Enthalpy and Adiabatic Changes
|
|
|
- Paul Gallagher
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Enthalpy and Adiabatic Changes Chapter 2 of Atkins: The First Law: Concepts Sections of Atkins Exercises 2.15(a), 2.16(a), 2.18(a), 2.28(a); Problem 2.10 Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-1
2 Problem from Last Time A sample of 70. mmol of Kr(g) expands reversibly and isothermally at 373 K from 5.25 cm 3 to 6.29 cm 3. The internal energy of the sample is known to increase by 83.5 J. Using the virial equation of state up to the second virial coefficient (B = cm 3 mol -1 ), calculate w, q, and H for this process. Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-2
3 Enthalpy and Adiabatic Changes Chapter 2 of Atkins: The First Law: Concepts Sections of Atkins Enthalpy Definition of Enthalpy Measurement of Enthalpy Variation of Enthalpy with Temperature Relation Between Heat Capacities Adiabatic Change Work of Adiabatic Change Heat Capacity and Adiabats Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-3
4 Enthalpy For a system that changes volume, the internal energy is not equal to the heat supplied, as for a fixed volume system Some energy supplied as heat to the system returns to surroundings as expansion work: du < dq When heat is supplied to the system at a constant pressure, there is a change in another thermodynamic state function known as enthalpy, H Mathematically, enthalpy is H = U + pv Change in enthalpy is equal to heat supplied to the system at constant pressure dh = dq (const p) H = q p Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-4
5 Enthalpy: Why does H=q p? 1. Infinitesimal change in state of system: U changes to U + du, p changes to p + dp, V changes to V + dv, so H=U + p V becomes = U + du + pv + pdv + Vdp + dpdv 2. The product of two infinitesimal quantities, dp dv, disappears. Since H= U + pv, we write H + dh = H + du + pdv + Vdp 3. Substitute in du = dq + dw H + dh = ( U + du)+ p + dp dh = du + pdv + Vdp ( )( V + dv) dh = dq + dw + pdv + Vdp 4. System is in mechanical equilibrium with surroundings at pressure p, so there is only expansion work, and dw = -pdv, so that dh = dq + Vdp 5. Impose condition that heating is done at constant pressure, so dp=0 dh = dq (constant p, w e = 0) Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-5
6 Measurement of Change in Enthalpy, H An adiabatic bomb calorimeter or an adiabatic flame calorimeter can be used to measure H by watching the T that happens as the result of physical or chemical changes occurring at constant pressure. The adiabatic flame calorimeter measures T resulting from combustion of a substance in O 2 (g) At constant pressure an element is immersed in a T- controlled water bath - combustion occurs when a known amount of reactant is burned, and T is then monitored The adiabatic bomb calorimeter measures U during a change, from which H can be calculated (in this case, solids and liquids have such small molar volumes that H m = U m + pv m U m ) In the case of liquids and solids, processes are accompanied by a very small V, so there is negligible work done on surroundings Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-6
7 Relation of Internal Energy and Enthalpy For a perfect gas, the internal energy and enthalpy can be related by For a measurable change in enthalpy H = U + pv = U + nrt H = U + n gas RT Where n gas is the change of moles of gas in the reaction. For instance 3 NO(g) N 2 O(g) + NO 2 (g) 3 mol of gas are replaced by 2 mol of gas, so at 298 K H = U + ( 1 mol)rt or H U = 2.5 kj Why is the difference negative? (The change in H is less than the change in internal energy) The system contracts as the number of moles of gas decreases (energy is moved to the system from the surroundings). Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-7
8 Variation of Enthalpy with Temperature Enthalpy of substance increases as T is raised How H changes is dependent on the conditions, most important being constant pressure The heat capacity at constant pressure is an extensive property, defined as C p = H T For infinitesimal changes in pressure p dh = C p dt (at constant pressure) and for measurable changes H = C p T (at constant pressure) and heat at constant pressure q p = C p T Also: intensive property of molar heat capacity at constant pressure, C p,m Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-8
9 Variations and Relations of Heat Capacities Variation of heat capacity is negligible for small temperature ranges - good for noble gases - however, if accurate treatment is necessary C p,m ( J K -1 mol -1 )= a + bt + c a b/(10-3 K -1 ) c/(10 5 K 2 ) T 2 Graphite Where a, b and c are empirical parameters independent of T CO 2 (g) H 2 O(l) N 2 (g) At constant pressure, most systems expand when heated, and do work on the surroundings while losing internal energy. Therefore some energy supplied as heat returns back to the surroundings as expansion work. Temperature of a system rises less than when heating at constant volume, implying larger heat capacity: Heat capacity of a system at constant pressure is larger than its heat capacity at constant volume (to be derived in Chapter 3) C p C V = nr Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-9
