Chapter Introduction Section 1: Transforming the Roman World Section 2:Feudalism Section 3:Growth of European Kingdoms Section 4:Byzantine Empire and
|
|
|
- Felicity Booth
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Chapter Introduction Section 1: Transforming the Roman World Section 2:Feudalism Section 3:Growth of European Kingdoms Section 4:Byzantine Empire and Crusades Visual Summary
3 How important is the location of a city? From ancient times, Carcassonne was important because of its location near the Pyrenees Mountains. The Romans built fortifications on the hilltop and each ruler added to them until the 1600s. A fortified city like Carcassonne, with a double ring of defensive walls and 53 towers, could hold out for months against an army. In this chapter you will learn about the beginning of the Middle Ages. What was the advantage of locating a city on a hilltop? Why might castles and fortified towns become impractical?
4
5
6 Transforming the Roman World Why was Rome the center of the Christian world at the beginning of the period?
7 Feudalism What purpose does a strong central government serve?
8 The Growth of European Kingdoms How do you think the Magna Carta affected the development of the U.S. government?
9 Byzantine Empire and Crusades What was the purpose of the Crusades?
10 The BIG Idea Ideas, Beliefs, and Values The new European civilization combined Germanic, Roman, and Christian elements.
11 Content Vocabulary wergild monasticism ordeal missionary bishopric nun pope abbess monk Academic Vocabulary excluded ensure
12 People and Places Clovis Gregory I Saint Benedict Pépin Charlemagne Carolingian Empire
13 Do you think that in our society, every personal crime should have a monetary value paid as a fine to the victim? A. Yes B. No A. A B. B
14 The New Germanic Kingdoms (cont.) By 500 A.D., the Western Roman Empire had been replaced by Germanic kingdoms that eventually excluded Romans from holding power. Clovis established the kingdom of the Franks. He was the first Germanic ruler to convert to Christianity and become allied with the Roman Catholic Church. New Germanic Kingdoms, A.D. 500
15 The New Germanic Kingdoms (cont.) As Germans and Romans intermarried, they created a new society. This impacted the Germanic legal system. The Germans devised a legal system based on a fine called a wergild which was paid by the wrongdoer to the victim s family. The value of the fine varied according to social status, so it cost more to commit an offense against a noble than a slave.
16 The New Germanic Kingdoms (cont.) The ordeal was a system to establish guilt or innocence through a physical trial. It was based on the belief in divine intervention.
17 What was the significance of Clovis s conversion to Christianity? A. It changed Germanic law. B. It prevented the spread of Islam in Western Europe. C. It divided the Germanic kingdoms. D. It unified the Franks and the Roman Catholic Church.
18 The Role of the Church The Bishop of Rome became the leader of the Christian Church.
19 The Role of the Church (cont.) By the end of the 4th century, Christianity had become the dominant religion of the Roman Empire, and the Church developed a system of organization. Priests led parishes; groups of parishes became known as bishoprics that were led by bishops. Bishoprics were, in turn, under the authority of an archbishop.
20 The Role of the Church (cont.) The head of the Catholic Church became known as the pope. Gregory I, pope from 590 to 604, strengthened the power of the papacy. He converted non- Christians and increased his spiritual authority over the Church. The practice of living the life of a monk is known as monasticism. Saint Benedict wrote a series of rules that became the model for monasticism. A Monk s Daily Timetable
21 The Role of the Church (cont.) Monks became Christian heroes in the new European civilization, providing religious and moral leadership. Monks became the missionaries that converted Western Europe to Catholicism. By 1050, most of Western Europe was Catholic. Women could become nuns and live in convents, which were headed by abbesses.
22 How did Catholic monks impact Western European society? A. Education and morality B. Architecture C. Military training D. Latin languages
23 The Carolingian Empire Charlemagne expanded the Frankish kingdom and created the Carolingian Empire.
24 The Carolingian Empire (cont.) Pépin was a chief officer of the Frankish kingdom who assumed the kingship for himself and his family. His son was Charles the Great. Charles the Great, or Charlemagne, was an intelligent leader and fierce warrior who expanded the Frankish kingdom, creating the Carolingian Empire. The Carolingian Empire
25 The Carolingian Empire (cont.) The Carolingian Empire was the largest European empire in history at the time. Charlemagne sent out messengers called the missi dominici to ensure that his wishes were enacted. In 800, Charlemagne was crowned emperor of the Roman Empire by the pope. This event symbolized the joining of Roman, Germanic, and Christian elements.
26 The Carolingian Empire (cont.) Charlemagne s strong desire to promote learning and education is often referred to as the Carolingian Renaissance.
27 What was given to Charlemagne by the pope in 800? A. The Roman army B. All the gold in Rome C. The castle in Rome D. The title of Roman Emperor
28
29 The BIG Idea Order and Security The collapse of central authority in Europe led to a new political order known as feudalism.
30 Content Vocabulary feudalism vassal knight fief feudal contract tournament chivalry Academic Vocabulary enabled contract
31 People and Places Magyars Hungary Vikings Normandy Eleanor of Aquitaine
32 When a team loses a coach who is a strong leader, the team is automatically weakened. A. Agree B. Disagree A. A B. B
33 The End of the Carolingian Empire Vikings, Magyars, and Muslims invaded Europe during the ninth and tenth centuries.
34 The End of the Carolingian Empire (cont.) After Charlemagne s death in 814, Europe was invaded by foreign powers. The most devastating attacks came from the Vikings. The Scandinavian warriors used longboats that enabled them to attack towns and villages far from the coast. Invasions of Europe,
35 The End of the Carolingian Empire (cont.) Frankish rulers gave the Vikings land in Normandy and converted the Norsemen to Christianity. The Vikings were made a part of European civilization. Invasions of Europe,
36 Which of the following was not an invading force in ninth-century Europe? A. Muslims B. Vikings C. Egyptians D. Magyars
37 The Development of Feudalism A system of lords and vassals spread throughout Europe after the collapse of the Carolingian Empire.
38 The Development of Feudalism (cont.) As a result of invasions, the people of Western Europe turned to local lords for protection. This led to a social and political system known as feudalism. Vassals were men who served a lord in a military capacity. Feudalism
39 The Development of Feudalism (cont.) Knights came to dominate European warfare for nearly 500 years. Knights had a high degree of social prestige and formed the backbone of European aristocracy.
