COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN I
|
|
|
- Joseph Cobb
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION CAREER-TECHNICAL EDUCATION/TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION DEPARTMENT COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN I COURSE PHILOSOPHY Computer Aided Design is a constantly evolving field which affects the way everyday products are designed, prototyped, and manufactured. Students enrolled in CAD I become proficient with various CAD functions, terminology, and career opportunities in related fields. Each participant will demonstrate the safe operation of tools, computer equipment, and plotters in their quest to design and analyze solutions to real-world problems within time constraints. Students will create computer-generated single view, orthographic, isometric, and three-dimensional drawings in preparation for advanced high school and post-secondary education programs and/or industry. COURSE DESCRIPTION Grade Level: 9-12 Department: Career-Technical Education Technology Education Course Title: Credits: 5 Course Code: BOARD OF EDUCATION INITIAL ADOPTION DATE: AUGUST 30, 2010
2 Course Philosophy In order to prepare students for the 21 st century workforce it is important to impart the knowledge and skills students will require at an early stage. will focus on providing students with the information they need to be productive members of the design and industrial world. Through the use of traditional methods and hands-on problem solving, students will be engaged in a host of real world problem solving activities. By immersing students in an experience that mimics industry, they will be better prepared to continue their education in this field and have an understanding for how the world around them is designed and produced. Course Description is a one year, five credit course designed for students who may be considering post secondary training in related areas, such as Mechanical Engineering, Product Design, or Industrial Design. The CAD courseware includes, but is not limited to, 2D and 3D design, parametric modeling, engineering drawings, as well as Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) technology. Students learn by creating computergenerated single view, orthographic, isometric, and 3D designs along with constructing models/prototypes. The CAD course will increase the students awareness of various facets of engineering fields including manufacturing techniques, design trends, design styles, CAD functions, and creating prototypes for presentation to clients. Skills in communication, mathematics, science, leadership, teamwork, and problem solving are reinforced in this course.
3 Curriculum Map Relevant Standards F C.1,2,5,6, O C.1-6; D.1-3; E.5; F C O.1,13-18, 22,29-33,36,46-51,67, A F O.58; O(1) B.1-3; C. 1-3; D.1; E (1) A F O(1).2,5, B.6, 18, 24, C.1, F.2; G.1, Enduring Understandings Self-management is a key to maximizing efficiency and preventing accidents. Working with other people is an important skill for life and the workplace. Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the work place. The design/engineering process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Proficiencies with various tools and menus of a computer program will greatly assist the efficiency of work. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. Essential What are some organizational skills? How are organizational skills beneficial to an employee/employer relationship? Why is time management important? Why are safety precautions important in the workplace? What characteristics are essential to a functional team? What are the benefits of working in a team environment as opposed to individually? How do inappropriate behaviors and characteristics affect productivity? How is work done on a computer created and stored? What is the benefit of a computer network? What is the purpose of various file types? What are the components of the design/engineering process? How is the design/engineering process carried out, and what are the steps? How is a final product affected by the design/engineering process? How do sketches play a role in creating a solid model? How does a CAD program help you create a design? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create the changes? How can one navigate through the various options of a CAD program? What is the difference between using your hand to drawn design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter a design as opposed to altering it digitally? Who is known as a major contributor in CAD? What are the benefits of digital CAD technology in product development? Diagnostic (before) Do Now Ice Breaker Pretest Student Survey Oral / Discussion Anticipatory Set s Formative (during) Quizzes Chapter Test Written Assignments Oral Observations Participatory Rubrics Role Play Interviews Journals Research Assignments Summative (after) Portfolios Performance Mid Terms Final Exam Projects Based Learning Rubric 4
4 Relevant Standards F.1, 3, B(1).9, 75, B B(1).1, 2, 15; D.3, C.1, B.1, B(1).1, 9, B.2, A.1, B.1, 2 Enduring Understandings CAD requires knowledge of proper technique. CAD programs allow products to be presented to clients prior to production. CAD programs are fundamental to the development of technological products. Essential What are the basic CAD terminologies for creating models? What are some of the key features that should be understood when designing a product? Why is it important to follow proper procedure in creating a model? How does proper dimensioning affect a product? How do various parts come together to form sub assemblies? What are the key features in renderings? Why is it important to know various file types? Why are presentations important? How is a product presentation conducted? What are some ways in which CAD models can be presented to clients? Why is solid model rendering important? How has the timeline of product development been affected by CAD technologies? What is the difference between CAD and CAM? Why is it important to know how to use CAD CAM Software together? How is rapid prototyping used in the development of a product? Diagnostic (before) Do Now Pretest Student Survey Oral / Discussion Anticipatory Set s Formative (during) Journals Quizzes Chapter Test Observations Participatory Rubrics Interviews Written Assignments Oral Summative (after) Portfolios Projects Based Learning Rubric Performance Mid Terms Final Exam B(1).7, 54-58, C.55, E.4, D.2 Use of various designs and information adheres to legal and ethical laws. What are the consequences of copying and pasting other peoples work without permission? What ethical guidelines need to be followed when producing ideas and designs? Why are patents important in the development of technological products and systems? Research Assignments 5
5 Unit Title Unit 1: Teamwork, Self Management, and Health & Safety Course Proficiencies and Pacing Unit Understandings and Goals Self-management is a key to maximizing efficiency and preventing accidents. Working with other people is an important skill for life and the workplace. Students will be able to identify and implement proper safety in a work environment. Students will also understand the importance of collaboration and effective teamwork skills. Recommended Duration 2 weeks Unit 2: Introduction to Design Unit 3: Sketching and Drawing Unit 4: CAD - History and Introduction Unit 5: Creating a Simple Model. Unit 6: Dimensions and Constraints The design/engineering process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD programs are fundamental to the development of technological products. Use of various designs and information adheres to legal and ethical laws. Students will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the design/engineering process and put it into practice. Students will be able to identify basic technical drawings and describe e their importance to the design/engineering process. Students will be able to identify the impact and use of computer technology in product development. The design process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD requires knowledge of proper technique. Students will be able to demonstrate an understanding of various sketching techniques as well as drawing types. Students will develop an appreciation for the use of computers in drafting and design work. Students will be able to identify the early influences in CAD technology. Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the work place. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. Students will understand the historical background that lead to the innovation of CAD and how it was first used. Student will be able to identify the various menus, toolbars, windows, and work areas of the CAD program. Students will also understand how to create specific file types, save file, and format preferences. Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the work place. The design process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. Students will understand the need to have a valid sketch prior to creating a solid. Students will understand the concept of parametric modeling and shape before size. Students will understand the importance of selecting the appropriate drawing plane. Students will understand the primary extrude feature. Students will be able to troubleshoot common errors. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD requires knowledge of proper technique. Students will describe the importance of dimensioning and tolerances Students will understand the interaction between sketching dimensions and the resulting solid mode, as well as geometric and parametric relationships. 2-3 weeks 2-3 weeks 2 weeks 2 weeks 3 weeks 6
6 7 Unit Title Unit 7: Engineering Drawing Unit 8: Drawing Output Unit 9: Patterns and Copies Unit 10: Revolve Unit 11: Sweep/Loft Unit 12: Rendering Unit 13: Assemblies Unit 14: Rapid Prototyping Unit 15: Careers and Professionalism Unit Understandings and Goals Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the work place. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD requires knowledge of proper technique. CAD programs allow products to be presented to clients prior to production. Students will be producing engineering drawings based on 3D models and parts. Students will be able to identify proper drawing styles and their individual components. Students will understand the proper dimensioning techniques. Students will understand how to create a title block and scale their drawing to specific. Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the workplace. Students will understand how to format their drawings and models for out put to an assortment of printers and plotters. Students will be able to duplicate and mirror visual objects within their design to create patterns and several instances of the same shape. Students will be able to understand the relationship between a profile and the axis it is rotated about using revolve or a similar feature. Students will be able to project a profile along a given path to create a new solid object that may be of an irregular shape. CAD programs allow products to be presented to clients prior to production. Students will be able to apply materials and textures to a designed product to give it a realistic appearance for presentation. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. The design process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Students will be able to take multiple designed components and join them together within the program to make a complete final product. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD Programs are fundamental to the development of technological products. The design process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Students will be able to create a design and then use a rapid prototyping method to create a tangible 3D model. Working with other people is an important skill for life and the workplace. CAD programs allow products to be presented to clients prior to production. Students will be able to create a final product using CAD/CAM software to quickly create a prototype of their ideas for presentation. Recommended Duration 2 weeks 1 weeks 2 weeks 2 weeks 4 weeks 2 weeks 3 weeks 3 weeks 2 weeks
7 8 Unit #1: Teamwork, Self Management, and Health & Safety Enduring Understandings: Self-management is a key to maximizing efficiency and preventing accidents. Working with other people is an important skill for life and the workplace. Essential : What are some organizational skills? How are organizational skills beneficial to an employee/employer relationship? Why is time management important? Why are safety precautions important in the workplace? What characteristics are essential to a functional team? What are the benefits of working in a team environment as opposed to individually? How do inappropriate behaviors and characteristics affect productivity? Unit Goals: Students will be able to identify and implement proper safety in a work environment. Students will also understand the importance of collaboration and effective teamwork skills. Duration of Unit: 2 weeks NJCCCS: C.1-6, D.1-3, E.5, F.1, F.1, C.1,2,5,6,11-13, C.14-24, O.1,13-18, 22,29-33,36,38-51,67,68 Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, Instructional Resources Teaching and Skills and What are common organizational skills needed in the workplace? How does time management affect productivity? What are the governing bodies that set safety laws? What is Personal Protective Equipment? What are some key characteristics and advantages of team work? Proper record keeping is critical In order to meet goals, a timeline with objectives must be set. Model methods of organizing materials and resources for projects. Implement safety procedures in the classroom. Identify safety signage and the hazard the symbol is warning against. Model methods for maximizing personal productivity in a safe environment. Model social characteristics that are beneficial to groups. Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Pacing Chart Class Expectations/Rules SMART responders Role playing of teachers and students. Teacher/ Students demonstrating good and bad organization. Discussions of class procedures and expectations Presentation on classroom and occupational safety procedures, PPE and hazardous signage. Divide class into 3 or 4 teams. Students will compete in a quiz bowl testing their safety sign/symbol knowledge. Use whatever is available to ring in (call bell, whistle etc.) Winning team receives extra credit. Presentation on appropriate characteristics for team work and collaboration. Review of articles on team work skill with a reflection provided by the students and shared with others. Notebook Responses to discussion questions Journal Threaded Discussion Groups Midterm/Final Exam A hands-on approach to assignments and projects is recommended as the most effective method of learning. Students that fall behind may be teamed up with students whom excel in particular topics. Teacher should always adjust learning environment based on reluctant learners or special education needs.
