Microscopy and Cytology
|
|
|
- Hugh Harmon
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microscopy and Cytology Item per class per bench 1. DI Water 6 bottles 1 bottle 2. Methylene Blue 6 bottles 1 bottle 3. Iodine 6 bottles 1 bottle 4. Slide boxes with letter e and thread slides 6 boxes 1 box 5. Slides and cover slips for wet mounts 1box each Varies 6. Toothpicks 6 boxes 1 box 7. Sharpie markers 6 makers 1 marker 8. Model of Cells 2 models Fresh Materials 1. Onion cells 1 onion 1 sample 2. Elodea (aquarium plant) 1 plant 1 leaf 0
2 Microscopy and Cytology Abstract In today s lab you will be viewing tissue samples from plants and animals under the microscope and identifying the various cellular organelles found in each cell type. Because you may be somewhat unfamiliar with the organelles of the cell, it is highly encouraged that you review your textbook for more information on cellular organelles as well as the cell types that you will be viewing today. 1. Using the Compound (light) Microscope Before you can use the microscope in a laboratory setting, you must first learn how it works as well as the function of each part. In this exercise, you will use your assigned microscope to identify each part as well as write a short description of its function. Results: Stage Power switch Ocular Lens Objective Lenses Base Diaphragm Course Focus Fine Focus Light Source Condenser It is the place where you place your slide Turns on the Microscope The place where you look at your sample You can switch them for greater magnification Base of the Microscope used for support Determines the intensity of light Focus your sample Helps focusing with more detail Where the light comes out Focus light into sample Figure 1. Description and function of the components of a light compound microscope. Be prepared to identify parts of the microscope and be able to describe their function! 1
3 2
4 2. Orientations of Images Through the Microscope As light passes through the various slides that you will look at today, that light becomes refracted by the pieces of glass placed in the objective and ocular lenses of the microscope. The result is that the orientation of the subject on the slide being viewed is inverted. This means that the particular specimen you are studying will appear to have rotated 180 from the orientation that it is in when viewed with the naked eye. Here you will practice orienting yourself with this concept by studying a slide of the letter e. 1. Open your slide box and find the slide that has the letter e on it. 2. Place the slide on the microscope so that when you look down at it, the e is in the correct orientation as though you were reading it on a page. 3. Based off of the information in the introductory paragraph draw the e in the orientation that you expect it to be in when you view it on the microscope: 4. Turn on the light source, and set the microscope to the objective. 5. Use the ocular lenses and the focus adjustment knob to bring the image into focus. In the space provided, draw the e as it appears when viewed through the microscope: 3. The Objective Lenses & Depth of Focus Differences Between Objectives. Aside from magnification, the resolution (amount of detail), field of view (total visible surface area of the slide), and depth of focus (how much the focus knobs can be moved while still keeping the image in focus) differ between each of the objective lenses. Using the microscope and what you know about each of these characteristics and objective lenses, fill in the table below. Using a numeric scale (1-4 where 1=greatest and 4=least), rank each of the objectives compared to one another in each listed category. Objective Field of View Resolution Depth of Focus 4X X X X 4 1 Figure 2. Differing characteristics between the microscope objective lenses. 3
5 Using depth of focus, look at a prepared slide with three colored threads (yellow, green, and blue) at 4x and then 10x. 1. Start by viewing the thread using the 4x objective, and bring the slide into focus using the coarse focus adjustment knob. 2. Once the slide is in focus, use the fine focus adjustment knob to focus on the different colored threads. Using this, try to determine which thread is on top, which is in the middle, and which is on the bottom. Color of the thread on top: Color of the thread in the middle: Color of the thread on the bottom: 3. Now change the objective to the 10x objective, and bring the colored thread slide into focus. Again use the fine focus adjustment knob to bring the different colored threads into focus, and attempt to determine which is on top, which is in the middle, and which is on the bottom. Color of the thread on top: Color of the thread in the middle: Color of the thread on the bottom: Questions on depth of focus: 1. When using the fine focus adjustment knob, did each colored thread stay in focus longer when viewed under the 4x objective or under the 10x objective? Depth of focus is defined as how much the focus knob(s) can be moved while still keeping the image in focus. If the depth of focus of an objective lens is high, then the focus knob(s) must be moved more to observe a change in focus of the image. If the depth of focus of an objective lens is lower, the focus knobs do not have to be moved as much to make the image go out of focus. 2. Knowing this and based on your observations of the thread slide, which of the two objective lenses (4x) or (10x) had greater depth of focus, and which had the lesser depth of focus? Greater depth of focus: Lesser depth of focus: 4