10 Adiabatic Changes What changes occur when a gas expands adiabatically? - Work is done - internal energy falls - Temperature of the working gas falls - Kinetic energy of the molecules falls with average speed of the molecules U of ideal gas with T and V expressed in two steps U results solely from the second step, if C V is indep. of T, so: U = C V ( T f T i )= C V T Adiabatic expansion, q = 0, and U =w ad w ad = C V T The work done during an adiabatic expansion of a perfect gas is proportional to the temperature difference between the initial and final states (mean E K T) Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-10
11 Reversible Adiabatic Changes To calculate the work done by adiabatic expansion, w ad, T must be related to V (which we know from the perfect gas law). Consider a reversible case, p = p ext at all times, so as a gas adiabatically (q = 0) expands by dv, and the work done is dw = -p dv Perfect gas: du = C V dt. Now, since du = dw for adiabatic changes, C V dt = pdv Integrate for measurable changes, after subbing in p = nrt/v C V T f T i dt T = nr V f V i dv V C V ln T f = nrln V f With c = C v /nr, and identities a ln x = ln x a and ln(x/y) = ln (y/x) ln T f T i c = ln V i V f Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-11 T i T f = T i V i V f 1 c V i
12 Adiabatic Changes U = C V q = 0 ( T f T i )= C V T V f T f c = V i T i c where c = C V,m R T f = T i V i V f 1 c At left, the variation in T is shown for reversible adiabatic expanding gas for different values of c - falls steeply for low C V,m Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-12
13 Reversible Adiabatic Changes II Initial and final states of an ideal gas satisfy the perfect gas law, no matter what the change of state: p i V i p f V f = T i T f We have shown that for reversible adiabatic change, the temperature changes, such that 1 c T i T f = V f 1 c = V i R C V,m = and 1 c = γ 1 R C V,m + C V,m C V,m 1 = R + C V,m C V,m 1= C p,m C V,m 1= γ 1 Combine these expressions: p i V i γ = p f V f γ Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-13
14 Heat Capacity Ratio and Adiabats So for a reversible adiabatic change pv γ = constant where γ is the heat capacity ratio of a substance γ = C p,m C V,m Heat capacity at constant pressure > heat capacity at constant volume γ = C V,m + R C V,m =1+ R C V,m Monatomic perfect gas, C V,m = (3/2)R, γ = 5/3 Polyatomic perfect gas, C V,m = 3R, γ = 4/3 Pressure declines more steeply for adiabat than for isotherm, because of temperature decrease in the former case! Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-14
15 Problem 1 Calculate the final T of a sample of CO 2 of mass 16.0 g that is expanded reversibly and adiabatically from 500. ml at K to 2.00 L. The value of C p,m for CO 2 is J K -1 mol -1 T f /T i = (V i /V f ) 1/c where c = C v /R = (C p R)/R T f = 200 K Remember: C p (J/K) = C v (J/K) + nr (moles*j/mol-k) C p,m (J/mol-K) = C v,m (J/mol-K) + R (J/mol-K) Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-15
16 Problem 2 Calculate the final p of a sample of H 2 O(g) of mass 1.4 g that is expanded reversibly and adiabatically from an initial T of 300. K and a volume of 1.0 L to a final volume of 3.0 L. The value of γ for H 2 O(g) is 1.3 P f = P i (V i /V f ) γ P i = nrt/v i P f = 0.46 atm Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-16
17 Problem 3 When 2.0 mol of CO 2 is heated at a constant pressure of 1.25 atm, its temperature increases from 250 K to 277 K. Calculate q, H, and U for this process. The value of C p,m for CO 2 is J K -1 mol -1 H = q p = C p T = 2.0 x 10 3 J U = H nr T = 1.6 x 10 3 J Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-17
18 Problem mol of CO 2 is originally confined in a 15.0 L vessel at 280. K and then adiabatically expanded against a constant pressure of 78.5 kpa until the volume has increased by a factor of 4.0. Calculate q, w, T, H, and U for this process. The value of C p,m for CO 2 is J K -1 mol -1 q = 0 w = -P ext V = -3.5 x 10 3 J U = -3.5 x10 3 J T = U/C v,m = U/(C p,m nr) = -24 K H = U + nr T = -4.5 x 10 3 J Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-18
19 Problem 5 One mole of an alkane CnH2n+2 is burned in excess oxygen to form CO2(g) and H2O(g) at K and 1 bar pressure. At constant pressure, the heat released in the process is found to be kj. It is also found that 20 g of the alkane occupies a volume of L at K and 2 atm pressure. Determine the standard partial molar enthalpy of the alkane. Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-19
20 Problem 5 - Key PV = nrt Mol. Weight = mrt/pv = g Mol Weight = n (2n+2) = g n = 4 C 4 H 10(l) O 2(g) 4CO 2(g) + 5H 2 O (l) H comb = 4 H CO2 + 5 H H2O 6.5 H O2 H C4H10 H C4H10 = 4 H CO2 + 5 H H2O 6.5 H O2 H comb = 4( ) + 5( ) 0 ( ) = kj Prof. Mueller Chemistry Fall 2003 Lecture 7-20
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 4 Solutions 1 Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally and reversibly at 98 K from 1 atm to 00 atm Calculate q, w, ΔU, and ΔH For an isothermal
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 4 Solutions 1 Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally and reversibly at 98 K from 1 atm to 00 atm Calculate q, w, ΔU, and ΔH For an isothermal
a) Use the following equation from the lecture notes: = ( 8.314 J K 1 mol 1) ( ) 10 L
 hermodynamics: Examples for chapter 4. 1. One mole of nitrogen gas is allowed to expand from 0.5 to 10 L reversible and isothermal process at 300 K. Calculate the change in molar entropy using a the ideal
