Chapter 3 Crystal Binding. Phys 175A Dr. Ray Kwok SJSU
|
|
|
- Rebecca Bailey
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 Crystal Binding Phys 175A Dr. Ray Kwok SJSU
2 4 basis categories
3 Molecular Bonds Introduction To understand the crystal binding, one should understand how molecules bind together The bonding mechanisms in a molecule are fundamentally due to electric forces The forces are related to a potential energy function A stable molecule would be expected at a configuration for which the potential energy function has its minimum value
4 Features of Molecular Bonds The force between atoms is repulsive at very small separation distances This repulsion is partially electrostatic and partially due to the exclusion principle Due to the exclusion principle, some electrons in overlapping shells are forced into higher energy states The energy of the system increases as if a repulsive force existed between the atoms The force between the atoms is attractive at larger distances (e.g. due to shifted charge distribution, induced dipole-dipole interaction)
5 Potential Energy Function The potential energy for a system of two atoms can be expressed in the form A B U( r ) = + n m r r r is the internuclear separation distance m and n are small integers (usually) A is associated with the attractive force B is associated with the repulsive force
6 Graph U(x) At large separations, the slope of the curve is positive Corresponds to a net attractive force (F = du/dr) At the equilibrium separation distance, the attractive and repulsive forces just balance At this point the potential energy is a minimum The slope is zero (F=0)
7 Molecular Bonds Types Simplified models of molecular bonding include Ionic Covalent van der Waals Hydrogen
8 Ionic Bonding Ionic bonding occurs when two atoms combine in such a way that one or more outer electrons are transferred from one atom to the other Ionic bonds are fundamentally caused by the Coulomb attraction between oppositely charged ions (e.g. Na + Cl )
9 Ionic Bonding, cont. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is called Ionization Energy. (Na + ) The amount of energy gained by adding an electron (from far away E=0) to an atom (E<0) is called the Electron Affinity of the atom. (Cl ) The Binding Energy (or Dissociation Energy) is the amount of energy needed to break the molecular bonds and produce neutral atoms
10 Ionic Bonding, NaCl Example The graph shows the total energy of the molecule vs the internuclear distance The minimum energy is at the equilibrium separation distance Binding energy = 4.2 ev
11 Ionic Bonding,final The energy of the molecule is lower than the energy of the system of two neutral atoms It is said that it is energetically favorable for the molecule to form The system of two atoms can reduce its energy by transferring energy out of the system and forming a molecule
12 Covalent Bonding A covalent bond between two atoms is one in which electrons supplied by either one or both atoms are shared by the two atoms Covalent bonds can be described in terms of atomic wave functions The example will be two hydrogen atoms forming H 2 (bonding energy 4.48 ev)
13 Covalent bonds Bonding can occur without outright removal or addition of an electron. In these types of bonds, the connection occurs through orbital overlap.
14 Wave Function Two Atoms Far Apart Each atom has a wave function (1s 1 ) 1 r ao ψ1 s( r ) = e πa There is little overlap between the wave functions of the two atoms when they are far away from each other 3 o
15 Wave Function Molecule The two atoms are brought close together The wave functions overlap and form the compound wave shown The probability amplitude is larger between the atoms than on either side
16 Covalent Bonding, Final The probability is higher that the electrons associated with the atoms will be located between them This can be modeled as if there were a fixed negative charge between the atoms, exerting attractive Coulomb forces on both nuclei The result is an overall attractive force between the atoms, resulting in the covalent bond
17 Van der Waals Bonding Two neutral molecules are attracted to each other by weak electrostatic forces called van der Waals forces (typically 0.1 ev) Atoms that do not form ionic or covalent bonds are also attracted to each other by van der Waals forces The van der Waals force is due to the fact that the molecule has a charge distribution with positive and negative centers at different positions in the molecule
18 Van der Waals Bonding, cont. As a result of this charge distribution, the molecule may act as an electric dipole Because of the dipole electric fields, two molecules can interact such that there is an attractive force between them Remember, this occurs even though the molecules are electrically neutral e.g. Liquid nitrogen molecules N 2
19 Types of Van der Waals Forces Dipole-dipole force An interaction between two molecules each having a permanent electric dipole moment Dipole-induced dipole force A polar molecule having a permanent dipole moment induces a dipole moment in a nonpolar molecule
20 Types of Van der Waals Forces, cont. Dispersion force An attractive force occurs between two nonpolar molecules The interaction results from the fact that, although the average dipole moment of a nonpolar molecule is zero, the average of the square of the dipole moment is nonzero because of charge fluctuations The two nonpolar molecules tend to have dipole moments that are correlated in time so as to produce van der Waals forces
21 Hydrogen Bonding In addition to covalent bonds, a hydrogen atom in a molecule can also form a hydrogen bond (weak 0.5 ev) Using water (H 2 O) as an example There are two covalent bonds in the molecule The electrons from the hydrogen atoms are more likely to be found near the oxygen atom than the hydrogen atoms
22 Hydrogen Bonding H 2 O cont. This leaves essentially bare protons at the positions of the hydrogen atoms The negative end of another molecule can come very close to the proton This bond is strong enough to form a solid crystalline structure
23 Hydrogen Bonding, Final The hydrogen bond is relatively weak compared with other electrical bonds Hydrogen bonding is a critical mechanism for the linking of biological molecules and polymers DNA is an example
24 Bonding in Solids Bonds in solids can be of the following types Ionic Covalent Metallic
