School of Technology Field of study Electrical Engineering (0714)
|
|
|
- Brett Bell
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AUTUMN SEMESTER 2016 NOTE! Period Study level ECTS cr Course number Course Attendance required in both semesters Attendance required in both semesters M1 = 1 st year Master M2 = 2 nd year Master 1 M1 6 BL30A0400 Design of an Electrical Machine 1-2 M1 5 BL40A1201 Digital Control Design 2-3 M2 8 BL30A1001 Electrical Drives 1 M1 5 BL20A0401 Electricity Market 1 M1 2 BL50A0600 Electromagnetic Compatibility in Power Electronics 1-2 M1 6 BL40A1601 Embedded System Design 1-2 M1 4 BL40A1100 Embedded System Programming 1-2 M1 6 BL30A0600 Power Electronics 2-3 M1 3 BL20A0201 Power Exchange Game for Electricity Markets 1-2 M2 5 BL40A1000 Real-time Operating Systems and Programs Preliminary course descriptions on pages 2-7. See final course descriptions in Study Guide in Uni portal (June 2016). Learning agreement is created in Mobility-Online system during application process. More information about applying, i.e. Guide for Applicants, is available on > Apply to LUT > Exchange studies Course registration is done online before the semester start. Method of registration and deadlines are announced in Uni portal (Studies and services > Enrolment > Course registration) Course schedules are published in Uni portal in July (7)
2 BL30A0400 DESIGN OF AN ELECTRICAL MACHINE 6 ECTS cr Year and Period M.Sc. (Tech.) 1 Period 1 Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Juha Pyrhönen 1. perform a basic design of a rotating electrical machine, 2. name the simplest winding arrangements and other components of the machine, 3. explain the torque production process in electrical machines, 4. calculate the main data (equivalent circuit parameters) of an electrical machine from machine geometric and winding designs, 5. list the most important materials used in magnetic circuits and windings, 6. model the machine with an equivalent circuit, 7. compare machine designs with each other by using the per unit presentation of machines, 8. use phasor diagrams in the machine analysis, 9. discuss the problems of insulation systems and heat transfer. Electromagnetic principles used in machine design, the magnetic circuit of an electric machine, the windings of an electric machine, impacts of the structure of the electric motor on the motor characteristics, calculation of the parameters of an equivalent circuit from the dimensions of the machine (resistances, inductances), effective-value phasor diagrams for different machine types, principles of electric machine design, insulation materials and systems heat transfer. Suitable also for doctoral studies. Modes of Study Lectures, tutorials and assignment supervision 48 h, 1st period. The design assignment of an electric machine. Written examination. Total workload 156 h. 0-5, written examination 100 %. Satisfactorily completed assignment required. Study materials Pyrhönen, Jokinen, Hrabovcova: Design of Rotating Electrical Machines. Students are recommended to have completed BL30A0000 Electric Circuits, BL10A0100 Basics of Electric Engineering. BL40A1201 DIGITAL CONTROL DESIGN 5 ECTS cr Digital Control Design Postdoctoral Researcher, D.Sc. (Tech.) Rafal Jastrzebski 1. build plant models of simple electromechanical systems and discretise them, 2. describe and explain the example control systems, interpret system responses and control design specifications in time continuous and time discrete domains, 3. compare and discriminate between different discretisation techniques and different control design methods, 4. relate knowledge from the areas such as system modelling, model discretisation, design of a digital control in a discrete time domain, computer simulation and digital implementation, 5. design and implement digital state-space controllers and transfer function controllers, 6. apply the selected control design methods and system modelling concepts to new control problems that involve various electromechanical systems. Different discretisation methods, discretisation of plants with time delay. State feedback, state estimation (predictive, current, reduced order, constant and sinusoidal disturbance estimation), sate-space control design (pole placement, optimal control, integral state augmentation and reference control) and polynomial control design (deadbeat control, cancelation of poles and zeros, integral control, reference control). Fundamentals of a multivariable control system. Simulation of 2(7)
3 Modes of Study Further Information a digital control system with Simulink. Programming of digital control for a microprocessor. Control design examples including control of real MIMO industrial systems. Application of MATLAB in control design. 12 h of lectures, 12 h of tutorials, 1st period. 2 h of lectures, 2 h of tutorials, 6-12 h of demonstration lectures, 10 h of project work in computer class, written examination, 2nd period. Project assignment, 3rd period. Total workload 130 h. 0-5, examination 100 %. Satisfactorily completed assignment required. BL40A0200 Control Systems Introduction and BL40A0501 Digital Control, Introduction. This course has 1-15 places for open university students. More information on the web site for open BL30A1001 ELECTRICAL DRIVES 8 ECTS cr Electrical Drives The course will be given in English. Year and Period M.Sc. (Tech.) 2 Period 2-3 Person in Charge: Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Juha Pyrhönen 1. describe the principles of scalar, vector and direct torque control of rotating field machines, 2. model the behaviour of different synchronous and asynchronous machines by using vector equivalent circuits and vector diagrams, 3. name the main ideas of the electromagnetic design and performance of different rotating machines, 4. select a suitable electrical machine for a certain purpose and evaluate their thermal limits in cyclic operation, 5. define the most important power electronic converters and their properties in different applications, 6. discuss the principles of PWM, space vector modulation and DTC, 7. discuss the adverse effects of PWM systems on motor behaviour and the wave nature of the motor cable. Theory of electric motor drives, operation and vector equivalent circuits. Synchronous machine drives, asynchronous machine drives, synchronous reluctance machine drives, permanent magnet synchronous machine drives, switched reluctance motor drives. Torque production in different machines. Power electronic converters suitable for motor and generator drives. Scalar control, vector control, direct flux linkage control and direct torque control (DTC). Motor cable wave nature, bearing currents. Modes of Study Lectures or seminars 24 h, tutorials 24 h, 2nd period. Lectures or seminars 24 h, tutorials 24 h, 3rd period. Independent study 112 h. Total workload 208 h. 0-5, written examination 100 %. Study materials Pyrhönen, Juha: Electrical Drives, lecture material. The students are recommended to have completed the courses BL30A0000 Electric Circuits, BL10A0100 Basics of Electric Engineering, BL30A0200 Laboratory Course in Electrical Engineering, BL30A0500 Introduction to Electrical Drives and BL30A0800 Electromagnetic Components and to have attended the courses BL30A0400 Design of an Electrical Machine and BL30A0900 Power Electronic Components. 3(7)
