Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton
|
|
|
- Clara Barnett
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs and pelvic & pectoral girdles 7-1
2 Types of Bones 5 basic types of bones: long = compact short = spongy except surface flat = plates of compact enclosing spongy irregular = variable sesamoid = develop in tendons or ligaments (patella) Sutural bones = in joint between skull bones 7-2
3 Bone Surface Markings Surface features-- rough area, groove, openings, process Specific functions passageway for blood vessels and nerves joint formation muscle attachment & contraction 7-3
4 Bone Surface Markings from Table 7.2 Foramen = opening Fossa = shallow depression Sulcus = groove Meatus = tubelike passageway or canal Condyle = large, round protuberance Facet = smooth flat articular surface Trochanter = very large projection Tuberosity = large, rounded, roughened projection Learning the terms found in this Table will simplify your study of the skeleton. 7-4
5 The Skull 8 Cranial bones protect brain & house ear ossicles muscle attachment for jaw, neck & facial muscles 14 Facial bones protect delicate sense organs -- smell, taste, vision support entrances to digestive and respiratory systems 7-5
6 The 8 Cranial Bones Frontal Parietal (2) Temporal (2) Occipital Sphenoid Ethmoid 7-6
7 Frontal Bone Forehead, roof of orbits, & anterior cranial floor Frontal suture gone by age 6 7-7
8 Parietal sides & roof of cranial cavity Temporal zygomatic process forms part of arch Parietal & Temporal Bones 7-8
9 Temporal and Occipital bones Temporal Occipital 7-9
10 Sphenoid bone Base of skull Pterygoid processes are attachment sites for jaw muscles 7-10
11 Sphenoid in Anterior View Resembles a bat (the mammal) 7-11
12 Sphenoid from Superior View Lesser wing & greater wing Sella turcica holds pituitary gland Optic foramen 7-12
13 Ethmoid Bone Cranial floor, lateral nasal walls & nasal septum Cribriform plate & olfactory foramina Crista galli for attachment of membranes cover the brain 7-13
14 Ethmoid bone Perpendicular plate is upper part of nasal septum Nasal concha filters & warms air 7-14
15 14 Facial Bones Nasal (2) Maxillae (2) Zygomatic (2) Mandible (1) Lacrimal (2) Palatine (2) Inferior nasal conchae (2) Vomer (1) 7-15
16 Maxillary bones Floor of orbit, floor of nasal cavity or hard palate Maxillary sinus Alveolar processes hold upper teeth Cleft palate is lack of union of maxillary bones 7-16
17 Zygomatic Bones Cheekbones Lateral wall of orbit along with sphenoid Part of zygomatic arch along with part of temporal 7-17
18 Lacrimal Bones Lacrimal bones part of medial wall of orbit lacrimal fossa houses lacrimal sac 7-18
19 Palatine & Vomer Palatine part of hard palate Vomer posterior part of nasal septum 7-19
20 Mandible Alveolar processes for lower teeth 7-20
21 Sutures Lambdoid suture unites parietal and occipital Sagittal suture unites 2 parietal bones 7-21
22 Sutures Coronal suture unites frontal and both parietal bones Squamous suture unites parietal and temporal bones 7-22
23 Paranasal Sinuses Paired cavities in ethmoid, sphenoid, frontal and maxillary Lined with mucous membranes and open into nasal cavity Resonating chambers for voice, lighten the skull Sinusitis is inflammation of the membrane (allergy) 7-23
24 Fontanels of the Skull at Birth. Dense connective tissue membrane-filled spaces (soft spots) Unossified at birth but close early in a child's life. Fetal skull passes through the birth canal. Rapid growth of the brain during infancy 7-24
25 Nasal Septum Divides nasal cavity into left and right sides Formed by vomer, perpendicular plate of ethmoid and septal cartilage Deviated septum does not line in the midline developmental abnormality or trauma 7-25
26 U-shaped single bone Hyoid Bone Articulates with no other bone of the body Suspended by ligament and muscle from skull Supports the tongue & provides attachment for tongue, neck and pharyngeal muscles 7-26
27 Vertebral Column Backbone or spine built of 26 vertebrae Five vertebral regions cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck thoracic vertebrae ( 12 ) in the thorax lumbar vertebrae ( 5 ) in the low back region sacrum (5, fused) coccyx (4, fused) 7-27
28 Intervertebral Discs Between adjacent vertebrae absorbs vertical shock Permit various movements of the vertebral column Fibrocartilagenous ring with a pulpy center 7-28
29 Normal Curves of the Vertebral Column Primary curves thoracic and sacral are formed during fetal development Secondary curves cervical is formed when infant raises head at 4 months lumbar forms when infant sits up & begins to walk at 1 year 7-29
30 Thorax Bony cage flattened from front to back Sternum (breastbone) Ribs 1-7 are true ribs (vertebrosternal) 8-12 are false ribs (vertebrochondral) are floating Costal cartilages Bodies of the thoracic vertebrae 7-30
31 Sternum Manubrium 1st & 2nd ribs Body costal cartilages of 2-10 ribs Xiphoid ossifies by 40 CPR position 7-31
32 Herniated (Slipped) Disc Protrusion of the nucleus pulposus Most commonly in lumbar region Pressure on spinal nerves causes pain Surgical removal of disc after laminectomy 7-32
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
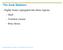 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
The Axial Skeleton. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
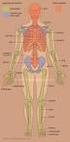 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Anatomy of Bones and Joints
 C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
The Skeleton. The word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up THE AXIAL SKELETON THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
relating to head, neck, and trunk 206 bones organized into structural framework Skeleton relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis
 Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
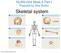 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM. 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200)
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
Problems. Knowing. back of the
 Introduction Welcome to BodyZone Physiotherapy patient resource about Cervical Spine Problems. Knowing the main parts of your neck and how these parts work is important as you learn to care for your neck
Introduction Welcome to BodyZone Physiotherapy patient resource about Cervical Spine Problems. Knowing the main parts of your neck and how these parts work is important as you learn to care for your neck
OBJECTIVE: List and describe the functions of the skeletal system. D. Storage depot for minerals and homeostasis
 Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
The Human Skeleton. Bone and Bone Growth
 The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column
 Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum. S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD.