25 Ionic Bonds in Solids The dominant interaction between ions is through the Coulomb force Many crystals are formed by ionic bonding (I-VII, II-VI) e.g. NaCl Ions are closed electronic shells. [e.g. LiF, Li (1s 2 2s) becomes Li + (1s 2 ), F (1s 2 2s 2 2p 5 ) becomes F (1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 )]
26 Electrostatic Energy The net effect of all the interactions is a negative electric potential energy U attractive = e αke r 2 α is a dimensionless number known as the Madelung constant The value of α depends only on the crystalline structure of the solid
27 Total Energy in a Crystalline Solid As the constituent ions of a crystal are brought close together, a repulsive force exists The potential energy term B/r m accounts for this repulsive force This repulsive force is a result of electrostatic forces and the exclusion principle
28 Total Energy in a Crystalline Solid, cont The total potential energy of the crystal is U 2 e = α k + r B r t o t a l e m The minimum value, U o, is called the ionic cohesive energy of the solid It represents the energy needed to separate the solid into a collection of isolated positive and negative ions
29 Ionic Bonds, NaCl Example The crystalline structure is shown (a) Each positive sodium ion is surrounded by six negative chlorine ions (b) Each chlorine ion is surrounded by six sodium ions (c)
30 Na-Cl Na ev Na + + e - (ionization energy = 5.14 ev) Cl + e - Cl ev (electron affinity = 3.61 ev) Na + + Cl NaCl ev (cohesive energy = 7.9 ev) i.e. the energy per molecule of NaCl is ( ) = 6.4 ev lower than the energy of separated neutral atoms.
31 More properties of Ionic Crystals They form relatively stable, hard crystals They are poor electrical conductors They contain no free electrons (filled shells) Each electron is bound tightly to one of the ions They have high melting points
32 Properties of Solids with Covalent Bonds Properties include Usually very hard Due to the large atomic cohesive energies High bond energies High melting points Good electrical conductors
33 More about Covalent Bonds Share electrons (usually 2 e - ) Directional (along orbital that share e - ) Electrons tend to localize between atoms Prefer anti-parallel spins (Pauli) Act as glue to atoms No clear cut range to be ionic or covalent
34 Cohesive Energies for Some Covalent Solids
35 Covalent Bond Example Diamond Each carbon atom in a diamond crystal is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms This forms a tetrahedral structure
36 Metallic Solids Metallic bonds are generally weaker than ionic or covalent bonds The outer electrons in the atoms of a metal are relatively free to move through the material (high mobility) The number of such mobile electrons in a metal is large (high carrier density) High electrical conductivity (& thermal)
37 Metallic Solids, cont. The metallic structure can be viewed as a sea or gas of nearly free electrons surrounding a lattice of positive ions The bonding mechanism is the attractive force between the entire collection of positive ions and the electron gas
38 Properties of Metallic Solids Light interacts strongly with the free electrons in metals Visible light is absorbed and re-emitted quite close to the surface (reflective) This accounts for the shiny nature of metal surfaces (screening, plasma frequency) High electrical conductivity More discussions on metal later.
Type of Chemical Bonds
 Type of Chemical Bonds Covalent bond Polar Covalent bond Ionic bond Hydrogen bond Metallic bond Van der Waals bonds. Covalent Bonds Covalent bond: bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared
Type of Chemical Bonds Covalent bond Polar Covalent bond Ionic bond Hydrogen bond Metallic bond Van der Waals bonds. Covalent Bonds Covalent bond: bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared
Crystalline solids. A solid crystal consists of different atoms arranged in a periodic structure.
 Crystalline solids A solid crystal consists of different atoms arranged in a periodic structure. Crystals can be formed via various bonding mechanisms: Ionic bonding Covalent bonding Metallic bonding Van
Crystalline solids A solid crystal consists of different atoms arranged in a periodic structure. Crystals can be formed via various bonding mechanisms: Ionic bonding Covalent bonding Metallic bonding Van
Section 3: Crystal Binding
 Physics 97 Interatomic forces Section 3: rystal Binding Solids are stable structures, and therefore there exist interactions holding atoms in a crystal together. For example a crystal of sodium chloride
Physics 97 Interatomic forces Section 3: rystal Binding Solids are stable structures, and therefore there exist interactions holding atoms in a crystal together. For example a crystal of sodium chloride
CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding
 CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding SECTION 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding OBJECTIVES 1. Define Chemical bond. 2. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonding.. 4. Explain
CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding SECTION 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding OBJECTIVES 1. Define Chemical bond. 2. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonding.. 4. Explain
Chapter 2. Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding
 Chapter 2. Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding Interatomic Bonding Bonding forces and energies Primary interatomic bonds Secondary bonding Molecules Bonding Forces and Energies Considering the interaction
Chapter 2. Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding Interatomic Bonding Bonding forces and energies Primary interatomic bonds Secondary bonding Molecules Bonding Forces and Energies Considering the interaction
H 2O gas: molecules are very far apart
 Non-Covalent Molecular Forces 2/27/06 3/1/06 How does this reaction occur: H 2 O (liquid) H 2 O (gas)? Add energy H 2O gas: molecules are very far apart H 2O liquid: bonding between molecules Use heat
Non-Covalent Molecular Forces 2/27/06 3/1/06 How does this reaction occur: H 2 O (liquid) H 2 O (gas)? Add energy H 2O gas: molecules are very far apart H 2O liquid: bonding between molecules Use heat
A pure covalent bond is an equal sharing of shared electron pair(s) in a bond. A polar covalent bond is an unequal sharing.
 CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW
 Answer the following questions. CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW 1. What are the three kinds of bonds which can form between atoms? The three types of Bonds are Covalent, Ionic and Metallic. Name Date Block 2.
Answer the following questions. CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW 1. What are the three kinds of bonds which can form between atoms? The three types of Bonds are Covalent, Ionic and Metallic. Name Date Block 2.
CHAPTER 10: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES: THE UNIQUENESS OF WATER Problems: 10.2, 10.6,10.15-10.33, 10.35-10.40, 10.56-10.60, 10.101-10.
 CHAPTER 10: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES: THE UNIQUENESS OF WATER Problems: 10.2, 10.6,10.15-10.33, 10.35-10.40, 10.56-10.60, 10.101-10.102 10.1 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN IONS Ion-ion Interactions and Lattice Energy
CHAPTER 10: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES: THE UNIQUENESS OF WATER Problems: 10.2, 10.6,10.15-10.33, 10.35-10.40, 10.56-10.60, 10.101-10.102 10.1 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN IONS Ion-ion Interactions and Lattice Energy
Which substance contains positive ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons? A) O2(s) B) Cu(s) C) CuO(s) D) SiO2(s)
 BONDING MIDTERM REVIEW 7546-1 - Page 1 1) Which substance contains positive ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons? A) O2(s) B) Cu(s) C) CuO(s) D) SiO2(s) 2) The bond between hydrogen and oxygen in
BONDING MIDTERM REVIEW 7546-1 - Page 1 1) Which substance contains positive ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons? A) O2(s) B) Cu(s) C) CuO(s) D) SiO2(s) 2) The bond between hydrogen and oxygen in
CHAPTER 6 REVIEW. Chemical Bonding. Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 Name Date lass APTER 6 REVIEW hemical Bonding SETIN 1 SRT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. a A chemical bond between atoms results from the attraction between the valence
Name Date lass APTER 6 REVIEW hemical Bonding SETIN 1 SRT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. a A chemical bond between atoms results from the attraction between the valence
A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together is called a(n)
 Chemistry I ATOMIC BONDING PRACTICE QUIZ Mr. Scott Select the best answer. 1) A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together is
Chemistry I ATOMIC BONDING PRACTICE QUIZ Mr. Scott Select the best answer. 1) A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together is
Modern Construction Materials Prof. Ravindra Gettu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Modern Construction Materials Prof. Ravindra Gettu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 2 Lecture - 2 Part 2 of 2 Review of Atomic Bonding II We will continue
Modern Construction Materials Prof. Ravindra Gettu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 2 Lecture - 2 Part 2 of 2 Review of Atomic Bonding II We will continue
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Section Activity #1: Fill out the following table for biology s most common elements assuming that each atom is neutrally charged.
 LS1a Fall 2014 Section Week #1 I. Valence Electrons and Bonding The number of valence (outer shell) electrons in an atom determines how many bonds it can form. Knowing the number of valence electrons present
LS1a Fall 2014 Section Week #1 I. Valence Electrons and Bonding The number of valence (outer shell) electrons in an atom determines how many bonds it can form. Knowing the number of valence electrons present
3/5/2014. iclicker Participation Question: A. MgS < AlP < NaCl B. MgS < NaCl < AlP C. NaCl < AlP < MgS D. NaCl < MgS < AlP
 Today: Ionic Bonding vs. Covalent Bonding Strengths of Covalent Bonds: Bond Energy Diagrams Bond Polarities: Nonpolar Covalent vs. Polar Covalent vs. Ionic Electronegativity Differences Dipole Moments
Today: Ionic Bonding vs. Covalent Bonding Strengths of Covalent Bonds: Bond Energy Diagrams Bond Polarities: Nonpolar Covalent vs. Polar Covalent vs. Ionic Electronegativity Differences Dipole Moments
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Javier E. Horta, M.D., Ph.D. University of Massachusetts Lowell Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Javier E. Horta, M.D., Ph.D. University of Massachusetts Lowell Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
In the box below, draw the Lewis electron-dot structure for the compound formed from magnesium and oxygen. [Include any charges or partial charges.
 Name: 1) Which molecule is nonpolar and has a symmetrical shape? A) NH3 B) H2O C) HCl D) CH4 7222-1 - Page 1 2) When ammonium chloride crystals are dissolved in water, the temperature of the water decreases.
Name: 1) Which molecule is nonpolar and has a symmetrical shape? A) NH3 B) H2O C) HCl D) CH4 7222-1 - Page 1 2) When ammonium chloride crystals are dissolved in water, the temperature of the water decreases.
