Unit 5 Geometry. Using imperial, metric and conversions when necessary. Maximum area for a given perimeter
|
|
|
- Karen Carpenter
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 5 Geometry BIG PICTURE MAP 4C Foundations for College Mathematics Students will: Understand the relationships between imperial and metric units Consolidate understanding of perimeter, area, surface area, and volume through real-life problems Explore optimization of two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures Day Lesson Title Math Learning Goals Expectations 1 Exploring Relationships between Metric and Imperial Lesson Included *New Jan/08* Explore relationships that exist between inches and centimeters (measuring tools: string, both types of rulers, or tapes) Reading ruler, measuring tape (fraction) Create a scatter plot from the student s data Perform a linear regression and get the equation Connect to the actual conversion (inches <-> centimetres) GT1.1 Trundle wheel activity for perimeter Converting mixed imperial measurements <-> metric Example convert 5 1/8 to cm 3 Finding the area of rectangles, triangles, and circles, and of related composite shapes, in situations arising from realworld applications Using imperial, metric and conversions when necessary 4 Maximizing Area for a Given Perimeter Maximum area for a given perimeter Problem: Cagey Problem, Why are copper wires round? Lesson Included 5 Minimizing Minimum perimeter for a given area Perimeter Problem: Fencing Lesson Included *New Jan/08* 6 Jazz Day 7 Volume problems involving rectangular prisms, triangular prisms, cylinders, and composite figures Using imperial, metric and conversions when necessary Example: Volume of Concrete Pad in cubic meters with initial measurements in feet and inches. Example 8 x 4 x 4 8 Surface area problems involving rectangular prisms, triangular prisms, cylinders, and composite figures Using imperial, metric and conversions when necessary GT1.1 GT1. GT.,GT.1 GT.,GT.1 GT1.3 GT1.3 9 Maximum Volume of a Triangular Prism Lesson Included Maximum volume for a given surface area Using imperial, metric and conversions when necessary GT.3,GT.1 MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 1
2 10 Minimum Surface Area of a Cylinder Minimum surface area for a given volume Using imperial, metric and conversions when necessary GT.3,GT Lesson Included Keeping the Kandies Summative Included M.O.* Summative Task Packaging Project MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008)
3 Unit 5: Day 1: Exploring Relationships between Metric and Imperial Math Learning Goals: Minds On: 10 Explore relationships that exist between metric and imperial measuring systems Action: 35 Consolidate:30 Total=75 min Minds On Whole Class Discussion Put the titles Metric and Imperial on the board. Ask students to list several units of measure (for distance, weight or volume) and discuss whether the suggestions belong to the metric or imperial system. Determine if students are already aware of relationships between metric and imperial systems. (e.g. Some students may already know that there are.54 cm in an inch or that there are 1 inches in a foot.) Discuss where each system of measure is currently in use and the need to be able to convert between systems. Mathematical Process Focus: Reflecting Students reflect on prior knowledge of measurement units and conversions Action! Consolidate Debrief Exploration Skill Practice Pairs Investigation Explain to students that they will be measuring several objects around the classroom today in both metric and imperial units. They will then be required to perform a regression (as in unit of the course) to determine the relationship between the two units of measure. Distribute BLM to each pair to perform the investigation. Learning Skills/Observation/Mental Note: Assess teamwork skills as you circulate. Mathematical Process Focus: Connecting students connect prior knowledge of linear regression with finding a relationship between the lengths of inches and centimetres, yards and metres, etc. Whole Class Sharing Results For each activity, have students write their equation of the line of best fit on the board as shown in BLM Using the equations, decide on the appropriate conversion factor for each activity. Whole Class Board Note Using BLM as a guide, show students how to perform conversions of distances and areas. Whole Class Discussion Discuss other units of measure and their conversion factors. Give the example of the Gimli Glider incident to show the importance of proper/correct conversions (and to peak their interests). In particular, ask the students to determine how much fuel they were short for the flight (the plane needed,300kg of fuel, but was loaded with,300pounds instead) Home Activity or Further Classroom Consolidation Complete BLM 5.1. Assessment Opportunities Materials BLM BLM 5.1. BLM Measuring tapes with metric and imperial measures Graphing Calculators or statistics software When adding units to the list, question students whether they are distance, volume, mass, etc. When adding several measures of one type, ask students to order them by size (eg. If students say yards, inches and feet are all imperial distance measures, ask them which is biggest and which is smallest of the three given. Gimli Glider info can be found at: g/wiki/gimli_glider And the news report at: /IDC /that_was_then/life _society/gimli_glider MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 3
4 5.1.1: Metric and Imperial: What s the Relationship? Exploring Centimetres and Inches Data Collection 1. Measure 5 objects of varying sizes around the classroom.. Measure each object two times: once in centimetres and once in inches. 3. Record your results in the table. Object Length in Inches Length in Centimetres Analyze the data 4. Enter your data into a spreadsheet or graphing calculator. 5. Perform a linear regression to obtain the equation of the line of best fit. Line of Best Fit: Interpret your findings 6. Measure another object in the classroom in inches. Object: Length in inches: 7. Use your line of best fit to calculate the length in centimetres. 8. Now measure the item in centimetres. How close was your calculation to your measurement? 9. How do you convert lengths given in inches to centimetres? 10. How do you convert lengths given in centimetres to inches? MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 4
5 5.1.1: Metric and Imperial: What s the Relationship? (Continued) Exploring Centimetres and Inches You have determined a relationship between centimetres and inches, which can be used to convert lengths or distances. Now, you will determine a relationship to convert areas in inches and centimetres. Hypothesis 1. Do you think the relationship between inches and centimetres is the same as the relationship you found between centimetres and inches? Explain. (example: how would you convert 1 cm to inches?) Data Collection. Measure the area of 5 objects of varying sizes around the classroom. 3. Measure the area of each object two times: once in inches and once in centimetres. 4. Record your results in the table. Object Area in Inches Area in Centimetres Analyze the data 5. Enter your data into a spreadsheet or graphing calculator. 6. Perform a linear regression to obtain the equation of the line of best fit. Line of Best Fit: Interpret your findings 7. Do your findings agree or disagree with your hypothesis? Explain. 8. How do you convert areas given in inches to centimetres? 10. How do you convert areas given in centimetres to inches? MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 5