hermodynamics: Examples for chapter 4. 1. One mole of nitrogen gas is allowed to expand from 0.5 to 10 L reversible and isothermal process at 300 K. Calculate the change in molar entropy using a the ideal
Problem Set 3 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 (a) One mole of an ideal gas at 98 K is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 10 L to 10 L Determine the amount of work in Joules We start
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 (a) One mole of an ideal gas at 98 K is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 10 L to 10 L Determine the amount of work in Joules We start
Thermodynamics of Mixing
 Thermodynamics of Mixing Dependence of Gibbs energy on mixture composition is G = n A µ A + n B µ B and at constant T and p, systems tend towards a lower Gibbs energy The simplest example of mixing: What
Thermodynamics of Mixing Dependence of Gibbs energy on mixture composition is G = n A µ A + n B µ B and at constant T and p, systems tend towards a lower Gibbs energy The simplest example of mixing: What
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1
 Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Gibbs Free Energy and Chemical Potential. NC State University
 Chemistry 433 Lecture 14 Gibbs Free Energy and Chemical Potential NC State University The internal energy expressed in terms of its natural variables We can use the combination of the first and second
Chemistry 433 Lecture 14 Gibbs Free Energy and Chemical Potential NC State University The internal energy expressed in terms of its natural variables We can use the combination of the first and second
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 (10 points) 2 H 2 O 2 (aq) 2 H 2 O(l) + O 2 (g) The mass of an aqueous solution of H 2 O 2 is 6.951 g. The H 2 O 2 in the solution decomposes completely
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 (10 points) 2 H 2 O 2 (aq) 2 H 2 O(l) + O 2 (g) The mass of an aqueous solution of H 2 O 2 is 6.951 g. The H 2 O 2 in the solution decomposes completely
1 Exercise 2.19a pg 86
 In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
Module 5: Combustion Technology. Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels
 1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
Bomb Calorimetry. Example 4. Energy and Enthalpy
 Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
Standard Free Energies of Formation at 298 K. Average Bond Dissociation Energies at 298 K
 1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work. Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work.
 The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work. Compare fuel value of different compounds. What drives these reactions to proceed
The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work. Compare fuel value of different compounds. What drives these reactions to proceed
Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law
 Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
vap H = RT 1T 2 = 30.850 kj mol 1 100 kpa = 341 K
 Thermodynamics: Examples for chapter 6. 1. The boiling point of hexane at 1 atm is 68.7 C. What is the boiling point at 1 bar? The vapor pressure of hexane at 49.6 C is 53.32 kpa. Assume that the vapor
Thermodynamics: Examples for chapter 6. 1. The boiling point of hexane at 1 atm is 68.7 C. What is the boiling point at 1 bar? The vapor pressure of hexane at 49.6 C is 53.32 kpa. Assume that the vapor
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro. Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley Hills, Maqqwertd ygoijpk[l
 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
 Chapter 19: THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES 1. Evidence that a gas consists mostly of empty space is the fact that: A. the density of a gas becomes much greater when it is liquefied B. gases exert pressure
Chapter 19: THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES 1. Evidence that a gas consists mostly of empty space is the fact that: A. the density of a gas becomes much greater when it is liquefied B. gases exert pressure
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 2
 AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 N 2 (g) + 3 F 2 (g) 2 NF 3 (g) ΔH 298 = 264 kj mol 1 ; ΔS 298 = 278 J K 1 mol 1 The following questions relate to the synthesis reaction represented by the
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 N 2 (g) + 3 F 2 (g) 2 NF 3 (g) ΔH 298 = 264 kj mol 1 ; ΔS 298 = 278 J K 1 mol 1 The following questions relate to the synthesis reaction represented by the
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM (ICE METHOD)
 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM (ICE METHOD) Introduction Chemical equilibrium occurs when opposing reactions are proceeding at equal rates. The rate at which the products are formed from the reactants equals the
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM (ICE METHOD) Introduction Chemical equilibrium occurs when opposing reactions are proceeding at equal rates. The rate at which the products are formed from the reactants equals the
1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics
 Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
CHEMISTRY. Matter and Change. Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3. The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
Gas Laws. The kinetic theory of matter states that particles which make up all types of matter are in constant motion.
