BYLINE: Michael F. Goodchild, University of California, Santa Barbara,
|
|
|
- Sophie Lester
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TITLE: SPATIAL DATA ANALYSIS BYLINE: Michael F. Goodchild, University of California, Santa Barbara, SYNONYMS: spatial analysis, geographical data analysis, geographical analysis DEFINITION: Methods of data analysis perform logical or mathematical manipulations on data in order to test hypotheses, expose anomalies or patterns, or create summaries or views that expose particular traits. Data often refer to specific locations in some space. To qualify as spatial, the locations must be known and must affect the outcome of the analysis. While many spaces might be relevant, including the space of the human brain or the space of the human genome, the history of spatial data analysis is dominated by location in geographic space, in other words location on or near the surface of the Earth. Thus geographical and spatial are often essentially synonymous. More formally, spatial data analysis can be defined as a set of techniques devised for the manipulation of data whose outcomes are not invariant under relocation of the objects of interest in some space. The term exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) describes an important subset that emphasizes real-time interaction, the creation of multiple views of data, the search for patterns and anomalies, and the generation of new hypotheses as opposed to the formal testing of existing ideas. The term spatial data mining describes another important subset that emphasizes the analysis of very large volumes of spatial data. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: Berry and Marble [1] made one of the earliest efforts to assemble a systematic review of methods of spatial data analysis, drawing on a literature that had accumulated for many decades. Their interest was sparked in large part by what later became known as the Quantitative Revolution in Geography, a paradigm shift that originated at the University of Washington in the late 1950s and spread rapidly as the original group of graduate students found faculty positions. Bunge [2] summarized the core concept: that the analysis of patterns of phenomena on the Earth s surface could lead to a set of formal theories about the behavior of human and natural systems, and that the discovery of such theories would put the discipline of geography on a sound scientific footing. Substantial progress was made in the 1960s, particularly in the study of patterns of settlement and economic activity, and in the study of such physical phenomena as meandering rivers and stream channel networks. Beginning in the 1960s, the development of geographic information systems (GIS) provided a major impetus by creating a simple structure in which methods of spatial data analysis could be implemented. By the 1980s GIS had become a popular and rapidly growing software application, with a flourishing industry and tools to enable spatial data analysis, along with the necessary techniques for data acquisition, editing, and display. Today GIS is often portrayed as an engine for spatial data analysis, and many new techniques have been added to what are now literally thousands of methods. GIS finds application in virtually all disciplines that deal with the surface and near-surface of the 1
2 Earth, ranging from ecology and geology to sociology and political science [3]. It is extensively used in logistics, in planning and public decision making, in military and intelligence applications, and in the management of utility networks. While the use of computers to perform spatial data analysis was already well established in the 1960s, ESDA emerged rather later, when the graphics and interactive capabilities of computers had advanced sufficiently. By the early 1990s researchers were developing novel ways of linking multiple views using the windowing techniques that emerged at that time, and exploiting the high-resolution graphics that became available on standard personal computers. Today, interactive tools inspired by ESDA are widely available in GIS products, and more specialized software is also available (see, for example, GeoDa, Interest in spatial data mining has grown in the past decade, driven in part by the increasing availability of very large volumes of spatial data. For example, it is now routine to capture the location and time of use of credit and debit cards, and to apply sophisticated algorithms in an effort to detect fraudulent use. Heavy use of spatial data analysis is made by intelligence agencies, based on software that can examine telephone and traffic and detect references to places. SCIENTIFIC FUNDAMENTALS: Several approaches have been devised for organizing the thousands of techniques that qualify as spatial data analysis. Perhaps the commonest, represented by several recent textbooks and by the organization of some GIS user interfaces, is based on a taxonomy of spatial data types. Very broadly, one can capture variation within a space using either raster or vector structures; a raster structure is created by dividing the space into discrete, regularly shaped elements and describing the contents of each, while vector structures describe each feature present in the space as either a point, line, area, or volume, with associated attributes. Tomlin [4] and others have systematized the analysis of raster data in schemata described as map algebras, image algebras, or cartographic modeling, and several GIS have adopted these schemata in their user interfaces. In one such schema the analysis of raster data is described as either focal, local, zonal, or global: focal operations are performed independently on the contents of each cell; local operations are performed on a cell and its immediate neighborhood; zonal operations apply to contiguous patches of cells with identical descriptions; and global operations apply to the entire raster. To date a similarly simple systematization of vector operations has not been achieved. Instead, several textbooks (e.g., [5], [6]) organize methods of vector-based analysis according to the types of features being analyzed, focusing in turn on points, lines, areas, and volumes. For example, techniques for the analysis of sets of points might determine the degree of dispersion of the points; search for anomalous clusters; or find a shortest tour through the points. Some texts also provide descriptions of methods for the analysis of relationships or interactions between features. For example, retailers and traffic engineers commonly use methods of spatial data analysis to predict the numbers of trips 2
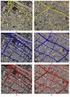
3 expected between home neighborhood areas and such destination points as shopping centers or places of work. Longley et al. [3] use a different organizing scheme that is designed to be more strongly related to user motivation, and to overcome some of the ambiguities inherent in an emphasis on data type. Their scheme assigns techniques to six categories, ordered by increasing conceptual sophistication: query and reasoning, measurement, transformation, descriptive summary, optimization, and hypothesis testing. Query and reasoning functions rely on the presentation of alternative views to the user. For example, a set of data on average income by US state might be presented as a map, as a table, as a histogram, and as a scatterplot in which average income is graphed against another variable such as percent with more than high-school education. The user gains insight by examining the alternative views, by querying specific values, or by selecting data items in one window and seeing them highlighted in the other windows. Measurement functions represent one of the earliest motivations for GIS. Manual methods for obtaining measures of such properties as area, length, slope, or shape from maps are notoriously inaccurate, tedious, and time-consuming, whereas it is trivial to obtain them from digital representations. Nevertheless digital representations are only approximations or generalizations of real phenomena, and many estimates exhibit representation-related biases. Transformation functions obtain new objects, or new properties of those objects. They include many key GIS functions, including buffering (the geometric dilation of points, lines, areas, or volumes), overlay (the computation of intersections between objects), and interpolation (the use of data from sample locations to estimate values at locations where no samples were taken). Figure 1 shows an example of buffering, using half-mile circles around points representing the schools of part of Los Angeles. The example was motivated by proposals to ban registered sex offenders from living within a specified distance of a school. [Figure 1 about here] Descriptive summaries include the widest range of spatial data analysis techniques. Standard univariate statistics such as the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and variance have equivalents in multidimensional spaces. Figure 2 shows the twodimensional equivalents of the mean and standard deviation applied to the black and white populations of Milwaukee, using data by census tract. A suite of summary statistics have been devised for measuring spatial dependence, a key property of many spaces based on the observation that measurements of many properties taken close together tend to be more similar than measurements taken far apart. The fields of spatial statistics and geostatistics are both based on this property, and provide ways of addressing it explicitly. Spatial heterogeneity, or the tendency for the properties of spaces to vary widely from one area to another, is also the subject of many forms of descriptive summary. The rapidly evolving field of local or place-based summaries (e.g., [7]) addresses the spatial 3