8 9 Unit #2: Introduction to Design Enduring Understandings: The design/engineering process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD programs are fundamental to the development of technological products. Use of various media and information adheres to legal and ethical laws. Essential : What are the components of the design/engineering process? How is the design process carried out, and what are the steps? How is a final product affected by the design process? What is the difference between using your hand to drawn design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter a design as opposed to altering it digitally? How has the timeline of product development been affected by CAD technologies? How is rapid prototyping used in the development of a product? What are the consequences of copying and pasting other peoples work without permission? Why are patents important in the development of technological products and systems? Unit Goals: Students will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the design/engineering process and put it into practice. Students will be able to identify basic technical drawings and describe e their importance to the design/engineering process. Students will be able to identify the impact and use of computer technology in product development. Duration of Unit: 2-3 weeks NJCCCS: C.1, D.2, G.1, F.2, A.1, B.1-3, C. 1-3, D.1, E.1, (1).11-12, B (1).1, B (1).7, B (1).9, B.2, B.6, B.18, B.24, B.54, B.55, B.56, B.57, B.58, C.55, E.4, Guiding / Topical How are products conceived? What role do conceptual sketches and drawings have in product development? How does computer technology influence product development? Content, Themes, Concepts, and Skills Definitions and examples of the design/engineering process. Utilize design/engineering process to complete an activity. Definitions and examples of basic technical drawings. 2 Dimensional (2D), 3Dimensional (3D): Identify various technical drawings and categorize them as 2D or 3D. Identify them the purpose of the drawings in the design/engineering process. Definitions and examples of Computer Aided Design (CAD) and Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) technologies. Identify various CAD programs and CAM technologies such as AutoCAD, Pro ENGINEER, Phinocerous, CNC Mills/Routers, CNC Laser Cutter/Engravers, 3D Printers Instructional Resources and Classroom supplies for technological learning activities (TLA) Examples from industry (rendered drawings, floor plans, sectional drawings) Current textbook and resource binder PowerPoint/SMART Notebook Presentation Product literature from manufactures. Sample products from manufactures, or classroom activities Teaching Students participate in simple Technological Learning Activity (TLA) Class discussion on process used I n order to create solution for TLA Completion of Design/Engineering Process Handout/Power Point Students share their sketches and drawings produced for previously competed TLA. Instructor shares drawings of student work such as CO2 Dragsters or Furniture design. Instructor facilitates a discussion as to how ideas for products such as cell phones, automobiles, and household furniture are developed. Instructor present methods that are utilized in modern manufacturing process such as CAD and CAM. Identifying specific examples such as the use of CAD programs to operate CNC mills. Instructor facilitates a discussion as to how ideas for products such as cell phones, automobiles, and household furniture are influenced through the use of computer technology. Project Article summaries Notebook Responses to discussion questions Journal Threaded Discussion Groups Midterm/Final Exam Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
9 10 Unit #3: Sketching and Drawing Enduring Understandings: The design/engineering process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or solve a problem. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD requires knowledge of proper technique. Essential : How is the design/engineering process carried out, and what are the steps? What is the difference between using your hand to drawn design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter a design as opposed to altering it digitally? Who is known as a major contributor in CAD? How does proper dimensioning affect a product? Unit Goals: Students will be able to demonstrate an understanding of various sketching techniques as well as drawing types. Students will develop an appreciation for the use of computers in drafting and design work. Students will be able to identify the early influences in CAD technology. Duration of Unit: 2-3 weeks NJCCCS: B.2, C.1, G.1, F.2, B.1-3, C. 1-3, D.1, E.1, F.1, F.3, (1).11-12, B (1).9, B.6, B.18, B.24, B.75 Guiding / Topical What purpose do sketches and drawings serve? How can technical drawings be categorized? What is the purpose of the various technical drawings? What are some specific elements similar to all technical drawings? Content, Themes, Concepts, and Skills Definitions of visual representations such as sketches, drawings, technical drawing, and rendering. Summarize the application of sketches, drawings, and renderings. Identify them the purpose of the drawings in the design/engineering process. Utilize basic techniques to produce sketches Definitions and examples of technical drawings. Identify various technical drawings and categorize them as 2D or 3D. Summarize Definitions and examples of technical drawings elements. Produce technical drawings utilizing the appropriate line types and styles. Instructional Resources and Current textbook and resource binders Examples of visual representation: sketches, drawings, renderings. PowerPoint/SMART Notebook Paper Pencils Teaching Display examples of sketches, drawings, and technical drawings. Engage students in a discussion that lists the similarities and differences. Have students brainstorm the purpose for the various types of visual representations. Students participate in teacher led exercise in sketching, including w=how to hold and use a pencil correctly, as well as techniques for using basic shapes to form more complicated designs. Presentation on the various technical drawing types. Engage students by asking them what purpose each drawing serves and whom it might be for. Students participate in an activity where they must match a drawing to the correct name. Students recreate drawings from handouts. Activity progresses by having students take a 3D drawing and creating a 2D drawing, or vice versa. Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience. Written tests and Project Article summaries Notebook Midterm/Final Exam
10 11 Unit #4: CAD History and Introduction Enduring Understandings: Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the work place. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. Essential : How is work done on a computer created and stored? What is the purpose of various file types? How does a CAD program help you create a design? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create the changes? How can one navigate through the various options of a CAD program? What is the difference between using your hand to drawn design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter a design as opposed to altering it digitally? Who is known as a major contributor in CAD? Unit Goals: Students will understand the historical background that lead to the innovation of CAD and how it was first used. Students will be able to identify the various menus, toolbars, windows, and work areas of the CAD program. Students will also understand how to create specific file types, save file, and format preferences. Duration of Unit: 2 weeks NJCCCS: 8.1.A , C.1, F.2-3, G.1, B.6, B.18, B.24, O.58, O (1).2, 5, 8-12 Guiding / Topical What lead to the development of CAD? How CAD was first utilized? How files are initially created? What is the purpose of various file types? How does one navigate through a program? What is the purpose of the user interface? How are features and drawings edited? Content, Themes, Concepts, and Skills Early development of CAD was primarily for aerospace and automotive industries. Types of models: wireframe, surface, solid and parametric. Identify and describe early developmental drawbacks of CAD systems Define various file types such as part, sketch, and drawing. File system architecture of program Create, save and retrieve various file types such as part, sketch, and drawing. Describe appropriate file types. Identify various areas of program workspace, such as tool bar, main window, progress bar or similar features Identify the purpose of the various navigation and display elements and describe how they are used in assisting usage of the program. Define basic operations such as Sketch and Extrude Identify integral icons for the creation of sketches and parts. Instructional Resources and Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Teaching PowerPoint Presentation on history of CAD, including early developers and uasage. Compare and contrast examples of various modeled parts and their drawings. Demonstrate the various types of files and describe the purpose of each one. Compare and discuss student responses to different topics relating to computer files. Compare and discuss student response to the similarities and differences between interface of CAD program and other computer programs. Demonstrate the application of the various display areas and navigation menus. Provide students with simple tutorials or guides to familiarizing them with interface. Demonstrate the ease of use of the program be creating a simple part and identifying key features and icons, as well as possible problems. Project Article summaries Notebook Responses to discussion questions Journal Threaded Discussion Groups Midterm/Final Exam Create, edit and save basic sketch or part file. Identify various icons and their functions. Provide students with simple tutorials or guides to familiarizing them with interface. Students complete information as they move through the tutorial. Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
11 12 Unit #5: Creating a Simple Model Enduring Understandings: Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the work place. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. Essential : How is work done on a computer created and stored? What is the benefit of a computer network? What is the purpose of various file types? How is a final product affected by the design/engineering process? How do sketches play a role in creating a solid model? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create the changes? What is the difference between using your hand to drawn design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter a design as opposed to altering it digitally? Unit Goals: Students will understand the need to have a valid sketch prior to creating a solid. Students will understand the concept of parametric modeling and shape before size. Students will understand the importance of selecting the appropriate drawing plane. Students will understand the primary extrude feature. Students will be able to troubleshoot common errors. Duration of Unit: 2 weeks NJCCCS: A.2, C.1, B.1-3, C. 1-3, D.1, E.1, G.1, F.2-3, B.6, B.18, B.24, O.58, O (1).2, 5, 8-12 Guiding / Topical What type of sketch is needed to produce a 3D part? Is it important to know the size of an object prior to designing? What are the three planes of a 3D part? How do you create a 3D object from a 2D drawing? Content, Themes, Concepts, and Skills Editing multiple shapes into a valid sketch. Create a valid 2D sketch that can be used for extrusion. Constraints Rough Dimensions Lateral; Frontal; Base Features; Extruding; Projecting Instructional Resources and PowerPoint or SMART Notebook LCD projector Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Teaching Demonstration on how to create a valid sketch. Discussion of what constitutes a valid sketch profile. Presentation on valid sketches and common errors Demonstration of digital readout of size. Demonstration of using dimension tools. Lecture describing the concept of planes; PowerPoint presentation on various planes. Discussion on relating planes to the planes in an orthographic projection. Discussion of how features work within a CAD program. Demonstration of Extruding and Projection features; lecture describing the relation of extrusion and projection to actual manufacturing techniques. Project Article summaries Journal Threaded Discussion Groups Midterm/Final Exam Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