 Name Period Gas Laws Kinetic energy is the energy of motion of molecules. Gas state of matter made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). Each atom or molecule is very far from other atoms or molecules.
Name Period Gas Laws Kinetic energy is the energy of motion of molecules. Gas state of matter made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). Each atom or molecule is very far from other atoms or molecules.
CHAPTER 12. Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory
 CHAPTER 12 Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory 1 Gases vs. Liquids & Solids Gases Weak interactions between molecules Molecules move rapidly Fast diffusion rates Low densities Easy to compress Liquids
CHAPTER 12 Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory 1 Gases vs. Liquids & Solids Gases Weak interactions between molecules Molecules move rapidly Fast diffusion rates Low densities Easy to compress Liquids
HEAT UNIT 1.1 KINETIC THEORY OF GASES. 1.1.1 Introduction. 1.1.2 Postulates of Kinetic Theory of Gases
 UNIT HEAT. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES.. Introduction Molecules have a diameter of the order of Å and the distance between them in a gas is 0 Å while the interaction distance in solids is very small. R. Clausius
UNIT HEAT. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES.. Introduction Molecules have a diameter of the order of Å and the distance between them in a gas is 0 Å while the interaction distance in solids is very small. R. Clausius
Chapter 18 Homework Answers
 Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.22. 18.24. 18.26. a. Since G RT lnk, as long as the temperature remains constant, the value of G also remains constant. b. In this case, G G + RT lnq. Since the reaction
Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.22. 18.24. 18.26. a. Since G RT lnk, as long as the temperature remains constant, the value of G also remains constant. b. In this case, G G + RT lnq. Since the reaction
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual
 Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
AS1 MOLES. oxygen molecules have the formula O 2 the relative mass will be 2 x 16 = 32 so the molar mass will be 32g mol -1
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (L) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.023 x 10 23 mol -1. Example
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (L) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.023 x 10 23 mol -1. Example
7. 1.00 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg = 101.325 kpa = 14.70 psi. = 0.446 atm. = 0.993 atm. = 107 kpa 760 torr 1 atm 760 mm Hg = 790.
 CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
F321 MOLES. Example If 1 atom has a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g 1 mole of atoms will have a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g x 6.02 x 10 23 = 7.
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
PV (0.775 atm)(0.0854 L) n = = = 0.00264 mol RT -1-1
 catalyst 2 5 g ¾¾¾¾ 2 4 g 2 g DH298 = rxn DS298 C H OH( ) C H ( ) + H O( ) 45.5 kj/mol ; = 126 J/(K mol ) ethanol ethene water rxn 1 atm 760 torr PV (0.775 atm)(0.0854 L) n = = = 0.00264 mol RT -1-1 (0.08206
catalyst 2 5 g ¾¾¾¾ 2 4 g 2 g DH298 = rxn DS298 C H OH( ) C H ( ) + H O( ) 45.5 kj/mol ; = 126 J/(K mol ) ethanol ethene water rxn 1 atm 760 torr PV (0.775 atm)(0.0854 L) n = = = 0.00264 mol RT -1-1 (0.08206
= 1.038 atm. 760 mm Hg. = 0.989 atm. d. 767 torr = 767 mm Hg. = 1.01 atm
 Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
ENTHALPY CHANGES FOR A CHEMICAL REACTION scaling a rxn up or down (proportionality) quantity 1 from rxn heat 1 from Δ r H. = 32.
 CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #10 Chapter 4 (Part II); Sections 4.6-4.10 Do the topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets: Enthalpy
CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #10 Chapter 4 (Part II); Sections 4.6-4.10 Do the topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets: Enthalpy
Exergy: the quality of energy N. Woudstra
 Exergy: the quality of energy N. Woudstra Introduction Characteristic for our society is a massive consumption of goods and energy. Continuation of this way of life in the long term is only possible if
Exergy: the quality of energy N. Woudstra Introduction Characteristic for our society is a massive consumption of goods and energy. Continuation of this way of life in the long term is only possible if
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Given: 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = -110.2 kj find ΔH for N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g).
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Given: 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = -110.2 kj find ΔH for N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g).