4 heterogeneity property directly, arguing that it is more important to determine how the results of spatial data analysis vary from one area to another than to attempt to extract single, global results. Another suite of summary statistics addresses the fragmentation of landscapes, with particularly strong applications in ecology. [Figure 2 about here] Methods of optimization focus on the design of spatial pattern rather than on its analysis. They include methods for optimum location of points (e.g., retail stores, schools), lines (e.g. roads, pipelines), and areas (e.g., political voting districts), as well as on the design of optimum routes (e.g., for delivery vehicles or school buses). Finally, methods of hypothesis testing address the process of inference, by which analysts reason from the analysis of a sample to conclusions about the larger world represented by the sample. Such methods are well known in statistical analysis, encompassing many well-known statistical tests, significance levels, and the formulation of null hypotheses. Unfortunately the application of such methods to spatial data is confounded by two major issues. First, it is rare for a sample of objects to be representative of any larger and welldefined set; instead, spatial data analysis is commonly applied to all of the objects that exist in a given study area. Second, it is also rare for objects distributed in space to be selected independently from any larger set; instead, the property of spatial dependence virtually ensures that nearby objects will have some degree of similarity. KEY APPLICATIONS As noted earlier, techniques of spatial data analysis can be applied to virtually all spaces, and all phenomena distributed within such spaces. Nevertheless, the vast majority of applications are found in geographic space, that is, the space defined by the surface and near-surface of the Earth, at spatial resolutions ranging from sub-meter to global. Many important applications have derived from the need to understand the mechanisms of disease, and particularly its transmission within human populations. The work of Dr. John Snow on cholera [8] is often cited as the seminal example, but today methods of spatial data analysis are routinely used to scan data on such diseases as cancer, searching for anomalous clusters and thus for potential causal mechanisms. Spatial data analysis has been central to the study of outbreaks of new diseases such as West Nile virus and SARS. Spatial data analysis has also been central to the study of landscape change, and related phenomena of urban sprawl, deforestation, desertification, and habitat destruction. Such analyses are often based on snapshots of landscape obtained from Earth-orbiting satellites, and can form the basis for sophisticated models of landscape change that can be used to investigate the future effects of management alternatives. Transportation applications are also particularly rich. Methods of spatial data analysis are routinely used to model traffic patterns, and to evaluate planning options, including new 4
5 roads, mass transit, and congestion pricing. The possibility of real-time tracking of vehicles using GPS has recently given this field new impetus. FUTURE DIRECTIONS The insights that can be obtained from spatial data analysis are limited by its essentially cross-sectional nature the need to draw inferences from snapshots obtained at one point in time. It is difficult, for example, to ascribe cause when no information is available about change through time. Thus there is great interest in the development of an improved suite of methods for spatiotemporal data analysis. In the past the lack of suitable data has been a major impediment, but today vast new sources are becoming available as the result of developments in satellite remote sensing, GPS tracking, and Internet-based data sharing. GIS owes much of its original stimulus to the paper map, which is of necessity flat. At global scales, analysis based on flattened or projected views of the Earth s surface can be misleading, and there is therefore strong interest in developing methods of spatial data analysis for the Earth s curved surface. This interest has been stimulated in part by the recent emergence of virtual globes, including Google Earth. CROSS REFERENCES: Geographic Information System, Spatial Data Types, Spatial Operations and Map Operations RECOMMENDED READING 1. Berry B. J. L., Marble D. F. (1968): Spatial Analysis: A Reader in Statistical Geography. Prentice Hall. 2. Bunge, W. (1966): Theoretical Geography. Gleerup. 3. Longley P. A., Goodchild M. F., Maguire D. J., Rhind D. W. (2005): Geographic Information Systems and Science. Wiley. 4. Tomlin C. D. (1990): Geographic Information Systems and Cartographic Modeling. Prentice Hall. 5. Haining R. P. (2003): Spatial Data Analysis: Theory and Practice. Cambridge University Press. 6. Bailey T. C., Gatrell A. C. (1995): Interactive Spatial Data Analysis. Longman. 7. Fotheringham A. S., Brunsdon C., Charlton M. (2002): Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships. Wiley. 8. Johnson S. (2006): The Ghost Map: The Story of London s Most Terrifying Epidemic and How It Changed Science, Cities, and the Modern World. Riverhead. 9. O Sullivan D., Unwin D. J. (2003): Geographic Information Analysis. Wiley. FIGURE CAPTIONS 1. The buffer operation. Half-mile buffers have been drawn around points representing the locations of schools in an area of central Los Angeles. Such buffers are often required by legislation; this example was motivated by a proposal to ban registered sex offenders from living within a prescribed distance of schools. 2. Two-dimensional equivalents of the mean and standard deviation. The larger ellipse shows the dispersion of the white population of Milwaukee around its centroid; the 5
6 smaller ellipse shows the greater concentration of the city s black population. The map shows percent black, using 1990 data by census tract. 6
GIS & Spatial Modeling
 Geography 4203 / 5203 GIS & Spatial Modeling Class 2: Spatial Doing - A discourse about analysis and modeling in a spatial context Updates Class homepage at: http://www.colorado.edu/geography/class_homepages/geog_4203
Geography 4203 / 5203 GIS & Spatial Modeling Class 2: Spatial Doing - A discourse about analysis and modeling in a spatial context Updates Class homepage at: http://www.colorado.edu/geography/class_homepages/geog_4203
Spatial Data Analysis
 14 Spatial Data Analysis OVERVIEW This chapter is the first in a set of three dealing with geographic analysis and modeling methods. The chapter begins with a review of the relevant terms, and an outlines
14 Spatial Data Analysis OVERVIEW This chapter is the first in a set of three dealing with geographic analysis and modeling methods. The chapter begins with a review of the relevant terms, and an outlines
A quick overview of geographic information systems (GIS) Uwe Deichmann, DECRG <udeichmann@worldbank.org>
 A quick overview of geographic information systems (GIS) Uwe Deichmann, DECRG Why is GIS important? A very large share of all types of information has a spatial component ( 80
A quick overview of geographic information systems (GIS) Uwe Deichmann, DECRG Why is GIS important? A very large share of all types of information has a spatial component ( 80
EXPLORING SPATIAL PATTERNS IN YOUR DATA
 EXPLORING SPATIAL PATTERNS IN YOUR DATA OBJECTIVES Learn how to examine your data using the Geostatistical Analysis tools in ArcMap. Learn how to use descriptive statistics in ArcMap and Geoda to analyze
EXPLORING SPATIAL PATTERNS IN YOUR DATA OBJECTIVES Learn how to examine your data using the Geostatistical Analysis tools in ArcMap. Learn how to use descriptive statistics in ArcMap and Geoda to analyze
WATER INTERACTIONS WITH ENERGY, ENVIRONMENT AND FOOD & AGRICULTURE Vol. II Spatial Data Handling and GIS - Atkinson, P.M.
