Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (
|
|
|
- Meghan Davis
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services ( Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one or more individuals selling products or services for profit. Nearly 100,000 new businesses are started in Canada each year, with most of them being founded by people who want freedom from ordinary jobs, a new challenge in life, or the advantage of earning extra money. Four topics to be discussed: 1. Business organization 2. Three main financial statements 3. The accounting equation 4. T Accounts Debits and Credits 1. Business organizations take one of three forms: 1. Sole proprietorship 2. Partnership 3. Corporation Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation A sole proprietorship, or single proprietorship, is a business owned by one person. No legal requirement is needed in order to start this form of business, other than to file for a business license and register the business name. While it is a separate entity for accounting purposes, it is not a separate legal entity from its owner, this means, that a court can order an owner to sell personal belongings to pay its debts. Tax authorities do not separate a proprietorship from its owner; the profits of the business are reported and taxed on the owner s personal income tax return. A partnership is owned by two or more personas called partners. As for a proprietorship, no special legal requirements must be met in order to start a partnership, other than to register the business name and get a business license. To run the business together, the partners need an oral or written agreement that usually indicates how the profits and losses are to be shared. Each partner s share of profits is reported and taxed on that partner s personal tax return. Like a proprietorship, a partnership does not have a separate legal entity from its owners. A Corporation is a business that has a separate legal entity and is responsible for its own acts and its own debts. It can enter into its own contracts, and it can buy, own, and sell property. Think of a corporation as a separate person, therefore, a corporation files its own tax return and pays tax on its profits. A corporation acts through its managers that hold a separate legal status and the managers are not responsible for the corporate acts and debts. Ownership, or equity, of the corporation is divided into units called shares. Owners of shares are called shareholders or in American terms stockholders. A shareholder can sell or transfer shares to another person without affecting the operations of a corporation.
2 2. Three Main Financial Statements 1. A balance sheet contains assets, liabilities, and owners equity. Creative Interiors Balance Sheet as at March 31, 2009 Assets Liabilities Cash $8,400 Accounts Payable $6,000 Supplies 3,600 Notes payable 200 Office Supplies 6,000 Total Liabilities $6,200 Sally Creative Capital 11,800 Total Liability and Total assets $18,000 Owners equity $18, Income statements contain income and expenses. Revenue Creative Interiors Income Statement March 1 31, 2009 Consulting Revenue $3800 Rental Revenue 300 Total Revenue $4,100 Operating Expenses Rent Expense $1000 Salaries Expense 700 Total Operating Expenses $1,700 Net Income $2, Trial balance contains all accounts. Assets, liabilities, owner equity, income, and expenses.
3 Creative Interiors Trial Balance as at March 31, 2009 Debits Credits Cash $8,400 Supplies 3,600 Office Furniture 6,000 Accounts payable $6,000 Notes Payable 200 Sally Creative Capital 11,800 Current Earnings 2,400 Consulting Revenue 3,800 Rent Revenue 300 Rent Expense 1,000 Salaries Expense 700 $22,100 $22, The Accounting Equation Notice on the balance sheet the two sections are the assets on one side and liabilities and owners equity are on the other side. The total assets of $18,000 equal the total liability and owner equity of $18,000. This equality is known as accounting equation. Assets = Liabilities Owner Equity Assets describe what Liabilities describe debts OE describes owner financing an organization has to pay to suppliers, bank (investment) and owner withdrawal. invested in, such as land loans, and government taxes. building, machinery, and cash on hand. Assets = Liabilities Owner Equity $25000 $15000 $10,000 Purchase of equipment Bank loan Owner investment
4 4. T Accounts Debits and Credits Assets Liabilities Owner Investment Revenues Expenses Owner Withdrawal
5 The Taccounts above are a helpful learning tool. It shows the effects of individual transactions on specific accounts. The Taccount is so named because it looks like the letter T. The left side of the Taccount is always called the debit side often abbreviated Dr. The right side is always called the credit side, often abbreviated Cr. The difference between total debits and total credits for an account is the account balance. When the sum of debits exceeds the sum of credits, the account has a debit balance. It has a credit balance when the sum of credits exceeds the sum of debits. When the sum of debits equals the sum of credits, the account has a zero balance. Office Supplies Accounts Payable Balance Balance = 400 total debits; = 260 total = 850 total debits; = 1,000 credit; debits are greater than credits, so the 140 total credits; credits are greater than debits, so balance is a debit ( ). the 150 balance is a credit (1, ). Analyzing transactions below are some transactions to show you how debits and credits rules and doubleentry accounting are useful in analyzing and processing transactions. 1. Investment by owner Dr. Cash Cr. 10,000 Dr. Sally Creative, Capital Cr. 10,000 Transaction: Sally Creative invested $10,000 in Creative Interiors on January 1, Analysis: Assets increase. Owner equity increase. Doubleentry: Debits the Cash asset account for $10,000. Credit The Sally Creative, Capital account in owner equity for $10,000.
