SAP TESTING PLANT SAMPLING GUIDE
|
|
|
- Aileen Lane
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SAP TESTING PLANT SAMPLING GUIDE
2 Hortus Plant Sampling Guide This guide is intended to help ensure that the correct plant part and number of leaves required for a sap test are being collected and sent to our laboratory for testing. This will allow for faster, more accurate testing of your sample, which in turn leads to you receiving your recommendation in the shortest turnaround time. If you require further information please do not hesitate to call us on to speak to one of our friendly, knowledgeable staff.
3 Plant Sampling Select the correct leaf consult sampling guide. For young or small crops a larger sample will be required. Select an average representative area in the field for monitoring. Select average representative plants avoid diseased plants. Collect enough sample for 5ml sap consult manual for leaf numbers. Do not mix varieties in the sample as there may be some variation. Sample from 8am 3pm, but monitor the same time each week. Do not sample immediately after rain note heat or cold stresses. Note fertiliser and irrigation times and application rates if possible.
4 Handling and Transport Use plastic bags. Collect dry samples. Keep cool and dry (don t freeze or sit on dash in direct sun). Send via the fastest form of delivery to minimise time in transit. Apply Keep cool and dry stickers if available. Do not over pack compression will cause deterioration.
5 Analysis Request Form Please fill in all information on the Analysis Request Form (ARF). This can be done online by logging in using your unique user ID (your address and a password). Simply register online to set up your online profile. Please indicate what sort of recommendation you require on the ARF as this will also influence the price you are charged for your results. A detailed ARF gives us a complete understanding of the growing conditions of your crop and lets us know if you are concerned about specific problems or symptoms and allows us to address these in our recommendations. It also ensures we generate the appropriate optimal level for your particular situation. The ARF can be completed online at our preferred and easiest option. You can also download a single hardcopy form from our website or order a carbon copy booklet of 50 forms.
6 Asparagus Take stems from the top 20cm of the plant. Take at least 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at fern formation; and monitor monthly to mature fern stage.
7 Aster Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant, or out from the crown of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 70 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Send the whole leaves to the laboratory. Begin sampling at 10 leaf stage. Monitor fortnightly until flowering peak. 1st fully expanded leaf
8 Avocado First fully expanded leaf Take the first fully expanded leaves on the latest flush. Sample at least 60 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Begin sampling at fruit set, then monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are: early fruit set when fruit size is about 25 mm when fruit is 50mm when fruit reaches mature size
9 Baby beets Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf out from the crown of the plant. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The petiole and midrib of the leaf is required. 1st fully expanded leaf from growing point
10 Banana Take the first fully unrolled leaf out from the crown, and chop off about 25 cm of the midrib of the leaf, from where the leaf blade begins. At least 6 leaves required - the larger the sample the more representative it is of the whole block. If the sample is too bulky the midribs can be split longitudinally, and half discarded. (i.e. 12 half midribs is a better sample than 6 entire midribs, for the same volume.) Begin sampling when suckers are 2m high, and continue fortnightly or monthly as required. 30cm section of midrib from 1st unrolled leaf
11 Basil Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. Take at least 70 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and the midrib. Begin sampling at 5 true leaf stage. Sample weekly or fortnightly until harvest. First fully expanded leaf
12 Beans Petiole to send Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. The trifoliate leaf is formed of three smaller leaflets - BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaflets. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the leaflets can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded. Strip the leaf blades only, leaving the whole petiole and the three smaller offshoots. Beans begin sampling at 5 true leaf stage. Sample weekly or fortnightly to pod fill stage.
13 Brassicas 1st fully expanded leaf Take first fully expanded leaf out from the growing point of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take 20 to 30 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole (leaf stalk) and the midrib. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the midrib and discarded. Begin sampling at five leaf stage, continue to heading stage, weekly or fortnightly.
14 Capsicum Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant, or out from the crown of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Send the whole leaves to the laboratory. First fully expanded leaf Begin sampling at early budding. Monitor weekly or fortnightly until harvest. Sampling of long harvest crops can continue through harvest.
15 Carambola It is best to sample non-fruiting terminals. Take compound leaves that are almost fully expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 40 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Begin sampling at pre-flowering stage, monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage as below. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are - one month pre-flowering beginning of flowering early fruit set when fruit size is about 25 mm
16 Carnations Take first fully expanded leaf down from the growing point of the plant. The leaf to sample is usually the third or fourth leaf. Sample the leaf back to the node of the stem. The part sampled is the whole leaf and midrib. Take at least 80 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling when first new leaves reach mature stage. Sample fortnightly or monthly. Sample this leaf
17 Carrots, Turnips & Beets Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf out from the crown of the plant. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Whole leaves are required for carrots, and the midrib of beet, and parsnips etc. 1st fully expanded leaf from growing point Carrots: begin sampling at 5-6 leaf stage. Sample fortnightly or every three weeks to bulking up stage.
18 Celery Take the top three nodes from the stalk from the first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf out from the crown of the plant. Take at least 30 stalks, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at 5-6 leaf stage. Sample fortnightly or every three weeks to pre-harvest stage.
19 Chervil Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and the midrib. Begin sampling at 5 true leaf stage. Sample weekly or fortnightly until harvest.
20 Chives Send 20 whole plants after removing the roots. For larger plants cut the collar at the top end of the bulb, remove green leaves, and send the leaf blades. Most bulb crops can be sampled from the time of bulb formation to last fertigation.
21 Christmas Bush Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the third or fourth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaflets. Take at least leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the whole leaf and petiole. 1st fully expanded leaf Sampling should commence from the new flush in spring and continue monthly during the main growing season or while vegetative growth is being produced.
22 Chrysanthemum Take first fully expanded leaf down from the growing point of the plant. The leaf to sample is usually the fourth or fifth leaf down. The part sampled is the petiole and midrib. Take at least 70 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling when first new leaves reach mature stage. Sample fortnightly or monthly. Take the whole compound leaf
23 Citrus Sample non-fruiting terminals only. Take leaves that are about 3/4 expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 40 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are one month pre-flowering beginning of flowering early fruit set when fruit size is about 25 mm Monitoring program 1st mature leaf of current flush Begin sampling at pre-flowering stage, monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage.
24 Coffee Take the first fully expanded leaves on the latest flush. Sample at least 40 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Begin sampling at fruit set, then monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage. First fully expanded leaf
25 Coriander Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and the midrib. Begin sampling at 5 true leaf stage. Sample weekly or fortnightly until harvest.
26 Corn Select the first leaf with a visible dewlap. Select the thickest stalk in each stool. Take at least leaves per sample, selected randomly through the sampling area. Avoid distorted of stunted plants Send whole leaves from young plants, but remove the leaf tips to leave 30 cm of leaf when sampling more mature plants. Sampling can begin from about 30 cm high (V5). Sample fortnightly or as required, depending on fertigation frequency. If necessary, seedlings (V1-V4) can be sampled by sending 30 whole plants.
27 Cotton Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded. Send the petioles or leaf stalks to the Lab. Sampling times for cotton are: squaring 2-3 weeks later, late flowering 2-3 weeks later, late boll set/early boll fill 2-3 weeks later, mid-late boll fill late boll fill
28 Cucumber 1st fully expanded leaf Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the runner, or out from the crown of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the block. Up to 50 leaves may be required if petioles are very small. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded.
29 Custard Apple It is best to sample non-fruiting terminals. Take leaves that are about 3/4 expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 40 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Usual sampling times for are: one month pre-flowering beginning of flowering early fruit set when fruit size is about 25 mm when fruit size is about 75 mm
30 Eggplant First fully expanded leaf Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant, or out from the crown of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the block. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and the midrib of the leaf. Begin sampling at budding, continue weekly or fortnightly until harvest. May continue sampling during harvest.
31 Fennel Take the top 20cm of the plant. Take at least 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at budding; and monitor fortnightly to mid-harvest.
32 Gerberas Take first fully expanded leaf out from the crown of the plant. This will be the leaf that is almost fully expanded and starting to change colour to a darker green. The part sampled is the petiole and midrib. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling when first new leaves reach mature stage. Sample fortnightly or monthly. Sample this leaf
33 Grapes Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the runner. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE PETIOLE. Take at least 60 leaves, randomly across the block and increase number if petioles are small. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the leaves of grapes and discarded. Begin sampling when canes are 30 cm long. Continue weekly or fortnightly to harvest. Strategic sampling times are 30 cm canes, early flowering, early fruit set, fruit fill, pre-harvest, and postharvest.