6 3. Based off of your answer to question 2, if you were to have viewed the thread slide under the 10x and 40x objective lenses, which do you hypothesize would have had the greater depth of focus, and which would have had the lesser depth of focus? Greater depth of focus: Lesser depth of focus: 3 Preparing Wet Mounts for Microscopy This exercise is directed towards increasing your understanding about preparing wet mounts on microscopic slides and using the compound light microscope. Because microscopes are utilized in all biological classes that follow Biology 1406, it is crucial that you get hands on time and understand how to correctly and efficiently use the microscope. To ensure that you receive this beneficial training, it is highly recommended that if you and your partner choose to divide up tasks, you each take turns using the microscope, so that you can both practice scanning slides, changing objectives, and bringing the slides into focus. Plant cell Animal cell Elodea leaf: 1. Place a drop of water on a microscope slide. 2. Pluck a leaf from the Elodea and place it in the center of the drop of water with its topside facing upwards. 3. Place a coverslip over the leaf. 4. Add one drop of Iodine to the edge of the coverslip, and allow it to diffuse over the leaf. 5. What objective are you going to initially scan this slide with? 4X Check with your instructor to verify that you have selected the correct objective. 6. After you have verified the initial objective, you may slowly move upward in magnification. However, for the leaf, you should NEVER use the 100X objective or the microscope oil. Results: (Verify the answers to these questions with your partner, then verify them with the other group at your table, and, finally, verify them with your instructor) 5
7 a) Please draw the cell as you observe it in the area provided, and label any organelles that you can see: b) Observe this cell. Is it a plant or animal cell? What observations did you use to make your conclusion? Plant cells, because it contains a cell wall. c) What organelles can you see at this magnification level? Indicate those you can see with a checkmark in the appropriate box in figure 3. Write out the functions of each organelle listed. Organelle Observed? At What Magnification Function Nucleus 40x Contains all genes needed to control activities Cell Wall 4x Structural support and protection Plasma Membrane 40x Cells outer membrane, not to be confused with cell wall. Chloroplasts 40x Conduct Photosynthesis. Vacuole n/a Contain organic and inorganic molecules such as enzymes. Cytoplasm 40x Fluid that fills cells. Nucleoli Figure 3. Identification and function of cellular organelles in plant cells (leaf). d) Note which organelles you were not able to see. Why do you think that you are unable to see them? Can you think of any steps that you could take that would help you to better visualize them? Vacuole, might need a different staining method to display 6
8 e) Field of view refers to the diameter of the field, or area of the slide that you are able to observe under a given magnification. When you increase the magnification by changing the objective lens, what do you notice about the breadth of the field or area of the slide that you can see? In other words, do you see more and more of the Elodea leaf as you increase magnification (field of view increasing?) or less and less of the leaf as you increase magnification (field of view decreasing?). You can see less of the Elodea leaf but you are able to see in more detail the sample Take time to identify all of the above mentioned structures in the pictures provided on your bench top. Make sure that you can identify these structures and their functions! Onion cell 1. Remove a fleshy leaf from a red onion and snap the leaf backward to remove a thin layer of epidermis. 2. Place a drop of water on a microscope slide and place the piece of onion in the middle of the drop. 3. Place a coverslip over the slide, add a drop of Iodine at the edge of the cover slip, and allow it to disperse across the sample. 4. Place the slide on the stage of the microscope. 5. What objective are you going to initially scan this slide with? 4x Check with your instructor to verify that you have selected the correct objective. 6. After you have verified the initial objective, you may slowly move upward in magnification. However, for the onion cells, you should NEVER use the 100X objective or the microscope oil. Results: (Verify the answers to these questions with your partner, then verify them with the other group at your table, and, finally, verify them with your instructor.) a. Please draw the cell as you observe it in the area provided, and label any organelles that you can see: 7
9 b) Observe this cell. Is it a plant or animal cell? What observations did you use to make your conclusion? Plant cell, the cell wall is visible. c) What organelles can you see at this magnification level? Indicate those you can see with a checkmark in the appropriate box in figure 4. Write out the functions of each organelle listed. Observed? At What Organelle Function Magnification Nucleus 40x Contains all genes needed to control activities Cell Wall 10x Structural support and protection Plasma Membrane 40x Cells outer membrane, not to be confused with cell wall. Chloroplasts n/a Conduct Photosynthesis. Vacuole n/a Contain organic and inorganic molecules such as enzymes. Cytoplasm 40x Fluid that fills cells. Nucleoli Figure 4. Identification and function of cellular organelles in plant cells (onion). d) Note which organelles you were not able to see. Why do you think that you are unable to see them? Can you think of any steps that you could take that would help you to better visualize them? Vacuole, might need a different staining method to display Stained Cheek cell 1. Gently scrape the inside of your mouth with a toothpick. 2. Obtain one microscope slide and place a drop of water in the center of it. 3. Stir the end of the toothpick into the drop of water. 4. Place a coverslip over the slide. 5. Place the slide on the stage of the microscope. 6. What objective are you going to initially scan this slide with? 4x Check with your instructor to verify that you have selected the correct objective. 7. After you have verified the initial objective, you may slowly move upward in magnification. However, for the cheek cells, you should NEVER use the 100X objective or the microscope oil. 8. What color are the cheek cells before you perform the staining? Transparent 8