6 5.1.1: Metric and Imperial: What s the Relationship? (Continued) Exploring Metres and Yards Data Collection 1. Measure 5 objects of varying sizes around the classroom.. Measure each object two times: once in metres and once in yards. 3. Record your results in the table. Object Length in Metres Length in Yards Analyze the data 4. Enter your data into a spreadsheet or graphing calculator. 5. Perform a linear regression to obtain the equation of the line of best fit. Line of Best Fit: Interpret your findings 6. Measure another object in the classroom in metres. Object: Length in metres: 7. Use your line of best fit to calculate the length in yards. 8. Now measure the item in yards. How close was your calculation to your measurement? 9. How do you convert lengths given in metres to yards? 10. How do you convert lengths given in yards to metres? MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 6
7 5.1.: Metric and Imperial Conversions 1. Perform the following conversions using the relationships determined in class today. a) 15 cm = inches b) 0 inches = cm c) 7 3/8 inches = cm d) 10.4 cm = inches e) 6 yards = m f) 18 m = yards g) 4 yards feet = m h) 16 m 5 cm = yards. Another set of distance measurements commonly used are miles and kilometres. a) What unit of distance do you think is longer, a mile or a kilometre? b) There are 1760 yards in a mile. Convert this number to metres. c) How many metres are in a kilometre? d) Which unit of distance is longer, the mile or the kilometre? e) Determine the relationship between miles and kilometres based on your above calculations. 3. Converting areas is not the same as converting distances. Below is a different method you can use to convert areas in different units of measurement if you already know the appropriate conversions for lengths. Convert 16 miles to km by following the steps outlined below. a) Consider 1 mile. Convert the side lengths to kilometres. 1 mile 1 mile 1 mile? km? km? km b) Calculate the area in km. c) Use the information obtained in parts a) and b) to convert 16 miles to km. 4. Use any method to convert 30 inches 3 to cm 3. MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 7
8 5.1.3: Metric and Imperial Conversions (Teacher Notes) Board Note (for Consolidation): Line of Best Fit Line of Best Fit Line of Best Fit (Inches Centimetres) (Inches Centimetres ) (Metres Yards) (Have students write their lines of best fit for each of these scenarios on the board.) There are approximately.54 cm in an inch. There are approximately 6.45 cm in an inch. There are approximately 1.09 yards in a metre. Performing Conversions 1. Perform the following conversions using the relationships determined in class today. a) 5 7/8 inches = cm b) 1. cm = inches inch inch 1 y = = cm 54. x cm = 54. x ( 1. )( 1) =. 54y 1x = ( 54. )( ) 1. = y 54. x 14. 9cm y 83. inches c) 3 yards 1 foot = m d) 14 m 33 cm = yards e) 4 cm = inches f) 15 inches = cm inch 1 z = cm ( 4)( 1) = (. 54) y 4 (. 54) = y y 65. inches. A Canadian Football League playing field is 110 yards by 65 yards. Determine the area of the football field in m. * Allow students to try this question as a think-pair-share. Hopefully you will see at least different solutions (determine the area, then convert to metric; convert the dimensions to metric then determine the area) Instead of,300 kg of fuel, they had,300 pounds on board MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 8
9 Unit 5: Day 5: Minimizing Perimeter Math Learning Goals: Minds On: 10 Determine minimum perimeter for a given area. Compare minimizing perimeter for a set area with maximizing area for a set perimeter Action: 45 Materials Geometer s Sketchpad U5L5_GSP1 BLM BLM 5.5. Consolidate:0 Total=75 min Assessment Opportunities Minds On Think, Pair, Share Discussion Put two questions on the board: 1. Determine the dimensions of the right triangle with a maximum area where the perimeter must be 3 inches.. Determine the dimensions of the right triangle with a minimum perimeter where the area must be 40 inches. Have students discuss with a partner the similarities and differences between these two questions. During the discussion, prompt students to focus on what information is given, what is required to be found, and what process might you go through to solve the problems. Point out to students that the first question was from the previous day s lesson and the second question will be the focus of today s lesson. Action! Individual Investigation Distribute BLM to students and direct them to the GSP file that they should use as an aid in completing the investigation. Reasoning and Proving/Observation/Mental Note: Circulate and give students feedback on their work. Mathematical Process Focus: Reasoning and Proving students are required to investigate several different options and must argue why the option they chose is the best one. Students should have access to U5L5_GSP1 Consolidate Debrief Student Grouping Instructional Strategy Distribute BLM 5.5. and instruct students on how to manually find the dimensions now that we have determined some special relationships (Refer to BLM 5.5. (Teacher notes). (i.e. That the optimal dimensions for a rectangle must be a square and that the optimal dimensions for a right triangle is a right isosceles triangle.) Concept Practice Home Activity or Further Classroom Consolidation Complete questions 1 and at the bottom of BLM 5.5. MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 9
10 5.5.1: Park Beautification A local park s officials have been given a grant to beautify its facilities. Along with new playground equipment and repainting of all the buildings, a garden is to be planted somewhere on the grounds. Three different locations have been chosen for the garden. However, the brick used to line the perimeter of the garden is quite expensive. You will examine the three different locations for a garden area of 0 m and decide which option will be cheapest to border with the chosen brick. Using Geometer s Sketchpad, open the provided file and examine the three different options. Option 1: A Circular Garden with Fountain The beautification committee has chosen the centre of the park as its first option. They would like to build a circular garden and place a fountain in the middle. In this case, there will only be one possible set of dimensions. Determine the radius and circumference of a circle with an area of 0m. Area = 0m Radius = Circumference = Option : A Rectangular Garden Surrounding the Park Sign The committee s second option is near the entrance of the park. Here, the garden would surround the welcome sign to the park. For this case, you must consider at least 8 different dimensions for the length and width of the garden. Remember, you would like an area of 0m and you are trying to minimize the perimeter of the garden. Length Width Area Perimeter Hypothesis: Based on your trials, what do you think are the best dimensions of the garden for this option? MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 10
11 5.5.1: Park Beautification (Continued) Option 3: A Right Triangular Garden Near the Playground The committee s final option is in a corner of the park near the playground. For this case, you must consider at least 8 different dimensions for the height and base of the right triangle. Remember, you would like an area of 0m and you are trying to minimize the perimeter of the garden. Height Base Area Perimeter Hypothesis: Based on your trials, what do you think are the best dimensions of the garden for this option? Selecting the Best Option You have now had a chance to investigate several different options for the placement of a garden in the park. What recommendation would you make to the park beautification committee based on your research? Be sure to justify your recommendation. MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 11