12 13 Unit #6: Dimensions and Constraints Enduring Understandings: Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. CAD requires knowledge of proper technique. Essential : What is the difference between using your hand to drawn design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter a design as opposed to altering it digitally? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create the changes? How can one navigate through the various options of a CAD program? What are some of the key features that should be understood when designing a product? How does proper dimensioning affect a product? Why is it important to know various file types? Unit Goals: Students will be able to describe the importance of dimensioning and tolerances Students will understand the interaction between sketching dimensions and the resulting solid model, as well as geometric and parametric relationships. Duration of Unit: 3 weeks NJCCCS: B.2, A.2, C.1, G.1, F.1-3, B.6, B.18, B.24, B.75, B (1).9, O (1).2, 5, 8-12 Guiding / Topical What role do constraints play in a parametric model? What role do dimensions play in drawings? How are dimensions created in CAD? What types of geometric constraints can be placed on a feature or sketch? What types of parametric constraints can be placed on a feature or sketch? Content, Themes, Concepts, and Skills Constraints determine how big or small a part is when compared to a given value or proportion. They include dimensional, geometric, or parametric. Identify and describe what constraints regulate the look and size of a part. Parts can be constrained by using a specific dimensional value. Apply appropriate dimensions. Parts can be constrained by using various geometric constraints. Apply appropriate geometric constraints. Parts can be constrained by using proportional constraints so that when value is changed several others change because of their parametric constraint. Apply appropriate parametric constraints. Instructional Resources and Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Teaching Compare and discuss student responses to their description of constraints. Presentation on various CAD constraints such as dimensional, geometric and parametric. Provide students with simple tutorials or guides to familiarizing them with the dimension constraints of sketches and features. Provide students with simple tutorials or guides to familiarizing them with the geometric constraints of sketches and features. Provide students with simple tutorials or guides to familiarizing them with the parametric constraints of sketches and features. Project Article summaries Notebook Responses to discussion questions Journal Threaded Discussion Groups Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
13 14 Unit #7: Engineering Drawing Enduring Understandings: CAD requires knowledge of proper technique. CAD programs allow products to be presented to clients prior to production. Essential : What is the difference between using your hand to drawn design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter an design as opposed to altering it digitally? Who is known as a major contributor in CAD? Unit Goals: Students will be producing engineering drawings based on 3D models and parts. Students will be able to identify proper drawing styles and their individual components. ] Students will understand the proper dimensioning techniques. Students will understand how to create a title block and scale their drawing to specific. Duration of Unit: 2 weeks NJCCCS: B.6, B.18, B.24, C.1, G.1, F.2 Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, and Instructional Resources and Teaching Skills What is the purpose of a technical drawing? What are the various forms of technical drawings? Why are dimensioning standards important? What are the dimensions on a drawing used for? How do dimensions affect the overall presentation of the drawing? What is the purpose of a title block? What information should be included on a title block? Technical drawings are used to represent objects in a host of various methods, each having its own advantage and disadvantage. Identify and describe the various types of technical drawings and the purpose Placement of dimensions is important and creates a more effective and accurate representation. Properly place dimensions on a part drawing. Title blocks communicate key information about a drawing as well as provide a neat and organized means of presentation. Produce a title block with space for such key information, but not limited to: scale, creator, date and revision Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Presentation of various technical drawings and their purpose and usage of technical drawings. Compare and discuss student responses to the various technical drawings. Demonstration of dimension placement. PowerPoint on dimensioning standards/ dimensioning conventions. Lecture on importance of accurate dimensioning. Self guided tutorial Design activity in which students create their own title block to utilize throughout the year. Project Midterm/Final Exam Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
14 15 Unit #8: Drawing Output Enduring Understandings: Knowing how to create, save, retrieve, and produce electronic work is essential in the workplace. Essential : How is work done on a computer created and stored? What is the benefit of a computer network? What is the purpose of various file types? How do sketches play a role in creating a solid model? How does a CAD program help you create a design? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create changes? How can one navigate through the various options of a CAD program? Unit Goal: Students will understand how to format their drawings and models for output to an assortment of printers and plotters. Duration of Unit: 1 week NJCCCS: 8.1.A.12.1, F.2, O.58, O(1) A.2, F.3, O(1),(2),(5), O(8)-(12) Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, Instructional Resources and Teaching and Skills What are some common output types of drawings? What factors affect the quality of the output? What are standard paper sizes? Identify and describe the various methods of outputting designs and part such as: Digital PDF Plot Full Color Render Identify and describe purpose of various paper sizes. Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Demonstration of print command and preparation of drawing/part file to output device. Compare and discuss student responses to examples of printed and plotted part files. Self guided tutorial Project Standard Sizes ANSI Skill: Produce an appropriate sized drawing of efficient quality and detail. Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Midterm/Final Exam Output device such as HP Design Jet 510 Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
15 16 Unit #9: Patterns and Copies Enduring Understanding: Essential : How do sketches play a role in creating a solid model? How does a CAD program help you create a design? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create changes? How can one navigate through the various options of a CAD program? Unit Goal: Students will be able to duplicate and mirror visual objects within their design to create patterns and several instances of the same shape. Duration of Unit: 2 weeks NJCCCS: A.2, F.3, O (1), (2), (5), O (8)-(12) Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, and Instructional Resources and Teaching Skills How can we replicate a drawing or feature in a CAD program? What is the difference between mirroring and duplicating something? Methods of duplicating features and sketches differ among CAD programs, desired outcome, and methodologies. Pattern Duplicate Mirror Study Guides/Handouts Demonstrate various methods of duplicating features and sketches in CAD program. Identify key commands and steps needed to reach required effect. Compare and discuss student responses to the Revolve command Project Identify and describe the various tools and commands used to replicate features and sketches. PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Self guided tutorial Design activity in which feature needs to be utilized. How do you duplicate a shape? How do you mirror a shape? Pattern (or similar) command and how it is used to duplicate a feature or drawing. Replicate a feature by creating a pattern or copy in a linear or radial format. Mirror (or similar) command and how it is used to duplicate a feature or drawing. Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Self guided tutorial Design activity in which feature needs to be utilized. Midterm/Final Exams Replicate a feature by creating a pattern or copy in a linear or radial format. Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
16 17 Unit #10: Revolve Enduring Understanding: Essential : How do sketches play a role in creating a solid model? How does a CAD program help you create a design? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create changes? How can one navigate through the various options of a CAD program? Unit Goal: Students will be able to understand the relationship between a profile and the axis it is rotated about using revolve or a similar feature. Duration of Unit: 2 weeks NJCCCS: A.2, F.3, O (1), (2), (5), O (8)-(12) Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, and Instructional Resources and Teaching Skills How does a sketch need to be designed if it is going to be revolved? When is using a revolve function an appropriate choice? Revolve command is a method of creating a 3D feature using a 2D sketch and a rotational point, commonly known as a center line. Profile Revolve Centerline Produce a Revolve feature by producing a valid sketch and centerline. Then imputing the number of degrees to revolve the sketch around the centerline. Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Demonstrate the method of revolving a profile around a center line. Identify key commands and steps needed to reach required effect. Compare and discuss student responses to the Revolve command Self guided tutorial Design activity in which feature needs to be utilized. Project Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Midterm/Final Exams Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
17 18 Unit #11: Sweep/Loft Enduring Understanding: Essential : How do sketches play a role in creating a solid model? How does a CAD program help you create a design? What part of the CAD editing program helps you create changes? How can one navigate through the various options of a CAD program? Unit Goal: Students will be able to project a profile along a given path to create a new solid object that may be of an irregular shape. Duration of Unit: 4 weeks NJCCCS: A.2, F.3, O (1), (2), (5), O (8)-(12) Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Instructional Resources and Teaching Concepts, and Skills How can one use a 2D drawing to create a 3D feature along a path? When would it be useful to sweep a profile along a path to aide in your design? When is appropriate to loft two features together? Identify the method of using two 2D sketches to form a sweep feature. Profile Sweep Skills: Sweeping a profile along a path to create complex shapes The method of creating a 3D feature from 2D sketches on varying planes is known as a Loft Profile Loft Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Presentation on the various methods of taking two or more 2D sketches and creating a 3D feature. Identify key commands and steps needed to reach required effect. Compare and contrast the similarities and differences of a Sweep and Loft, while identifying appropriate uses of each command. Self guided tutorial Design activity in which feature needs to be utilized. Project Midterm/Final Exams Utilize dissimilar 2D shapes create a complex irregular 3D feature. Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