6 2. Purchase supplies for cash Dr. Supplies Cr Dr. Cash Cr. 10,000 2,500 Transaction: Creative Interiors purchases supplies by paying $2,500 cash. Analysis: Assets increase. Assets decrease. These changes the composition of assets, but does not change the total amount of assets. Doubleentry: Debit the Supplies asset account for $2500. Credit the Cash asset account for $ Purchase furniture and supplies on credit. Dr. Supplies Cr. 2,500 1,100 Dr. Furniture Cr. 6,000 Transaction: Creative Interiors purchases $1,100 of supplies and $6,000 of furniture on credit. Creative interiors signs a promissory note for the $6,000 of furniture. Analysis: Assets increases. Liabilities increases. Doubleentry: Debit two asset accounts: Supplies for $1,100 and furniture for $6000. Credit two liability accounts: Accounts payable for $1,100 and Notes Payable for $6000. Dr. Accounts Payable Cr. 1,100 Dr. Notes Payable Cr. 6,000
7 4. Services rendered for cash. Dr. Cash Cr. 10,000 2,500 2,200 Transaction: Creative Interiors provided consulting services to a Customer and immediately collected $2,200 cash. Analysis: Assets increase. Dr. Revenue Cr. Doubleentry: Debit the Cash asset account for $2,200. Credit the Consulting Revenue account for $2,200. 2, Payment of expenses in cash. Dr. Salaries Expense Cr. 700 Transaction: Creative Interiors pays $700 cash for Employee s salary for the pay period ending on January 14. ` Analysis: Assets decrease. Dr. Cash Cr. 10,000 2,500 2, Doubleentry: Debit the Salaries expense account For $700. Credit the Cash asset account for $700
8 Other Bookkeeping and Accounting Resources
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET. Initial Paid-in Capital. An Example Entity. Transaction 2.
 The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
Chapter 1. Introduction to Accounting and Business
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
Financial Accounting. (Exam)
 Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
A Simple Model. The Accounting Equation
 An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
2 Transaction Analysis
 29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Bean Counter's Accounting and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet"
 Page 1 of 6 Bean Counter's ing and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet" Provided by: Bean Counter Source Documents ( Invoices, Checks, etc.) Journals -Transactions first recorded using Debits and s General Ledger
Page 1 of 6 Bean Counter's ing and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet" Provided by: Bean Counter Source Documents ( Invoices, Checks, etc.) Journals -Transactions first recorded using Debits and s General Ledger
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
1 Money and income Currency currency notes (banknotes) coins cash bank deposits BrE: note or banknote; on paper AmE: bill
 1 A B Money and income Currency The money used in a country euros, dollars, yen, etc. is its currency. Money in notes (banknotes) and coins is called cash. Most money, however, consists of bank deposits:
1 A B Money and income Currency The money used in a country euros, dollars, yen, etc. is its currency. Money in notes (banknotes) and coins is called cash. Most money, however, consists of bank deposits:
Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT. 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr APPLE COMPUTER, INC.