40 The Development of Feudalism (cont.) Vassals swore allegiance to a lord. In turn, the vassal was given a fief and political control of it. The lord and vassal relationship came to be characterized by a set of unwritten rules known as the feudal contract. Vassals had to perform military service and the lord had to provide land and protection.
41 What provided the most power in the system of feudalism? A. Religion B. Land C. Castles D. Money
42 Feudal Society Men and women of the nobility were guided by a code of ethical behavior and society s expectations of their roles.
43 Feudal Society (cont.) In Europe during the Middle Ages, society was dominated by men whose main concern was warfare. Nobles and knights attended tournaments, where the knights would demonstrate their fighting skills. Influenced by the Catholic Church, nobles and knights began to follow an idealized code of ethics called chivalry.
44
45 Feudal Society (cont.) Lower-class women had few rights, but aristocratic women had opportunities to play important roles. The lady of the castle supervised affairs for her husband s absence travel or war. Eleanor of Aquitaine was an influential woman who was married to the king of France, and later to the king of England.
46 Why were European tournaments important? A. European warriors trained and demonstrated fighting skills. B. They earned valuable money for the lords. C. They helped spread Christianity. D. They allowed European warriors to purchase land or supplies.
47 Please complete Code of Chivalry assignment pages
48 The BIG Idea Order and Security During the High Middle Ages, monarchs began to extend their power and build strong states.
49 Written documents outlining rights of citizens make governments more fair. A. Agree B. Disagree A. A B. B
50 England in the High Middle Ages King John of England put his seal on the Magna Carta in 1215, recognizing the rights of his nobles, and keeping the English monarch from ever becoming an absolute ruler.
51 England in the High Middle Ages (cont.) In 1066 William of Normandy defeated King Harold at the Battle of Hastings. William was crowned king of England, leading to a new English culture. Henry II, who ruled from 1154 to 1189, expanded the power of the king. Common law began to replace the varying codes of the kingdom. Europe, 1160
52 England in the High Middle Ages (cont.) Thomas á Becket was the archbishop of Canterbury who challenged Henry by claiming that only the Roman Catholic Church could try clerics. He was killed by knights who were loyal to Henry II. English nobles resented the growing power of the king and defeated the forces of King John at Runnymede.
53 England in the High Middle Ages (cont.) In 1215 the king was forced to put his seal on the document known as the Magna Carta. This document outlined the rights of the people and the king. During the thirteenth century, the English Parliament was created. This representative assembly dealt with taxes, politics, and law.
54 What document outlined the rights of the king and the people of England? A. Parliament B. Common law C. Magna Carta D. Feudal Charter
55 France in the Middle Ages One section of Charlemagne s empire became France.
56 France in the Middle Ages (cont.) The reign of Philip II Augustus was a turning point for the French monarchy. He added land and expanded the power and income of the monarchy.
57 France in the Middle Ages (cont.) Louis IX ruled for much of the thirteenth century and tried to bring justice to his people. He was later made a saint. Philip IV created a French parliament by meeting with the three estates of the kingdom: Clergy (first estate) Nobles (second estate) Townspeople and peasants (third estate)
58 Who would be included in the first estate of the French parliament? A. Clergy B. Nobles C. Townspeople D. Royalty
59 Central and Eastern Europe The Slavic peoples settled in central and eastern Europe, forming new kingdoms.
60 Central and Eastern Europe (cont.) The Slavic peoples were from central Europe. They eventually split into three groups: Western Slavs eventually formed the Polish and Bohemian kingdoms. These two groups were converted to Christianity and became part of the Roman Catholic Church.
61 Central and Eastern Europe (cont.) Eastern Slavs were converted to Orthodox Christianity by Byzantine missionaries. Southern Slavs included the Croats, Serbs, and Bulgarians. They were converted to Eastern Orthodoxy, except for the Croats, who accepted the Catholic Church. Slavic Peoples of Central and Eastern Europe
62
63 The BIG Idea Ideas, Beliefs, and Values The Byzantine Empire created a unique civilization that was eventually weakened by the Crusades.
64 Content Vocabulary patriarch schism Crusades infidel Academic Vocabulary legal enormous
65 All empires eventually get too large and then fall apart. A. Agree B. Disagree A. A B. B
66 From Eastern Roman Empire to Byzantine Empire The Eastern Roman Empire evolved into the smaller Byzantine Empire, which created a unique civilization in the eastern Mediterranean.
67 From Eastern Roman Empire to Byzantine Empire (cont.) Despite the fall of Rome, the Eastern Roman Empire continued to exist. Its political and cultural center was the city of Constantinople. Justinian became emperor of the Eastern Roman Empire in 527. Justinian expanded the empire to include Italy, part of Spain, North Africa, Asia Minor, Palestine, and Syria.
68 From Eastern Roman Empire to Byzantine Empire (cont.) Justinian s most important contribution was The Body of Civil Law, a codification of legal material in the empire. The Eastern Roman Empire soon lost much territory because of overspending on foreign conquest, Islamic invasions, and the success of the Bulgars in the Balkans. The Justinian Code
69 From Eastern Roman Empire to Byzantine Empire (cont.) The new, smaller empire was called the Byzantine Empire. The emperor appointed the head of the Eastern Orthodox Church, known as the patriarch, which gave him political and religious power in the empire.
70 From Eastern Roman Empire to Byzantine Empire (cont.) Justinian built the capital of Constantinople into a beautiful city that became a trading center between the Middle East and Europe. Justinian s greatest achievement other than The Body of Civil Law was the creation of the Hagia Sophia, a church with an enormous dome.
71 Why did Constantinople grow wealthy during the Middle Ages? A. Powerful army B. Unifying religion C. Production of silk and porcelain D. Strategic location for trade
72 New Heights and New Problems The Macedonians expanded the Byzantine Empire, but new threats arose in the late eleventh century.
73 New Heights and New Problems (cont.) Relations between the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church worsened during this period. A schism developed between the two main branches of Christianity. The Byzantine empire was threatened by the Turks and turned to Europe for help.