18 19 Unit #12: Rendering Enduring Understanding: CAD programs allow products to be presented to clients prior to production. Essential : Why are presentations important? How is a product presentation conducted? What are some ways in which CAD models can be presented to clients? Why is solid model rendering important? Unit Goal: Students will be able to apply materials and textures to a designed product to give it a realistic appearance for presentation. Duration of Unit: 2 weeks NJCCCS: B (1).1, B (1).2, D.3, C.1, B.15, B.1, B.2 Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, Instructional Resources and Teaching and Skills How can virtual parts be realistically represented? How do you render an object within a CAD program? What textures and materials can be applied to give a product a realistic appearance? What are the benefits of high quality renderings? Rendering is the production realistic models and images in CAD. Coloring Surface texturing Bump Mapping Lighting Shading Create realistic rendering of parts using available feature within CAD and through third party software. There are many benefits of having images when used in presentations. Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Presentation on the various rendering methodologies and their advantages and disadvantages. Discuss necessary steps in completing a renderings. Compare and discuss student responses to various rendered parts. Self guided tutorial Facilitate the creation of a rendering for a given target audience by using a stock part file. Project Product Create realistic rendering of parts using available feature within CAD and through third party software. Community Resources Printer/Plotter Streaming Videos Students work in small collaborative groups to identify desired textures, coloring, and shading to have the greatest impact. Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
19 20 Unit #13: Assemblies Enduring Understanding: Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. Essential : What is the difference between using your hand to draw a design as opposed to a computer? What is the difference between using your hand to alter a design as opposed to altering it digitally? Who is known as a major contributor in CAD? What are the benefits of digital CAD technology in product development? Unit Goal: Students will be able to take multiple designed components and join them together within the program to make a complete final product. Duration of Unit: 3 weeks NJCCCS: B.6, B.18, B.24, C.1, G.1, F.2 Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, and Instructional Resources and Teaching Skills What is an assembly? How are assembly drawings used in manufacturing? How are parts of an assembly placed together? How is an assembly drawing created? Placing parts together to create more complex parts is known as an Assembly. There are various methods of doing this. Assembly Files Mating Constraints Assembly Drawings Identify and describe the various methods of assembly as well as the constraints that regulate how they are made. Placement and alignment of parts in an assembly realy on constraints they are: Mate, Mate Offset, Align, Align Offset, Insert, Orient Define and describe key components for assembly drawings and the information that they contain. Create an assembly using pre made parts and various placement constraints. Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Community Resources Printer/Plotter Streaming Videos 3D printer(optional) Presentation on the various assembly methodologies and their advantages and disadvantages. Discuss necessary components of an assembly drawing. Compare and discuss student responses to various assembly drawings from engineering drawings to assembly instructions from household items such as IKEA furniture. Demonstration of various assembly constraints to allow students to create definitions and descriptions of each. Handout of matching various assembly constraints with graphic representations of constraints. Demonstration of how CAD drawings are used in manufacturing operations. Design and model a product that uses multiple parts and multiple saved drawings for assembling together. Project Midterm/Final Exams CNC Router(optional) Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
20 21 Unit #14: Rapid Prototyping Enduring Understanding: Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify work. Essential : How has the timeline of product development been affected by CAD technologies? What is the difference between CAD and CAM? Why is it important to know how to use CAD CAM Software together? How is rapid prototyping used in the development of a product? Unit Goal: Students will be able to create a final product using CAD/CAM software to quickly create a prototype of their ideas for presentation to client. Duration of Unit: 3 weeks NJCCCS: B (1).1, B (1).9, B.2, A.1, B.1, B.2, Guiding / Topical Content, Themes, Concepts, and Instructional Resources and Teaching Skills What is rapid prototyping? What equipment or software is necessary to create prototypes? What are the benefits of rapid prototyping versus traditional methods? How is rapid prototyping performed? Identify and describe various methods of rapid prototyping used in industry and education. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Stereo lithography (SLA) Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) Electron Beam Melting (EBM) 3D printing (3DP) CNC Router CNC milling machine The process of presentation of prototypes and models over the years has varied and evolved. Identify and describe various methods of prototype presentations throughout history. The process of preparing part files for prototyping consists of assorted software and hardware. CAD/CAM Post Processing Output files, such as STL Changing of tooling and material ; Study Guides/Handouts PowerPoint or SMART Notebook Texts similar to Parametric Modeling with Pro Engineer Wildfire 4.0 or Designing with Pro/DESKTOP Printer/Plotter Streaming Videos 3D printer(optional) CNC Router(optional) Definitions of various types of rapid prototyping. Sample of various technologies such as 3D printing or Laminated Object Manufacturing. Description of current equipment available for use. Creation of comparison chart between various technologies highlighting each strengths and weaknesses. Student design and create a product for rapid prototyping. Design and model a product for consumer manufacture. Create a presentation for a product of your design that will persuade investors to back the product. Written tests and Project Rubrics Midterm/Final Exams Create a part using one of the methods of rapid prototyping. Students with individual learning styles can be assisted through adjustments in assessment standards, one-to-one teacher support, additional testing time, and use of visual and auditory teaching methods A wide variety of and strategies complement the individual learning experience.
HONORS BUSINESS COMPUTER SYSTEMS
 FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION SPECIALIZED LEARNING CENTER HONORS BUSINESS COMPUTER SYSTEMS COURSE PHILOSOPHY Technology literacy is
FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION SPECIALIZED LEARNING CENTER HONORS BUSINESS COMPUTER SYSTEMS COURSE PHILOSOPHY Technology literacy is
Computer Aided Drafting in Engineering
 Unit 17: Computer Aided Drafting in Engineering Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose A/600/0267 BTEC National This unit gives learners the knowledge and skills
Unit 17: Computer Aided Drafting in Engineering Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose A/600/0267 BTEC National This unit gives learners the knowledge and skills
JEFFERSON TOWNSHIP PUBLIC SCHOOLS RELATED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY CURRICULUM TITLE: 3D COMPUTER GRAPHICS GRADE: 10-12
 JEFFERSON TOWNSHIP PUBLIC SCHOOLS RELATED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY CURRICULUM TITLE: 3D COMPUTER GRAPHICS GRADE: 10-12 Grade 10-12 Related Arts and Technology Curriculum Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS JEFFERSON TOWNSHIP
JEFFERSON TOWNSHIP PUBLIC SCHOOLS RELATED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY CURRICULUM TITLE: 3D COMPUTER GRAPHICS GRADE: 10-12 Grade 10-12 Related Arts and Technology Curriculum Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS JEFFERSON TOWNSHIP
Kankakee Community College
 Kankakee Community College Course prefix and number: DRFT 2134 Course title: AutoCAD III Semester: Fall 2014 Credit hours: 4 Lecture hours: 2.5 Lab hours: 3 Catalog description: Prerequisite: DRFT 2114,
Kankakee Community College Course prefix and number: DRFT 2134 Course title: AutoCAD III Semester: Fall 2014 Credit hours: 4 Lecture hours: 2.5 Lab hours: 3 Catalog description: Prerequisite: DRFT 2114,
West Sound Technical Skills Center 101 National Avenue N. Bremerton WA 98312
 West Sound Technical Skills Center 101 National Avenue N. Bremerton WA 98312 Instructor: Tony Sharpe Phone: 360-473-0585 Fax: 360-478-5090 Email: tony.sharpe@bremertonschools.org Hours: 7:30 a.m. 3:00
West Sound Technical Skills Center 101 National Avenue N. Bremerton WA 98312 Instructor: Tony Sharpe Phone: 360-473-0585 Fax: 360-478-5090 Email: tony.sharpe@bremertonschools.org Hours: 7:30 a.m. 3:00
MENU PLANNING AND HOSPITALITY GOVERNANCE
 FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION CULINARY ARTS ACADEMY MENU PLANNING AND HOSPITALITY GOVERNANCE COURSE PHILOSOPHY The Freehold Regional High School District s
FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION CULINARY ARTS ACADEMY MENU PLANNING AND HOSPITALITY GOVERNANCE COURSE PHILOSOPHY The Freehold Regional High School District s
Design. Design. Certificates. Contact Information. Full-Time Faculty. Associate Degrees. Associate in Arts Degrees. Certificate of Achievement
 Design Associate in Arts Degrees Architectural Design Computer-Aided Drafting Computer-Aided Drafting and Design Mechanical Design Students may earn one of the above-named associate degrees by completing
Design Associate in Arts Degrees Architectural Design Computer-Aided Drafting Computer-Aided Drafting and Design Mechanical Design Students may earn one of the above-named associate degrees by completing
Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE
 Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Computer Aided Drafting & Design Course Number: 7163 Department: Career and Technical Education Grade(s): 9-12 Level(s): Academic Credit:
Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Computer Aided Drafting & Design Course Number: 7163 Department: Career and Technical Education Grade(s): 9-12 Level(s): Academic Credit:
2014 New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards - Technology
 2014 New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards - Technology Content Area Standard Strand Grade Level bands Technology 8.2 Technology Education, Engineering, Design, and Computational Thinking - Programming:
2014 New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards - Technology Content Area Standard Strand Grade Level bands Technology 8.2 Technology Education, Engineering, Design, and Computational Thinking - Programming:
Ministry of Education Course Title: Learning Strategies 1: Skills For Success in Secondary School
 Course Outline School Name: Toronto Prep School Ministry of Education Course Title: Learning Strategies 1: Skills For Success in Secondary School Grade Level: 9 Open Ministry Course Code: GLS10 Teacher's
Course Outline School Name: Toronto Prep School Ministry of Education Course Title: Learning Strategies 1: Skills For Success in Secondary School Grade Level: 9 Open Ministry Course Code: GLS10 Teacher's
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools
 Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools F1 in Schools Race Car In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s digital prototyping strategy
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools F1 in Schools Race Car In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s digital prototyping strategy
Computer Integrated Manufacturing Course Description
 Computer Integrated Manufacturing Course Description Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) is the study of manufacturing planning, integration, and implementation of automation. The course explores manufacturing