 SPATIAL DATA HANDLING AND GIS Atkinson, P.M. School of Geography, University of Southampton, UK Keywords: data models, data transformation, GIS cycle, sampling, GIS functionality Contents 1. Background
SPATIAL DATA HANDLING AND GIS Atkinson, P.M. School of Geography, University of Southampton, UK Keywords: data models, data transformation, GIS cycle, sampling, GIS functionality Contents 1. Background
Geostatistics Exploratory Analysis
 Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Exploratory Analysis Carlos Alberto Felgueiras cfelgueiras@isegi.unl.pt
Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Exploratory Analysis Carlos Alberto Felgueiras cfelgueiras@isegi.unl.pt
SPATIAL ANALYSIS IN GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. A DATA MODEL ORffiNTED APPROACH
 POSTER SESSIONS 247 SPATIAL ANALYSIS IN GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. A DATA MODEL ORffiNTED APPROACH Kirsi Artimo Helsinki University of Technology Department of Surveying Otakaari 1.02150 Espoo,
POSTER SESSIONS 247 SPATIAL ANALYSIS IN GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. A DATA MODEL ORffiNTED APPROACH Kirsi Artimo Helsinki University of Technology Department of Surveying Otakaari 1.02150 Espoo,
Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies. 13 th May 2004. Content. What is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies 13 th May 2004 Content Introduction to GIS Data concepts Data input Analysis Applications selected examples What is GIS? Geographic Information
Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies 13 th May 2004 Content Introduction to GIS Data concepts Data input Analysis Applications selected examples What is GIS? Geographic Information
Identifying Schools for the Fruit in Schools Programme
 1 Identifying Schools for the Fruit in Schools Programme Introduction This report identifies New Zeland publicly funded schools for the Fruit in Schools programme. The schools are identified based on need.
1 Identifying Schools for the Fruit in Schools Programme Introduction This report identifies New Zeland publicly funded schools for the Fruit in Schools programme. The schools are identified based on need.
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
BYLINE: Michael F. Goodchild, University of California, Santa Barbara, www.geog.ucsb.edu/~good
 TITLE: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM BYLINE: Michael F. Goodchild, University of California, Santa Barbara, www.geog.ucsb.edu/~good SYNONYMS: geospatial information system, spatial information system DEFINITION:
TITLE: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM BYLINE: Michael F. Goodchild, University of California, Santa Barbara, www.geog.ucsb.edu/~good SYNONYMS: geospatial information system, spatial information system DEFINITION:
Introduction to GIS. Dr F. Escobar, Assoc Prof G. Hunter, Assoc Prof I. Bishop, Dr A. Zerger Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
 Introduction to GIS 1 Introduction to GIS http://www.sli.unimelb.edu.au/gisweb/ Dr F. Escobar, Assoc Prof G. Hunter, Assoc Prof I. Bishop, Dr A. Zerger Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
Introduction to GIS 1 Introduction to GIS http://www.sli.unimelb.edu.au/gisweb/ Dr F. Escobar, Assoc Prof G. Hunter, Assoc Prof I. Bishop, Dr A. Zerger Department of Geomatics, The University of Melbourne
Geography 4203 / 5203. GIS Modeling. Class (Block) 9: Variogram & Kriging
 Geography 4203 / 5203 GIS Modeling Class (Block) 9: Variogram & Kriging Some Updates Today class + one proposal presentation Feb 22 Proposal Presentations Feb 25 Readings discussion (Interpolation) Last
Geography 4203 / 5203 GIS Modeling Class (Block) 9: Variogram & Kriging Some Updates Today class + one proposal presentation Feb 22 Proposal Presentations Feb 25 Readings discussion (Interpolation) Last
Data, Measurements, Features
 Data, Measurements, Features Middle East Technical University Dep. of Computer Engineering 2009 compiled by V. Atalay What do you think of when someone says Data? We might abstract the idea that data are
Data, Measurements, Features Middle East Technical University Dep. of Computer Engineering 2009 compiled by V. Atalay What do you think of when someone says Data? We might abstract the idea that data are
A STATISTICS COURSE FOR ELEMENTARY AND MIDDLE SCHOOL TEACHERS. Gary Kader and Mike Perry Appalachian State University USA
 A STATISTICS COURSE FOR ELEMENTARY AND MIDDLE SCHOOL TEACHERS Gary Kader and Mike Perry Appalachian State University USA This paper will describe a content-pedagogy course designed to prepare elementary
A STATISTICS COURSE FOR ELEMENTARY AND MIDDLE SCHOOL TEACHERS Gary Kader and Mike Perry Appalachian State University USA This paper will describe a content-pedagogy course designed to prepare elementary
What is GIS? Geographic Information Systems. Introduction to ArcGIS. GIS Maps Contain Layers. What Can You Do With GIS? Layers Can Contain Features
 What is GIS? Geographic Information Systems Introduction to ArcGIS A database system in which the organizing principle is explicitly SPATIAL For CPSC 178 Visualization: Data, Pixels, and Ideas. What Can
What is GIS? Geographic Information Systems Introduction to ArcGIS A database system in which the organizing principle is explicitly SPATIAL For CPSC 178 Visualization: Data, Pixels, and Ideas. What Can
DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT
 270 COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT Degrees Offered: B.A., M.S. Chair: Liu, Shih-Sien ( 劉 士 仙 ) The Department Established in 1986, the Department of Transportation Management
270 COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT Degrees Offered: B.A., M.S. Chair: Liu, Shih-Sien ( 劉 士 仙 ) The Department Established in 1986, the Department of Transportation Management
Using Spatial Statistics In GIS
 Using Spatial Statistics In GIS K. Krivoruchko a and C.A. Gotway b a Environmental Systems Research Institute, 380 New York Street, Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA b Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;
Using Spatial Statistics In GIS K. Krivoruchko a and C.A. Gotway b a Environmental Systems Research Institute, 380 New York Street, Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA b Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;
Teaching a Progression of Courses in Geographic Information Science at Higher Education Institutions
 Teaching a Progression of Courses in Geographic Information Science at Higher Education Institutions Michael A. McAdams, Ali Demirci, Ahmet Karaburun, Mehmet Karakuyu, Süleyman İncekara Geography Department,
Teaching a Progression of Courses in Geographic Information Science at Higher Education Institutions Michael A. McAdams, Ali Demirci, Ahmet Karaburun, Mehmet Karakuyu, Süleyman İncekara Geography Department,
14 MAY/JUNE 2002 A CS IT BULLETIN
 14 MAY/JUNE 2002 A CS IT BULLETIN AGSM BULLETIN MAY/JUNE 2002 '15 Most of us are aware that GIS has now permeated all of the fields of surveying and mapping. This is true from the surveyor in the field,
14 MAY/JUNE 2002 A CS IT BULLETIN AGSM BULLETIN MAY/JUNE 2002 '15 Most of us are aware that GIS has now permeated all of the fields of surveying and mapping. This is true from the surveyor in the field,
Principles and Practices of Data Integration
 Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
Data Integration Data integration is the process of combining data of different themes, content, scale or spatial extent, projections, acquisition methods, formats, schema, or even levels of uncertainty,
