COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
|
|
|
- Adela Morrison
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit 1. Prepare trial balance on the worksheet. 2. Enter adjustment data. 3. Enter adjusted balances 4. Extend adjusted balance to appropriate columns. 5. Calculate income/loss and complete the worksheet. 1
2 Steps in the Accounting Cycle 9. Prepare post-closing trial balance 8. Journalize and post closing entries 1. Source Documents: Analyse Transactions 2. Journalize the transactions 3. Post to ledger accounts 4. Prepare a trial balance 7. Prepare financial statements 6. Prepare adjusted trial balance 5. Journalize and post adjusting entries Closing the Books What is closing the books for? How would you do it? 2
3 Closing Entry Concepts The final stage of the accounting cycle is to prepare the accounts for the next fiscal period. To do this, you must understand which accounts have balances that continue from one period to the next and which do not. Closing Entry Concepts Continued When a new accounting period begins, the revenue and expense accounts should show zero balances so that they contain only data that refer to the new period. This allows the calculation of net income according to the matching principle, which states: Revenue for each accounting period is matched with expenses for that accounting period to determine the net income or net loss. 3
4 Purpose of Closing Entries 1. Updates the owner s capital account in the ledger by transferring net income (loss) and owner s drawings to owner s capital. 2. Prepares the temporary accounts (revenue, expense, drawings) for the next period s postings by reducing their balances to zero. Closing Entries The revenue and expense accounts are reduced to zero by a process called closing the books. Closing the books is the process by which revenue and expense accounts are reduced to zero of the end of each accounting period. Closing the accounts is sometimes called clearing the accounts. 4
5 Real Accounts and Nominal Accounts Real Accounts All asset and liability accounts, as well as the owner's capital account, are considered to be real accounts. Real accounts have balances that continue into the next fiscal period. Examples of real accounts are Bank, Vehicles, and Accounts Payable. Real Accounts and Nominal Accounts Nominal Accounts Nominal accounts (Revenue, Expense, and Drawings) have balances that do not continue into the next fiscal period. Nominal accounts, with the exception of the Drawings account, are related to the income statement, and the income statement deals only with a single fiscal period. All nominal accounts begin each fiscal period with a nil balance. 5
6 Real Accounts and Nominal Accounts Income Summary A special nominal account, called the Income Summary account, is used only during the closing entry process. The Income Summary account summarizes the revenues and expenses of the period. The temporary balance in this account represents either the amount of net income or the amount of net loss. Real Accounts and Nominal Accounts Other names for REAL and NOMINAL accounts are PERMANENT and TEMPORARY accounts. These alternative terms help you remember which accounts will continue to have balances (PERMANENT) and which will be closed out (TEMPORARY). 6
7 Temporary Versus Permanent TEMPORARY (NOMINAL) These accounts are closed PERMANENT (REAL) These accounts are not closed All revenue accounts All asset accounts All expense accounts All liability accounts Owner s drawings ** Owner s capital account (Income Statement / Drawings Accounts) (Balance Sheet Accounts) Diagram of the Closing Process Normal Dr. Balance (INDIVIDUAL) EXPENSES Cr. to close Dr. to close (INDIVIDUAL) REVENUES Normal Cr. Balance OWNER S CAPITAL 1 Expenses Opening Balance Revenues 1 Debit each revenue account for its balance, and credit the owner s capital account for total revenues. 2 Debit the owner s capital account for total expenses, and credit each expense account for its balance. 7
8 Diagram of the Closing Process Expenses Drawings OWNER S CAPITAL Opening Balance Revenues Ending Balance 3 Normal Dr. Balance OWNER S DRAWINGS Cr. to close 3 Debit owner s capital for the balance in the owner s drawings account and credit owner s drawings for the same amount Summary In summary, there are 4 steps involved in closing the books: 1. Close the revenue accounts into Income Summary. 2. Close the expense accounts into Income Summary. 3. Close Income Summary into Capital. 4. Close Drawings into Capital. 8