Energy and Chemical Reactions. Characterizing Energy:
 Energy and Chemical Reactions Energy: Critical for virtually all aspects of chemistry Defined as: We focus on energy transfer. We observe energy changes in: Heat Transfer: How much energy can a material
Energy and Chemical Reactions Energy: Critical for virtually all aspects of chemistry Defined as: We focus on energy transfer. We observe energy changes in: Heat Transfer: How much energy can a material
Problem Solving. Stoichiometry of Gases
 Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Stoichiometry of Gases Now that you have worked with relationships among moles, mass, and volumes of gases, you can easily put these to work in stoichiometry calculations.
Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Stoichiometry of Gases Now that you have worked with relationships among moles, mass, and volumes of gases, you can easily put these to work in stoichiometry calculations.
Technical Thermodynamics
 Technical Thermodynamics Chapter 2: Basic ideas and some definitions Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Egon Hassel University of Rostock, Germany Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Ship Building Institute of Technical
Technical Thermodynamics Chapter 2: Basic ideas and some definitions Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Egon Hassel University of Rostock, Germany Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Ship Building Institute of Technical
Thermochemical equations allow stoichiometric calculations.
 CHEM 1105 THERMOCHEMISTRY 1. Change in Enthalpy ( H) Heat is evolved or absorbed in all chemical reactions. Exothermic reaction: heat evolved - heat flows from reaction mixture to surroundings; products
CHEM 1105 THERMOCHEMISTRY 1. Change in Enthalpy ( H) Heat is evolved or absorbed in all chemical reactions. Exothermic reaction: heat evolved - heat flows from reaction mixture to surroundings; products
Lecture Notes: Gas Laws and Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT).
 CHEM110 Week 9 Notes (Gas Laws) Page 1 of 7 Lecture Notes: Gas Laws and Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT). Gases Are mostly empty space Occupy containers uniformly and completely Expand infinitely Diffuse
CHEM110 Week 9 Notes (Gas Laws) Page 1 of 7 Lecture Notes: Gas Laws and Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT). Gases Are mostly empty space Occupy containers uniformly and completely Expand infinitely Diffuse
k 2f, k 2r C 2 H 5 + H C 2 H 6
 hemical Engineering HE 33 F pplied Reaction Kinetics Fall 04 Problem Set 4 Solution Problem. The following elementary steps are proposed for a gas phase reaction: Elementary Steps Rate constants H H f,
hemical Engineering HE 33 F pplied Reaction Kinetics Fall 04 Problem Set 4 Solution Problem. The following elementary steps are proposed for a gas phase reaction: Elementary Steps Rate constants H H f,
IB Chemistry. DP Chemistry Review
 DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry
 CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
Combustion Calorimetry
 ombustion alorimetry 1 Please Note: Each lab group will be required to pick the compound they use in this experiment. The compound must contain only carbon and hydrogen or carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
ombustion alorimetry 1 Please Note: Each lab group will be required to pick the compound they use in this experiment. The compound must contain only carbon and hydrogen or carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology. Experiment 9. Physical Chemistry
 Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology Experiment 9 Physical Chemistry Calorimetry Abstract The heat of combustion of Naphthalene
Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology Experiment 9 Physical Chemistry Calorimetry Abstract The heat of combustion of Naphthalene
Thermochemistry. r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc. Ron Robertson
 Thermochemistry r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc Ron Robertson I. What is Energy? A. Energy is a property of matter that allows work to be done B. Potential and Kinetic Potential energy
Thermochemistry r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc Ron Robertson I. What is Energy? A. Energy is a property of matter that allows work to be done B. Potential and Kinetic Potential energy
Lecture 14 Chapter 19 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory of Gases. Chapter 20 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Lecture 14 Chapter 19 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory of Gases Now we to look at temperature, pressure, and internal energy in terms of the motion of molecules and atoms? Relate to the 1st Law of Thermodynamics
Lecture 14 Chapter 19 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory of Gases Now we to look at temperature, pressure, and internal energy in terms of the motion of molecules and atoms? Relate to the 1st Law of Thermodynamics
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION. 37 74 20 40 60 80 m/e
 CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
 Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Final Exam CHM 3410, Dr. Mebel, Fall 2005
 Final Exam CHM 3410, Dr. Mebel, Fall 2005 1. At -31.2 C, pure propane and n-butane have vapor pressures of 1200 and 200 Torr, respectively. (a) Calculate the mole fraction of propane in the liquid mixture
Final Exam CHM 3410, Dr. Mebel, Fall 2005 1. At -31.2 C, pure propane and n-butane have vapor pressures of 1200 and 200 Torr, respectively. (a) Calculate the mole fraction of propane in the liquid mixture
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
Chapter 3. Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Chapter 13 - Chemical Equilibrium
 Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Intro A. Chemical Equilibrium 1. The state where the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with time. All reactions carried out in a closed vessel
Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Intro A. Chemical Equilibrium 1. The state where the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with time. All reactions carried out in a closed vessel
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
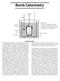 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
EXERCISES. 16. What is the ionic strength in a solution containing NaCl in c=0.14 mol/dm 3 concentration and Na 3 PO 4 in 0.21 mol/dm 3 concentration?
