We use the cardinal points to establish direction. The principal cardinal points are north, south, east and west.
|
|
|
- Roy Robertson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT 1. THE REPRESENTATION OF THE EARTH. 1. How is the earth represented? Globes and maps The earth is spherical. However it is not a perfect sphere. It is slightly flattened at the poles..globes represent the earth accurately, because they have a similar shape, but they do not contain detailed information..maps are the most common representation of the earth. They provide detailed information. Establishing direction We use the cardinal points to establish direction. The principal cardinal points are north, south, east and west. Some elements in nature can help us. For example, the sun rises in the east and sets in the west, and the North Star always indicates north. A compass is an instrument with a magnetic needle which always points north. A compass helps us find our way in a forest, at sea or even in a city if we get lost.
2 2. What types of maps are there? Types of maps There are three types of maps:.physical maps give information on relief, and show mountains, rivers, etc..thematic maps give information on particular subjects: climate, vegetation, etc..political maps give information on countries, borders, etc. A) B)
3 Activities 1.Look at the maps above On which map can you identify? a. Countries b. Climates c. Capital cities and boundaries d. Seas Is map A physical, thematic or political? Is map B physical, thematic or political? 2.Now study map B more closely a. Symbols like colours, lines and points are used on maps. What symbols are used on this map? b. What does colour represent? c. Which are the coldest continents? d. In which continent is the biggest desert? e. Which continents have a Mediterranean climate? 3.Look for different types of thematic maps in your book What are they about? 3.How do we locate places on maps? Meridians and parallels A series of imaginary vertical and horizontal lines enables us to identify the exact location of Places on Earth.Meridians are semicircles which go from one pole to the other. The prime meridian (0º) (Greenwich meridian) is the point of reference for other meridians. It divides the Earth into two hemispheres: the western hemisphere and the eastern hemisphere.
4
5 .Parallels are circles which are perpendicular to the meridians. The Equator is the most important parallel and is the point of reference for the other parallels. It is at the same distance from both poles. It divides the Earth into two hemispheres: the northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere. The Equator divides the Earth into the Northern and southern hemispheres Other important parallels, from North to South, are:.the Arctic circle.the Tropic of Cancer.The Tropic of Capricorn.The Antarctic Circle Latitude and longitude
6 Latitude and longitude indicate geographical coordinates: the exact location of a place on the Earth. Latitude is measured by using the parallels which start at the Equator (0º). At the poles there are 90º. They are north (N) or south (S). Longitude is measured by using the meridians which start at the prime meridian (0º). They run vertically from 0º to 180º to the west (W), and 0º to 180º to the east (E). All locations on a line have the same longitude. The combination of latitude and longitude gives us the geographical coordinates of a place. The numbers on the right and left of the map indicate latitude The numbers at the top and bottom of the map indicate longitude Activity Identify the coordinates Look carefully at the lines of latitude and longitude. What are the coordinates of the three cities? Complete the table. City Latitude longitude Buenos Aires 38º S Oslo 10º E Beijing
7 4. How do we represent scale on a map? Scale Maps are reduced representations of reality. Scale indicates the difference between the size of something in the real world and its size on a map. Scale can be indicated in two different ways on a map:.numeric scale is expressed as a fraction. The numerator represents a unit on a map, for example, 1cm. The denominator represents its size in the real world. A scale of 1/20 means that 1 cm. on the map is equal to 20 cm. on the ground..graphic scale (bar scale) is a bar or line divided into equal segments, usually 1 cm. The numbers on the bar indicate the actual size which each segment represents.
8 Activity Plan a car trip through Spain beginning in Madrid. Measure the distances between the cities using the scale and a ruler. Then complete the table. Madrid-Sevilla Alicante-Valencia Zaragoza-Barcelona Zaragoza-Bilbao Barcelona-Sevilla Approximate distance in Kilometres
Grades 3-5. Benchmark A: Use map elements or coordinates to locate physical and human features of North America.
