Course: AG 534 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction
|
|
|
- Karen Anderson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course: AG 53 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction Unit Objective CAERT Lesson Plan Library Unit Problem Area Les son Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 1,2, 3 Introduction to Animal Science Match terms associated with an introduction to the livestock industry to their correct definitions. Introduction to Animal Science Name the types of livestock. Animal. Plant & Soil Science Introduction to Animal Science Name the products and services livestock provide. Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 2 Introduction to Animal Science Identify the sources of Idaho cash farm receipts. Introduction to Animal Science Identify Idaho s rank in the nation s agriculture for crops, livestock and livestock products. Introduction to Animal Science Distinguish between primary and secondary food sources. Introduction to Animal Science Describe reasons for and against using livestock Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 2 as a food source. Introduction to Animal Science List three specific careers in each of the seven Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 3 areas of livestock industry employment. Introduction to Animal Science Develop an opinion on the future of livestock Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 1 production.. Introduction to Animal Science Conduct a community survey on the types of livestock raised in the area. Introduction to Animal Science e familiar with current employment information in Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 3 the livestock industry. Introduction to Animal Science Explain general laboratory procedures, equipment Animal. Plant & Soil Science A 1 2- and report writing. Introduction to Animal Science Demonstrate the use of a compound microscope Agriscience C 3 1 The Organisms Define terms related to the organisms. Agriscience C 5 1 The Organisms List the seven categories of the classification system in order from largest to smallest. The Organisms Outline the classification system for humans. The Organisms The Organisms The Organisms List three traits that help place an organism into a kingdom. List and define the five kingdoms in the classification system. State two biological principles for each of the categories that demonstrate commonness among organisms. The Organisms Outline the classification of the major livestock animals in the United States. The Organisms Examine cells from the five kingdoms
2 The Organisms Classify organisms Cell Structure Match terms associated with cell structure to their Agriscience C 3 1 correct definitions. Cell Structure List three things which define a cell. Agriscience C 3 1 Cell Structure State the four basic ideas of the cell theory. Agriscience C 3 1 Cell Structure List three ways that cells can differ from one Agriscience C 3 1 another Cell Structure Label the correct parts of an animal cell Agriscience C 3 1 Cell Structure List and describe the cell components and their Agriscience C 3 1 functions. Cell Structure Name and describe the functions of the cell Agriscience C 3 1 organelles. Cell Structure Describe the difference between plant and animal Agriscience C 3 1 cells. Cell Structure List and describe the functions of the major types Agriscience C 5 2 of specialized animal cells. Cell Structure Identify and describe cells. Cell Structure Study cell parts. Agriscience C 3 1 Cell Structure Identify differences between plant and animals Agriscience C 3 1 cells. Functions of the Cell Match terms associated with cell function to the Agriscience C 3 1 correct definitions. Functions of the Cell Explain the different ways materials can pass iological Science Application 2 7 through a cell membrane (Cellular Transport). in Agriculture Functions of the Cell List three reasons why photosynthesis is the most Animal, Plant & Soil Science C 3 3 important process in the world. Functions of the Cell Explain the processes involved in photosynthesis. Animal, Plant & Soil Science C 3 3 Functions of the Cell List five factors that affect photosynthetic rate. Animal, Plant & Soil Science C 3 3 Functions of the Cell Explain the process of respiration. Functions of the Cell Outline the relationship between photosynthesis Animal, Plant & Soil Science C 3 and respiration. Functions of the Cell Explain the process of aerobic respiration. Animal, Plant & Soil Science C 3 Functions of the Cell Explain the process of fermentation. Animal, Plant & Soil Science C 3 Functions of the Cell Define homeostasis and explain how cells achieve this state. Functions of the Cell Study the movement of substances across iological Science Application 2 7 membranes. in Agriculture Animal Tissues, Systems and Describe the four primary animal tissues.
3 Animal Tissues, Systems and Identify the types of epithelial tissue when given a description of each. Animal Tissues, Systems and Identify the types of connective tissue when given a description of each. Animal Tissues, Systems and Identify the types of muscular tissue when given a description of each. Animal Tissues, Systems and Identify the types of nervous tissue when given a description of each. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the functions and list the three major organs Agriscience C 5 a of the circulatory system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the functions and list the seven major Agriscience C 5 2 organs of the digestive system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the function and list the two major organs of Agriscience C 5 2 the respiratory system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the function and list the two major organs of Agriscience C 5 2 the excretory system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the function and list the three major organs Agriscience C 5 2 of the nervous system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the function and list the major organ of the Agriscience C 5 2 endocrine system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the function and list the major organ of the Agriscience C 5 2 skeletal system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the function and lost the major organ of the Agriscience C 5 2 muscular system. Animal Tissues, Systems and State the function and list the two major organs of Agriscience C 5 2 the reproductive system. Animal Tissues, Systems and Discuss the nervous system anatomy. Agriscience C 5 2 Animal Tissues, Systems and Discuss the respiratory system. Agriscience C 5 2 Animal Tissues, Systems and Discuss the structure of the heart. Agriscience C 5 2 Define terms related to genetics and heredity. Animal, Plant & Soil Science iological Science in Ag Identify the phases of mitosis and meiosis. Explain why genes are important in animal iological Science in Ag breeding. List and describe the two ways in which genes control inherited traits. Animal, Plant & Soil Science iological Science in Ag Define dominant gene and recessive gene. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1
4 Define and give an example of incomplete Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 dominance. Demonstrate the use of the punnett square to predict the traits of the offspring when the male Animal, Plant & Soil Science iological Science in Ag and female carry heterozygous gene pairs of a given trait. Explain how the sex of the offspring is determined in mammals and poultry. Define and give and example of sex-linked characteristics. Animal, Plant & Soil Science iological Science in Ag Explain linkage, crossover and mutation. Animal, Plant & Soil Science iological Science in Ag Match traits of beef animals to their respective iological Science in Ag heritability estimates. Calculate estimated annual progress from genetic iological Science in Ag selection. Describe the components of the modified contemporary comparison system for dairy bull evaluation. List the pairs of chromosomes for each of the iological Science in Ag various species of livestock. Examine the phases of meiosis and mitosis. Predict inheritance. iological Science in Ag Study genetics by breeding fruit flies. Macroscopic Functional List the male primary and accessory sex organs Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 and the copulatory organ. Macroscopic Functional Describe the functions of the male reproductive Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 organs. Macroscopic Functional Label the reproductive tract of a bull. iological Science in Ag Macroscopic Functional Arrange in order the pathway of the spermatozoan iological Science in Ag in the male reproductive tract. Macroscopic Functional List four problems related to the temperature of the testes and the three structures that regulate the temperature. Macroscopic Functional Define monorchid and explain how it may be Macroscopic Functional determined in the stallion. Explain the cause of a scrotal hernia.
