4. ABSORPTION ABSORPTION MECHANISMS ABSORPTION TRANSPORT MECHANISMS. Nutrients can be absorbed by. Active Transport
|
|
|
- Maria Lloyd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4. ABSORPTION ABSORPTION MECHANISMS Once the digestive process is completed, the nutrients have to be transferred across the digestive tract epithelium into the intracellular space and eventually into circulation for distribution throughout the body. Absorption can take place by several means (Fig. 4-1). It can be carried out by pinocytocis, active transport and passive diffusion. Some elements such as water are absorbed exclusively by diffusion using osmotic forces. Ions can enter enterocytes by diffusion, but may need to be transported actively to the intracellular space. Molecules move across membranes following concentration gradients, thus moving from more concentrated to less concentrated pools. They also can follow electric gradients whereby they move to areas of opposite charge. Active Transport There are several active transport mechanisms (Fig. 4-2). One uses metabolic energy in the form of ATP to drive Na +, K +. The ATPase pump creates an intracellular electronegative environment by lowering the concentration of Na + as a result of being pumped out into the intracellular space. In pumping Na + out, K + is brought into the cell. To prevent accumulation of intracellular K +, the cell has leak channels that permit the escape of K + into the intracellular space (Fig. 4-3). Co-transport A second mechanism is called co-transport or symport and consists of using the lower Na + concentration in the cell to attract two Na + at the same time than a third molecule, which could be a monosaccharide or an amino acid. A special protein binds all three components in the outside of the cell. As the Na + enters into the cell, it flips the protein and internalizes the desired molecule. Upon release of the Na +, the protein changes its conformation and releases the ABSORPTION Nutrients can be absorbed by o Pinocytocis o Active transport o Diffusion Water is absorbed entirely by diffusion (osmosis) o Can also be secreted that way Ions diffuse into enterocytes and are transported to intracellular space Molecules move across membranes following gradient o Concentration (to lower) o Electric (to opposite charge) Figure 4-1. Basic mechanism of absorption TRANSPORT MECHANISMS Active transport uses metabolic energy o Na +, K +, ATPase pump Create intracellular electronegative environment Lower Na + concentration Co-transport or symport o Carries 2 Na + and 1 glucose o Depends on Na + gradient Exchangers or antiports o Switch Na + for H + o Uses Na + gradients Figure 4-2. Mechanism of active transport used in absorption of nutrients molecule inside the cell. Finally, the empty molecule reverts to its original position, ready to pick up more cargo outside the cell (Fig. 4-3). V BS 122 Physiology II 31
2 CARBOHYDRATE ABSORPTION Directly linked to membranous phase digestion o Hydrolyzed monosaccharides transported actively into the cell by transport carrier proteins o Powered by Na + gradient Moved through basolateral space by diffusion Figure 4-3. Mechanism of co-transport of materials into the enterocytes using sodium gradient created by ATP driven sodium pump Figure 4-4. General aspects of carbohydrate absorption Antiports The third mechanism of transport is the use of exchangers or antiports. In these cases, a Na + is exchanged with an H + generating a Na + gradient, which is used to move molecules across the cell membrane. CARBOHYDRATE ABSORPTION All molecules of glucose are internalized using the co-transport system which uses Na + gradient. The passage of glucose from the epithelial cell to the intracellular space is done through facilitated diffusion via leak channels of the basolateral membrane (Fig. 4-4). Figure 4-6. Flow and migration of nutrients through the intestine towards the enterocyte for membranous digestion and absorption Figure 4-5. Internalization of monosaccharides after membranous digestion Galactose is absorbed using the same mechanism of Na + cotransport that permit the absorption of glucose (Figs. 4-3, 4-5). Fructose, however, operates in a different manner. Fructose is internalized into the cell by facilitated diffusion. This is a much slower system than the co-transport, thus, less fructose can be absorbed in a given time. Once fructose is in the cell, it is phosphorylated and converted to glucose before it is released into the intracellular space (Fig. 4-5). The flow of materials in the small intestine has different velocities depending on the position within the lumen of the intestine. Molecules in the center move faster than those closer to the wall (Fig. 4-6). In order to be able to internalize the V BS 122 Physiology II 32
