Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
|
|
|
- Russell Adams
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it do? 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study the body s only mitotic neurons. These neurons are the 4. What is Cranial Nerve II called, and what does it do? 5. What is Cranial Nerve III called, and what does 6. What is Cranial Nerve IV called, and what does 7. What is Cranial Nerve V called, and what does it do? 8. What hole does Cranial Nerve V pass through in the skull? There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves, numbered with Roman numerals. Make sure you know the NAME AND the Roman numerals! I Olfactory II Optic III Occulomotor IV Trochlear V Trigeminal VI Abducens VII Facial VIII Vestibulocochlear IX Glossopharyngeal X Vagus XI Accessory Nerve XII Hypoglossal OLFACTORY nerves Transmits the sense of smell. olfactory receptors II. OPTIC NERVE: Transmits visual information from the eye s retina. III Occulomotor Nerve: this controls most of the extrinsic muscles of the eye (that move the eyeball). They also have parasympathetic innervation in the iris (pupil) and cilliary (controls the lens). IV. Trochlear Nerve: supplies one of the extrinsic eye muscles V. Trigeminal Nerve: This is the main sensory nerve of the face. It has a large branch that passes through the foramen ovale of the skull. 9. Irritation of CN V is called what? Problems with CN-V are called TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA, which is excruciating pain in the face from nerve inflammation. 10. What is Cranial Nerve VI called, and what does VI: Abducens controls one of the eye muscles (lateral rectus). 11. What is Cranial Nerve VII called, and what does 12. A person who cannot blink or smile may have damage to what nerve? VII Facial Nerve: This innervates the muscles of facial expression and salivary glands. VII Facial Nerve
2 13. A person who cannot easily taste sweet, sour, or salty substances has damage to what nerve? 14. The primary gustatory (taste) cortex is located in which lobe of the brain? 15. Bell s Palsy is damage to what nerve? What other disorder does it look like? 16. What is Cranial Nerve VIII called, and what does 17. What is Cranial Nerve IX called, and what three things does A person who cannot easily taste sweet, sour, or salty substances has damage to what nerve? VII Facial Nerve Temporal lobe (in the insula) BELL S PALSY is damage of the facial nerve Needs to be distinguished from a stroke. VIII. VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR nerve transmits hearing and balance. IX: GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL signals the pharynx to constrict (along with X) during swallowing. Innervates top of tongue Carries information from baroreceptors 18. What is Cranial Nerve X called, and what four things does 19. Which cranial nerve travels into the abdomen? X Vagus Nerve 20. The majority of all parasympathetic fibers are X Vagus Nerve from what cranial nerve? 21. What is Cranial Nerve XI called, and what does 22. What is Cranial Nerve XII called, and what does X Vagus Nerve Parasympathetic supply to organs Moves the larynx during speech Signals pharynx to constrict during swallowing (with CN IX) Carries information from baroreceptors XI: ACCESSORY NERVE enters the skull through foramen magnum and leaves through the jugular foramen. It just supplies the shoulder muscles. XII. HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE (hypo=under; glossal=tongue) - supplies the under surface of the tongue. 23. What does damage to Cranial Nerve XII cause? Damage causes impairment of speech. 24. Where does spinal cord begin and end? FORAMEN MAGNUM. It goes to L1-2. In infants, it ends at L4-5, because it doesn t grow as fast as the rest of the body. 25. What is the spinal cord called beyond L1-2? CAUDA EQUINA ( Horse s tail ), which exit through the intervertebral foramina. 26. Where does the SACRAL PLEXUS exit the spinal cord? 27. What spinal nerve has a number that does not correspond to a vertebra? The SACRAL PLEXUS is made up of the spinal nerves exiting the spinal cord from the level of L4 to S5. There is a spinal nerve C8, although there is no C8 vertebrae.