9 Journalizing and Posting the Closing Entries Closing Entry No. 1 Don t forget to post to the General Ledger Journalizing and Posting the Closing Entries Closing Entry No. 2 9
10 Journalizing and Posting the Closing Entries Don t forget to post to the General Ledger Closing Entry No. 3 Journalizing and Posting the Closing Entries Closing Entry No. 4 Don t forget to post to the General Ledger 10
11 Closing Entries STOP AND CHECK 1. Does the balance in your Owner s Capital account equal the ending capital balance reported in the Balance Sheet and Statement of Owner s Equity? 2. Are all of your temporary account balances zero? Post - Closing Trial Balance After all closing entries have been journalized and posted, a post-closing trial balance is prepared. The purpose of this trial balance is to prove the equality of the permanent (balance sheet) account balances that are carried forward into the next accounting period. 11
12 Post - Closing Trial Balance Pioneer Advertising Agency Post-Closing Trial Balance October 31, 2012 After Adjustment Debit Credit Cash $ 15,200 The post-closing trial Accounts Receivable 200 Advertising Supplies balance is prepared 1,000 Prepaid Insurance from the permanent 550 Office Equipment accounts in the ledger. 5,000 Accumulated Amortization $ 83 Notes Payable The post-closing trial 5,000 Accounts Payable 2,500 balance provides evidence Unearned Revenue 800 Salaries Payable that the journalizing and 1,200 Interest Payable posting of closing entries 25 C.R. Byrd, Capital has been properly 12,342 $ 21,950 $ 21,950 completed. Steps in the Accounting Cycle 9. Prepare post-closing trial balance 8. Journalize and post closing entries 7. Prepare financial statements 1. Source Documents: Analyse Transactions 6. Prepare adjusted trial balance 2. Journalize the transactions 3. Post to ledger accounts 4. Prepare a trial balance 5. Journalize and post adjusting entries 12
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle
 Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 16
 Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
Closing the Books Section 7 Accounting 11
 Closing the Books At the end of a fiscal year once all the transactions for the entity have been recorded, the revenue and expense accounts must be closed out to a zero balance. These accounts have been
Closing the Books At the end of a fiscal year once all the transactions for the entity have been recorded, the revenue and expense accounts must be closed out to a zero balance. These accounts have been
Chapter 3. Adjusting the accounts. Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals
 1 Chapter 3 Adjusting the accounts Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare adjusting entries for prepaid expenses originally recorded in an expense account
1 Chapter 3 Adjusting the accounts Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare adjusting entries for prepaid expenses originally recorded in an expense account
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET
 Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
Objective Evidence. Unit of Measurement. Accounting Period Cycle. Business Entity. Going Concern. Adequate Disclosure. Matching Expenses with Revenue
 Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
Accounting Concept: A source document is prepared for each transaction Objective Evidence Accounting Concept: Business transactions are stated in numbers that have common values; that is, using a common
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements
 CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCOUNTING LIFEPAC 7 ADJUSTING & CLOSING ENTRIES
 Unit 7 ACCOUNTING LIFEPAC 7 ADJUSTING & CLOSING ENTRIES CONTENTS I. ADJUSTING ENTRIES.............................. 3 The Purpose of the Worksheet....................... 3 The Need for Adjustments..........................
Unit 7 ACCOUNTING LIFEPAC 7 ADJUSTING & CLOSING ENTRIES CONTENTS I. ADJUSTING ENTRIES.............................. 3 The Purpose of the Worksheet....................... 3 The Need for Adjustments..........................