3 carbohydrates, the membranous digestion has to take place. For the membrane bound enzymes to work, the sugars have to be in the area of the unstirred water layer and then get into the glycocalix. Once attached to the digestive enzymes, the molecules of monosaccharides are in very close proximity with the apical epithelial membrane where the co-transport system or facilitated diffusion takes place. PROTEIN ABSORPTION The absorption of protein is very similar to that of carbohydrates. The main difference is that at the end of the membranous digestion there are still many di and tripeptides, which can be absorbed into the enterocytes. These peptides are then hydrolyzed by enzymes located inside the enterocytes and the individual amino acids released by passive diffusion through the basolateral membrane into the intracellular space (Figs. 4-7, 4-8). PROTEIN ABSORPTION Similar to carbohydrates Also di and tripeptides internalized into enterocytes Digested by internal enzymes Released to intracellular space as free amino acids Figure 4-7. General aspects of protein absorption LIPID ABSORPTION The mechanism for lipid absorption is a little more complex Figure 4-8. Membranous digestion, absorption and intracellular digestion of small peptides by than that of carbohydrates or proteins. After digestion is enterocytes completed, we find micelles in the lumen of the small intestine. The micelle contacts the apical membrane of the enterocytes. The monoglycerides, as well as the cholesterol and LIPID ABSORPTION IN JEJUNUM Micelles contact enterocytes Most lipid components diffuse into enterocyte o Monoglycerides o Cholesterol o Vitamin A Free fatty acids are transported by membrane bound proteins o Fatty acid binding protein Bile acids continue in lumen Figure 4-9. Steps in lipid absorption What is left of the micelle, in the lumen of the small intestine, are vitamin A, diffuse from the micelle into the enterocyte. The free fatty acids have to be carried out by a series of membrane bound proteins called fatty acid binding proteins (Figs. 4-9, 4-11). BILE ACIDS Reach the ileum Are absorbed by Na + co-transport system Routed through the portal vasculature directly to liver They are recycled into gallbladder Figure Routes followed by bile acids V BS 122 Physiology II 33
4 the bile salts which are immediately reused in the formation of new micelles during the digestive process. Eventually, the bile salts reach the ileum where they are absorbed by a Na + co-transport system and routed through the portal system to the liver. In the liver, they are recycled into the lumen of the intestine or to the gallbladder forming the previously described enterohepatic circulation (Fig. 4-10). After the incorporation of all digested components into the enterocyte, the fatty acids and monoglycerides are transported to the endoplasmic reticulum where they are reconverted to triglycerides (Fig. 4-11).Here the cholesterol is reesterified and all of these are packed into chylomicrons (Fig ) in such a way that the cholesterol esters and the triglycerides form the core which is surrounded by phospholipids, cholesterol and proteins. The entire surface component makes the chylomicron water-soluble (Fig. 4-13). RECONSTITUTION Fatty acids, monoglycerides are converted into triglycerides o Endoplasmic reticulum Cholesterol is re-esterified Packed into chylomicrons o Core cholesterol ester and triglycerides o Surface phospholipids, cholesterol and proteins (water soluble) Figure Transfer of lipids from a micelle to the inside of the enterocyte by active transport and diffusion The chylomicrons (Fig. 4-15) are then released through the basolateral membrane into the intracellular space where they are picked up in the lymphatics, to reach the thoracic duct which empties into the vena cava. High concentrations of chylomicrons, as a result of a fatty meal, can generate lipemia or a white colour in plasma (Fig. 4-14). Figure Formation of chylomicrons EXPULSION Released through basolateral membrane Can not enter circulation Are transported through lymphatics Enter thoracic duct Empty into vena cava Causes lipemia (white colour in plasma) after a fatty meal Figure Expulsion of chylomicrons from enterocytes Figure Formation of chylomicrons in the enterocytes V BS 122 Physiology II 34
5 Figure Composition of a chylomicron WATER AND ELECTROLYTES ABSORPTION The absorption of water takes place by osmosis and may follow the paracellular route (moves between the cells through the tight junctions) or the intracellular route (enters the cell through the apical membrane and leaves the cell to the intracellular space through the basolateral membrane). Usually when the nutrients are absorbed and diffuse to the intercellular space (monosaccharides, amino acids, chylomicrons) they create an osmotic gradient which brings water from the ingesta. When these particles enter the capillaries they again create an osmotic pressure which attracts water into the villi microcirculation. (Figs. 4-16, 4-17). WATER ABSORPTION Trans cellular absorption By osmotic pressure o Created by other absorbed solutes (food) Then diffuses into capillary Under pressure can leave to intestinal lumen via tight junctions (paracellular) Figure Mechanism of water absorption Furthermore, within the villi there is counter-current transfer of water from the incoming arterial blood to the closely apposed venous return. This generates a more concentrated blood at the tip of the villi, where water is drawn by osmosis from the intracellular space. This process is similar to that used in the kidney. In the villi, the concentration at the entry point is 300 mosm while at the tip it may reach concentration of 600 mosm (Fig. 4-18). All the absorption of water takes place in a transcellular manner (Fig. 4-19). Figure Absorption of water in the intestine V BS 122 Physiology II 35
