MODULE SIX. Impact of Alcohol on Fetal Development
|
|
|
- Mervin Willis
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MODULE SIX Impact of Alcohol on Fetal Development Teratogens Paternal Alcohol Use Fetal Development Brain Function Basic Brain Anatomy Impact of Alcohol on a Developing Fetal Brain
2 Impact of Alcohol on Fetal Development TERATOGENS A teratogen is an environmental substance that interferes with the normal development of the fetus, causing fetal death or congenital abnormalities (a condition or defect that exists at birth) (University of Virginia, 2006). Teratogens can be classified into four categories (Berk & Shanker, 2006), including: radiation maternal infections (measles/rubella, HIV, hepatitis) chemicals (mercury, lead) drugs, such as thalidomide (a drug given to pregnant women for morning sickness that caused birth defects) and alcohol Alcohol is the most common teratogen used by women during pregnancy. Alcohol is called a neurobehavioural teratogen because it can cause injury to the brain that results in behavioural problems. Stratten, Howe, & Battaglia (1996) state that of all the substances of abuse (including cocaine, heroin, and marijuana), alcohol produces by far the most serious neurobehavioural effects in the fetus. The harm done by alcohol and other teratogens is not always straightforward. There are many factors that determine the resulting damage. These are: dose or amount of exposure genetic makeup and resilience of the mother and developing infant time of exposure other influences, such as nutrition, medical care, and the interplay with other teratogens The time of alcohol exposure is especially important given the concept of sensitive periods of development (Berk & Shanker, 2006). A sensitive period (critical period) is a span of time in which a specific body part and/or system are in rapid development, and therefore, the effects of a teratogen can be most devastating. For example, although the brain develops throughout the entire pregnancy, it goes through a highly sensitive period between 4-12 weeks, the embryonic period. If alcohol is consumed during this period of rapid brain development, damage can be most severe. Page 1
3 Alcohol s potential effects on the developing fetus central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) include (Chudley et al., 2005): cell death interference with neural connections changes in the normal migration of cells reducing the neuronal pathways, or connections, between cells altering the neurochemistry reducing myelination of the axons PATERNAL ALCOHOL USE There is little known about the effect of paternal drinking before conception on pregnancy and outcomes (Passaro et al., 1998). It is important, however, to note that there have not been any cases of FASD documented where there was no maternal alcohol use during pregnancy (Abel, 1998). Alcohol consumed by the mother can only affect the fetus after the placenta and umbilical cord are established. There have been studies involving animals and the paternal use of alcohol. These studies have shown that paternal use of alcohol among animals is associated with a number of genetic conditions, birth defects, reduced fertility, reduced percentage of pregnancies carried to term, fetal development, and higher fetal mortality (Cicero et al., 1994; Tanaka, Suzuki, & Arima, 1982). There have also been behavioural attributes associated with paternal exposure to alcohol. These include: hyperactivity, changes in adult locomotor activity, decreased ability to deal with stress, and a variety of learning and memory deficits (Cicero, 1994; Bielawski & Abel, 1996; Ledig et al., 1998; Abel, 1993). While it is impossible to extrapolate these findings to humans, it is important to consider the genetic implications of alcohol exposure derived from the field of animal studies (Gearing et al., 2005, pp 3). FETAL DEVELOPMENT In order to understand how alcohol creates damage in a developing fetus, one needs to have a basic understanding of how a baby develops throughout pregnancy. Knowledge about how alcohol interferes with normal fetal development is also important. The Beginning of Life At the very beginning stage of pregnancy, the egg and sperm fuse to form the developing baby called a zygote. The single cell multiplies for the first two weeks, and becomes a blastocyst, a hollow ball of cells. At about day 7 9, implantation occurs; that is, the blastocyst connects itself to the lining of the woman s uterus (Bolane, 1991). At this time, there are a number of structures that begin to form. These structures include the amnion, chorion, yolk sac, placenta and umbilical cord and their roles, described on the next page, are to nourish and protect the developing zygote (Berk & Shanker, 2006). Page 2