 EXERISES 1. The standard enthalpy of reaction is 512 kj/mol and the standard entropy of reaction is 1.60 kj/(k mol) for the denaturalization of a certain protein. Determine the temperature range where
EXERISES 1. The standard enthalpy of reaction is 512 kj/mol and the standard entropy of reaction is 1.60 kj/(k mol) for the denaturalization of a certain protein. Determine the temperature range where
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion using a bomb calorimeter TEC
 Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Phys222 W11 Quiz 1: Chapters 19-21 Keys. Name:
 Name:. In order for two objects to have the same temperature, they must a. be in thermal equilibrium.
Name:. In order for two objects to have the same temperature, they must a. be in thermal equilibrium.
CHEM 105 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99. = -163 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Ni(CO) 4 (g) = -260 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Cr(CO) 6 (g)
 CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
Thermodynamics. Chapter 13 Phase Diagrams. NC State University
 Thermodynamics Chapter 13 Phase Diagrams NC State University Pressure (atm) Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function
Thermodynamics Chapter 13 Phase Diagrams NC State University Pressure (atm) Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Spring 2009. kj mol 125 0-229 -92. H f. H rxn = Σ H f (products) - Σ H f (reactants)
 Spring 2009 2. The reaction of an elemental halogen with an alkane is a very common reaction. The reaction between chlorine and butane is provided below. (NOTE: Questions a d and f pertain to this reaction.)
Spring 2009 2. The reaction of an elemental halogen with an alkane is a very common reaction. The reaction between chlorine and butane is provided below. (NOTE: Questions a d and f pertain to this reaction.)
Boyles Law. At constant temperature the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure on the gas 1 P = P
 Boyles Law At constant temperature the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure on the gas 1 or k 1 Boyles Law Example ressure olume Initial 2.00 atm 100 cm 3
Boyles Law At constant temperature the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure on the gas 1 or k 1 Boyles Law Example ressure olume Initial 2.00 atm 100 cm 3
1. What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula PO and a gram-molecular mass of 284 grams?
 Name: Tuesday, May 20, 2008 1. What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula PO and a gram-molecular mass of 284 grams? 2 5 1. P2O 5 3. P10O4 2. P5O 2 4. P4O10 2. Which substance
Name: Tuesday, May 20, 2008 1. What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula PO and a gram-molecular mass of 284 grams? 2 5 1. P2O 5 3. P10O4 2. P5O 2 4. P4O10 2. Which substance
Gases. States of Matter. Molecular Arrangement Solid Small Small Ordered Liquid Unity Unity Local Order Gas High Large Chaotic (random)
 Gases States of Matter States of Matter Kinetic E (motion) Potential E(interaction) Distance Between (size) Molecular Arrangement Solid Small Small Ordered Liquid Unity Unity Local Order Gas High Large
Gases States of Matter States of Matter Kinetic E (motion) Potential E(interaction) Distance Between (size) Molecular Arrangement Solid Small Small Ordered Liquid Unity Unity Local Order Gas High Large
Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics 1
 Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
2. The percent yield is the maximum amount of product that can be produced from the given amount of limiting reactant.
 UNIT 6 stoichiometry practice test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. moles F 1. The mole ratio is a comparison of how many grams of one substance are required to participate in
UNIT 6 stoichiometry practice test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. moles F 1. The mole ratio is a comparison of how many grams of one substance are required to participate in
CLASSICAL CONCEPT REVIEW 8
 CLASSICAL CONCEPT REVIEW 8 Kinetic Theory Information concerning the initial motions of each of the atoms of macroscopic systems is not accessible, nor do we have the computational capability even with
CLASSICAL CONCEPT REVIEW 8 Kinetic Theory Information concerning the initial motions of each of the atoms of macroscopic systems is not accessible, nor do we have the computational capability even with
Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry
 Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry Introduction This experiment measures the enthalpy change when a system consisting of a known amount of a substance in the presence of excess oxygen is quantitatively
Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry Introduction This experiment measures the enthalpy change when a system consisting of a known amount of a substance in the presence of excess oxygen is quantitatively
Compressible Fluids. Faith A. Morrison Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University November 4, 2004
 94 c 2004 Faith A. Morrison, all rights reserved. Compressible Fluids Faith A. Morrison Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University November 4, 2004 Chemical engineering
94 c 2004 Faith A. Morrison, all rights reserved. Compressible Fluids Faith A. Morrison Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University November 4, 2004 Chemical engineering
Unit 2: Quantities in Chemistry
 Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002
 CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
Mr. Bracken. Multiple Choice Review: Thermochemistry
 Mr. Bracken AP Chemistry Name Period Multiple Choice Review: Thermochemistry 1. If this has a negative value for a process, then the process occurs spontaneously. 2. This is a measure of how the disorder
Mr. Bracken AP Chemistry Name Period Multiple Choice Review: Thermochemistry 1. If this has a negative value for a process, then the process occurs spontaneously. 2. This is a measure of how the disorder
AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board: Connecting Students to College Success The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to
AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board: Connecting Students to College Success The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to
Test Review # 9. Chemistry R: Form TR9.13A
 Chemistry R: Form TR9.13A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Collision theory. In order for a reaction to occur, particles of the reactant must collide. Not all collisions cause reactions.