 2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
EasyPC Training. Accounting Basics
 EasyPC Training Accounting Basics Contents Accounting Basics... 3 The Accounting Equation... 3 Assets... 3 Liabilities... 3 Owner s Equity... 3 The Balance Sheet... 5 Double Entry Bookkeeping... 6 Ledger
EasyPC Training Accounting Basics Contents Accounting Basics... 3 The Accounting Equation... 3 Assets... 3 Liabilities... 3 Owner s Equity... 3 The Balance Sheet... 5 Double Entry Bookkeeping... 6 Ledger
Chapter 4: Accounting Records
 Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries
 Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
Basic Accounting Principles
 Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Accounting Basics, Part 1
 Accounting Basics, Part 1 Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts, Journals and, Ledger Part 1 What s Here Introduction Business Types Business Organization Professional Advice
Accounting Basics, Part 1 Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts, Journals and, Ledger Part 1 What s Here Introduction Business Types Business Organization Professional Advice
Baseline Assessment. Date Accounting 1
 Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
A = L + OE. Transaction 1 Assets = Liabilitites + Owners equity + 1,000,000 Cash + 1,000,000 Common stock
 FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Henry Jarva Aalto University, Spring 2015 Student name: EXERCISE 1. Provide journal entries for Transactions 5 8, Adjusting Entries 2 7, and prepare Exhibit 1. 2. Calculate
FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Henry Jarva Aalto University, Spring 2015 Student name: EXERCISE 1. Provide journal entries for Transactions 5 8, Adjusting Entries 2 7, and prepare Exhibit 1. 2. Calculate
MODULE 6 Financial Statements
 Introduction. 102 Projected Outcomes 103 Facilitators Notes. 104 What is Accounting. 104 The Accounting Equation.. 105 Accounting Terminology 106 Assets 106 Liabilities. 106 Owner s Equity, Partner s Equity,
Introduction. 102 Projected Outcomes 103 Facilitators Notes. 104 What is Accounting. 104 The Accounting Equation.. 105 Accounting Terminology 106 Assets 106 Liabilities. 106 Owner s Equity, Partner s Equity,
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping
 Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Authored for ENMU Tutoring Services. By Jessica Huff
 By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting
 When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
Chapter 2. Analyzing transactions
 1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
Assessment Schedule 2010 Accounting: Prepare financial statements and related accounting entries for sole proprietors (90224)
 NCEA Level 2 Accounting (90224) 2010 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2010 Accounting: Prepare financial statements and related accounting entries for sole proprietors (90224) Evidence Statement ONE Part
NCEA Level 2 Accounting (90224) 2010 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2010 Accounting: Prepare financial statements and related accounting entries for sole proprietors (90224) Evidence Statement ONE Part
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed
 Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Accounting Basics. Prepared for First Year MBA
 Accounting Basics Prepared for First Year MBA Overview S No Particulars 01 Introduction to Accounting 02 Accounting Equation 03 Types of Transactions 04 Purchase and Sales 05 Types of Accounts 06 Golden
Accounting Basics Prepared for First Year MBA Overview S No Particulars 01 Introduction to Accounting 02 Accounting Equation 03 Types of Transactions 04 Purchase and Sales 05 Types of Accounts 06 Golden
Management & Principles of Accounting Date: 09/11/2015 Introduction to financial accounting Basic concepts and tools
 Management & Principles of Accounting Date: 09/11/2015 Introduction to financial accounting Basic concepts and tools Patrizia Tettamanzi Sophie Goodman Source: Kimmel/Weygandt/Kieso Financial Accounting
Management & Principles of Accounting Date: 09/11/2015 Introduction to financial accounting Basic concepts and tools Patrizia Tettamanzi Sophie Goodman Source: Kimmel/Weygandt/Kieso Financial Accounting
Definition of Accounting
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201
 The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
CASH FLOW STATEMENT. MODULE - 6A Analysis of Financial Statements. Cash Flow Statement. Notes
 MODULE - 6A Cash Flow Statement 30 CASH FLOW STATEMENT In the previous lesson, you have learnt various types of analysis of financial statements and its tools such as comparative statements, common size
MODULE - 6A Cash Flow Statement 30 CASH FLOW STATEMENT In the previous lesson, you have learnt various types of analysis of financial statements and its tools such as comparative statements, common size
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle
 Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Learning Objectives: Quick answer key: Question # Multiple Choice True/False. 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information.