4 A membrane called the amnion forms around the zygote and this protects the zygote with amniotic fluid. This fluid maintains a constant temperature and provides a soft ride ; a cushion against the movements of the mother. The yolk sac produces blood cells for the baby until the developing liver, spleen and bone marrow are able to do their jobs. The chorion is a further layer of protection and surrounds the amnion. The chorion develops tiny, hair-like blood vessels that will burrow into the wall of the uterus, and the placenta then begins to develop. The placenta brings the mother s and embryo s blood systems close together but does not allow them to mix (Berk & Shanker, 2006). The membrane that separates the systems allows nutrients and oxygen from the mother s bloodstream to enter the embryo s bloodstream through the process of diffusion into the umbilical vein. Fetal waste products are then returned to the mother via the umbilical arteries to the placenta and through the protective membrane into the maternal blood vessels. Once this system of exchange exists between the mother and the developing baby, anything in the mother s blood can now cross over to the baby s blood. Three Trimesters of Pregnancy Pregnancy is divided into three equal parts or trimesters. Each trimester is approximately 12 weeks (3 months) long. Table 6.1: Development of zygote, embryo & fetus within three trimesters of pregnancy First Trimester 0-12 weeks Second Trimester weeks Third Trimester weeks 0-3 weeks: Zygote 3-9 weeks: Embryo 9-12 weeks: Fetus Fetus Fetus First Trimester (0-3 months) The first trimester is a time when the cells of the zygote divide, become implanted in the lining of the uterus and develop the necessities to continue life. Alcohol consumed at this time may cause cell death or problems with implantation (Berk & Shanker, 2006). Three weeks after the sperm cell enters the egg, the developing baby is no longer referred to as a zygote, and is now called an embryo. During the five weeks the baby is called an embryo (3-9 weeks), the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and major organs develop. In fact, the heart starts to beat 3 weeks after conception and brain waves are recorded at 6 weeks. This is the most sensitive period for damage to the CNS and the structure of the face (Berk & Shanker, 2006). This is a time when the most damage occurs to all body parts and systems. It is important to note that maternal use of alcohol past this stage of development can still damage the growing fetus. Page 3
5 At nine weeks, the baby is now referred to as a fetus (Berk & Shanker, 2006). This is often referred to as the period of growth and finishing. The brain, spinal cord, organs and muscles become more organized and begin to work together. Connections are made so that the fetus has the capability for movement and behaviour. This is when ultrasounds reveal kicking, arm and hand movements, thumb sucking, and mouth opening. By 12 weeks, all of the body systems, with the exception of the immune system, are working. Second Trimester (3-6 months) In the second trimester of pregnancy, the developing fetus continues to grow and mature. The mother can usually begin to feel her baby moving inside her at around 4½ months. By the end of the second trimester, most of the brain s neurons are present. Details such as eyelashes, eyebrows, and hair are apparent. Third Trimester (6-9 months) Development from this point on is mostly size and maturation. The brain, however, continues to develop during the entire pregnancy. The cerebral cortex, the basis of human intelligence, gets bigger. During this period of brain development, the grooves and convolutions characteristic of adult brains deepen, thereby increasing brain size and capacity without increasing head size. Maternal use of alcohol can damage the fetus and the brain at any point during the pregnancy. BRAIN FUNCTION The brain is extremely complex and no one completely understands its capacities. Once fully developed, the adult brain weighs between 1 and 1.5 kg (about 3 pounds) containing about 100 billion nerve cells. Ongoing neuroscience research continues to discover new information that extends our understanding of human behaviour and functioning. Page 4
6 BASIC BRAIN ANATOMY The brain is divided into three parts. Table 6.2: Parts of the Brain Structure Forebrain Midbrain Hindbrain Description includes the cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus and is the largest part of the brain with the highest intellectual functioning located at the top of the brain stem, it contains centres that receive information and then make sense of it; relays auditory and visual information contains the pons, medulla oblongata and the cerebellum and acts somewhat like the body s computer, regulating automatic processes The following anatomical description of the brain includes the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellum and the brain stem. Cerebrum: This is the largest brain structure. It is identified by a grooved appearance and is the top portion of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, the right and the left. The cerebrum