Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
|
|
|
- Tabitha Judith Marshall
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS: WHAT ADVANCE PREPARATION, IF ANY, IS REQUIRED OF THE TEACHER FOR THIS LESSON? Review Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems due to large number of terms and definitions. LEARNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this lesson learners will be able to: 1) Locate and name at least five parts of each of the male and female reproductive systems. [knowledge] LIFE SKILLS DEMONSTRATED IN THIS LESSON: 1) Seek information about sexual and reproductive anatomy. RESOURCE MATERIALS FOR TEACHER: Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems MATERIALS FOR LEARNER: None
2 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I This lesson is enhanced when learners have the following background knowledge: Content from the International Technical Guidance on Sexuality Education Key Concept 4 Human Development; 4.1 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology; Level I PROCEDURE: Step 1) 5 minutes Begin the lesson by informing learners that, Today we are going to learn about the human reproductive system. The male and female reproductive systems are composed of external and internal organs. Ask students what function the reproductive system has in our bodies. Responses should include: To produce the sperm and egg cells that allow us to reproduce To transport and sustain these cells To nurture the developing offspring To produce hormones Next, explain by saying, The lesson will provide an overview of the body parts that everyone has that allow them to reproduce later in life, if they so choose, and explain the functions of each of the reproductive organs. Understanding one s body and how it works is important to staying healthy. Step 2) 35 minutes Write on the chalkboard three columns: Male/Female/Both. Explain the activity by saying the following, Next we will brainstorm the sexual and reproductive anatomy we all have and try to determine if it s a male part, female part, or body part everyone has. Let s also keep in mind that some people s bodies don t fit neatly into one category or another and they might be born with ambiguous genitalia. Those people are called intersex and see me if you want more information about that. Let s now think of the names of the parts of the body, both inside and outside, that are part of the reproductive system. [Teacher s Note: For more information about intersex, please go to Intersex-Ally.pdf] Write the body parts in the correct column on the board using the Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems. Add in any body parts the class does not list. As you list the body parts in one of the three columns, briefly define each reproductive body part, where it is in the body and what it does. Use the Reproductive Visuals 4 5 to aid with the review of the male and female reproductive systems as appropriate. [Teacher s Note: Please do not feel that you must convey every bit of information in the Teacher Background. Most of the information is provided as background on Reproductive Systems for you and to allow you to supplement what your learners know and are curious about.] Step 3) 5 minutes Conclude by telling learners that these are the main sexual and reproductive male and female body parts, each with a very specific function. Explain that the second part of the lesson on another day will allow learners to better understand how the parts on the inside of the body work. Ask learners the following question and have each learner share their response in rapid succession. What is one new piece of information you are leaving today s lesson with?
3 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I KEY MESSAGES OF LESSON: 1) Knowing the male and female reproductive anatomy and the function of each part is important to understanding how your body works and to ultimately staying healthy. ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES AT CONCLUSION OF LESSON: Teachers can have learners list at least two body parts and their functions for females and two body parts for males on a piece of paper to submit for assessment of the learning objectives. HOMEWORK WITH FOCUS ON FAMILY INVOLVEMENT ACTIVITIES: None POSSIBLE ADAPTATIONS: Large class size None Limited materials/technology None Adapted from: Family Life and Sexual Health High School Version, Lesson 2: Reproductive System; Public Health Seattle & King County, Revised