12 5.5.: Calculating Dimensions: Maximum Area / Minimum Perimeter 1. Determine the perimeter of a circle with an area of 144 inches.. Determine the minimum perimeter of a rectangle with an area of 18 mm. 3. Determine the minimum perimeter of a right-angled triangle with an area of 5 ft. Maximizing Area and Minimizing Perimeter: Practise Complete the following questions on lined paper. 1. Determine the maximum area for each of the following shapes. a) a circle with a circumference of 15 cm. b) a rectangle with a perimeter of 34 m. c) a right-angled triangle with a perimeter of 18 mm.. Determine the minimum perimeter for each of the following shapes. a) a circle with an area of 56 yards. b) a rectangle with an area of 9 inches. c) a right-angled triangle with an area of 13 dam. 3. Determine the minimum amount of fencing needed for each of the following: (Note: you will have to create a table for these ones) a) A rectangle garden to be fenced on all 4 sides, with an area of 9 yards. b) A rectangle garden only to be fenced on 3 sides, with an area of 18 yards. c) A rectangle garden only to be fenced on sides, with an area of 36 yards. d) What do you notice about your answers from a c? Why do you think this is the case? MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 1
13 5.5.: Calculating Dimensions: Maximum Area / Minimum Perimeter (Teacher Notes) 1. Determine the perimeter of a circle with an area of 144 inches. A = πr C = π r 144 = πr C = π( 68.) 144 πr = π π C = 4. 7inches 144 π = r 144 π = r r = 68. inches. Determine the minimum perimeter of a rectangle with an area of 18 mm. To get optimal dimensions, we must have a square, so l=w A = l P = 4 l 18 = l P = 44 (.) 18 = l P = 168. mm l = 4. mm 3. Determine the minimum perimeter of a right-angled triangle with an area of 5 ft. A bh = We know from yesterday s work: 5 = bh P = b 104 = bh P = ( 10. ) P = feet but b=h since we have an isosceles triangle 104 = b 104 = b b = 10. feet MAP 4C: Unit 5 Geometry (January January 008) 13
Tallahassee Community College PERIMETER
 Tallahassee Community College 47 PERIMETER The perimeter of a plane figure is the distance around it. Perimeter is measured in linear units because we are finding the total of the lengths of the sides
Tallahassee Community College 47 PERIMETER The perimeter of a plane figure is the distance around it. Perimeter is measured in linear units because we are finding the total of the lengths of the sides
VOLUME of Rectangular Prisms Volume is the measure of occupied by a solid region.
 Math 6 NOTES 7.5 Name VOLUME of Rectangular Prisms Volume is the measure of occupied by a solid region. **The formula for the volume of a rectangular prism is:** l = length w = width h = height Study Tip:
Math 6 NOTES 7.5 Name VOLUME of Rectangular Prisms Volume is the measure of occupied by a solid region. **The formula for the volume of a rectangular prism is:** l = length w = width h = height Study Tip:
Show that when a circle is inscribed inside a square the diameter of the circle is the same length as the side of the square.
 Week & Day Week 6 Day 1 Concept/Skill Perimeter of a square when given the radius of an inscribed circle Standard 7.MG:2.1 Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic twodimensional
Week & Day Week 6 Day 1 Concept/Skill Perimeter of a square when given the radius of an inscribed circle Standard 7.MG:2.1 Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic twodimensional
Imperial Length Measurements
 Unit I Measuring Length 1 Section 2.1 Imperial Length Measurements Goals Reading Fractions Reading Halves on a Measuring Tape Reading Quarters on a Measuring Tape Reading Eights on a Measuring Tape Reading
Unit I Measuring Length 1 Section 2.1 Imperial Length Measurements Goals Reading Fractions Reading Halves on a Measuring Tape Reading Quarters on a Measuring Tape Reading Eights on a Measuring Tape Reading
Characteristics of the Four Main Geometrical Figures
 Math 40 9.7 & 9.8: The Big Four Square, Rectangle, Triangle, Circle Pre Algebra We will be focusing our attention on the formulas for the area and perimeter of a square, rectangle, triangle, and a circle.
Math 40 9.7 & 9.8: The Big Four Square, Rectangle, Triangle, Circle Pre Algebra We will be focusing our attention on the formulas for the area and perimeter of a square, rectangle, triangle, and a circle.
Geometry Notes VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA
 Volume and Surface Area Page 1 of 19 VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the volume of given geometric figures. Calculate
Volume and Surface Area Page 1 of 19 VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the volume of given geometric figures. Calculate
How do you compare numbers? On a number line, larger numbers are to the right and smaller numbers are to the left.
 The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
Perimeter, Area and Volume What Do Units Tell You About What Is Being Measured? Overview
 Perimeter, Area and Volume What Do Units Tell You About What Is Being Measured? Overview Summary of Lessons: This set of lessons was designed to develop conceptual understanding of the unique attributes
Perimeter, Area and Volume What Do Units Tell You About What Is Being Measured? Overview Summary of Lessons: This set of lessons was designed to develop conceptual understanding of the unique attributes
Perimeter, Area, and Volume
 Perimeter, Area, and Volume Perimeter of Common Geometric Figures The perimeter of a geometric figure is defined as the distance around the outside of the figure. Perimeter is calculated by adding all
Perimeter, Area, and Volume Perimeter of Common Geometric Figures The perimeter of a geometric figure is defined as the distance around the outside of the figure. Perimeter is calculated by adding all
Area of Parallelograms (pages 546 549)
 A Area of Parallelograms (pages 546 549) A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The base is any one of the sides and the height is the shortest distance (the length of a perpendicular
A Area of Parallelograms (pages 546 549) A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The base is any one of the sides and the height is the shortest distance (the length of a perpendicular
Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 314 318)
 Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 34 38) Any side of a parallelogram or triangle can be used as a base. The altitude of a parallelogram is a line segment perpendicular to the base
Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 34 38) Any side of a parallelogram or triangle can be used as a base. The altitude of a parallelogram is a line segment perpendicular to the base
Basic Math for the Small Public Water Systems Operator
 Basic Math for the Small Public Water Systems Operator Small Public Water Systems Technology Assistance Center Penn State Harrisburg Introduction Area In this module we will learn how to calculate the
Basic Math for the Small Public Water Systems Operator Small Public Water Systems Technology Assistance Center Penn State Harrisburg Introduction Area In this module we will learn how to calculate the
Teacher Page Key. Geometry / Day # 13 Composite Figures 45 Min.
 Teacher Page Key Geometry / Day # 13 Composite Figures 45 Min. 9-1.G.1. Find the area and perimeter of a geometric figure composed of a combination of two or more rectangles, triangles, and/or semicircles
Teacher Page Key Geometry / Day # 13 Composite Figures 45 Min. 9-1.G.1. Find the area and perimeter of a geometric figure composed of a combination of two or more rectangles, triangles, and/or semicircles
Finding Volume of Rectangular Prisms
 MA.FL.7.G.2.1 Justify and apply formulas for surface area and volume of pyramids, prisms, cylinders, and cones. MA.7.G.2.2 Use formulas to find surface areas and volume of three-dimensional composite shapes.
MA.FL.7.G.2.1 Justify and apply formulas for surface area and volume of pyramids, prisms, cylinders, and cones. MA.7.G.2.2 Use formulas to find surface areas and volume of three-dimensional composite shapes.
Convert between units of area and determine the scale factor of two similar figures.
 CHAPTER 5 Units of Area c GOAL Convert between units of area and determine the scale factor of two. You will need a ruler centimetre grid paper a protractor a calculator Learn about the Math The area of
CHAPTER 5 Units of Area c GOAL Convert between units of area and determine the scale factor of two. You will need a ruler centimetre grid paper a protractor a calculator Learn about the Math The area of
Calculating Area, Perimeter and Volume
 Calculating Area, Perimeter and Volume You will be given a formula table to complete your math assessment; however, we strongly recommend that you memorize the following formulae which will be used regularly
Calculating Area, Perimeter and Volume You will be given a formula table to complete your math assessment; however, we strongly recommend that you memorize the following formulae which will be used regularly
The teacher gives the student a ruler, shows her the shape below and asks the student to calculate the shape s area.
 Complex area Georgia is able to calculate the area of a complex shape by mentally separating the shape into familiar shapes. She is able to use her knowledge of the formula for the area of a rectangle
Complex area Georgia is able to calculate the area of a complex shape by mentally separating the shape into familiar shapes. She is able to use her knowledge of the formula for the area of a rectangle
Demystifying Surface Area and Volume
 Demystifying Surface and Volume CYLINDER 1. Use the net of the cylinder provided. Measure in centimeters and record the radius of the circle, and the length and width of the rectangle. radius = length
Demystifying Surface and Volume CYLINDER 1. Use the net of the cylinder provided. Measure in centimeters and record the radius of the circle, and the length and width of the rectangle. radius = length
Geometry Notes PERIMETER AND AREA
 Perimeter and Area Page 1 of 57 PERIMETER AND AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the area of given geometric figures. Calculate the perimeter
Perimeter and Area Page 1 of 57 PERIMETER AND AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the area of given geometric figures. Calculate the perimeter
Surface Area Quick Review: CH 5
 I hope you had an exceptional Christmas Break.. Now it's time to learn some more math!! :) Surface Area Quick Review: CH 5 Find the surface area of each of these shapes: 8 cm 12 cm 4cm 11 cm 7 cm Find
I hope you had an exceptional Christmas Break.. Now it's time to learn some more math!! :) Surface Area Quick Review: CH 5 Find the surface area of each of these shapes: 8 cm 12 cm 4cm 11 cm 7 cm Find
YOU MUST BE ABLE TO DO THE FOLLOWING PROBLEMS WITHOUT A CALCULATOR!
 DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - SIMPLE GEOMETRIC FIGURES Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you! YOU MUST
DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - SIMPLE GEOMETRIC FIGURES Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you! YOU MUST
Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets
 Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets Year One Maths Target Sheet Key Statement KS1 Maths Targets (Expected) These skills must be secure to move beyond expected. I can compare, describe and solve
Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets Year One Maths Target Sheet Key Statement KS1 Maths Targets (Expected) These skills must be secure to move beyond expected. I can compare, describe and solve
Solids. Objective A: Volume of a Solids
 Solids Math00 Objective A: Volume of a Solids Geometric solids are figures in space. Five common geometric solids are the rectangular solid, the sphere, the cylinder, the cone and the pyramid. A rectangular
Solids Math00 Objective A: Volume of a Solids Geometric solids are figures in space. Five common geometric solids are the rectangular solid, the sphere, the cylinder, the cone and the pyramid. A rectangular
Geometry and Measurement
 The student will be able to: Geometry and Measurement 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the principles of geometry and measurement and operations using measurements Use the US system of measurement for
The student will be able to: Geometry and Measurement 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the principles of geometry and measurement and operations using measurements Use the US system of measurement for
Measurement Length, Area and Volume
 Length, Area and Volume Data from international studies consistently indicate that students are weaker in the area of measurement than any other topic in the mathematics curriculum Thompson & Preston,
Length, Area and Volume Data from international studies consistently indicate that students are weaker in the area of measurement than any other topic in the mathematics curriculum Thompson & Preston,
FCAT FLORIDA COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST. Mathematics Reference Sheets. Copyright Statement for this Assessment and Evaluation Services Publication
 FCAT FLORIDA COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST Mathematics Reference Sheets Copyright Statement for this Assessment and Evaluation Services Publication Authorization for reproduction of this document is hereby
FCAT FLORIDA COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST Mathematics Reference Sheets Copyright Statement for this Assessment and Evaluation Services Publication Authorization for reproduction of this document is hereby
1. Kyle stacks 30 sheets of paper as shown to the right. Each sheet weighs about 5 g. How can you find the weight of the whole stack?
 Prisms and Cylinders Answer Key Vocabulary: cylinder, height (of a cylinder or prism), prism, volume Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) [Note: The purpose of these questions is
Prisms and Cylinders Answer Key Vocabulary: cylinder, height (of a cylinder or prism), prism, volume Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) [Note: The purpose of these questions is
Lesson 18 Pythagorean Triples & Special Right Triangles
 Student Name: Date: Contact Person Name: Phone Number: Teas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills Eit Level Math Review Lesson 18 Pythagorean Triples & Special Right Triangles TAKS Objective 6 Demonstrate
Student Name: Date: Contact Person Name: Phone Number: Teas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills Eit Level Math Review Lesson 18 Pythagorean Triples & Special Right Triangles TAKS Objective 6 Demonstrate
16 Circles and Cylinders
 16 Circles and Cylinders 16.1 Introduction to Circles In this section we consider the circle, looking at drawing circles and at the lines that split circles into different parts. A chord joins any two
16 Circles and Cylinders 16.1 Introduction to Circles In this section we consider the circle, looking at drawing circles and at the lines that split circles into different parts. A chord joins any two
Unit 10 Grade 7 Volume of Right Prisms
 Unit 10 Grade 7 Volume of Right Prisms Lesson Outline Big Picture Students will: develop and apply the formula: Volume = area of the base height to calculate volume of right prisms; understand the relationship
Unit 10 Grade 7 Volume of Right Prisms Lesson Outline Big Picture Students will: develop and apply the formula: Volume = area of the base height to calculate volume of right prisms; understand the relationship
MEASUREMENTS. U.S. CUSTOMARY SYSTEM OF MEASUREMENT LENGTH The standard U.S. Customary System units of length are inch, foot, yard, and mile.
 MEASUREMENTS A measurement includes a number and a unit. 3 feet 7 minutes 12 gallons Standard units of measurement have been established to simplify trade and commerce. TIME Equivalences between units
MEASUREMENTS A measurement includes a number and a unit. 3 feet 7 minutes 12 gallons Standard units of measurement have been established to simplify trade and commerce. TIME Equivalences between units
Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1. 2. 3. 12in
 Area Review Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1 A 2 bh or A bh 2 Solve: Find the area of each triangle. 1. 2. 3. 5in4in 11in 12in 9in 21in 14in 19in 13in
Area Review Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1 A 2 bh or A bh 2 Solve: Find the area of each triangle. 1. 2. 3. 5in4in 11in 12in 9in 21in 14in 19in 13in
Perimeter. 14ft. 5ft. 11ft.
 Perimeter The perimeter of a geometric figure is the distance around the figure. The perimeter could be thought of as walking around the figure while keeping track of the distance traveled. To determine
Perimeter The perimeter of a geometric figure is the distance around the figure. The perimeter could be thought of as walking around the figure while keeping track of the distance traveled. To determine
Scope and Sequence KA KB 1A 1B 2A 2B 3A 3B 4A 4B 5A 5B 6A 6B
 Scope and Sequence Earlybird Kindergarten, Standards Edition Primary Mathematics, Standards Edition Copyright 2008 [SingaporeMath.com Inc.] The check mark indicates where the topic is first introduced
Scope and Sequence Earlybird Kindergarten, Standards Edition Primary Mathematics, Standards Edition Copyright 2008 [SingaporeMath.com Inc.] The check mark indicates where the topic is first introduced
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116
 MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
Lateral and Surface Area of Right Prisms
 CHAPTER A Lateral and Surface Area of Right Prisms c GOAL Calculate lateral area and surface area of right prisms. You will need a ruler a calculator Learn about the Math A prism is a polyhedron (solid
CHAPTER A Lateral and Surface Area of Right Prisms c GOAL Calculate lateral area and surface area of right prisms. You will need a ruler a calculator Learn about the Math A prism is a polyhedron (solid
Volume of Pyramids and Cones
 Volume of Pyramids and Cones Objective To provide experiences with investigating the relationships between the volumes of geometric solids. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms
Volume of Pyramids and Cones Objective To provide experiences with investigating the relationships between the volumes of geometric solids. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 These students are setting up a tent. How do the students know how to set up the tent? How is the shape of the tent created? How could students find the amount of material needed to make the tent? Why
These students are setting up a tent. How do the students know how to set up the tent? How is the shape of the tent created? How could students find the amount of material needed to make the tent? Why
Perimeter is the length of the boundary of a two dimensional figure.
 Section 2.2: Perimeter and Area Perimeter is the length of the boundary of a two dimensional figure. The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference. The perimeter of any two dimensional figure whose
Section 2.2: Perimeter and Area Perimeter is the length of the boundary of a two dimensional figure. The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference. The perimeter of any two dimensional figure whose
TEKS TAKS 2010 STAAR RELEASED ITEM STAAR MODIFIED RELEASED ITEM
 7 th Grade Math TAKS-STAAR-STAAR-M Comparison Spacing has been deleted and graphics minimized to fit table. (1) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student represents and uses numbers in
7 th Grade Math TAKS-STAAR-STAAR-M Comparison Spacing has been deleted and graphics minimized to fit table. (1) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student represents and uses numbers in
43 Perimeter and Area
 43 Perimeter and Area Perimeters of figures are encountered in real life situations. For example, one might want to know what length of fence will enclose a rectangular field. In this section we will study
43 Perimeter and Area Perimeters of figures are encountered in real life situations. For example, one might want to know what length of fence will enclose a rectangular field. In this section we will study
Section 7.2 Area. The Area of Rectangles and Triangles
 Section 7. Area The Area of Rectangles and Triangles We encounter two dimensional objects all the time. We see objects that take on the shapes similar to squares, rectangle, trapezoids, triangles, and
Section 7. Area The Area of Rectangles and Triangles We encounter two dimensional objects all the time. We see objects that take on the shapes similar to squares, rectangle, trapezoids, triangles, and
Measurement. Volume It All Stacks Up. Activity:
 Measurement Activity: TEKS: Overview: Materials: Grouping: Time: Volume It All Stacks Up (7.9) Measurement. The student solves application problems involving estimation and measurement. The student is
Measurement Activity: TEKS: Overview: Materials: Grouping: Time: Volume It All Stacks Up (7.9) Measurement. The student solves application problems involving estimation and measurement. The student is
Pizza! Pizza! Assessment
 Pizza! Pizza! Assessment 1. A local pizza restaurant sends pizzas to the high school twelve to a carton. If the pizzas are one inch thick, what is the volume of the cylindrical shipping carton for the
Pizza! Pizza! Assessment 1. A local pizza restaurant sends pizzas to the high school twelve to a carton. If the pizzas are one inch thick, what is the volume of the cylindrical shipping carton for the
Student Outcomes. Lesson Notes. Classwork. Exercises 1 3 (4 minutes)
 Student Outcomes Students give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle. Students know the formula for the area of a circle and use it to solve problems.
Student Outcomes Students give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle. Students know the formula for the area of a circle and use it to solve problems.
CHAPTER 8, GEOMETRY. 4. A circular cylinder has a circumference of 33 in. Use 22 as the approximate value of π and find the radius of this cylinder.
 TEST A CHAPTER 8, GEOMETRY 1. A rectangular plot of ground is to be enclosed with 180 yd of fencing. If the plot is twice as long as it is wide, what are its dimensions? 2. A 4 cm by 6 cm rectangle has
TEST A CHAPTER 8, GEOMETRY 1. A rectangular plot of ground is to be enclosed with 180 yd of fencing. If the plot is twice as long as it is wide, what are its dimensions? 2. A 4 cm by 6 cm rectangle has
Areas of Polygons. Goal. At-Home Help. 1. A hockey team chose this logo for their uniforms.
 -NEM-WBAns-CH // : PM Page Areas of Polygons Estimate and measure the area of polygons.. A hockey team chose this logo for their uniforms. A grid is like an area ruler. Each full square on the grid has
-NEM-WBAns-CH // : PM Page Areas of Polygons Estimate and measure the area of polygons.. A hockey team chose this logo for their uniforms. A grid is like an area ruler. Each full square on the grid has
Overview. Essential Questions. Grade 8 Mathematics, Quarter 4, Unit 4.3 Finding Volume of Cones, Cylinders, and Spheres
 Cylinders, and Spheres Number of instruction days: 6 8 Overview Content to Be Learned Evaluate the cube root of small perfect cubes. Simplify problems using the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders,
Cylinders, and Spheres Number of instruction days: 6 8 Overview Content to Be Learned Evaluate the cube root of small perfect cubes. Simplify problems using the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders,
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 6th Grade Unit 8
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
Grade 5 Work Sta on Perimeter, Area, Volume
 Grade 5 Work Sta on Perimeter, Area, Volume #ThankATeacher #TeacherDay #TeacherApprecia onweek 6. 12. Folder tab label: RC 3 TEKS 5(4)(H) Perimeter, Area, and Volume Cover: Reporting Category 3 Geometry
Grade 5 Work Sta on Perimeter, Area, Volume #ThankATeacher #TeacherDay #TeacherApprecia onweek 6. 12. Folder tab label: RC 3 TEKS 5(4)(H) Perimeter, Area, and Volume Cover: Reporting Category 3 Geometry
9 Area, Perimeter and Volume
 9 Area, Perimeter and Volume 9.1 2-D Shapes The following table gives the names of some 2-D shapes. In this section we will consider the properties of some of these shapes. Rectangle All angles are right
9 Area, Perimeter and Volume 9.1 2-D Shapes The following table gives the names of some 2-D shapes. In this section we will consider the properties of some of these shapes. Rectangle All angles are right
Measurement with Reasoning
 compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
STUDY PLUS MATHS ON THE FARM LESSON 1
 STUDY PLUS MATHS ON THE FARM LESSON 1 Key word Lesson Starter Main Activity Plenary Resources Convert between units of area Acre hectare square metre square feet Setting the scene photo-story of Arrallas
STUDY PLUS MATHS ON THE FARM LESSON 1 Key word Lesson Starter Main Activity Plenary Resources Convert between units of area Acre hectare square metre square feet Setting the scene photo-story of Arrallas
BPS Math Year at a Glance (Adapted from A Story Of Units Curriculum Maps in Mathematics K-5) 1
 Grade 4 Key Areas of Focus for Grades 3-5: Multiplication and division of whole numbers and fractions-concepts, skills and problem solving Expected Fluency: Add and subtract within 1,000,000 Module M1:
Grade 4 Key Areas of Focus for Grades 3-5: Multiplication and division of whole numbers and fractions-concepts, skills and problem solving Expected Fluency: Add and subtract within 1,000,000 Module M1:
Cylinder Volume Lesson Plan
 Cylinder Volume Lesson Plan Concept/principle to be demonstrated: This lesson will demonstrate the relationship between the diameter of a circle and its circumference, and impact on area. The simplest
Cylinder Volume Lesson Plan Concept/principle to be demonstrated: This lesson will demonstrate the relationship between the diameter of a circle and its circumference, and impact on area. The simplest
Measurement: Converting Distances
 Measurement: Converting Distances Measuring Distances Measuring distances is done by measuring length. You may use a different system to measure length differently than other places in the world. This
Measurement: Converting Distances Measuring Distances Measuring distances is done by measuring length. You may use a different system to measure length differently than other places in the world. This
Quick Reference ebook
 This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
Metric Units of Length
 7.2 Metric Units of Length 7.2 OBJECTIVES. Know the meaning of metric prefixes 2. Estimate metric units of length 3. Convert metric units of length NOTE Even in the United States, the metric system is
7.2 Metric Units of Length 7.2 OBJECTIVES. Know the meaning of metric prefixes 2. Estimate metric units of length 3. Convert metric units of length NOTE Even in the United States, the metric system is
Area is a measure of how much space is occupied by a figure. 1cm 1cm
 Area Area is a measure of how much space is occupied by a figure. Area is measured in square units. For example, one square centimeter (cm ) is 1cm wide and 1cm tall. 1cm 1cm A figure s area is the number
Area Area is a measure of how much space is occupied by a figure. Area is measured in square units. For example, one square centimeter (cm ) is 1cm wide and 1cm tall. 1cm 1cm A figure s area is the number
How does one make and support a reasonable conclusion regarding a problem? How does what I measure influence how I measure?
 Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Mathematics Grade/Course Grade 7 Unit 3 Two and Three Dimensional Geometry Duration 23 instructional days (+4 days reteaching/enrichment)
Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Mathematics Grade/Course Grade 7 Unit 3 Two and Three Dimensional Geometry Duration 23 instructional days (+4 days reteaching/enrichment)
2nd Semester Geometry Final Exam Review
 Class: Date: 2nd Semester Geometry Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The owner of an amusement park created a circular
Class: Date: 2nd Semester Geometry Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The owner of an amusement park created a circular
UNIT 1 MASS AND LENGTH
 UNIT 1 MASS AND LENGTH Typical Units Typical units for measuring length and mass are listed below. Length Typical units for length in the Imperial system and SI are: Imperial SI inches ( ) centimetres
UNIT 1 MASS AND LENGTH Typical Units Typical units for measuring length and mass are listed below. Length Typical units for length in the Imperial system and SI are: Imperial SI inches ( ) centimetres
Volume of Right Prisms Objective To provide experiences with using a formula for the volume of right prisms.