Course 803401 DSS. Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
 Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803401 DSS Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization CS/MIS Department Information Sharing
Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803401 DSS Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization CS/MIS Department Information Sharing
Workshop: Using Spatial Analysis and Maps to Understand Patterns of Health Services Utilization
 Enhancing Information and Methods for Health System Planning and Research, Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES), January 19-20, 2004, Toronto, Canada Workshop: Using Spatial Analysis and Maps
Enhancing Information and Methods for Health System Planning and Research, Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES), January 19-20, 2004, Toronto, Canada Workshop: Using Spatial Analysis and Maps
CHAPTER-24 Mining Spatial Databases
 CHAPTER-24 Mining Spatial Databases 24.1 Introduction 24.2 Spatial Data Cube Construction and Spatial OLAP 24.3 Spatial Association Analysis 24.4 Spatial Clustering Methods 24.5 Spatial Classification
CHAPTER-24 Mining Spatial Databases 24.1 Introduction 24.2 Spatial Data Cube Construction and Spatial OLAP 24.3 Spatial Association Analysis 24.4 Spatial Clustering Methods 24.5 Spatial Classification
Reading Questions. Lo and Yeung, 2007: 2 19. Schuurman, 2004: Chapter 1. 1. What distinguishes data from information? How are data represented?
 Reading Questions Week two Lo and Yeung, 2007: 2 19. Schuurman, 2004: Chapter 1. 1. What distinguishes data from information? How are data represented? 2. What sort of problems are GIS designed to solve?
Reading Questions Week two Lo and Yeung, 2007: 2 19. Schuurman, 2004: Chapter 1. 1. What distinguishes data from information? How are data represented? 2. What sort of problems are GIS designed to solve?
Geovisualization. Geovisualization, cartographic transformation, cartograms, dasymetric maps, scientific visualization (ViSC), PPGIS
 13 Geovisualization OVERVIEW Using techniques of geovisualization, GIS provides a far richer and more flexible medium for portraying attribute distributions than the paper mapping which is covered in Chapter
13 Geovisualization OVERVIEW Using techniques of geovisualization, GIS provides a far richer and more flexible medium for portraying attribute distributions than the paper mapping which is covered in Chapter
Big Ideas in Mathematics
 Big Ideas in Mathematics which are important to all mathematics learning. (Adapted from the NCTM Curriculum Focal Points, 2006) The Mathematics Big Ideas are organized using the PA Mathematics Standards
Big Ideas in Mathematics which are important to all mathematics learning. (Adapted from the NCTM Curriculum Focal Points, 2006) The Mathematics Big Ideas are organized using the PA Mathematics Standards
Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
 Turban, Aronson, and Liang Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
Turban, Aronson, and Liang Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
Sanjeev Kumar. contribute
 RESEARCH ISSUES IN DATAA MINING Sanjeev Kumar I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, Pusa, New Delhi-110012 sanjeevk@iasri.res.in 1. Introduction The field of data mining and knowledgee discovery is emerging as a
RESEARCH ISSUES IN DATAA MINING Sanjeev Kumar I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, Pusa, New Delhi-110012 sanjeevk@iasri.res.in 1. Introduction The field of data mining and knowledgee discovery is emerging as a
REGIONAL CENTRE FOR TRAINING IN AEROSPACE SURVEYS (RECTAS) MASTER IN GEOINFORMATION PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT
 REGIONAL CENTRE FOR TRAINING IN AEROSPACE SURVEYS (RECTAS) MASTER IN GEOINFORMATION PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME DESCRIPTION October 2014 1. The programme The academic programme shall be referred
REGIONAL CENTRE FOR TRAINING IN AEROSPACE SURVEYS (RECTAS) MASTER IN GEOINFORMATION PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME DESCRIPTION October 2014 1. The programme The academic programme shall be referred
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Economics 1
 Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Economics 1 Henry G. Overman (London School of Economics) 5 th January 2006 Abstract: Geographical Information Systems (GIS) are used for inputting, storing,
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Economics 1 Henry G. Overman (London School of Economics) 5 th January 2006 Abstract: Geographical Information Systems (GIS) are used for inputting, storing,
Geographically weighted visualization interactive graphics for scale-varying exploratory analysis
 Geographically weighted visualization interactive graphics for scale-varying exploratory analysis Chris Brunsdon 1, Jason Dykes 2 1 Department of Geography Leicester University Leicester LE1 7RH cb179@leicester.ac.uk
Geographically weighted visualization interactive graphics for scale-varying exploratory analysis Chris Brunsdon 1, Jason Dykes 2 1 Department of Geography Leicester University Leicester LE1 7RH cb179@leicester.ac.uk
Why Taking This Course? Course Introduction, Descriptive Statistics and Data Visualization. Learning Goals. GENOME 560, Spring 2012
 Why Taking This Course? Course Introduction, Descriptive Statistics and Data Visualization GENOME 560, Spring 2012 Data are interesting because they help us understand the world Genomics: Massive Amounts
Why Taking This Course? Course Introduction, Descriptive Statistics and Data Visualization GENOME 560, Spring 2012 Data are interesting because they help us understand the world Genomics: Massive Amounts
How To Write A Data Analysis
 Mathematics Probability and Statistics Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction
Mathematics Probability and Statistics Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WHAT IS A GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM? A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer-based tool for mapping and analyzing spatial data. GIS technology integrates
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WHAT IS A GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM? A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer-based tool for mapping and analyzing spatial data. GIS technology integrates
Raster Operations. Local, Neighborhood, and Zonal Approaches. Rebecca McLain Geography 575 Fall 2009. Raster Operations Overview
 Raster Operations Local, Neighborhood, and Zonal Approaches Rebecca McLain Geography 575 Fall 2009 Raster Operations Overview Local: Operations performed on a cell by cell basis Neighborhood: Operations
Raster Operations Local, Neighborhood, and Zonal Approaches Rebecca McLain Geography 575 Fall 2009 Raster Operations Overview Local: Operations performed on a cell by cell basis Neighborhood: Operations
FROM GIS TO GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SCIENCE IN UNIVERSITY EDUCATION
 FROM GIS TO GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SCIENCE IN UNIVERSITY EDUCATION Prof. Kirsi VIRRANTAUS, Chair of FIG Commission 2, Finland Key words: Geographic Information Science, spatial analysis, spatial modelling,
FROM GIS TO GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SCIENCE IN UNIVERSITY EDUCATION Prof. Kirsi VIRRANTAUS, Chair of FIG Commission 2, Finland Key words: Geographic Information Science, spatial analysis, spatial modelling,
Numerical Algorithms Group. Embedded Analytics. A cure for the common code. www.nag.com. Results Matter. Trust NAG.