4 Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems MALE PART PENIS (made up of shaft, glans, and foreskin) FORESKIN WHAT IT IS / WHAT IT DOES Allows passage of urine and semen Provides sensation (has many nerve endings) The average penis measures 3 4 inches when it's not erect (flaccid) and 5 7 inches when erect Protects the glans of the penis Provides sensation Males who have been circumcised don t have one SCROTUM Muscular sac which is shorter when cold, longer when warm Holds testes Controls temperature Provides sensation TESTES (also called testicles) EPIDIDYMIS SPERMATAZOA (sperm) SPERMATIC CORDS Produces sperm and sex hormones (androgens and testosterone) Each is made of 500 1,200 feet of tightly coiled tubes Allows maturation of sperm Cell from a man called sperm Sperm carry the strings of genes (called chromosomes) or DNA instructions in case the sperm meets with an egg cell and fertilizes it Suspends the testicles Supply blood to the testicles Provide sensation Carry sperm from the testicles VAS DEFERENS Provides storage for sperm Allow passage of sperm Provides sensation Carries sperm from the testes
5 Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems MALE PART SEMINAL VESICLES SEMEN WHAT IT IS / WHAT IT DOES Contributes fructose (sugar) to semen for nourishing the sperm Helps sperm live longer and travel better About a teaspoon per ejaculation Contains hundreds of millions of sperm PROSTATE GLAND Produces most of the fluid that makes up semen COWPER S GLAND (also called bulbourethral glands) Pair of glands Produces pre ejaculatory fluid (called pre cum ) that cleans the urethra to protect sperm. Some pre ejaculatory fluid may contain sperm
6 Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems FEMALE PART UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) CERVIX WHAT IT IS / WHAT IT DOES Houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby Allows nutrient & waste exchange with placenta during pregnancy Nourishes an embryo before a placenta grows The bottom section of the uterus Produces fluids to help sperm travel Produces a mucus plug to keep out germs during pregnancy VAGINA Allows passage of sperm Produces fluid daily to cleanse and lubricate itself and help sperm travel Allows passage of shed endometrium during menstrual period Allows passage of baby Provides sensation (has many nerve endings especially in outer third) A collapsed tube, like a deflated balloon Three inches long when not aroused and five to six inches long when aroused and very stretchy Is the middle of the three openings between a female s legs HYMEN Membrane some females have that partly covers the vaginal opening Some girls are both without a hymen May be stretched during use of a tampon, having finger inserted or during sexual intercourse OVUM (also called egg cell ) Carries strings of genes called chromosomes which mix with chromosomes of sperm if fertilization occurs They dissolve in the Fallopian tube after about 24 hours if not fertilized
7 Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems FEMALE PART OVARY WHAT IT IS / WHAT IT DOES Provide storage for the ovum (eggs) Allow maturation of the ovum Produce sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone and androgens) FALLOPIAN TUBES Allow passage of ovum toward uterus Allow passage of sperm from uterus FIMBRIA Guides a mature ovum, when it is released from an ovary, into a Fallopian tube Fringe like or finger like outer ends of the Fallopian tubes SKENE S GLANDS Area of firm tissue towards the front wall of the vagina surrounding the urethra Responds to pressure sometimes causing orgasm that may or may not produce fluid (the fluid is not urine) Also known as the Graffenberg spot (G spot) or the female prostate gland VULVA (made up of labia majora, labia minora, and clitoris) Protect opening of urethra and vagina, as eyelids protect eyes Provide sensation (has many nerve endings) Labia are folds of skin Outer labia (labia majora) have pubic hair CLITORIS (made up of shaft, crura [internal branches], glans and hood) CLITORIAL HOOD Provides sensation (has many nerve endings) Each internal branch of erectile tissue is about 3.5 inches long The glans (the visible part) is usually.25.5 inches long, comparable in size to a pearl at the front of the vulva where the labia meet Protects the glans of the clitoris Provides sensation (has many nerve endings) Like a cap, mostly covers the clitoris when it is not erect
8 Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems BOTH MALE AND FEMALE NAVEL WHAT IT IS / WHAT IT DOES Allows passage of oxygen and nourishment before birth After birth it serves no purpose Not part of the reproductive system ABDOMEN (also called the belly) BUTTOCKS Contains most of our internal organs The part of the body between the rib cage and pelvis Provides cushion for tail bone and aids in walking and standing Contains muscle for movement Not part of the reproductive system PELVIS Bowl shaped bone structure that supports and protects the internal reproductive organs Men s and women s pelvises are shaped differently so that women can give birth if they choose CILIA BLADDER Hair like structures which line the Fallopian tubes and the epididymis Sweep an ovum down the Fallopian tube or the sperm cells through the epididymis Provides storage for urine Not part of the reproductive system URETHRA Allows passage of urine In males allows passage of semen In males is the tube inside the penis In females it is below the clitoris and above the opening to the vagina Not part of the reproductive system Some females ejaculate a clear fluid that is not urine from their urethra during orgasm. This is normal and natural and women should not think they are urinating during orgasm if this happens. ANUS Allows passage of bowel movements (feces) Provides sensation (has many nerve endings) The opening from the rectum and lower intestines Not part of the reproductive system