5 Macroscopic Functional Indicate where sperm is mixed with the accessory Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 fluids first to become semen. Macroscopic Functional Describe the differences between the penis iological Science in Ag structure of the bull and stallion. Microscopic of Define terms related to microscopic anatomy and spermatogenesis. Microscopic of Match cell types to their correct descriptions. Microscopic of Match reproductive organs to their correct cell types. Microscopic of Identify the types of cells found in the scrotum, parietal vaginal tunic, testis, visceral vaginal tunic and seminiferous tubules. Microscopic of Describe the function of the sustentacular cells. Microscopic of Identify the primary cells found in the seminiferous tubules. Microscopic of Explain spermatogenesis in detail, from its iological Science in Ag beginning to the mature spermatozoa. Microscopic of Diagram to show how many spermatozoa form iological Science in Ag from one spermatogonia. Microscopic of Indicate the number of days to complete iological Science in Ag spermatogenesis in the bull, ram and boar. Microscopic of List two factors that arrest spermatogenesis in iological Science in Ag bulls. Describe a hormone. Identify the complete hormone names from the abbreviations. Identify the action of the major reproductive hormones. Describe puberty. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 List and describe the factors affecting attainment Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 of puberty. Describe the relationship of size, weight and age to puberty. List and discuss factors to consider when selecting breeding stock at puberty. Define gonadotropic.
6 reeding Soundness Describe the functions of the four parts of the hypophysis. List the effects of testosterone on secondary sex Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 characteristics in the bull. List the bull-to-cow ration when using young bulls for the first time and when using mature bulls. Explain the process of mating. iological Science in Ag Describe the composition of semen. iological Science in Ag List the point of semen disposition in the female by the bull, ram, boar and stallion. Describe the passage of sperm through the tract iological Science in Ag during ejaculation. List the males that have fractionated ejaculated and describe t he three fractions of each. Describe the various methods of collecting semen and one advantage and disadvantage of each. Describe in detail the use of the artificial vagina iological Science in Ag for collecting semen from the bull, ram, boar and stallion. Describe in detail the use of the electroejaculate for collecting semen from the bull and ram. Name the parts of the sperm cell. iological Science in Ag Label the types of abnormal sperm. iological Science in Ag Describe the three factors used in semen evaluation. iological Science in Ag Describe the quality of bovine semen based on color, foreign material, wave pattern and progressive motility. Evaluate semen based on color, foreign material, wave pattern, motility and abnormal sperm. Collect and evaluate sperm. iological Science in Ag List and describe in detail the criteria used for evaluating the outward signs of fertility in the male.
7 reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness reeding Soundness List the internal reproductive organs that are evaluated for breeding soundness. Explain how the internal reproductive organs that are evaluated for breeding soundness. Describe two problems that may be found when evaluating the internal reproductive organs for breeding soundness. List and discuss the kinds of performance records which might be used when selecting breeding stock. Explain how a pedigree might be used when selecting breeding stock. List the desirable and undesirable characteristics to look for when evaluating beef breeding stock. Match the parts of a dairy cow to a description of how they should look in an ideal animal. Distinguish between desirable and undesirable general appearance, body capacity, mammary system and dairy character when evaluating dairy animals. Describe the components of the modified contemporary comparison system for bull evaluation. List desirable and undesirable characteristics of breeding swine. Describe the reasons for considering various selection factors when choosing quality swine breeding stock. Describe the primary difference between sheep selection and selection of other meat animals. List characteristics to avoid when selecting breeding sheep. Discuss the processing of fresh bull semen, including the extenders used. List and describe the three methods of processing frozen sperm. List the five components of semen extender. Explain how to calculate semen extension for processing fresh semen when given volume, Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 2 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 1- Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 1 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 2 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 2 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 2 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 3 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 3 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 Animal, Plant & Soil Science 2 iological Science in Ag 3 3-2
8 concentration, motility, normality, and number of viable cells per insemination. List six advantages and three disadvantages of packaging semen in straws. List four advantages and five disadvantages of packaging semen in ampules. List four advantages and six disadvantages of packaging semen in pellets. Explain which methos of selecting a sire is most effective. Explain what NR means. Identify the parts of the female reproductive tract. Animal, Plant & Soil Science iological Science in Ag Match the parts of the female reproductive tract to Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 their correct descriptions. iological Science in Ag List the order of the ovum pathway in the female Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 reproductive tract. iological Science in Ag Identify the function and the three portions of the broad ligament. List the three functions of the follicle. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 Describe the corpus hemorrhagicum. Describe the corpus luteum and state its function. Describe the corpus albicans and state its two functions. Describe the differences in the ovaries of the cow, ewe, sow, and mare. State the two general functions of the oviduct. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 Match structures of the oviduct with their correct functions and descriptions. Explain how the sow s oviduct differs from the cow s oviduct. Explain how the mare s oviduct differed from the cow s oviduct. Explain how the ewe s oviduct differs from the cow s oviduct.