 Grades 3-5 Students use knowledge of geographic locations, patterns and processes to show the interrelationship between the physical environment and human activity, and to explain the interactions that
Grades 3-5 Students use knowledge of geographic locations, patterns and processes to show the interrelationship between the physical environment and human activity, and to explain the interactions that
The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT MIDDLE SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes NAME: CLASS VI SEC: ROLL NO: DATE:.04.2015 I NAME THE FOLLOWING: 1. A small spherical model of the Earth:
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT MIDDLE SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes NAME: CLASS VI SEC: ROLL NO: DATE:.04.2015 I NAME THE FOLLOWING: 1. A small spherical model of the Earth:
Solar Angles and Latitude
 Solar Angles and Latitude Objectives The student will understand that the sun is not directly overhead at noon in most latitudes. The student will research and discover the latitude ir classroom and calculate
Solar Angles and Latitude Objectives The student will understand that the sun is not directly overhead at noon in most latitudes. The student will research and discover the latitude ir classroom and calculate
World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+
 World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+ Activity Goal To use the global grid system of latitude and longitude to find specific locations on a world map. Materials Needed: A pencil, a ruler,
World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+ Activity Goal To use the global grid system of latitude and longitude to find specific locations on a world map. Materials Needed: A pencil, a ruler,
Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars
 Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars Vocabulary List Adult Education at Scienceworks Pre-visit Activity 1: What is longitude and latitude? Activity 2: Using the Southern Cross to find
Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars Vocabulary List Adult Education at Scienceworks Pre-visit Activity 1: What is longitude and latitude? Activity 2: Using the Southern Cross to find
Lines on Maps and Globes. Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4
 Lines on Maps and Globes Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4 Fourth Grade Social Studies Standard Map: Chart/Globe The learner will be able to use maps, charts, graphs, and globes
Lines on Maps and Globes Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4 Fourth Grade Social Studies Standard Map: Chart/Globe The learner will be able to use maps, charts, graphs, and globes
Week 1. Week 2. Week 3
 Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Stage 4. Geography. Blackline Masters. By Karen Devine
 1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
Coordinate Systems. Orbits and Rotation
 Coordinate Systems Orbits and Rotation Earth orbit. The earth s orbit around the sun is nearly circular but not quite. It s actually an ellipse whose average distance from the sun is one AU (150 million
Coordinate Systems Orbits and Rotation Earth orbit. The earth s orbit around the sun is nearly circular but not quite. It s actually an ellipse whose average distance from the sun is one AU (150 million
The Basics of Navigation
 The Basics of Navigation Knowledge of map reading and the use of the compass is an indispensable skill of bushcraft. Without this skill, a walker is a passenger and mere follower on a trip. To become a
The Basics of Navigation Knowledge of map reading and the use of the compass is an indispensable skill of bushcraft. Without this skill, a walker is a passenger and mere follower on a trip. To become a
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
Celestial Observations
 Celestial Observations Earth experiences two basic motions: Rotation West-to-East spinning of Earth on its axis (v rot = 1770 km/hr) (v rot Revolution orbit of Earth around the Sun (v orb = 108,000 km/hr)
Celestial Observations Earth experiences two basic motions: Rotation West-to-East spinning of Earth on its axis (v rot = 1770 km/hr) (v rot Revolution orbit of Earth around the Sun (v orb = 108,000 km/hr)
Sun Earth Relationships
 1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere tilts away from sun) 23.5 2 Solar radiation
1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere tilts away from sun) 23.5 2 Solar radiation
Geography I Pre Test #1
 Geography I Pre Test #1 1. The sun is a star in the galaxy. a) Orion b) Milky Way c) Proxima Centauri d) Alpha Centauri e) Betelgeuse 2. The response to earth's rotation is a) an equatorial bulge b) polar
Geography I Pre Test #1 1. The sun is a star in the galaxy. a) Orion b) Milky Way c) Proxima Centauri d) Alpha Centauri e) Betelgeuse 2. The response to earth's rotation is a) an equatorial bulge b) polar
compass Encyclopedic Entry
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
SOUTH AMERICA CONTENTS. What s in This Book... 2. Section 1: South America in the World... 3. Section 2: Political Divisions of South America...