10 9. Now take the slide and place a drop of methylene blue on the edge of the coverslip; draw the stain across the coverslip by placing a paper towel or tissue on the opposite side of the coverslip. 10. Again place the slide on the stage of the microscope. 11. What objective are you going to initially scan this slide with? 4x Check with your instructor to verify that you have selected the correct objective. 12. After you have verified the initial objective, you may slowly move upward in magnification. However, for the leaf, you should NEVER use the 100X objective or the microscope oil. 13. What color are the cheek cells after the staining? Blue Results: (Verify the answers to these questions with your partner, then verify them with the other group at your table, and, finally, verify them with your instructor) a) Please draw the cell as you observe it in the area provided, and label any organelles that you can see: b) Observe this cell. Is it a plant or animal cell? What observations did you use to make your conclusion? Animal Cell, it lacks cell wall. 9
11 c) What organelles can you see at this magnification level? Indicate those you can see with a checkmark in the appropriate box in the figure 5. Write out the functions of each organelle listed. Observed? At What Organelle Function Magnification Nucleus 40x Contains all genes needed to control activities Cell Wall n/a Structural support and protection Plasma Membrane 40x Cells outer membrane, not to be confused with cell wall. Chloroplasts n/a Conduct Photosynthesis. Vacuole n/a Contain organic and inorganic molecules such as enzymes. Cytoplasm 40x Fluid that fills cells. Nucleoli Figure 5. Identification and function of cellular organelles in mammalian cells. d) Note which organelles you were not able to see. Why do you think that you are unable to see them? Can you think of any steps that you could take that would help you to better visualize them? In the animal cell, different organelles will not appear due to different type of cell. Take time to identify all of the above mentioned structures in the pictures provided on your bench top. Make sure that you can identify these structures and their functions! 10
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
OBJECTIVES PROCEDURE. Lab 2- Bio 160. Name:
 Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Students will identify these animal cell structures: Students should properly answer the pre-activity cell membrane, nucleus. questions.
 WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
Care and Use of the Compound Microscope
 Revised Fall 2011 Care and Use of the Compound Microscope Objectives After completing this lab students should be able to 1. properly clean and carry a compound and dissecting microscope. 2. focus a specimen
Revised Fall 2011 Care and Use of the Compound Microscope Objectives After completing this lab students should be able to 1. properly clean and carry a compound and dissecting microscope. 2. focus a specimen
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist You may refer to pages 66-67, 72-73 in your textbook for a general discussion of microscopes.
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist You may refer to pages 66-67, 72-73 in your textbook for a general discussion of microscopes.
BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test
 BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test 1. Why is the microscope in our lab called a compound microscope? 2. How do you calculate total magnification? 3. What is the lowest and the maximal magnification
BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test 1. Why is the microscope in our lab called a compound microscope? 2. How do you calculate total magnification? 3. What is the lowest and the maximal magnification
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
 1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology
 Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Use of the Microscope and Cytology
 Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Cells. Introduction WSBCTC 1
 Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Exercise 2. The Compound Light Microscope
 6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
Animal & Plant Cell Slides
 Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
Pre-Lab Questions. 1. What is cell theory? 2. What do all cells contain? 3. What is a prokaryote? 4. What is a eukaryote? 5. What is an organelle?
 Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
Biology. STANDARD II: Objective 3. Osmosis Inquiry Labs
 Biology STANDARD II: Objective 3 Osmosis Inquiry Labs Background Knowledge: Students should have used a microscope before and be familiar with the parts. They should also know how to make a wet mount slide.
Biology STANDARD II: Objective 3 Osmosis Inquiry Labs Background Knowledge: Students should have used a microscope before and be familiar with the parts. They should also know how to make a wet mount slide.
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity
 Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
Osmosis Demonstration Lab
 Osmosis Demonstration Lab Objectives The student will: 1) Observe the effects of different concentrations of salt solutions on potato cores. 2) Infer the relationship between weight loss and rate of osmosis.
Osmosis Demonstration Lab Objectives The student will: 1) Observe the effects of different concentrations of salt solutions on potato cores. 2) Infer the relationship between weight loss and rate of osmosis.
GRADE 7: Life science 1. UNIT 7L.1 7 hours. Specialised cells. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Key vocabulary and technical terms
 GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY
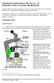 MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
MICROSCOPY. To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope.
 MICROSCOPY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope. To demonstrate skill in the use of ocular and stage micrometers for measurements of cell size. To recognize
MICROSCOPY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope. To demonstrate skill in the use of ocular and stage micrometers for measurements of cell size. To recognize
3.1 Cells and cell function
 BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY
 EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
EXPERIMENT #1: MICROSCOPY Brightfield Compound Light Microscope The light microscope is an important tool in the study of microorganisms. The compound light microscope uses visible light to directly illuminate
LAB 3 Use of the Microscope
 LAB 3 Use of the Microscope Introduction In this laboratory you will be learning how to use one of the most important tools in biology the compound light microscope to view a variety of specimens. You
LAB 3 Use of the Microscope Introduction In this laboratory you will be learning how to use one of the most important tools in biology the compound light microscope to view a variety of specimens. You
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Membrane Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis, and Membrane Transport Introduction... 2 Diffusion and osmosis as related to cellular processes... 2 The hotter the medium, the faster the molecules diffuse... 2 TASK 1: TEMPERATURE
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Membrane Transport Introduction... 2 Diffusion and osmosis as related to cellular processes... 2 The hotter the medium, the faster the molecules diffuse... 2 TASK 1: TEMPERATURE
MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES
 EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
A Fishy Tale. Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope
 A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
Using a Microscope to See Different Types of Cells
 Using a Microscope to See Different Types of Cells copyright 2003 by Dr. Vivianne Nachmias, University of Pennsylvania All organisms are made up of cells - a cell is the simplest collection of matter that
Using a Microscope to See Different Types of Cells copyright 2003 by Dr. Vivianne Nachmias, University of Pennsylvania All organisms are made up of cells - a cell is the simplest collection of matter that
Living things: Cells Living things:
 unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Chapter 4. Microscopy, Staining, and Classification. Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell North Carolina State University
 Chapter 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell North Carolina State University Microscopy and Staining 2012 Pearson Education Inc.
Chapter 4 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell North Carolina State University Microscopy and Staining 2012 Pearson Education Inc.
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Biology Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Biology for Achievement Standard 91160 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Biology for Achievement Standard 91160 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard
Compound microscope (Hund)
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Compound microscope (Hund) 15 16 17 18 19 20 1) Eyepieces (magnifies 10x), one with diopter adjustment, 2) Interp[upillary adjustment, 3) Head, 4) Revolving nosepiece,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Compound microscope (Hund) 15 16 17 18 19 20 1) Eyepieces (magnifies 10x), one with diopter adjustment, 2) Interp[upillary adjustment, 3) Head, 4) Revolving nosepiece,
Discovering cells. The fi rst drawing of cells
 Discovering cells Living things are made of cells. Just as bricks and planks of wood are the building blocks for houses, cells are the building blocks of living things. Cells, although they are very small,
Discovering cells Living things are made of cells. Just as bricks and planks of wood are the building blocks for houses, cells are the building blocks of living things. Cells, although they are very small,
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction
 Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Figure 1. Basic structure of the leaf, with a close up of the leaf surface showing Stomata and Guard cells.
 BIOL100 Laboratory Assignment 3: Analysis of Stomata Name: Stomata (singular=stoma) are the respiratory control structures in plants (see Figure 1 below). They are essentially small holes in the surface
BIOL100 Laboratory Assignment 3: Analysis of Stomata Name: Stomata (singular=stoma) are the respiratory control structures in plants (see Figure 1 below). They are essentially small holes in the surface
Where is Mitosis Most Common in the Onion Root?
 Where is Mitosis Most Common in the Onion Root? Faith Loyd Biology Miss Carpenter February 20, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis, and Prediction The problem in this lab is: To analyze data to see whether mitosis
Where is Mitosis Most Common in the Onion Root? Faith Loyd Biology Miss Carpenter February 20, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis, and Prediction The problem in this lab is: To analyze data to see whether mitosis
THE COMPOUND MICROSCOPE
 THE COMPOUND MICROSCOPE In microbiology, the microscope plays an important role in allowing us to see tiny objects that are normally invisible to the naked eye. It is essential for students to learn how
THE COMPOUND MICROSCOPE In microbiology, the microscope plays an important role in allowing us to see tiny objects that are normally invisible to the naked eye. It is essential for students to learn how
Cellular Membranes I. BACKGROUND MATERIAL
 Cellular Membranes Objectives: 1. To explore the nature of cellular membranes by investigating environmental conditions which stress them. 2. To learn methods for measuring the extent of stress on the
Cellular Membranes Objectives: 1. To explore the nature of cellular membranes by investigating environmental conditions which stress them. 2. To learn methods for measuring the extent of stress on the
Unit 5 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Unit 5 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Advanced Concepts What is the abbreviated name of this molecule? What is its purpose? What are the three parts of this molecule? Label each part with the
Unit 5 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Advanced Concepts What is the abbreviated name of this molecule? What is its purpose? What are the three parts of this molecule? Label each part with the
Impressions of a Stoma
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells
 Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells Background: Because of their rapid growth, the cells of the root tips of plants undergo rapid cell division. Ornamental onion root tips cells
Laboratory Observing the Cell Cycle of Onion Root Tip Cells Background: Because of their rapid growth, the cells of the root tips of plants undergo rapid cell division. Ornamental onion root tips cells
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
7.2 Cells: A Look Inside
 CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 7.2 Cells: A Look Inside Imagine a factory that makes thousands of cookies a day. Ingredients come into the factory, get mixed and baked, then the cookies are packaged.
CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 7.2 Cells: A Look Inside Imagine a factory that makes thousands of cookies a day. Ingredients come into the factory, get mixed and baked, then the cookies are packaged.
CLIL lesson for TKT CLIL Chiara Cappa Liceo Scientifico Respighi - Piacenza. CLIL lesson on cells
 CLIL lesson on cells Time: 1 hour Number of students: 20 Age: 14-15 Level: Pre-intermediate (B1) Subject: Biology Learning outcomes: at the end of the lesson students should be able to: o describe the
CLIL lesson on cells Time: 1 hour Number of students: 20 Age: 14-15 Level: Pre-intermediate (B1) Subject: Biology Learning outcomes: at the end of the lesson students should be able to: o describe the
The Cell Grade Ten. Estimated Duration: Three hours
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark A Explain that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms, that once life originated all cells come from pre-existing cells,
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark A Explain that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms, that once life originated all cells come from pre-existing cells,
Do Not Write on this Quiz Paper (südamlik aitäh)
 1. This makes ribosomes. Cell Organelle Quiz Do Not Write on this Quiz Paper (südamlik aitäh) a. Rough ER c. Golgi apparatus (body) b. Nucleolus d. Mitochondria 2. This is an energy producing organelle.
1. This makes ribosomes. Cell Organelle Quiz Do Not Write on this Quiz Paper (südamlik aitäh) a. Rough ER c. Golgi apparatus (body) b. Nucleolus d. Mitochondria 2. This is an energy producing organelle.
7.1 What Are Cells? You are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. CHAPTER 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 7.1 What Are Cells? Look closely at the skin on your arm. Can you see that it is made of cells? Of course not! Your skin cells are much too small to see with your eyes. Now
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 7.1 What Are Cells? Look closely at the skin on your arm. Can you see that it is made of cells? Of course not! Your skin cells are much too small to see with your eyes. Now
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB)
 Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion
 Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion The plasma membrane enclosing every cell is the boundary that separates the cell from its external environment. It is not an impermeable barrier, but like all biological membranes,
Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion The plasma membrane enclosing every cell is the boundary that separates the cell from its external environment. It is not an impermeable barrier, but like all biological membranes,
7.2 Cell Structure. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Summary. Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and many specialized structures.
 7.2 Cell Structure Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the role of vacuoles, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton. Identify the role of ribosomes, endoplasmic
7.2 Cell Structure Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the role of vacuoles, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton. Identify the role of ribosomes, endoplasmic
DIFFUSION (HYPERTONIC, HYPOTONIC, & ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS) THE GUMMY BEAR LAB PASS
 DIFFUSION (HYPERTONIC, HYPOTONIC, & ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS) THE GUMMY BEAR LAB PASS Have you ever wondered why your fingers have wrinkles after soaking in a bath tub? Your students have probably wondered the
DIFFUSION (HYPERTONIC, HYPOTONIC, & ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS) THE GUMMY BEAR LAB PASS Have you ever wondered why your fingers have wrinkles after soaking in a bath tub? Your students have probably wondered the
Lab 4: Diffusion and Osmosis
 Lab 4: Diffusion and Osmosis Introduction The cell membrane encloses the contents of all cells, organelles and many cytoplasmic inclusions, and regulates what gets in and out. This is called selective
Lab 4: Diffusion and Osmosis Introduction The cell membrane encloses the contents of all cells, organelles and many cytoplasmic inclusions, and regulates what gets in and out. This is called selective
14 The ability of the lenses to distinguish fine detail and structure is called a. Illumination b. Magnification c. Refractive index d.
 1 2 Assume you stain Bacillus by applying malachite green with heat and then counterstain with safranin. Through the microscope, the green structures are a. cell walls. b. capsules. c. endospores. d. flagella.