9 Microscopic Female Functional Microscopic Female Functional Microscopic Female Functional Microscopic Female Functional Microscopic Female Functional Microscopic Female Functional Microscopic Female Functional List and describe the three types of uteruses. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 Describe the caruncles and state their function. Describe the uterus of the cow and ewe, sow and Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 the mare. List five functions of the uterus. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 List the three functions of the cervix. Describe the cow s cervix structure. Animal, Plant & Soil Science iological Science in Ag Describe how the cervix of the ewe, sow and mare differs from that of the cow. State the functions of the vagina. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 Describe the structure of the vagina. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 Describe and list the function of the vestibule. State the function of the vulva and clitoris. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 1 Examine the anatomy of the female reproductive tract. Describe in detail a follicle, corpus hemorrhagicum, corpus luteum, corpus albicans, and an atretic follicle. List and describe the steps in follicular growth. Describe cell division during oogenesis List the types of cells found in the oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina, vestibule and vulva. Indicate where the majority of the oocytes are located at birth. Explain how one would distinguish between a follicle and a corpus luteum by palpation in the cow. Indicate when the myometrium is most active iological Science in Ag 3 3-2
10 Female Female Female Female Female Female List the hormones originating in the hypothalamus, hypophysis and the gonads that are related to female reproduction. Identify the target organs of the various hormones related to female reproduction. Identify the action of each of the various hormones related to female reproduction. Describe the four factors related to puberty and their effects. List the ages and ranges for the onset of puberty in the various species. Explain why one would want to shorten the prepubertal interval. Describe the following terms: proestrus, estrus, metestrus, diestrus, an anestrus Describe in detail the symptoms of estrus in the cow. Describe in detail the symptoms of estrus in the ewe. Describe in detail the symptoms of estrus in the sow. Describe in detail the symptoms of estrus in the mare. Describe the growth of ovarian structures through an estrous cycle. Indicate the length of the estrous cycle for the cow, sow, ewe, and mare. Describe the activity of the oviduct at the time of ovulation. Explain the menstrual cycle and how the cyclic pattern of women differs from that of the domestic animals. List six advantages and four disadvantages of synchronized ovulation. List the various compounds used for ovulation control and the class (or classes) of livestock they are used for. Distinguish between the action of progesterone, progesterogens, and prostaglandins for ovulation control. iological Science in Ag Animal, Plant and Soils Science A iological Science in Ag 3 3-1
11 Explain why it is necessary to have a functional CL before suing prostaglandins. Explain why two injections of prostaglandins are iological Science in Ag needed to control ovulation. Explain why intramuscular injection requires a higher dosage than intrauterine injections. Explain the difference between prostaglandin and prostaglandin analogue. List the detrimental side effects that are present in swine when synchronized with progestogens. Outline a general plan for breeding sheep in anestrus. Outline a method for increasing the number of pigs per litter. List the four programs used to superovulate mares. State the hormone sequence that is used to superovulate a cow. Explain why one would want to breed calves before they normally reach puberty. List seven advantages of artificial insemination of iological Science in Ag the cow. List four disadvantages of artificial insemination of iological Science in Ag the cow. Describe the signs of estrus in cows. iological Science in Ag State which sign of estrus is the most important iological Science in Ag with regard to time of insemination. Describe the three methods of checking for estrus iological Science in Ag in cattle. List the necessary records need in an artificial iological Science in Ag insemination program. Explain the A.M. P.M. insemination rule. iological Science in Ag Indicate the optimum time for insemination for iological Science in Ag cows. Label equipment necessary for artificial iological Science in Ag insemination. Describe and outline the steps of the rectocervical iological Science in Ag technique for artificially inseminating a cow. Indicate the best temperature of thaw frozen semen to be used immediately. iological Science in Ag 3 1-3
12 List five advantages and three disadvantages of artificial insemination of the ewe. Explain why sheep artificial insemination is so poorly accepted in the United States. Discuss five areas of management of a sheep artificial insemination program. Indicate the optimum time of insemination for ewes. Describe and outline the steps of the speculum technique for artificially inseminating a ewe. List five advantages and five disadvantages of artificial insemination of the sow. Discuss three areas of management of a swine artificial insemination program. Fertilization and Embryo Describe the mechanisms involved in sperm and ovum transport. Fertilization and Embryo List in order the barriers to sperm penetration of the ovum. Fertilization and Embryo Define syngamy. Fertilization and Embryo Indicate where fertilization takes place. Fertilization and Embryo Indicate how long it takes sperm to reach the point of fertilization in the cow, ewe, and sow. Fertilization and Embryo Explain where sperm is deposited in the normal copulation of the horse. Fertilization and Embryo List six advantages and four disadvantages of embryo transplants. Fertilization and Embryo Discuss synchronization, condition, superovulation and insemination as related to embryo transfer. Fertilization and Embryo Describe the main reason for transferring embryos in swine. Fertilization and Embryo Describe in outline form the surgical procedure for embryo transplant in the cow. Fertilization and Embryo Describe in outline form the non-surgical procedure for embryo transplant in the cow. Fertilization and Embryo Describe in outline form the surgical procedure for embryo transplant in the ewe. Fertilization and Embryo Describe in outline form the surgical procedure for iological Science in Ag iological Science in Ag iological Science in Ag iological Science in Ag iological Science in Ag Animal, Plant and Soils Science
13 embryo transplant in the sow. Fertilization and Embryo Describe in outline form the non-surgical procedure for embryo transplant in the sow. Fertilization and Embryo Describe in outline form the non-surgical procedure for embryo transplant in the mare. Fertilization and Embryo Distinguish between good and bad eggs. iotechnology Define biotechnology. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 6 iotechnology List four broad applications of biotechnology in Animal, Plant & Soil Science 5 agriculture iotechnology List four common uses of biotechnology in agricultural science that have been around for Animal, Plant & Soil Science 5 6 some time. iotechnology List and explain the three major techniques of Animal, Plant & Soil Science 6 biotechnology. iotechnology Describe five current genetic research projects in plants of major impact on agriculture. iotechnology Describe five current genetic research projects in animals of major impact on agriculture. iotechnology List four areas of biotechnology applications in Animal, Plant & Soil Science 5 food processing. iotechnology Describe four areas of public concern about Animal, Plant & Soil Science 6 3 biotechnology. iotechnology Match the occurrence in the history of genetic engineering to the correct year of occurrence. iotechnology List eight areas of career opportunities in iotechnology biotechnology. List eight specific occupational titles in agricultural biotechnology. iotechnology Determine the ethics of biotechnology. Animal, Plant & Soil Science 6 3 iotechnology Research a career in biotechnology. iotechnology Make yogurt. List the gestation lengths for the cow, mare, sow and ewe. Describe the importance of progesterone to maintenance of pregnancy. Indicate the source of progesterone in the cow, mare, sow and ewe. List and describe the three stages of development of prenatal young.