34 Industrial Hemp Select the youngest fully expanded leaf back from the growing point BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaflets. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the leaflets can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded. Begin sampling at 30cm in height. Sample fortnightly to flowering stage. 1st fully expanded leaf
35 Kangaroo Paw Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the second or third leaf out from the growing point of the plant, or out from the crown of the plant. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Send the entire leaves to the laboratory. Begin sampling when first able to sample appropriate part. Monitor monthly until flowering. 1st fully expanded leaf
36 Kiwi Fruit Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the runner. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the block. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and midrib. Begin sampling when vines reach 1 m and sample monthly until midharvest.
37 Lemon Grass Take the first fully expanded leaf. The part to be tested is the midrib of the leaves. Send leaves from across the sampling area.
38 Lettuce & Cabbage Take wrapper leaf, close to head maturity. Take at least 15 leaves, randomly across the block. The part to be tested is the midrib of the leaf. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the midrib and discarded. Begin sampling at 3-4 weeks and sample weekly or fortnightly until two weeks before harvest.
39 Loquats Sample non-fruiting terminals only. Take leaves that are almost fully expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 50 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Begin sampling at early fruit set, then monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are - one month pre-flowering beginning of flowering early fruit set at fruit fill stage
40 Lucerne Take the top 20cm of the plant. Take at least 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at budding; and monitor fortnightly to mid-harvest.
41 Lychee Sample non-fruiting terminals only. Take leaves that are almost fully expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 200 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Begin sampling at pre-flowering stage, monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage as below. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are - one month pre-flowering beginning of flowering early fruit set when fruit size is about 25 mm
42 Macadamia First fully expanded leaf Take the first fully expanded leaves on the latest flush. Sample at least 200 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Begin sampling at fruit set, then monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are - early fruit set when fruit size is about 25 mm when fruit is 50mm when fruit reaches mature size
43 Mango 1st fully expanded leaf Sample non-fruiting terminals only. Take leaves that are about 3/4 expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 70 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Begin sampling at early fruit set, then monthly to harvest, or sample by crop stage. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are - one month pre-flowering beginning of flowering early fruit set when fruit size is about 25 mm at fruit fill stage
44 Mint Take the top 20cm of the plant. Take at least 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at budding; and monitor fortnightly to midharvest.
45 Olives Sample non-fruiting terminals only. Take leaves that are fully expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 70 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Monitoring program Begin sampling when first leaves of new flush reach maturity. Sample fortnightly or monthly to peak harvest. 1st fully expanded leaf
46 Onions, Garlic & Leek For spring onions and young onions, send 20 whole plants after removing the leaf tips and roots. Be sure to include the collar at the base of the leaf, as this is the part to be tested. For larger plants cut the collar at the top end of the bulb, remove green leaves, and send the collars collars is enough. Most bulb crops can be sampled from the time of bulb formation to last fertigation.
47 Parsley Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and the midrib. Begin sampling at 5 true leaf stage. Sample weekly or fortnightly until harvest.
48 Passionfruit Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the runner. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 70 leaves, randomly across the block. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and midrib. Begin sampling when vines reach 1 m and sample monthly until midharvest. 1st fully expanded leaf
49 Paw Paw Take the youngest fully expanded leaf out from the crown, and remove the petiole. At least 10 petioles required. Petioles should be approximately 25 cm long. Leaf blades can be removed before dispatching sample. Sample from budding, monthly to harvest. Petiole of first fully expanded leaf
50 Peanut Take the first fully expanded leaf from the growing tip of the plant. The trifoliate leaf is formed of three smaller leaflets BE SURE TO TAKE THE WHOLE LEAF AND PETIOLE, not just the leaflets. Take at least 50 leaves randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching the leaflets can be stripped off and discarded. Strip the leaf blades only leaving the petiole and the three smaller offshoots. Begin sampling when the first new leaves reach the mature stage. Sample every 2-4 weeks until the plants start to shut down. Important times are pre-flowering, pegging and nut sizing.
51 Peas & Snow Peas Take the top 20cm of the plant. Take at least 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at budding; and monitor fortnightly to midharvest.
52 Pistachio Nuts Sample non-fruiting terminals only. Take leaves that are fully expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 50 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Monitoring program Begin sampling when first leaves of new flush reach maturity. Sample fortnightly or monthly to peak harvest. 1st fully expanded leaf
53 Potato First fully expanded leaf Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. The compound leaf is formed of several/ many smaller leaflets - BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaflets. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. In potatoes, this should be from 15 to 30 cm long, depending on the stage of the crop. For ease of dispatching, the leaflets can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded. Begin sampling at 4-5 leaf stage. Sample fortnightly to bulking up stage.
54 Rhubarb Take the stalk from the first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf out from the crown of the plant. Take at least 30 stalks, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at 5-6 leaf stage. Sample fortnightly or every three weeks to "preharvest" stage.
55 Rocket Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk and the midrib. Begin sampling at 5 true leaf stage. Sample weekly or fortnightly until harvest.
56 Rose Take first fully expanded leaf from the growing point of the plant. The compound leaf is formed of five smaller leaflets - BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaflets. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling when first new leaves reach mature stage. Sample fortnightly or monthly. Take the whole compound leaf
57 Rosemary Take the top cm of the new growth. Take at least 20 to 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area.
58 1st fully expanded leaf Sage Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 40 leaves, randomly across the block. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded.. Begin when the plant begins to start significant vertical growth and continue every 2-4 weeks until harvest.
59 Stone & Pome Fruit Sample non-fruiting terminals only. Take leaves that are fully expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 30 leaves through the orchard, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height, at up to three different points around the tree. Monitoring program Begin sampling when first leaves of new flush reach maturity. Sample fortnightly or monthly to peak harvest. 1st fully expanded leaf
60 Strawberry Take first fully expanded leaf out from the crown of the plant. The trifoliate leaf is formed of three smaller leaflets - BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF AND PETIOLE, not just the leaflets. Take at least 70 leaves, randomly across the sampling area. Send petiole The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the leaflets can be stripped off the stalk and discarded. Strip the leaf blades only, leaving the whole petiole and the three smaller offshoots. Begin sampling when first new leaves reach mature stage. Sample fortnightly until the end of the main harvest period.
61 Sugarcane, Sorghum & Maize Select the first leaf with a visible dewlap. Select the thickest stalk in each stool. Take at least leaves per sample, selected randomly through the sampling area. Avoid distorted or stunted plants Send whole leaves from young plants, but remove the leaf tips to leave 30 cm of leaf when sampling more mature plants. Sampling can begin from about 30 cm high, in conjunction with Quick Soil test. Sample fortnightly or as required, depending on fertigation frequency. If necessary, seedlings can be sampled by sending 30 whole plants.
62 Sweet Potato Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant, or out from the crown of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 50 leaves, randomly across the block. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded. 1st fully expanded leaf Begin when runners are 50 cm long, continue fortnightly to bulking up.
63 Tarragon Take the top 20cm of the plant. Take at least 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at budding; and monitor fortnightly to midharvest.
64 Timber Trees 1st fully expanded leaf Take leaves that are about 3/4 expanded on the latest flush. Sample at least 80 leaves through the plantation, no more than 3 per tree. Sample at about shoulder height if possible, (or from limbs that have been recently removed) at up to three different points around the tree. Usual sampling times for sap analyses are - as required during main growing period of the year main sampling period is during the first 2-4 years of tree establishment
65 Tomato 1st fully expanded leaf Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the plant. The compound leaf is formed of several/many smaller leaflets - BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaflets. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the block. The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. In tomatoes, this should be from 15 to 30 cm long, depending on the stage of the crop. For ease of dispatching, the leaflets should be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded. Tomatoes begin sampling at first flowering, continue weekly or fortnightly until harvest. May continue sampling trellised crops after harvest has begun.
66 Thyme Take the top 5-10 cm of the new growth. Take at least 40 to 50 tops, randomly across the sampling area.
67 Vine Cucurbits Watermelon, rockmelon, honeydew & pumpkin. First fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the runner, or out from the crown of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the block. Up to 50 leaves may be required if petioles are very small. 1st fully expanded leaf The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded.
68 Watercress Take the top 20cm of the plant. Take at least 30 tops, randomly across the sampling area. Begin sampling at budding; and monitor fortnightly to midharvest.
69 Wheat, Barley & Oats (early stage) Sample the whole above ground part of the plant. The whole plant is sampled up until tillering begins. Send plants per sample, selected randomly through the sampling area. Avoid distorted of stunted plants in the sampling area. Usually a single sample is sufficient from this growth stage.
70 Wheat, Barley & Oats (tillering) Sample the first fully expanded leaf and sheath with a visible dewlap. This part is sampled up until the flag leaf emerges. Send leaves per sample, selected randomly through the sampling area. Avoid distorted of stunted plants in the sampling area. Usually a single sample is sufficient from this growth stage. Leaf with visible dewlap
71 Wheat, Barley & Oats (flag leaf stage) Sample the flag leaf and sheath down to the last node. The flag leaf will be the final leaf that emerges before the grain head emerges. Send leaves per sample, selected randomly through the sampling area. Avoid distorted of stunted plants in the sampling area. Usually a single sample is sufficient from this growth stage. Flag Leaf, final leaf before grain head
72 Zucchini & Squash Take first fully expanded leaf - usually the fourth or fifth leaf back from the growing point of the runner, or out from the crown of the plant. BE SURE TO TAKE WHOLE LEAF, not just the leaf blade. Take at least 30 leaves, randomly across the block. Up to 50 leaves may be required if petioles are very small. No more than 20 leaves may be required for zucchinis. 1st fully expanded leaf The part to be tested is the petiole, or leaf stalk. For ease of dispatching, the blades can be stripped off the leaf stalk and discarded.
Consumer Horticulture
 Purdue Extension Consumer Horticulture Container and Raised Bed Gardening HORT-186-W Purdue Extension Consumer Horticulture Indiana Vegetable Planting Calendar Michael N. Dana and B. Rosie Lerner HO-186-W
Purdue Extension Consumer Horticulture Container and Raised Bed Gardening HORT-186-W Purdue Extension Consumer Horticulture Indiana Vegetable Planting Calendar Michael N. Dana and B. Rosie Lerner HO-186-W
CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS
 142 APPENDIX 3 CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS A new crop ification, the Indicative Classification (ICC) has been developed for the 2010 round of agricultural censuses, and is given at the end of this appendix.
142 APPENDIX 3 CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS A new crop ification, the Indicative Classification (ICC) has been developed for the 2010 round of agricultural censuses, and is given at the end of this appendix.
COMMERCIAL AGRICULTURE PROJECT ENTREPRENEURSHIP TRAINING COURSE OUTLINE: SMALLHOLDER FARMER S CONTEXT
 COMMERCIAL AGRICULTURE PROJECT ENTREPRENEURSHIP TRAINING COURSE OUTLINE: SMALLHOLDER FARMER S CONTEXT Prepared and Compiled by: Brian M Touray, MSc Program Development Advisor CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF TOURISM
COMMERCIAL AGRICULTURE PROJECT ENTREPRENEURSHIP TRAINING COURSE OUTLINE: SMALLHOLDER FARMER S CONTEXT Prepared and Compiled by: Brian M Touray, MSc Program Development Advisor CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF TOURISM
Horticulture Information Leaflet 33-E
 Department of Horticultural Science Horticulture Information Leaflet 33-E Revised 9/93 -- Author Reviewed 8/97 VEGETABLE CROP IRRIGATION Douglas C. Sanders, Extension Horticultural Specialist Distributed
Department of Horticultural Science Horticulture Information Leaflet 33-E Revised 9/93 -- Author Reviewed 8/97 VEGETABLE CROP IRRIGATION Douglas C. Sanders, Extension Horticultural Specialist Distributed
YOUR FARM. AT WORK. CORPORATE WELLNESS PROGRAMS
 YOUR FARM. AT WORK. CORPORATE WELLNESS PROGRAMS Join your coworkers outside to help plant, maintain, and harvest organic produce from your company s own urban farm. Green City Growers corporate wellness
YOUR FARM. AT WORK. CORPORATE WELLNESS PROGRAMS Join your coworkers outside to help plant, maintain, and harvest organic produce from your company s own urban farm. Green City Growers corporate wellness
IMPORT STATUS OF PLANT COMMODITIES & RELATED ITEMS: ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA
 IMPORT STATUS OF PLANT COMMODITIES & RELATED ITEMS: ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA Country of Export All Countries All planting material, plant cuttings, live plants, cut flowers & ornamentals without an import permit
IMPORT STATUS OF PLANT COMMODITIES & RELATED ITEMS: ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA Country of Export All Countries All planting material, plant cuttings, live plants, cut flowers & ornamentals without an import permit
SQUARE FOOT GARDENING. An Educational Class Presented by Harvest Farm Community Garden March 2010
 SQUARE FOOT GARDENING An Educational Class Presented by Harvest Farm Community Garden March 2010 All New Square Foot Gardening: Grow More in Less Space! By Mel Bartholomew www.squarefootgardening.com It
SQUARE FOOT GARDENING An Educational Class Presented by Harvest Farm Community Garden March 2010 All New Square Foot Gardening: Grow More in Less Space! By Mel Bartholomew www.squarefootgardening.com It
NUTRITION EDUCATION CARDS AND HOSPITALITY TRAINING FOR SCHOOL NUTRITION SERVICES STAFF
 SWEET RED PEPPERS All red peppers start out green, then turn red. Red peppers have calcium for healthy bones. WINTER SQUASH Squash has Vitamin A for healthy eyes. Orange vegetables help you have healthy
SWEET RED PEPPERS All red peppers start out green, then turn red. Red peppers have calcium for healthy bones. WINTER SQUASH Squash has Vitamin A for healthy eyes. Orange vegetables help you have healthy
101 Horseshoe Lake Road Monroe, LA 71201 (318) 387-5647, office (318) 387-8404, fax. Split Unit of Unit of. Item Number Product Description Group
 000945 CLEMENTINES CITRUS CS 001230 GRAPEFRUIT 32-48 Case CITRUS 8/5# CS 001650 LEMONS 165 CASE CITRUS CS 001660 LEMONS 200 CASE CITRUS 5# CS 001630 LEMONS 95/115 CITRUS CS 001840 LIMES 200 COUNT 40# CITRUS
000945 CLEMENTINES CITRUS CS 001230 GRAPEFRUIT 32-48 Case CITRUS 8/5# CS 001650 LEMONS 165 CASE CITRUS CS 001660 LEMONS 200 CASE CITRUS 5# CS 001630 LEMONS 95/115 CITRUS CS 001840 LIMES 200 COUNT 40# CITRUS
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!
 Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
Vegetable Planting Guide For Eastern North Carolina
 North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service NC STATE UNIVERSITY Vegetable Guide For Eastern North Carolina Getting Started There is much to consider when planning a vegetable garden. When is the right
North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service NC STATE UNIVERSITY Vegetable Guide For Eastern North Carolina Getting Started There is much to consider when planning a vegetable garden. When is the right
(Adopted April 25, 2003, Amended May 22, 2009)
 DRC GOOD ARRIVAL GUIDELINES (Adopted April 25, 2003, Amended May 22, 2009) Section 16 of the DRC Trading Standards policy on grade and condition standards for commodities stipulates: With regard to grade
DRC GOOD ARRIVAL GUIDELINES (Adopted April 25, 2003, Amended May 22, 2009) Section 16 of the DRC Trading Standards policy on grade and condition standards for commodities stipulates: With regard to grade
4.5 CSA Crop Planning
 4.5 CSA Crop Planning Lecture Outline 3 Exercise 5 Appendices 1. Calculating Weekly and Seasonal Harvest Goals 9 2. Calculating the Number of Plants Per Sowing 11 Required to Meet Harvest Goals 3. Determining
4.5 CSA Crop Planning Lecture Outline 3 Exercise 5 Appendices 1. Calculating Weekly and Seasonal Harvest Goals 9 2. Calculating the Number of Plants Per Sowing 11 Required to Meet Harvest Goals 3. Determining
Learning Prompt 3 - Mr McGee and the Biting Flea
 Learning Prompt 3 - Mr McGee and the Biting Flea In this learning prompt, we re going to look at lists and routines, using the story of Belinda the Cow to show children how breaking a routine is the key
Learning Prompt 3 - Mr McGee and the Biting Flea In this learning prompt, we re going to look at lists and routines, using the story of Belinda the Cow to show children how breaking a routine is the key
Llewellyn's Moon Sign Book
 PLANTING BY THE MOON "Shine on, Shine on harvest moon" is the song lyric which Texans can sing most of the year because of the long production period. Most growers ignore the phases of the moon when the
PLANTING BY THE MOON "Shine on, Shine on harvest moon" is the song lyric which Texans can sing most of the year because of the long production period. Most growers ignore the phases of the moon when the
** In the beginning it is best to limit your food options. We have provided 3 examples for each meal. You will do best by sticking to this.
 Female Fat Loss Formula Diet: This is the diet you will follow. There are no foods that are off limits, but rather foods that are emphasized and those that are minimized. Here are the general rules you
Female Fat Loss Formula Diet: This is the diet you will follow. There are no foods that are off limits, but rather foods that are emphasized and those that are minimized. Here are the general rules you
Plant tissue analysis is used as a diagnostic tool to
 From: Plant Nutrient Management in Hawaii s Soils, Approaches for Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture J. A. Silva and R. Uchida, eds. College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, University of
From: Plant Nutrient Management in Hawaii s Soils, Approaches for Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture J. A. Silva and R. Uchida, eds. College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, University of
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
HOME FREEZING GUIDE FOR FRESH VEGETABLES
 HOME FREEZING GUIDE F FRESH VEGETABLES Freezing most vegetables at home is a fast, convenient way to preserve produce at their peak maturity and nutritional quality. The following links provide information
HOME FREEZING GUIDE F FRESH VEGETABLES Freezing most vegetables at home is a fast, convenient way to preserve produce at their peak maturity and nutritional quality. The following links provide information
Guidelines for Harvesting Vegetables
 Guidelines for Harvesting Vegetables From Cornell Cooperative Extension, Chemung County More gardening information at www.gardening.cornell.edu Knowing when to harvest your vegetables is as important as
Guidelines for Harvesting Vegetables From Cornell Cooperative Extension, Chemung County More gardening information at www.gardening.cornell.edu Knowing when to harvest your vegetables is as important as
Plant Parts and Their Function
 Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Protein Values in Foods
 Protein Values in Foods This document is used as reference material to support the Alternative Health Improvement Center s Newsletter article: Eat your Protein! Stay Healthy! located at http://ahicatlanta.com/articles/eat-your-protein-to-stay-healthy.html.
Protein Values in Foods This document is used as reference material to support the Alternative Health Improvement Center s Newsletter article: Eat your Protein! Stay Healthy! located at http://ahicatlanta.com/articles/eat-your-protein-to-stay-healthy.html.
2016 WILLIAMSBURG FARMERS MARKET VENDOR APPLICATION 2016 Application Part I
 Visit: 2016 WILLIAMSBURG FARMERS MARKET VENDOR APPLICATION 2016 Application Part I Business/Farm Name: Owner(s) Name: Date Began: Mailing Address: Business Location(s): City/County: Business Phone: Cell:
Visit: 2016 WILLIAMSBURG FARMERS MARKET VENDOR APPLICATION 2016 Application Part I Business/Farm Name: Owner(s) Name: Date Began: Mailing Address: Business Location(s): City/County: Business Phone: Cell:
Corn Tissue Sampling WHEN AND HOW
 WHEN AND HOW Corn Tissue Sampling After the grower, farm, field and plant tissue work order have been created within the Nutra-Links Crop Intelligence software; 1. Print the field s work order and take
WHEN AND HOW Corn Tissue Sampling After the grower, farm, field and plant tissue work order have been created within the Nutra-Links Crop Intelligence software; 1. Print the field s work order and take
Table 9 Page 12 Q13. Which of the following produce items have you purchased FRESH (NOT frozen, canned or dried) in the past 12 months?
 Banner 1 Table 1 Page 1 Q5. What is your household income? Table 2 Page 2 Q6. What is your marital status? Table 3 Page 3 Q7. How many dependent children do you have? Table 4 Page 4 Q8. In which state
Banner 1 Table 1 Page 1 Q5. What is your household income? Table 2 Page 2 Q6. What is your marital status? Table 3 Page 3 Q7. How many dependent children do you have? Table 4 Page 4 Q8. In which state
Low Oxalate Diet. Cereals and Cereal Products. Milk and Milk Products
 Low Oxalate Diet Oxalate can be found in healthy plant foods. What can become confusing for some patients is that they have already been put on dietary restrictions because of some other medical conditions
Low Oxalate Diet Oxalate can be found in healthy plant foods. What can become confusing for some patients is that they have already been put on dietary restrictions because of some other medical conditions
To offer you the best quality of our products we need your order 14 days in advance of your event.
 Mövenpick Restaurant Zur Historischen Mühle Components for your menu On the following sites you will find our selection of dishes which you can combine to an multi-course menu. Our menus are offered in
Mövenpick Restaurant Zur Historischen Mühle Components for your menu On the following sites you will find our selection of dishes which you can combine to an multi-course menu. Our menus are offered in
Fillings and toppings for Sandwiches
 Fillings and toppings for Sandwiches Fillings for Sandwiches Curried egg Lean ham & egg Beef with wasabi mayonnaise Turkey, cranberry & avocado Ham, cheese & relish Tuna mayonnaise & chives Fillings for
Fillings and toppings for Sandwiches Fillings for Sandwiches Curried egg Lean ham & egg Beef with wasabi mayonnaise Turkey, cranberry & avocado Ham, cheese & relish Tuna mayonnaise & chives Fillings for
Postharvest Management of Commercial Horticultural Crops STORAGE CONDITIONS FRUITS & VEGETABLES
 Postharvest Management of Commercial Horticultural Crops STORAGE CONDITIONS FRUITS & VEGETABLES By Karen L. B. Gast Once a crop is harvested, it is almost impossible to improve its quality. Losses of horticultural
Postharvest Management of Commercial Horticultural Crops STORAGE CONDITIONS FRUITS & VEGETABLES By Karen L. B. Gast Once a crop is harvested, it is almost impossible to improve its quality. Losses of horticultural
Crop production. 0 5 10 15 million ha. 0 5 10 15 20 million tonnes PART 1. CHART 7: Harvested area of the most important crops in Central Asia (2010)
 PART 1 Crop production is the most important crop in the region of Europe and Central Asia. More than 80 million hectares of land are dedicated to growing wheat, of which 240 were produced in 2010. is
PART 1 Crop production is the most important crop in the region of Europe and Central Asia. More than 80 million hectares of land are dedicated to growing wheat, of which 240 were produced in 2010. is
Harvesting and Preparing Vegetables for Exhibit
 Harvesting and Preparing Vegetables for Exhibit Reviewed by Dr. Ronald Smith Extension Horticulturist Raymond Wagner Retired 4 H Youth Specialist Robert G. Askew Retired Extension Horticulturist Formatted
Harvesting and Preparing Vegetables for Exhibit Reviewed by Dr. Ronald Smith Extension Horticulturist Raymond Wagner Retired 4 H Youth Specialist Robert G. Askew Retired Extension Horticulturist Formatted
fruits and seeds, roots and stems,
 Lesson time: two 45-60 minute sessions Vocabulary: fruits, seeds, roots, stems, flowers and leaves fruits and seeds, roots and stems, flowers and leaves Description Students learn six plant parts and learn
Lesson time: two 45-60 minute sessions Vocabulary: fruits, seeds, roots, stems, flowers and leaves fruits and seeds, roots and stems, flowers and leaves Description Students learn six plant parts and learn
Planting and Harvesting Guide for Piedmont Vegetables and Herbs
 Planting and arvesting Guide for Piedmont Vegetables and erbs Created by Doug Jones, Piedmont Biofarm Debbie Roos, North Carolina Cooperative xtension, Chatham County Center Read First: ow to Use this
Planting and arvesting Guide for Piedmont Vegetables and erbs Created by Doug Jones, Piedmont Biofarm Debbie Roos, North Carolina Cooperative xtension, Chatham County Center Read First: ow to Use this
Central North Carolina Planting Calendar for Annual Vegetables, Fruits, and Herbs
 Central North Carolina Planting Calendar for Annual Vegetables, Fruits, and Herbs Central North Carolina is a wonderful place to garden. Almost any type of vegetable or fruit can be grown successfully
Central North Carolina Planting Calendar for Annual Vegetables, Fruits, and Herbs Central North Carolina is a wonderful place to garden. Almost any type of vegetable or fruit can be grown successfully
Product List. Not all items are stocked Some require 24 / 48 hour notice Please call for availability
 Product List Not all items are stocked Some require 24 / 48 hour notice Please call for availability Apples Empire 100 CT Case Bananas No Gas 40LB Case Apples Empire 88 CT Case Bananas On Turn Case Half
Product List Not all items are stocked Some require 24 / 48 hour notice Please call for availability Apples Empire 100 CT Case Bananas No Gas 40LB Case Apples Empire 88 CT Case Bananas On Turn Case Half
Your child s diet with Dietary Fructose Intolerance (DFI)
 Your child s diet with Dietary Fructose Intolerance (DFI) What is Dietary Fructose Intolerance (DFI)? Dietary Fructose Intolerance is when your child has problems digesting and absorbing the fructose in
Your child s diet with Dietary Fructose Intolerance (DFI) What is Dietary Fructose Intolerance (DFI)? Dietary Fructose Intolerance is when your child has problems digesting and absorbing the fructose in
Company Headquarters Hapag-Lloyd AG Keep Cool Regional Head Offices Europe: Hapag-Lloyd AG America: Hapag-Lloyd (America) Inc.
 Keep Cool We Care Fresher at the destination Our reefer containers provide environmentally friendly technology, reliable temperatures as low as 35 C/ 31 F and a variety of precise controlling alternatives
Keep Cool We Care Fresher at the destination Our reefer containers provide environmentally friendly technology, reliable temperatures as low as 35 C/ 31 F and a variety of precise controlling alternatives
Unit 3 Lesson 5: People Need Plants
 Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
A guide for handling for cabbage, carrot, hot pepper, lettuce, sweet potato and tomato. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
 A guide for handling for cabbage, carrot, hot pepper, lettuce, sweet potato and tomato Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations A guide for handling for cabbage 1. HARVESTING Harvesting
A guide for handling for cabbage, carrot, hot pepper, lettuce, sweet potato and tomato Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations A guide for handling for cabbage 1. HARVESTING Harvesting
The Glycemic Index of Foods
 What is the Glycemic Index (GI)? It is a method used to classify carbohydrate containing foods, according to the effect that they may have on blood sugar levels. It is claimed that the higher the GI number,
What is the Glycemic Index (GI)? It is a method used to classify carbohydrate containing foods, according to the effect that they may have on blood sugar levels. It is claimed that the higher the GI number,
Production of horticultural crops is
 PRODUCTION OF FRESH FRUITS AND VEGETABLES AS IT RELATES TO DIRECT MARKETING Robert E. Call 1 Production of horticultural crops is a highly technical interplay of science, art, hard work and salesmanship.
PRODUCTION OF FRESH FRUITS AND VEGETABLES AS IT RELATES TO DIRECT MARKETING Robert E. Call 1 Production of horticultural crops is a highly technical interplay of science, art, hard work and salesmanship.
WHITE ASPARAGUS "EXTRA PIECES. 1 KG. 660 gr. 425 gr. Units per Box: 12 Boxes per Pallet: 100 Reference: 01-1001 Net weight: Drained net weight:
 ^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 6/8 Pieces. 1 Kg. ^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 9/12 Pieces. 1 Kg. ^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 13/16 Pieces. 1 Kg. ^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 17/24 Pieces. 1
^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 6/8 Pieces. 1 Kg. ^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 9/12 Pieces. 1 Kg. ^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 13/16 Pieces. 1 Kg. ^ White Asparagus "Extra Qual." 17/24 Pieces. 1
RECOMMENDED FOOD INGREDIENTS for TCM DIAGNOSIS
 General Guidelines for Diet/Foods according to TCM 1. use rice, oats, buckwheat as main grains 2. small portions of meat (chicken, turkey), fish (e.g. salmon, trout, tuna, white fish) and seafoods (e.g.
General Guidelines for Diet/Foods according to TCM 1. use rice, oats, buckwheat as main grains 2. small portions of meat (chicken, turkey), fish (e.g. salmon, trout, tuna, white fish) and seafoods (e.g.
Diet and coumarin anticoagulants: warfarin (Coumadin ), nicoumalone (Sintrom )
 NOTES \bookfoldsheets0\bookfoldsheets0\book Diet and coumarin anticoagulants: warfarin (Coumadin ), nicoumalone (Sintrom ) Leaflet prepared by Rita Uckardas, Dt.P., in collaboration with Stéphanie Caron,
NOTES \bookfoldsheets0\bookfoldsheets0\book Diet and coumarin anticoagulants: warfarin (Coumadin ), nicoumalone (Sintrom ) Leaflet prepared by Rita Uckardas, Dt.P., in collaboration with Stéphanie Caron,
o d Propagation and Moon Planting Fact Sheet
 o d Propagation and Moon Planting Fact Sheet Propagation Propagation is actually quite simple and requires very little effort on your part. Most seeds are ready to go, complete with all the nutrients and
o d Propagation and Moon Planting Fact Sheet Propagation Propagation is actually quite simple and requires very little effort on your part. Most seeds are ready to go, complete with all the nutrients and
Family Meals Grocery Lists
 Family Meals Grocery Lists Print off these helpful tips and 6 weeks of grocery lists from the Family Meals Cookbook to help make your shopping easier. You can print off the entire list or simply select
Family Meals Grocery Lists Print off these helpful tips and 6 weeks of grocery lists from the Family Meals Cookbook to help make your shopping easier. You can print off the entire list or simply select
reacts to the allergen by producing an antibody knows as immunoglobulin E (IgE).
 FOOD INTOLERANCE, Management Plan by Dr. Sue Shepherd and Dr. Peter Gibson ALL ABOUT FOOD - Food allergy or food hypersensitivity are quite uncommon. These are reactions to a protein in the food and involve
FOOD INTOLERANCE, Management Plan by Dr. Sue Shepherd and Dr. Peter Gibson ALL ABOUT FOOD - Food allergy or food hypersensitivity are quite uncommon. These are reactions to a protein in the food and involve
Drip Fertigation in Horticultural crops
 Drip Fertigation in Horticultural crops G. Sri Krishna, Research Associate, Agricultural Research Station, Utukur, Kadapa - 516003 Mail: srikrishna12@rediffmail.com Application of Fertilizers to plantation,
Drip Fertigation in Horticultural crops G. Sri Krishna, Research Associate, Agricultural Research Station, Utukur, Kadapa - 516003 Mail: srikrishna12@rediffmail.com Application of Fertilizers to plantation,
Eating well: first year of life Food photo cards
 Eating well: first year of life Food photo cards For information on how to use these food photo cards, see Eating Well First Year of Life Practical Guide. ISBN 978-1-89-782030-8 Eating Well: First Year
Eating well: first year of life Food photo cards For information on how to use these food photo cards, see Eating Well First Year of Life Practical Guide. ISBN 978-1-89-782030-8 Eating Well: First Year
National Retail Report - Fruits and Vegetables
 Fruit and Vegetable Market News Division Agricultural Marketing Service National Retail Report - Fruits and Vegetables Websites: www.marketnews.usda.gov/mnp/fv-home and http://www.ams.usda.gov/mnreports/fvwretail.pdf
Fruit and Vegetable Market News Division Agricultural Marketing Service National Retail Report - Fruits and Vegetables Websites: www.marketnews.usda.gov/mnp/fv-home and http://www.ams.usda.gov/mnreports/fvwretail.pdf
Science of Life Explorations
 Science of Life Explorations Celebrate the Growing Year: The Farmer s Year A Farmer s Year While you are in school or on a vacation, farmers are working hard to provide us with the foods we eat and the
Science of Life Explorations Celebrate the Growing Year: The Farmer s Year A Farmer s Year While you are in school or on a vacation, farmers are working hard to provide us with the foods we eat and the
AIJN Guideline for Vegetable Juices and Nectars
 AIJN Guideline for Vegetable Juices and Nectars 1. INTRODUCTION This guideline is applicable without prejudice to the national legislation of each Member State and/or Code of Practice and cannot be used
AIJN Guideline for Vegetable Juices and Nectars 1. INTRODUCTION This guideline is applicable without prejudice to the national legislation of each Member State and/or Code of Practice and cannot be used
The Alkaline Foods Chart
 The Alkaline Foods Chart Complete List of Alkaline Foods & Acidic Food ph Ratings (http://www.acidalkalinediet.com) * You should aim for a 70/30 ratio between alkaline and acid foods. There is no need
The Alkaline Foods Chart Complete List of Alkaline Foods & Acidic Food ph Ratings (http://www.acidalkalinediet.com) * You should aim for a 70/30 ratio between alkaline and acid foods. There is no need
Growing Vegetables at Home
 Visit us on the Web: www.gardeninghelp.org Growing Vegetables at Home Vegetable gardening is a rewarding hobby that has many benefits not the least of which is getting exercise and growing fresh food.
Visit us on the Web: www.gardeninghelp.org Growing Vegetables at Home Vegetable gardening is a rewarding hobby that has many benefits not the least of which is getting exercise and growing fresh food.
CALIFORNIA AGRICULTURAL WATER USE: KEY BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 NEED TO KNOW CALIFORNIA AGRICULTURAL WATER USE: KEY BACKGROUND INFORMATION Author: Heather Cooley INTRODUCTION Water plays a substantial and vital role in California s agricultural sector. Given the long-term
NEED TO KNOW CALIFORNIA AGRICULTURAL WATER USE: KEY BACKGROUND INFORMATION Author: Heather Cooley INTRODUCTION Water plays a substantial and vital role in California s agricultural sector. Given the long-term
Risk Assessment Study on. Nitrate and Nitrite in Vegetables Available in Hong Kong. ~ Summary~
 Risk Assessment Study on Nitrate and Nitrite in Vegetables Available in Hong Kong ~ Summary~ Purpose This paper summarises the main findings of the risk assessment study on nitrate and nitrite in vegetables
Risk Assessment Study on Nitrate and Nitrite in Vegetables Available in Hong Kong ~ Summary~ Purpose This paper summarises the main findings of the risk assessment study on nitrate and nitrite in vegetables
Blood Group Diet. The O - Blood Group FOODS THAT ENCOURAGE WEIGHT GAIN FOODS THAT ENCOURAGE WEIGHT LOSS
 The O - Blood Group Beans, Sugar, Sweet Corn, Cabbage, Mustard, Lentils, Bread, Cereal Kelp, Red meats, White Meat, Seafood, Liver, Broccoli MEAT Beef, Chicken, Ostrich, Game Lamb Hake, Salmon, Sardines,
The O - Blood Group Beans, Sugar, Sweet Corn, Cabbage, Mustard, Lentils, Bread, Cereal Kelp, Red meats, White Meat, Seafood, Liver, Broccoli MEAT Beef, Chicken, Ostrich, Game Lamb Hake, Salmon, Sardines,
Adult portion size examples - approximately equivalent to 80g in weight
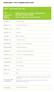 FRUIT - Adult portion size = 80g Fruit (Always check labels for additives) Adult portion size examples - approximately equivalent to 80g in weight (As eaten, edible portion, drained if canned) Apple: fresh
FRUIT - Adult portion size = 80g Fruit (Always check labels for additives) Adult portion size examples - approximately equivalent to 80g in weight (As eaten, edible portion, drained if canned) Apple: fresh
ALL CHURCH FAST GUIDELINES. January 11-31. (21 Days)
 2008 ALL CHURCH FAST GUIDELINES January 11-31 (21 Days) Guidelines for Observing the Daniel Fast This Daniel Fast is designed to lead to spiritual insight. (Daniel 1:17) As for these four boys, God gave
2008 ALL CHURCH FAST GUIDELINES January 11-31 (21 Days) Guidelines for Observing the Daniel Fast This Daniel Fast is designed to lead to spiritual insight. (Daniel 1:17) As for these four boys, God gave
GUIDELINES FOR GARDEN SHOW SHOWING VEGETABLES
 GUIDELINES FOR GARDEN SHOW SHOWING VEGETABLES POTATOES. Always wash the potatoes carefully trying not to break the skin- Choose even sized tubers of similar shape. White potatoes are all white. Coloured
GUIDELINES FOR GARDEN SHOW SHOWING VEGETABLES POTATOES. Always wash the potatoes carefully trying not to break the skin- Choose even sized tubers of similar shape. White potatoes are all white. Coloured
Nourishing Yin. Appointments: 0208 515 0820 Fax: 0208 940 8533 Email: enquiries@naturalgynae.com www.naturalgynae.com
 Nourishing Yin Avoid foods that stimulate energy use Consume cooling foods and dairy products More sweet, sour and salty foods Less pungent and bitter foods Barley Spelt Alfalfa Sprouts Artichoke Asparagus
Nourishing Yin Avoid foods that stimulate energy use Consume cooling foods and dairy products More sweet, sour and salty foods Less pungent and bitter foods Barley Spelt Alfalfa Sprouts Artichoke Asparagus
Pick plans for fresh vegetables
 Production Insurance Plan Overview Fresh Market Vegetable Production Pick plans for fresh vegetables Connecting producers with programs What you need to know about protecting your fresh market vegetables
Production Insurance Plan Overview Fresh Market Vegetable Production Pick plans for fresh vegetables Connecting producers with programs What you need to know about protecting your fresh market vegetables
1800 Calorie Meal Plan. Jessica Iannotta Department of Nutritional Sciences UMDNJ School of Health Related Professions
 1800 Calorie Meal Plan Meal Portion Food Calories DAY 1 Breakfast 1 cup Hot Oatmeal, cooked, unsweetened 150 1 banana 120 1 Amy s Bean & Rice Burrito 280 (in the frozen foods section of your grocery store
1800 Calorie Meal Plan Meal Portion Food Calories DAY 1 Breakfast 1 cup Hot Oatmeal, cooked, unsweetened 150 1 banana 120 1 Amy s Bean & Rice Burrito 280 (in the frozen foods section of your grocery store
RIPPLE Africa Step by Step Fruit Tree planting Guide
 RIPPLE Africa Step by Step Fruit Tree planting Guide NOTES ON FRUIT PRODUCTION Aim and Objective The aim and objective of RIPPLE Africa as an organisation is to make Nkhata Bay District one of the leading
RIPPLE Africa Step by Step Fruit Tree planting Guide NOTES ON FRUIT PRODUCTION Aim and Objective The aim and objective of RIPPLE Africa as an organisation is to make Nkhata Bay District one of the leading
List of low carb (and low glycemic) Foods
 List of low carb (and low glycemic) Foods Very Low Carb 1-5 g (Not Artichokes Asparagus Baby corn Bamboo shoots Bean sprouts Bok choy Broccoli Brussels sprouts Cabbages Cauliflower Celery Chilies Chinese
List of low carb (and low glycemic) Foods Very Low Carb 1-5 g (Not Artichokes Asparagus Baby corn Bamboo shoots Bean sprouts Bok choy Broccoli Brussels sprouts Cabbages Cauliflower Celery Chilies Chinese
Patient Information: Low FODMAP Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Patient Information: Low FODMAP Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome WHAT ARE FODMAPS? FODMAP is the acronym for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides and Polyols, a group of short-chain
Patient Information: Low FODMAP Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome WHAT ARE FODMAPS? FODMAP is the acronym for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides and Polyols, a group of short-chain
City of Ann Arbor Farmers Market 2016 Daytime Vendor Application Checklist To be completed by the applicant/vendor before turning into market office
 City of Ann Arbor Farmers Market 2016 Daytime Vendor Application Checklist To be completed by the applicant/vendor before turning into market office Please ensure you have completed all of the following
City of Ann Arbor Farmers Market 2016 Daytime Vendor Application Checklist To be completed by the applicant/vendor before turning into market office Please ensure you have completed all of the following
MICHIGAN Senior Project FRESH/Market FRESH SENIOR FARMERS MARKET NUTRITION PROGRAM MARKET MASTER S GUIDEBOOK
 MICHIGAN Senior Project FRESH/Market FRESH SENIOR FARMERS MARKET NUTRITION PROGRAM MARKET MASTER S GUIDEBOOK Revised 2/2014 MICHIGAN OFFICE OF SERVICES TO THE AGING SENIOR PROJECT FRESH/MARKET FRESH THE
MICHIGAN Senior Project FRESH/Market FRESH SENIOR FARMERS MARKET NUTRITION PROGRAM MARKET MASTER S GUIDEBOOK Revised 2/2014 MICHIGAN OFFICE OF SERVICES TO THE AGING SENIOR PROJECT FRESH/MARKET FRESH THE
Fibe. Fiber and water work together in bowel regulation. Be sure to drink eight to ten (8 ounce) glasses of
 r Fibe An important part of a healthy diet is eating a variety of fiber-rich foods, including whole-grain breads and cereals, fruits and vegetables, beans and nuts. Fiber is an important part of your diet.
r Fibe An important part of a healthy diet is eating a variety of fiber-rich foods, including whole-grain breads and cereals, fruits and vegetables, beans and nuts. Fiber is an important part of your diet.
Recipe #1 2-3 cups of greens of your choice, 2 cups papaya, 2 oranges No water necessary
 Victoria Boutenko's Favourite Blend well: 6 leaves of red leaf lettuce 1/4 bunch of fresh basil 1/2 lime (juiced) 1/2 red onion 2 celery sticks 1/4 avocado Sergei Boutenko's Favourite Blend well: 5 kale
Victoria Boutenko's Favourite Blend well: 6 leaves of red leaf lettuce 1/4 bunch of fresh basil 1/2 lime (juiced) 1/2 red onion 2 celery sticks 1/4 avocado Sergei Boutenko's Favourite Blend well: 5 kale
Easy Herb Recipes. Place the strawberries, mint leaves, orange juice, and yogurt in your blender. Blend until thick and smooth.
 Strawberry Smoothie Easy Herb Recipes Serves: 1 1 cup unsweetened frozen strawberries 1 teaspoon coarsely chopped mint leaves ½ cup 100% orange juice ½ cup lowfat vanilla yogurt Place the strawberries,
Strawberry Smoothie Easy Herb Recipes Serves: 1 1 cup unsweetened frozen strawberries 1 teaspoon coarsely chopped mint leaves ½ cup 100% orange juice ½ cup lowfat vanilla yogurt Place the strawberries,
ECONOMIC CONTRIBUTION OF NORTH CAROLINA AGRICULTURE AND AGRIBUSINESS
 ECONOMIC CONTRIBUTION OF NORTH CAROLINA AGRICULTURE AND AGRIBUSINESS $76 BILLION Agriculture and Agribusiness, including the farming, processing, wholesaling and retailing of food, natural fiber and forestry
ECONOMIC CONTRIBUTION OF NORTH CAROLINA AGRICULTURE AND AGRIBUSINESS $76 BILLION Agriculture and Agribusiness, including the farming, processing, wholesaling and retailing of food, natural fiber and forestry
Standard Food Panel: IgA/IgG/IgE Complete Report
 Standard Food Panel: IgA/IgG/IgE Complete Report 13500 Linden Ave North Seattle, Washington 98133 USA Physician: Patient: Accession #: Age: Sex: Collected: IgA IgG IgE 58 F 2009-04-22 Received: 2009-05-01
Standard Food Panel: IgA/IgG/IgE Complete Report 13500 Linden Ave North Seattle, Washington 98133 USA Physician: Patient: Accession #: Age: Sex: Collected: IgA IgG IgE 58 F 2009-04-22 Received: 2009-05-01
ASK ABOUT OUR DAILY SPECIALS. Cabbage Taco $12.00 Cabbage stuffed with nutmeat, tomato, avocado, onions and sauce
 Each item is carefully selected for its exquisite taste and nutritional value. Meals are prepared fresh upon ordering. Please allow at least 25 minutes for preparation. Prices are subject to change due
Each item is carefully selected for its exquisite taste and nutritional value. Meals are prepared fresh upon ordering. Please allow at least 25 minutes for preparation. Prices are subject to change due
Perspectives of water efficient and saline agriculture. November 25th, Greet Blom-Zandstra
 Perspectives of water efficient and saline agriculture November 25th, Greet Blom-Zandstra Outline Current and future problems Effects of drought or salinity on plants Plant responses Anticipation in agricultural
Perspectives of water efficient and saline agriculture November 25th, Greet Blom-Zandstra Outline Current and future problems Effects of drought or salinity on plants Plant responses Anticipation in agricultural
WORKING DOCUMENT SANTE 10684/2015 Rev0 [AnnexIIIA] Pesticide residues and maximum residue levels (mg/kg)
![WORKING DOCUMENT SANTE 10684/2015 Rev0 [AnnexIIIA] Pesticide residues and maximum residue levels (mg/kg) WORKING DOCUMENT SANTE 10684/2015 Rev0 [AnnexIIIA] Pesticide residues and maximum residue levels (mg/kg)](/thumbs/40/21125591.jpg) 0100000 FRUITS, FRESH or FROZEN; TREE NUTS 0110000 Citrus fruits 0.015 0110010 Grapefruits 0110020 Oranges 0110030 Lemons 0110040 Limes 0110050 Mandarins 0110990 Others 0120000 Tree nuts 0.01* 0120010
0100000 FRUITS, FRESH or FROZEN; TREE NUTS 0110000 Citrus fruits 0.015 0110010 Grapefruits 0110020 Oranges 0110030 Lemons 0110040 Limes 0110050 Mandarins 0110990 Others 0120000 Tree nuts 0.01* 0120010
II. Vegetative Propagation. Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting
 II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
27.3.2009 Official Journal of the European Union L 81/3
 27.3.2009 Official Journal of the European Union L 81/3 COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 256/2009 of 23 March 2009 amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and
27.3.2009 Official Journal of the European Union L 81/3 COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 256/2009 of 23 March 2009 amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and
Low-Fructose Food Choices
 Patient and Family Education Low-Fructose Food Choices For your child with fructose malabsorption Fructose is a kind of sugar. Fructose malabsorption happens when your child s body has problems breaking
Patient and Family Education Low-Fructose Food Choices For your child with fructose malabsorption Fructose is a kind of sugar. Fructose malabsorption happens when your child s body has problems breaking
Educator Lesson Plan Kitchen Calculations
 The Culinary Institute of America s Educator Lesson Plan Kitchen Calculations Menus used in the dining room give both the waitstaff and guests important information about what your establishment offers,
The Culinary Institute of America s Educator Lesson Plan Kitchen Calculations Menus used in the dining room give both the waitstaff and guests important information about what your establishment offers,
1. According to the Food Guide Pyramid, how many daily servings do we need of fruits?
 NAME HOUR VIDEO WORKSHEET 1. According to the Food Guide Pyramid, how many daily servings do we need of fruits? 2. How many daily servings do we need of vegetables according to the Food Guide Pyramid?
NAME HOUR VIDEO WORKSHEET 1. According to the Food Guide Pyramid, how many daily servings do we need of fruits? 2. How many daily servings do we need of vegetables according to the Food Guide Pyramid?