9 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part II TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part II SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS: WHAT ADVANCE PREPARATION, IF ANY, IS REQUIRED OF THE TEACHER FOR THIS LESSON? Review Teacher Background on Reproductive Systems from Part I due to large number of terms and definitions. Make copies of materials listed below and prepare visuals needed for lesson. Prepare enlarged illustrations of the male and female genitals and reproductive organs for classes that are bigger than 25. LEARNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this lesson learners will be able to: 1) Describe the path of an egg (ovum) during menstruation. [knowledge] 2) Describe the path of a sperm during ejaculation. [knowledge] 3) Understand there is a wide range of normal anatomy. [knowledge] LIFE SKILLS DEMONSTRATED IN THIS LESSON: 1) Seek information about sexual and reproductive anatomy. 2) Collaborate with others to put the reproductive system together in a small group activity. RESOURCE MATERIALS FOR TEACHER: Reproductive System Visuals 4 5 (made larger if not distributing to students) Labelled body parts for classroom activity, one set per class or small group Seven pairs of scissors Chalkboard and chalk A few pieces of tape MATERIALS FOR LEARNER: Reproductive System Worksheets 4 5 ONLY One copy per learner
10 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part II This lesson is enhanced when learners have the following background knowledge: Content from the International Technical Guidance on Sexuality Education Key Concept 4 Human Development; 4.1 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology; Level I PROCEDURE: Step 1) 2 minutes Begin the lesson by informing learners that, Today we are going to learn more about the human reproductive system. Remind students that the male and female reproductive systems are composed of external and internal organs, which function to produce the sperm and egg cells that allow us to reproduce, to transport and sustain these cells, to nurture the developing offspring, and to make hormones. Next, explain by saying, This lesson will build on what we learned in the first part of the lesson in order to better understand how the internal organs work. Knowing how your body works can help you explain to a health care provider should you have a question or think there might be a problem. It will also help you later when there are lessons about birth control and sexually transmitted infections. Step 2) 20 minutes Ask for six volunteers and give each volunteer one piece from the female reproductive system puzzle. Ask volunteers to cut out their body part and then try and tape their pieces together on the chalkboard correctly to form the female internal reproductive system. As you review the female system, make sure to describe the path of the ovum by saying something like, The ovum or egg leaves the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube through the cervix and into the uterus. During this time, if there are no sperm that join with the egg, the ovum and lining of the uterus shed and leave the body through the vagina approximately once a month, which is called her menstrual period. Help learners using the Reproductive System Visual #5 as needed. Thank learners and have them return to their seats. Step 3) 20 minutes Repeat the same procedure for the male system by asking for eight different volunteers. Give each volunteer one piece from the male reproductive system puzzle. Ask volunteers to cut out their body part and then try and tape their pieces together on the chalkboard correctly to form the male reproductive system. Make sure to describe the path of a sperm from being made in the testicles by saying something like, The sperm are made in the testicles and take time to mature in the epididymis before traveling through the vas deferens, mixing with fluid from the prostate and seminal vesicles to form the fluid called semen that eventually leaves through the urethra in the penis during ejaculation. Help learners using the Reproductive System Visual #4 as needed. Thank learners and have them return to their seats. Step 4) 3 minutes As closure for the lesson, remind learners that there is a wide range of what bodies can look like and almost all physical appearances are considered perfectly normal. Ask learners the following question and have each learner share their response in rapid succession. What is one new piece of information you are leaving today s lesson with?