14 Parturition and the Postpartum Parturition and the Postpartum Parturition and the Postpartum List and describe the three cell layers of the gastrula. List and describe the three extraembryonic membranes. List the age of the embryo developmental periods of the calf. List the age of the embryo developmental periods of the lamb. List the age of the embryo developmental periods of the pig. List the age of the embryo developmental periods of the foal. List the three types of placentae structure, the layers of cell types in each, and the species in which each is found. List and describe the three placentae shapes and the species in which each is found. List four reasons for pregnancy determination. Name five distinct indications of pregnancy detectable in rectal examination. Name the techniques used in pregnancy testing of ewes and sows. List the determining characteristics for age of the fetus in the cow at 30 days of gestation, 120 days of gestation, and 270 days of gestation. Pregnancy test a cow using rectal examination. Define terms associated with parturition and the postpartum period. List the six factors influencing parturition. Explain what changes occur in progesterone and estrogen at parturition in the cow, ewe, sow, and mare. Describe the process of parturition in the cow and ewe. Describe the process of parturition in the mare. Parturition and the Postpartum Parturition and the Postpartum Parturition and the Postpartum List the problems that may arise during the birth of
15 a calf and methods of alleviating them. Parturition and the Postpartum List the problems that may arise during the birth of a lamb and methods of alleviating them. Parturition and the Postpartum List the problems that may arise during the birth of piglets and the methods of alleviating them. Parturition and the Postpartum List the problems that may arise during the birth of a foal and the methods of alleviating them. Parturition and the Postpartum Discuss the relationship of the postpartum period to ensuing estrous activity and conception in the cow. Parturition and the Postpartum Discuss the relationship of the postpartum period to ensuing estrous activity and conception in the ewe. Parturition and the Postpartum Discuss the relationship of the postpartum period to ensuing estrous activity and conception in the sow. Parturition and the Postpartum Discuss the relationship of the postpartum period to ensuing estrous activity and conception in the mare. Reproductive Diseases Identify symptoms of major reproductive diseases. Reproductive Diseases List the necessary specimens needed for diagnosing by the veterinarian or diagnostic laboratory. Reproductive Diseases Identify the five diseases transmitted by coitus only (venereal diseases). Reproductive Diseases Describe the importance of preventive measures and the need for the veterinarian and diagnostic laboratory. Reproductive Diseases Indicate the hormone that may be deficient during gestation. Reproductive Diseases Explain what causes torsion of the umbilical cord and why it would cause abortion.
Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology
 Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Reproductive Anatomy and Fertility
 Describe the functions of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems. Analyze factors that affect male and female fertility. Outline the process of estrous and estrus. UNIT Objectives 4 Discuss
Describe the functions of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems. Analyze factors that affect male and female fertility. Outline the process of estrous and estrus. UNIT Objectives 4 Discuss
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction. Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Artificial Insemination in Cattle
 Artificial Insemination in Cattle Introduction This slide show is designed to introduce students to artificial insemination in cattle. However, it is only a brief overview and further training is necessary
Artificial Insemination in Cattle Introduction This slide show is designed to introduce students to artificial insemination in cattle. However, it is only a brief overview and further training is necessary
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
ANP 504 : ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION COURSE LECTURERS
 ANP 504 : ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION COURSE LECTURERS DR. A. O. LADOKUN DR. J. O. DR. J. A. DARAMOLA ABIONA COURSE OUTLINE PART I The Role of AI and Reproduction in Livestock Improvement 1. Advantages and
ANP 504 : ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION COURSE LECTURERS DR. A. O. LADOKUN DR. J. O. DR. J. A. DARAMOLA ABIONA COURSE OUTLINE PART I The Role of AI and Reproduction in Livestock Improvement 1. Advantages and
PRODUCERS can choose to use natural
 Artificial Insemination PRODUCERS can choose to use natural or artificial means of breeding their animals. Technology has advanced in the last 30 to 40 years to allow animal producers to use means other
Artificial Insemination PRODUCERS can choose to use natural or artificial means of breeding their animals. Technology has advanced in the last 30 to 40 years to allow animal producers to use means other
A POWERFUL IN VITRO FERTILIZATION
 A POWERFUL During the past 50 years technological advances in the field of bovine reproduction have led to some dramatic changes in the way cattle look, reproduce, perform, and even taste. Artificial Insemination
A POWERFUL During the past 50 years technological advances in the field of bovine reproduction have led to some dramatic changes in the way cattle look, reproduce, perform, and even taste. Artificial Insemination
ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015)
 1 ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015) Instructor: Dr. Eduardo L. Gastal, DVM, MS, PhD Room: AG 129; Phone: 453-1774; E-mail: [email protected] Office hours: MWF 11-12 a.m.;
1 ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015) Instructor: Dr. Eduardo L. Gastal, DVM, MS, PhD Room: AG 129; Phone: 453-1774; E-mail: [email protected] Office hours: MWF 11-12 a.m.;
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Tech Prep Articulation
 Tech Prep Articulation Agriculture & Natural Resources Tech Prep Education: Tech Prep education in Missouri is an articulated two-year secondary and two or more year post-secondary education program which:
Tech Prep Articulation Agriculture & Natural Resources Tech Prep Education: Tech Prep education in Missouri is an articulated two-year secondary and two or more year post-secondary education program which:
Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle
 AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
Proceedings, Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle September 11 and 12, 2007, Billings, Montana NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REPRODUCTION IN CATTLE
 Proceedings, Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle September 11 and 12, 2007, Billings, Montana NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REPRODUCTION IN CATTLE George E. Seidel, Jr. Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology
Proceedings, Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle September 11 and 12, 2007, Billings, Montana NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REPRODUCTION IN CATTLE George E. Seidel, Jr. Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproductive technologies. Lecture 15 Introduction to Breeding and Genetics GENE 251/351 School of Environment and Rural Science (Genetics)
 Reproductive technologies Lecture 15 Introduction to Breeding and Genetics GENE 251/351 School of Environment and Rural Science (Genetics) Animal Breeding in a nutshell Breeding objectives Trait measurement
Reproductive technologies Lecture 15 Introduction to Breeding and Genetics GENE 251/351 School of Environment and Rural Science (Genetics) Animal Breeding in a nutshell Breeding objectives Trait measurement
INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION APICHAI POONCHAI D.V.M.
 INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION APICHAI POONCHAI D.V.M. In natural mating a bull mounts a cow & ejuculates his semen in her vagina INTRODUCTION In A.I. Semen is collected from a bull in an artificial
INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION APICHAI POONCHAI D.V.M. In natural mating a bull mounts a cow & ejuculates his semen in her vagina INTRODUCTION In A.I. Semen is collected from a bull in an artificial
Artificial Insemination (AI) in Cattle
 Artificial Insemination (AI) in Cattle Most dairy cows are bred by AI Less common in beef cattle Commonly, bulls are used for all breeding under pasture conditions Less commonly, bulls are used as clean-up
Artificial Insemination (AI) in Cattle Most dairy cows are bred by AI Less common in beef cattle Commonly, bulls are used for all breeding under pasture conditions Less commonly, bulls are used as clean-up
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Artificial Insemination in Cattle. Objectives. What are the advantages and disadvantages of AI?
 ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Artificial Insemination in Cattle Objectives 1) To provide an overview of the process of artificial insemination (AI) in cattle. 2) To gain an understanding
ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Artificial Insemination in Cattle Objectives 1) To provide an overview of the process of artificial insemination (AI) in cattle. 2) To gain an understanding
Terms: The following terms are presented in this lesson (shown in bold italics and on PowerPoint Slides 2 and 3):
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
Impact of reproductive technologies on improved genetics in beef cattle
 Impact of reproductive technologies on improved genetics in beef cattle JE Kinder 1, JM Osborne 1, ME Davis 1, ML Day 1 1 The Ohio State University, Department of Animal Sciences, Columbus, Ohio 43210,
Impact of reproductive technologies on improved genetics in beef cattle JE Kinder 1, JM Osborne 1, ME Davis 1, ML Day 1 1 The Ohio State University, Department of Animal Sciences, Columbus, Ohio 43210,
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Artificial Insemination Programs for Cattle
 Artificial Insemination Programs for Cattle Use of Artificial Insemination Artificial insemination (AI) is the most widely used assisted reproductive technology. Although AI is much more widely used in
Artificial Insemination Programs for Cattle Use of Artificial Insemination Artificial insemination (AI) is the most widely used assisted reproductive technology. Although AI is much more widely used in
licle by expressing estrus (heat) and producing an LH surge. The LH surge causes ovulation, which begins the heifer s first cycle.
 publication 400-02 Estrus Synchronization for Heifers John B. Hall, Department of Animal and Poultry Sciences, Virginia Tech Amanda Liles, Department of Animal and Poultry Sciences, Virginia Tech W. Dee
publication 400-02 Estrus Synchronization for Heifers John B. Hall, Department of Animal and Poultry Sciences, Virginia Tech Amanda Liles, Department of Animal and Poultry Sciences, Virginia Tech W. Dee
Artificial Insemination in Dairy Cattle 1
 Whole Document Navigator (Click Here) Artificial Insemination in Dairy Cattle 1 D. W. Webb 2 Artificial insemination (AI) is a process by which sperm are collected from the male, processed, stored and
Whole Document Navigator (Click Here) Artificial Insemination in Dairy Cattle 1 D. W. Webb 2 Artificial insemination (AI) is a process by which sperm are collected from the male, processed, stored and
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE
 UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE I (180)
 DESCRIPTION The first assessment in a series, Agricultural Science I provides foundational knowledge for careers in animal science, plant science, horticulture, natural resources, or agricultural systems
DESCRIPTION The first assessment in a series, Agricultural Science I provides foundational knowledge for careers in animal science, plant science, horticulture, natural resources, or agricultural systems
Articulated Credit. Agriculture & Natural Resources Tech Prep Education:
 Articulated Credit Agriculture & Natural Resources Tech Prep Education: Tech Prep education in Missouri is an articulated two-year secondary and two or more year post-secondary education program which:
Articulated Credit Agriculture & Natural Resources Tech Prep Education: Tech Prep education in Missouri is an articulated two-year secondary and two or more year post-secondary education program which:
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Unit #5 Human Growth and Development 6 th Grade - Chapter 7, 8 7 th Grade - Chapter 12 8 th Grade - Chapter 16, 17
 8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
Small Animal Science and Technology
 Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Test Code: 2003 / Version: 01 Copyright 2011 General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information Written Assessment
Measuring What Matters in Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Test Code: 2003 / Version: 01 Copyright 2011 General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information Written Assessment
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit B: Anatomy and Physiology of Poultry Lesson 4: Artificial Poultry Reproduction Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit B: Anatomy and Physiology of Poultry Lesson 4: Artificial Poultry Reproduction Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial Insemination (AI) and Oestrus Synchronisation of Beef Cattle
 Artificial Insemination (AI) and Oestrus Synchronisation of Beef Cattle Information compiled by Endell Veterinary Group, Paragon Veterinary Group and RAFT Solutions/Bishopton Cattle Breeding Services.