 SOUTH CONTENTS What s in This Book 2 Section 1: 3 Section 2: Political Divisions of 1 Section 3: Physical Features of 41 Section 4: Valuable Resources of 67 Section : n Culture 89 Section 6: Assessment
SOUTH CONTENTS What s in This Book 2 Section 1: 3 Section 2: Political Divisions of 1 Section 3: Physical Features of 41 Section 4: Valuable Resources of 67 Section : n Culture 89 Section 6: Assessment
The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems. Long History of Mapping. The Earth is Flat. Long History of Mapping
 The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems Intro to Mapping & GIS The Earth is Flat Day to day, we live life in a flat world sun rises in east, sets in west sky is above, ground is below
The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems Intro to Mapping & GIS The Earth is Flat Day to day, we live life in a flat world sun rises in east, sets in west sky is above, ground is below
Earth-Sun Relationships. The Reasons for the Seasons
 Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
defined largely by regional variations in climate
 1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
Lines of Latitude and Longitude
 ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
Navigation: Latitude and Longitude
 Sextants and Chronometers Help Sailors Find Their Position at Sea Latitude lines run horizontally across the globe and are used to measure distances north and south of the equator. Sailors used a sextant
Sextants and Chronometers Help Sailors Find Their Position at Sea Latitude lines run horizontally across the globe and are used to measure distances north and south of the equator. Sailors used a sextant
Newton s Law of Gravity
 Gravitational Potential Energy On Earth, depends on: object s mass (m) strength of gravity (g) distance object could potentially fall Gravitational Potential Energy In space, an object or gas cloud has
Gravitational Potential Energy On Earth, depends on: object s mass (m) strength of gravity (g) distance object could potentially fall Gravitational Potential Energy In space, an object or gas cloud has
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
Tropical Horticulture: Lecture 2
 Lecture 2 Theory of the Tropics Earth & Solar Geometry, Celestial Mechanics The geometrical relationship between the earth and sun is responsible for the earth s climates. The two principal movements of
Lecture 2 Theory of the Tropics Earth & Solar Geometry, Celestial Mechanics The geometrical relationship between the earth and sun is responsible for the earth s climates. The two principal movements of
Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007
 Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007 1. In the illustration shown below what navigational features are represented by A, B, and C? Note that A is a critical city in defining
Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007 1. In the illustration shown below what navigational features are represented by A, B, and C? Note that A is a critical city in defining
Where on Earth are the daily solar altitudes higher and lower than Endicott?
 Where on Earth are the daily solar altitudes higher and lower than Endicott? In your notebooks, write RELATIONSHIPS between variables we tested CAUSE FIRST EFFECT SECOND EVIDENCE As you increase the time
Where on Earth are the daily solar altitudes higher and lower than Endicott? In your notebooks, write RELATIONSHIPS between variables we tested CAUSE FIRST EFFECT SECOND EVIDENCE As you increase the time
Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide
 Name: Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide There are three main sections to this module: terrestrial coordinates, celestial equatorial coordinates, and understanding how the ecliptic is related to
Name: Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide There are three main sections to this module: terrestrial coordinates, celestial equatorial coordinates, and understanding how the ecliptic is related to
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES
 6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation
 4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation 4.1 Details on Great Circles In fig. GN 4.1 two Great Circle/Rhumb Line cases are shown, one in each hemisphere. In each case the shorter distance between
4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation 4.1 Details on Great Circles In fig. GN 4.1 two Great Circle/Rhumb Line cases are shown, one in each hemisphere. In each case the shorter distance between
Chapter 19 Magnetic Forces and Fields
 Chapter 19 Magnetic Forces and Fields Student: 3. The magnetism of the Earth acts approximately as if it originates from a huge bar magnet within the Earth. Which of the following statements are true?