 Embedded Analytics A cure for the common code www.nag.com Results Matter. Trust NAG. Executive Summary How much information is there in your data? How much is hidden from you, because you don t have access
Embedded Analytics A cure for the common code www.nag.com Results Matter. Trust NAG. Executive Summary How much information is there in your data? How much is hidden from you, because you don t have access
MASTERS OF PHILOSOPHY (M. PHIL.) GEOGRAPHY DETAILED SYLLABUS SESSION 2013-14
 MASTERS OF PHILOSOPHY (M. PHIL.) GEOGRAPHY DETAILED SYLLABUS SESSION 2013-14 UNIT - I PAPER I RESEARCH METHODOLOGY THEORY AND TECHNIQUES Research: Definition, Importance and Meaning of research, Characteristics
MASTERS OF PHILOSOPHY (M. PHIL.) GEOGRAPHY DETAILED SYLLABUS SESSION 2013-14 UNIT - I PAPER I RESEARCH METHODOLOGY THEORY AND TECHNIQUES Research: Definition, Importance and Meaning of research, Characteristics
Applying GIS Analysis to Archaeological Research in Canada
 Applying GIS Analysis to Archaeological Research in Canada T A L K B Y D R. K I S H A S U P E R N A N T P R E S E N T E D A T G E O A L B E R T A 2 0 1 3 S E P T E M B E R 2 3, 2 0 1 3 Overview Review
Applying GIS Analysis to Archaeological Research in Canada T A L K B Y D R. K I S H A S U P E R N A N T P R E S E N T E D A T G E O A L B E R T A 2 0 1 3 S E P T E M B E R 2 3, 2 0 1 3 Overview Review
Spatial Data Mining for Customer Segmentation
 Spatial Data Mining for Customer Segmentation Data Mining in Practice Seminar, Dortmund, 2003 Dr. Michael May Fraunhofer Institut Autonome Intelligente Systeme Spatial Data Mining, Michael May, Fraunhofer
Spatial Data Mining for Customer Segmentation Data Mining in Practice Seminar, Dortmund, 2003 Dr. Michael May Fraunhofer Institut Autonome Intelligente Systeme Spatial Data Mining, Michael May, Fraunhofer
SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS
 SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: Geographic information systems and Map projections. Content that needs to be covered for examination
SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: Geographic information systems and Map projections. Content that needs to be covered for examination
Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping
 Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping NRS 516, Spring 2016 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural
Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping NRS 516, Spring 2016 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural
Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems
 LIBER QUARTERLY, ISSN 1435-5205 LIBER 1999. All rights reserved K.G. Saur, Munich. Printed in Germany Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems by PIOTR CICHOCINSKI ABSTRACT This paper presents
LIBER QUARTERLY, ISSN 1435-5205 LIBER 1999. All rights reserved K.G. Saur, Munich. Printed in Germany Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems by PIOTR CICHOCINSKI ABSTRACT This paper presents
Tracking System for GPS Devices and Mining of Spatial Data
 Tracking System for GPS Devices and Mining of Spatial Data AIDA ALISPAHIC, DZENANA DONKO Department for Computer Science and Informatics Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Sarajevo Zmaja
Tracking System for GPS Devices and Mining of Spatial Data AIDA ALISPAHIC, DZENANA DONKO Department for Computer Science and Informatics Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Sarajevo Zmaja
DIABLO VALLEY COLLEGE CATALOG 2015-2016
 GEOGRAPHY GEOG Tish Young, Dean Physical Sciences and Engineering Division Physical Sciences Building, Room 263 Possible career opportunities Geography is an interdisciplinary study focusing on the spatial
GEOGRAPHY GEOG Tish Young, Dean Physical Sciences and Engineering Division Physical Sciences Building, Room 263 Possible career opportunities Geography is an interdisciplinary study focusing on the spatial
Chapter 5. Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data. Visualization
 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization 5-1 Learning Objectives
Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization 5-1 Learning Objectives
Data Visualization Techniques and Practices Introduction to GIS Technology
 Data Visualization Techniques and Practices Introduction to GIS Technology Michael Greene Advanced Analytics & Modeling, Deloitte Consulting LLP March 16 th, 2010 Antitrust Notice The Casualty Actuarial
Data Visualization Techniques and Practices Introduction to GIS Technology Michael Greene Advanced Analytics & Modeling, Deloitte Consulting LLP March 16 th, 2010 Antitrust Notice The Casualty Actuarial
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS
 INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
A GIS helps you answer questions and solve problems by looking at your data in a way that is quickly understood and easily shared.