Chemistry R: Form TR9.13A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Collision theory. In order for a reaction to occur, particles of the reactant must collide. Not all collisions cause reactions.
Guide to Chapter 13. Chemical Equilibrium
 Guide to Chapter 13. Chemical Equilibrium We will spend five lecture days on this chapter. During the first class meeting we will focus on how kinetics makes a segue into equilibrium. We will learn how
Guide to Chapter 13. Chemical Equilibrium We will spend five lecture days on this chapter. During the first class meeting we will focus on how kinetics makes a segue into equilibrium. We will learn how
Reading: Moore chapter 18, sections 18.6-18.11 Questions for Review and Thought: 62, 69, 71, 73, 78, 83, 99, 102.
 Thermodynamics 2: Gibbs Free Energy and Equilibrium Reading: Moore chapter 18, sections 18.6-18.11 Questions for Review and Thought: 62, 69, 71, 73, 78, 83, 99, 102. Key Concepts and skills: definitions
Thermodynamics 2: Gibbs Free Energy and Equilibrium Reading: Moore chapter 18, sections 18.6-18.11 Questions for Review and Thought: 62, 69, 71, 73, 78, 83, 99, 102. Key Concepts and skills: definitions
Name Class Date. Section: Calculating Quantities in Reactions. Complete each statement below by writing the correct term or phrase.
 Skills Worksheet Concept Review Section: Calculating Quantities in Reactions Complete each statement below by writing the correct term or phrase. 1. All stoichiometric calculations involving equations
Skills Worksheet Concept Review Section: Calculating Quantities in Reactions Complete each statement below by writing the correct term or phrase. 1. All stoichiometric calculations involving equations
The Gas Laws. Our Atmosphere. Pressure = Units of Pressure. Barometer. Chapter 10
 Our Atmosphere The Gas Laws 99% N 2 and O 2 78% N 2 80 70 Nitrogen Chapter 10 21% O 2 1% CO 2 and the Noble Gases 60 50 40 Oxygen 30 20 10 0 Gas Carbon dioxide and Noble Gases Pressure Pressure = Force
Our Atmosphere The Gas Laws 99% N 2 and O 2 78% N 2 80 70 Nitrogen Chapter 10 21% O 2 1% CO 2 and the Noble Gases 60 50 40 Oxygen 30 20 10 0 Gas Carbon dioxide and Noble Gases Pressure Pressure = Force
EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor
 EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
Molar Mass of Butane
 Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
Give all answers in MKS units: energy in Joules, pressure in Pascals, volume in m 3, etc. Only work the number of problems required. Chose wisely.
 Chemistry 45/456 0 July, 007 Midterm Examination Professor G. Drobny Universal gas constant=r=8.3j/mole-k=0.08l-atm/mole-k Joule=J= Nt-m=kg-m /s 0J= L-atm. Pa=J/m 3 =N/m. atm=.0x0 5 Pa=.0 bar L=0-3 m 3.
Chemistry 45/456 0 July, 007 Midterm Examination Professor G. Drobny Universal gas constant=r=8.3j/mole-k=0.08l-atm/mole-k Joule=J= Nt-m=kg-m /s 0J= L-atm. Pa=J/m 3 =N/m. atm=.0x0 5 Pa=.0 bar L=0-3 m 3.