4 BL20A0401 ELECTRICITY MARKET 5 ECTS cr Electricity Market Year and Period M.Sc. (Tech.) 1 Period 1 Person in Charge: Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Jarmo Partanen, Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Satu Viljainen 1. describe the characteristics of the different business sectors in the Nordic electricity market, 2. explain electricity price formation, 3. model electricity consumption, 4. explain the operation principle of the power exchange, 5. identify and describe the products of the power exchange, 6. select the right risk management method for electricity trade, 7. describe the tasks of the different parties in an electric power system in maintaining technical and commercial power balance, 8. conduct the balance settlement, 9. price the products of electricity trade and distribution and describe why and how electricity distribution business is regulated. The development of electricity markets, loads on the electricity network and load forecasts, power exchange, electricity trade, balance management, the fundamentals of pricing and regulation of distribution business. The course is related to sustainability. Modes of Study 28 h of lectures, 14 h of tutorials, 1st period. Independent studies. Written examination. Total workload 130 h. The lectures focus on the core learning objectives in the topic. Successful completion of the course requires student s active independent work. 0-5, examination 100%. Study materials Material distributed in class. 4(7)
5 BL50A0600 ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY IN POWER ELECTRONICS 2 ECTS cr Electromagnetic compatibility in power electronics Year and Period M.Sc. (Tech.) 1 Period 1 D.Sc. (Tech.) Juhamatti Korhonen, Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Pertti Silventoinen Person in Charge: Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Pertti Silventoinen 1. describe the coupling mechanisms of electromagnetic interferences in power electronics, 2. name the most significant sources of electromagnetic emissions in power electronic systems, 3. recognise and be aware of cable reflection in electrical drives, 4. list the suitable filter types for common mode filtering, du/dt filtering and harmonics filtering. Power electronics as an interference source, network harmonics, reflection phenomena of cables, conductive RF interference, interference radiation of power electronics, filtering techniques of conductive interferences. Modes of Study 12 h of lectures, 1st period. Written examination. Independent work 40 h. Total workload 55 h. 0-5, written examination 100 %. Study materials Moodle. Further Information Recommended: Basic knowledge of electromagnetism and electromagnetic fields This course has 1-10 places for open university students. More information on the web site for open BL40A1601 EMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN 6 ECTS cr Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Jero Ahola Upon completion of the course the student will be able to program with VHDL hardware design language and design and implement digital systems by using programmable logic circuits. Circuit design of digital electronics with programmable logic circuits. Principles of digital circuit design, system level synthesis, hardware design languages. Modes of Study Lectures 12 h, exercises, 12 h, 1st period. Lectures 12 h, exercises, 12 h, assignment, 2nd period. Examination. Total workload 156 h. 0-5, examination 100 %. Satisfactorily completed assignment required. Basics of digital design and digital electronics, basics of programming. Further Information This course has 1-15 places for open university students. More information on the web site for open BL40A1100 EMBEDDED SYSTEM PROGRAMMING 4 ECTS cr Embedded System Programming Associate Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Tuomo Lindh 1. apply C language and its structures to embedded system programming, 2. form complex data types such as structures, unions and buffers and use these in order to maintain information of different entities (e.g. processing units), 3. control the registers of a micro controller using C-language, 4. use different PUs of a micro controller. Design tools, C-language in embedded system programming, utilisation of a microcontroller environment (registers, timers, buses, A/D conversion etc.). Typical data structures, typical 5(7)
6 Modes of Study Study materials Further Information program structures in real-time applications. Programming the Windows interface, basic properties of real-time operating systems. 12 h of lectures, 12 h of tutorials, 1st period. 12 h of lectures, 12 h of tutorials, 2nd period. Assignment. Written examination. Total workload 104 h. 0-5, assignment 1 20 %, examination 80 %. Satisfactorily completed assignment 2 required. Wolf, W.: Computers as components: principles of embedded computing system design. Lecture notes. Basics of C language. This course has 1-5 places for open university students. More information on the web site for open BL30A0600 POWER ELECTRONICS 6 ECTS cr Power Electronics Associate Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Lasse Laurila 1. demonstrate good general knowledge of the different basic main circuits in modern power electronics, 2. describe the features and functions of different rectifiers, switch-mode converters and inverters, 3. calculate and simulate typical design tasks of the aforementioned circuits, 4. describe the joint operation of static converters and loads as well as the network interferences caused by converters and alternatives to reduce these interferences. Operation of the main circuits of different power converters: rectifiers (single and three-phase), DC-DC switch mode converters and power supplies (buck, boost, buck-boost, Cúk, flyback, forward), inverters (single and three-phase), resonance converters (ZVS, ZCS). Characteristics and operation. Pulse width modulation (PWM). Harmonic components. Simulation of power electronic circuits. Modes of Study 12 h of lectures, 12 h of tutorials, 1st period. 12 h of lectures, 12 h of tutorials, 2nd period. Written examination. Independent study 108 h. Total workload 156 h. 0-5, examination 100 %. Possible extra assignments to gather extra points to the exam. Study materials Mohan, Undeland, Robbins: Power Electronics, converters, applications, and design, where applicable. BL30A0000 Electric Circuits. Integration and derivation (esp. sine and cosine functions). FFT. Laplace transforms. BL20A0201 POWER EXCHANGE GAME FOR ELECTRICITY MARKETS 3 ECTS cr Power Exchange Game for Electricity Markets Year and Period M.Sc. (Tech.) 1 Period 2-3 Doctoral Student, M.Sc. (Tech.) Petri Valtonen Person in Charge: Professor, D.Sc. (Tech.) Satu Viljainen Plan electricity purchase and sale in an economically viable way, recognize the most common risk management instruments and basic mechanisms of demand response in electricity markets, and exploit financial products of the power exchange in risk management and trade electricity in day ahead and intraday markets. These skills will be practised in a power exchange game, after which the student will be able to analyse and interpret the game results. 6(7)