Artificial Insemination (AI) and Oestrus Synchronisation of Beef Cattle Information compiled by Endell Veterinary Group, Paragon Veterinary Group and RAFT Solutions/Bishopton Cattle Breeding Services.
GnRH Based Estrus Synchronization Systems for Beef Cows
 GnRH Based Estrus Synchronization Systems for Beef Cows John B. Hall, Extension Animal Scientist, Beef, Virginia Tech W. Dee Whittier, Extension Specialist and Professor, Virginia-Maryland Regional College
GnRH Based Estrus Synchronization Systems for Beef Cows John B. Hall, Extension Animal Scientist, Beef, Virginia Tech W. Dee Whittier, Extension Specialist and Professor, Virginia-Maryland Regional College
G. Cliff Lamb. North Florida Research and Education Center, Marianna, Florida University of Florida. Introduction
 COST ANALYSIS OF IMPLEMENTING A SYNCHRONIZATION OR AI PROGRAM-USING DECISION-AID TOOLS G. Cliff Lamb North Florida Research and Education Center, Marianna, Florida University of Florida Introduction Estrous
COST ANALYSIS OF IMPLEMENTING A SYNCHRONIZATION OR AI PROGRAM-USING DECISION-AID TOOLS G. Cliff Lamb North Florida Research and Education Center, Marianna, Florida University of Florida Introduction Estrous
Appendix J. Genetic Implications of Recent Biotechnologies. Appendix Contents. Introduction
 Genetic Improvement and Crossbreeding in Meat Goats Lessons in Animal Breeding for Goats Bred and Raised for Meat Will R. Getz Fort Valley State University Appendix J. Genetic Implications of Recent Biotechnologies
Genetic Improvement and Crossbreeding in Meat Goats Lessons in Animal Breeding for Goats Bred and Raised for Meat Will R. Getz Fort Valley State University Appendix J. Genetic Implications of Recent Biotechnologies
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Animal Sciences. Timed-Artificial Insemination in Beef Cows: What are the Options?
 Purdue Extension Animal Sciences AS-575-W Timed-Artificial Insemination in Beef Cows: What are the Options? Allen Bridges, Scott Lake, Ron Lemenager, and Matt Claeys, Purdue Beef Team, Department of Animal
Purdue Extension Animal Sciences AS-575-W Timed-Artificial Insemination in Beef Cows: What are the Options? Allen Bridges, Scott Lake, Ron Lemenager, and Matt Claeys, Purdue Beef Team, Department of Animal
MINISTRY OF LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT SMALLHOLDER DAIRY COMMERCIALIZATION PROGRAMME. Artificial Insemination (AI) Service
 MINISTRY OF LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT SMALLHOLDER DAIRY COMMERCIALIZATION PROGRAMME Artificial Insemination (AI) Service 1 1.0 Introduction The fertility of a dairy cattle is very important for a dairy farmer
MINISTRY OF LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT SMALLHOLDER DAIRY COMMERCIALIZATION PROGRAMME Artificial Insemination (AI) Service 1 1.0 Introduction The fertility of a dairy cattle is very important for a dairy farmer
Beef Cattle Handbook
 Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-1000 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Adapted from Beef Improvement Federation Beef Performance Glossary John Hough, Amercian Hereford Association David Notter,
Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-1000 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Adapted from Beef Improvement Federation Beef Performance Glossary John Hough, Amercian Hereford Association David Notter,
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Master Curriculum Topic Study: Human Body Systems
 Master Curriculum Topic Study: Human Body Systems Session C Section I: Culminating Ideas for Adult Literacy 1. The fundamental building block of organisms is cells. a. Cells combine to form tissues, which
Master Curriculum Topic Study: Human Body Systems Session C Section I: Culminating Ideas for Adult Literacy 1. The fundamental building block of organisms is cells. a. Cells combine to form tissues, which
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
TIMING THE FERTILE PERIOD OF THE BITCH: BRIEF REVIEW
 TIMING THE FERTILE PERIOD OF THE BITCH: BRIEF REVIEW Canine Reproduction Seminar Dr. Scarlette Gotwals Stages of the Estrous Cycle Proestrus: Estrus: Diestrus: Anestrus: Vulvar swelling and bloody vaginal
TIMING THE FERTILE PERIOD OF THE BITCH: BRIEF REVIEW Canine Reproduction Seminar Dr. Scarlette Gotwals Stages of the Estrous Cycle Proestrus: Estrus: Diestrus: Anestrus: Vulvar swelling and bloody vaginal
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Artificial Reproductive Technologies I: insemination
 Artificial Reproductive Technologies I: insemination Cinzia Allegrucci LO s List the main advantages and disadvantages of artificial insemination (AI) Explain methods for evaluating volume and concentration,
Artificial Reproductive Technologies I: insemination Cinzia Allegrucci LO s List the main advantages and disadvantages of artificial insemination (AI) Explain methods for evaluating volume and concentration,
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A COMPARISON OF SEMEN THAWING FOR ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION IN CATTLE MIR CENTER, ANGELO STATE UNIVERSITY, SAN ANGELO, TEXAS
 A COMPARISON OF SEMEN THAWING FOR ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION IN CATTLE MIR CENTER, ANGELO STATE UNIVERSITY, SAN ANGELO, TEXAS A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Angelo State University
A COMPARISON OF SEMEN THAWING FOR ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION IN CATTLE MIR CENTER, ANGELO STATE UNIVERSITY, SAN ANGELO, TEXAS A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Angelo State University
Artificial Insemination Training Program
 Artificial Insemination Training Program HISTORY First AI research reports 200 years ago. A long ago, Arabs obtained semen from mated mares belonging to rival groups during night hours to inseminate their
Artificial Insemination Training Program HISTORY First AI research reports 200 years ago. A long ago, Arabs obtained semen from mated mares belonging to rival groups during night hours to inseminate their
Herd Navigator and reproduction management
 Herd Navigator and reproduction management 1. Reproductive management Efficient and profitable reproduction management in a dairy herd requires routine and time-consuming manual heat detection and proper
Herd Navigator and reproduction management 1. Reproductive management Efficient and profitable reproduction management in a dairy herd requires routine and time-consuming manual heat detection and proper
Animal Pharming: The Industrialization of Transgenic Animals December 1999
 Animal Pharming: The Industrialization of Transgenic Animals December 1999 Animal pharming, the process of using transgenic animals to produce human drugs, is staking its claim in a lucrative world market.