Chapter 19 Magnetic Forces and Fields Student: 3. The magnetism of the Earth acts approximately as if it originates from a huge bar magnet within the Earth. Which of the following statements are true?
OBJECTIVES. Identify the means by which latitude and longitude were created and the science upon which they are based.
 Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: isolines, gradient, topographic map, contour interval, hachured lines, profile, latitude, longitude, hydrosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, elevation, model EARTH
Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: isolines, gradient, topographic map, contour interval, hachured lines, profile, latitude, longitude, hydrosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, elevation, model EARTH
Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond
 Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
An Introduction to Coordinate Systems in South Africa
 An Introduction to Coordinate Systems in South Africa Centuries ago people believed that the earth was flat and notwithstanding that if this had been true it would have produced serious problems for mariners
An Introduction to Coordinate Systems in South Africa Centuries ago people believed that the earth was flat and notwithstanding that if this had been true it would have produced serious problems for mariners
Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems
 Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems How do we model the earth? Datums Datums mathematically describe the surface of the Earth. Accounts for mean sea level, topography, and gravity models. Projections
Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems How do we model the earth? Datums Datums mathematically describe the surface of the Earth. Accounts for mean sea level, topography, and gravity models. Projections
How do you find a place on a globe? How do you look up a place based on latitude and longitude?
 Why are globes tilted? Most Replogle globes are made to tilt at an angle of 23.5º to match the actual tilt of the earth in relationship to our sun. Incidentally, it is this tilting of the earth relative
Why are globes tilted? Most Replogle globes are made to tilt at an angle of 23.5º to match the actual tilt of the earth in relationship to our sun. Incidentally, it is this tilting of the earth relative
Noon Sun Angle = 90 Zenith Angle
 Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
Unit One Study Guide
 Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
IAntarcticaI. IArctic Ocean I. Where in the World? Arctic Ocean. Pacific Ocean. Pacific Ocean. Atlantic Ocean. North America.
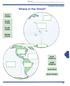 Name ------------------------------ Where in the World? Continents and s Arctic Pacific Pacific Atlantic.1.... 0" o ". North America South America Antarctica Arctic 261 Name Where in the World Continents
Name ------------------------------ Where in the World? Continents and s Arctic Pacific Pacific Atlantic.1.... 0" o ". North America South America Antarctica Arctic 261 Name Where in the World Continents
The following words and their definitions should be addressed before completion of the reading:
 Seasons Vocabulary: The following words and their definitions should be addressed before completion of the reading: sphere any round object that has a surface that is the same distance from its center
Seasons Vocabulary: The following words and their definitions should be addressed before completion of the reading: sphere any round object that has a surface that is the same distance from its center
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE?
 MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE? Grade Level: Kindergarten Presented by: Karen Davis and Tamara Young, Tate Elementary, Van Buren, AR Length of unit:5 lessons I. ABSTRACT A. This unit focuses
MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE? Grade Level: Kindergarten Presented by: Karen Davis and Tamara Young, Tate Elementary, Van Buren, AR Length of unit:5 lessons I. ABSTRACT A. This unit focuses
USING MAPS AND GLOBES
 USING MAPS AND GLOBES Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, Colorado Springs Charter Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately one week (five
USING MAPS AND GLOBES Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, Colorado Springs Charter Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately one week (five
Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon
 Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon Background: You can measure your latitude in earth's northern hemisphere by finding out the altitude of the celestial equator from the southern
Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon Background: You can measure your latitude in earth's northern hemisphere by finding out the altitude of the celestial equator from the southern
Which month has larger and smaller day time?
 ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector. Destination #3
 Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
CONTENTS. Page 3 What is orienteering? Page 4 Activity: orienteering map bingo. Page 5 Activity: know your colours. Page 6 Choosing your compass
 THE RIGHT DIRECTION SCOUT ORIENTEER ACTIVITY BADGE CONTENTS Page What is orienteering? Page 4 Activity: orienteering map bingo Page 5 Activity: know your colours Page 6 Choosing your compass Page 7 Activity:
THE RIGHT DIRECTION SCOUT ORIENTEER ACTIVITY BADGE CONTENTS Page What is orienteering? Page 4 Activity: orienteering map bingo Page 5 Activity: know your colours Page 6 Choosing your compass Page 7 Activity:
Searching Land Records thru the BLM General Land Office Records.
 Searching Land Records thru the BLM General Land Office Records. Land Records can be an exciting addition to your family history search. The United States Government transferred ownership of land to millions
Searching Land Records thru the BLM General Land Office Records. Land Records can be an exciting addition to your family history search. The United States Government transferred ownership of land to millions
Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons
 Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you
Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones
 Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS
 INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures. Seasons & Sun's Distance. Solstice & Equinox. Seasons & Solar Intensity
 Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Send all inquiries to: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 8787 Orion Place Columbus, Ohio 43240-4027 ISBN 0-07-824996-1. Printed in the United States of America
 Copyright by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to reproduce the material contained herein on the condition that such material be reproduced only for classroom use;
Copyright by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to reproduce the material contained herein on the condition that such material be reproduced only for classroom use;
UNIT I INTRODUCTION. This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
Solar energy and the Earth s seasons
 Solar energy and the Earth s seasons Name: Tilt of the Earth s axis and the seasons We now understand that the tilt of Earth s axis makes it possible for different parts of the Earth to experience different
Solar energy and the Earth s seasons Name: Tilt of the Earth s axis and the seasons We now understand that the tilt of Earth s axis makes it possible for different parts of the Earth to experience different
UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System
 Practical Cartographer s Reference #01 UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System 180 174w 168w 162w 156w 150w 144w 138w 132w 126w 120w 114w 108w 102w 96w 90w 84w 78w 72w 66w 60w 54w 48w 42w
Practical Cartographer s Reference #01 UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System 180 174w 168w 162w 156w 150w 144w 138w 132w 126w 120w 114w 108w 102w 96w 90w 84w 78w 72w 66w 60w 54w 48w 42w
Earth In Space Chapter 3
 Earth In Space Chapter 3 Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Earth casts a circular shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Ships were observed to disappear below the
Earth In Space Chapter 3 Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Earth casts a circular shadow on the moon during a lunar eclipse Shape of the Earth Ancient Greeks Ships were observed to disappear below the
Allows teachers to print reports for individual students or an entire class.
 Map and Globe Skills Developed by teachers and geography specialists, Map and Globe Skills provides the strategies, skills and practice your students need to develop a strong understanding of basic mapping
Map and Globe Skills Developed by teachers and geography specialists, Map and Globe Skills provides the strategies, skills and practice your students need to develop a strong understanding of basic mapping
Use WITH Investigation 4, Part 2, Step 2
 INVESTIGATION 4 : The Sundial Project Use WITH Investigation 4, Part 2, Step 2 EALR 4: Earth and Space Science Big Idea: Earth in Space (ES1) Projects: Tether Ball Pole Sundial Globe and a Light Indoors
INVESTIGATION 4 : The Sundial Project Use WITH Investigation 4, Part 2, Step 2 EALR 4: Earth and Space Science Big Idea: Earth in Space (ES1) Projects: Tether Ball Pole Sundial Globe and a Light Indoors
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum
 Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston
 Chapter 6: SOLAR GEOMETRY Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston SOLAR GEOMETRY AS A DETERMINING FACTOR OF HEAT GAIN, SHADING AND THE POTENTIAL OF DAYLIGHT PENETRATION...
Chapter 6: SOLAR GEOMETRY Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston SOLAR GEOMETRY AS A DETERMINING FACTOR OF HEAT GAIN, SHADING AND THE POTENTIAL OF DAYLIGHT PENETRATION...