is called the thinking part of the brain. The nerve centers for thought, communication, personality, the senses and voluntary movement are in the cerebrum (Encyclopedia Britannica & Fine, 2008). Within the cerebrum there are four main sections/lobes. Table 6.3: Four Lobes of the Cerebrum Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Parietal Lobe Frontal Lobe Description located at the back of the brain processes visual images by interpreting the signals sent by the eyes located above the ear and behind the temple processes sound and, in turn, language because the temporal lobe is connected to the hippocampus, it also functions in memory formation and retention (Encyclopedia Britannica & Fine, 2008). located behind the frontal lobe and at the top of the head integrates information from various bodily senses such as touch, pressure and pain passes this information to the cerebral cortex and only then can the information be processed in the parietal lobe. largest of the lobes and is located behind the forehead responsible for the executive functioning of the brain. It is the intelligence centre of the brain performs abstract intellectual functions such as understanding cause and effect and connecting consequences to the preceding action, as well as being the centre for critical thinking, problem solving, decision making, self-control and self regulation controls complex movement and speech. Page 5
7 The cerebrum also contains the basal ganglia and corpus callosum. Basal ganglia are structures deep within the cerebrum that are very important in fine motor coordination. Corpus callosum is a thick flat bundle of nerve fibres that transfers information between the two hemispheres of the brain so that the two halves can work together to analyze situations. Diencephalon : This part of the brain contains the thalamus and hypothalamus, along with a number of other components including the pituitary gland. The diencephalon is located below the cerebrum. (Society for Neuroscience, 2008; Parker, 2007). Table 6.4: Parts of the Diencephalon Structure Thalamus Hypothalamus Description relays most of the sensory and motor information to the various parts of the cerebrum shaped like two eggs, which are masses of nerve tissue. located below the thalamus and secretes hormones helps to control the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system, which maintains the constant conditions of the body. sympathetic division mobilizes the energy and resources of the body, while the parasympathetic division conserves energy and resources is essential to what an individual finds rewarding from sex, music, alcohol and drugs to maternal behaviour. (Gibb, 2007) Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located at the bottom and back of the brain and is connected to the brain stem. It is divided into two hemispheres, contains approximately half of the brain s neurons and provides the coordination of voluntary movement. If one of the hemispheres of the cerebellum is damaged, the same side of the body and its movement will be affected. (Encyclopedia Britannica & Fine, 2008). Table 6.5: Parts of the Cerebellum Structure Description Parts of Structure Brainstem located at the base of the brain and the top of the spinal cord and reaches into approximately the middle of the brain or at a level behind the eyes Medulla oblongata is responsible for the automatic functions that keep the body alive such as the heartbeat and breathing Pons, helps to regulate automatic functions and sends messages from the spinal cord to the forebrain and back again. The midbrain is the top of the brainstem. Page 6
8 Limbic System referred to as the primitive brain, influences instinctive behaviour such as the fight or flight reaction to a situation behaviours triggered by the limbic system can be controlled most of the time by the higher functioning components of the brain Amygdala is located beneath the hypothalamus; it plays an important role in emotional responses such as fear, anger, sexual desire and how the individual relates to the world and people around him or her. Hippocampus helps in the recognition of new experiences and amalgamating memories to help the individual in his or her responses to situation. Neurotransmission in the Brain There are over 100 billion neurons in the brain and many more glial cells that support the neurons. The components of the brain communicate with each other. This communication within the brain and with other systems of the body happens because of the nerves and neurons in the brain and body. Table 6.6: Neurons and Parts of Neurons Structure Neuron Axons Dendrites Synapse Glial Cells Description has a cell body with a nucleus along with branch-like structures that are called axons and dendrites. These branch-like structures send and receive messages. send signals away from the cell body to other neurons receive signals from other neurons and move them toward the cell body of the neuron. is the very small gap between two neurons that allows neurotransmission to occur through an electrical impulse that causes a chemical to be released from the sending neuron to the receiving neuron. are cells that surround, support, protect and feed the neurons. If neurotransmission within the brain is altered, individuals may have difficulties with things like sleep, depression and anxiety or insensitivity to pain. Page 7