 A Geographic Information System (GIS) integrates hardware, software, and data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information. GIS allows us to view,
A Geographic Information System (GIS) integrates hardware, software, and data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information. GIS allows us to view,
MEng, BSc Applied Computer Science
 School of Computing FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MEng, BSc Applied Computer Science Year 1 COMP1212 Computer Processor Effective programming depends on understanding not only how to give a machine instructions
School of Computing FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MEng, BSc Applied Computer Science Year 1 COMP1212 Computer Processor Effective programming depends on understanding not only how to give a machine instructions
Objectives. Raster Data Discrete Classes. Spatial Information in Natural Resources FANR 3800. Review the raster data model
 Spatial Information in Natural Resources FANR 3800 Raster Analysis Objectives Review the raster data model Understand how raster analysis fundamentally differs from vector analysis Become familiar with
Spatial Information in Natural Resources FANR 3800 Raster Analysis Objectives Review the raster data model Understand how raster analysis fundamentally differs from vector analysis Become familiar with
Chapter 111. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics. Subchapter B. Middle School
 Middle School 111.B. Chapter 111. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics Subchapter B. Middle School Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter B issued under the Texas Education
Middle School 111.B. Chapter 111. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics Subchapter B. Middle School Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter B issued under the Texas Education
The Scientific Data Mining Process
 Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
School of Public Health and Health Services Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics
 School of Public Health and Health Services Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Graduate Certificate Public Health Microbiology and Emerging Infectious Diseases 2011-2012 Program Directors for
School of Public Health and Health Services Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Graduate Certificate Public Health Microbiology and Emerging Infectious Diseases 2011-2012 Program Directors for
The Use of Geographic Information Systems in Risk Assessment
 The Use of Geographic Information Systems in Risk Assessment With Specific Focus on the RiVAMP Methodology Presented by Nadine Brown August 27, 2012 Climate Studies Group Mona Climate Change Workshop Presentation
The Use of Geographic Information Systems in Risk Assessment With Specific Focus on the RiVAMP Methodology Presented by Nadine Brown August 27, 2012 Climate Studies Group Mona Climate Change Workshop Presentation
Street Address: 1111 Franklin Street Oakland, CA 94607. Mailing Address: 1111 Franklin Street Oakland, CA 94607
 Contacts University of California Curriculum Integration (UCCI) Institute Sarah Fidelibus, UCCI Program Manager Street Address: 1111 Franklin Street Oakland, CA 94607 1. Program Information Mailing Address:
Contacts University of California Curriculum Integration (UCCI) Institute Sarah Fidelibus, UCCI Program Manager Street Address: 1111 Franklin Street Oakland, CA 94607 1. Program Information Mailing Address:
Information Visualization WS 2013/14 11 Visual Analytics
 1 11.1 Definitions and Motivation Lot of research and papers in this emerging field: Visual Analytics: Scope and Challenges of Keim et al. Illuminating the path of Thomas and Cook 2 11.1 Definitions and
1 11.1 Definitions and Motivation Lot of research and papers in this emerging field: Visual Analytics: Scope and Challenges of Keim et al. Illuminating the path of Thomas and Cook 2 11.1 Definitions and
Technology has transformed the way in which science is conducted. Almost
 Chapter 1 Educational Technology in the Science Classroom Glen Bull and Randy L. Bell Technology has transformed the way in which science is conducted. Almost every aspect of scientific exploration has
Chapter 1 Educational Technology in the Science Classroom Glen Bull and Randy L. Bell Technology has transformed the way in which science is conducted. Almost every aspect of scientific exploration has
APPLICATIONS AND RESEARCH ON GIS FOR THE REAL ESTATE
 APPLICATIONS AND RESEARCH ON GIS FOR THE REAL ESTATE Chengda Lin, Lingkui Meng, Heping Pan School of Remote Sensing Information Engineering Wuhan University, 129 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430079, China Tel: (86-27)-8740-4336
APPLICATIONS AND RESEARCH ON GIS FOR THE REAL ESTATE Chengda Lin, Lingkui Meng, Heping Pan School of Remote Sensing Information Engineering Wuhan University, 129 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430079, China Tel: (86-27)-8740-4336
Spatial Analysis of Accessibility to Health Services in Greater London
 Spatial Analysis of Accessibility to Health Services in Greater London Centre for Geo-Information Studies University of East London June 2008 Contents 1. The Brief 3 2. Methods 4 3. Main Results 6 4. Extension
Spatial Analysis of Accessibility to Health Services in Greater London Centre for Geo-Information Studies University of East London June 2008 Contents 1. The Brief 3 2. Methods 4 3. Main Results 6 4. Extension
MEng, BSc Computer Science with Artificial Intelligence
 School of Computing FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MEng, BSc Computer Science with Artificial Intelligence Year 1 COMP1212 Computer Processor Effective programming depends on understanding not only how to give
School of Computing FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MEng, BSc Computer Science with Artificial Intelligence Year 1 COMP1212 Computer Processor Effective programming depends on understanding not only how to give
KEY WORDS: Geoinformatics, Geoinformation technique, Remote Sensing, Information technique, Curriculum, Surveyor.