7 Electricity purchase/sale, OTC markets, physical products on the power exchange (spot and elbas), financial products on the power exchange (forwards, futures and options), risk management. Modes of Study Lectures 8 h, weekly game situation practice 40 h, 2nd and 3rd period. Written homework, intermediate report and final report. Total workload 78 h. The lectures focus on the key learning objectives in the topic. Successful completion of the course requires student s active independent work. 0-5, written report 100%. Study materials Material handed out in class. BL20A0400 Sähkömarkkinat BL40A1000 REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEMS AND PROGRAMS 5 ECTS cr Real-time Operating Systems and Programs Year and Period M.Sc. (Tech.) 2 Period 1-2 Post-Doctoral Researcher, D.Sc. (Tech.) Alexander Smirnov 1. use the services of a real-time operating system, 2. design the architecture of an application program using a real-time operating system as its basis, 3. implement a simple real-time operating system using the C language. Basic concepts of a real-time system. Services provided by a real-time operating system: task management, time management, semaphores, mutual exclusion semaphores (mutex), event flags, mailboxes, message queues and memory management. Implementation of a real-time operating system: context switch, interrupt management. Processor-specific parts of a real-time operating system and adapting the real-time operating system to a new processor. Modes of Study 18 h of lectures, 12 h of tutorials, 1st period. 18 h of lectures, 12 h of tutorials, assignment, 2nd period. Written examination. Total workload 130 h. 0-5, examination 100 %. Satisfactorily completed assignment required. Study materials Labrosse, J.J.: MicroC/OS-II The Real-Time Kernel (2nd Edition). BL40A1100 Embedded System Programming. 7(7)
Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive in Speed Control Of Induction Motor
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 78-7461, p-issn: 319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 5 (December 013) PP: 36-41 Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 78-7461, p-issn: 319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 5 (December 013) PP: 36-41 Modelling, Simulation and Performance Analysis of A Variable Frequency Drive
Degree programme in Automation Engineering
 Degree programme in Automation Engineering Course descriptions of the courses for exchange students, 2014-2015 Autumn 2014 21727630 Application Programming Students know the basis of systems application
Degree programme in Automation Engineering Course descriptions of the courses for exchange students, 2014-2015 Autumn 2014 21727630 Application Programming Students know the basis of systems application
PSE 6031 SYLLABUS (Tentative)
 PSE 6031 SYLLABUS (Tentative) Power Electronics (3 credits) Friday Afternoon: 1:00-3:00 PM 15 Virtual Class Meetings (no face-face meetings) Pre-requisites: All coursework to qualify for the upper division
PSE 6031 SYLLABUS (Tentative) Power Electronics (3 credits) Friday Afternoon: 1:00-3:00 PM 15 Virtual Class Meetings (no face-face meetings) Pre-requisites: All coursework to qualify for the upper division
Syllabus: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering
 Syllabus: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Instructors Dr.-Ing. Saša Bukvić-Schäfer Email: [email protected] Dr.-Ing. Antonio Notholt-Vergara Email: [email protected] Syllabus: Fundamentals
Syllabus: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Instructors Dr.-Ing. Saša Bukvić-Schäfer Email: [email protected] Dr.-Ing. Antonio Notholt-Vergara Email: [email protected] Syllabus: Fundamentals
Poznan University of Technology Faculty of Electrical Engineering
 Poznan University of Technology Faculty of Electrical Engineering Contact Person: Pawel Kolwicz Vice-Dean Faculty of Electrical Engineering [email protected] List of Modules Academic Year: 2015/16
Poznan University of Technology Faculty of Electrical Engineering Contact Person: Pawel Kolwicz Vice-Dean Faculty of Electrical Engineering [email protected] List of Modules Academic Year: 2015/16
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
Anais Volume 1 COBEP99 UFPR UFSM
 COBEP99 UFPR UFSM 5 e Congresso Brasileiro de Eletronica de Potencia The 5~ Brazilian Power Electronics Conference Foz do Iguagu, Parana, Brasil 19 a 23 de setembro de 1999 Anais Volume 1 UB/TIB Hannover
COBEP99 UFPR UFSM 5 e Congresso Brasileiro de Eletronica de Potencia The 5~ Brazilian Power Electronics Conference Foz do Iguagu, Parana, Brasil 19 a 23 de setembro de 1999 Anais Volume 1 UB/TIB Hannover
CSEN301 Embedded Systems Trimester 1
 Victoria University of Wellington (VUW) course offering for NZ-EU Joint Mobility Project Novel Sensing Technologies and Instrumentation in Environmental Climate Change Monitoring 1. General The Victoria
Victoria University of Wellington (VUW) course offering for NZ-EU Joint Mobility Project Novel Sensing Technologies and Instrumentation in Environmental Climate Change Monitoring 1. General The Victoria
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING The master degree programme of Teacher Training in Electronical Engineering is designed to develop graduates competencies in the field of Curriculum Development and Instructional
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING The master degree programme of Teacher Training in Electronical Engineering is designed to develop graduates competencies in the field of Curriculum Development and Instructional
INDUCTION MOTOR PERFORMANCE TESTING WITH AN INVERTER POWER SUPPLY, PART 2
 INDUCTION MOTOR PERFORMANCE TESTING WITH AN INVERTER POWER SUPPLY, PART 2 By: R.C. Zowarka T.J. Hotz J.R. Uglum H.E. Jordan 13th Electromagnetic Launch Technology Symposium, Potsdam (Berlin), Germany,
INDUCTION MOTOR PERFORMANCE TESTING WITH AN INVERTER POWER SUPPLY, PART 2 By: R.C. Zowarka T.J. Hotz J.R. Uglum H.E. Jordan 13th Electromagnetic Launch Technology Symposium, Potsdam (Berlin), Germany,
Simulation of VSI-Fed Variable Speed Drive Using PI-Fuzzy based SVM-DTC Technique
 Simulation of VSI-Fed Variable Speed Drive Using PI-Fuzzy based SVM-DTC Technique B.Hemanth Kumar 1, Dr.G.V.Marutheshwar 2 PG Student,EEE S.V. College of Engineering Tirupati Senior Professor,EEE dept.
Simulation of VSI-Fed Variable Speed Drive Using PI-Fuzzy based SVM-DTC Technique B.Hemanth Kumar 1, Dr.G.V.Marutheshwar 2 PG Student,EEE S.V. College of Engineering Tirupati Senior Professor,EEE dept.