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
1.4.6-1.4.8 Gas Laws. Heat and Temperature
 1.4.6-1.4.8 Gas Laws Heat and Temperature Often the concepts of heat and temperature are thought to be the same, but they are not. Perhaps the reason the two are incorrectly thought to be the same is because
1.4.6-1.4.8 Gas Laws Heat and Temperature Often the concepts of heat and temperature are thought to be the same, but they are not. Perhaps the reason the two are incorrectly thought to be the same is because
Sample Problem: STOICHIOMETRY and percent yield calculations. How much H 2 O will be formed if 454 g of. decomposes? NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + 2 H 2 O
 STOICHIOMETRY and percent yield calculations 1 Steps for solving Stoichiometric Problems 2 Step 1 Write the balanced equation for the reaction. Step 2 Identify your known and unknown quantities. Step 3
STOICHIOMETRY and percent yield calculations 1 Steps for solving Stoichiometric Problems 2 Step 1 Write the balanced equation for the reaction. Step 2 Identify your known and unknown quantities. Step 3
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Chapter 19 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Concept Check 19.1 You have a sample of 1.0 mg of solid iodine at room temperature. Later, you notice that the iodine has sublimed (passed into the vapor state).
Chapter 19 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Concept Check 19.1 You have a sample of 1.0 mg of solid iodine at room temperature. Later, you notice that the iodine has sublimed (passed into the vapor state).
Heat and Work. First Law of Thermodynamics 9.1. Heat is a form of energy. Calorimetry. Work. First Law of Thermodynamics.
 Heat and First Law of Thermodynamics 9. Heat Heat and Thermodynamic rocesses Thermodynamics is the science of heat and work Heat is a form of energy Calorimetry Mechanical equivalent of heat Mechanical
Heat and First Law of Thermodynamics 9. Heat Heat and Thermodynamic rocesses Thermodynamics is the science of heat and work Heat is a form of energy Calorimetry Mechanical equivalent of heat Mechanical
Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010)
 Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION Heat released in a chemical reaction can be determined experimentally by using an adiabatic calorimeter. The reaction
Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION Heat released in a chemical reaction can be determined experimentally by using an adiabatic calorimeter. The reaction
Chemistry 13: States of Matter
 Chemistry 13: States of Matter Name: Period: Date: Chemistry Content Standard: Gases and Their Properties The kinetic molecular theory describes the motion of atoms and molecules and explains the properties
Chemistry 13: States of Matter Name: Period: Date: Chemistry Content Standard: Gases and Their Properties The kinetic molecular theory describes the motion of atoms and molecules and explains the properties
Statistical Mechanics, Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas. 8.01t Nov 22, 2004
 Statistical Mechanics, Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas 8.01t Nov 22, 2004 Statistical Mechanics and Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Old & Fundamental Understanding of Heat (I.e. Steam) Engines Part of Physics Einstein
Statistical Mechanics, Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas 8.01t Nov 22, 2004 Statistical Mechanics and Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Old & Fundamental Understanding of Heat (I.e. Steam) Engines Part of Physics Einstein
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
Test 5 Review questions. 1. As ice cools from 273 K to 263 K, the average kinetic energy of its molecules will
 Name: Thursday, December 13, 2007 Test 5 Review questions 1. As ice cools from 273 K to 263 K, the average kinetic energy of its molecules will 1. decrease 2. increase 3. remain the same 2. The graph below
Name: Thursday, December 13, 2007 Test 5 Review questions 1. As ice cools from 273 K to 263 K, the average kinetic energy of its molecules will 1. decrease 2. increase 3. remain the same 2. The graph below
87 16 70 20 58 24 44 32 35 40 29 48 (a) graph Y versus X (b) graph Y versus 1/X
 HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
Thermodynamics AP Physics B. Multiple Choice Questions
 Thermodynamics AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the name of the following statement: When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium
Thermodynamics AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the name of the following statement: When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium
Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law
 Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law Some chemical reactions are endothermic and proceed with absorption of heat while others are exothermic and proceed with an evolution of heat. The magnitude
Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law Some chemical reactions are endothermic and proceed with absorption of heat while others are exothermic and proceed with an evolution of heat. The magnitude
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems
 Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1. A chemical equation. (C-4.4)
 Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS System: Quantity of matter (constant mass) or region in space (constant volume) chosen for study. Closed system: Can exchange energy but not mass; mass is constant
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS System: Quantity of matter (constant mass) or region in space (constant volume) chosen for study. Closed system: Can exchange energy but not mass; mass is constant
States of Matter CHAPTER 10 REVIEW SECTION 1. Name Date Class. Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
Gases and Kinetic-Molecular Theory: Chapter 12. Chapter Outline. Chapter Outline
 Gases and Kinetic-Molecular heory: Chapter Chapter Outline Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases Composition of the Atmosphere and Some Common Properties of Gases Pressure Boyle s Law: he Volume-Pressure
Gases and Kinetic-Molecular heory: Chapter Chapter Outline Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases Composition of the Atmosphere and Some Common Properties of Gases Pressure Boyle s Law: he Volume-Pressure
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
CHEMISTRY GAS LAW S WORKSHEET
 Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The volume of a fixed mass of gas is
Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The volume of a fixed mass of gas is