Digit - Rostlina. Co-operation programme Flanders and Czech Republic. Katholieke Hogeschool Kempen. Presentation
 3 Digit - Rostlina 16 Oktober 2003 Co-operation programme Flanders and Czech Republic Katholieke Hogeschool Kempen Vorselaar Lier Turnhout Geel Teacher training 765 Health care 450 Health care 394 1 institute
3 Digit - Rostlina 16 Oktober 2003 Co-operation programme Flanders and Czech Republic Katholieke Hogeschool Kempen Vorselaar Lier Turnhout Geel Teacher training 765 Health care 450 Health care 394 1 institute
Fiber. What is fiber? Fiber is a part of plant food. There are two types of fiber:
 Fiber An important part of a healthy diet is eating fiber-rich foods. This handout will explain what fiber is, where it s found, and how to increase the amount of fiber in your diet. What is fiber? Fiber
Fiber An important part of a healthy diet is eating fiber-rich foods. This handout will explain what fiber is, where it s found, and how to increase the amount of fiber in your diet. What is fiber? Fiber
Growing Herbs from Seed
 Growing Herbs from Seed Every home with a kitchen should have a kitchen herb garden. Why? Because using fresh herbs from your garden, rather than dried herbs from a jar, will liven up your meals and rejuvenate
Growing Herbs from Seed Every home with a kitchen should have a kitchen herb garden. Why? Because using fresh herbs from your garden, rather than dried herbs from a jar, will liven up your meals and rejuvenate
AGFACTS AGFACTS AGFACTS
 AGFACTS AGFACTS AGFACTS www.agric.nsw.gov.au Boron deficiency in pastures and field crops Agfact P1.AC.1, 2nd edition 2004 B.S. Dear, former Principal Research Scientist R.G. Weir, former Special Chemist
AGFACTS AGFACTS AGFACTS www.agric.nsw.gov.au Boron deficiency in pastures and field crops Agfact P1.AC.1, 2nd edition 2004 B.S. Dear, former Principal Research Scientist R.G. Weir, former Special Chemist
your easy guide to home-grown, garden-fresh vegetables vegetable growing chart
 Vegetable Planner your easy guide to home-grown, garden-fresh vegetables vegetable growing chart At-a-glance guide to sowing and harvesting times for most popular vegetables. This chart covers 18 months
Vegetable Planner your easy guide to home-grown, garden-fresh vegetables vegetable growing chart At-a-glance guide to sowing and harvesting times for most popular vegetables. This chart covers 18 months
Pumpkin Soup. Miguel Maestre Recipe. Ingredients. Method
 Pumpkin Soup 1.5kg butternut pumpkin Sea salt and freshly ground black pepper 1 bulb garlic, cut in half horizontally Handful of thyme, oregano and rosemary sprigs 1½ tbsp olive oil 2 onion, peeled and
Pumpkin Soup 1.5kg butternut pumpkin Sea salt and freshly ground black pepper 1 bulb garlic, cut in half horizontally Handful of thyme, oregano and rosemary sprigs 1½ tbsp olive oil 2 onion, peeled and
Storing fruits and vegetables from the home garden
 A3823 Storing fruits and vegetables from the home garden Teryl Roper, Karen Delahaut, Barb Ingham It s possible to have crisp, homegrown apples well into November, and to use tender potatoes and crunchy
A3823 Storing fruits and vegetables from the home garden Teryl Roper, Karen Delahaut, Barb Ingham It s possible to have crisp, homegrown apples well into November, and to use tender potatoes and crunchy
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
Seed Processing Plant
 Seed Processing Plant Y 50 Years of Experience - Your Guarentee Consultancy based on experience At Cimbria, we have built up a profound and market leading specialist know-how within development and turn-key
Seed Processing Plant Y 50 Years of Experience - Your Guarentee Consultancy based on experience At Cimbria, we have built up a profound and market leading specialist know-how within development and turn-key
Effective Financing Statement (EFS)
 Fax 307.777.5339 For Office Use Only Effective Financing Statement (EFS) 1. Contact and Send Acknowledgment To: a. Name and Phone of Contact at Filer (optional) b. PAD Account # to be Charged c. Send Acknowledgement
Fax 307.777.5339 For Office Use Only Effective Financing Statement (EFS) 1. Contact and Send Acknowledgment To: a. Name and Phone of Contact at Filer (optional) b. PAD Account # to be Charged c. Send Acknowledgement
Van Vugt Kruiden B.V.
 Van Vugt Kruiden B.V. - A complete overview - Van Vugt Kruiden B.V. Voorweg 18 Tel: +1 (0)180-65660 E-mail: info@vanvugtkruiden.nl 988 CG Ridderkerk Fax: +1 (0)180-6560 Website: www.vanvugtkruiden.nl W
Van Vugt Kruiden B.V. - A complete overview - Van Vugt Kruiden B.V. Voorweg 18 Tel: +1 (0)180-65660 E-mail: info@vanvugtkruiden.nl 988 CG Ridderkerk Fax: +1 (0)180-6560 Website: www.vanvugtkruiden.nl W
Perth Market Authority: Assess and define the Perth Market traders share of the wholesale fruit and vegetable market
 Perth Market Authority: Assess and define the Perth Market traders share of the wholesale fruit and vegetable market Assessment for the year ending 30 June 2014 February 2015 Martin Kneebone, Managing
Perth Market Authority: Assess and define the Perth Market traders share of the wholesale fruit and vegetable market Assessment for the year ending 30 June 2014 February 2015 Martin Kneebone, Managing
Appendix A Food Sources of Vitamins and Minerals
 Appendix A Food Sources of Vitamins and Minerals Appendix A 229 Appendix A Food Sources of Vitamins and Minerals Vitamin A (Retinol) Food Amount IU* Liver 3 oz 45,400 Crab 2 cup,680 Egg medium 590 Fats
Appendix A Food Sources of Vitamins and Minerals Appendix A 229 Appendix A Food Sources of Vitamins and Minerals Vitamin A (Retinol) Food Amount IU* Liver 3 oz 45,400 Crab 2 cup,680 Egg medium 590 Fats
dlife s 2010 BEST Low Carb Snack List!
 dlife s 2010 BEST Low Carb Snack List! Note: GL* and GI** values are included where available for each snack food. DAIRY Full-fat (4%) cottage cheese Serving Size: 1/2 Cup; Carbs: 6g; Fiber: 0g; Calories:
dlife s 2010 BEST Low Carb Snack List! Note: GL* and GI** values are included where available for each snack food. DAIRY Full-fat (4%) cottage cheese Serving Size: 1/2 Cup; Carbs: 6g; Fiber: 0g; Calories:
Understanding the Carbohydrate Portions in Gluten Free Foods 1 Portion/Exchange = 15g
 Understanding the Carbohydrate Portions in luten Free Foods 1 Portion/Exchange = 15g Know your Carbohydrate Foods Dairy Fruit Starchy vegetables Breads, cereals, rice, pasta/noodles, biscuits, flour(s)
Understanding the Carbohydrate Portions in luten Free Foods 1 Portion/Exchange = 15g Know your Carbohydrate Foods Dairy Fruit Starchy vegetables Breads, cereals, rice, pasta/noodles, biscuits, flour(s)
(Non-legislative acts) REGULATIONS
 15.4.2010 Official Journal of the European Union L 94/1 II (Non-legislative acts) REGULATIONS COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 304/2010 of 9 April 2010 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of
15.4.2010 Official Journal of the European Union L 94/1 II (Non-legislative acts) REGULATIONS COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 304/2010 of 9 April 2010 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of
OVERVIEW MARKET ALERTS GOOD BUYS. February 4, 2016
 February 4, 2016 OVERVIEW The weather has improved and we have seen tremendous improvement with commodities in the Yuma growing region. Lettuce, Cauliflower, Broccoli are all plentiful and the price is
February 4, 2016 OVERVIEW The weather has improved and we have seen tremendous improvement with commodities in the Yuma growing region. Lettuce, Cauliflower, Broccoli are all plentiful and the price is
APPROVED FOOD LIST JAMIE EASON S LIVEFIT 12-WEEK TRAINER
 LEAN PROTEINS Sole Flounder Cod Halibut Mahi-mahi Red snapper Orange ruffy (Limit, high in mercury) Ahi tuna (Limit, high in mercury) Swordfish (Limit, high in mercury) Tilapia Grouper Corvina Cobia White
LEAN PROTEINS Sole Flounder Cod Halibut Mahi-mahi Red snapper Orange ruffy (Limit, high in mercury) Ahi tuna (Limit, high in mercury) Swordfish (Limit, high in mercury) Tilapia Grouper Corvina Cobia White
Part 1: Knowing how to identify the problem. Author: Damon Polta, Friendly Aquaponics Farm Manager. For free distribution.
 Diseases, Deficiencies, and Toxicities in Plants Part 1: Knowing how to identify the problem. Author: Damon Polta, Friendly Aquaponics Farm Manager. For free distribution. Diseases Beet Western Yellow
Diseases, Deficiencies, and Toxicities in Plants Part 1: Knowing how to identify the problem. Author: Damon Polta, Friendly Aquaponics Farm Manager. For free distribution. Diseases Beet Western Yellow