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson
 Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Intermolecular forces- forces of attraction and repulsion between molecules that hold molecules, ions, and atoms together. Intramolecular - forces of chemical bonds within a molecule
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Intermolecular forces- forces of attraction and repulsion between molecules that hold molecules, ions, and atoms together. Intramolecular - forces of chemical bonds within a molecule
ANSWER KEY. Energy Levels, Electrons and IONIC Bonding It s all about the Give and Take!
 ANSWER KEY Energy Levels, Electrons and IONIC Bonding It s all about the Give and Take! From American Chemical Society Middle School Chemistry Unit: Chapter 4 Content Statements: Distinguish the difference
ANSWER KEY Energy Levels, Electrons and IONIC Bonding It s all about the Give and Take! From American Chemical Society Middle School Chemistry Unit: Chapter 4 Content Statements: Distinguish the difference
Chemistry 1050 Chapter 13 LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS 1. Exercises: 25, 27, 33, 39, 41, 43, 51, 53, 57, 61, 63, 67, 69, 71(a), 73, 75, 79
 Chemistry 1050 Chapter 13 LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS 1 Text: Petrucci, Harwood, Herring 8 th Edition Suggest text problems Review questions: 1, 5!11, 13!17, 19!23 Exercises: 25, 27, 33, 39, 41, 43, 51, 53, 57,
Chemistry 1050 Chapter 13 LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS 1 Text: Petrucci, Harwood, Herring 8 th Edition Suggest text problems Review questions: 1, 5!11, 13!17, 19!23 Exercises: 25, 27, 33, 39, 41, 43, 51, 53, 57,
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three types: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms Ionic Bonding
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three types: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms Ionic Bonding
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
Bonding Practice Problems
 NAME 1. When compared to H 2 S, H 2 O has a higher 8. Given the Lewis electron-dot diagram: boiling point because H 2 O contains stronger metallic bonds covalent bonds ionic bonds hydrogen bonds 2. Which
NAME 1. When compared to H 2 S, H 2 O has a higher 8. Given the Lewis electron-dot diagram: boiling point because H 2 O contains stronger metallic bonds covalent bonds ionic bonds hydrogen bonds 2. Which
KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER - molecules in matter are always in motion - speed of molecules is proportional to the temperature
 1 KINETIC TERY F MATTER - molecules in matter are always in motion - speed of molecules is proportional to the temperature TE STATES F MATTER 1. Gas a) ideal gas - molecules move freely - molecules have
1 KINETIC TERY F MATTER - molecules in matter are always in motion - speed of molecules is proportional to the temperature TE STATES F MATTER 1. Gas a) ideal gas - molecules move freely - molecules have
6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties
 324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
Bonding in Elements and Compounds. Covalent
 Bonding in Elements and Compounds Structure of solids, liquids and gases Types of bonding between atoms and molecules Ionic Covalent Metallic Many compounds between metals & nonmetals (salts), e.g. Na,
Bonding in Elements and Compounds Structure of solids, liquids and gases Types of bonding between atoms and molecules Ionic Covalent Metallic Many compounds between metals & nonmetals (salts), e.g. Na,
Lewis Dot Notation Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Polar Covalent Bonds Lewis Dot Notation Revisited Resonance
 Lewis Dot Notation Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Polar Covalent Bonds Lewis Dot Notation Revisited Resonance Lewis Dot notation is a way of describing the outer shell (also called the valence shell) of an
Lewis Dot Notation Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Polar Covalent Bonds Lewis Dot Notation Revisited Resonance Lewis Dot notation is a way of describing the outer shell (also called the valence shell) of an
Chapter Outline. Review of Atomic Structure Electrons, Protons, Neutrons, Quantum mechanics of atoms, Electron states, The Periodic Table
 Review of Atomic Structure Electrons, Protons, Neutrons, Quantum mechanics of atoms, Electron states, The Periodic Table Atomic Bonding in Solids Bonding Energies and Forces Periodic Table Chapter Outline
Review of Atomic Structure Electrons, Protons, Neutrons, Quantum mechanics of atoms, Electron states, The Periodic Table Atomic Bonding in Solids Bonding Energies and Forces Periodic Table Chapter Outline
Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
 Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Problems to try at end of chapter: Answers in Appendix I: 1,3,5,7b,9b,15,17,23,25,29,31,33,45,49,51,53,61 13.1 Properties of Liquids 1. Liquids take the shape of their container,
Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Problems to try at end of chapter: Answers in Appendix I: 1,3,5,7b,9b,15,17,23,25,29,31,33,45,49,51,53,61 13.1 Properties of Liquids 1. Liquids take the shape of their container,
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
Bonds. Bond Length. Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Bond Energy. Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Bonds hapter 8 Bonding: General oncepts Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Bond Energy Bond Length It is the energy required to break a bond. The distance where
Bonds hapter 8 Bonding: General oncepts Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Bond Energy Bond Length It is the energy required to break a bond. The distance where
POLAR COVALENT BONDS Ionic compounds form repeating. Covalent compounds form distinct. Consider adding to NaCl(s) vs. H 2 O(s):
 POLAR COVALENT BONDS Ionic compounds form repeating. Covalent compounds form distinct. Consider adding to NaCl(s) vs. H 2 O(s): Sometimes when atoms of two different elements form a bond by sharing an
POLAR COVALENT BONDS Ionic compounds form repeating. Covalent compounds form distinct. Consider adding to NaCl(s) vs. H 2 O(s): Sometimes when atoms of two different elements form a bond by sharing an
Intermolecular Forces
 Intermolecular Forces: Introduction Intermolecular Forces Forces between separate molecules and dissolved ions (not bonds) Van der Waals Forces 15% as strong as covalent or ionic bonds Chapter 11 Intermolecular
Intermolecular Forces: Introduction Intermolecular Forces Forces between separate molecules and dissolved ions (not bonds) Van der Waals Forces 15% as strong as covalent or ionic bonds Chapter 11 Intermolecular
Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces
 Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces Not quite the type of Force we re talking about Before we talk about noncovalent molecular forces, let s talk very briefly about covalent bonds. The Illustrated
Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces Not quite the type of Force we re talking about Before we talk about noncovalent molecular forces, let s talk very briefly about covalent bonds. The Illustrated
AS Chemistry Revision Notes Unit 1 Atomic Structure, Bonding And Periodicity
 AS Chemistry Revision Notes Unit Atomic Structure, Bonding And Periodicity Atomic Structure. All atoms have a mass number, A (the number of nucleons), and a proton number, Z (the number of protons). 2.