Computer Integrated Manufacturing Course Description Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) is the study of manufacturing planning, integration, and implementation of automation. The course explores manufacturing
AUTOCAD / DRAFTING COURSE SYLLABUS 2015-2016
 AUTOCAD / DRAFTING COURSE SYLLABUS 2015-2016 Course Description The AutoCAD/Drafting program at the TCTC is a two-year class designed to allow the student access to the basic principles of computer-aided
AUTOCAD / DRAFTING COURSE SYLLABUS 2015-2016 Course Description The AutoCAD/Drafting program at the TCTC is a two-year class designed to allow the student access to the basic principles of computer-aided
SolidWorks. SolidWorks Teacher Guide. and Student Courseware
 SolidWorks SolidWorks Teacher Guide and Student Courseware SolidWorks Corporation Outside the U.S.: +1-978-371-5011 300 Baker Avenue Fax: +1-978-371-7303 Concord, Massachusetts 01742 USA Email: info@solidworks.com
SolidWorks SolidWorks Teacher Guide and Student Courseware SolidWorks Corporation Outside the U.S.: +1-978-371-5011 300 Baker Avenue Fax: +1-978-371-7303 Concord, Massachusetts 01742 USA Email: info@solidworks.com
AutoCAD 3D. MicroStation. Courseware Issued (Optional) AutoCAD (30 Days Trial Version) Reference Guide Project Workbook
 2D CAD Introduction Isometric drawings File management Perspective drawings Orthographic drawings Annotations and Dimensions View management Team work Display management Layout management Layer management
2D CAD Introduction Isometric drawings File management Perspective drawings Orthographic drawings Annotations and Dimensions View management Team work Display management Layout management Layer management
Creating 2D Drawings from 3D AutoCAD Models
 Creating 2D Drawings from 3D AutoCAD Models David Piggott CrWare, LP GD205-2P This class explores the various techniques in creating 2D part and assembly drawings from 3D AutoCAD models. As part of the
Creating 2D Drawings from 3D AutoCAD Models David Piggott CrWare, LP GD205-2P This class explores the various techniques in creating 2D part and assembly drawings from 3D AutoCAD models. As part of the
Robotics Engineering
 Robotics Engineering COURSE OF STUDY BHPRSD Technology Education Department Written by: Kyle O Donnell, Steve Arena, Ygor Carvalho, Laura Whitaker Date: November 2014 Supervisor: Glenn Smith Approved by:
Robotics Engineering COURSE OF STUDY BHPRSD Technology Education Department Written by: Kyle O Donnell, Steve Arena, Ygor Carvalho, Laura Whitaker Date: November 2014 Supervisor: Glenn Smith Approved by:
HACKETTSTOWN, NEW JERSEY. Computer Animation Grades 10-12 CURRICULUM GUIDE FINAL DRAFT. July 2014
 HACKETTSTOWN, NEW JERSEY Computer Animation Grades 10-12 CURRICULUM GUIDE FINAL DRAFT July 2014 Mr. David C. Mango, Superintendent Ms. Nadia Inskeep, Director of Curriculum & Instruction Developed by:
HACKETTSTOWN, NEW JERSEY Computer Animation Grades 10-12 CURRICULUM GUIDE FINAL DRAFT July 2014 Mr. David C. Mango, Superintendent Ms. Nadia Inskeep, Director of Curriculum & Instruction Developed by:
SOUTHWESTERN MICHIGAN COLLEGE SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY Niles Campus COURSE SYLLABUS Winter Semester 2005
 SOUTHWESTERN MICHIGAN COLLEGE SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY Niles Campus COURSE SYLLABUS Winter Semester 2005 COURSE TITLE: ADVANCED CAD/AUTOCAD COURSE NO: CADD 203 SECTION # 2410 CREDITS/CONTACTS: Credit Hours
SOUTHWESTERN MICHIGAN COLLEGE SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY Niles Campus COURSE SYLLABUS Winter Semester 2005 COURSE TITLE: ADVANCED CAD/AUTOCAD COURSE NO: CADD 203 SECTION # 2410 CREDITS/CONTACTS: Credit Hours
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools
 F1 in Schools race car Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s Digital Prototyping strategy
F1 in Schools race car Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s Digital Prototyping strategy
Transportation, Distribution, and Logistics
 Transportation, Distribution, and Logistics Unit 1: Introduction Content Standard(s) and 1. Summarize purpose, rules, and regulations relative to the transportation, distribution, and logistics industry.
Transportation, Distribution, and Logistics Unit 1: Introduction Content Standard(s) and 1. Summarize purpose, rules, and regulations relative to the transportation, distribution, and logistics industry.
Precision Manufacturing Regional Alliance Project (PMRAP) Accelerated Weekend Program. Springfield Technical Community College.
 Precision Manufacturing Regional Alliance Project (PMRAP) Accelerated Weekend Program At Springfield Technical Community College Summary Report Precision Manufacturing Regional Alliance Project (PMRAP)
Precision Manufacturing Regional Alliance Project (PMRAP) Accelerated Weekend Program At Springfield Technical Community College Summary Report Precision Manufacturing Regional Alliance Project (PMRAP)
Total Credits for Diploma of Interior Design and Decoration 63
 Diploma of Interior Design and Decoration programme Code: MSF50213 Program Description The BHCK Diploma of Interior design and Decoration provides the skills and knowledge required to perform design and
Diploma of Interior Design and Decoration programme Code: MSF50213 Program Description The BHCK Diploma of Interior design and Decoration provides the skills and knowledge required to perform design and
Computer Aided Drafting & Computer Graphic Design. Advisory Committee. Program Update TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Computer Aided Drafting & Computer Graphic Design Advisory Committee Program Update TABLE OF CONTENTS Program Data 1. Enrollment 2. Graduates 3. Demographics 4. Program Costs Student Success Others 1.
Computer Aided Drafting & Computer Graphic Design Advisory Committee Program Update TABLE OF CONTENTS Program Data 1. Enrollment 2. Graduates 3. Demographics 4. Program Costs Student Success Others 1.
Computer Aided Design (CAD), ME 530.414, JHU Professor Dan Stoianovici, dss@jhu.edu
 Computer Aided Design (CAD), ME 530.414, JHU Professor Dan Stoianovici, dss@jhu.edu COURSE DESCRIPTION: The course outlines modern solid modeling design, analysis, simulation, and manufacturing of mechanical
Computer Aided Design (CAD), ME 530.414, JHU Professor Dan Stoianovici, dss@jhu.edu COURSE DESCRIPTION: The course outlines modern solid modeling design, analysis, simulation, and manufacturing of mechanical
CAD/CAM in schools initiative
 CAD/CAM in schools initiative 10 years on... where are we now? John Lee June 2009 what is CAD/CAM? Engineering Design & development Rapid prototyping Virtual testing DATA management Production scheduling
CAD/CAM in schools initiative 10 years on... where are we now? John Lee June 2009 what is CAD/CAM? Engineering Design & development Rapid prototyping Virtual testing DATA management Production scheduling
Rapid prototyping. CAD / lecture. October 5, 2010. TO&I Vermelding onderdeel organisatie
 1 Rapid prototyping is: Rapid prototyping is an additive (layered) digital fabrication technology Layers of material are added forming the final 3d physical model The digital data of the virtual 3d model
1 Rapid prototyping is: Rapid prototyping is an additive (layered) digital fabrication technology Layers of material are added forming the final 3d physical model The digital data of the virtual 3d model
Digital 3D Animation
 Elizabethtown Area School District Digital 3D Animation Course Number: 753 Length of Course: 1 semester 18 weeks Grade Level: 11-12 Elective Total Clock Hours: 120 hours Length of Period: 80 minutes Date
Elizabethtown Area School District Digital 3D Animation Course Number: 753 Length of Course: 1 semester 18 weeks Grade Level: 11-12 Elective Total Clock Hours: 120 hours Length of Period: 80 minutes Date
Luna Community College 2012-2015. Drafting Technology Curriculum Profile
 Revised: July 2012 Luna Community College 2012-2015 Drafting Technology Curriculum Profile Content Page Program Goals 2 Degree Requirements 3 Course Descriptions and Outcomes 5 Assessment. 10 Standard
Revised: July 2012 Luna Community College 2012-2015 Drafting Technology Curriculum Profile Content Page Program Goals 2 Degree Requirements 3 Course Descriptions and Outcomes 5 Assessment. 10 Standard
CASPER COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS Course Number and Title: ENTK 2510-01 CAD 3D Modeling. Lecture Hours: 2 Lab Hours:4 Credit Hours: 4
 Semester/Year: Spring 2016 CASPER COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS Course Number and Title: ENTK 2510-01 CAD 3D Modeling Lecture Hours: 2 Lab Hours:4 Credit Hours: 4 Class Time: 1:00 3:50 Days: Monday and Wednesday
Semester/Year: Spring 2016 CASPER COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS Course Number and Title: ENTK 2510-01 CAD 3D Modeling Lecture Hours: 2 Lab Hours:4 Credit Hours: 4 Class Time: 1:00 3:50 Days: Monday and Wednesday
LEAVING CERT DCG SCHEME OF WORK
 2010-11 LEAVING CERT DCG SCHEME OF WORK ST OLIVER S COMMUNITY COLLEGE Mission statement The technology department aspires to provide a safe, stimulating environment where all students can develop their
2010-11 LEAVING CERT DCG SCHEME OF WORK ST OLIVER S COMMUNITY COLLEGE Mission statement The technology department aspires to provide a safe, stimulating environment where all students can develop their
Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 4.0 Basic Design
 Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
CAD/ CAM Prof. P. V. Madhusudhan Rao Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 03 What is CAD/ CAM
 CAD/ CAM Prof. P. V. Madhusudhan Rao Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 03 What is CAD/ CAM Now this lecture is in a way we can say an introduction
CAD/ CAM Prof. P. V. Madhusudhan Rao Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 03 What is CAD/ CAM Now this lecture is in a way we can say an introduction
o Ivy Tech DESN 102- Technical Graphics DESN 103- CAD Fundamentals
 Indiana Department of Education Academic Course Framework ARCHITECHTURAL DRAFTING AND DESIGN I Architectural Drafting and Design I Gives students a basic understanding of the detailing skills commonly
Indiana Department of Education Academic Course Framework ARCHITECHTURAL DRAFTING AND DESIGN I Architectural Drafting and Design I Gives students a basic understanding of the detailing skills commonly
An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD
 An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD Faculty of Technology University of Plymouth Drake Circus Plymouth PL4 8AA These notes are to be used in conjunction with the AutoCAD software
An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD Faculty of Technology University of Plymouth Drake Circus Plymouth PL4 8AA These notes are to be used in conjunction with the AutoCAD software
INDUSTRIAL DESIGN (534)
 DESCRIPTION This instructional course prepares individuals to apply technical knowledge and skills to develop and create concepts that optimize the function, value, and appearance of products for the benefit
DESCRIPTION This instructional course prepares individuals to apply technical knowledge and skills to develop and create concepts that optimize the function, value, and appearance of products for the benefit
Theoretical and Experimental Contributions Regarding the Optimization of Rapid Prototyping Technologies
 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA FACULTY OF MACHINE BUILDING Theoretical and Experimental Contributions Regarding the Optimization of Rapid Prototyping Technologies Doctoral thesis ABSTRACT Scientific
TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA FACULTY OF MACHINE BUILDING Theoretical and Experimental Contributions Regarding the Optimization of Rapid Prototyping Technologies Doctoral thesis ABSTRACT Scientific
Product Design (Part 4)
 Product Design (Part 4) Engineering Drawing Chapter 16 Drawing Standards Line conventions and lettering- ANSI/ASME Y14.2M-1992 Multiview and sectional view drawings- ANSI/ASME Y14.3M-1994 Pictorial drawing-ansi/asme
Product Design (Part 4) Engineering Drawing Chapter 16 Drawing Standards Line conventions and lettering- ANSI/ASME Y14.2M-1992 Multiview and sectional view drawings- ANSI/ASME Y14.3M-1994 Pictorial drawing-ansi/asme
DRAFTING AND DESIGN. For additional program information see: http://www.hillcollege.edu/students/teched/drafting/.