Animal Pharming: The Industrialization of Transgenic Animals December 1999 Animal pharming, the process of using transgenic animals to produce human drugs, is staking its claim in a lucrative world market.
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
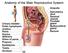 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
THE STIMULATION OF OVULATION DURING HIGH TEMPERATURE, AN TECHNIQUE OF FERTILITY INCREASING IN COWS
 THE STIMULATION OF OVULATION DURING HIGH TEMPERATURE, AN TECHNIQUE OF FERTILITY INCREASING IN COWS TURMALAJ L.*; RAPTI DH.*; LIKA E.*; GRIZELJ J.**; VINCE S.** * Veterinary Medicine Faculty, Tirane, Albania.
THE STIMULATION OF OVULATION DURING HIGH TEMPERATURE, AN TECHNIQUE OF FERTILITY INCREASING IN COWS TURMALAJ L.*; RAPTI DH.*; LIKA E.*; GRIZELJ J.**; VINCE S.** * Veterinary Medicine Faculty, Tirane, Albania.
BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER
 BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER Good management No shortcuts PLAN AHEAD AVOID STRESS Some examples of how stress is induced are: Mixing groups or individual animals together that have not previously been together.
BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER Good management No shortcuts PLAN AHEAD AVOID STRESS Some examples of how stress is induced are: Mixing groups or individual animals together that have not previously been together.
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
2016 Protocols for Synchronization of Estrus and Ovulation in Beef Cows and Heifers
 2016 Protocols for Synchronization of Estrus and Ovulation in Beef Cows and Heifers Biotechnology presents beef producers with an unprecedented opportunity to improve herd genetics. Producers have more
2016 Protocols for Synchronization of Estrus and Ovulation in Beef Cows and Heifers Biotechnology presents beef producers with an unprecedented opportunity to improve herd genetics. Producers have more
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY: Academic Explorations Grades 7 and 8
 Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY: Academic Explorations Grades 7 and 8 Text: Mader s Understanding Human Anatomy & Physiology; 7 th Edition. TOPIC/OBJECTIVES HOW 1 Welcome and Introduction Ice Breaker
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY: Academic Explorations Grades 7 and 8 Text: Mader s Understanding Human Anatomy & Physiology; 7 th Edition. TOPIC/OBJECTIVES HOW 1 Welcome and Introduction Ice Breaker
Reproductive Management of Sheep and Goats
 A l a b a m a A & M a n d A u b u r n U n i v e r s i t i e s ANR-1316 Reproductive Management of Sheep and Goats The success of a sheep and goat operation depends on the number of lambs and kids raised,
A l a b a m a A & M a n d A u b u r n U n i v e r s i t i e s ANR-1316 Reproductive Management of Sheep and Goats The success of a sheep and goat operation depends on the number of lambs and kids raised,
Von Mäusen und Menschen E - 1
 Von Mäusen und Menschen E - 1 Mus musculus: Genetic Portrait of the House Mouse E - 3 Outline Mouse genome Mouse life cycle Transgenic protocols Addition of genes by nuclear injection Removal of genes
Von Mäusen und Menschen E - 1 Mus musculus: Genetic Portrait of the House Mouse E - 3 Outline Mouse genome Mouse life cycle Transgenic protocols Addition of genes by nuclear injection Removal of genes
Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers
 Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright CIBT This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the direction of the original recipient. All
Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Copyright CIBT This work may be copied by the original recipient from CIBT to provide copies for users working under the direction of the original recipient. All
THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS. J. S. Stevenson
 Dairy Day 1998 THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS J. S. Stevenson Summary Management of the estrous cycle is now more practical than it was a decade ago because of our understanding
Dairy Day 1998 THE WHY, HOW-TO, AND COST OF PROGRAMED AI BREEDING OF DAIRY COWS J. S. Stevenson Summary Management of the estrous cycle is now more practical than it was a decade ago because of our understanding
Revised Spring 2006 1
 It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
ANIMAL GENETICS SOLUTIONS
 THE NATIONAL ANIMAL GENETIC RESOURCES CENTRE AND DATABANK NAGRC & DB) COLLABORATION WITH IAEA AND OTHER STAKEHOLDERS IN ANGR DEVELOPMENT INTERLAKEN, SWITZERLAND SEPT. 2007 ANIMAL GENETICS SOLUTIONS Vision
THE NATIONAL ANIMAL GENETIC RESOURCES CENTRE AND DATABANK NAGRC & DB) COLLABORATION WITH IAEA AND OTHER STAKEHOLDERS IN ANGR DEVELOPMENT INTERLAKEN, SWITZERLAND SEPT. 2007 ANIMAL GENETICS SOLUTIONS Vision
Artificial Insemination of Cattle
 Artificial Insemination of Cattle Animal Reproduction: 3850N Jacky Whitehead Nicole Black April 5, 2006 With the global market becoming so interdependent, it has opened the doors for livestock producers,
Artificial Insemination of Cattle Animal Reproduction: 3850N Jacky Whitehead Nicole Black April 5, 2006 With the global market becoming so interdependent, it has opened the doors for livestock producers,
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
MCAS Biology. Review Packet
 MCAS Biology Review Packet 1 Name Class Date 1. Define organic. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2. All living things are made up of 6 essential elements: SPONCH. Name the six elements of life. S N P C O H 3. Elements
MCAS Biology Review Packet 1 Name Class Date 1. Define organic. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2. All living things are made up of 6 essential elements: SPONCH. Name the six elements of life. S N P C O H 3. Elements