Mapping Russia s vegetation zones
 Mapping Russia s vegetation zones biome is the name for a vegetation zone that can be mapped on a global scale, as shown below. Russia is such a large country that it contains several world biomes. In
Mapping Russia s vegetation zones biome is the name for a vegetation zone that can be mapped on a global scale, as shown below. Russia is such a large country that it contains several world biomes. In
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS THINGS
 CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
6. The greatest atmospheric pressure occurs in the 1) troposphere 3) mesosphere 2) stratosphere 4) thermosphere
 1. The best evidence of the Earth's nearly spherical shape is obtained through telescopic observations of other planets photographs of the Earth from an orbiting satellite observations of the Sun's altitude
1. The best evidence of the Earth's nearly spherical shape is obtained through telescopic observations of other planets photographs of the Earth from an orbiting satellite observations of the Sun's altitude
Where in the World is the arctic?
 Where in the World is the arctic? Summary: Students map the arctic in relation to their home in order to learn the location and countries of the arctic. Grade Level: 3-4; 5-8; K-2 Time one class period.
Where in the World is the arctic? Summary: Students map the arctic in relation to their home in order to learn the location and countries of the arctic. Grade Level: 3-4; 5-8; K-2 Time one class period.
Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions
 Chapter 2 Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions 2.1 Purpose The main goal of this lab is for you to gain an understanding of how the sky changes during the night and over the course of a year. We will
Chapter 2 Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions 2.1 Purpose The main goal of this lab is for you to gain an understanding of how the sky changes during the night and over the course of a year. We will
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense
 WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Wendy S. Hyndman, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Doreen W. Jennings, Lincoln
WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Wendy S. Hyndman, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Doreen W. Jennings, Lincoln
MULTI-LEVEL LESSON PLAN GUIDE Earth, Moon, and Beyond
 1 MULTI-LEVEL LESSON PLAN GUIDE Earth, Moon, and Beyond Jeni Gonzales e-mail: JeniLG7@aol.com SED 5600 Dr. Michael Peterson December 18, 2001 1 2 Unit Plan: Multi-level- Earth, Moon, and Beyond Theme:
1 MULTI-LEVEL LESSON PLAN GUIDE Earth, Moon, and Beyond Jeni Gonzales e-mail: JeniLG7@aol.com SED 5600 Dr. Michael Peterson December 18, 2001 1 2 Unit Plan: Multi-level- Earth, Moon, and Beyond Theme:
6. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows the average monthly temperature of two cities A and B.
 1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
1 213 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading C A vessel heading ENE is on a course of. A. 022.5 C. 067.5 B. 045.0 D. 090.0
 1 213 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading C A vessel heading ENE is on a course of. A. 022.5 C. 067.5 B. 045.0 D. 090.0 2 214 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading A A vessel heading ESE is on a course of. A. 112.5
1 213 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading C A vessel heading ENE is on a course of. A. 022.5 C. 067.5 B. 045.0 D. 090.0 2 214 Ref: Compass, Boxing, Heading A A vessel heading ESE is on a course of. A. 112.5
Vessels reporting duties on the NSR
 The Arctic 2030 Project: Feasibility and Reliability of Shipping on the Northern Sea Route and Modeling of an Arctic Marine Transportation & Logistics System 1-st Industry Seminar: NSR s Legislation, Tariff
The Arctic 2030 Project: Feasibility and Reliability of Shipping on the Northern Sea Route and Modeling of an Arctic Marine Transportation & Logistics System 1-st Industry Seminar: NSR s Legislation, Tariff
Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic
 Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic Summary: Students graph sea ice extent (area) in both polar regions (Arctic and Antarctic) over a three-year period to learn about seasonal variations
Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic Summary: Students graph sea ice extent (area) in both polar regions (Arctic and Antarctic) over a three-year period to learn about seasonal variations
Ch.1. Name: Class: Date: Matching
 Name: Class: Date: Ch.1 Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. technology e. democracy b. diffusion f. extended family c. exports g. interdependence d. climate 1. goods sent to markets
Name: Class: Date: Ch.1 Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. technology e. democracy b. diffusion f. extended family c. exports g. interdependence d. climate 1. goods sent to markets
BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY A UNIT OF STUDY. Includes Two Videos... 1. WATER AND LANDFORMS 2. CLIMATE AND NATURAL RESOURCES.
 BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY A UNIT OF STUDY Includes Two Videos... 1. WATER AND LANDFORMS 2. CLIMATE AND NATURAL RESOURCES Teacher's Guide Video Produced by VIDEO DIALOG, INC. Teacher's Guide and Blackline Master
BASICS OF GEOGRAPHY A UNIT OF STUDY Includes Two Videos... 1. WATER AND LANDFORMS 2. CLIMATE AND NATURAL RESOURCES Teacher's Guide Video Produced by VIDEO DIALOG, INC. Teacher's Guide and Blackline Master
Experiment 5: Magnetic Fields of a Bar Magnet and of the Earth
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 Experiment 5: Magnetic Fields of a Bar Magnet and of the Earth OBJECTIVES 1. To examine the magnetic field associated with a
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 Experiment 5: Magnetic Fields of a Bar Magnet and of the Earth OBJECTIVES 1. To examine the magnetic field associated with a
EARTH SCIENCES - TYPES OF MAPS TEACHER GUIDE
 EARTH SCIENCES - TYPES OF MAPS TEACHER GUIDE MATERIALS: Electronic Reader - Maps 5 different types of maps (see lab) inflatable globes local topographical map Objective: To understand the uses and importance
EARTH SCIENCES - TYPES OF MAPS TEACHER GUIDE MATERIALS: Electronic Reader - Maps 5 different types of maps (see lab) inflatable globes local topographical map Objective: To understand the uses and importance
Solar Heating Basics. 2007 Page 1. a lot on the shape, colour, and texture of the surrounding
 2007 Page 1 Solar Heating Basics Reflected radiation is solar energy received by collectorsfrom adjacent surfaces of the building or ground. It depends a lot on the shape, colour, and texture of the surrounding
2007 Page 1 Solar Heating Basics Reflected radiation is solar energy received by collectorsfrom adjacent surfaces of the building or ground. It depends a lot on the shape, colour, and texture of the surrounding
Chapter Overview. Seasons. Earth s Seasons. Distribution of Solar Energy. Solar Energy on Earth. CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Introduction to Geography
 High School Unit: 1 Lesson: 1 Suggested Duration: 3 days Introduction to Lesson Synopsis: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to geography and geography terminology, to teach students about
High School Unit: 1 Lesson: 1 Suggested Duration: 3 days Introduction to Lesson Synopsis: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to geography and geography terminology, to teach students about
The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual
 The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual 'What's the good of Mercator's North Poles and Equators, Tropics, Zones
The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual 'What's the good of Mercator's North Poles and Equators, Tropics, Zones
MGL Avionics. MapMaker 2. User guide
 MGL Avionics MapMaker 2 User guide General The MGL Avionics MapMaker application is used to convert digital map images into the raster map format suitable for MGL EFIS systems. Note: MapMaker2 produces
MGL Avionics MapMaker 2 User guide General The MGL Avionics MapMaker application is used to convert digital map images into the raster map format suitable for MGL EFIS systems. Note: MapMaker2 produces
CHAPTER 9 SURVEYING TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
 CHAPTER 9 SURVEYING TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS Surveying Terms 9-2 Standard Abbreviations 9-6 9-1 A) SURVEYING TERMS Accuracy - The degree of conformity with a standard, or the degree of perfection attained
CHAPTER 9 SURVEYING TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS Surveying Terms 9-2 Standard Abbreviations 9-6 9-1 A) SURVEYING TERMS Accuracy - The degree of conformity with a standard, or the degree of perfection attained
SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS
 SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: Geographic information systems and Map projections. Content that needs to be covered for examination
SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: Geographic information systems and Map projections. Content that needs to be covered for examination
Map reading made easy
 Map reading made easy What is a map? A map is simply a plan of the ground on paper. The plan is usually drawn as the land would be seen from directly above. A map will normally have the following features:
Map reading made easy What is a map? A map is simply a plan of the ground on paper. The plan is usually drawn as the land would be seen from directly above. A map will normally have the following features:
Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives
 Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives Standard 1: Citizenship characterize and good citizenship by building social networks of reciprocity and trustworthiness (Civic Dispositions).
Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives Standard 1: Citizenship characterize and good citizenship by building social networks of reciprocity and trustworthiness (Civic Dispositions).
11A Plate Tectonics. What is plate tectonics? Setting up. Materials
 11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY. Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in
 ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
Experiment P-17 Magnetic Field Strength
 1 Experiment P-17 Magnetic Field Strength Objectives To learn about basic properties of magnets. To study the relationship between magnetic field strength and the distance from the magnet. Modules and
1 Experiment P-17 Magnetic Field Strength Objectives To learn about basic properties of magnets. To study the relationship between magnetic field strength and the distance from the magnet. Modules and
STANDARD 3.1 Greece & Rome. STANDARD 3.2 - Mali
 2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
Follow That Hurricane!
 Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Shape Dictionary YR to Y6
 Shape Dictionary YR to Y6 Guidance Notes The terms in this dictionary are taken from the booklet Mathematical Vocabulary produced by the National Numeracy Strategy. Children need to understand and use
Shape Dictionary YR to Y6 Guidance Notes The terms in this dictionary are taken from the booklet Mathematical Vocabulary produced by the National Numeracy Strategy. Children need to understand and use
A Few Facts about Antarctica
 A Few Facts about Antarctica Antarctica is the continent that surrounds the South Pole, the southernmost point at the bottom of the earth. Antarctica is a continent because it is land that is covered by
A Few Facts about Antarctica Antarctica is the continent that surrounds the South Pole, the southernmost point at the bottom of the earth. Antarctica is a continent because it is land that is covered by
Stellar, solar, and lunar demonstrators
 Stellar, solar, and lunar demonstrators Rosa M. Ros, Francis Berthomieu International Astronomical Union, Technical University of Catalonia (Barcelona, España), CLEA (Nice, France) Summary This worksheet
Stellar, solar, and lunar demonstrators Rosa M. Ros, Francis Berthomieu International Astronomical Union, Technical University of Catalonia (Barcelona, España), CLEA (Nice, France) Summary This worksheet
ACTIVITY 1 Hemispheres of the World
 Name Date Class CTIVITY 1 s of the World Directions: Use your textbook to answer the questions below. 1. What line of latitude is used to divide the earth into Northern and Southern s? 2. What line of
Name Date Class CTIVITY 1 s of the World Directions: Use your textbook to answer the questions below. 1. What line of latitude is used to divide the earth into Northern and Southern s? 2. What line of
Motion & The Global Positioning System (GPS)
 Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
EPSG. Coordinate Reference System Definition - Recommended Practice. Guidance Note Number 5
 European Petroleum Survey Group EPSG Guidance Note Number 5 Coordinate Reference System Definition - Recommended Practice Revision history: Version Date Amendments 1.0 April 1997 First release. 1.1 June
European Petroleum Survey Group EPSG Guidance Note Number 5 Coordinate Reference System Definition - Recommended Practice Revision history: Version Date Amendments 1.0 April 1997 First release. 1.1 June
3D Drawing. Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces
 3D Drawing Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces The following document helps describe the basic process for generating a 3D representation of a simple 2D plan. For this exercise we will be
3D Drawing Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces The following document helps describe the basic process for generating a 3D representation of a simple 2D plan. For this exercise we will be
Geometry and Geography
 Geometry and Geography Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles March 12, 2011 1 Pedagogical Advice I have been leading mathematical circles using this topic for many years,
Geometry and Geography Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles March 12, 2011 1 Pedagogical Advice I have been leading mathematical circles using this topic for many years,