6 Figure Counter current mechanism of water absorption Figure Trans cellular absorption of water by enterocytes Under abnormal conditions, when there is an inflammation and there is more intracellular water, this creates the reverse process and water is transported from the intracellular space to the lumen of the intestine. This transport takes place exclusively through the paracellular route (Fig. 4-20). Water is also secreted by the endothelial cells in the crypt area. Usually, the majority of the ingested and secreted water is absorbed by the small intestine, leaving a relatively small amount to be excreted in the feces. A disruption to this balance causes diarrhoea. Figure Paracellular release of water into the lumen of the intestine V BS 122 Physiology II 36
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
4. Biology of the Cell
 4. Biology of the Cell Our primary focus in this chapter will be the plasma membrane and movement of materials across the plasma membrane. You should already be familiar with the basic structures and roles
4. Biology of the Cell Our primary focus in this chapter will be the plasma membrane and movement of materials across the plasma membrane. You should already be familiar with the basic structures and roles
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Modes of Membrane Transport
 Modes of Membrane Transport Transmembrane Transport movement of small substances through a cellular membrane (plasma, ER, mitochondrial..) ions, fatty acids, H 2 O, monosaccharides, steroids, amino acids
Modes of Membrane Transport Transmembrane Transport movement of small substances through a cellular membrane (plasma, ER, mitochondrial..) ions, fatty acids, H 2 O, monosaccharides, steroids, amino acids
Cell Membrane Structure (and How to Get Through One)
 Cell Membrane Structure (and How to Get Through One) A cell s membrane is a wall of sorts that defines the boundaries of a cell. The membrane provides protection and structure for the cell and acts as
Cell Membrane Structure (and How to Get Through One) A cell s membrane is a wall of sorts that defines the boundaries of a cell. The membrane provides protection and structure for the cell and acts as
OVERVIEW OF LIPID METABOLISM
 VERVIEW F LIPID METABLISM Date: September 20, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am 8:50 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve Chaney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building stephen_chaney@med.unc.edu 9663286 *Please
VERVIEW F LIPID METABLISM Date: September 20, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am 8:50 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve Chaney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building stephen_chaney@med.unc.edu 9663286 *Please
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT
 BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BMLS II / B Pharm II / BDS II VJ Temple
BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BMLS II / B Pharm II / BDS II VJ Temple
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Part A Multiple Choice 1. The fluid mosaic model describes membranes as having A. a set of protein channels separated by phospholipids. B. a bilayer of phospholipids in
Membrane Structure and Function Part A Multiple Choice 1. The fluid mosaic model describes membranes as having A. a set of protein channels separated by phospholipids. B. a bilayer of phospholipids in
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Physiology of Digestive system II
 Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function -plasma membrane acts as a barrier between cells and the surrounding. -plasma membrane is selective permeable -consist of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates -major lipids
Membrane Structure and Function -plasma membrane acts as a barrier between cells and the surrounding. -plasma membrane is selective permeable -consist of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates -major lipids
Mammalian Physiology. Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption
 Mammalian Physiology Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption 1UNLV UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 33 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the digestive secretions
Mammalian Physiology Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption 1UNLV UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 33 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the digestive secretions
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Absorption of Drugs. Transport of a drug from the GI tract
 Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
CHAPTER 5.1 5.2: Plasma Membrane Structure
 CHAPTER 5.1 5.2: Plasma Membrane Structure 1. Describe the structure of a phospholipid molecule. Be sure to describe their behavior in relationship to water. 2. What happens when a collection of phospholipids
CHAPTER 5.1 5.2: Plasma Membrane Structure 1. Describe the structure of a phospholipid molecule. Be sure to describe their behavior in relationship to water. 2. What happens when a collection of phospholipids
1.1.2. thebiotutor. AS Biology OCR. Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport. Module 1.2 Cell Membranes. Notes & Questions.
