Digestive System, Part 1
|
|
|
- Jerome Woods
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Objectives: Digestive System, Part 1 Discuss the general functions and anatomy of the digestive tract, including accessory structures. First, an overview of the tubular nature of the digestive system. Describe the individual organs of the system, including a discussion of the gross and microscopic anatomy. Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
2 Digestive System Overview AKA: Digestive Tract Alimentary Tract or Canal GI tract Gut Muscular, hollow tube, from the lips to the anus + Various accessory organs
3 Digestive System Overview The function of the system as a whole is processing food in such a way that nutrients can be absorbed and residues eliminated." Individual parts function in:! Ingestion Propulsion Mechanical digestion and segmentation Chemical and enzymatic digestion Secretion Absorption Compaction Excretion and elimination (defecation)
4 Membranes Peritoneum - generic serous membrane in abdominal cavity Parietal and Visceral Peritoneum Retroperitoneal vs. (intra)peritoneal" Mesenteries (p 669)- double sheets of peritoneum, surrounding and suspending portions of the digestive organs Greater omentum - "fatty apron", hangs anteriorly from stomach; double layer encloses fat Lesser omentum - between stomach and liver Mesentery proper - suspends and wraps the small intestine Mesocolon - suspends and wraps the colon, parts are transverse mesocolon sigmoid mesocolon Fig. 22.6!
5 General Organization
6 Structure of Small Intestinal Wall Plicae circulares circular pleats around the interior of the small intestine Villi minute finger-like projections, contain capillaries & lacteals Microvilli sub-microscopic size, projections on simple columnar cells Function of all three? Crypts at bottom of villi Cell regeneration (mitosis)" Glands mucus, enzymes" "
7 Smooth Muscle, a review One nucleus Nonstriated Actin and myosin present Slow, sustained contraction Communication Varicosities Gap junctions
8 Histological Organization Tube made up of four layers. 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa 4. Serosa = Visceral Peritoneum Modifications along its length as needed.
9 The 4 Layers of the Gut 1) Mucosa Epithelium - usually simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells; may be stratified squamous if protection needed, e.g., esophagus Lamina propria areolar connective tissue deep to epithelium Muscularis mucosae -produces folds - plicae (small intestine) or rugae (stomach) Fig 23.7!
10 The 4 Layers of the Gut 2) Submucosa made up of loose connective tissue contains submucosal plexus and blood vessels Fig 23.7!
11 The 4 Layers of the Gut 3) Muscularis externa smooth muscle, usually two layers (controlled by the myenteric plexus; source of peristalsis ) - inner layer: circular outer layer: longitudinal Fig 23.7!
12 The 4 Layers of the Gut 4) Serosa visceral layer of mesentery (contiguous with the peritoneum) or adventitia depending on location Fig 23.7!
13 Repetitio est mater studiorum
14 Oral Cavity AKA buccal cavity or mouth - lined with oral mucosa (type of epithelium?) Lips = labia Labial frenulum Hard and soft palates - form roof of mouth Tongue - skeletal muscle Lingual frenulum Salivary glands - three pairs Teeth Fauces = opening to pharynx
15 Types and Numbers of Teeth Dental succession" "Deciduous (1 o, baby, milk) teeth - 20, replaced by" "Permanent teeth - 32 teeth"
16 Structure of Teeth Crown - exposed surface of tooth Neck - boundary between root and crown Fig 23.14! Enamel - outer surface Dentin bone-like, but noncellular Pulp cavity - hollow with blood vessels and nerves Root canal - canal length of root Gingival sulcus - where gum and tooth meet Periodontal Ligament
17 Three pairs of Salivary Glands L / day for " digestion (?)" lubrication (swallowing) moistening (tasting)" Parotid lateral side of face, anterior to ear, drain by parotid duct to vestibule near 2nd upper molar Submandibular medial surface of mandible drain near lingual frenulum drain posterior to lower molars Sublingual in floor of mouth - drain near lingual frenulum
18 Mumps Swollen, painful parotid salivary glands (parotitis) on one or both sides of the face " Etiology: Mumps virus (Myxovirus)" Fever and sometimes orchitis, pancreatitis etc.! About 1/3 of infected people do not show symptoms" Effective vaccine (MMR) since 1967!