 0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
Understanding Accounting Reports. www.brightpearl.com
 Understanding Accounting Reports Whats inside You ll often hear the term management accounts - but how often do you use this information to actually manage your business on a day to day basis? It may well
Understanding Accounting Reports Whats inside You ll often hear the term management accounts - but how often do you use this information to actually manage your business on a day to day basis? It may well
4. Business Accounting
 4. Business Accounting Nobody was ever meant to remember or invent what he did with every cent. Robert Frost Questions 1. What is the purpose of accounting? 2. What are the main types of accounting? 3.
4. Business Accounting Nobody was ever meant to remember or invent what he did with every cent. Robert Frost Questions 1. What is the purpose of accounting? 2. What are the main types of accounting? 3.
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle
 Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Chapter 4. Accounting Records: Structure and Terminology The process of accounting documentation
 Chapter 4 Accounting Records: Structure and Terminology The process of accounting documentation 1 Basic Element of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting
Chapter 4 Accounting Records: Structure and Terminology The process of accounting documentation 1 Basic Element of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting
HERE'S A TIP. Double Entry Accounting. Debits and Credits
 Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Merchandising Businesses
 Learning Objectives LO1 Distinguish among service, retail merchandising, and wholesale merchandising businesses. LO2 Identify differences between a sole proprietorship and a corporation. LO3 Explain the
Learning Objectives LO1 Distinguish among service, retail merchandising, and wholesale merchandising businesses. LO2 Identify differences between a sole proprietorship and a corporation. LO3 Explain the
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
PREPARING FINAL ACCOUNTS. part
 15_1312MH_CH09 27/1/05 8:38 am Page 87 PREPARING part 3 FINAL ACCOUNTS 9 The final accounts of sole traders 10 Accounting principles, concepts and policies 11 Depreciation and fixed assets 12 Bad debts
15_1312MH_CH09 27/1/05 8:38 am Page 87 PREPARING part 3 FINAL ACCOUNTS 9 The final accounts of sole traders 10 Accounting principles, concepts and policies 11 Depreciation and fixed assets 12 Bad debts
T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements
 2 T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM maintains an office for the practice of veterinary medicine. The account balances as of September 1 are given
2 T Accounts, Debits and Credits, Trial Balance, and Financial Statements DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM maintains an office for the practice of veterinary medicine. The account balances as of September 1 are given
Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis
 1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
Chapter 14. 1 Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 Chapter 14 1 Identify the purposes of the statement of cash flows Distinguish among operating, investing, and financing cash flows Prepare the statement of cash flows by the indirect method Identify noncash
Chapter 14 1 Identify the purposes of the statement of cash flows Distinguish among operating, investing, and financing cash flows Prepare the statement of cash flows by the indirect method Identify noncash
Financial Statements. Chapter 19 Study Guide
 Financial Statements Chapter 19 Study Guide Financial Statements Discuss the nature of a consolidated financial statement? Understand the relationship between the work sheet and the financial statements.
Financial Statements Chapter 19 Study Guide Financial Statements Discuss the nature of a consolidated financial statement? Understand the relationship between the work sheet and the financial statements.
Preparing Financial Statements
 Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
CHAE Review. Capital Leases & Forms of Business
 CHAE Review Financial Statements, Capital Leases & Forms of Business This is a complete review of the two volume text book, Certified Hospitality Accountant Executive Study Guide, as published by The Educational
CHAE Review Financial Statements, Capital Leases & Forms of Business This is a complete review of the two volume text book, Certified Hospitality Accountant Executive Study Guide, as published by The Educational
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings
 Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
LIABILITIES. Liabilities are claims against your Assets. They are something that you have to repay to someone else.