 thebiotutor AS Biology OCR Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport Module 1.2 Cell Membranes Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. The main
thebiotutor AS Biology OCR Unit F211: Cells, Exchange & Transport Module 1.2 Cell Membranes Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. The main
FIGURE 2.18. A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged) and hydrophilic (attracted to water).
 PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
7. A selectively permeable membrane only allows certain molecules to pass through.
 CHAPTER 2 GETTING IN & OUT OF CELLS PASSIVE TRANSPORT Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells. Some substances can cross the cell membrane
CHAPTER 2 GETTING IN & OUT OF CELLS PASSIVE TRANSPORT Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells. Some substances can cross the cell membrane
Cell Biology - Part 2 Membranes
 Cell Biology - Part 2 Membranes The organization of cells is made possible by membranes. Membranes isolate, partition, and compartmentalize cells. 1 Membranes isolate the inside of the cell from the outside
Cell Biology - Part 2 Membranes The organization of cells is made possible by membranes. Membranes isolate, partition, and compartmentalize cells. 1 Membranes isolate the inside of the cell from the outside
Weds 5/20/15. Membranes - finish last lecture outline. Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system
 Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
The Lipid Bilayer Is a Two-Dimensional Fluid
 The Lipid Bilayer Is a Two-Dimensional Fluid The aqueous environment inside and outside a cell prevents membrane lipids from escaping from bilayer, but nothing stops these molecules from moving about and
The Lipid Bilayer Is a Two-Dimensional Fluid The aqueous environment inside and outside a cell prevents membrane lipids from escaping from bilayer, but nothing stops these molecules from moving about and
Six major functions of membrane proteins: Transport Enzymatic activity
 CH 7 Membranes Cellular Membranes Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane. Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. The fluid mosaic
CH 7 Membranes Cellular Membranes Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane. Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. The fluid mosaic
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer. α-helix transmembrane domain. Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide
 Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer α-helix transmembrane domain Hydrophobic R groups of a.a. interact with fatty acid chains Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide Polar a.a. Hydrophilic
Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer α-helix transmembrane domain Hydrophobic R groups of a.a. interact with fatty acid chains Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide Polar a.a. Hydrophilic
Biological cell membranes
 Unit 14: Cell biology. 14 2 Biological cell membranes The cell surface membrane surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the cell s contents and the environment. The cell membrane has multiple
Unit 14: Cell biology. 14 2 Biological cell membranes The cell surface membrane surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the cell s contents and the environment. The cell membrane has multiple
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science
 Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Cell Transport and Plasma Membrane Structure
 Cell Transport and Plasma Membrane Structure POGIL Guided Inquiry Learning Targets Explain the importance of the plasma membrane. Compare and contrast different types of passive transport. Explain how
Cell Transport and Plasma Membrane Structure POGIL Guided Inquiry Learning Targets Explain the importance of the plasma membrane. Compare and contrast different types of passive transport. Explain how
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
General Protein Metabolism
 General Protein Metabolism Protein Digestion Dietary proteins are very large complex molecules that cannot be absorbed from the intestine. To be absorbed, dietary proteins must be digested to small simple
General Protein Metabolism Protein Digestion Dietary proteins are very large complex molecules that cannot be absorbed from the intestine. To be absorbed, dietary proteins must be digested to small simple
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Lipid Metabolism. Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college
 Lipid Metabolism Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college Lipids - Heterogenous group of biomolecules - Water insoluble (hydrophobic) - Soluble in organic and non-polar solvents acetone,
Lipid Metabolism Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college Lipids - Heterogenous group of biomolecules - Water insoluble (hydrophobic) - Soluble in organic and non-polar solvents acetone,
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet
 NAME ANSWER KEY DATE PERIOD Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet Composition of the Cell Membrane & Functions The cell membrane is also called the PLASMA membrane and is made of a phospholipid BI-LAYER.