 DRAFTING AND DESIGN For additional program information see: http://www.hillcollege.edu/students/teched/drafting/. Certificate of Completion in Basic Computer Aided Drafting Major Code: 6055 TSI (Testing)
DRAFTING AND DESIGN For additional program information see: http://www.hillcollege.edu/students/teched/drafting/. Certificate of Completion in Basic Computer Aided Drafting Major Code: 6055 TSI (Testing)
After this activity, you will be able to:
 CAD Tutorial - 1 Purpose: Introduce you to solid modeling and basic solid modeling functions. Importance: Solid Modeling is a way for scientists and engineers to geometrically model their work, check for
CAD Tutorial - 1 Purpose: Introduce you to solid modeling and basic solid modeling functions. Importance: Solid Modeling is a way for scientists and engineers to geometrically model their work, check for
Autodesk Revit Architecture 2011 Professional Massmodeling Rendering Video Tutorial
 Autodesk Revit Architecture 2011 Professional Massmodeling Rendering Video Tutorial Instructor Handout Created by: Marvi Basha, Klaus Hyden und Philipp Müller Autodesk Student Experts TU Graz September
Autodesk Revit Architecture 2011 Professional Massmodeling Rendering Video Tutorial Instructor Handout Created by: Marvi Basha, Klaus Hyden und Philipp Müller Autodesk Student Experts TU Graz September
CATIA Wireframe & Surfaces TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Wireframe & Surfaces... 2 Pull Down Menus... 3 Edit... 3 Insert... 4 Tools... 6 Generative Shape Design Workbench... 7 Bottom Toolbar... 9 Tools... 9 Analysis... 10
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 Wireframe & Surfaces... 2 Pull Down Menus... 3 Edit... 3 Insert... 4 Tools... 6 Generative Shape Design Workbench... 7 Bottom Toolbar... 9 Tools... 9 Analysis... 10
Alphacam Art combines Vectric s Aspire artistic design software with the market leading Alphacam manufacturing software.
 Alphacam Art Alphacam Art - CNC Routing For Artists & Ideal Jewellery Cad Cam Software Alphacam Art combines Vectric s Aspire artistic design software with the market leading Alphacam manufacturing software.
Alphacam Art Alphacam Art - CNC Routing For Artists & Ideal Jewellery Cad Cam Software Alphacam Art combines Vectric s Aspire artistic design software with the market leading Alphacam manufacturing software.
Columbus State Community College Construction Science and Engineering Technology Department Mechanical Engineering Technology
 Columbus State Community College Construction Science and Engineering Technology Department Mechanical Engineering Technology COURSE: Mech 1145 CAD I Semester: Spring 2014 Instructor: Shane Bendele Phone:
Columbus State Community College Construction Science and Engineering Technology Department Mechanical Engineering Technology COURSE: Mech 1145 CAD I Semester: Spring 2014 Instructor: Shane Bendele Phone:
Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD
 Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD Overview By Prof. D. M. Kulkarni Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD http://www.phindia.com/bookdetail_forth.php?isbn=978-81-203-3783-1 Team of Authors Dr. Dhananjay M.
Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD Overview By Prof. D. M. Kulkarni Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD http://www.phindia.com/bookdetail_forth.php?isbn=978-81-203-3783-1 Team of Authors Dr. Dhananjay M.
LITCHFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Core Curriculum Scope and Sequence {Interior Design}
 LITCHFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Core Curriculum Scope and Sequence {Interior Design} CT Frameworks/ Standards Content and Skill Objectives Students will be able to: Assessments Resources Architecture 2-3 weeks
LITCHFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Core Curriculum Scope and Sequence {Interior Design} CT Frameworks/ Standards Content and Skill Objectives Students will be able to: Assessments Resources Architecture 2-3 weeks
o Ivy Tech DESN 105- Architectural Design I DESN 113- Intermediate CAD o Vincennes University ARCH 221- Advanced Architectural Software Applications
 Indiana Department of Education Academic Course Framework ARCHITECHTURAL DRAFTING AND DESIGN II Architectural Drafting and Design II presents a history and survey of architecture and focuses on the creative
Indiana Department of Education Academic Course Framework ARCHITECHTURAL DRAFTING AND DESIGN II Architectural Drafting and Design II presents a history and survey of architecture and focuses on the creative
Expert Panel Sample Booklet. Workforce Education Implementation Evaluation. SRI International
 Expert Panel Sample Booklet Workforce Education Implementation Evaluation SRI International Introduction Welcome to the Expert Panel. During this session you will rate different qualities of classroom
Expert Panel Sample Booklet Workforce Education Implementation Evaluation SRI International Introduction Welcome to the Expert Panel. During this session you will rate different qualities of classroom
COURSE TITLE: ARCHITECTURAL DRAFTING GRADES 11 & 12 LENGTH: FULL YEAR SCHOOLS: RUTHERFORD HIGH SCHOOL RUTHERFORD, NEW JERSEY DATE:
 COURSE TITLE: ARCHITECTURAL DRAFTING GRADES 11 & 12 LENGTH: FULL YEAR SCHOOLS: RUTHERFORD HIGH SCHOOL RUTHERFORD, NEW JERSEY DATE: Fall 2014 Architectural Drafting 2 Rutherford High School Rutherford,
COURSE TITLE: ARCHITECTURAL DRAFTING GRADES 11 & 12 LENGTH: FULL YEAR SCHOOLS: RUTHERFORD HIGH SCHOOL RUTHERFORD, NEW JERSEY DATE: Fall 2014 Architectural Drafting 2 Rutherford High School Rutherford,
AC 2011-151: TEACHING SURFACE MODELING TO CAD/CAM TECH- NOLOGISTS
 AC 2011-151: TEACHING SURFACE MODELING TO CAD/CAM TECH- NOLOGISTS Derek M. Yip-Hoi, Western Washington University Derek Yip-Hoi has a Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Michigan. He
AC 2011-151: TEACHING SURFACE MODELING TO CAD/CAM TECH- NOLOGISTS Derek M. Yip-Hoi, Western Washington University Derek Yip-Hoi has a Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Michigan. He
Learning Autodesk. Modeling, Analysis and Animation SDC. Randy H. Shih. Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.
 Learning Autodesk Inventor 2012 Modeling, Analysis and Animation Randy H. Shih SDC Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Visit the following
Learning Autodesk Inventor 2012 Modeling, Analysis and Animation Randy H. Shih SDC Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Visit the following
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY LESSON PLANS
 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY LESSON PLANS GRADE 11. LESSON PLAN 1. Lesson Plan: Personal finance Number f Activities : 3 Duration : +/- 13H30 Week : 1-3 Date: Context : Personal finance management, Business context.
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY LESSON PLANS GRADE 11. LESSON PLAN 1. Lesson Plan: Personal finance Number f Activities : 3 Duration : +/- 13H30 Week : 1-3 Date: Context : Personal finance management, Business context.
Course Overview Name of Course: Child Care I Name of Department: Family and Consumer Science
 Course Overview Name of Course: Child Care I Name of Department: Family and Consumer Science The Child Care Career Program This is a three year program designed to give students interested in a career
Course Overview Name of Course: Child Care I Name of Department: Family and Consumer Science The Child Care Career Program This is a three year program designed to give students interested in a career
Completion/Revision Date Approved by Board of Education on November 16, 2009
 Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Microsoft Word Essentials Course Number: Department: Career and Technical Education Grade(s): 9-12 Level(s): Academic Credit: 1/2 Course
Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Microsoft Word Essentials Course Number: Department: Career and Technical Education Grade(s): 9-12 Level(s): Academic Credit: 1/2 Course
PREREQUISITE FOR ALL ONLINE CLASSES: You must have basic Computer and Internet skills with a highspeed Internet connection and an E-mail address.
 SPRING/SUMMER 2015 ONLINE CLASSES What to Expect with these Online Courses All classes meet online. Just turn on your computer. Go to the Internet. Enter Online classroom. Your instructor will give you
SPRING/SUMMER 2015 ONLINE CLASSES What to Expect with these Online Courses All classes meet online. Just turn on your computer. Go to the Internet. Enter Online classroom. Your instructor will give you
MET 306. Activity 8a. Mechanism Design Creo 2.0 Level 7 POINT A GROUND LINK LINK 1 LINK 2 LINK 3 POINT B 10/15/2010 1
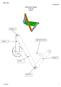 Mechanism Design Creo 2.0 Level 7 POINT A LINK 1 GROUND LINK LINK 2 LINK 3 POINT B 10/15/2010 1 Download parts ground, key, link_1, link_2, link_3 and pulley from the V:/MET_306/Activity_8_Creo drive.
Mechanism Design Creo 2.0 Level 7 POINT A LINK 1 GROUND LINK LINK 2 LINK 3 POINT B 10/15/2010 1 Download parts ground, key, link_1, link_2, link_3 and pulley from the V:/MET_306/Activity_8_Creo drive.