 Accounting 101 ASSETS An Asset is something that you own, that has value, and will generate a future benefit. Assets are good. Eg.) Cash, accounts receivable, GST receivable, inventory, equipment, land,
Accounting 101 ASSETS An Asset is something that you own, that has value, and will generate a future benefit. Assets are good. Eg.) Cash, accounts receivable, GST receivable, inventory, equipment, land,
Analyzing Business Transactions Using T Accounts
 pri639_ch03_053-088.qxd 9/7/3 4:54 PM Page 53 Analyzing Business Transactions Using T Accounts Chapter 3 When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 876, and gave birth to www.att.com the company
pri639_ch03_053-088.qxd 9/7/3 4:54 PM Page 53 Analyzing Business Transactions Using T Accounts Chapter 3 When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 876, and gave birth to www.att.com the company
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements
 CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems. Functional Area Systems. Lecture 4
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis
 HOSP 1860 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis A business must always have a balance between what it owns and what it owes. This is shown by the basic accounting
HOSP 1860 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis A business must always have a balance between what it owns and what it owes. This is shown by the basic accounting
Financial Statements Tutorial
 Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Principles of Financial Accounting ACC-101-TE. TECEP Test Description
 Principles of Financial Accounting ACC-101-TE TECEP Test Description This TECEP is an introduction to the field of financial accounting. It covers the accounting cycle, merchandising concerns, and financial
Principles of Financial Accounting ACC-101-TE TECEP Test Description This TECEP is an introduction to the field of financial accounting. It covers the accounting cycle, merchandising concerns, and financial
A Simple Model. Introduction to Financial Statements
 Introduction to Financial Statements NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These notes are intended to supplement the videos on ASimpleModel.com. They are not to be used as stand alone study aids, and are not written
Introduction to Financial Statements NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These notes are intended to supplement the videos on ASimpleModel.com. They are not to be used as stand alone study aids, and are not written
BUSINESS ACCOUNTS. sample documents. sourced from www.osbornebooks.co.uk
 BUSINESS ACCOUNTS sample documents sourced from www.osbornebooks.co.uk Sample documents document page invoice 3 statement 4 double-entry accounts 5 cash book 6 petty cash book 7 extended trial balance
BUSINESS ACCOUNTS sample documents sourced from www.osbornebooks.co.uk Sample documents document page invoice 3 statement 4 double-entry accounts 5 cash book 6 petty cash book 7 extended trial balance
Essentials of Financial Statement Analysis
 Essentials of Financial Statement Analysis An Introduction to Financial Statement Analysis Gregory Mostyn, CPA Worthy and James Publishing www.worthyjames.com Essentials of Financial Statement Analysis
Essentials of Financial Statement Analysis An Introduction to Financial Statement Analysis Gregory Mostyn, CPA Worthy and James Publishing www.worthyjames.com Essentials of Financial Statement Analysis
CENTRE FOR CONTINUING EDUCATION BBA (AVIATION OPERATION)
 CENTRE FOR CONTINUING EDUCATION BBA (AVIATION OPERATION) BATCH: SEMESTER: NAME: ROLL NO: ASSIGNMENT 1 & 2 FOR BUSINESS ACCOUNTING BBCF 131 UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & ENERGY STUDIES Assignment-1 Note: All
CENTRE FOR CONTINUING EDUCATION BBA (AVIATION OPERATION) BATCH: SEMESTER: NAME: ROLL NO: ASSIGNMENT 1 & 2 FOR BUSINESS ACCOUNTING BBCF 131 UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & ENERGY STUDIES Assignment-1 Note: All
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs
 ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
Accounting Is a Language. Financial Accounting: The Balance Sheet BALANCE SHEET. Accounting Information. Assets. Balance Sheet: Layout
 Accounting Is a Language Financial Accounting: The Balance Sheet Richard S. Barr Purpose: providing information Financial Statements Summarize accounting information Examples We need to know what the numbers
Accounting Is a Language Financial Accounting: The Balance Sheet Richard S. Barr Purpose: providing information Financial Statements Summarize accounting information Examples We need to know what the numbers
The Nature of Accounting Systems
 Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
Accruals and prepayments
 5 Accruals and prepayments this chapter covers... In the last chapter we have looked at the preparation of financial statements or final accounts using the extended trial balance, or spreadsheet, approach.
5 Accruals and prepayments this chapter covers... In the last chapter we have looked at the preparation of financial statements or final accounts using the extended trial balance, or spreadsheet, approach.