The Work Sheet and the Closing Process
 C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
The Accounting Cycle Completed
 5 The Accounting Cycle Completed Adjusting, Closing, and Post-Closing Trial Balance THE BIG PICTURE You are planning your school schedule for next term. Your goal is to take a full course load and find
5 The Accounting Cycle Completed Adjusting, Closing, and Post-Closing Trial Balance THE BIG PICTURE You are planning your school schedule for next term. Your goal is to take a full course load and find
Accrual accounting ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING. ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING continued. Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 Accrual accounting concepts PowerPoint presentation by Anne Abraham University of Wollongong 2009 John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING Accrual-based accounting
Chapter 3 Accrual accounting concepts PowerPoint presentation by Anne Abraham University of Wollongong 2009 John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd ACCRUAL VERSUS CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING Accrual-based accounting
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Advanced Accounting. Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business
 Advanced Accounting Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business Financial statements are used to summarize financial info and then are used to evaluate the financial position and progress
Advanced Accounting Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business Financial statements are used to summarize financial info and then are used to evaluate the financial position and progress
Baseline Assessment. Date Accounting 1
 Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and
 Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000.
 Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Accumulated Depreciation Equipment
 Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
The Accounting Cycle Completed
 5 The Accounting Cycle Completed T HE B IG P ICTURE Accountants have come a long way from the old stereotype of bean counter a pale figure with a green eyeshade who tends cloth-bound ledgers and journals
5 The Accounting Cycle Completed T HE B IG P ICTURE Accountants have come a long way from the old stereotype of bean counter a pale figure with a green eyeshade who tends cloth-bound ledgers and journals
Accounting Principles Dr. Mishari Alfraih. Adjusting the Accounts
 Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle
 Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and
Chapter 2. Analyzing transactions
 1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations
 Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
> DO IT! Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts. Timing Concepts. Adjusting Entries for Deferrals D-12. Solution
 Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 6: Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 Chapter 6: Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should recognize that financial statements can be used to evaluate net profit or loss, return on investments,
Chapter 6: Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should recognize that financial statements can be used to evaluate net profit or loss, return on investments,
Periodicity Assumption... Time Period Assumption... Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts
 Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 4th Ed. CHAPTER 4 Kimmel, Weygandt, Kieso Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts KEY THINGS WE LL DO: Refresh and expand Ch.3 concepts. Differentiate
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 4th Ed. CHAPTER 4 Kimmel, Weygandt, Kieso Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts KEY THINGS WE LL DO: Refresh and expand Ch.3 concepts. Differentiate
The worksheet for Hancock Company shows the following in the financial statement
 Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1
 Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1 We will explore the effect of standard processes in SAP Business One on Financial Reports: such as the Balance Sheet, the Trial Balance, and the Profit and
Welcome to the financial reports topic. 5-1-1 We will explore the effect of standard processes in SAP Business One on Financial Reports: such as the Balance Sheet, the Trial Balance, and the Profit and
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System
 CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
Accounting 300A-10A The Operating Cycle: Worksheet/Closing Entries Page 1
 Accounting 3A-1A The Operating Cycle: Worksheet/Closing Entries Page 1 THE WORKSHEET and CLOSING ENTRIES I. Review of Key Concepts and Terms: A. The purpose of the worksheet 1. To show that the accounts
Accounting 3A-1A The Operating Cycle: Worksheet/Closing Entries Page 1 THE WORKSHEET and CLOSING ENTRIES I. Review of Key Concepts and Terms: A. The purpose of the worksheet 1. To show that the accounts
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings
 Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures
 Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives
 CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
Financial Accounting. (Exam)
 Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint. Accounting-Advanced. Test Code: 3900 / Version: 01
 Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Accounting-Advanced Test Code: 3900 / Version: 01 Measuring What Matters Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Journalizing Journalize an opening entry
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Accounting-Advanced Test Code: 3900 / Version: 01 Measuring What Matters Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Journalizing Journalize an opening entry
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines
 Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
Accounting II Second Semester Final
 Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Time Period Assumption
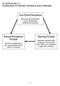 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
Statement of Cash Flows
 PREPARING THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS: THE INDIRECT METHOD OF REPORTING CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES The work sheet method described in the text book is not the recommended approach. We will provide
PREPARING THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS: THE INDIRECT METHOD OF REPORTING CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES The work sheet method described in the text book is not the recommended approach. We will provide
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET. Initial Paid-in Capital. An Example Entity. Transaction 2.