74 Why did a schism develop between Catholics and Orthodox Christians? A. Catholics demanded taxes B. Orthodox Christians did not recognize the pope C. Orthodox Christians were tolerant of other religions D. Catholic popes wanted Orthodox Christian lands
75 The Crusades The Crusades had a significant effect on medieval society in both the East and the West.
76 The Crusades (cont.) From the eleventh to the thirteenth centuries, European Christians carried out a series of Crusades to regain the Holy Land from the Muslims. Pope Urban II saw the Crusades as an opportunity to free Jerusalem and Palestine from the infidels. The Crusades
77 The Crusades (cont.) The First Crusade was made up of mostly French warriors who retook Jerusalem in A horrible massacre of the inhabitants ensued. The Crusaders set up Christian kingdoms on the coast.
78 The Crusades (cont.) By 1140, the Muslims began to strike back, and St. Bernard of Clairvaux called for a Second Crusade. Muslim forces under Saladin recaptured Jerusalem in After Saladin s death, Pope Innocent III initiated the Fourth Crusade. The crusaders sacked Constantinople in a petty dispute between Italian and Byzantine leaders.
79 The Crusades (cont.) Effects of the Crusades: Wealth for the Italian port cities Increased attacks on Jews Breakdown of feudalism Development of nation-states
80 Which country was not involved in the Crusades? A. Germany B. Spain C. England D. France
81
82 MEDIEVAL EUROPE and the Church Germanic rulers, especially the Franks, ruled the old Western Roman Empire. Charlemagne expanded Frankish rule and promoted learning, centered in monasteries.
83 The FEUDAL ECONOMY Viking attacks in Europe led to decentralized governments and a new feudal system, which was based on military service in return for land grants. England and France were the first to build strong centralized states in Western Europe, while Russia developed around Kiev.
84 Rise and Fall of BYZANTIUM For centuries after Rome s fall, a wealthy Byzantine Empire dominated trade in the eastern Mediterranean. As the Turks of the Ottoman Empire grew powerful, Byzantine rulers in Constantinople were threatened. Religious zeal and a spirit of conquest inspired European Crusaders, but Constantinople finally fell in 1453.
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97 Chapter Transparencies Menu Chapter Transparency Unit Time Line Transparency Cause-and-Effect Transparency Select a transparency to view.
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105 wergild money for a man, the value of a person in money, depending on social status; in Germanic society, a fine paid by a wrongdoer to the family of the person he or she had injured or killed
106 ordeal a means of determining guilt in Germanic law, based on the idea of divine intervention; if the accused person was unharmed after a physical trial, he or she was presumed innocent
107 bishopric a group of Christian communities, or parishes, under the authority of a bishop
108 pope the bishop of Rome and head of the Roman Catholic Church
109 monk a man who separates himself from ordinary human society in order to dedicate himself to God; monks live in monasteries headed by abbots
110 monasticism practice of living the life of a monk
111 missionary a person sent out to carry a religious message
112 nun a woman who separates herself from ordinary human society in order to dedicate herself to God; nuns live in convents headed by abbesses
113 abbess the head of a convent
114 excluded not counted or included
115 ensure to make sure
116 feudalism political and social system that developed during the Middle Ages when royal governments were no longer able to defend their subjects; nobles offered protection and land in return for service
117 vassal under feudalism, a man who served a lord in a military capacity
118 knight under feudalism, a member of the heavily armored cavalry
119 fief under feudalism, a grant of land made to a vassal; the vassal held political authority within his fief
120 feudal contract under feudalism, the unwritten rules that determined the relationship between a lord and his vassal
121 tournament under feudalism, a series of martial activities such as jousts designed to keep knights busy during peacetime and help them prepare for war
122 chivalry in the Middle Ages, the ideal of civilized behavior that developed among the nobility; it was a code of ethics that knights were supposed to uphold
123 enabled made possible
124 contract a binding agreement between two or more people or parties
125 common law a uniform system of law that developed in England based on court decisions and on customs and usage rather than on written law codes; replaced law codes that varied from place to place
126 Magna Carta the Great Charter of rights, which King John was forced by the English nobles to sign at Runnymeade in 1215
127 Parliament in thirteenth-century England, the representative government that emerged; it was composed of two knights from every county, two people from every town, and all of the nobles and bishops throughout England
128 estate one of the three classes into which French society was divided before the revolution: the clergy (first estate), the nobles (second estate), and the townspeople (third estate); a landed property, usually with a large house on it
129 challenge a summons that is often stimulating, inciting, or threatening
130 document an original or official paper that gives proof of or support to
131 patriarch the head of the Eastern Orthodox Church, originally appointed by the Byzantine emperor
132 schism the separation between the two great branches of Christianity that occurred when the Roman Pope Leo IX and the Byzantine patriarch Michael Cerularius excommunicated each other in 1054
133 Crusades military expeditions carried out by European Christians in the Middle Ages to regain the Holy Land from the Muslims
134 infidel an unbeliever; a term applied to the Muslims during the Crusades
135 legal relating to law; founded on law
136 enormous huge; vast; immense
137 To use this Presentation Plus! product: Click the Forward button to go to the next slide. Click the Previous button to return to the previous slide. Click the Home button to return to the Chapter Menu. Click the Transparency button from the Chapter Menu, Chapter Introduction slides, or Visual Summary slides to access the transparencies that are relevant to this chapter. From within a section, click on this button to access the relevant Daily Focus Skills Transparency. Click the Return button in a feature to return to the main presentation. Click the History Online button to access online textbook features. Click the Reference Atlas button to access the Interactive Reference Atlas. Click the Exit button or press the Escape key [Esc] to end the slide show. Click the Help button to access this screen. Links to Presentation Plus! features such as Maps in Motion, Graphs in Motion, Charts in Motion, Concepts in Motion, and figures from your textbook are located at the bottom of relevant screens.
138 This slide is intentionally blank.
Note Taking Study Guide THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE Focus Question: What made the Byzantine empire rich and successful for so long, and why did it finally crumble? As you read this section in your textbook,
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE Focus Question: What made the Byzantine empire rich and successful for so long, and why did it finally crumble? As you read this section in your textbook,
Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church
 Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Directions Read each False statement below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word
Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Directions Read each False statement below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word
World History Middle Ages Test
 World History Middle Ages Test 1. Europe became a feudal society because a. Europeans needed to defend themselves against constant raids and invasions. b. overpopulation required that a more efficient
World History Middle Ages Test 1. Europe became a feudal society because a. Europeans needed to defend themselves against constant raids and invasions. b. overpopulation required that a more efficient
Late Medieval Period (WHI.12)
 Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
How did the histories of the Byzantine Empire and Western Europe differ during the era of third-wave civilizations?