3 28. CROSS SECTION OF THE SPINAL CORD CENTRAL CANAL, GREY MATTER, WHITE MATTER, POSTERIOR MEDIAN SULCUS, ANTERIOR MEDIAN FISSURE, DORSAL HORN, VENTRAL HORN, DORSAL ROOT, DORSAL ROOT GANGLION, VENTRAL ROOT, and SPINAL NERVE 29. Define a GANGLION (plural is ganglia) Ganglion = a group of neuron cell bodies. 30. Are they motor or sensory? Some are motor, some are sensory. 31. Are they in the CNS, PNS, or both? All ganglia are in the PNS only 32. Where are the cell bodies of the sensory neurons Posterior root ganglion of the spinal nerves located? 33. Most synapses are in what part of the nervous Most synapses are in the CNS system? 34. Define SENSORY NEURONS: 35. Where do they come in to the spinal cord? 36. Where is their cell body 37. Where do they synapse 38. What pathway do they take to the brain 39. In what part of the brain do they terminate? 40. Axons in the DORSAL COLUMN PATHWAY go to what part of the brain? SENSORY NEURONS come in through the posterior root, their cell body is in the posterior root ganglion, and its axon goes into the posterior horn and synapses in the grey matter. It also sends a branch to an area of the white matter called the DORSAL COLUMN PATHWAY, which goes into the brain (thalamus). Thalamus
4 Regarding LOWER MOTOR NEURONS: 41. Where is their cell body 42. Where does their axon exit the spinal cord 43. Where do they synapse LMN s have their cell body in the anterior horn (of the gray matter), and their axon goes out the anterior root, and synapses in a muscle. 44. Where are the cell bodies of interneurons? Their cell bodies are in the dorsal half of the gray matter in the spinal cord. 45. Where do interneurons synapse? on the cell body of the motor neuron 46. What is another name for interneurons? association neurons 47. The complexity of the CNS can be attributed to The complexity of the CNS can be attributed to what? Interneurons 48. Where is the site of neuronal integration? Grey matter 49. What is the correct path of a simple spinal Receptor, afferent neuron, integration center, efferent reflex? neuron, effector 50. What types of sensory information are conveyed Pain and temperature toward the brain in the spinothalamic tracts? 51. What region of the brain interprets signals for Somatosensory association area touch and temperature? 52. What are the 3 nerves that form a simple reflex Sensory, lower motor, and interneuron forms the arc? SIMPLE REFLEX ARC. 53. Example of a withdrawal reflex. 54. Simple reflex behavior involves how many If you touch a hot stove, the sensory input comes into the spinal cord, the association neurons send the information to the lower motor neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows it. Simple reflex behavior involves three nerves, and no
5 nerves? 55. Any brain involvement? 56. Are the automatic or voluntary events? brain involvement. Reflexes are automatic events. 57. Define reflexes: 58. Are they motor, sensory, or both 59. Are they fast or slow 60. Are they voluntary or involuntary 61. Do they involve one or multiple synapses 62. What is an example of a three-neuron reflex? KNEE-JERK REFLEX 63. How does a sensory signal get from a finger to the brain? 64. What is the difference between a nerve and a tract? 65. WHAT IS AN UPPER MOTOR NEURON? 66. What is a LOWER (SOMATIC) MOTOR NEURON? They involve both motor and sensory neurons, they are rapid, involuntary, and they involve multiple synapses. SENSORY TOUCH SPINAL NERVE POSTERIOR ROOT GANGLION POSTERIOR ROOT POSTERIOR HORN TRACT THALAMUS Inside the brain nerves are called tracts; outside the brain, they are called nerves (for example, optic and olfactory nerves are outside the CNS, while optic and olfactory tracts are inside the CNS) Upper motor neuron: cell body is in the brain, synapses on a lower motor neuron (in the spinal cord) Lower motor neuron: cell body is in the spinal cord, and synapses on skeletal muscle. Primary motor cortex 67. What region of the brain contains the upper motor neurons? 68. When the nerves leave the spinal cord, they a plexus. travel together in what? One of these is known as the brachial plexus (in the 69. Give one example armpit; innervates the muscles of the arm). 70. Starting at the spinal cord and preceding rami, trunks, divisions, cords laterally, the subdivisions of a plexus are in what order? 71. What do PROPRIOCEPTION neurons sense? the amount of force and movement in muscles and joints 72. What tract do they travel in? Proprioception nerves travel up the spinocerebellar tract. 73. An example of a test for proprioception is? Close eyes and touch finger to nose. 74. Symptoms of an upper motor neuron disease Cannot move extremity on their own (paralysis) but reflexes are present 75. Symptoms of a lower motor neuron disease Cannot move extremity on their own (paralysis) and reflexes are also not present 76. How many spinal nerves are there? 31 Pairs 77. What region of the spinal cord do spinal nerves exit? OUTSIDE of vertebral canal Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral 78. Are spinal nerves motor or sensory or both? They are motor and sensory