AS Chemistry Revision Notes Unit Atomic Structure, Bonding And Periodicity Atomic Structure. All atoms have a mass number, A (the number of nucleons), and a proton number, Z (the number of protons). 2.
Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding
 Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding 6.1 Organizing the Elements I. The Periodic Law A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements
Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding 6.1 Organizing the Elements I. The Periodic Law A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements
SHAPES OF MOLECULES (VSEPR MODEL)
 1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
Chapter 10 Liquids & Solids
 1 Chapter 10 Liquids & Solids * 10.1 Polar Covalent Bonds & Dipole Moments - van der Waals constant for water (a = 5.28 L 2 atm/mol 2 ) vs O 2 (a = 1.36 L 2 atm/mol 2 ) -- water is polar (draw diagram)
1 Chapter 10 Liquids & Solids * 10.1 Polar Covalent Bonds & Dipole Moments - van der Waals constant for water (a = 5.28 L 2 atm/mol 2 ) vs O 2 (a = 1.36 L 2 atm/mol 2 ) -- water is polar (draw diagram)
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134)
 Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134) 1. Helium atoms do not combine to form He 2 molecules, What is the strongest attractive
Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134) 1. Helium atoms do not combine to form He 2 molecules, What is the strongest attractive
ATOMS AND BONDS. Bonds
 ATOMS AND BONDS Atoms of elements are the simplest units of organization in the natural world. Atoms consist of protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (negative charge). The
ATOMS AND BONDS Atoms of elements are the simplest units of organization in the natural world. Atoms consist of protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (negative charge). The
Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond)
 Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond) Weak bonds are those forces of attraction that, in biological situations, do not take a large amount of energy to break. For example, hydrogen bonds are broken by energies
Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond) Weak bonds are those forces of attraction that, in biological situations, do not take a large amount of energy to break. For example, hydrogen bonds are broken by energies
Why? Intermolecular Forces. Intermolecular Forces. Chapter 12 IM Forces and Liquids. Covalent Bonding Forces for Comparison of Magnitude
 1 Why? Chapter 1 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids Why is water usually a liquid and not a gas? Why does liquid water boil at such a high temperature for such a small molecule? Why does ice float on water?
1 Why? Chapter 1 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids Why is water usually a liquid and not a gas? Why does liquid water boil at such a high temperature for such a small molecule? Why does ice float on water?
Unit 3: Quantum Theory, Periodicity and Chemical Bonding. Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry & Intermolecular Forces
 onour Chemistry Unit 3: Quantum Theory, Periodicity and Chemical Bonding Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry & Intermolecular orces 10.1: Molecular Geometry Molecular Structure: - the three-dimensional
onour Chemistry Unit 3: Quantum Theory, Periodicity and Chemical Bonding Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry & Intermolecular orces 10.1: Molecular Geometry Molecular Structure: - the three-dimensional
Question 4.2: Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements: Mg, Na, B, O, N, Br.
 Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories
Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories
Chapter 4: Structure and Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
 Chapter 4: Structure and Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds 4.1 Chemical Bonding o Chemical Bond - the force of attraction between any two atoms in a compound. o Interactions involving valence
Chapter 4: Structure and Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds 4.1 Chemical Bonding o Chemical Bond - the force of attraction between any two atoms in a compound. o Interactions involving valence
Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems
 Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems 1. What are the SI units for a. Wavelength of light b. frequency of light c. speed of light Meter hertz (s -1 ) m s -1 (m/s) 2. T/F (correct
Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems 1. What are the SI units for a. Wavelength of light b. frequency of light c. speed of light Meter hertz (s -1 ) m s -1 (m/s) 2. T/F (correct
The Properties of Water
 1 Matter & Energy: Properties of Water, ph, Chemical Reactions EVPP 110 Lecture GMU Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 The Properties of Water 3 Water - Its Properties and Its Role in the Fitness of Environment importance
1 Matter & Energy: Properties of Water, ph, Chemical Reactions EVPP 110 Lecture GMU Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 The Properties of Water 3 Water - Its Properties and Its Role in the Fitness of Environment importance
CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING Active Learning Questions: 3-9, 11-19, 21-22 End-of-Chapter Problems: 1-36, 41-59, 60(a,b), 61(b,d), 62(a,b), 64-77, 79-89, 92-101, 106-109, 112, 115-119 An American chemist
CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING Active Learning Questions: 3-9, 11-19, 21-22 End-of-Chapter Problems: 1-36, 41-59, 60(a,b), 61(b,d), 62(a,b), 64-77, 79-89, 92-101, 106-109, 112, 115-119 An American chemist
7.4. Using the Bohr Theory KNOW? Using the Bohr Theory to Describe Atoms and Ions
 7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
Molecular Geometry and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland Community College for the use of this experiment.