 CURRICULUM OF GEOINFORMATICS INTEGRATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Kirsi VIRRANTAUS*, Henrik HAGGRÉN** Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Department of Surveying
CURRICULUM OF GEOINFORMATICS INTEGRATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Kirsi VIRRANTAUS*, Henrik HAGGRÉN** Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Department of Surveying
FUTURE VIEWS OF FIELD DATA COLLECTION IN STATISTICAL SURVEYS
 FUTURE VIEWS OF FIELD DATA COLLECTION IN STATISTICAL SURVEYS Sarah Nusser Department of Statistics & Statistical Laboratory Iowa State University nusser@iastate.edu Leslie Miller Department of Computer
FUTURE VIEWS OF FIELD DATA COLLECTION IN STATISTICAL SURVEYS Sarah Nusser Department of Statistics & Statistical Laboratory Iowa State University nusser@iastate.edu Leslie Miller Department of Computer
Geospatial Sciences: From Ph.D. to Google Earth
 Geospatial Sciences: From Ph.D. to Google Earth Dr. Ronald Briggs The University of Texas at Dallas Program in Geospatial Information Sciences briggs@utdallas.edu From Ph.D. to Google Earth 1990 2008 You
Geospatial Sciences: From Ph.D. to Google Earth Dr. Ronald Briggs The University of Texas at Dallas Program in Geospatial Information Sciences briggs@utdallas.edu From Ph.D. to Google Earth 1990 2008 You
Utilizing spatial information systems for non-spatial-data analysis
 Jointly published by Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Scientometrics, and Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht Vol. 51, No. 3 (2001) 563 571 Utilizing spatial information systems for non-spatial-data analysis
Jointly published by Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Scientometrics, and Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht Vol. 51, No. 3 (2001) 563 571 Utilizing spatial information systems for non-spatial-data analysis
096 Professional Readiness Examination (Mathematics)
 096 Professional Readiness Examination (Mathematics) Effective after October 1, 2013 MI-SG-FLD096M-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW
096 Professional Readiness Examination (Mathematics) Effective after October 1, 2013 MI-SG-FLD096M-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW
A Correlation of. to the. South Carolina Data Analysis and Probability Standards
 A Correlation of to the South Carolina Data Analysis and Probability Standards INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how Stats in Your World 2012 meets the indicators of the South Carolina Academic Standards
A Correlation of to the South Carolina Data Analysis and Probability Standards INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how Stats in Your World 2012 meets the indicators of the South Carolina Academic Standards
Raster Data Structures
 Raster Data Structures Tessellation of Geographical Space Geographical space can be tessellated into sets of connected discrete units, which completely cover a flat surface. The units can be in any reasonable
Raster Data Structures Tessellation of Geographical Space Geographical space can be tessellated into sets of connected discrete units, which completely cover a flat surface. The units can be in any reasonable
Field Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing
 Field Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing Section A: Introduction Chapter 1: GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork 1 GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork The widespread use of computers
Field Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing Section A: Introduction Chapter 1: GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork 1 GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork The widespread use of computers
USING SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS FOR INFORMATION VISUALIZATION AND KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY IN COMPLEX GEOSPATIAL DATASETS
 USING SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS FOR INFORMATION VISUALIZATION AND KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY IN COMPLEX GEOSPATIAL DATASETS Koua, E.L. International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation (ITC).
USING SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS FOR INFORMATION VISUALIZATION AND KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY IN COMPLEX GEOSPATIAL DATASETS Koua, E.L. International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation (ITC).
Data Driven Discovery In the Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences
 Data Driven Discovery In the Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences Simon Appleford, Marshall Scott Poole, Kevin Franklin, Peter Bajcsy, Alan B. Craig, Institute for Computing in the Humanities, Arts,
Data Driven Discovery In the Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences Simon Appleford, Marshall Scott Poole, Kevin Franklin, Peter Bajcsy, Alan B. Craig, Institute for Computing in the Humanities, Arts,
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Exploration is a process of discovery. In the database exploration process, an analyst executes a sequence of transformations over a collection of data structures to discover useful
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Exploration is a process of discovery. In the database exploration process, an analyst executes a sequence of transformations over a collection of data structures to discover useful
Bowdoin Computer Science
 Bowdoin Science What is computer science, what are its applications in other disciplines, and its impact in society? 101: Introduction to CS Pre-requisites: none Assumes no prior knowledge of programming
Bowdoin Science What is computer science, what are its applications in other disciplines, and its impact in society? 101: Introduction to CS Pre-requisites: none Assumes no prior knowledge of programming
GIS. Digital Humanities Boot Camp Series
 GIS Digital Humanities Boot Camp Series GIS Fundamentals GIS Fundamentals Definition of GIS A geographic information system (GIS) is used to describe and characterize spatial data for the purpose of visualizing
GIS Digital Humanities Boot Camp Series GIS Fundamentals GIS Fundamentals Definition of GIS A geographic information system (GIS) is used to describe and characterize spatial data for the purpose of visualizing
4.1 Exploratory Analysis: Once the data is collected and entered, the first question is: "What do the data look like?"
 Data Analysis Plan The appropriate methods of data analysis are determined by your data types and variables of interest, the actual distribution of the variables, and the number of cases. Different analyses
Data Analysis Plan The appropriate methods of data analysis are determined by your data types and variables of interest, the actual distribution of the variables, and the number of cases. Different analyses
SUMMER SCHOOL ON ADVANCES IN GIS
 SUMMER SCHOOL ON ADVANCES IN GIS Six Workshops Overview The workshop sequence at the UMD Center for Geospatial Information Science is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of current state-of-the-art
SUMMER SCHOOL ON ADVANCES IN GIS Six Workshops Overview The workshop sequence at the UMD Center for Geospatial Information Science is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of current state-of-the-art
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Introduction to Geographical. Information Systems. Government 1008. Lecture 1: Introduction to Course and Content Sumeeta Srinivasan
 Government 1008 Introduction to Geographical Information Systems Lecture 1: Introduction to Course and Content Sumeeta Srinivasan Reference: Longley, Goodchild, et al. Geographic Information Systems and
Government 1008 Introduction to Geographical Information Systems Lecture 1: Introduction to Course and Content Sumeeta Srinivasan Reference: Longley, Goodchild, et al. Geographic Information Systems and
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Probability and Statistics
 South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Probability and Statistics South Carolina College- and Career-Ready Mathematical Process Standards The South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR)
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Probability and Statistics South Carolina College- and Career-Ready Mathematical Process Standards The South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR)
DATA QUALITY IN GIS TERMINOLGY GIS11
 DATA QUALITY IN GIS When using a GIS to analyse spatial data, there is sometimes a tendency to assume that all data, both locational and attribute, are completely accurate. This of course is never the