 How did the histories of the Byzantine Empire and Western Europe differ during the era of third-wave civilizations? Western Europe. Frankish Kingdoms. Roman Catholic Church. Holy Roman Empire. Eastern
How did the histories of the Byzantine Empire and Western Europe differ during the era of third-wave civilizations? Western Europe. Frankish Kingdoms. Roman Catholic Church. Holy Roman Empire. Eastern
The Frankish Empire. The Franks and the Origins of the Frankish Empire
 The Frankish Empire The Germanic tribe known as the Franks established and ruled the Frankish Empire, in the ancient territory of Gaul (largely encompassing modern-day France and parts of modern-day Germany),
The Frankish Empire The Germanic tribe known as the Franks established and ruled the Frankish Empire, in the ancient territory of Gaul (largely encompassing modern-day France and parts of modern-day Germany),
Home work. Fill in the Blanks Use your study sheet to find the correct answers. BETWEEN ANCIENT AND MODERN
 Date: 1 BETWEEN ANCIENT AND MODERN The Middle Ages is the period between a and m history. The early period of the Middle Ages is known as the D Ages because the great c of G and R had fallen. Life during
Date: 1 BETWEEN ANCIENT AND MODERN The Middle Ages is the period between a and m history. The early period of the Middle Ages is known as the D Ages because the great c of G and R had fallen. Life during
Ninth Grade History & Social Science World History I
 SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
IMPACT OF THE CRUSADES DBQ
 IMPACT OF THE CRUSADES DBQ This task is based on the accompanying documents. Some of these documents have been edited for the purpose of this task. This task is designed to test your ability to work with
IMPACT OF THE CRUSADES DBQ This task is based on the accompanying documents. Some of these documents have been edited for the purpose of this task. This task is designed to test your ability to work with
Introduction. In Chapter 37, you learned how the emperor
 Introduction In Chapter 37, you learned how the emperor Constantine moved his capital from Rome to the ancient city of Byzantium in 330 C.E. This city eventually became known as Constantinople. After Constantine
Introduction In Chapter 37, you learned how the emperor Constantine moved his capital from Rome to the ancient city of Byzantium in 330 C.E. This city eventually became known as Constantinople. After Constantine
The Legacy of the Roman Empire and the Middle Ages in the West
 The Legacy of the Roman Empire and the Middle Ages in the West The Roman Empire reigned from 27 BCE to 476 CE throughout the Mediterranean world, including parts of Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.
The Legacy of the Roman Empire and the Middle Ages in the West The Roman Empire reigned from 27 BCE to 476 CE throughout the Mediterranean world, including parts of Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.
Roman Law. Justinian Code. The Dark Ages 9/9/2012
 Roman Law This was the legal system that began in early Rome (451 B.C.E.), and was the basis of Law for Western Europe, except England. As the Roman Empire grew, laws became more complex and the profession
Roman Law This was the legal system that began in early Rome (451 B.C.E.), and was the basis of Law for Western Europe, except England. As the Roman Empire grew, laws became more complex and the profession
How did the Crusades affect Europe and the Middle East?
 Focus Lesson - The Impact of the Crusades Merchant ships in the harbor at Naples after the Crusades How did the Crusades affect Europe and the Middle East? The Results of the End of the Medieval Crusades
Focus Lesson - The Impact of the Crusades Merchant ships in the harbor at Naples after the Crusades How did the Crusades affect Europe and the Middle East? The Results of the End of the Medieval Crusades
The sea protected the city on three sides. A huge wall protected the fourth. A chain was stretched across the north harbor for even more protection.
 Constantinople: The City of Constantine Constantine I was dissatisfied with Rome as his capital. He rebuilt Istanbul and renamed it Constantinople. Rome, Latin speaking, and pagan began its slow decline.
Constantinople: The City of Constantine Constantine I was dissatisfied with Rome as his capital. He rebuilt Istanbul and renamed it Constantinople. Rome, Latin speaking, and pagan began its slow decline.
History of Law in Society
 History of Law in Society Laws in Canada Our legal system has its origins in many cultures including aspects of Mosaic Law, Greek Law, Roman Law, French Law, and British Laws. In Canada, we are also influenced
History of Law in Society Laws in Canada Our legal system has its origins in many cultures including aspects of Mosaic Law, Greek Law, Roman Law, French Law, and British Laws. In Canada, we are also influenced
History 318: The Byzantine Empire Fall, 1995 Professor Abrahamse
 History 318: The Byzantine Empire Fall, 1995 Professor Abrahamse Office: MHB (McIntosh Humanities Building) 207 985-5381 E-Mail: DABRAHAM@CSULB.EDU Office Hours: Thurs. 5-6:30 or by appointment Assigned
History 318: The Byzantine Empire Fall, 1995 Professor Abrahamse Office: MHB (McIntosh Humanities Building) 207 985-5381 E-Mail: DABRAHAM@CSULB.EDU Office Hours: Thurs. 5-6:30 or by appointment Assigned
Benchmark C Describe the characteristics of feudal societies and the transition to the Renaissance and Reformation in Europe.
 Feudalism in Japan and Europe Connection: History Benchmark C Describe the characteristics of feudal societies and the transition to the Renaissance and Reformation in Europe. Indicator 3 Describe the
Feudalism in Japan and Europe Connection: History Benchmark C Describe the characteristics of feudal societies and the transition to the Renaissance and Reformation in Europe. Indicator 3 Describe the
(1) The Byzantine Empire. (2) The Rise of Russia. (3) Shaping Eastern Europe.
 Chapter 10 - The Byzantine Empire and Russia. (330-1613). (1) The Byzantine Empire. (2) The Rise of Russia. (3) Shaping Eastern Europe. Constantinople. Justinian. Kiev. Fall. Ivan. Romanov. becomes. Byzantine.
Chapter 10 - The Byzantine Empire and Russia. (330-1613). (1) The Byzantine Empire. (2) The Rise of Russia. (3) Shaping Eastern Europe. Constantinople. Justinian. Kiev. Fall. Ivan. Romanov. becomes. Byzantine.