6 79. What do lower motor neurons do? Carry motor commands to the skeletal muscles
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Ventral Surface. The Cranial Nerves 4/5/2010. Review: Spinal Nerves
 The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
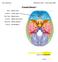 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Lu L m u b m a b r a rta T p a Figure 12.30
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
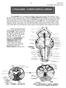 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises
 1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28
 The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Brain & Mind. Bicester Community College Science Department
 B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15
 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System 468 Comparison of the Autonomic and Somatic Motor Systems 468 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System 468 Comparison of the Autonomic and Somatic Motor Systems 468 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system
 Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Best Teaching Practices Conference. Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY. Class: X. TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System
 Best Teaching Practices Conference Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY Class: X TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System OBJECTIVES: Use Information Technology to enable the students to: Explain the general
Best Teaching Practices Conference Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY Class: X TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System OBJECTIVES: Use Information Technology to enable the students to: Explain the general
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab. Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Lecture One: Brain Basics
 Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
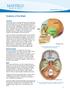 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Central control of the autonomic nervous system
 Central control of the autonomic nervous system John Morris Hypothalamus as an integrative centre regulating the ANS Involved in homeostasis stress responses anticipatory responses Sympathetic and para
Central control of the autonomic nervous system John Morris Hypothalamus as an integrative centre regulating the ANS Involved in homeostasis stress responses anticipatory responses Sympathetic and para
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES. On completion of this chapter, you will be able to:
 CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission
CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex
 Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System I. An Overview of Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System, p. 496 Figure 15-1 Specialized cells called sensory
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System I. An Overview of Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System, p. 496 Figure 15-1 Specialized cells called sensory
Cranial Nerves. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve
 Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Cranial Nerves CHAPTER 15 CLINICAL CASE
 CHAPTER 15 Cranial Nerves CLINICAL CASE OLFACTORY NERVE (CN I) OPTIC NERVE (CN II) OCULOMOTOR NERVE (CN III) TROCHLEAR NERVE (CN IV) TRIGEMINAL NERVE (CN V) ABDUCENT NERVE (CN VI) FACIAL NERVE (CN VII)
CHAPTER 15 Cranial Nerves CLINICAL CASE OLFACTORY NERVE (CN I) OPTIC NERVE (CN II) OCULOMOTOR NERVE (CN III) TROCHLEAR NERVE (CN IV) TRIGEMINAL NERVE (CN V) ABDUCENT NERVE (CN VI) FACIAL NERVE (CN VII)
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
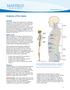 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Meninges of Cord. Spinal Roots and Nerve. 31 Pairs of Spinal Nerves. White Matter Columns 2/24/2014. Book Fig. 8.1. Book Fig. 8.3
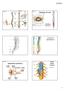 Book Fig. 8.3 Book Fig. 8.1 Meninges of Cord Filum terminale ------- strand connecting end of cord to coccyx to keep cord centered 31 Pairs of Spinal Nerves Book Fig. 8.7 Spinal Roots and Nerve White Matter
Book Fig. 8.3 Book Fig. 8.1 Meninges of Cord Filum terminale ------- strand connecting end of cord to coccyx to keep cord centered 31 Pairs of Spinal Nerves Book Fig. 8.7 Spinal Roots and Nerve White Matter
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION. Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology
 PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd.
 About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Exploring Creation with Advanced Biology ~ Schedule for 2015-2016 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Date:
 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Angela Wilkin May 2013
 Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential
 Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