 Molecular and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland ommunity ollege for the use of this experiment. Objectives To construct molecular models for covalently bonded atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions
Molecular and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland ommunity ollege for the use of this experiment. Objectives To construct molecular models for covalently bonded atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions
4.5 Physical Properties: Solubility
 4.5 Physical Properties: Solubility When a solid, liquid or gaseous solute is placed in a solvent and it seems to disappear, mix or become part of the solvent, we say that it dissolved. The solute is said
4.5 Physical Properties: Solubility When a solid, liquid or gaseous solute is placed in a solvent and it seems to disappear, mix or become part of the solvent, we say that it dissolved. The solute is said
BOND TYPES: THE CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCES
 BOND TYPES: THE CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCES Every (pure) substance has a unique set of intrinsic properties which distinguishes it from all other substances. What inferences, if any can be made from a
BOND TYPES: THE CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCES Every (pure) substance has a unique set of intrinsic properties which distinguishes it from all other substances. What inferences, if any can be made from a
Laboratory 11: Molecular Compounds and Lewis Structures
 Introduction Laboratory 11: Molecular Compounds and Lewis Structures Molecular compounds are formed by sharing electrons between non-metal atoms. A useful theory for understanding the formation of molecular
Introduction Laboratory 11: Molecular Compounds and Lewis Structures Molecular compounds are formed by sharing electrons between non-metal atoms. A useful theory for understanding the formation of molecular
The strength of the interaction
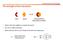 The strength of the interaction Host Guest Supramolecule (host-guest complex) When is the host capable to recognize the guest? How do we define selectivity Which element will we use to design the host
The strength of the interaction Host Guest Supramolecule (host-guest complex) When is the host capable to recognize the guest? How do we define selectivity Which element will we use to design the host
Objectives. PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics. Constituents of Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Basic Atomic Theory
 PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
Chapter 6 Assessment. Name: Class: Date: ID: A. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 6 Assessment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When an atom loses an electron, it forms a(n) a. anion. c.
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 6 Assessment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When an atom loses an electron, it forms a(n) a. anion. c.
Matter, Materials, Crystal Structure and Bonding. Chris J. Pickard
 Matter, Materials, Crystal Structure and Bonding Chris J. Pickard Why should a theorist care? Where the atoms are determines what they do Where the atoms can be determines what we can do Overview of Structure
Matter, Materials, Crystal Structure and Bonding Chris J. Pickard Why should a theorist care? Where the atoms are determines what they do Where the atoms can be determines what we can do Overview of Structure
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of the Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of the Chemical Bonding 1. There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol for a phosphorus atom. (a). 4, 2 (b). 2, 4 (c). 4, 3 (d). 2, 3 Explanation: Read the question
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of the Chemical Bonding 1. There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol for a phosphorus atom. (a). 4, 2 (b). 2, 4 (c). 4, 3 (d). 2, 3 Explanation: Read the question
100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals.
 2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
A REVIEW OF GENERAL CHEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES
 A REVIEW OF GENERAL CEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Draw Lewis (electron dot and line) structural formulas for simple compounds and ions from molecular
A REVIEW OF GENERAL CEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Draw Lewis (electron dot and line) structural formulas for simple compounds and ions from molecular
Molecular Models in Biology
 Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
VAPORIZATION IN MORE DETAIL. Energy needed to escape into gas phase GAS LIQUID. Kinetic energy. Average kinetic energy
 30 VAPORIZATION IN MORE DETAIL GAS Energy needed to escape into gas phase LIQUID Kinetic energy Average kinetic energy - For a molecule to move from the liquid phase to the gas phase, it must acquire enough
30 VAPORIZATION IN MORE DETAIL GAS Energy needed to escape into gas phase LIQUID Kinetic energy Average kinetic energy - For a molecule to move from the liquid phase to the gas phase, it must acquire enough
States of Matter CHAPTER 10 REVIEW SECTION 1. Name Date Class. Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
CHAPTER 10 REVIEW States of Matter SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Identify whether the descriptions below describe an ideal gas or a real gas. ideal gas
Name Block Date Ch 17 Atomic Nature of Matter Notes Mrs. Peck. atoms- the smallest particle of an element that can be identified with that element
 Name Block Date Ch 17 Atomic Nature of Matter Notes Mrs. Peck atoms- the smallest particle of an element that can be identified with that element are the building blocks of matter consists of protons and
Name Block Date Ch 17 Atomic Nature of Matter Notes Mrs. Peck atoms- the smallest particle of an element that can be identified with that element are the building blocks of matter consists of protons and
Elements in the periodic table are indicated by SYMBOLS. To the left of the symbol we find the atomic mass (A) at the upper corner, and the atomic num
 . ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
Chapter NP-1. Nuclear Physics. Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES
 Chapter NP-1 Nuclear Physics Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES 1.1 CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 2.0 COMPOSITION OF ATOMS 2.1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Chapter NP-1 Nuclear Physics Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES 1.1 CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 2.0 COMPOSITION OF ATOMS 2.1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Name: Class: Date: 3) The bond angles marked a, b, and c in the molecule below are about,, and, respectively.
 Name: Class: Date: Unit 9 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The basis of the VSEPR model of molecular bonding is. A) regions of
Name: Class: Date: Unit 9 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The basis of the VSEPR model of molecular bonding is. A) regions of
19.1 Bonding and Molecules
 Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
The Periodic Table: Periodic trends
 Unit 1 The Periodic Table: Periodic trends There are over one hundred different chemical elements. Some of these elements are familiar to you such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Each one has
Unit 1 The Periodic Table: Periodic trends There are over one hundred different chemical elements. Some of these elements are familiar to you such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Each one has
Self Assessment_Ochem I
 UTID: 2013 Objective Test Section Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct answer; please carefully bubble your choice on the scantron sheet.
UTID: 2013 Objective Test Section Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct answer; please carefully bubble your choice on the scantron sheet.
3 Atomic Structure 15
 3 Atomic Structure 15 3.1 Atoms You need to be familiar with the terms in italics The diameter of the nucleus is approximately 10-15 m and an atom 10-10 m. All matter consists of atoms. An atom can be
3 Atomic Structure 15 3.1 Atoms You need to be familiar with the terms in italics The diameter of the nucleus is approximately 10-15 m and an atom 10-10 m. All matter consists of atoms. An atom can be
PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes.
 1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
Test Bank - Chapter 4 Multiple Choice
 Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
 Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases 1 According to Brønsted and Lowry, an acid-base reaction is defined in terms of a proton transfer. By this definition, the reaction of Cl in water is: Cl(aq) + Cl (aq) +
Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases 1 According to Brønsted and Lowry, an acid-base reaction is defined in terms of a proton transfer. By this definition, the reaction of Cl in water is: Cl(aq) + Cl (aq) +
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Materials Molecules Atoms Atoms = protons (p) + neutrons (n) + electrons (e) Protons and neutrons are made of quarks Quantitative measurements need units:
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Materials Molecules Atoms Atoms = protons (p) + neutrons (n) + electrons (e) Protons and neutrons are made of quarks Quantitative measurements need units:
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Modified by Dr. Daniela R. Radu Why This Chapter? Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Modified by Dr. Daniela R. Radu Why This Chapter? Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER
 KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER The kinetic-molecular theory is based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion. The theory can be used to explain the properties of solids, liquids,
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER The kinetic-molecular theory is based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion. The theory can be used to explain the properties of solids, liquids,
Chapter 5 Student Reading
 Chapter 5 Student Reading THE POLARITY OF THE WATER MOLECULE Wonderful water Water is an amazing substance. We drink it, cook and wash with it, swim and play in it, and use it for lots of other purposes.
Chapter 5 Student Reading THE POLARITY OF THE WATER MOLECULE Wonderful water Water is an amazing substance. We drink it, cook and wash with it, swim and play in it, and use it for lots of other purposes.
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies
 Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the ionic compounds NaF, CsI, and CaO in order of increasing lattice energy. Analyze From the formulas for three
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the ionic compounds NaF, CsI, and CaO in order of increasing lattice energy. Analyze From the formulas for three
Chapter 4, Lesson 5: Energy Levels, Electrons, and Ionic Bonding
 Chapter 4, Lesson 5: Energy Levels, Electrons, and Ionic Bonding Key Concepts The attractions between the protons and electrons of atoms can cause an electron to move completely from one atom to the other.
Chapter 4, Lesson 5: Energy Levels, Electrons, and Ionic Bonding Key Concepts The attractions between the protons and electrons of atoms can cause an electron to move completely from one atom to the other.
(1) e.g. H hydrogen that has lost 1 electron c. anion - negatively charged atoms that gain electrons 16-2. (1) e.g. HCO 3 bicarbonate anion
 GS106 Chemical Bonds and Chemistry of Water c:wou:gs106:sp2002:chem.wpd I. Introduction A. Hierarchy of chemical substances 1. atoms of elements - smallest particles of matter with unique physical and
GS106 Chemical Bonds and Chemistry of Water c:wou:gs106:sp2002:chem.wpd I. Introduction A. Hierarchy of chemical substances 1. atoms of elements - smallest particles of matter with unique physical and
Explain the ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds and give one example for each type of bonds.
 Problem 1 Explain the ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds and give one example for each type of bonds. Ionic Bonds Two neutral atoms close to each can undergo an ionization process in order
Problem 1 Explain the ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds and give one example for each type of bonds. Ionic Bonds Two neutral atoms close to each can undergo an ionization process in order
We will not be doing these type of calculations however, if interested then can read on your own
 Chemical Bond Lattice Energies and Types of Ions Na (s) + 1/2Cl 2 (g) NaCl (s) ΔH= -411 kj/mol Energetically favored: lower energy Like a car rolling down a hill We will not be doing these type of calculations
Chemical Bond Lattice Energies and Types of Ions Na (s) + 1/2Cl 2 (g) NaCl (s) ΔH= -411 kj/mol Energetically favored: lower energy Like a car rolling down a hill We will not be doing these type of calculations
Name Class Date. What is ionic bonding? What happens to atoms that gain or lose electrons? What kinds of solids are formed from ionic bonds?
 CHAPTER 1 2 Ionic Bonds SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is ionic bonding? What happens to atoms that gain or lose
CHAPTER 1 2 Ionic Bonds SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is ionic bonding? What happens to atoms that gain or lose
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: States of Matter In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. The kinetic-molecular
Questions on Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Questions on Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Circle the Correct Answer: 1) Which ion below has a noble gas electron configuration? A) Li 2+ B) Be 2+ C) B2+ D) C2+ E) N 2-2) Of the ions below,
Questions on Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Circle the Correct Answer: 1) Which ion below has a noble gas electron configuration? A) Li 2+ B) Be 2+ C) B2+ D) C2+ E) N 2-2) Of the ions below,
The elements of the second row fulfill the octet rule by sharing eight electrons, thus acquiring the electronic configuration of neon, the noble gas o
 2. VALENT BNDING, TET RULE, PLARITY, AND BASI TYPES F FRMULAS LEARNING BJETIVES To introduce the basic principles of covalent bonding, different types of molecular representations, bond polarity and its
2. VALENT BNDING, TET RULE, PLARITY, AND BASI TYPES F FRMULAS LEARNING BJETIVES To introduce the basic principles of covalent bonding, different types of molecular representations, bond polarity and its
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING
 CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules
 5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules What you will accomplish in this experiment This experiment will give you an opportunity to draw Lewis structures of covalent compounds, then use those
5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules What you will accomplish in this experiment This experiment will give you an opportunity to draw Lewis structures of covalent compounds, then use those
Chemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1
 hemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1 ARB SKELETS arbon has a unique role in the cell because of its ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Thus carbon atoms can join to form chains.
hemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1 ARB SKELETS arbon has a unique role in the cell because of its ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Thus carbon atoms can join to form chains.
PROTONS AND ELECTRONS
 reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
chemrevise.org 19/08/2013 Periodicity N Goalby chemrevise.org
 chemrevise.org 19/8/213 eriodicity Goalby chemrevise.org locks An s-block element will always have an electronic structure where the outer electron is filling a s-sublevel. kewise the outer electron of
chemrevise.org 19/8/213 eriodicity Goalby chemrevise.org locks An s-block element will always have an electronic structure where the outer electron is filling a s-sublevel. kewise the outer electron of
Chapter 17. How are acids different from bases? Acid Physical properties. Base. Explaining the difference in properties of acids and bases
 Chapter 17 Acids and Bases How are acids different from bases? Acid Physical properties Base Physical properties Tastes sour Tastes bitter Feels slippery or slimy Chemical properties Chemical properties
Chapter 17 Acids and Bases How are acids different from bases? Acid Physical properties Base Physical properties Tastes sour Tastes bitter Feels slippery or slimy Chemical properties Chemical properties
UNIT 2 PRACTICE EXAM (Part 1: General Chemistry)
 UIT 2 PRACTICE EXAM (Part 1: General Chemistry) 1. Which would be the best definition of an ionic bond? a. The attraction between the partial positive region of one molecule and the partial negative region
UIT 2 PRACTICE EXAM (Part 1: General Chemistry) 1. Which would be the best definition of an ionic bond? a. The attraction between the partial positive region of one molecule and the partial negative region
Ionic and Metallic Bonding
 Ionic and Metallic Bonding BNDING AND INTERACTINS 71 Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 1, 3 5, 7 12, 14, 15, 18 20 Essential Understanding Ions form when atoms gain or lose
Ionic and Metallic Bonding BNDING AND INTERACTINS 71 Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 1, 3 5, 7 12, 14, 15, 18 20 Essential Understanding Ions form when atoms gain or lose
Paper 1 (7405/1): Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme
 AQA Qualifications A-level Chemistry Paper (7405/): Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme 7405 Specimen paper Version 0.5 MARK SCHEME A-level Chemistry Specimen paper 0. This question is marked
AQA Qualifications A-level Chemistry Paper (7405/): Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme 7405 Specimen paper Version 0.5 MARK SCHEME A-level Chemistry Specimen paper 0. This question is marked
Exercises Topic 2: Molecules
 hemistry for Biomedical Engineering. Exercises Topic 2 Authors: ors: Juan Baselga & María González Exercises Topic 2: Molecules 1. Using hybridization concepts and VSEPR model describe the molecular geometry
hemistry for Biomedical Engineering. Exercises Topic 2 Authors: ors: Juan Baselga & María González Exercises Topic 2: Molecules 1. Using hybridization concepts and VSEPR model describe the molecular geometry