19 Esophagus Lined with noncornified stratified squamous epithelium Food boluses propelled by peristalsis of both skeletal and smooth muscle (gravity, too) Hiatus; lower esophageal sphincter GERD Hiatal hernia
20 Stomach Cardiac Sphincter (?)" Cardia" Fundus" Body" Pyloric antrum" Pylorus" Pyloric sphincter" Greater and Lesser Curvatures" Greater Omentum"
21 Stomach Rugae or Rugal Folds" Pylorus" Pyloric sphincter"
22 Circulation
23 Histology of Stomach Type of epithelium lining stomach? Gastric pits shallow pits, external half rapidly reproduces for replacement Gastric glands deep in lamina propria, 3 types of cells 1. Parietal cells (produce HCl and intrinsic factor B 12 ) 2. Chief cells (produce pepsinogen) 3. Enteroendocrine cells G cells (several hormones including gastrin which stimulates both parietal and chief cells)
24 Ulcers Mucosal erosion of stomach or duodenum GERD NSAIDs Helicobacter pylori Stress?? Dx by esophagogastroduodenoscopy Endoscopy video"
25 Review:
26
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE
 CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System
 General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
Digestive system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Oral cavity Alimentary Canal Accessory organs teeth salivary glands liver gall bladder pancreas appendix Components Functions Motility
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Oral cavity Alimentary Canal Accessory organs teeth salivary glands liver gall bladder pancreas appendix Components Functions Motility
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
26. Digestive System
 26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15
 Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
SEER Training Modules
 http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI)
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI) I. A tube traveling through the body
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI) I. A tube traveling through the body
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Digestive System Digestive Tract
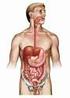 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Classifications of animals: ruminant vs non-ruminant carnivore: meat-eating herbivore: plant-eating omnivore: both meat and plant-eating
 Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes The Gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestive tract. Accessory organs. Digestive System Overview
 Digestive System Digestive System The process of chemically and physically breaking down foods into simpler forms that can be absorbed is called digestion. The digestive system can be divided into two
Digestive System Digestive System The process of chemically and physically breaking down foods into simpler forms that can be absorbed is called digestion. The digestive system can be divided into two
Functions of the digestive system
 Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Continuing Education Independent Study Series
 Continuing Education Independent Study Series Professional Development Manager Association of Surgical Technologists Englewood, Colorado Association of Surgical Technologists Publication made possible
Continuing Education Independent Study Series Professional Development Manager Association of Surgical Technologists Englewood, Colorado Association of Surgical Technologists Publication made possible
The Digestive System
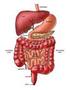 The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Small & Large Intestines
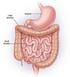 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14
 Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Overview of the Digestive System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46506 1 Overview of the Digestive System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46506 1 Overview of the Digestive System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
The Digestive System
 16 The Digestive System FOCUS: The function of the digestive system is to take in food, break it down into smaller compounds, and absorb those compounds so that the body can use them. This process provides
16 The Digestive System FOCUS: The function of the digestive system is to take in food, break it down into smaller compounds, and absorb those compounds so that the body can use them. This process provides
Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
II. General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
h. Large intestine 3
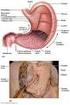
 (1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
(1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
Digestion. Processing of food Types. Mechanical (physical) Chemical. Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix. Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis
 Digestive System Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases Ingestion
Digestive System Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases Ingestion
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Study Guide Digestive System
 Study Guide Digestive System 1. Digestion is breakdown of complex food molecules like starch into smaller molecules like glucose that can pass through the cell membranes of intestine and get absorbed into
Study Guide Digestive System 1. Digestion is breakdown of complex food molecules like starch into smaller molecules like glucose that can pass through the cell membranes of intestine and get absorbed into
The Digestive System. - teeth, tongue, gall bladder, and glands (salivary glands, liver, pancreas).