11 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part II KEY MESSAGES OF LESSON: 1) There is a wide range of normal when it comes to how people s bodies look. 2) Knowing the male and female reproductive anatomy and the function of each part is important to understanding how your body works and to ultimately staying healthy. ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES AT CONCLUSION OF LESSON: Teachers can ask learners to write down the one piece of new information they are leaving the lesson with and submit for assessment of the learning objectives. HOMEWORK WITH FOCUS ON FAMILY INVOLVEMENT ACTIVITIES: None POSSIBLE ADAPTATIONS: Large class size With a large group, you can conduct the reproductive system puzzles in teams as a competition or in small groups. Limited materials/technology Instead of using the puzzle pieces, the teacher can assign a different part of the reproductive system to each volunteer (or learner within a small group) and ask them to draw on the chalkboard, so that the picture becomes more complete as each volunteer adds their drawing. The teacher may need to draw the different organs along the side of the chalkboard so that volunteers can use this for reference when adding their drawing to the chalkboard. Adapted from: Family Life and Sexual Health High School Version, Lesson 2: Reproductive System; Public Health Seattle & King County, Revised
12 PREGNANCY VISUAL 4: Reproductive System Visual 4 Male Internal View Male Internal View VAS DEFERENS SEMINAL VESICLE BLADDER PUBIC BONE PUBIC HAIR ANUS PROSTATE GLAND COWPER S GLAND PENIS EPIDIDYMIS TESTIS SCROTUM URETHRA
13 PREGNANCY VISUAL 5: Reproductive System Visual 5 Female Internal View Male Internal View FIMBRIA OVARY FALLOPIAN TUBES UTERUS BLADDER PUBIC BONE CERVIX PUBIC HAIR SHAFT OF CLITORIS GLANS OF CLITORIS URETHRA SKENE S GLANDS LABIA VAGINA ANUS
14 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 1 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 1 TESTICLE
15 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 2 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 2 TESTICLE
16 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 3 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 3 VAS DEFERENS
17 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 4 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 4 VAS DEFERENS
18 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 5 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 5 PROSTATE GLAND COWPER S GLAND
19 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 6 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 6 SEMINAL VESICLE
20 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 7 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 7 SEMINAL VESICLE
21 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 8 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 8 PENIS
22 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 9 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 9 UTERUS
23 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 10 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 10 VAGINA
24 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 11 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 11 FALLOPIAN TUBE
25 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 12 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 12 FALLOPIAN TUBE
26 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 13 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 13 OVARY
27 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 14 Reproductive System Puzzle Part 14 OVARY
28
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3
 Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Unit #5 Human Growth and Development 6 th Grade - Chapter 7, 8 7 th Grade - Chapter 12 8 th Grade - Chapter 16, 17
 8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
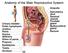 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Agenda: 1. Help students learn about health and major body systems. 2. Introduce the reproductive system
 FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-6.3:
 GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1
 Mary Wenstrom Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1 Health Education Grade 10 Content Area: Sexuality Education Health Literacy: Effective Communicator and Critical Thinker Life Skills: Understanding Adolescence,
Mary Wenstrom Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1 Health Education Grade 10 Content Area: Sexuality Education Health Literacy: Effective Communicator and Critical Thinker Life Skills: Understanding Adolescence,
II. III. 2004 Core Knowledge National Conference, Grade Level, (Unit Name Here) 1
 Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Growing up what s it all about?
 4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
Here we will talk about:
 Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE
 Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Revised Spring 2006 1
 It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
Grade 6, Theme Three
 Family Letter Grade 6, Theme Three Dear Family, We are ready to begin Theme Three of Fully Alive, our Family Life program. Because the partnership of home, church, and school is so important, this letter
Family Letter Grade 6, Theme Three Dear Family, We are ready to begin Theme Three of Fully Alive, our Family Life program. Because the partnership of home, church, and school is so important, this letter
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
identify the physical, interpersonal, and emotional aspects of healthy human beings
 Lesson Four Title: Theme: Time: Materials: You, Your Body and Puberty Puberty for Boys and Girls 110 minutes External Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz External
Lesson Four Title: Theme: Time: Materials: You, Your Body and Puberty Puberty for Boys and Girls 110 minutes External Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz External
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury
 Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
associated with puberty for boys and girls.
 Lesson 5 Puberty Overview In this informational lesson, students learn about puberty. Small groups brainstorm physical, emotional and social changes they think occur The class discusses and evaluates the
Lesson 5 Puberty Overview In this informational lesson, students learn about puberty. Small groups brainstorm physical, emotional and social changes they think occur The class discusses and evaluates the
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up. (for boys and girls)
 What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
Patient & Family Guide 2015 Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer www.nshealth.ca Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer What is the prostate? The prostate is one of the male sex glands. It makes seminal fluid
Chapter 28: Reproductive System
 I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Boys and Puberty. about body changes and other stuff!
 Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! In this booklet, we ve got together a heap of information so that you can be informed about the important stuff.
Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! In this booklet, we ve got together a heap of information so that you can be informed about the important stuff.
That being said, consider the following as you decide whether or not a vasectomy is your best option for birth control.
 Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Penis Enlargement Exercises
 Penis Enlargement Exercises Chapter 1 How do Penis Exercises Work? What Can it Do For You? Pg 2 Chapter 2 Before You Start: Safety Tips Pg 3 Chapter 3 Pg 4 Measuring Your Penis Chapter 4 Penis exercises
Penis Enlargement Exercises Chapter 1 How do Penis Exercises Work? What Can it Do For You? Pg 2 Chapter 2 Before You Start: Safety Tips Pg 3 Chapter 3 Pg 4 Measuring Your Penis Chapter 4 Penis exercises
Questions, Questions, Questions
 1 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and your
1 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and your
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Sexuality for the Woman With Cancer Cancer, sex, and sexuality
 Sexuality for the Woman With Cancer Cancer, sex, and sexuality When you first learned you had cancer, you probably thought mostly of survival. But after a while other questions may have started coming
Sexuality for the Woman With Cancer Cancer, sex, and sexuality When you first learned you had cancer, you probably thought mostly of survival. But after a while other questions may have started coming
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING
 NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING 1 MODULE 1: SEX AND SEXUALITY Unit 1: The Concepts of Sex and Sexuality Unit 2: Human
NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING 1 MODULE 1: SEX AND SEXUALITY Unit 1: The Concepts of Sex and Sexuality Unit 2: Human
Boys and. about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM
 Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 2 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM In
Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 2 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM In
Let s talk aboutpuberty
 Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3:
 PUBERTY CHANGES Lesson 2 GRADE 4 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3: Describe physical, emotional and social changes that occur during puberty; e.g., menstruation, secondary sexual characteristics, changing identity
PUBERTY CHANGES Lesson 2 GRADE 4 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3: Describe physical, emotional and social changes that occur during puberty; e.g., menstruation, secondary sexual characteristics, changing identity
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Some activities need additional guidance, or can be expanded: These are your testicles, this is where semen and sperm is made.
 P UBERTY This section includes: Teachers Notes changes - Female changes - Male Inside a boys body Inside a girls body Inside our bodies Boys growing up Girls growing up Hormones Coping with emotions Being
P UBERTY This section includes: Teachers Notes changes - Female changes - Male Inside a boys body Inside a girls body Inside our bodies Boys growing up Girls growing up Hormones Coping with emotions Being
FAMILY LIFE EDUCATION ACPS Fifth Grade
 Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
CHAPTER 22: THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS. 3. Define the terms meiosis, DNA, somatic cells, gametes, diploid, haploid and zygote.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Vasectomy What happens under normal conditions? What is a vasectomy? How is a vasectomy performed?
 Vasectomy The decision to proceed with a vasectomy is a very personal one. It is important that you have a clear understanding of what a vasectomy is and what it is not. Most patients can expect to recover
Vasectomy The decision to proceed with a vasectomy is a very personal one. It is important that you have a clear understanding of what a vasectomy is and what it is not. Most patients can expect to recover
Puberty is the name given to the physical changes that happen between childhood and adulthood
 LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse. Your Body s Design for Bladder Control
 National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse Your Body s Design for Bladder Control BLADDER Let s talk about bladder control for women. There s treatment that works. CONTROL Let s Talk
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse Your Body s Design for Bladder Control BLADDER Let s talk about bladder control for women. There s treatment that works. CONTROL Let s Talk
Perineal Stretching/Massage By Carolyn Hastie
 The Perineum Perineal Stretching/Massage The perineum is that amazing, stretchy muscle and skin between your anus and your yoni (we use the word yoni instead of vagina, because vagina means sheath for
The Perineum Perineal Stretching/Massage The perineum is that amazing, stretchy muscle and skin between your anus and your yoni (we use the word yoni instead of vagina, because vagina means sheath for
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System. Major Organs. Function: producing offspring. External Reproductive Organs
 Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
There are four areas where you can expect changes to occur as your hormone therapy progresses.
 You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
INTRODUCTION A PARTICIPATORY PROGRAMME ON SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FOR WOMEN AND GIRLS A TOOLKIT FOR FACILITATORS
 INTRODUCTION A PARTICIPATORY PROGRAMME ON SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FOR WOMEN AND GIRLS A TOOLKIT FOR FACILITATORS 01 02 Acknowledgements This toolkit was made possible through the financial support
INTRODUCTION A PARTICIPATORY PROGRAMME ON SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FOR WOMEN AND GIRLS A TOOLKIT FOR FACILITATORS 01 02 Acknowledgements This toolkit was made possible through the financial support
Vasectomy Services Patient Information
 Vasectomy Services Patient Information Vasectomy Vasectomy Please read this information leaflet and consent form carefully, and bring it with you to your appointment. Please ask the doctor any questions
Vasectomy Services Patient Information Vasectomy Vasectomy Please read this information leaflet and consent form carefully, and bring it with you to your appointment. Please ask the doctor any questions
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3:
 GRADE 7-9 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT QUICK LESSON SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Quick Lesson GRADE 7-9 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual
GRADE 7-9 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT QUICK LESSON SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Quick Lesson GRADE 7-9 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual
