Lymph Transport and Immunity
|
|
|
- Eleanore Mills
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lymph Transport and Immunity Outline The Lymphatic System Lymph Vessels Lymphoid Organs Nonspecific Defenses Barriers Inflammatory Response Specific Defenses Antibodies T Cells Induced Immunity Active versus Passive Immunity Immunity Side Effects Allergies Blood Typing 2 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 1
2 The Lymphatic System Consists of lymphatic vessels and the lymphoid organs Three main homeostatic functions: Lymphatic capillaries take up and return excess fluid to the bloodstream Lacteals receive lipoproteins and transport them to the bloodstream Helps defend body against disease 3 Lymphatic System 4 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 2
3 The Lymphatic Organs 5 Lymphatic System One-way system that begins with lymphatic capillaries Take up fluid that has been diffused from, and not reabsorbed by, blood capillaries Edema - Localized swelling due to accumulation of tissue fluid Lymph flows one way From a capillary to ever-larger lymphatic vessels Finally to a lymphatic duct, which enters a subclavian vein 6 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 3
4 Lymphoid Organs Lymph Nodes - Capsule surrounding two distinct regions, cortex and medulla Lymphocytes congregate in cortex when fighting off a pathogen Macrophages concentrated in medulla - cleanse lymph Lymph nodes named for their location 7 Tonsils Lymphoid Organs Patches of lymphatic tissue located around the pharynx First to encounter pathogens that enter via the nose and mouth Spleen Located in upper left region of abdominal cavity just beneath diaphragm Cleanses blood 8 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 4
5 Thymus Gland Lymphoid Organs Located along trachea behind the sternum in upper thoracic cavity Produces thymic hormones Red Bone Marrow Origin for all types of blood cells Area of maturation for most white blood cells 9 Immune System Nonspecific Defenses Barriers to entry serve as mechanical barriers Skin Mucous membranes lining respiratory, digestive, and urinary tracts 10 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 5
6 Nonspecific Defenses Inflammatory Reaction Damaged cells and mast cells release histamine and kinins Capillaries dilate and become more permeable Enlarged capillaries cause skin to redden Swollen area and kinins stimulate free nerve endings causing pain 11 Inflammatory Reaction Neutrophils and monocytes migrate to the site of injury Neutrophils and mast cells phagocytize pathogens Monocytes differentiate into macrophages 12 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 6
7 Inflammatory Response 13 Complement System A collection of plasma proteins Activated when pathogens enter the body Complements certain immune responses Interferon binds to receptors of noninfected cells Causes them to prepare for possible attack Produce substances that interfere with viral replication 14 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 7
8 Action of the Complement System Against a bacterium 15 Specific Defenses An antigen is any foreign substance that stimulates the immune system to react Lymphocytes capable of recognizing antigens Have antigen receptors on plasma membrane Protein s shape allow it to combine with a specific antigen 16 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 8
9 Specific Defenses Immunity primarily the result of B lymphocytes B cells give rise to plasma cells Produce antibodies T lymphocytes T cells directly attack cells that bear non-self proteins 17 T Cells Requirements for T cell antigen recognition: Antigen must be presented by an antigenpresenting cell Antigen is first linked to a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein in the plasma membrane Cytokines - signaling chemicals that stimulate various immune cells 18 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 9
10 Cytotoxic T Cells Types of T Cells Destroy antigen-bearing cells Contain Perforins Helper T Cells Regulate immunity by secreting cytokines 19 Humoral (antibody-mediated) immune response Antigen (1st exposure) Engulfed by Cell-mediated immune response Key Stimulates Gives rise to Antigenpresenting cell B cell Helper T cell Cytotoxic T cell Memory Helper T cells Plasma cells Memory B cells Antigen (2nd exposure) Memory Cytotoxic T cells Active Cytotoxic T cells Secreted antibodies Defend against extracellular pathogens by binding to antigens, thereby neutralizing pathogens or making them better targets for phagocytes and complement proteins. Defend against intracellular pathogens and cancer by binding to and lysing the infected cells or cancer cells. 20 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 10
11 Key Humoral (antibody-mediated) immune response Stimulates Gives rise to Antigen (1st exposure) Engulfed by Antigenpresenting cell B cell Helper T cell Memory Helper T cells Plasma cells Memory B cells Antigen (2nd exposure) Secreted antibodies Defend against extracellular pathogens 21 Cell-mediated immune response Antigen (1st exposure) Engulfed by Antigenpresenting cell Key Stimulates Gives rise to Helper T cell Cytotoxic T cell Memory Helper T cells Antigen (2nd exposure) Memory Cytotoxic T cells Active Cytotoxic T cells Defend against intracellular pathogens 22 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 11
12 Helper T Cells: A Response to Nearly All Antigens A surface protein called CD4 binds the class II MHC molecule This binding keeps the helper T cell joined to the antigen-presenting cell while activation occurs Activated helper T cells secrete cytokines that stimulate other lymphocytes 23 Antigenpresenting cell Bacterium Peptide antigen Humoral immunity (secretion of antibodies by plasma cells) Cytokines B cell Class II MHC molecule CD4 TCR (T cell receptor) Helper T cell Cytotoxic T cell Cell-mediated immunity (attack on infected cells) 24 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 12
13 Cytotoxic T Cells: A Response to Infected Cells Cytotoxic T cells are the effector cells in cellmediated immune response Cytotoxic T cells make CD8, a surface protein that greatly enhances interaction between a target cell and a cytotoxic T cell BindingtoaclassIMHCcomplexonaninfected cell activates a cytotoxic T cell and makes it an active killer The activated cytotoxic T cell secretes proteins that destroy the infected target cell 25 Cytotoxic T cell Perforin Granzymes CD8 Class I MHC molecule TCR Target cell Peptide antigen 26 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 13
14 Cytotoxic T cell CD8 Class I MHC molecule TCR Perforin Granzymes Pore Target cell Peptide antigen 27 Released cytotoxic T cell Cytotoxic T cell Perforin Granzymes CD8 Class I MHC molecule TCR Pore Dying target cell Target cell Peptide antigen 28 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 14
15 Cell-mediated Immunity 29 B Cells: A Response to Extracellular Pathogens The humoral response is characterized by secretion of antibodies by B cells Activation of B cells is aided by cytokines and antigen binding to helper T cells Clonal selection of B cells generates antibody-secreting plasma cells, the effector cells of humoral immunity 30 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 15
16 Antigen-presenting cell Bacterium Peptide antigen B cell Class II MHC molecule TCR CD4 Helper T cell Activated helper T cell Cytokines Clone of plasma cells Clone of memory B cells Endoplasmic reticulum of plasma cell Secreted antibody molecules 2 µm 31 Antigen-presenting cell Bacterium Peptide antigen Class II MHC molecule TCR CD4 Helper T cell 32 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 16
17 Antigen-presenting cell Bacterium Peptide antigen B cell Class II MHC molecule TCR CD4 Cytokines Helper T cell Activated helper T cell 33 Antigen-presenting cell Bacterium Peptide antigen B cell Class II MHC molecule TCR CD4 Clone of plasma cells Secreted Cytokines antibody molecules Helper T cell Activated helper T cell Clone of memory B cells 34 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 17
18 Fig Antigen molecules B cells that differ in antigen specificity Antigen receptor Antibody molecules Clone of memory cells Clone of plasma cells 35 Endoplasmic reticulum of plasma cell 2 µm 36 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 18
19 How many antibody classes do have we? Antibody Classes The five major classes of antibodies, or immunoglobulins, differ in distribution and function Polyclonal antibodies are the products of many different clones of B cells following exposure to a microbial antigen Monoclonal antibodies are prepared from a single clone of B cells grown in culture 38 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 19
20 Immunoglobins IgG - Main antibody type in circulation IgM - Found in circulation Largest antibody IgA - Found in secretions IgD - Found on surface of immature B cells IgE - Found as antigen receptors on basophils in blood and on mast cells in tissue 39 Fig Class of Immunoglobulin (Antibody) Distribution Function IgM (pentamer) J chain First Ig class Promotes neutralization and cross- produced after initial exposure to linking of antigens; antigen; then its very effective in concentration in complement system the blood declines activation IgG (monomer) Most abundant Ig class in blood; also present in tissue fluids Promotes opsonization, neutralization, and cross-linking of antigens; less effective in activation of complement system than IgM Only Ig class that crosses placenta, thus conferring passive immunity on fetus IgA (dimer) J chain Present in secretions such as tears, saliva, mucus, and breast milk Provides localized defense of mucous membranes by cross-linking and neutralization of antigens Secretory component Presence in breast milk confers passive immunity on nursing infant IgE (monomer) Present in blood at low concentrations Triggers release from mast cells and basophils of histamine and other chemicals that cause allergic reactions IgD (monomer) Transmembrane region Present primarily on surface of B cells that have not been exposed to antigens Acts as antigen receptor in the antigen-stimulated proliferation and differentiation of B cells (clonal selection) 40 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 20
21 41 Fig a Class of Immunoglobulin (Antibody) Distribution Function IgM (pentamer) J chain First Ig class produced after initial exposure to antigen; then its concentration in the blood declines Promotes neutralization and crosslinking of antigens; very effective in complement system activation 42 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 21
22 43 Fig b Class of Immunoglobulin (Antibody) Distribution Function IgG (monomer) Most abundant Ig class in blood; also present in tissue fluids Promotes opsonization, neutralization, and cross-linking of antigens; less effective in activation of complement system than IgM Only Ig class that crosses placenta, thus conferring passive immunity on fetus 44 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 22
23 45 The Role of Antibodies in Immunity Neutralization occurs when a pathogen can no longer infect a host because it is bound to an antibody Opsonization occurs when antibodies bound to antigens increase phagocytosis Antibodies together with proteins of the complement system generate a membrane attack complex and cell lysis 46 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 23
24 Viral neutralization Virus Opsonization Bacterium Macrophage Activation of complement system and pore formation Complement proteins Formation of membrane attack complex Flow of water and ions Pore Foreign cell 47 Fig c Class of Immunoglobulin (Antibody) IgA (dimer) J chain Distribution Present in secretions such as tears, saliva, mucus, and breast milk Function Provides localized defense of mucous membranes by cross-linking and neutralization of antigens Secretory component Presence in breast milk confers passive immunity on nursing infant 48 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 24
25 49 50 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 25
26 51 Fig d Class of Immunoglobulin (Antibody) IgE (monomer) Distribution Present in blood at low concentrations Function Triggers release from mast cells and basophils of histamine and other chemicals that cause allergic reactions 52 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 26
27 53 54 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 27
28 Fig e Class of Immunoglobulin (Antibody) Distribution Function IgD (monomer) Transmembrane region Present primarily on surface of B cells that have not been exposed to antigens Acts as antigen receptor in the antigen-stimulated proliferation and differentiation of B cells (clonal selection) 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 28
29 57 58 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 29
30 Antibody-Mediated Immunity Clonal selection theory: The antigen selects which lymphocyte will Undergo clonal expansion, and Produce more lymphocytes If the same antigen enters the system again Memory B cells quickly divide Give rise to more lymphocytes capable of quickly producing antibodies 59 Structure of an Antibody 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 30
31 Structure of an Antibody 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 31
32 63 64 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 32
33 Overview of Nonspecific and Specific Defenses 65 Active Immunity Induced Immunity Immunization Pathogens or pathogen products treated to remove virulence Dependent upon memory B cells & memory T cells capable of responding to lower doses of antigen 66 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 33
34 Active Immunity Due to Immunizations 67 Passive immunity Passive Immunity Occurs when an individual is given prepared antibodies (immunoglobins) to combat a disease Short-lived Newborns are often passively immune due to mother s blood 68 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 34
35 Passive Immunity 69 Cytokines and Immunity Cytokines Signaling molecules produced by lymphocytes, monocytes, or other cells Both interferon and interleukins have been used as immunotherapeutic drugs Enhance the ability of the individual s T cells (and B cells) to fight cancer 70 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 35
36 Production of Monoclonal Antibodies 71 Allergies Immunity Side Effects Hypersensitivities to substances that ordinarily would not harm the body Immediate Response IgE antibodies Delayed Response Memory T cells 72 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 36
37 Immunity Side Effects Blood Type Reactions ABO blood typing Two self antigens - A and B If same antigen and its antibody are present in the blood, agglutination occurs Rh blood typing People that are Rh have Rh factor People that are Rh - do not have Rh factor Rh - individuals may produce antibodies to Rh factor if exposed 73 Blood Transfusions 74 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 37
38 Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn 75 Immunity Side Effects Tissue Rejection Antibodies and cytotoxic T cells bring about destruction of foreign tissues in the body Immune system is correctly distinguishing between self and nonself Autoimmune Diseases Cytotoxic T cells or antibodies mistakenly attack the body s own cells 76 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 38
39 Review The Lymphatic System Lymph Vessels Lymphoid Organs Nonspecific Defenses Barriers Inflammatory Response Specific Defenses Antibodies T Cells Induced Immunity Active versus Passive Immunity Immunity Side Effects Allergies Blood Typing 77 國立交通大學生物科技學系陳文亮老師 39
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237)
 Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Immunity. Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity
 Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education. Su et al.
 Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Unit Four. Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
Core Topic 2. The immune system and how vaccines work
 Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins that compete with animal A) Antibodies. B) Red blood cells. C) Transferrin. D) White blood cells. E) Receptors.
 Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
The Human Immune System
 The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer
 Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6
 CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity
 Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Immune and Lymphatic Systems
 1. All of the following organs actively FIGHT pathogens EXCEPT: a. Cervical lymph nodes b. Tonsils c. Spleen d. Thymus e. Axillary lymph nodes 2. T lymphocytes gain immunocompetence within the: a. Bone
1. All of the following organs actively FIGHT pathogens EXCEPT: a. Cervical lymph nodes b. Tonsils c. Spleen d. Thymus e. Axillary lymph nodes 2. T lymphocytes gain immunocompetence within the: a. Bone
IMMUNE SYSTEM. The body s defense against:
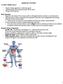 The body s defense against: IMMUNE SYSTEM disease causing organisms or infectious agents malfunctioning cells or abnormal body cells as cancer foreign cells or particles Basic Immunity Depends on the ability
The body s defense against: IMMUNE SYSTEM disease causing organisms or infectious agents malfunctioning cells or abnormal body cells as cancer foreign cells or particles Basic Immunity Depends on the ability
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
The Immune System. How your immune system works. Organs of the Immune System
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION The Immune System How your immune system works The immune system is a network of special cells, tissues, and organs that defend the body against attacks from foreign invaders,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION The Immune System How your immune system works The immune system is a network of special cells, tissues, and organs that defend the body against attacks from foreign invaders,
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
Immune System Memory Game
 Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health
 SCHOLAR Study Guide SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health Authored by: Eoin McIntyre Reviewed by: Sheena Haddow Previously authored by: Mike Cheung Eileen Humphrey Eoin McIntyre
SCHOLAR Study Guide SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health Authored by: Eoin McIntyre Reviewed by: Sheena Haddow Previously authored by: Mike Cheung Eileen Humphrey Eoin McIntyre
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
MISSION DEBRIEFING: Teacher Guide
 Activity on the IMMUNE SYSTEM: The Body Fights Back In this activity, the students will use a hands-on approach to learn about the immune system and how it fights off pathogens that invade the body. They
Activity on the IMMUNE SYSTEM: The Body Fights Back In this activity, the students will use a hands-on approach to learn about the immune system and how it fights off pathogens that invade the body. They
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System
 The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name Date Class. This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread.
 Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Objectives Surface Barriers: Skin and Mucosae 1. Explain the roles of the skin and mucous membranes in the innate defense. 2. List and discuss the secretions
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Objectives Surface Barriers: Skin and Mucosae 1. Explain the roles of the skin and mucous membranes in the innate defense. 2. List and discuss the secretions
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
 Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity CHAPTER 4 04/05/15. Different Immunoglobulins
 Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
Antibody Structure, and the Generation of B-cell Diversity B cells recognize their antigen without needing an antigen presenting cell CHAPTER 4 Structure of Immunoglobulin G Different Immunoglobulins Differences
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation. B cell maturation
 B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer
 Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Some terms: An antigen is a molecule or pathogen capable of eliciting an immune response
 Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6)
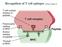 Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
Exercise 9: Blood. Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826.
 Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Immunology. B lymphocytes & Antibodies. 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected]
 Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected] What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected] What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Hypersensitivity. TYPE I Hypersensitivity Classic allergy. Allergens. Characteristics of allergens. Allergens. Mediated by IgE attached to Mast cells.
 Gel and Coombs classification of hypersensitivities. Hypersensitivity Robert Beatty Type I Type II Type III Type IV MCB150 IgE Mediated IgG/IgM Mediated IgG Mediated T cell Classic Allergy rbc lysis Immune
Gel and Coombs classification of hypersensitivities. Hypersensitivity Robert Beatty Type I Type II Type III Type IV MCB150 IgE Mediated IgG/IgM Mediated IgG Mediated T cell Classic Allergy rbc lysis Immune
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Biology 2402 CHAPTER 22 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Pathogens are disease-producing organisms. Survival and good health depends on
Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Biology 2402 CHAPTER 22 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Pathogens are disease-producing organisms. Survival and good health depends on
Understanding the Immune System
 Understanding the Immune System How It Works U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Cancer Institute Understanding
Understanding the Immune System How It Works U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Cancer Institute Understanding
Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute
 Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Immunity and how vaccines work
 1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1
 Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity
 Immunologie II für Naturwissenschaftler Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity Beda M. Stadler Institute of Immunology Inselspital Bern, Switzerland http://www.immunology.unibe.ch/teaching/imm2/immuno2.htm
Immunologie II für Naturwissenschaftler Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity Beda M. Stadler Institute of Immunology Inselspital Bern, Switzerland http://www.immunology.unibe.ch/teaching/imm2/immuno2.htm
Understanding the Immune System
 Understanding the Immune System How It Works U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Artwork by Jeanne Kelly Understanding
Understanding the Immune System How It Works U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Artwork by Jeanne Kelly Understanding
Immunology and Blood Groups
 Immunology and Blood Groups An infectious disease is caused by pathogens, where they are said to be parasitic. Pathogens are organisms that live on or in their host, and gain nutrients from that host.
Immunology and Blood Groups An infectious disease is caused by pathogens, where they are said to be parasitic. Pathogens are organisms that live on or in their host, and gain nutrients from that host.
Immunity Unit Test Z
 Immunity Unit Test Z Name MB Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the pathogens in Figure 31.1 cause disease by taking over healthy
Immunity Unit Test Z Name MB Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the pathogens in Figure 31.1 cause disease by taking over healthy
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
SYSTEM Teacher Pages THE IMMUNE. Your students will learn:
 Grade Level 3-5 Sergeant Cell s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Activity Summary Comparing immune cells with a police team, the webquest activity guides students to research the immune system online.
Grade Level 3-5 Sergeant Cell s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Activity Summary Comparing immune cells with a police team, the webquest activity guides students to research the immune system online.
Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists. Lesson 9.1 Objectives. Chapter 9 Lymphatic and Immune Pathologies. Lymphatic System Overview
 Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists Chapter 9 Lymphatic and Immune Pathologies Lesson 9.1 Objectives Discuss anatomic structures and physiologic processes related to the lymphatic system. Describe
Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists Chapter 9 Lymphatic and Immune Pathologies Lesson 9.1 Objectives Discuss anatomic structures and physiologic processes related to the lymphatic system. Describe
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Candy Antigens and Antibodies
 LAB ACTIVITY: Candy Antigens and Antibodies TEACHER S EDITION Curricular Links: Biology 20, Science 30 Class Time: 1 period Suggested Answers: Question 1: What is the main function of red blood cells?
LAB ACTIVITY: Candy Antigens and Antibodies TEACHER S EDITION Curricular Links: Biology 20, Science 30 Class Time: 1 period Suggested Answers: Question 1: What is the main function of red blood cells?
Chapter 18. Blood Types
 Chapter 18 Blood Types Blood Types blood types and transfusion compatibility are a matter of interactions between plasma proteins and erythrocytes Karl Landsteiner discovered blood types A, B and O in
Chapter 18 Blood Types Blood Types blood types and transfusion compatibility are a matter of interactions between plasma proteins and erythrocytes Karl Landsteiner discovered blood types A, B and O in
gamma globulins immunoglobulin myeloma proteins monoclonal antibodies mab
 Antibodies Molecular structure Antibodies are plasma glycoproteins, called gamma globulins because of their mobility in an electric field and immunoglobulin (Ig) because of their role in immunity. Antibodies
Antibodies Molecular structure Antibodies are plasma glycoproteins, called gamma globulins because of their mobility in an electric field and immunoglobulin (Ig) because of their role in immunity. Antibodies
Thought for the Day. Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis
 Thought for the Day Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Section 2 Lecture
Thought for the Day Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Section 2 Lecture
Food allergy /anaphylaxis
 Food allergy /anaphylaxis A food allergy or hypersensitivity is an abnormal response to a food that is triggered by the immune system. Allergic reactions are often mild, but can be sometimes very dangerous.
Food allergy /anaphylaxis A food allergy or hypersensitivity is an abnormal response to a food that is triggered by the immune system. Allergic reactions are often mild, but can be sometimes very dangerous.
Blood. Blood. Blood Composition. Blood Composition. Fractionation & Hemopoesis
 Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Inflammation and Healing. Review of Normal Defenses. Review of Normal Capillary Exchange. BIO 375 Pathophysiology
 Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Mechanical barriers are a crucial first line of defence. It would be impossible to provide an exhaustive list. Two examples are:
 Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Dendritic Cells: A Basic Review *last updated May 2003
 *last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
*last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) [email protected] 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org
 Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) [email protected] 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) [email protected] 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
VPM 152. INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators
 General Pathology VPM 152 INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION Definition: any messenger that acts on blood vessels, inflammatory cells or other cells to contribute to an
General Pathology VPM 152 INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION Definition: any messenger that acts on blood vessels, inflammatory cells or other cells to contribute to an
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14
 Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Antibody Function & Structure
 Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
The Adaptive Immune System
 Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS.
 TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy. Chapter 7
 Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy Chapter 7 An unborn baby makes no IgG (antibody) and only slowly starts producing it after birth. However, starting at about the sixth month of pregnancy, the
The lymphatic system and the immune system
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 [email protected] www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 [email protected] www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52
 P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY The lymphatic system consists of a fluid called lymph, vessels that convey lymph called lymphatics, and a number of structures
P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY The lymphatic system consists of a fluid called lymph, vessels that convey lymph called lymphatics, and a number of structures