The social structure of the Medieval world
 Medieval Society & Medieval Architecture The social structure of the Medieval world First order: Oratores, those who pray Second order: Bellatores, those who fight Third order: Laboratores, those who work
Medieval Society & Medieval Architecture The social structure of the Medieval world First order: Oratores, those who pray Second order: Bellatores, those who fight Third order: Laboratores, those who work
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies. Semester 1
 World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
Introduction. Byzantine Conquest - Justinian
 Introduction In 324 the Roman Emperor Constantine was very concerned about the barbarian invasions, which were literally at the gates of Rome. So Constantine moved the Empire s capital to a little known
Introduction In 324 the Roman Emperor Constantine was very concerned about the barbarian invasions, which were literally at the gates of Rome. So Constantine moved the Empire s capital to a little known
5- Why did the Shogun rule Japan?
 Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
Chapter 1. The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650
 Chapter 1 The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650 The Renaissance The Renaissance was a period of history that sought to join the middle ages to the modern times. This age grew into one of the most culturally
Chapter 1 The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650 The Renaissance The Renaissance was a period of history that sought to join the middle ages to the modern times. This age grew into one of the most culturally
The Sudanic African Empires: Ghana / Mali / Songhay & The Swahili City States of East Africa
 The Sudanic African Empires: Ghana / Mali / Songhay & The Swahili City States of East Africa AP World History Mr. Blankenship Ghana Mali Songhay Swahili States The Kingdom of Ghana emerged c. 5 th century
The Sudanic African Empires: Ghana / Mali / Songhay & The Swahili City States of East Africa AP World History Mr. Blankenship Ghana Mali Songhay Swahili States The Kingdom of Ghana emerged c. 5 th century
YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons)
 YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons) Contents Include: The United Kingdom and the Union Jack Kings and Queens The Magna Carta Charles I Parliament The Prime Minister Suggested Teacher Resources:
YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons) Contents Include: The United Kingdom and the Union Jack Kings and Queens The Magna Carta Charles I Parliament The Prime Minister Suggested Teacher Resources:
The failure of the Spanish Armada in 1588 permanently crippled the Spanish navy.
 AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
The Protestant Reformation
 The Protestant Reformation Mr. Montreuil April 2015 1 The Big Picture I can explain how the Protestant Reformation impacted Europe religiously, politically, & socially. This Lesson I can identify Reformation
The Protestant Reformation Mr. Montreuil April 2015 1 The Big Picture I can explain how the Protestant Reformation impacted Europe religiously, politically, & socially. This Lesson I can identify Reformation
The Roman Catholic Church had a large influence on life during the Middle Ages. It was the center of every village and town.
 Catholic Influence The Roman Catholic Church had a large influence on life during the Middle Ages. It was the center of every village and town. Daily Life To become a king, vassal, or knight you went through
Catholic Influence The Roman Catholic Church had a large influence on life during the Middle Ages. It was the center of every village and town. Daily Life To become a king, vassal, or knight you went through
Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government
 CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
Byzantium: Teacher s Guide
 Byzantium: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 9-12 Curriculum Focus: World History Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description Rome fell in 476, but the empire moved east and lasted another thousand
Byzantium: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 9-12 Curriculum Focus: World History Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description Rome fell in 476, but the empire moved east and lasted another thousand
AFRICAN KINGDOMS. Ghana. Around AD 800 the rulers of many farming villages united to create the kingdom of Ghana.
 AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
Reformation Lesson Plan. Central Historical Question: Why did Luther challenge the Catholic Church?
 Reformation Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Why did Luther challenge the Catholic Church? Materials: Reformation PowerPoint Copies of Documents A and B Copies of Reformation: Guiding Questions
Reformation Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Why did Luther challenge the Catholic Church? Materials: Reformation PowerPoint Copies of Documents A and B Copies of Reformation: Guiding Questions
World History Unit 4 Empires and Kingdoms: Growth and Expansion
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the World History Course. World History Unit 4
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the World History Course. World History Unit 4
Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline
 Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline 509 BCE: Tarquin the Proud, the last king of Rome, was overthrown by a group of patricians upset over his abuse of power. The Roman Republic was proclaimed. 494 BCE:
Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline 509 BCE: Tarquin the Proud, the last king of Rome, was overthrown by a group of patricians upset over his abuse of power. The Roman Republic was proclaimed. 494 BCE:
World History: The Byzantine Empire Lesson 6
 World History: The Byzantine Empire Lesson 6 Learning Objective: Students will review the impact and facts surrounding the Byzantine Empire through short chunks, chews, checks followed by a review graph.
World History: The Byzantine Empire Lesson 6 Learning Objective: Students will review the impact and facts surrounding the Byzantine Empire through short chunks, chews, checks followed by a review graph.
Middle Ages Research Project
 Assigned On: Wednesday, March 2 Due On: Friday, March 25 Middle Ages Research Project By Royal Proclamation of the 7 th Grade Court Hear ye, hear ye! Loyal citizens of Jeffersonshire! The Royal Court of
Assigned On: Wednesday, March 2 Due On: Friday, March 25 Middle Ages Research Project By Royal Proclamation of the 7 th Grade Court Hear ye, hear ye! Loyal citizens of Jeffersonshire! The Royal Court of
An Overview of Western Civilization
 The Six Major Periods of Western Civilization (BCE = BC; CE = AD) 1. Mesopotamia, Egypt, & Hebrews (3000-500 BCE) 2. Ancient Greece (1200-200 BCE) 3. Ancient Rome (753 BCE - 476 CE) -----------------------------------------------------------------
The Six Major Periods of Western Civilization (BCE = BC; CE = AD) 1. Mesopotamia, Egypt, & Hebrews (3000-500 BCE) 2. Ancient Greece (1200-200 BCE) 3. Ancient Rome (753 BCE - 476 CE) -----------------------------------------------------------------
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
Africa Before the Slave Trade
 Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social
 Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social results of the agricultural revolution? 3. What are the
Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social results of the agricultural revolution? 3. What are the
Note Taking Study Guide THE GREEK ROOTS OF DEMOCRACY
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide THE GREEK ROOTS OF DEMOCRACY Focus Question: What ideas arose in ancient Greece that contributed to the development of democratic values in the modern world? As you read
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide THE GREEK ROOTS OF DEMOCRACY Focus Question: What ideas arose in ancient Greece that contributed to the development of democratic values in the modern world? As you read
Ancient Rome Unit Plan Unit Overview Rationale Goals and Essential questions Objectives
 Ancient Rome Unit Plan Name: Laura Johnson Unit Overview This unit will focus on Ancient Rome, the rise of the Roman Republic, the transition of that republic to an empire, and the fall of that empire.