 The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Internal Anatomy. Figure 2. The bones of the avian skull (a) lateral view (b) posterior view (c) sclerotic ring.
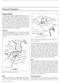 Internal Anatomy Skeletal System The skeletal system (Figure 1) is highly modified to meet the structural and energetic demands of flight. Throughout the skeleton are examples of three types of adaptive
Internal Anatomy Skeletal System The skeletal system (Figure 1) is highly modified to meet the structural and energetic demands of flight. Throughout the skeleton are examples of three types of adaptive
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Chapter 10. All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES
 Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions
 Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE
 2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report
 The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report BACK INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Back Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report BACK INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Back Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
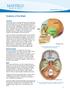 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF).
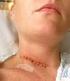 Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery (ACDF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra,
6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues
 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues Cartilage Location and basic structure Found throughout adult body Ear and epiglottis Articular cartilages and costal cartilage Larynx, trachea, and nose Intervertebral discs,
6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues Cartilage Location and basic structure Found throughout adult body Ear and epiglottis Articular cartilages and costal cartilage Larynx, trachea, and nose Intervertebral discs,
Unilateral Nasal Polyps
 Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Normal CT scan of the chest
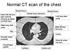 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Spine University s Guide to Kinetic MRIs Detect Disc Herniations
 Spine University s Guide to Kinetic MRIs Detect Disc Herniations 2 Introduction Traditionally, doctors use a procedure called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose disc injuries. Kinetic magnetic
Spine University s Guide to Kinetic MRIs Detect Disc Herniations 2 Introduction Traditionally, doctors use a procedure called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose disc injuries. Kinetic magnetic
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF).
 Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
Patient Information. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery (LLIF). Understanding your spine Disc Between each pair of vertebrae there is a disc that acts as a cushion to protect the vertebra, allows
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals
 Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals 6 Bones and skeletal system Contents Bones Introduction Classification of Bones Bone Structure Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Chemical Composition
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals 6 Bones and skeletal system Contents Bones Introduction Classification of Bones Bone Structure Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Chemical Composition
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
1 )~ ~V? 1) I, \ Chapter One: Introduction. b. g._----- h. 1. _ )...lii('---:-----':----;-~.k.-- h... I l«=~.. \! a. _. a. _. e. _
 Chapter One: Introduction ANATOMICAL POSITION AND TERMS OF DIRECTION When studying the human body it is important to place the body in anatomical position. Anatomical position is described as the body
Chapter One: Introduction ANATOMICAL POSITION AND TERMS OF DIRECTION When studying the human body it is important to place the body in anatomical position. Anatomical position is described as the body
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3)
 Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Observing Vertebrate Skeletons
 Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Human, Male, White. Bone Clones Osteological Evaluation Report. Product Number: 1 intact mandible. General observations:
 Human, Male, White Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-107 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
Human, Male, White Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-107 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
Wellness & Lifestyles Australia
 Wellness & Lifestyles Australia MANUAL HANDLING IN AGED CARE AND THE HEALTH CARE INDUSTRY E-BOOK prepared by Wellness & Lifestyles Australia 2007,2008,2009 Table of Contents Page No. IMPORTANT NOTICE...
Wellness & Lifestyles Australia MANUAL HANDLING IN AGED CARE AND THE HEALTH CARE INDUSTRY E-BOOK prepared by Wellness & Lifestyles Australia 2007,2008,2009 Table of Contents Page No. IMPORTANT NOTICE...
Skeletal System. Skeletal Anatomy. bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework
 Skeletal System bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework bone is active tissue:!5-7% bone mass/week Functions of Skeletal System: 1. Support strong and relatively
Skeletal System bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework bone is active tissue:!5-7% bone mass/week Functions of Skeletal System: 1. Support strong and relatively