1 2 Assume you stain Bacillus by applying malachite green with heat and then counterstain with safranin. Through the microscope, the green structures are a. cell walls. b. capsules. c. endospores. d. flagella.
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Look at the back of this paper
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Look at the back of this paper
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
CORAL REEF ECOLOGY. Objectives Students will learn that coral is an animal. Students will learn the differences between plant and animal cells.
 CORAL REEF ECOLOGY Concepts Scientific method Difference between plants and animals cells HCPS III Benchmarks SC 4.1.2 SC 4.4.1 Duration 2 hours Source Material PRISM Vocabulary Cell Cell Membrane Cytosol
CORAL REEF ECOLOGY Concepts Scientific method Difference between plants and animals cells HCPS III Benchmarks SC 4.1.2 SC 4.4.1 Duration 2 hours Source Material PRISM Vocabulary Cell Cell Membrane Cytosol
EXTRACTION OF DNA FROM CALF THYMUS CELLS Revised 2/1/96 Introduction
 Revised 2/1/96 Introduction Cells may be classified into two primary types depending on whether they have a discrete nucleus (eukaryotic) or do not (prokaryotic). Prokaryotes include bacteria, such as
Revised 2/1/96 Introduction Cells may be classified into two primary types depending on whether they have a discrete nucleus (eukaryotic) or do not (prokaryotic). Prokaryotes include bacteria, such as
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS SIMILARITIES IN PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Cells vary widely in structure and function, even within the same organism. The human body, for example, has more than 200 different types of cells, each with a specialized
Chapter 3. Cell Division. Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.
 Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) A - liver; 1 B -brain; 1 C - heart; 1 D - lung; 1 E - kidney; 1. (b) (i) E/kidney; 1. (ii) C/heart; 1.
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 A - liver; 1 B -brain; 1 C - heart; 1 D - lung; 1 E - kidney; 1 (b) (i) E/kidney; 1 C/heart; 1 (iii) B/brain; 1 (iv) D/lungs; 1 QUESTIONSHEET 2 (i) artery; 1 eye; 1 (iii) stomach; 1 (iv)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 A - liver; 1 B -brain; 1 C - heart; 1 D - lung; 1 E - kidney; 1 (b) (i) E/kidney; 1 C/heart; 1 (iii) B/brain; 1 (iv) D/lungs; 1 QUESTIONSHEET 2 (i) artery; 1 eye; 1 (iii) stomach; 1 (iv)
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis
 Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
Cell Unit Practice Test #1
 ell Unit Practice Test #1 Name: ate: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell?. mitochondria.
ell Unit Practice Test #1 Name: ate: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell?. mitochondria.
Fig. 1. Background. Name: Class: Date:
 Background Bubbles make a great stand in for cell membranes. They re fluid, flexible, and can self-repair. Bubbles and cell membranes are alike because their parts are so similar. If you could zoom down
Background Bubbles make a great stand in for cell membranes. They re fluid, flexible, and can self-repair. Bubbles and cell membranes are alike because their parts are so similar. If you could zoom down
MT-30 & MT-90 Series. Advanced Academic Microscopes/ Advanced Academic Polarizing Microscope INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Introduction With your purchase of an MT-30/MT-90 series type microscope you have chosen for a quality product. The MT-30/MT-90 series type microscopes are developed for use at schools and laboratories.
Introduction With your purchase of an MT-30/MT-90 series type microscope you have chosen for a quality product. The MT-30/MT-90 series type microscopes are developed for use at schools and laboratories.
Draw one line from each structure in List A to the correct information about the structure in List B.
 Q. The drawing shows the cell of a bacterium. (a) List A gives the four structures labelled on the diagram. List B includes information about each structure. Draw one line from each structure in List A
Q. The drawing shows the cell of a bacterium. (a) List A gives the four structures labelled on the diagram. List B includes information about each structure. Draw one line from each structure in List A
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
The Cell. Grade 8 Activity Plan
 The Cell Grade 8 Activity Plan Plant Cell Project Objectives: 1. To identify cell organelles and their functions. 2. To demonstrate the difference between plant and animal cells. Keywords/concepts: cells,
The Cell Grade 8 Activity Plan Plant Cell Project Objectives: 1. To identify cell organelles and their functions. 2. To demonstrate the difference between plant and animal cells. Keywords/concepts: cells,
Leaf Structure and Transpiration
 10 LESSON Leaf Structure and Transpiration INTRODUCTION Have you wondered what happens to all that water that disappears from the reservoir of your growing system? Although some might have evaporated from
10 LESSON Leaf Structure and Transpiration INTRODUCTION Have you wondered what happens to all that water that disappears from the reservoir of your growing system? Although some might have evaporated from
CHAPTER 3 OBSERVING MICROORGANISMS THROUGH A MICROSCOPE. I. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT - See Table 3.1 in text. + Fig. 3.2
 CHAPTER 3 OBSERVING MICROORGANISMS THROUGH A MICROSCOPE I. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT - See Table 3.1 in text. + Fig. 3.2 II. MICROSCOPY: THE INSTRUMENTS A. COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPY Figure 3.3 1. Have ocular
CHAPTER 3 OBSERVING MICROORGANISMS THROUGH A MICROSCOPE I. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT - See Table 3.1 in text. + Fig. 3.2 II. MICROSCOPY: THE INSTRUMENTS A. COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPY Figure 3.3 1. Have ocular
Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different?
 Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
B2 1 Cells, Tissues and Organs
 B2 Cells, Tissues and Organs 5 minutes 5 marks Page of 7 Q. The diagram shows a bacterium. On the drawing, name the structures labelled A, B, C and D. (Total 4 marks) Q2. (a) The diagrams show cells containing
B2 Cells, Tissues and Organs 5 minutes 5 marks Page of 7 Q. The diagram shows a bacterium. On the drawing, name the structures labelled A, B, C and D. (Total 4 marks) Q2. (a) The diagrams show cells containing
DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY. To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques.
 DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques. To observe flagella in prepared slides stained by specific flagellar stains. II.
DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques. To observe flagella in prepared slides stained by specific flagellar stains. II.
Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students
 Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students Activity Title: Quick Hit Goal of Activity: To perform formative and summative assessments
Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students Activity Title: Quick Hit Goal of Activity: To perform formative and summative assessments
In order to be useful, a smear must have the following qualities:
 Smear Preparation and Simple Stain Objectives: Make bacterial smear slides (usually called smears) Distinguish cells on these slides using a simple stain procedure Unstained microbial cells are nearly
Smear Preparation and Simple Stain Objectives: Make bacterial smear slides (usually called smears) Distinguish cells on these slides using a simple stain procedure Unstained microbial cells are nearly
Cells Vocabulary List & Definitions
 Cells Vocabulary List & Definitions cytoplasm mitochondrion nucleolus nucleus organ tissue vacuole cell membrane cell wall chlorophyll chloroplast chromosome inherited genetic material in a cell not specified
Cells Vocabulary List & Definitions cytoplasm mitochondrion nucleolus nucleus organ tissue vacuole cell membrane cell wall chlorophyll chloroplast chromosome inherited genetic material in a cell not specified
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
Forensic Science: The Basics. Microscopy
 Forensic Science: The Basics Microscopy Chapter 6 Jay A. Siegel,Ph.D. Power point presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College, Peru Nebraska Presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College CRC Press,
Forensic Science: The Basics Microscopy Chapter 6 Jay A. Siegel,Ph.D. Power point presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College, Peru Nebraska Presentation by Greg Galardi, Peru State College CRC Press,
Given these characteristics of life, which of the following objects is considered a living organism? W. X. Y. Z.
 Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis
 Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points)
 Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
The Effects of Caffeine of Mitosis Rates. Justin Filbert Berwick Area Senior High School 9 th Grade
 The Effects of Caffeine of Mitosis Rates Justin Filbert Berwick Area Senior High School 9 th Grade Research: Caffeine Sources The top 5 Soft Drinks for the year 2013: 1. Coca-Cola (2.83 mg/fl oz) 2. Diet
The Effects of Caffeine of Mitosis Rates Justin Filbert Berwick Area Senior High School 9 th Grade Research: Caffeine Sources The top 5 Soft Drinks for the year 2013: 1. Coca-Cola (2.83 mg/fl oz) 2. Diet
Microscopy. MICROSCOPY Light Electron Tunnelling Atomic Force RESOLVE: => INCREASE CONTRAST BIODIVERSITY I BIOL1051 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MICROSCOPES
 BIODIVERSITY I BIOL1051 Microscopy Professor Marc C. Lavoie [email protected] MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MICROSCOPES MAGNIFY RESOLVE: => INCREASE CONTRAST Microscopy 1. Eyepieces 2. Diopter adjustment
BIODIVERSITY I BIOL1051 Microscopy Professor Marc C. Lavoie [email protected] MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MICROSCOPES MAGNIFY RESOLVE: => INCREASE CONTRAST Microscopy 1. Eyepieces 2. Diopter adjustment
Investigating cells. Cells are the basic units of living things (this means that all living things are made up of one or more cells).