 Volume of Right Prisms Objective To provide experiences with using a formula for the volume of right prisms. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game
Volume of Right Prisms Objective To provide experiences with using a formula for the volume of right prisms. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game
The GED math test gives you a page of math formulas that
 Math Smart 643 The GED Math Formulas The GED math test gives you a page of math formulas that you can use on the test, but just seeing the formulas doesn t do you any good. The important thing is understanding
Math Smart 643 The GED Math Formulas The GED math test gives you a page of math formulas that you can use on the test, but just seeing the formulas doesn t do you any good. The important thing is understanding
SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME
 SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME In this unit, we will learn to find the surface area and volume of the following threedimensional solids:. Prisms. Pyramids 3. Cylinders 4. Cones It is assumed that the reader has
SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME In this unit, we will learn to find the surface area and volume of the following threedimensional solids:. Prisms. Pyramids 3. Cylinders 4. Cones It is assumed that the reader has
Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key
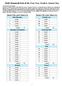 Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key Instructions to the teacher: In order to continue with the Math Mammoth Grade 7 Complete Worktext, I recommend that the student score a minimum of
Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key Instructions to the teacher: In order to continue with the Math Mammoth Grade 7 Complete Worktext, I recommend that the student score a minimum of
Florida Department of Education/Office of Assessment January 2012. Grade 6 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Achievement Level Descriptions
 Florida Department of Education/Office of Assessment January 2012 Grade 6 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Achievement Level Descriptions Grade 6 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Reporting Category Fractions, Ratios, Proportional
Florida Department of Education/Office of Assessment January 2012 Grade 6 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Achievement Level Descriptions Grade 6 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Reporting Category Fractions, Ratios, Proportional
ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Thursday, January 28, 2016 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only
 ALGEBRA I (COMMON CORE) The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Thursday, January 28, 2016 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The
ALGEBRA I (COMMON CORE) The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Thursday, January 28, 2016 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The
GAP CLOSING. Volume and Surface Area. Intermediate / Senior Student Book
 GAP CLOSING Volume and Surface Area Intermediate / Senior Student Book Volume and Surface Area Diagnostic...3 Volumes of Prisms...6 Volumes of Cylinders...13 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders...18
GAP CLOSING Volume and Surface Area Intermediate / Senior Student Book Volume and Surface Area Diagnostic...3 Volumes of Prisms...6 Volumes of Cylinders...13 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders...18
Lesson 11: Volume with Fractional Edge Lengths and Unit Cubes
 Lesson : Volume with Fractional Edge Lengths and Unit Cubes Student Outcomes Students extend their understanding of the volume of a right rectangular prism with integer side lengths to right rectangular
Lesson : Volume with Fractional Edge Lengths and Unit Cubes Student Outcomes Students extend their understanding of the volume of a right rectangular prism with integer side lengths to right rectangular
ACTIVITY: Finding a Formula Experimentally. Work with a partner. Use a paper cup that is shaped like a cone.
 8. Volumes of Cones How can you find the volume of a cone? You already know how the volume of a pyramid relates to the volume of a prism. In this activity, you will discover how the volume of a cone relates
8. Volumes of Cones How can you find the volume of a cone? You already know how the volume of a pyramid relates to the volume of a prism. In this activity, you will discover how the volume of a cone relates
STATE GOAL 7: Estimate, make and use measurements of objects, quantities and relationships and determine acceptable
 C 1 Measurement H OW MUCH SPACE DO YOU N EED? STATE GOAL 7: Estimate, make and use measurements of objects, quantities and relationships and determine acceptable levels of accuracy Statement of Purpose:
C 1 Measurement H OW MUCH SPACE DO YOU N EED? STATE GOAL 7: Estimate, make and use measurements of objects, quantities and relationships and determine acceptable levels of accuracy Statement of Purpose:
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving
Developing Conceptual Understanding of Number. Set J: Perimeter and Area
 Developing Conceptual Understanding of Number Set J: Perimeter and Area Carole Bilyk [email protected] Wayne Watt [email protected] Perimeter and Area Vocabulary perimeter area centimetres right angle Notes
Developing Conceptual Understanding of Number Set J: Perimeter and Area Carole Bilyk [email protected] Wayne Watt [email protected] Perimeter and Area Vocabulary perimeter area centimetres right angle Notes
MATH 110 Landscape Horticulture Worksheet #4
 MATH 110 Landscape Horticulture Worksheet #4 Ratios The math name for a fraction is ratio. It is just a comparison of one quantity with another quantity that is similar. As a Landscape Horticulturist,
MATH 110 Landscape Horticulture Worksheet #4 Ratios The math name for a fraction is ratio. It is just a comparison of one quantity with another quantity that is similar. As a Landscape Horticulturist,
Modeling in Geometry
 Modeling in Geometry Overview Number of instruction days: 8-10 (1 day = 53 minutes) Content to Be Learned Mathematical Practices to Be Integrated Use geometric shapes and their components to represent
Modeling in Geometry Overview Number of instruction days: 8-10 (1 day = 53 minutes) Content to Be Learned Mathematical Practices to Be Integrated Use geometric shapes and their components to represent
EDEXCEL FUNCTIONAL SKILLS PILOT TEACHER S NOTES. Maths Level 2. Chapter 5. Shape and space
 Shape and space 5 EDEXCEL FUNCTIONAL SKILLS PILOT TEACHER S NOTES Maths Level 2 Chapter 5 Shape and space SECTION H 1 Perimeter 2 Area 3 Volume 4 2-D Representations of 3-D Objects 5 Remember what you
Shape and space 5 EDEXCEL FUNCTIONAL SKILLS PILOT TEACHER S NOTES Maths Level 2 Chapter 5 Shape and space SECTION H 1 Perimeter 2 Area 3 Volume 4 2-D Representations of 3-D Objects 5 Remember what you
Kristen Kachurek. Circumference, Perimeter, and Area Grades 7-10 5 Day lesson plan. Technology and Manipulatives used:
 Kristen Kachurek Circumference, Perimeter, and Area Grades 7-10 5 Day lesson plan Technology and Manipulatives used: TI-83 Plus calculator Area Form application (for TI-83 Plus calculator) Login application
Kristen Kachurek Circumference, Perimeter, and Area Grades 7-10 5 Day lesson plan Technology and Manipulatives used: TI-83 Plus calculator Area Form application (for TI-83 Plus calculator) Login application
B = 1 14 12 = 84 in2. Since h = 20 in then the total volume is. V = 84 20 = 1680 in 3
 45 Volume Surface area measures the area of the two-dimensional boundary of a threedimensional figure; it is the area of the outside surface of a solid. Volume, on the other hand, is a measure of the space
45 Volume Surface area measures the area of the two-dimensional boundary of a threedimensional figure; it is the area of the outside surface of a solid. Volume, on the other hand, is a measure of the space
12 Surface Area and Volume
 12 Surface Area and Volume 12.1 Three-Dimensional Figures 12.2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volumes of Pyramids
12 Surface Area and Volume 12.1 Three-Dimensional Figures 12.2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volumes of Pyramids
12-1 Representations of Three-Dimensional Figures
 Connect the dots on the isometric dot paper to represent the edges of the solid. Shade the tops of 12-1 Representations of Three-Dimensional Figures Use isometric dot paper to sketch each prism. 1. triangular
Connect the dots on the isometric dot paper to represent the edges of the solid. Shade the tops of 12-1 Representations of Three-Dimensional Figures Use isometric dot paper to sketch each prism. 1. triangular
Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters
 Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters Name Lesson 8.1: Areas of Rectangle (and Square) and Parallelograms How do we measure areas? Area is measured in square units. The type of the square unit you choose
Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters Name Lesson 8.1: Areas of Rectangle (and Square) and Parallelograms How do we measure areas? Area is measured in square units. The type of the square unit you choose
Applications for Triangles
 Not drawn to scale Applications for Triangles 1. 36 in. 40 in. 33 in. 1188 in. 2 69 in. 2 138 in. 2 1440 in. 2 2. 188 in. 2 278 in. 2 322 in. 2 none of these Find the area of a parallelogram with the given
Not drawn to scale Applications for Triangles 1. 36 in. 40 in. 33 in. 1188 in. 2 69 in. 2 138 in. 2 1440 in. 2 2. 188 in. 2 278 in. 2 322 in. 2 none of these Find the area of a parallelogram with the given
Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: You can see why this works with the following diagrams:
 Area Review Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1 A 2 bh or A bh 2 You can see why this works with the following diagrams: h h b b Solve: Find the area of
Area Review Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1 A 2 bh or A bh 2 You can see why this works with the following diagrams: h h b b Solve: Find the area of
Task: Representing the National Debt 7 th grade
 Tennessee Department of Education Task: Representing the National Debt 7 th grade Rachel s economics class has been studying the national debt. The day her class discussed it, the national debt was $16,743,576,637,802.93.