NAME ANSWER KEY DATE PERIOD Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet Composition of the Cell Membrane & Functions The cell membrane is also called the PLASMA membrane and is made of a phospholipid BI-LAYER.
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
Lipids. Classifying Lipids
 (Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, sphingolipids, and cholesterol (together with proteins)
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, sphingolipids, and cholesterol (together with proteins)
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages. The Plasma Membrane Structure and Function. Phospholipids. I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II.
 BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
CELL MEMBRANES, TRANSPORT, and COMMUNICATION. Teacher Packet
 AP * BIOLOGY CELL MEMBRANES, TRANSPORT, and COMMUNICATION Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the production
AP * BIOLOGY CELL MEMBRANES, TRANSPORT, and COMMUNICATION Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the production
Lecture 6: Cholesterol (Ch. 9.1e, 9.2b, 19.7b,c) & Lipoproteins (Ch. 10.3*, 19.1, 19.7b,c)
 Lecture 6: Cholesterol (Ch. 9.1e, 9.2b, 19.7b,c) & Lipoproteins (Ch. 10.3*, 19.1, 19.7b,c) Next lecture: Fatty Acid Oxidation (Ch. 19.2), Ketone Bodies (Ch. 19.3) and Fatty Acid Biosynthesis (Ch. 19.4)
Lecture 6: Cholesterol (Ch. 9.1e, 9.2b, 19.7b,c) & Lipoproteins (Ch. 10.3*, 19.1, 19.7b,c) Next lecture: Fatty Acid Oxidation (Ch. 19.2), Ketone Bodies (Ch. 19.3) and Fatty Acid Biosynthesis (Ch. 19.4)
Mammalian Physiology. Cellular Membranes Membrane Transport UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 1 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Cellular Membranes Membrane Transport UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 1 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the structure of the cell membrane
Mammalian Physiology Cellular Membranes Membrane Transport UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 1 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the structure of the cell membrane
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Date: Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George. Score: 1) A cell with 1% solute concentration is placed in a beaker with a 5% solute concentration.
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
Homeostasis and Transport Module A Anchor 4
 Homeostasis and Transport Module A Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - Buffers play an important role in maintaining homeostasis in organisms. - To maintain homeostasis, unicellular organisms grow, respond to the
Homeostasis and Transport Module A Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - Buffers play an important role in maintaining homeostasis in organisms. - To maintain homeostasis, unicellular organisms grow, respond to the
17. The Digestion and Absorption of Food. Regulation of Gastrointestinal Processes
 chapter C H A P T E R 17 _ The Digestion and Overview: of the Gastrointestinal Organs Structure of the Gastrointestinal Tract Wall Digestion and Absorption Carbohydrate Protein Fat Vitamins Water and Minerals
chapter C H A P T E R 17 _ The Digestion and Overview: of the Gastrointestinal Organs Structure of the Gastrointestinal Tract Wall Digestion and Absorption Carbohydrate Protein Fat Vitamins Water and Minerals
Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End!
 Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End! General Chemical Principles 1. bonds are characterized by the sharing of electrons between the participating atoms. a. hydrogen b.
Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End! General Chemical Principles 1. bonds are characterized by the sharing of electrons between the participating atoms. a. hydrogen b.
Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet
 Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Composition of the Cell Membrane & Functions The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane and is made of a phospholipid bilayer. The phospholipids have a hydrophilic
Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Composition of the Cell Membrane & Functions The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane and is made of a phospholipid bilayer. The phospholipids have a hydrophilic
Chapter 26: The Urinary System
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Membrane Transport. Extracellular Concentration of X
 Use the following graph to answer questions 1 and 2. Rate of diffusion of X into the cell 1. Which of the following processes is represented by the above graph? c. Active transport 2. Molecule X is most
Use the following graph to answer questions 1 and 2. Rate of diffusion of X into the cell 1. Which of the following processes is represented by the above graph? c. Active transport 2. Molecule X is most
Section 7-3 Cell Boundaries
 Note: For the past several years, I ve been puzzling how to integrate new discoveries on the nature of water movement through cell membranes into Chapter 7. The Section below is a draft of my first efforts
Note: For the past several years, I ve been puzzling how to integrate new discoveries on the nature of water movement through cell membranes into Chapter 7. The Section below is a draft of my first efforts
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism)
 Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT (PASSIVE and ACTIVE) Webquest
 Name: Period: CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT (PASSIVE and ACTIVE) Webquest PART I: CELL MEMBRANES WEBSITE #1: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap1101 1. What is the BASIC UNIT of LIFE?
Name: Period: CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT (PASSIVE and ACTIVE) Webquest PART I: CELL MEMBRANES WEBSITE #1: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap1101 1. What is the BASIC UNIT of LIFE?
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 2. Goals/ What You Need to Know Goals What You Need to Know
 Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane. AP Biology
 Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane More than just a barrier Expanding our view of cell membrane beyond just a phospholipid bilayer barrier phospholipids plus Fluid Mosaic Model In 1972, S.J.
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane More than just a barrier Expanding our view of cell membrane beyond just a phospholipid bilayer barrier phospholipids plus Fluid Mosaic Model In 1972, S.J.
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Digestive system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Total body water ~(60% of body mass): Intracellular fluid ~2/3 or ~65% Extracellular fluid ~1/3 or ~35% fluid. Interstitial.
 http://www.bristol.ac.uk/phys-pharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.htmlpharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.html Physiology of the Cell Membrane Membrane proteins and their roles (channels,
http://www.bristol.ac.uk/phys-pharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.htmlpharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.html Physiology of the Cell Membrane Membrane proteins and their roles (channels,
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1. Lipids:
 (Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Classifying Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, p sphingolipids, p and cholesterol
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Classifying Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, p sphingolipids, p and cholesterol
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION
 LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse
 PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling CELL MEMBRANE. Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook
 Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling CELL MEMBRANE Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook HOW DOES THE LAB RELATE TO THE NEXT CHAPTER? SURFACE AREA: the entire outer covering of a cell that enables materials pass.
Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling CELL MEMBRANE Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook HOW DOES THE LAB RELATE TO THE NEXT CHAPTER? SURFACE AREA: the entire outer covering of a cell that enables materials pass.
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function
 Name Period Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Explain what is meant when
Name Period Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Explain what is meant when
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Small & Large Intestines
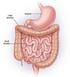 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Version 1.0. General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 2011. Biology BIOL1. (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease. Final.
 Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 2011 Biology BIOL1 (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and
Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 2011 Biology BIOL1 (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Chapter 25. The Small Intestine (The Absorption of Nutrients)
 hapter 25 The Small Intestine (The Absorption of Nutrients) Small Intestine nearly all chemical digestion and nutrient absorption occurs in small intestine the longest part of the digestive tract 2.7 to
hapter 25 The Small Intestine (The Absorption of Nutrients) Small Intestine nearly all chemical digestion and nutrient absorption occurs in small intestine the longest part of the digestive tract 2.7 to
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM. Section B: Enzymes
 CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
RAD 223. Radiography physiology. Lecture Notes. First lecture: Cell and Tissue
 RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal
 exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