Design of Solar Power Optimizer And Eliminating Leakage Current In Multi-Level Inverter For PV Systems
 Design of Solar Power Optimizer And Eliminating Leakage Current In Multi-Level Inverter For PV Systems A. Asaph 1, Dr. P. Selvan 2 1 PG Scholar, 2 Head of the Department, Erode Sengunthar Engineering College,
Design of Solar Power Optimizer And Eliminating Leakage Current In Multi-Level Inverter For PV Systems A. Asaph 1, Dr. P. Selvan 2 1 PG Scholar, 2 Head of the Department, Erode Sengunthar Engineering College,
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Bi-directional Power System for Laptop Computers
 Bi-directional Power System for Laptop Computers Terry L. Cleveland Staff Applications Engineer Microchip Technology Inc. [email protected] Abstract- Today the typical laptop computer uses
Bi-directional Power System for Laptop Computers Terry L. Cleveland Staff Applications Engineer Microchip Technology Inc. [email protected] Abstract- Today the typical laptop computer uses
Principles of Adjustable Frequency Drives
 What is an Adjustable Frequency Drive? An adjustable frequency drive is a system for controlling the speed of an AC motor by controlling the frequency of the power supplied to the motor. A basic adjustable
What is an Adjustable Frequency Drive? An adjustable frequency drive is a system for controlling the speed of an AC motor by controlling the frequency of the power supplied to the motor. A basic adjustable
Introduction. Harmonics and IEEE 519 Page 1 of 19
 Introduction In an ideal power system, the voltage supplied to customer equipment, and the resulting load current are perfect sine waves. In practice, however, conditions are never ideal, so these waveforms
Introduction In an ideal power system, the voltage supplied to customer equipment, and the resulting load current are perfect sine waves. In practice, however, conditions are never ideal, so these waveforms
Technology for Next-generation Reduced-size High-performance Inverter
 Technology for Next-generation Reduced-size High-performance Inverter 28 Technology for Next-generation Reduced-size High-performance Inverter Naoki Kurihara Shuichi Tachihara Kenhachiro Minamide Satoshi
Technology for Next-generation Reduced-size High-performance Inverter 28 Technology for Next-generation Reduced-size High-performance Inverter Naoki Kurihara Shuichi Tachihara Kenhachiro Minamide Satoshi
New Pulse Width Modulation Technique for Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Umesha K L, Sri Harsha J, Capt. L. Sanjeev Kumar
 New Pulse Width Modulation Technique for Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Umesha K L, Sri Harsha J, Capt. L. Sanjeev Kumar Abstract In this paper, various types of speed control methods for the three
New Pulse Width Modulation Technique for Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Umesha K L, Sri Harsha J, Capt. L. Sanjeev Kumar Abstract In this paper, various types of speed control methods for the three
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies
 Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
Analysis of Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation VSI Induction Motor on various conditions
 Analysis of Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation VSI Induction Motor on various conditions Padma Chaturvedi 1, Amarish Dubey 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Maharana Pratap Engineering College,
Analysis of Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation VSI Induction Motor on various conditions Padma Chaturvedi 1, Amarish Dubey 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Maharana Pratap Engineering College,
WIND TURBINE TECHNOLOGY
 Module 2.2-2 WIND TURBINE TECHNOLOGY Electrical System Gerhard J. Gerdes Workshop on Renewable Energies November 14-25, 2005 Nadi, Republic of the Fiji Islands Contents Module 2.2 Types of generator systems
Module 2.2-2 WIND TURBINE TECHNOLOGY Electrical System Gerhard J. Gerdes Workshop on Renewable Energies November 14-25, 2005 Nadi, Republic of the Fiji Islands Contents Module 2.2 Types of generator systems
FREQUENCY CONTROLLED AC MOTOR DRIVE
 FREQUENCY CONTROLLED AC MOTOR DRIVE 1.0 Features of Standard AC Motors The squirrel cage induction motor is the electrical motor motor type most widely used in industry. This leading position results mainly
FREQUENCY CONTROLLED AC MOTOR DRIVE 1.0 Features of Standard AC Motors The squirrel cage induction motor is the electrical motor motor type most widely used in industry. This leading position results mainly
Cable Solutions for Servo and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD)
 Cable Solutions for Servo and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) Electric drive systems with continuous torque and speed control are widespread today. They allow an optimal adjustment of the drive with respect
Cable Solutions for Servo and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) Electric drive systems with continuous torque and speed control are widespread today. They allow an optimal adjustment of the drive with respect
Associate Degree of Applied Engineering (Renewable Energy Technologies) OVERVIEW OF SUBJECT REQUIREMENTS
 Course Associate Degree of Applied Engineering (Renewable Energy Technologies) Course Number HE20502 Location Newcastle, Ultimo, Mt Druitt OVERVIEW OF SUBJECT REQUIREMENTS Note: This document is intended
Course Associate Degree of Applied Engineering (Renewable Energy Technologies) Course Number HE20502 Location Newcastle, Ultimo, Mt Druitt OVERVIEW OF SUBJECT REQUIREMENTS Note: This document is intended
POWER SYSTEM HARMONICS. A Reference Guide to Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures AN ALLEN-BRADLEY SERIES OF ISSUES AND ANSWERS
 A Reference Guide to Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures AN ALLEN-BRADLEY SERIES OF ISSUES AND ANSWERS By: Robert G. Ellis, P. Eng., Rockwell Automation Medium Voltage Business CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...
A Reference Guide to Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures AN ALLEN-BRADLEY SERIES OF ISSUES AND ANSWERS By: Robert G. Ellis, P. Eng., Rockwell Automation Medium Voltage Business CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...
REMOTE HOST PROCESS CONTROL AND MONITORING OF INDUSTRY APPLIANCES
 REMOTE HOST PROCESS CONTROL AND MONITORING OF INDUSTRY APPLIANCES 1 Abinath.T.R, 2 Sudhakar.V, 3 Sasikala.S 1,2 UG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Info Institute of Engineering,
REMOTE HOST PROCESS CONTROL AND MONITORING OF INDUSTRY APPLIANCES 1 Abinath.T.R, 2 Sudhakar.V, 3 Sasikala.S 1,2 UG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Info Institute of Engineering,
Mathematical Modelling of PMSM Vector Control System Based on SVPWM with PI Controller Using MATLAB
 Mathematical Modelling of PMSM Vector Control System Based on SVPWM with PI Controller Using MATLAB Kiran Boby 1, Prof.Acy M Kottalil 2, N.P.Ananthamoorthy 3 Assistant professor, Dept of EEE, M.A College
Mathematical Modelling of PMSM Vector Control System Based on SVPWM with PI Controller Using MATLAB Kiran Boby 1, Prof.Acy M Kottalil 2, N.P.Ananthamoorthy 3 Assistant professor, Dept of EEE, M.A College
PROGRAM CRITERIA FOR ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 PROGRAM CRITERIA FOR ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Scope These program criteria apply to programs having titles involving Electrical Engineering Technology including: electrical engineering, electrical
PROGRAM CRITERIA FOR ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Scope These program criteria apply to programs having titles involving Electrical Engineering Technology including: electrical engineering, electrical
ONR/NSF-Sponsored Faculty/Industry Workshop
 ONR/NSF-Sponsored Faculty/Industry Workshop Reforming Power-Related Curriculum Power Electronics Presenter: Hariharan Krishnaswami Assistant Professor University of Texas at San Antonio New Electric Power
ONR/NSF-Sponsored Faculty/Industry Workshop Reforming Power-Related Curriculum Power Electronics Presenter: Hariharan Krishnaswami Assistant Professor University of Texas at San Antonio New Electric Power
Control Development and Modeling for Flexible DC Grids in Modelica
 Control Development and Modeling for Flexible DC Grids in Modelica Andreas Olenmark 1 Jens Sloth 2 Anna Johnsson 3 Carl Wilhelmsson 3 Jörgen Svensson 4 1 One Nordic AB, Sweden, [email protected].