Dr. G van der Veen (BVSc) Technical manager: Ruminants [email protected]
 Dr. G van der Veen (BVSc) Technical manager: Ruminants [email protected] GENETICS NUTRITION MANAGEMENT Improved productivity and quality GENETICS Breeding programs are: Optimize genetic progress
Dr. G van der Veen (BVSc) Technical manager: Ruminants [email protected] GENETICS NUTRITION MANAGEMENT Improved productivity and quality GENETICS Breeding programs are: Optimize genetic progress
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION STUDY
 ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION STUDY KOSOVO CLUSTER AND BUSINESS SUPPORT PROJECT 30 September 2005 This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development. It was prepared
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION STUDY KOSOVO CLUSTER AND BUSINESS SUPPORT PROJECT 30 September 2005 This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development. It was prepared
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
CURRICULUM MAP (Revised 6.15.07)
 (Revised 6.15.07) Below is an outline of the Living Environment course that uses the Glencoe NY State Living Environment textbook. Please note that there is more depth in the book than is needed for the
(Revised 6.15.07) Below is an outline of the Living Environment course that uses the Glencoe NY State Living Environment textbook. Please note that there is more depth in the book than is needed for the
(Received 29th July 1963)
 EGG TRANSFER IN SHEEP EFFECT OF DEGREE OF SYNCHRONIZATION BETWEEN DONOR AND RECIPIENT, AGE OF EGG, AND SITE OF TRANSFER ON THE SURVIVAL OF TRANSFERRED EGGS N. W. MOORE and J. N. SHELTON Jf.S. W. and The
EGG TRANSFER IN SHEEP EFFECT OF DEGREE OF SYNCHRONIZATION BETWEEN DONOR AND RECIPIENT, AGE OF EGG, AND SITE OF TRANSFER ON THE SURVIVAL OF TRANSFERRED EGGS N. W. MOORE and J. N. SHELTON Jf.S. W. and The
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
Animal Reproduction. Male Reproduction. # lectures for cumulative test # 02 book 12. Reproductive cyclicity: terminology and basic concepts 1-9 13
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, [email protected] 17 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, [email protected] 17 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Life Cycles. Background. Procedure
 Purpose: This lesson introduces students to the six major livestock species raised in Minnesota. Students will learn terms for mothers, fathers, and young and explore the life cycle of a typical farm animal.
Purpose: This lesson introduces students to the six major livestock species raised in Minnesota. Students will learn terms for mothers, fathers, and young and explore the life cycle of a typical farm animal.
Pregnancy Rates Per Artificial Insemination for Cows and Heifers Inseminated at a Synchronized Ovulation or Synchronized Estrus 1
 Pregnancy Rates Per Artificial Insemination for Cows and Heifers Inseminated at a Synchronized Ovulation or Synchronized Estrus 1 J. R. PURSLEY,*,2 M. C. WILTBANK,*,3 J. S. STEVENSON, J. S. OTTOBRE, H.
Pregnancy Rates Per Artificial Insemination for Cows and Heifers Inseminated at a Synchronized Ovulation or Synchronized Estrus 1 J. R. PURSLEY,*,2 M. C. WILTBANK,*,3 J. S. STEVENSON, J. S. OTTOBRE, H.
Department of Physiology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine University of Khartoum. Proposal for M. Sc. in Applied Physiology (Courses and Dissertation)
 Department of Physiology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine University of Khartoum Proposal for M. Sc. in Applied Physiology (Courses and Dissertation) 1 1. Introduction: The Department of Physiology is a
Department of Physiology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine University of Khartoum Proposal for M. Sc. in Applied Physiology (Courses and Dissertation) 1 1. Introduction: The Department of Physiology is a
240Tutoring Life Science Study Material
 240Tutoring Life Science Study Material This information is a sample of the instructional content and practice questions found on the 240Tutoring GACE Early Childhood Education. This information is meant
240Tutoring Life Science Study Material This information is a sample of the instructional content and practice questions found on the 240Tutoring GACE Early Childhood Education. This information is meant
Artificial Insemination Technique. Dairy Integrated Reproductive Management. Dr. M.L. O Connor The Pennsylvania State University. Reproductive Anatomy
 Artificial Insemination Technique IRM-12 Dairy Integrated Reproductive Management Dr. M.L. O Connor The Pennsylvania State University Many dairy producers are artificially breeding their own cattle. A
Artificial Insemination Technique IRM-12 Dairy Integrated Reproductive Management Dr. M.L. O Connor The Pennsylvania State University Many dairy producers are artificially breeding their own cattle. A
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 th Edition, 2015 Marieb
 A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy Marieb To the Next Generation Science Standards Life A Correlation of, HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct an explanation
A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy Marieb To the Next Generation Science Standards Life A Correlation of, HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct an explanation
REPRODUCTION IN DONKEYS
 REPRODUCTION IN DONKEYS Stephen R. Purdy, DVM Department of Veterinary and Animal Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA INTRODUCTION This is an overview of the practical aspects of male and
REPRODUCTION IN DONKEYS Stephen R. Purdy, DVM Department of Veterinary and Animal Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA INTRODUCTION This is an overview of the practical aspects of male and
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