Hamilton Southeastern Schools Ivy Tech Community College Technical Education Partnership
 Hamilton Southeastern Schools Ivy Tech Community College Technical Education Partnership Students enrolled in one of these programs will complete 5 college technical education courses, earning 15-16 college
Hamilton Southeastern Schools Ivy Tech Community College Technical Education Partnership Students enrolled in one of these programs will complete 5 college technical education courses, earning 15-16 college
Models of a Vending Machine Business
 Math Models: Sample lesson Tom Hughes, 1999 Models of a Vending Machine Business Lesson Overview Students take on different roles in simulating starting a vending machine business in their school that
Math Models: Sample lesson Tom Hughes, 1999 Models of a Vending Machine Business Lesson Overview Students take on different roles in simulating starting a vending machine business in their school that
Why is it important to do use your hands and traditional tools to create simple designs before jumping on to the computer?
 Intro to Graphic Design Essential Questions Unit 1: Traditional Tools Why is it important to sketch your ideas away from the computer instead of sketching on the computer and believing your solution is
Intro to Graphic Design Essential Questions Unit 1: Traditional Tools Why is it important to sketch your ideas away from the computer instead of sketching on the computer and believing your solution is
Robotics & Automation
 Robotics & Automation Levels: Grades 10-12 Units of Credit: 1.0 CIP Code: 21.0117 Core Code: 38-01-00-00-130 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: 612 COURSE DESCRIPTION Robotics & Automation is a lab-based,
Robotics & Automation Levels: Grades 10-12 Units of Credit: 1.0 CIP Code: 21.0117 Core Code: 38-01-00-00-130 Prerequisite: None Skill Test: 612 COURSE DESCRIPTION Robotics & Automation is a lab-based,
COURSE DES1010: SKETCH, DRAW & MODEL. Prerequisite:
 COURSE DES1010: SKETCH, DRAW & MODEL Level: Prerequisite: Description: Parameters: Outcomes: Introductory None Students are introduced to observational sketching, drawing and modelling, and to a selection
COURSE DES1010: SKETCH, DRAW & MODEL Level: Prerequisite: Description: Parameters: Outcomes: Introductory None Students are introduced to observational sketching, drawing and modelling, and to a selection
Project 4.1 Puzzle Design Challenge
 Project 4.1 Puzzle Design Challenge Introduction Have you ever looked at a product that has been well-designed? Do you find yourself asking questions such as, How did the designer think of that idea? or
Project 4.1 Puzzle Design Challenge Introduction Have you ever looked at a product that has been well-designed? Do you find yourself asking questions such as, How did the designer think of that idea? or
School District of the Chathams Curriculum Profile
 Program of Study: Fine Arts Course Title: Drawing Grade Level: 9-12 PURPOSE/ COURSE DESCRIPTION School District of the Chathams Curriculum Profile Drawing focuses on black and white or monochromatic rendering
Program of Study: Fine Arts Course Title: Drawing Grade Level: 9-12 PURPOSE/ COURSE DESCRIPTION School District of the Chathams Curriculum Profile Drawing focuses on black and white or monochromatic rendering
Working Drawing and Assemblies. Chapter 10
 Working Drawing and Assemblies Chapter 10 Objectives 1.Define working drawings. 2. Describe how working drawings are used in industry. 3. List the major components of a complete set of working drawings.
Working Drawing and Assemblies Chapter 10 Objectives 1.Define working drawings. 2. Describe how working drawings are used in industry. 3. List the major components of a complete set of working drawings.
Tri-District Technology Curriculum
 . Tri-District Technology Curriculum 2012 Grades K-6 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School Mr. Richard Freedman Principal
. Tri-District Technology Curriculum 2012 Grades K-6 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School Mr. Richard Freedman Principal
New Developments in College Algebra
 NORTHERN ESSEX COMMUNITY COLLEGE New Developments in College Algebra A Summer Mathematics Workshop Liliana Brand, Habib Maagoul, Linda Murphy, Nancy Nickerson, and Jim Sullivan 7/10/2009 This document
NORTHERN ESSEX COMMUNITY COLLEGE New Developments in College Algebra A Summer Mathematics Workshop Liliana Brand, Habib Maagoul, Linda Murphy, Nancy Nickerson, and Jim Sullivan 7/10/2009 This document
BUILDING DIGITAL LITERACY PURPOSE DEFINING DIGITAL LITERACY USING THIS GUIDE
 BUILDING PURPOSE In today s society, it is critical for students to be able to use the vast amount of technology available to them. Computer literacy will provide students with skills they need to succeed
BUILDING PURPOSE In today s society, it is critical for students to be able to use the vast amount of technology available to them. Computer literacy will provide students with skills they need to succeed
RAPID PROTOTYPING. Learning Objectives: By the end of the lecture the student should be able to: Explain the fundamentals of Rapid Prototyping
 RAPID PROTOTYPING Learning Objectives: By the end of the lecture the student should be able to: Explain the fundamentals of Rapid Prototyping Outline and explain differences of Rapid Prototyping Technologies
RAPID PROTOTYPING Learning Objectives: By the end of the lecture the student should be able to: Explain the fundamentals of Rapid Prototyping Outline and explain differences of Rapid Prototyping Technologies
To develop an understanding of the basic principles of drawing using AutoCAD. 3) Deduce the intersection lines for intersected cylinders.
 PROGRAMME: COURSE NAME: NATIONAL DIPLOMA IN INTERIOR DESIGN COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN (2D) COURSE CODE: ARC 213 DURATION: 0 4 4 UNITS: GOAL: GENERAL OBJECTIVES: 4 UNIT To develop an understanding of the basic
PROGRAMME: COURSE NAME: NATIONAL DIPLOMA IN INTERIOR DESIGN COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN (2D) COURSE CODE: ARC 213 DURATION: 0 4 4 UNITS: GOAL: GENERAL OBJECTIVES: 4 UNIT To develop an understanding of the basic
CATIA V5 Surface Design
 CATIA V5 Training Foils CATIA V5 Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 August 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_V5S_FI_V5R19 1 Lesson 1: Introduction to Generative Shape Design About this Course Introduction CATIA is a robust
CATIA V5 Training Foils CATIA V5 Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 August 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_V5S_FI_V5R19 1 Lesson 1: Introduction to Generative Shape Design About this Course Introduction CATIA is a robust
CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS
 Susan H. Carper Old Dominion University OTED 785 Fall 2002 CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS DEFINITION OF MICROSOFT OFFICE Microsoft Office is a software suite that includes several productivity applications. Microsoft
Susan H. Carper Old Dominion University OTED 785 Fall 2002 CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS DEFINITION OF MICROSOFT OFFICE Microsoft Office is a software suite that includes several productivity applications. Microsoft
Autodesk Fusion 360 Badge Guide: Design an F1 in Schools Trophy
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Badge Guide: Design an F1 in Schools Trophy Abstract: Gain basic understanding of creating 3D models in Fusion 360 by designing an F1 in Schools trophy. This badge may be claimed by
Autodesk Fusion 360 Badge Guide: Design an F1 in Schools Trophy Abstract: Gain basic understanding of creating 3D models in Fusion 360 by designing an F1 in Schools trophy. This badge may be claimed by
3D Printing and Structural Analysis: Is There an Alternative to FE Analysis for Quick Design Info & for FEM Validation?
 Orange County Chapter 3D Printing and Structural Analysis: Is There an Alternative to FE Analysis for Quick Design Info & for FEM Validation? FW Palmieri, Ph.D. 3/24/2014 Copyright 2014 Raytheon Company.
Orange County Chapter 3D Printing and Structural Analysis: Is There an Alternative to FE Analysis for Quick Design Info & for FEM Validation? FW Palmieri, Ph.D. 3/24/2014 Copyright 2014 Raytheon Company.
Engineering/Quality Management
 Engineering/Quality Management Third Level Courses Certificate in Quality Management, Lean Six Sigma and Creativity Certificate in Fundamentals of Quality Assurance Certificate in Quality Management Certificate
Engineering/Quality Management Third Level Courses Certificate in Quality Management, Lean Six Sigma and Creativity Certificate in Fundamentals of Quality Assurance Certificate in Quality Management Certificate
B.M.C. Durfee High School Honors Precalculus Course Syllabus 2012-2013
 Course: Precalculus (10301) Credits: 1 Instructor: Mrs. Brogan-Price Room #: 334 e-mail: jbrogan@fallriverschools.org Web Page: http://fallriverschools.org/jbrogan-price.cfm School Phone Number: 508-675-8100
Course: Precalculus (10301) Credits: 1 Instructor: Mrs. Brogan-Price Room #: 334 e-mail: jbrogan@fallriverschools.org Web Page: http://fallriverschools.org/jbrogan-price.cfm School Phone Number: 508-675-8100
All in the Family: Creating Parametric Components in Autodesk Revit
 All in the Family: Creating Parametric Components in Autodesk Revit Matt Dillon D C CADD AB2100 The key to mastering Autodesk Revit Architecture, Autodesk Revit MEP, or Autodesk Revit Structure software
All in the Family: Creating Parametric Components in Autodesk Revit Matt Dillon D C CADD AB2100 The key to mastering Autodesk Revit Architecture, Autodesk Revit MEP, or Autodesk Revit Structure software
TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
 The Technology Education Department offers an elective course of study to all students at Hinsdale Central. Technology Education courses help students meet the elective arts requirement. Our program of
The Technology Education Department offers an elective course of study to all students at Hinsdale Central. Technology Education courses help students meet the elective arts requirement. Our program of
Civil Engineering and Architecture (CEA) Detailed Outline
 Civil Engineering and Architecture (CEA) Detailed Outline Unit 1: Overview of Civil Engineering and Architecture (23 days) Lesson 1.1: History of Civil Engineering and Architecture 1. Many features of
Civil Engineering and Architecture (CEA) Detailed Outline Unit 1: Overview of Civil Engineering and Architecture (23 days) Lesson 1.1: History of Civil Engineering and Architecture 1. Many features of
2013-2014 Career and Technical Education Gold Seal
 2013-2014 Career and Technical Education Gold Seal FLORIDA GOLD SEAL VOCATIONAL SCHOLARS AWARD http://www.floridastudentfinancialaid.org/ssfad/bf/gsvrequire.htm The Florida Gold Seal Vocational Scholars
2013-2014 Career and Technical Education Gold Seal FLORIDA GOLD SEAL VOCATIONAL SCHOLARS AWARD http://www.floridastudentfinancialaid.org/ssfad/bf/gsvrequire.htm The Florida Gold Seal Vocational Scholars
Computer Technology: Literacy and Usage KINDERGARTEN. Standard 1.0 Students will understand basic operations and concepts of technology.