Control Development and Modeling for Flexible DC Grids in Modelica Andreas Olenmark 1 Jens Sloth 2 Anna Johnsson 3 Carl Wilhelmsson 3 Jörgen Svensson 4 1 One Nordic AB, Sweden, [email protected].
Control of a Three Phase Induction Motor using Single Phase Supply
 Control of a Three Phase Induction Motor using Single Phase Supply G. R. Sreehitha #1, A. Krishna Teja *2, Kondenti. P. Prasad Rao #3 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, K L University,
Control of a Three Phase Induction Motor using Single Phase Supply G. R. Sreehitha #1, A. Krishna Teja *2, Kondenti. P. Prasad Rao #3 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, K L University,
MsC in Advanced Electronics Systems Engineering
 MsC in Advanced Electronics Systems Engineering 1 2 General overview Location: Dijon, University of Burgundy, France Tuition Fees : 475 / year Course Language: English Course duration: 1 year Level: Second
MsC in Advanced Electronics Systems Engineering 1 2 General overview Location: Dijon, University of Burgundy, France Tuition Fees : 475 / year Course Language: English Course duration: 1 year Level: Second
Weighted Total Mark. Weighted Exam Mark
 CMP2204 Operating System Technologies Period per Week Contact Hour per Semester Total Mark Exam Mark Continuous Assessment Mark Credit Units LH PH TH CH WTM WEM WCM CU 45 30 00 60 100 40 100 4 Rationale
CMP2204 Operating System Technologies Period per Week Contact Hour per Semester Total Mark Exam Mark Continuous Assessment Mark Credit Units LH PH TH CH WTM WEM WCM CU 45 30 00 60 100 40 100 4 Rationale
METHODOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULATION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MACHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULATOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS.
 SEDM 24 June 16th - 18th, CPRI (Italy) METHODOLOGICL CONSIDERTIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULTION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MCHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULTOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS. Áron Szûcs BB Electrical
SEDM 24 June 16th - 18th, CPRI (Italy) METHODOLOGICL CONSIDERTIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULTION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MCHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULTOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS. Áron Szûcs BB Electrical
AC Induction Motor Slip What It Is And How To Minimize It
 AC Induction Motor Slip What It Is And How To Minimize It Mauri Peltola, ABB Oy, Helsinki, Finland The alternating current (AC) induction motor is often referred to as the workhorse of the industry because
AC Induction Motor Slip What It Is And How To Minimize It Mauri Peltola, ABB Oy, Helsinki, Finland The alternating current (AC) induction motor is often referred to as the workhorse of the industry because
Hybrid Systems Specialisation Syllabus
 Hybrid Systems Specialisation Syllabus Contents: 1. Basics of electric power systems 2. Energy generation in isolated systems 3. Electric power systems 4. Economics and socio-economics -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hybrid Systems Specialisation Syllabus Contents: 1. Basics of electric power systems 2. Energy generation in isolated systems 3. Electric power systems 4. Economics and socio-economics -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Modeling and Simulation of a Novel Switched Reluctance Motor Drive System with Power Factor Improvement
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 3 (1): 1649-1654, 2006 ISSN 1546-9239 2006 Science Publications Modeling and Simulation of a Novel Switched Reluctance Motor Drive System with Power Factor Improvement
American Journal of Applied Sciences 3 (1): 1649-1654, 2006 ISSN 1546-9239 2006 Science Publications Modeling and Simulation of a Novel Switched Reluctance Motor Drive System with Power Factor Improvement
Simulation and Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive
 Simulation and Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive C.S.Sharma, Tali Nagwani Abstract Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation variable speed drives are increasingly applied in many new industrial
Simulation and Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive C.S.Sharma, Tali Nagwani Abstract Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation variable speed drives are increasingly applied in many new industrial
VICOR WHITE PAPER. The Sine Amplitude Converter Topology Provides Superior Efficiency and Power Density in Intermediate Bus Architecture Applications
 The Sine Amplitude Converter Topology Provides Superior Efficiency and Power Density in Intermediate Bus Architecture Applications Maurizio Salato, Applications Engineering, Vicor Corporation Contents
The Sine Amplitude Converter Topology Provides Superior Efficiency and Power Density in Intermediate Bus Architecture Applications Maurizio Salato, Applications Engineering, Vicor Corporation Contents
Reliable World Class Insights Your Silicon Valley Partner in Simulation ANSYS Sales, Consulting, Training & Support
 www.ozeninc.com [email protected] (408) 732 4665 1210 E Arques Ave St 207 Sunnyvale, CA 94085 Reliable World Class Insights Your Silicon Valley Partner in Simulation ANSYS Sales, Consulting, Training &
www.ozeninc.com [email protected] (408) 732 4665 1210 E Arques Ave St 207 Sunnyvale, CA 94085 Reliable World Class Insights Your Silicon Valley Partner in Simulation ANSYS Sales, Consulting, Training &
Edison Memorial Lecture
 Edison Memorial Lecture Organized by Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi Jointly with IEEE PELS IES & PES IAS Delhi Chapter Date: Time: Venue: 22 th Nov., 2012 5.00 PM IIA 106, Bharti School,
Edison Memorial Lecture Organized by Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi Jointly with IEEE PELS IES & PES IAS Delhi Chapter Date: Time: Venue: 22 th Nov., 2012 5.00 PM IIA 106, Bharti School,
Alternative and Renewable Energy Systems
 Alternative and Renewable Energy Systems Known as the standard for technical training systems in use across virtually every industry and around the globe, Lab-Volt is now using its expertise to provide
Alternative and Renewable Energy Systems Known as the standard for technical training systems in use across virtually every industry and around the globe, Lab-Volt is now using its expertise to provide
Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application
 Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application A.Thiyagarajan Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Karpagam Institute of Technology
Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application A.Thiyagarajan Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Karpagam Institute of Technology
Power Electronic Circuits
 Power Electronic Circuits Assoc. Prof. Dr. H. İbrahim OKUMUŞ Karadeniz Technical University Engineering Faculty Department of Electrical And Electronics 1 DC to DC CONVERTER (CHOPPER) General Buck converter
Power Electronic Circuits Assoc. Prof. Dr. H. İbrahim OKUMUŞ Karadeniz Technical University Engineering Faculty Department of Electrical And Electronics 1 DC to DC CONVERTER (CHOPPER) General Buck converter
Transformerless UPS systems and the 9900 By: John Steele, EIT Engineering Manager
 Transformerless UPS systems and the 9900 By: John Steele, EIT Engineering Manager Introduction There is a growing trend in the UPS industry to create a highly efficient, more lightweight and smaller UPS
Transformerless UPS systems and the 9900 By: John Steele, EIT Engineering Manager Introduction There is a growing trend in the UPS industry to create a highly efficient, more lightweight and smaller UPS
Understanding SMD Power Inductors. Application Note. July 2011
 Understanding SMD Power Inductors July 2011 Application Note Power inductors play an important role in voltage conversion applications by yielding lower core losses. They are also used to store energy,
Understanding SMD Power Inductors July 2011 Application Note Power inductors play an important role in voltage conversion applications by yielding lower core losses. They are also used to store energy,
The details of the programme are given below. For a short description of the courses, Click here.