Tennessee Department of Education Task: Representing the National Debt 7 th grade Rachel s economics class has been studying the national debt. The day her class discussed it, the national debt was $16,743,576,637,802.93.
MATH 100 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM
 MATH 100 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Lecture Version Name: ID Number: Instructor: Section: Do not open this booklet until told to do so! On the separate answer sheet, fill in your name and identification number
MATH 100 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Lecture Version Name: ID Number: Instructor: Section: Do not open this booklet until told to do so! On the separate answer sheet, fill in your name and identification number
Calculating the Surface Area of a Cylinder
 Calculating the Measurement Calculating The Surface Area of a Cylinder PRESENTED BY CANADA GOOSE Mathematics, Grade 8 Introduction Welcome to today s topic Parts of Presentation, questions, Q&A Housekeeping
Calculating the Measurement Calculating The Surface Area of a Cylinder PRESENTED BY CANADA GOOSE Mathematics, Grade 8 Introduction Welcome to today s topic Parts of Presentation, questions, Q&A Housekeeping
Unit #3: Investigating Quadratics (9 days + 1 jazz day + 1 summative evaluation day) BIG Ideas:
 Unit #3: Investigating Quadratics (9 days + 1 jazz day + 1 summative evaluation day) BIG Ideas: Developing strategies for determining the zeroes of quadratic functions Making connections between the meaning
Unit #3: Investigating Quadratics (9 days + 1 jazz day + 1 summative evaluation day) BIG Ideas: Developing strategies for determining the zeroes of quadratic functions Making connections between the meaning
Problem Solving Students will demonstrate their ability to solve problems in mathematics including problems with open-ended answers.
 Title: Designing Our School Garden Brief Overview: This performance-based assessment integrates geometric problem solving with real-world application. Students will design a garden with a variety of flowers
Title: Designing Our School Garden Brief Overview: This performance-based assessment integrates geometric problem solving with real-world application. Students will design a garden with a variety of flowers
A Resource for Free-standing Mathematics Qualifications
 To find a maximum or minimum: Find an expression for the quantity you are trying to maximise/minimise (y say) in terms of one other variable (x). dy Find an expression for and put it equal to 0. Solve
To find a maximum or minimum: Find an expression for the quantity you are trying to maximise/minimise (y say) in terms of one other variable (x). dy Find an expression for and put it equal to 0. Solve
Grade 6 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Sample Questions
 Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
Chapter 4: Area, Perimeter, and Volume. Geometry Assessments
 Chapter 4: Area, Perimeter, and Volume Geometry Assessments Area, Perimeter, and Volume Introduction The performance tasks in this chapter focus on applying the properties of triangles and polygons to
Chapter 4: Area, Perimeter, and Volume Geometry Assessments Area, Perimeter, and Volume Introduction The performance tasks in this chapter focus on applying the properties of triangles and polygons to
Area and Volume Equations
 Area and Volume Equations MODULE 16? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use area and volume equations to solve real-world problems? LESSON 16.1 Area of Quadrilaterals 6.8.B, 6.8.D LESSON 16. Area of Triangles
Area and Volume Equations MODULE 16? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use area and volume equations to solve real-world problems? LESSON 16.1 Area of Quadrilaterals 6.8.B, 6.8.D LESSON 16. Area of Triangles
Measurement/Volume and Surface Area Long-Term Memory Review Grade 7, Standard 3.0 Review 1
 Review 1 1. Explain how to convert from a larger unit of measurement to a smaller unit of measurement. Include what operation(s) would be used to make the conversion. 2. What basic metric unit would be
Review 1 1. Explain how to convert from a larger unit of measurement to a smaller unit of measurement. Include what operation(s) would be used to make the conversion. 2. What basic metric unit would be
Grade 8 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Sample Questions
 Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
Mathematical Modeling and Optimization Problems Answers
 MATH& 141 Mathematical Modeling and Optimization Problems Answers 1. You are designing a rectangular poster which is to have 150 square inches of tet with -inch margins at the top and bottom of the poster
MATH& 141 Mathematical Modeling and Optimization Problems Answers 1. You are designing a rectangular poster which is to have 150 square inches of tet with -inch margins at the top and bottom of the poster
Unit 4 Grade 7 Composite Figures and Area of Trapezoids
 Unit 4 Grade 7 Composite Figures and Area of Trapezoids Lesson Outline Big Picture Students will: investigate, develop a strategy to find the area of and solve problems involving trapezoids; apply number
Unit 4 Grade 7 Composite Figures and Area of Trapezoids Lesson Outline Big Picture Students will: investigate, develop a strategy to find the area of and solve problems involving trapezoids; apply number
Grade 4 Mathematics Measurement: Lesson 1
 Grade 4 Mathematics Measurement: Lesson 1 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
Grade 4 Mathematics Measurement: Lesson 1 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
Objective To introduce a formula to calculate the area. Family Letters. Assessment Management
 Area of a Circle Objective To introduce a formula to calculate the area of a circle. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game Family Letters Assessment
Area of a Circle Objective To introduce a formula to calculate the area of a circle. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game Family Letters Assessment
Fourth Grade Math Standards and "I Can Statements"
 Fourth Grade Math Standards and "I Can Statements" Standard - CC.4.OA.1 Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and
Fourth Grade Math Standards and "I Can Statements" Standard - CC.4.OA.1 Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and