 Computer Technology: Literacy and Usage KINDERGARTEN Standard 1.0 Students will understand basic operations and concepts of technology. 1.1. Students will demonstrate an understanding of the nature and
Computer Technology: Literacy and Usage KINDERGARTEN Standard 1.0 Students will understand basic operations and concepts of technology. 1.1. Students will demonstrate an understanding of the nature and
Modeling in Geometry
 Modeling in Geometry Overview Number of instruction days: 8-10 (1 day = 53 minutes) Content to Be Learned Mathematical Practices to Be Integrated Use geometric shapes and their components to represent
Modeling in Geometry Overview Number of instruction days: 8-10 (1 day = 53 minutes) Content to Be Learned Mathematical Practices to Be Integrated Use geometric shapes and their components to represent
Combined Curriculum Document Technology High School
 Big Idea: Information, Communication and Productivity High School Students demonstrate a sound understanding of the nature and operations of technology systems. Students use technology to learn, to communicate,
Big Idea: Information, Communication and Productivity High School Students demonstrate a sound understanding of the nature and operations of technology systems. Students use technology to learn, to communicate,
PARAMETRIC MODELING. David Rosen. December 1997. By carefully laying-out datums and geometry, then constraining them with dimensions and constraints,
 1 of 5 11/18/2004 6:24 PM PARAMETRIC MODELING David Rosen December 1997 The term parametric modeling denotes the use of parameters to control the dimensions and shape of CAD models. Think of a rubber CAD
1 of 5 11/18/2004 6:24 PM PARAMETRIC MODELING David Rosen December 1997 The term parametric modeling denotes the use of parameters to control the dimensions and shape of CAD models. Think of a rubber CAD
INTERIOR DESIGN COURSE DESCRIPTIONS
 INTERIOR DESIGN COURSE DESCRIPTIONS The proposed curriculum adheres to the guidelines of the Council of Design Professional Standards. BA Year 2 30 credits DES 201 Theory of Art and Design This course
INTERIOR DESIGN COURSE DESCRIPTIONS The proposed curriculum adheres to the guidelines of the Council of Design Professional Standards. BA Year 2 30 credits DES 201 Theory of Art and Design This course
DESIGN. College of the Arts. Career Possibilities. Undergraduate Programs. Bachelor of Arts in Design (120 Units) 342 Design 2015-2016 CSULB Catalog
 DESIGN College of the Arts Department Chair: Martin Herman Department Office: Design (DESN), Room 101 Telephone / FAX: (562) 985 5089 / (562) 985 2284 Website: http://www.csulb.edu/depts/design/ Undergraduate
DESIGN College of the Arts Department Chair: Martin Herman Department Office: Design (DESN), Room 101 Telephone / FAX: (562) 985 5089 / (562) 985 2284 Website: http://www.csulb.edu/depts/design/ Undergraduate
Basic Computer Skills Module 2. Software Concepts
 Basic Computer Skills Module 2 Software Concepts Basic Computer Skills Module 2 Software Basics Summary Goal: Know the fundamentals of operating systems. SMART Objectives: Specific, Measurable, Achievable,
Basic Computer Skills Module 2 Software Concepts Basic Computer Skills Module 2 Software Basics Summary Goal: Know the fundamentals of operating systems. SMART Objectives: Specific, Measurable, Achievable,
Solid Edge structural frames and weldments
 Solid Edge structural frames and weldments White Paper Intelligent, process-specific applications that speed time to manufacturing. White Paper Solid Edge structural frames and weldments 2 Contents Solid
Solid Edge structural frames and weldments White Paper Intelligent, process-specific applications that speed time to manufacturing. White Paper Solid Edge structural frames and weldments 2 Contents Solid
Faculty Dr. Arafat Al-Naim, Dr. Rania Fawzi, Dr. Mohamed Galib, Dr. Majed Kamal Eldeen, Dr. Mohamed Sedeeq, Moh d Musa (M.A.)
 Graphic Design Department The Graphic Design Department at Zarqa University is committed to provide a high quality Design education and teaching new media skills. The Department offers a four-year bachelor
Graphic Design Department The Graphic Design Department at Zarqa University is committed to provide a high quality Design education and teaching new media skills. The Department offers a four-year bachelor
Graphic Design: Introduction to Typography
 Lesson 6 Graphic Design: Introduction to Typography What is Design? What is Graphic Design? How is Graphic Design different from Fine Art? LESSON OVERVIEW/OBJECTIVES Students will learn about design and
Lesson 6 Graphic Design: Introduction to Typography What is Design? What is Graphic Design? How is Graphic Design different from Fine Art? LESSON OVERVIEW/OBJECTIVES Students will learn about design and
COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN (CAD) 2D, ARCHITECTURE
 COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN (CAD) 2D, ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW ornamentation or cabinetry. PURPOSE Participants have the opportunity to use complex computer graphic skills, tools, and processes to develop representations
COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN (CAD) 2D, ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW ornamentation or cabinetry. PURPOSE Participants have the opportunity to use complex computer graphic skills, tools, and processes to develop representations
AutoCAD 2009. New Icon Quick Reference
 AutoCAD 2009 New Quick Reference Contents Chapter 1 New Quick Reference..................... 1 Toolbars................................... 1 3D Navigation Toolbar........................ 1 CAD Standards
AutoCAD 2009 New Quick Reference Contents Chapter 1 New Quick Reference..................... 1 Toolbars................................... 1 3D Navigation Toolbar........................ 1 CAD Standards
CATIA Functional Tolerancing & Annotation TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation...2 Pull-down Menus...3 Insert...3 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation Workbench...4 Bottom Toolbar Changes...5 3D Grid Toolbar...5
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation...2 Pull-down Menus...3 Insert...3 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation Workbench...4 Bottom Toolbar Changes...5 3D Grid Toolbar...5
Online Teaching and Learning
 Teaching online requires faculty members to shift their roles from instructor to facilitator or coach. Content shifts to customized materials and learning includes many active components. Simonson, Smaldino,
Teaching online requires faculty members to shift their roles from instructor to facilitator or coach. Content shifts to customized materials and learning includes many active components. Simonson, Smaldino,
Computer Aided Design and Drafting (CAD)
 Oakland Community College 2015-2016 Catalog 1 Computer Aided Design and Drafting (CAD) CAD 1050 Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) This course is designed to cover the fundamentals as well as
Oakland Community College 2015-2016 Catalog 1 Computer Aided Design and Drafting (CAD) CAD 1050 Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) This course is designed to cover the fundamentals as well as
Chapter 1. Creating Sketches in. the Sketch Mode-I. Evaluation chapter. Logon to www.cadcim.com for more details. Learning Objectives
 Chapter 1 Creating Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketch Mode-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Use various tools to create a geometry. Dimension a sketch. Apply constraints to
Chapter 1 Creating Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketch Mode-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Use various tools to create a geometry. Dimension a sketch. Apply constraints to
ENGINEERING, TECHNOLOGY, AND DESIGN
 ENGINEERING, TECHNOLOGY, AND DESIGN The Engineering, Technology and Design Department fosters student learning that will develop 21st century competencies in a constantly changing technological environment.
ENGINEERING, TECHNOLOGY, AND DESIGN The Engineering, Technology and Design Department fosters student learning that will develop 21st century competencies in a constantly changing technological environment.
Putting into Practice Surface Modeling Exercise Using Kayak Project: Experience with Advanced CATIA Course
 Putting into Practice Surface Modeling Exercise Using Kayak Project: Experience with Advanced CATIA Course Eric Leonhardt and Veekit O Charoen Department of Engineering Technology Western Washington University,
Putting into Practice Surface Modeling Exercise Using Kayak Project: Experience with Advanced CATIA Course Eric Leonhardt and Veekit O Charoen Department of Engineering Technology Western Washington University,
Innovation From Concept to Production
 Industrial Design Product Development Rapid Prototypes 3D Mold Design Short Run Production Legacy Data Translation Paradigm Engineering, Inc. is built on a foundation of innovation. Our unique expertise
Industrial Design Product Development Rapid Prototypes 3D Mold Design Short Run Production Legacy Data Translation Paradigm Engineering, Inc. is built on a foundation of innovation. Our unique expertise
SolidWorks: Mirror, Revolve, and. Introduction to Robotics
 SolidWorks: Mirror, Revolve, and Circular Pattern Introduction to Robotics Let s Review At this point we have learned the following: Extrude Boss/Base Extruded Cut Adding Relations and Dimensions Linear
SolidWorks: Mirror, Revolve, and Circular Pattern Introduction to Robotics Let s Review At this point we have learned the following: Extrude Boss/Base Extruded Cut Adding Relations and Dimensions Linear
FOLSOM CORDOVA UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT COMPUTER GAME DESIGN
 FOLSOM CORDOVA UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT COMPUTER GAME DESIGN Date: January 2016 Proposed Grade Level(s): Grade 6-8 Grading: A-F Prerequisite(s): None Course Length: Year Subject Area: Technology Elective
FOLSOM CORDOVA UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT COMPUTER GAME DESIGN Date: January 2016 Proposed Grade Level(s): Grade 6-8 Grading: A-F Prerequisite(s): None Course Length: Year Subject Area: Technology Elective