 MASTER S PROGRAMMES Through the Post Graduate School in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, three forms of Master s programmes are offered. The programme structure of the International MSc programme
MASTER S PROGRAMMES Through the Post Graduate School in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, three forms of Master s programmes are offered. The programme structure of the International MSc programme
Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Drives. AC Drives Using PWM Techniques
 Drives AC Drives Using PWM Techniques Power Conversion Unit The block diagram below shows the power conversion unit in Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) drives. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
Drives AC Drives Using PWM Techniques Power Conversion Unit The block diagram below shows the power conversion unit in Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) drives. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
Product Data Bulletin
 Product Data Bulletin Power System Harmonics Causes and Effects of Variable Frequency Drives Relative to the IEEE 519-1992 Standard Raleigh, NC, U.S.A. INTRODUCTION This document describes power system
Product Data Bulletin Power System Harmonics Causes and Effects of Variable Frequency Drives Relative to the IEEE 519-1992 Standard Raleigh, NC, U.S.A. INTRODUCTION This document describes power system
Development of High Frequency Link Direct DC to AC Converters for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC)
 Development of High Frequency Link Direct DC to AC Converters for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) Dr. Prasad Enjeti Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering College Station, TX -
Development of High Frequency Link Direct DC to AC Converters for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) Dr. Prasad Enjeti Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering College Station, TX -
CONVENTIONALLY reduced order models are being
 Co-Simulation of an Electric Traction Drive Christoph Schulte and Joachim Böcker Abstract For the simulation of electrical drives, reducedorder models or simple look-up tables are often used in order to
Co-Simulation of an Electric Traction Drive Christoph Schulte and Joachim Böcker Abstract For the simulation of electrical drives, reducedorder models or simple look-up tables are often used in order to
THIS paper reports some results of a research, which aims to investigate the
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 22, no. 2, August 2009, 227-234 Determination of Rotor Slot Number of an Induction Motor Using an External Search Coil Ozan Keysan and H. Bülent Ertan
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 22, no. 2, August 2009, 227-234 Determination of Rotor Slot Number of an Induction Motor Using an External Search Coil Ozan Keysan and H. Bülent Ertan
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF SVPWM INVERTER FED PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR DRIVE
 MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF SVPWM INVERTER FED PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR DRIVE Devisree Sasi 1, Jisha Kuruvilla P Final Year M.Tech, Dept. of EEE, Mar Athanasius College of Engineering, Kothamangalam,
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF SVPWM INVERTER FED PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR DRIVE Devisree Sasi 1, Jisha Kuruvilla P Final Year M.Tech, Dept. of EEE, Mar Athanasius College of Engineering, Kothamangalam,
Design and Simulation of Z-Source Inverter for Brushless DC Motor Drive
 Science Arena Publications Specialty Journal of Electronic and Computer Sciences Available online at www.sciarena.com 2015, Vol, 1 (1): 30-34 Design and Simulation of Z-Source Inverter for Brushless DC
Science Arena Publications Specialty Journal of Electronic and Computer Sciences Available online at www.sciarena.com 2015, Vol, 1 (1): 30-34 Design and Simulation of Z-Source Inverter for Brushless DC
Lab 14: 3-phase alternator.
 Lab 14: 3-phase alternator. Objective: to obtain the no-load saturation curve of the alternator; to determine the voltage regulation characteristic of the alternator with resistive, capacitive, and inductive
Lab 14: 3-phase alternator. Objective: to obtain the no-load saturation curve of the alternator; to determine the voltage regulation characteristic of the alternator with resistive, capacitive, and inductive
NATIONAL SUN YAT-SEN UNIVERSITY
 NATIONAL SUN YAT-SEN UNIVERSITY Department of Electrical Engineering (Master s Degree, Doctoral Program Course, International Master's Program in Electric Power Engineering) Course Structure Course Structures
NATIONAL SUN YAT-SEN UNIVERSITY Department of Electrical Engineering (Master s Degree, Doctoral Program Course, International Master's Program in Electric Power Engineering) Course Structure Course Structures
Three-port DC-DC Converters to Interface Renewable Energy Sources with Bi-directional Load and Energy Storage Ports
 Three-port DC-DC Converters to Interface Renewable Energy Sources with Bi-directional Load and Energy Storage Ports A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
Three-port DC-DC Converters to Interface Renewable Energy Sources with Bi-directional Load and Energy Storage Ports A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
Relationship between large subject matter areas
 H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER;
H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER;
ÇANKAYA UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Architecture
 ÇANKAYA UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Course Definition Form This form should be used for both a new elective or compulsory course being proposed and curricula development processes
ÇANKAYA UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Course Definition Form This form should be used for both a new elective or compulsory course being proposed and curricula development processes
GPS & GSM BASED REAL-TIME VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM.