Starting a Small Business
 Starting a Small Business Starting and managing a business takes motivation, desire and talent. It also takes research and planning. Like a chess game, success in small business starts with decisive and
Starting a Small Business Starting and managing a business takes motivation, desire and talent. It also takes research and planning. Like a chess game, success in small business starts with decisive and
Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
Debit Cash. Journalizing Transactions. Problem 2-2b. Created 2009 By Michael Worthington Elizabeth City State University
 Journalizing Transactions Created 2009 By Michael Worthington Elizabeth City State University Lela Peterson transferred cash from a personal bank account to the account used for the business Entity states
Journalizing Transactions Created 2009 By Michael Worthington Elizabeth City State University Lela Peterson transferred cash from a personal bank account to the account used for the business Entity states
Summary. Introduction to Accounting. Chapter
 1 Chapter Introduction to Accounting Summary 1. Accounting consists of five stages: (1) recording (bookkeeping), (2) summarizing, (3) analyzing, (4) interpreting and (5) reporting the financial information
1 Chapter Introduction to Accounting Summary 1. Accounting consists of five stages: (1) recording (bookkeeping), (2) summarizing, (3) analyzing, (4) interpreting and (5) reporting the financial information
ICAP GROUP S.A. FINANCIAL RATIOS EXPLANATION
 ICAP GROUP S.A. FINANCIAL RATIOS EXPLANATION OCTOBER 2006 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. FINANCIAL RATIOS FOR COMPANIES (INDUSTRY - COMMERCE - SERVICES) 4 2.1 Profitability Ratios...4 2.2 Viability
ICAP GROUP S.A. FINANCIAL RATIOS EXPLANATION OCTOBER 2006 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. FINANCIAL RATIOS FOR COMPANIES (INDUSTRY - COMMERCE - SERVICES) 4 2.1 Profitability Ratios...4 2.2 Viability
The Profit & Loss Account Accounting for Revenue & Expenses
 The Profit & Loss Account Accounting for Revenue & Expenses Chapter 3 Luby & O Donoghue (2005) Profit & Loss Account The main reason why people set up in business is to make a profit. The profit and loss
The Profit & Loss Account Accounting for Revenue & Expenses Chapter 3 Luby & O Donoghue (2005) Profit & Loss Account The main reason why people set up in business is to make a profit. The profit and loss
Debits and Credits: Analyzing and Recording Business Transactions
 63802_02_ch2_p039-076 2/26/09 11:30 AM Page 39 2 Debits and Credits: Analyzing and Recording Business Transactions DID YOU KNOW? In 2006 20% of sales came from Staples brands. The company plans to increase
63802_02_ch2_p039-076 2/26/09 11:30 AM Page 39 2 Debits and Credits: Analyzing and Recording Business Transactions DID YOU KNOW? In 2006 20% of sales came from Staples brands. The company plans to increase
Lesson 1. Business, Accounting, and You ASSIGNMENT 1: INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING. Why Study Accounting?
 Business, Accounting, and You Assignment 1 introduces three types of business and the entities used in creating these businesses. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial
Business, Accounting, and You Assignment 1 introduces three types of business and the entities used in creating these businesses. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial
Time Period Assumption
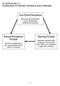 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
Publishers: Software Publication Pty Ltd [ABN 75078026150] Head Office Sydney Unit 10, 171 Gibbes Street Chatswood NSW 2067 1800 146 542
![Publishers: Software Publication Pty Ltd [ABN 75078026150] Head Office Sydney Unit 10, 171 Gibbes Street Chatswood NSW 2067 1800 146 542 Publishers: Software Publication Pty Ltd [ABN 75078026150] Head Office Sydney Unit 10, 171 Gibbes Street Chatswood NSW 2067 1800 146 542](/thumbs/30/13968171.jpg) Acknowledgments Copyright/Trademark Information: MYOB is the registered trademark of MYOB Technology Pty Ltd. Screen captures from MYOB Accounting v16 and v17 reproduced with permission. Copyright 2006
Acknowledgments Copyright/Trademark Information: MYOB is the registered trademark of MYOB Technology Pty Ltd. Screen captures from MYOB Accounting v16 and v17 reproduced with permission. Copyright 2006
Assets, Liabilities, and Net Worth
 Assets, Liabilities, and Net Worth C H A P T E R 3 OVERVIEW Assets, liabilities, and net worth are part of the language of finance. As such, it is important to understand both their composition and how