 The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Course Schedule Course Modules Review and Practice Exam Preparation Resources Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied
Course Schedule Course Modules Review and Practice Exam Preparation Resources Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems. Functional Area Systems. Lecture 4
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle STUDY OBJECTIVES The Navigator After studying this chapter, you should be Scan Study Objectives able to: Read Feature Story 1 Prepare a worksheet. Read Preview
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle STUDY OBJECTIVES The Navigator After studying this chapter, you should be Scan Study Objectives able to: Read Feature Story 1 Prepare a worksheet. Read Preview
Adjusting the Accounts
 HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
Completion of the Accounting Cycle
 8961dch04.qxd 10/9/03 8:17 AM Page 133 mac76 mac76:385_reb: Completion of the Accounting Cycle Chapter 4 THE NAVIGATOR Understand Concepts for Review Read Feature Story Scan Study Objectives Read Preview
8961dch04.qxd 10/9/03 8:17 AM Page 133 mac76 mac76:385_reb: Completion of the Accounting Cycle Chapter 4 THE NAVIGATOR Understand Concepts for Review Read Feature Story Scan Study Objectives Read Preview
Advanced District Concepts: More Fun With the Worksheet! 2014 Student Activity Conference
 ACCOUNTING Advanced District Concepts: More Fun With the Worksheet! 2014 Student Activity Conference UIL Accounting 2014 SAC Advanced District Concepts: Worksheet -2- Suggested Solving Strategy and Detailed
ACCOUNTING Advanced District Concepts: More Fun With the Worksheet! 2014 Student Activity Conference UIL Accounting 2014 SAC Advanced District Concepts: Worksheet -2- Suggested Solving Strategy and Detailed
MOUNTAIN VIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT
 MOUNTAIN VIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING I Curriculum Content Frameworks 0 Curriculum Content Frameworks COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING I Grade Levels: 0,, Course Code: 900 Prerequisite: Tech Prep
MOUNTAIN VIEW SCHOOL DISTRICT COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING I Curriculum Content Frameworks 0 Curriculum Content Frameworks COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING I Grade Levels: 0,, Course Code: 900 Prerequisite: Tech Prep
CHAPTER 4. Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
CHAPTER 3. BE3-2 Advertising. Dec. 31 Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 to adjust. BE3-3 Bere Co.
 CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
Adjusting and Closing Entries
 Adjusting and Closing Entries Adjusting and Closing entries tend to be difficult to grasp at first. A reason for this might be due to the type of transactions requiring adjustment, which tend to be unfamiliar.
Adjusting and Closing Entries Adjusting and Closing entries tend to be difficult to grasp at first. A reason for this might be due to the type of transactions requiring adjustment, which tend to be unfamiliar.
Bean Counter's Accounting and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet"
 Page 1 of 6 Bean Counter's ing and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet" Provided by: Bean Counter Source Documents ( Invoices, Checks, etc.) Journals -Transactions first recorded using Debits and s General Ledger
Page 1 of 6 Bean Counter's ing and Bookkeeping "Cheat Sheet" Provided by: Bean Counter Source Documents ( Invoices, Checks, etc.) Journals -Transactions first recorded using Debits and s General Ledger
Preparing Financial Statements
 Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University, Boone, NC 28608, [email protected] INTRODUCTION
 TEACHING PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING: HELPING STUDENTS IDENTIFY TEN DIFFERENCES WHEN COMPARING A TRIAL BALANCE, AN ADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE AND A BALANCE SHEET William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University,
TEACHING PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING: HELPING STUDENTS IDENTIFY TEN DIFFERENCES WHEN COMPARING A TRIAL BALANCE, AN ADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE AND A BALANCE SHEET William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University,
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II
 Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
How To Account For Revenue Under Accrual Accounting
 BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL
 CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS A general ledger is basic to an accounting system. The General Ledger of a fund is a summary record containing the balance of assets, liabilities, deferred revenues,
CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS A general ledger is basic to an accounting system. The General Ledger of a fund is a summary record containing the balance of assets, liabilities, deferred revenues,
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE
 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET
 CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
CHAPTER 12 ACCRUALS, DEFERRALS, AND THE WORKSHEET Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students may assess that an unexpected decline in sales would mean surplus inventory which would have to be reduced
She Wears A Bullet-Proof Vest:
 She Wears A Bullet-Proof Vest: Detailed Solving Steps for the 2014 Regional Accounting Exam s Work Sheet Problems Prepared by: LaVerne Funderburk, CPA UIL Accounting State Contest Director 2014 UIL Capital
She Wears A Bullet-Proof Vest: Detailed Solving Steps for the 2014 Regional Accounting Exam s Work Sheet Problems Prepared by: LaVerne Funderburk, CPA UIL Accounting State Contest Director 2014 UIL Capital
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ACCOUNTING-BASIC - PILOT. Test Code: 4100 Version: 01
 JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ACCOUNTING-BASIC - PILOT Test Code: 4100 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Journalizing Apply the accounting equation to journalize
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT ACCOUNTING-BASIC - PILOT Test Code: 4100 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Journalizing Apply the accounting equation to journalize
For More Course Tutorials Visit www.uoptutorial.com
 ACC 205 WEEK 2 EXERCISE ASSIGNMENT REVENUE AND EXPENSES(NEW) Click Here to Buy the Tutorial http://www.uoptutorial.com/index.php?route=product/p roduct&path=641&product_id=9760 For More Course Tutorials
ACC 205 WEEK 2 EXERCISE ASSIGNMENT REVENUE AND EXPENSES(NEW) Click Here to Buy the Tutorial http://www.uoptutorial.com/index.php?route=product/p roduct&path=641&product_id=9760 For More Course Tutorials
Chapter 5: Adjustments and the Worksheet
 Chapter 5: Adjustments and the Worksheet Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should suggest that accountants estimate the amount of wear and tear on the equipment. This expense should be charged
Chapter 5: Adjustments and the Worksheet Chapter Opener: Thinking Critically Students should suggest that accountants estimate the amount of wear and tear on the equipment. This expense should be charged
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 Chapter 9 Completing the Accounting Cycle ANSWERS TO SECTION 9.1 REVIEW QUESTIONS (text p. 307) The Adjustment Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 218 Accounting 1 Student
Chapter 9 Completing the Accounting Cycle ANSWERS TO SECTION 9.1 REVIEW QUESTIONS (text p. 307) The Adjustment Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 218 Accounting 1 Student
Chapter 1 Accounting in action
 Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I
 Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
How To Account For A Corporation
 Competency: Financial Statements 1. Describe the different types of financial statements; explain their purpose and compare the difference. 2. Prepare a trial balance, a worksheet (8 and 10 columns), and
Competency: Financial Statements 1. Describe the different types of financial statements; explain their purpose and compare the difference. 2. Prepare a trial balance, a worksheet (8 and 10 columns), and
3 Accrual Accounting & Income
 29366_10_ch3_p125-196 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 125 3 Accrual Accounting & Income SPOTLIGHT STARBUCKS CORPORATION Starbucks has changed coffee from a breakfast drink to an experience. The corporation began
29366_10_ch3_p125-196 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 125 3 Accrual Accounting & Income SPOTLIGHT STARBUCKS CORPORATION Starbucks has changed coffee from a breakfast drink to an experience. The corporation began
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs
 ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
SECTION 8.1 REVIEW QUESTIONS (page 275)
 CHAPTER 8 Completing the Accounting Cycle SECTION 8.1 REVIEW QUESTIONS (page 275) 1. Year-end financial statements are superior to interim financial statements because all accounts are brought up to date,
CHAPTER 8 Completing the Accounting Cycle SECTION 8.1 REVIEW QUESTIONS (page 275) 1. Year-end financial statements are superior to interim financial statements because all accounts are brought up to date,
COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
 ILLUSTRATION 24-1 OPERATING, INVESTING, AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES + Sales and Service Revenue Received Cost of Sales Paid Selling
ILLUSTRATION 24-1 OPERATING, INVESTING, AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES + Sales and Service Revenue Received Cost of Sales Paid Selling