 SG Biology Summary notes Investigating cells Sub-topic a: Investigating living cells Cells are the basic units of living things (this means that all living things are made up of one or more cells). Cells
SG Biology Summary notes Investigating cells Sub-topic a: Investigating living cells Cells are the basic units of living things (this means that all living things are made up of one or more cells). Cells
Chapter 1 Parts C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012
 Chapter 1 Parts C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012 Figure 1.1 illustrates the parts of an upright compound microscope and indicates the terminology that I use in these notes. Figure 1.1. Parts of a Compound
Chapter 1 Parts C. Robert Bagnell, Jr., Ph.D., 2012 Figure 1.1 illustrates the parts of an upright compound microscope and indicates the terminology that I use in these notes. Figure 1.1. Parts of a Compound
the plant & animal cell
 6.1 Basic unit of life Biology Biology Structure & functions of 06 the plant & animal cell In 1665, Robert Hooke observed a section of a cork using a microscope prepared by him. He discovered a structure
6.1 Basic unit of life Biology Biology Structure & functions of 06 the plant & animal cell In 1665, Robert Hooke observed a section of a cork using a microscope prepared by him. He discovered a structure
Plant and Animal Cells
 Plant and Animal Cells Cell Scientists Hans and Zacharias Janssen Dutch lens grinders, father and son produced first compound microscope (2 lenses) Robert Hooke (1665) English Scientist looked at a thin
Plant and Animal Cells Cell Scientists Hans and Zacharias Janssen Dutch lens grinders, father and son produced first compound microscope (2 lenses) Robert Hooke (1665) English Scientist looked at a thin
How To Use An Asbestos Microscope
 Asbestos Microscopes and Accessories Pyser-SGI has been supplying microscopes and accessories into Asbestos Laboratories for over 40 years PS12 Stage Micrometer with UKAS Certificate of Calibration - For
Asbestos Microscopes and Accessories Pyser-SGI has been supplying microscopes and accessories into Asbestos Laboratories for over 40 years PS12 Stage Micrometer with UKAS Certificate of Calibration - For
But what about the prokaryotic cells?
 Chapter 32: Page 318 In the past two chapters, you have explored the organelles that can be found in both plant and animal s. You have also learned that plant s contain an organelle that is not found in
Chapter 32: Page 318 In the past two chapters, you have explored the organelles that can be found in both plant and animal s. You have also learned that plant s contain an organelle that is not found in
UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and the Environment Situations. Cells
 Lesson Summaries HUMAN AND SOCIAL BIOLOGY UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and the Environment Situations Lesson 2 Cells OBJECTIVES At the end of this lesson you will be able to: a) Describe the structure of
Lesson Summaries HUMAN AND SOCIAL BIOLOGY UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and the Environment Situations Lesson 2 Cells OBJECTIVES At the end of this lesson you will be able to: a) Describe the structure of
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life H Biology Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life H Biology Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Protocol for Microscope Calibration
 Protocol for Microscope Calibration A properly calibrated system is essential for successful and efficient software use. The following are step by step instructions on how to calibrate the hardware using
Protocol for Microscope Calibration A properly calibrated system is essential for successful and efficient software use. The following are step by step instructions on how to calibrate the hardware using
The microscope is an important tool.
 KEY CONCEPT Microscopes allow us to see inside the cell. BEFORE, you learned Some organisms are unicellular and some are multicellular A microscope is necessary to study most cells The cell theory describes
KEY CONCEPT Microscopes allow us to see inside the cell. BEFORE, you learned Some organisms are unicellular and some are multicellular A microscope is necessary to study most cells The cell theory describes
06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE)
 DATA SHEET Order code Manufacturer code Description 06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE) The enclosed information is believed to be correct, Information may change without notice due to product
DATA SHEET Order code Manufacturer code Description 06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE) The enclosed information is believed to be correct, Information may change without notice due to product
Diffusion and Osmosis
 Diffusion and Osmosis OBJECTIVES: 1. To explore how different molecules move by diffusion and osmosis through semi-permeable membranes. 2. To understand how different concentration gradients affect the
Diffusion and Osmosis OBJECTIVES: 1. To explore how different molecules move by diffusion and osmosis through semi-permeable membranes. 2. To understand how different concentration gradients affect the
LAB 24 Transpiration
 Name: AP Biology Lab 24 LAB 24 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences
Name: AP Biology Lab 24 LAB 24 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences
Measuring the Point Spread Function of a Fluorescence Microscope
 Frederick National Laboratory Measuring the Point Spread Function of a Fluorescence Microscope Stephen J Lockett, PhD Principal Scientist, Optical Microscopy and Analysis Laboratory Frederick National
Frederick National Laboratory Measuring the Point Spread Function of a Fluorescence Microscope Stephen J Lockett, PhD Principal Scientist, Optical Microscopy and Analysis Laboratory Frederick National