Ancient Rome Unit Plan Name: Laura Johnson Unit Overview This unit will focus on Ancient Rome, the rise of the Roman Republic, the transition of that republic to an empire, and the fall of that empire.
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao
 Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Jainism Jainism also began in India; religion teaches ahimsa nonviolence - Jains believe all living things have souls and should not be hurt
 Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
: INTRODUCTION TO EUROPEAN HISTORY
 Course Title Course Code : INTRODUCTION TO EUROPEAN HISTORY : HST114 Recommended Study Year* : Year 1 No. of Credits/Term : 3 Mode of Tuition Class Contact Hours Category in Major Prog. Prerequisites Co-requisites
Course Title Course Code : INTRODUCTION TO EUROPEAN HISTORY : HST114 Recommended Study Year* : Year 1 No. of Credits/Term : 3 Mode of Tuition Class Contact Hours Category in Major Prog. Prerequisites Co-requisites
Name Date CIVILIZATIONS IN CONFLICT: BYZANTIUM, ISLAM AND THE CRUSADES Vocabulary
 1 Vocabulary ANGLO SAXONS- The general name applied to the Germanic tribes (Angles, Saxons, Frisians and Jutes) that settled in England after the Romans departed. The Anglo Saxons dominated England from
1 Vocabulary ANGLO SAXONS- The general name applied to the Germanic tribes (Angles, Saxons, Frisians and Jutes) that settled in England after the Romans departed. The Anglo Saxons dominated England from
GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET 6 - PAGE 1 of 22. The BYZANTINE EMPIRE (divided into 3 parts) PART 1: The BYZANTINE EMPIRE - INFLUENCE ON RUSSIA
 GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET 6 - PAGE 1 of 22 The BYZANTINE EMPIRE (divided into 3 parts) PART 1: The BYZANTINE EMPIRE - INFLUENCE ON RUSSIA (The Byzantine Empire influenced the development of early [Kievian]
GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET 6 - PAGE 1 of 22 The BYZANTINE EMPIRE (divided into 3 parts) PART 1: The BYZANTINE EMPIRE - INFLUENCE ON RUSSIA (The Byzantine Empire influenced the development of early [Kievian]
Muhammad Became the Prophet of Islam monotheistic, hajj, The Five Pillars of Islam include all of the following except
 World History Chapter 11 The Muslim World (622 1650) Session 1 Rise of Islam How did Muhammad become the prophet of Islam? What are the teachings of Islam? How did Islam help shape the way of life of its
World History Chapter 11 The Muslim World (622 1650) Session 1 Rise of Islam How did Muhammad become the prophet of Islam? What are the teachings of Islam? How did Islam help shape the way of life of its
Virginia SOL Review and Assessment Coach Table of Contents
 Table of Contents About This Book...............................................................vii VA Page Title Virginia Standards of Learning 1 Identifying, Analyzing, and Interpreting Primary and Secondary
Table of Contents About This Book...............................................................vii VA Page Title Virginia Standards of Learning 1 Identifying, Analyzing, and Interpreting Primary and Secondary
The Xenophile Historian
 The Xenophile Historian Map Gallery Map 1: The spread of civilization in thousand-year steps. The purple areas became civilized by 3000 B.C. Civilization spread to the green areas by 2000 B.C., yellow
The Xenophile Historian Map Gallery Map 1: The spread of civilization in thousand-year steps. The purple areas became civilized by 3000 B.C. Civilization spread to the green areas by 2000 B.C., yellow
I N V E S T I C E D O R O Z V O J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á N Í ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES
 ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
Renaissance and Reformation Study Guide and Notebook Checklist. **Use your notes and pages 34-57 and 146-148. Answers in Italics
 Renaissance and Reformation Study Guide and Notebook Checklist **Use your notes and pages 34-57 and 146-148 Answers in Italics 1. What is the Renaissance Movement the rebirth of? Art and learning 2. Where
Renaissance and Reformation Study Guide and Notebook Checklist **Use your notes and pages 34-57 and 146-148 Answers in Italics 1. What is the Renaissance Movement the rebirth of? Art and learning 2. Where
Table of Contents. Part One: Social Studies Curriculum
 Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
Civilizations in Conflict: Byzantium, Islam, and the Crusades
 Civilizations in Conflict: Byzantium, Islam, and the Crusades catalog #2259 Teacher s Guide Video Produced by... Chariot Productions Teacher s Guide by... Joe Sitkp Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED
Civilizations in Conflict: Byzantium, Islam, and the Crusades catalog #2259 Teacher s Guide Video Produced by... Chariot Productions Teacher s Guide by... Joe Sitkp Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED
TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY
 The Story of the World TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY Volume 1: Ancient Times Peace Hill Press Charles City, Virginia www.peacehillpress.com How to Use These Tests and Answer Key These Tests and their accompanying
The Story of the World TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY Volume 1: Ancient Times Peace Hill Press Charles City, Virginia www.peacehillpress.com How to Use These Tests and Answer Key These Tests and their accompanying
Ghana: A West African Trading Empire
 Ghana: A West African Trading Empire The kingdom of Ghana lasted from 500 C.E. to the 11 th century C.E. The kingdom arose from the Sahel of Africa and spread to the valley between the Senegal and Niger
Ghana: A West African Trading Empire The kingdom of Ghana lasted from 500 C.E. to the 11 th century C.E. The kingdom arose from the Sahel of Africa and spread to the valley between the Senegal and Niger
The Rise and Spread of Islam Study Guide
 The Rise and Spread of Islam Study Guide Terms: Bedouins: Nomadic people of Arabia who eventually became Islamic. Ka aba: Place believed where Abraham had worshipped. When Mohammed prayed there with the
The Rise and Spread of Islam Study Guide Terms: Bedouins: Nomadic people of Arabia who eventually became Islamic. Ka aba: Place believed where Abraham had worshipped. When Mohammed prayed there with the
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the similarities in the methods that various absolute monarchs used in the 1600s and 1700s to consolidate and increase their power. 9 8 Points
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the similarities in the methods that various absolute monarchs used in the 1600s and 1700s to consolidate and increase their power. 9 8 Points
The Tudor Myth. and the Place of the Stage
 The Tudor Myth and the Place of the Stage Shakespeare s History Plays Two tetralogies (series of four plays): First Tetralogy (1590-93): Henry VI, parts 1,2 and 3 Richard III Second Tetralogy (1595-1599):
The Tudor Myth and the Place of the Stage Shakespeare s History Plays Two tetralogies (series of four plays): First Tetralogy (1590-93): Henry VI, parts 1,2 and 3 Richard III Second Tetralogy (1595-1599):
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE.
 SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
World History: Essential Questions
 World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
The French Revolution Begins Close Read
 The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
World History Part I (to 1500 C.E.)
 Second Semester World History Part I (to 1500 C.E.) Dates Topic/Content/Skill S.O.L. Notes Unit 1, Geography Skills and Definitions 1/28-2/10 Maps as a visual representation of WG.1c geographic information
Second Semester World History Part I (to 1500 C.E.) Dates Topic/Content/Skill S.O.L. Notes Unit 1, Geography Skills and Definitions 1/28-2/10 Maps as a visual representation of WG.1c geographic information
The Roles of Men and Women
 The Roles of Men and Women For your exam, you will need to be able to discuss the following: How and why the roles of men and women have changed in the last century; What the different Christian attitudes
The Roles of Men and Women For your exam, you will need to be able to discuss the following: How and why the roles of men and women have changed in the last century; What the different Christian attitudes
History programmes of study: key stage 3
 History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
A SHORT HISTORY OF CHURCH BUILDING
 A SHORT HISTORY OF CHURCH BUILDING From its beginning, a critical part of Christianity has been the gathering of people worshipping together. By virtue of this activity, the place where they worship has
A SHORT HISTORY OF CHURCH BUILDING From its beginning, a critical part of Christianity has been the gathering of people worshipping together. By virtue of this activity, the place where they worship has
REVIEW FOR UNIT 1. Mr. Thorburn
 REVIEW FOR UNIT 1 Mr. Thorburn Introduction Purpose of law in society Differences between rules and laws Rule of Law: elements of Rule of Law, Meaning of Due Process, Roncarelli vs. Duplessis Relationship
REVIEW FOR UNIT 1 Mr. Thorburn Introduction Purpose of law in society Differences between rules and laws Rule of Law: elements of Rule of Law, Meaning of Due Process, Roncarelli vs. Duplessis Relationship
Unit 7 The Spread of Religions
 Unit 7 The Spread of Religions Section 1 Unit Materials Questions To Consider Question 1. How did Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam spread across the world, and why are they practiced so far from their
Unit 7 The Spread of Religions Section 1 Unit Materials Questions To Consider Question 1. How did Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam spread across the world, and why are they practiced so far from their
eb.com/>. eastern Africa, history of. Encyclopaedia Britannica Online. May 27,
 Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Daily Life in Aksum Aksum was a powerful and wealthy ancient kingdom. Located in East Africa, it was very influential between A.D. 50 and 600. During this time, goods from all over the ancient world were
Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks
 Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
it existed after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. However, by the end of their empire, its
 1 The Byzantine Empire s diplomatic tradition served it well for most of the thousand years it existed after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. However, by the end of their empire, its allies and enemies
1 The Byzantine Empire s diplomatic tradition served it well for most of the thousand years it existed after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. However, by the end of their empire, its allies and enemies
Summarize how Portugal built a trading empire
 Objectives Summarize how Portugal built a trading empire in. Analyze the rise of Dutch and Spanish dominance in the region. Understand how the decline of Mughal India affected European traders in the region.
Objectives Summarize how Portugal built a trading empire in. Analyze the rise of Dutch and Spanish dominance in the region. Understand how the decline of Mughal India affected European traders in the region.
Human Heritage A World History 2006
 Academic Content Standards Social Studies Minnesota Arizona Human Heritage A World History 2006 STANDARDS Strand 2: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1. Construct charts, graphs,
Academic Content Standards Social Studies Minnesota Arizona Human Heritage A World History 2006 STANDARDS Strand 2: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1. Construct charts, graphs,
German initiated battle in western europe that attempted to push back the allied advance that was un. Sample letter requesting financial assistance
 German initiated battle in western europe that attempted to push back the allied advance that was un. Sample letter requesting financial assistance from employer. German initiated battle in western europe
German initiated battle in western europe that attempted to push back the allied advance that was un. Sample letter requesting financial assistance from employer. German initiated battle in western europe
7 th Grade Instructional Guide Model Lesson 4: The Effects of the Crusades
 7 th Grade Instructional Guide Model Lesson 4: The Effects of the Crusades Standard 7.6.6 Discuss the causes and course of the religious Crusades and their effects on the Christian, Muslim, and Jewish
7 th Grade Instructional Guide Model Lesson 4: The Effects of the Crusades Standard 7.6.6 Discuss the causes and course of the religious Crusades and their effects on the Christian, Muslim, and Jewish
The Mongols and their impact on China and Korea
 The Mongols and their impact on China and Korea Nov. 6, 2012 Review What is the relationship of religion and philosophy to social structure? How much social mobility was there in pre-modern Asia? What
The Mongols and their impact on China and Korea Nov. 6, 2012 Review What is the relationship of religion and philosophy to social structure? How much social mobility was there in pre-modern Asia? What
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON
 UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
 Penguin Readers Factsheets Teacher s Notes A History of Britain By Fiona Beddall Summary More than 2,000 years of times past are brought to life in this lively and interesting account of Britain s history.
Penguin Readers Factsheets Teacher s Notes A History of Britain By Fiona Beddall Summary More than 2,000 years of times past are brought to life in this lively and interesting account of Britain s history.