 GPS & GSM BASED REAL-TIME VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM. Introduction: The Proposed design is cost-effective, reliable and has the function of accurate tracking. When large object or vehicles were spread out
GPS & GSM BASED REAL-TIME VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM. Introduction: The Proposed design is cost-effective, reliable and has the function of accurate tracking. When large object or vehicles were spread out
Project description. Power Electronics for Reliable and Energy efficient Renewable Energy Systems
 Project description Title: Power Electronics for Reliable and Energy efficient Renewable Energy Systems OBJECTIVES Principal objective Provide competence and decision basis for enabling reliable and energy
Project description Title: Power Electronics for Reliable and Energy efficient Renewable Energy Systems OBJECTIVES Principal objective Provide competence and decision basis for enabling reliable and energy
Solar Cybertech: A Competition of Digitally Controlled Vehicles Poweredby Solar Panels
 118 ELECTRONICS, VOL. 17, NO. 2, DECEMBER 2013 Solar Cybertech: A Competition of Digitally Controlled Vehicles Poweredby Solar Panels O. García, J. A. Oliver, D. Díaz, D. Meneses, P. Alou, M. Vasić, J.
118 ELECTRONICS, VOL. 17, NO. 2, DECEMBER 2013 Solar Cybertech: A Competition of Digitally Controlled Vehicles Poweredby Solar Panels O. García, J. A. Oliver, D. Díaz, D. Meneses, P. Alou, M. Vasić, J.
Occupational Profile: Electrical & Electronics Engineering Technician
 Occupational Profile: Electrical & Electronics Engineering Technician A competent Electrical & Electronics Engineering Technician should be able to demonstrate the following skills and competences: 1.
Occupational Profile: Electrical & Electronics Engineering Technician A competent Electrical & Electronics Engineering Technician should be able to demonstrate the following skills and competences: 1.
Harmonics in your electrical system
 Harmonics in your electrical system What they are, how they can be harmful, and what to do about them Abstract Harmonic currents, generated by non-linear electronic loads, increase power system heat losses
Harmonics in your electrical system What they are, how they can be harmful, and what to do about them Abstract Harmonic currents, generated by non-linear electronic loads, increase power system heat losses
Pulse Width Modulated (PWM)
 Control Technologies Manual PWM AC Drives Revision 1.0 Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Figure 1.8 shows a block diagram of the power conversion unit in a PWM drive. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
Control Technologies Manual PWM AC Drives Revision 1.0 Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Figure 1.8 shows a block diagram of the power conversion unit in a PWM drive. In this type of drive, a diode bridge rectifier
Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFE
 Data sheet Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFE The CM-PFE is a three-phase monitoring relay that monitors the phase parameter phase sequence and phase failure in three-phase mains. 2CDC 251 005 S0012 Characteristics
Data sheet Three-phase monitoring relay CM-PFE The CM-PFE is a three-phase monitoring relay that monitors the phase parameter phase sequence and phase failure in three-phase mains. 2CDC 251 005 S0012 Characteristics
A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER
 A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER 1 KARUNYA CHRISTOBAL LYDIA. S, 2 SHANMUGASUNDARI. A, 3 ANANDHI.Y 1,2,3 Electrical
A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER 1 KARUNYA CHRISTOBAL LYDIA. S, 2 SHANMUGASUNDARI. A, 3 ANANDHI.Y 1,2,3 Electrical
Academic year: 2015/2016 Code: IES-1-307-s ECTS credits: 6. Field of study: Electronics and Telecommunications Specialty: -
 Module name: Digital Electronics and Programmable Devices Academic year: 2015/2016 Code: IES-1-307-s ECTS credits: 6 Faculty of: Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunications Field of study: Electronics
Module name: Digital Electronics and Programmable Devices Academic year: 2015/2016 Code: IES-1-307-s ECTS credits: 6 Faculty of: Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunications Field of study: Electronics
UNIVERSITY OF YORK POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
 1 of 10 08/09/2014 14:47 Department of Electronics : Programme Specification - 2013/4 MSc : Internet and Wireless Computing Table of Contents Course Aims and Specification Diagrammatic Module Structure
1 of 10 08/09/2014 14:47 Department of Electronics : Programme Specification - 2013/4 MSc : Internet and Wireless Computing Table of Contents Course Aims and Specification Diagrammatic Module Structure
EET272 Worksheet Week 9
 EET272 Worksheet Week 9 answer questions 1-5 in preparation for discussion for the quiz on Monday. Finish the rest of the questions for discussion in class on Wednesday. Question 1 Questions AC s are becoming
EET272 Worksheet Week 9 answer questions 1-5 in preparation for discussion for the quiz on Monday. Finish the rest of the questions for discussion in class on Wednesday. Question 1 Questions AC s are becoming
AC/DC Power Supply Reference Design. Advanced SMPS Applications using the dspic DSC SMPS Family
 AC/DC Power Supply Reference Design Advanced SMPS Applications using the dspic DSC SMPS Family dspic30f SMPS Family Excellent for Digital Power Conversion Internal hi-res PWM Internal high speed ADC Internal
AC/DC Power Supply Reference Design Advanced SMPS Applications using the dspic DSC SMPS Family dspic30f SMPS Family Excellent for Digital Power Conversion Internal hi-res PWM Internal high speed ADC Internal
Future grid infrastructure Field tests of LVDC distribution
 Future grid infrastructure Field tests of LVDC distribution LUT LVDC Research Group: Andrey Lana, Pasi Nuutinen, Antti Pinomaa, Tero Kaipia, Pasi Peltoniemi, Aleksi Mattsson, Jarmo Partanen Introduction
Future grid infrastructure Field tests of LVDC distribution LUT LVDC Research Group: Andrey Lana, Pasi Nuutinen, Antti Pinomaa, Tero Kaipia, Pasi Peltoniemi, Aleksi Mattsson, Jarmo Partanen Introduction
Electric motor emulator versus rotating test rig
 DEVELOPMENT E l e c t r i c m o t o r s Electric motor emulator versus rotating test rig A controversial issue among experts is whether real-time model-based electric motor emulation can replace a conventional
DEVELOPMENT E l e c t r i c m o t o r s Electric motor emulator versus rotating test rig A controversial issue among experts is whether real-time model-based electric motor emulation can replace a conventional
Variable Frequency Drives - a Comparison of VSI versus LCI Systems
 Variable Frequency Drives - a Comparison of VSI versus LCI Systems Introduction TMEIC is a leader in the innovative design and manufacture of large ac variable f requency drive systems. TMEIC has been
Variable Frequency Drives - a Comparison of VSI versus LCI Systems Introduction TMEIC is a leader in the innovative design and manufacture of large ac variable f requency drive systems. TMEIC has been
High Frequency Power Quality
 High Frequency Power Quality Dr. Ing. Jos Knockaert, MSc [email protected] CE-ABLE Seminar 21st June 2016-1 Project: TETRA HFPQ funded by Dec 2014 Nov 2016 Main goals: - How to measure? - What are
High Frequency Power Quality Dr. Ing. Jos Knockaert, MSc [email protected] CE-ABLE Seminar 21st June 2016-1 Project: TETRA HFPQ funded by Dec 2014 Nov 2016 Main goals: - How to measure? - What are
Electric Commercial Vehicles - ECV 3. national seminar 8.10.2015
 Electric Commercial Vehicles - ECV 3. national seminar 8.10.2015 ECV2-LUT / Tubridi project Tubridi virtual platform and Hardware-In-Loop Result highlights Lasse Laurila, Paula Immonen, Jarkko Nokka LUT
Electric Commercial Vehicles - ECV 3. national seminar 8.10.2015 ECV2-LUT / Tubridi project Tubridi virtual platform and Hardware-In-Loop Result highlights Lasse Laurila, Paula Immonen, Jarkko Nokka LUT
BSc Bachelor of Science Electrical Engineering Sciences (240ECTS)
 BSc Bachelor of Science Electrical Engineering Sciences (240ECTS) Name of Study BSc - Bachelor of Science Electrical Engineering Sciences (240 ECTS) Introduction The mission of the Electrical Engineering
BSc Bachelor of Science Electrical Engineering Sciences (240ECTS) Name of Study BSc - Bachelor of Science Electrical Engineering Sciences (240 ECTS) Introduction The mission of the Electrical Engineering
Lab 8: DC generators: shunt, series, and compounded.
 Lab 8: DC generators: shunt, series, and compounded. Objective: to study the properties of DC generators under no-load and full-load conditions; to learn how to connect these generators; to obtain their
Lab 8: DC generators: shunt, series, and compounded. Objective: to study the properties of DC generators under no-load and full-load conditions; to learn how to connect these generators; to obtain their
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
MASSEY UNIVERSITY BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING with HONOURS TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORK ENGINEERING. Major Profile Description and Competency Framework
 Appendix 3.13 Telecommunications & Network Engineering Major Profile MASSEY UNIVERSITY BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING with HONOURS TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORK ENGINEERING Major Profile Description and Competency
Appendix 3.13 Telecommunications & Network Engineering Major Profile MASSEY UNIVERSITY BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING with HONOURS TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORK ENGINEERING Major Profile Description and Competency
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS
 SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe the different types of open single-phase motors used to drive
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe the different types of open single-phase motors used to drive
Design and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors
 Design and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors İbrahim ŞENGÖR, Abdullah POLAT, and Lale T. ERGENE Electrical and Electronic Faculty, İstanbul Technical University, 34469, Istanbul, TURKEY [email protected],
Design and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors İbrahim ŞENGÖR, Abdullah POLAT, and Lale T. ERGENE Electrical and Electronic Faculty, İstanbul Technical University, 34469, Istanbul, TURKEY [email protected],
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy Grid Integration. Jian Sun, Professor and Director Department of ECSE & Center for Future Energy Systems
 Smart Grid and Renewable Energy Grid Integration Jian Sun, Professor and Director Department of ECSE & Center for Future Energy Systems 1 How Smart Can We Make This Grid? 2 Smart Grid Drivers Need to Use
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy Grid Integration Jian Sun, Professor and Director Department of ECSE & Center for Future Energy Systems 1 How Smart Can We Make This Grid? 2 Smart Grid Drivers Need to Use
Electrical Drive Modeling through a Multiphysics System Simulation Approach
 Application Brief Electrical Drive Modeling through a The electric drive system is a key application in power electronics. Optimizing such complex mechatronic system requires in-depth analysis, expertise
Application Brief Electrical Drive Modeling through a The electric drive system is a key application in power electronics. Optimizing such complex mechatronic system requires in-depth analysis, expertise
E&I MAINTENANCE ENTRY TEST ENABLING OBJECTIVES. DESCRIBE hazards and precautions taken to avoid injury in the workplace.
 SAFETY Industrial DESCRIBE hazards and precautions taken to avoid injury in the workplace. Example #1: All of the following are common PPE used to perform maintenance activities EXCEPT: a. Safety Glasses
SAFETY Industrial DESCRIBE hazards and precautions taken to avoid injury in the workplace. Example #1: All of the following are common PPE used to perform maintenance activities EXCEPT: a. Safety Glasses
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
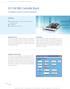 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
Power supplies. EE328 Power Electronics Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mutlu BOZTEPE Ege University, Dept. of E&E
 Power supplies EE328 Power Electronics Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mutlu BOZTEPE Ege University, Dept. of E&E EE328 POWER ELECTRONICS Outline of lecture Introduction to power supplies Modelling a power transformer
Power supplies EE328 Power Electronics Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mutlu BOZTEPE Ege University, Dept. of E&E EE328 POWER ELECTRONICS Outline of lecture Introduction to power supplies Modelling a power transformer
Advance Electronic Load Controller for Micro Hydro Power Plant
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 8 (2014) 1802-1810 D DAVID PUBLISHING Advance Electronic Load Controller for Micro Hydro Power Plant Dipesh Shrestha, Ankit Babu Rajbanshi, Kushal Shrestha and Indraman
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 8 (2014) 1802-1810 D DAVID PUBLISHING Advance Electronic Load Controller for Micro Hydro Power Plant Dipesh Shrestha, Ankit Babu Rajbanshi, Kushal Shrestha and Indraman
Electrical Engineering
 306 Electrical Engineering Paul Neudorfer, Ph.D., Chair Objectives Electrical engineering is concerned with the use of electrical energy for the benefit of society. The profession of electrical engineering
306 Electrical Engineering Paul Neudorfer, Ph.D., Chair Objectives Electrical engineering is concerned with the use of electrical energy for the benefit of society. The profession of electrical engineering
LINEAR MOTOR CONTROL IN ACTIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEMS
 LINEAR MOTOR CONTROL IN ACTIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEMS HONCŮ JAROSLAV, HYNIOVÁ KATEŘINA, STŘÍBRSKÝ ANTONÍN Department of Control Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University Karlovo
LINEAR MOTOR CONTROL IN ACTIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEMS HONCŮ JAROSLAV, HYNIOVÁ KATEŘINA, STŘÍBRSKÝ ANTONÍN Department of Control Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University Karlovo
Renewable Energy Sources Based Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor Drive
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 6 November 2014 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Renewable Energy Sources Based Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor Drive
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 6 November 2014 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Renewable Energy Sources Based Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor Drive