DATA QUALITY IN GIS When using a GIS to analyse spatial data, there is sometimes a tendency to assume that all data, both locational and attribute, are completely accurate. This of course is never the
Graduate Certificate in Systems Engineering
 Graduate Certificate in Systems Engineering Systems Engineering is a multi-disciplinary field that aims at integrating the engineering and management functions in the development and creation of a product,
Graduate Certificate in Systems Engineering Systems Engineering is a multi-disciplinary field that aims at integrating the engineering and management functions in the development and creation of a product,
BRIEF HISTORY OF GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 BRIEF HISTORY OF GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS Ian McHarg (1920-1981) 1981) the Father of GIS Ian L. McHarg was born and raised in Scotland. He came to the United States after World War II to get a
BRIEF HISTORY OF GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS Ian McHarg (1920-1981) 1981) the Father of GIS Ian L. McHarg was born and raised in Scotland. He came to the United States after World War II to get a
Chapter Contents Page No
 Chapter Contents Page No Preface Acknowledgement 1 Basics of Remote Sensing 1 1.1. Introduction 1 1.2. Definition of Remote Sensing 1 1.3. Principles of Remote Sensing 1 1.4. Various Stages in Remote Sensing
Chapter Contents Page No Preface Acknowledgement 1 Basics of Remote Sensing 1 1.1. Introduction 1 1.2. Definition of Remote Sensing 1 1.3. Principles of Remote Sensing 1 1.4. Various Stages in Remote Sensing
Big Data and Complex Networks Analytics. Timos Sellis, CSIT Kathy Horadam, MGS
 Big Data and Complex Networks Analytics Timos Sellis, CSIT Kathy Horadam, MGS Big Data What is it? Most commonly accepted definition, by Gartner (the 3 Vs) Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and high-variety
Big Data and Complex Networks Analytics Timos Sellis, CSIT Kathy Horadam, MGS Big Data What is it? Most commonly accepted definition, by Gartner (the 3 Vs) Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and high-variety
Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration and Master's Degree course description
 Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration and Master's Degree course description Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration Department s Compulsory Requirements Course Description (402102) Principles
Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration and Master's Degree course description Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration Department s Compulsory Requirements Course Description (402102) Principles
Technology Trends In Geoinformation
 Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: drkadir@jupem.gov.my www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: drkadir@jupem.gov.my www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
Assessment of Workforce Demands to Shape GIS&T Education
 Assessment of Workforce Demands to Shape GIS&T Education Gudrun Wallentin, Barbara Hofer, Christoph Traun gudrun.wallentin@sbg.ac.at University of Salzburg, Dept. of Geoinformatics Z_GIS, Austria www.gi-n2k.eu
Assessment of Workforce Demands to Shape GIS&T Education Gudrun Wallentin, Barbara Hofer, Christoph Traun gudrun.wallentin@sbg.ac.at University of Salzburg, Dept. of Geoinformatics Z_GIS, Austria www.gi-n2k.eu
Current Standard: Mathematical Concepts and Applications Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary
 Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary A student shall apply concepts of shape, space, and measurement to solve problems involving two- and three-dimensional shapes by demonstrating an understanding of:
Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary A student shall apply concepts of shape, space, and measurement to solve problems involving two- and three-dimensional shapes by demonstrating an understanding of:
An Overview of Knowledge Discovery Database and Data mining Techniques
 An Overview of Knowledge Discovery Database and Data mining Techniques Priyadharsini.C 1, Dr. Antony Selvadoss Thanamani 2 M.Phil, Department of Computer Science, NGM College, Pollachi, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
An Overview of Knowledge Discovery Database and Data mining Techniques Priyadharsini.C 1, Dr. Antony Selvadoss Thanamani 2 M.Phil, Department of Computer Science, NGM College, Pollachi, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction
 Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
A SOCIAL NETWORK ANALYSIS APPROACH TO ANALYZE ROAD NETWORKS INTRODUCTION
 A SOCIAL NETWORK ANALYSIS APPROACH TO ANALYZE ROAD NETWORKS Kyoungjin Park Alper Yilmaz Photogrammetric and Computer Vision Lab Ohio State University park.764@osu.edu yilmaz.15@osu.edu ABSTRACT Depending
A SOCIAL NETWORK ANALYSIS APPROACH TO ANALYZE ROAD NETWORKS Kyoungjin Park Alper Yilmaz Photogrammetric and Computer Vision Lab Ohio State University park.764@osu.edu yilmaz.15@osu.edu ABSTRACT Depending
Introduction to Geographical Data Visualization
 perceptual edge Introduction to Geographical Data Visualization Stephen Few, Perceptual Edge Visual Business Intelligence Newsletter March/April 2009 The important stories that numbers have to tell often
perceptual edge Introduction to Geographical Data Visualization Stephen Few, Perceptual Edge Visual Business Intelligence Newsletter March/April 2009 The important stories that numbers have to tell often
Course Descriptions: Undergraduate/Graduate Certificate Program in Data Visualization and Analysis
 9/3/2013 Course Descriptions: Undergraduate/Graduate Certificate Program in Data Visualization and Analysis Seton Hall University, South Orange, New Jersey http://www.shu.edu/go/dava Visualization and
9/3/2013 Course Descriptions: Undergraduate/Graduate Certificate Program in Data Visualization and Analysis Seton Hall University, South Orange, New Jersey http://www.shu.edu/go/dava Visualization and
New Tools for Spatial Data Analysis in the Social Sciences
 New Tools for Spatial Data Analysis in the Social Sciences Luc Anselin University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign anselin@uiuc.edu edu Outline! Background! Visualizing Spatial and Space-Time Association!
New Tools for Spatial Data Analysis in the Social Sciences Luc Anselin University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign anselin@uiuc.edu edu Outline! Background! Visualizing Spatial and Space-Time Association!
Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables
 Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables Praveen Kumar 1, Peter Bajcsy 2, David Tcheng 2, David Clutter 2, Vikas Mehra 1, Wei-Wen Feng 2, Pratyush
Using D2K Data Mining Platform for Understanding the Dynamic Evolution of Land-Surface Variables Praveen Kumar 1, Peter Bajcsy 2, David Tcheng 2, David Clutter 2, Vikas Mehra 1, Wei-Wen Feng 2, Pratyush
Dr. Shih-Lung Shaw s Research on Space-Time GIS, Human Dynamics and Big Data
 Dr. Shih-Lung Shaw s Research on Space-Time GIS, Human Dynamics and Big Data for Geography Department s Faculty Research Highlight October 12, 2014 Shih-Lung Shaw, Ph.D. Alvin and Sally Beaman Professor
Dr. Shih-Lung Shaw s Research on Space-Time GIS, Human Dynamics and Big Data for Geography Department s Faculty Research Highlight October 12, 2014 Shih-Lung Shaw, Ph.D. Alvin and Sally Beaman Professor
Software Engineering for Big Data. CS846 Paulo Alencar David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo
 Software Engineering for Big Data CS846 Paulo Alencar David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Big Data Big data technologies describe a new generation of technologies that aim
Software Engineering for Big Data CS846 Paulo Alencar David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Big Data Big data technologies describe a new generation of technologies that aim
Short-Term Forecasting in Retail Energy Markets
 Itron White Paper Energy Forecasting Short-Term Forecasting in Retail Energy Markets Frank A. Monforte, Ph.D Director, Itron Forecasting 2006, Itron Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction 4 Forecasting
Itron White Paper Energy Forecasting Short-Term Forecasting in Retail Energy Markets Frank A. Monforte, Ph.D Director, Itron Forecasting 2006, Itron Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction 4 Forecasting
Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis
 Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis Further Thoughts on Experimental Design 16 Individuals (8 each from two populations) with replicates Pop 1 Pop 2 Randomly sample 4 individuals
Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis Further Thoughts on Experimental Design 16 Individuals (8 each from two populations) with replicates Pop 1 Pop 2 Randomly sample 4 individuals