History of the Rule of Law
 History of the Rule of Law CONTEMPORARY FINE ART COLLECTION Since it opened in 1933, the Thomas J. Moyer Ohio Judicial Center has been home to numerous soaring and spectacular murals, and neoclassical,
History of the Rule of Law CONTEMPORARY FINE ART COLLECTION Since it opened in 1933, the Thomas J. Moyer Ohio Judicial Center has been home to numerous soaring and spectacular murals, and neoclassical,
Week 10: Chapter 9: Part 1: Terms
 Week 10: Chapter 9: Part 1: Terms Justinian - (483-565), called The Great, Byzantine emperor (527-65), who extended Byzantine rule in the West, beautified Constantinople (present-day İstanbul), and completed
Week 10: Chapter 9: Part 1: Terms Justinian - (483-565), called The Great, Byzantine emperor (527-65), who extended Byzantine rule in the West, beautified Constantinople (present-day İstanbul), and completed
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 15 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The first Aztecs were a. fishers from the west coast of Mexico. b. shepherds from the mountains
Chapter 15 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The first Aztecs were a. fishers from the west coast of Mexico. b. shepherds from the mountains
THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT
 THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT The political institutions of the United Kingdom are divided into the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. The last of these will be developed
THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT The political institutions of the United Kingdom are divided into the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. The last of these will be developed
My Magna Carta. an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds.
 My Magna Carta an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds. About the Competition The English-Speaking Union is delighted to present My Magna Carta an international creative writing
My Magna Carta an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds. About the Competition The English-Speaking Union is delighted to present My Magna Carta an international creative writing
Profile. Jerusalem University College
 Profile Jerusalem University College 6 Profile History Located on Mount Zion, adjacent to the southwest corner of the Old City wall, Jerusalem University College had its beginnings as the Institute of
Profile Jerusalem University College 6 Profile History Located on Mount Zion, adjacent to the southwest corner of the Old City wall, Jerusalem University College had its beginnings as the Institute of
40. To no one will we sell, to no one deny or delay right or justice
 THE RIGHT HONOURABLE THE LORD CHIEF JUSTICE Magna Carta 39. No free man shall be seized or imprisoned, or stripped of his rights or possessions, or outlawed or exiled, or deprived of his standing in any
THE RIGHT HONOURABLE THE LORD CHIEF JUSTICE Magna Carta 39. No free man shall be seized or imprisoned, or stripped of his rights or possessions, or outlawed or exiled, or deprived of his standing in any
Chapter 5 Test: Roman Rebublic/Empire
 Chapter 5 Test: Roman Rebublic/Empire Matching (1pt each) Match the terms to the descriptions. a. latifundia f. Virgil b. republic g. mercenaries c. Ptolemy h. legion d. heresy i. Augustine e. dictator
Chapter 5 Test: Roman Rebublic/Empire Matching (1pt each) Match the terms to the descriptions. a. latifundia f. Virgil b. republic g. mercenaries c. Ptolemy h. legion d. heresy i. Augustine e. dictator
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India?
 Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India? Unit X Quiz 2 1. When did the Suez Canal open? 2. Why was it initially difficult for European powers to control their
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India? Unit X Quiz 2 1. When did the Suez Canal open? 2. Why was it initially difficult for European powers to control their
Political/Military Events. Cultural/Religious Events
 Historical Timeline This timeline is limited to the major events that are directly related to the timeframe and the overall theme of the exhibition. Because the relationships between polytheistic religions,
Historical Timeline This timeline is limited to the major events that are directly related to the timeframe and the overall theme of the exhibition. Because the relationships between polytheistic religions,
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses
 Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
Advanced Placement Art History
 Advanced Placement Art History Syllabus Mr. Oram joram@dsdmail.net Textbooks: Gardner s Art Through the Ages Writing About Art by Sylvan Barnet On-line Resources: Art Study Online - The Book Companion
Advanced Placement Art History Syllabus Mr. Oram joram@dsdmail.net Textbooks: Gardner s Art Through the Ages Writing About Art by Sylvan Barnet On-line Resources: Art Study Online - The Book Companion
Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture
 Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture Ancient Greek Architecture The earliest buildings built in Greece in the New Stone Age are small houses or huts with wooden walls around them for protection. Later bigger
Ancient Greek Arts and Architecture Ancient Greek Architecture The earliest buildings built in Greece in the New Stone Age are small houses or huts with wooden walls around them for protection. Later bigger
Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform
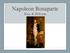 Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform Personal Life Born into a noble family on the French island of Corsica Quickly rose through the military, fighting for the Revolutionary army Supported the Jacobins Self-proclaimed
Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform Personal Life Born into a noble family on the French island of Corsica Quickly rose through the military, fighting for the Revolutionary army Supported the Jacobins Self-proclaimed
Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major.
 Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major. Note: if you take a History course that is cross listed and you take it under the
Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major. Note: if you take a History course that is cross listed and you take it under the
History. Bachelor of Arts Major in History. Objectives. Degree Offered. Major Offered. Minor Offered. International Studies.
 History 123 History Thomas W. Taylor, PhD, Chair Objectives Defying classification as either humanity or social science, history functions as both. It focuses on the values, as well as the ideas, personalities,
History 123 History Thomas W. Taylor, PhD, Chair Objectives Defying classification as either humanity or social science, history functions as both. It focuses on the values, as well as the ideas, personalities,
Ancient Ships of the Mediterranean
 Ancient Ships of the Mediterranean By: Brian Frantz Teacher: Mrs. ---- -------- Date Completed: February 5, 2001 Class: English Introduction There have been great discoveries of ancient artifacts in the
Ancient Ships of the Mediterranean By: Brian Frantz Teacher: Mrs. ---- -------- Date Completed: February 5, 2001 Class: English Introduction There have been great discoveries of ancient artifacts in the
Montezuma II. www.getworksheets.com
 Montezuma II Montezuma was the leader of the Aztecs, and he ruled from 1502 until 1520. He was born in 1480, and was trained to become a priest. He was born in Tenochtitlán, the capital of the Aztec Empire,
Montezuma II Montezuma was the leader of the Aztecs, and he ruled from 1502 until 1520. He was born in 1480, and was trained to become a priest. He was born in Tenochtitlán, the capital of the Aztec Empire,
THE EARLIEST KINGDOMS IN SOUTHERN AFRICA
 THE EARLIEST KINGDOMS IN SOUTHERN AFRICA Mapungubwe Read the following story of Mapungubwe: Arab traders were looking for gold. Chinese traders wanted ivory. Both ivory and gold were available on the plateau
THE EARLIEST KINGDOMS IN SOUTHERN AFRICA Mapungubwe Read the following story of Mapungubwe: Arab traders were looking for gold. Chinese traders wanted ivory. Both ivory and gold were available on the plateau
Name Class Date. Ancient China Section 4
 Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