Assets, Liabilities, and Net Worth C H A P T E R 3 OVERVIEW Assets, liabilities, and net worth are part of the language of finance. As such, it is important to understand both their composition and how
Accounting Banking Finance Society. Basic Financial Accounting
 Accounting Banking Finance Society Basic Financial Accounting Single Entry Bookkeeping Most of financial accounting is based on double-entry bookkeeping. To understand and appreciate the advantages of
Accounting Banking Finance Society Basic Financial Accounting Single Entry Bookkeeping Most of financial accounting is based on double-entry bookkeeping. To understand and appreciate the advantages of
Trading Profit and Loss Account
 Trading Profit and Loss Account Trading Account The trading account shows the income from sales and the direct costs of making those sales. It includes the balance of stocks at the start and end of the
Trading Profit and Loss Account Trading Account The trading account shows the income from sales and the direct costs of making those sales. It includes the balance of stocks at the start and end of the
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS
 C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
Introduction to Accounts
 Introduction to Accounts Copyright statement Sage (UK) Limited, 2012. All rights reserved We have written this guide to help you to use the software it relates to. We hope it will be read by and helpful
Introduction to Accounts Copyright statement Sage (UK) Limited, 2012. All rights reserved We have written this guide to help you to use the software it relates to. We hope it will be read by and helpful
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
Accg100 Accounting 1A. Lecture Notes
 Accg100 Accounting 1A Lecture Notes Semester 2, 2012 1 Table of Contents Lecture Notes Page Week 1: Introduction to Accounting, Ethics, 3 Business Entities, Financial Statements Week 2: Accounting for
Accg100 Accounting 1A Lecture Notes Semester 2, 2012 1 Table of Contents Lecture Notes Page Week 1: Introduction to Accounting, Ethics, 3 Business Entities, Financial Statements Week 2: Accounting for
The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis
 HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis Economic transactions must be classified into categories: assets, liabilities, and net worth. Assets (A) are resources
HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis Economic transactions must be classified into categories: assets, liabilities, and net worth. Assets (A) are resources
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
3. CONSOLIDATED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 3. CONSOLIDATED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (1) Consolidated Quarterly Balance Sheets September 30, 2014 and March 31, 2014 Supplementary Information 2Q FY March 2015 March 31, 2014 September 30, 2014
3. CONSOLIDATED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (1) Consolidated Quarterly Balance Sheets September 30, 2014 and March 31, 2014 Supplementary Information 2Q FY March 2015 March 31, 2014 September 30, 2014
Ratios and interpretation
 Unit Ratios and interpretation As we learnt in our earlier studies, accounting information is used to answer two key questions about a business: Is it making a profit? Are its assets sufficient to meet
Unit Ratios and interpretation As we learnt in our earlier studies, accounting information is used to answer two key questions about a business: Is it making a profit? Are its assets sufficient to meet
Section 2: The Bookkeeping Process (Module 3)
 Section 2: The Bookkeeping Process Dermott Crofton [email protected] 1 This Section of the Course Bookkeeping Process Double Entry Bookkeeping Rules of Debits and Credits The T-Account Representing transactions
Section 2: The Bookkeeping Process Dermott Crofton [email protected] 1 This Section of the Course Bookkeeping Process Double Entry Bookkeeping Rules of Debits and Credits The T-Account Representing transactions
Chapter 1 Accounting in action
 Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
COURSE GUIDELINE--Accounting
 COURSE GUIDELINE--Accounting Grade: 9- (Elective Course, offered one semester at a time) SUBJECT: Accounting TEACHER: Reimer STANDARD QTR. RESOURCES STRATEGIES ASSESSMENTS. Define accounting and explain
COURSE GUIDELINE--Accounting Grade: 9- (Elective Course, offered one semester at a time) SUBJECT: Accounting TEACHER: Reimer STANDARD QTR. RESOURCES STRATEGIES ASSESSMENTS. Define accounting and explain
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany. Introduction to Financial Accounting. David Annand. Based on International Financial Reporting Standards
 Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