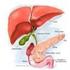 The Digestive System I. Overview A. Organs of the digestive system. 1. Alimentary canal (GI Tract): - continuous muscular tube, open at both ends. - digests food, absorbs digested fragments. 2. Accessory
The Digestive System I. Overview A. Organs of the digestive system. 1. Alimentary canal (GI Tract): - continuous muscular tube, open at both ends. - digests food, absorbs digested fragments. 2. Accessory
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Functions of Digestive System. The Digestive System. Digestive Processes. Anatomy. Digestive System. Melissa Gonzales McNeal 1. Layers of the GI tract
 The Digestive System Gastroenterology: study of digestive tract Heptologists study the liver General surgeons operate on most parts of the GI tract 1 Functions of Digestive System Protection Corrosive
The Digestive System Gastroenterology: study of digestive tract Heptologists study the liver General surgeons operate on most parts of the GI tract 1 Functions of Digestive System Protection Corrosive
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II Esophagus and Stomach. Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II Esophagus and Stomach Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine Learning Objectives 1. The esophagus is a typical hollow organ. 2. Know the histology of each of the layers
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II Esophagus and Stomach Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine Learning Objectives 1. The esophagus is a typical hollow organ. 2. Know the histology of each of the layers
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
PCB 4023 Cell Biology. Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs
 PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
The Digestive System. The organ system that processes food, extracts nutrients from it, and eliminates the residue.
 The Digestive System The organ system that processes food, extracts nutrients from it, and eliminates the residue. Digestive System The digestive system allows your body to obtain substances required to
The Digestive System The organ system that processes food, extracts nutrients from it, and eliminates the residue. Digestive System The digestive system allows your body to obtain substances required to
Lecture Notes on the Digestive System
 Lecture Notes on the Digestive System Function The function of the digestive system is to digest and absorb food. It consists of a tubular gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs that aid in digestion
Lecture Notes on the Digestive System Function The function of the digestive system is to digest and absorb food. It consists of a tubular gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs that aid in digestion
Digestive System. Part 4 Regulations and Maintenance
 Digestive System C H A P T E R Colorized SEM of the interior surface of the small intestine showing villi. 24 Every cell of the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the
Digestive System C H A P T E R Colorized SEM of the interior surface of the small intestine showing villi. 24 Every cell of the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
CH 23 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 CH 23 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This system is responsible for processing nutrients, which are required in order to produce energy and chemical building blocks via cellular respiration for cellular growth,
CH 23 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This system is responsible for processing nutrients, which are required in order to produce energy and chemical building blocks via cellular respiration for cellular growth,
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
Introduction. Digestive System. Physiology. Anatomy. Physiology. Alimentary Canal. Chapter 21
 Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Session 20. The Digestive Organs. Session Outline. Introduction. Unit 6 Digestive System
 Unit 6 Digestive System Session 20 The Digestive Organs Session Outline Introduction 20.1Alimentary tract 20.2 Mouth 20.3Tongue 20.4Teeth 20.5Oesophagus 20.6 Stomach 20.7Small intestine 20.8 large intestine
Unit 6 Digestive System Session 20 The Digestive Organs Session Outline Introduction 20.1Alimentary tract 20.2 Mouth 20.3Tongue 20.4Teeth 20.5Oesophagus 20.6 Stomach 20.7Small intestine 20.8 large intestine
Chapter 25. The Stomach Microscopic Anatomy and Gastric Function
 Chapter 25 The Stomach Microscopic Anatomy and Gastric Function Gross Anatomy of Stomach Diaphragm Lesser omentum Lesser curvature Pyloric region: Antrum Pyloric canal Pylorus Pyloric sphincter Fundic
Chapter 25 The Stomach Microscopic Anatomy and Gastric Function Gross Anatomy of Stomach Diaphragm Lesser omentum Lesser curvature Pyloric region: Antrum Pyloric canal Pylorus Pyloric sphincter Fundic
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Common features: - longitudinal tube through body - regional specializations along length - basic wall plan common to all vertebrate groups
 VERTEBRATE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Functions: - mechanical breakdown - big lumps of food to small - chemical breakdown - digestion monomers - absorption of monomers - compact waste feces, extract water eliminate
VERTEBRATE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Functions: - mechanical breakdown - big lumps of food to small - chemical breakdown - digestion monomers - absorption of monomers - compact waste feces, extract water eliminate
Chapter 24: The Digestive System. The Digestive System: An Overview, p. 863
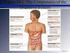 Chapter 24: The Digestive System The Digestive System: An Overview, p. 863 Objectives 1. Identify the organs of the digestive system and list their major functions. 2. Describe the functional histology
Chapter 24: The Digestive System The Digestive System: An Overview, p. 863 Objectives 1. Identify the organs of the digestive system and list their major functions. 2. Describe the functional histology
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
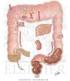 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Digestive System. Student Learning Objectives: Structures to be studied: Introduction
 Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion.
 CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
ii. Palatine tonsils - located between glossopalatine arch and pharyngopalatine arch iii. Function: guide food and air to laryngopharynx III.
 Digestive System I. Introduction I. Tube from mouth to anus, 30 ft. long II. Greatest portion below diaphragm III. Function: digestion and absorption II. Cross section through the coelom (body cavity)
Digestive System I. Introduction I. Tube from mouth to anus, 30 ft. long II. Greatest portion below diaphragm III. Function: digestion and absorption II. Cross section through the coelom (body cavity)
1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit
 Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
BIO 202 Digestive System Part I Overview and Mouth to Stomach
 1 BIO 202 Digestive System Part I Overview and Mouth to Stomach Function of the Digestive System Ingestion Taking food and water into the mouth Break down the food Mechanical digestion: chewing, mixing,
1 BIO 202 Digestive System Part I Overview and Mouth to Stomach Function of the Digestive System Ingestion Taking food and water into the mouth Break down the food Mechanical digestion: chewing, mixing,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
The Digestive System
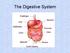 The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System 24-1
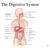 The Digestive System 24-1 Overview of GI tract Functions Mouth---bite, chew, swallow Pharynx and esophagus---- transport Stomach----mechanical disruption; absorption of water & alcohol Small intestine--chemical
The Digestive System 24-1 Overview of GI tract Functions Mouth---bite, chew, swallow Pharynx and esophagus---- transport Stomach----mechanical disruption; absorption of water & alcohol Small intestine--chemical
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
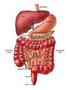 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
BILIOPANCREATIC DIVERSION WITH DUODENAL SWITCH SURGERY
 WITH DUODENAL SWITCH SURGERY Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Obesity. All decisions about surgical management of Obesity must be made in conjunction
WITH DUODENAL SWITCH SURGERY Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Obesity. All decisions about surgical management of Obesity must be made in conjunction
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Topography of the Mouth and Tooth Structure. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Topography of the Mouth and Tooth Structure. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Topography of the Mouth and Tooth Structure. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Introduction to Dental Anatomy
 Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
Anatomy of the Digestive System. The Digestive System. We need food for cellular utilization:
 The Digestive System We need food for cellular utilization:!nutrients as building blocks for synthesis!sugars, etc to break down for energy most food that we eat cannot be directly used by the body!too
The Digestive System We need food for cellular utilization:!nutrients as building blocks for synthesis!sugars, etc to break down for energy most food that we eat cannot be directly used by the body!too
Chapter 22: Digestive System
 Chapter 22: Digestive System Converts food into raw materials necessary for cell maintenance and growth Digestive System: Main Divisions of Digestive System: 1) Alimentary Canal (gastrointestinal tract)
Chapter 22: Digestive System Converts food into raw materials necessary for cell maintenance and growth Digestive System: Main Divisions of Digestive System: 1) Alimentary Canal (gastrointestinal tract)
Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems
 PMS /26/05 0:52 AM Page Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems Anthony McGrath INTRODUCTION The aim of this chapter is to increase the reader s understanding of the small and large bowel
PMS /26/05 0:52 AM Page Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems Anthony McGrath INTRODUCTION The aim of this chapter is to increase the reader s understanding of the small and large bowel
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