9 IMPACT OF ALCOHOL ON A DEVELOPING FETAL BRAIN Table 6.7: Impact of Alcohol on a Developing Fetal Brain Brain Area Type of Damage Impact Corpus Callosum Cerebellum Basal Ganglia Grey and White Matter Agenesis (failure to grow) Displacement Surface area reductions (anterior and posterior) Variability in shape Neuropsychological deficits, particularly impacting bimanual coordination, verbal learning and executive function Related to difficulties with balance, attention, conditioning, verbal learning and memory Smaller volume Smaller surface area Displacement Reduction in cranial vault size (space inside the skull that the brain occupies) Smaller volume Affects executive functioning, attention and response inhibition Abnormalities of density and distribution. Reduction in glucose metabolism Thalamus and Caudate Decreased cerebral blood flow Decrease dopamine and serotonin neurotransmission Cranium Reduction in cranial vault size (Fryer et al., 2009; Spadoni et al., 2006) Causes irregular cortical thinning Linked to executive dysfunction and visual processing deficits Delayed communication of sensory and motor information Decreases inhibition Page 8
10 Activities Activity 6.1: Alcohol Can Fry the Brain Purpose: To provide a visual representation or metaphor showing that alcohol can damage a fetus brain. Materials: One raw egg One wine glass One ounce of alcohol Instructions: Break the raw egg into the glass and add alcohol. Watch the clear part of the egg develop white streaks as the alcohol cooks it. This represents an infant s brain that is exposed to alcohol. Check back occasionally to see how it changes. Discussion: 1. If alcohol can do this to an egg, what affect does it have on a fetus? Activity 6.2: 4 Week Fetus Teaching Model Purpose: To provide a visual, life-like reference with details about the development that has occurred up to that time. Materials (found in the Resource Kit): Four week fetus from Maternal Source Laminated fetal development statement cards Instructions: If you have a small group, hand out laminated development description cards and have participants read them out loud to the group. Pass around the fetal model so participants can hold it in their hand if they wish. Discussion: 1. If there are pregnant women in the audience, relate it to them. Page 9
11 Activity 6.3: 12 Week Fetus Teaching Model Purpose: To provide a visual, life-like reference with details about the development that has occurred up to that time. Materials (found in the Resource Kit): 12 week fetus from Maternal Source Laminated fetal development statement cards Instructions: If you have a small group, hand out laminated development description cards and have participants read them out loud to the group. Pass around the fetal model so participants can hold it in their hand if they wish. Discussion: 1. If there are pregnant women in the audience, relate it to them. VIDEOS YouTube: Human Reproduction: Fertilization and Fetal Development YouTube: You Make Me Feel (ilathedreamer, 2008) DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. What are some common teratogens? Radiation Maternal infections (rubella, HIV, hepatitis) Chemicals (mercury, lead) Drugs (thalidomide, alcohol) 2. Can a father s alcohol use affect the fetus? Paternal alcohol use cannot cause FASD There have been some studies with animals that show that paternal use of alcohol is associated with some genetic conditions, birth defects, reduced fertility, and higher fetal mortality. There have also been some behavioural attributes associated with paternal alcohol use. These include: hyperactivity, changes in adult locomotor activity, decreased ability to deal with stress, and a variety of learning and memory deficits. Page 10
12 References Abel, E. L. (1993). Rat offspring sired by males treated with alcohol. Alcohol, 10(3), Abel, E. L. (1998). Protecting fetuses from certain harm. Politics and the Life Sciences, 17(2), Berk, L. E. & Shanker, S. G. (2006). Child development (2 nd ed.). Bielawski, D. M., & Abel, E. L. (1996). Acute treatment of paternal alcohol exposure produces malformations in offspring. Alcohol, 14(4), Bolane, J. E. (1991). Life unto life: Fetal growth and development. Rochester, NY: Childbirth Graphics Ltd. Chudley, A. E., Conry, J., Cook, J. L., Loock, C., Rosales, T., & LeBlanc, N. (2005). Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: Canadian guidelines for diagnosis. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 172(Suppl. 5), S1- S21. Cicero, T. J. (1994). Effects of paternal exposure to alcohol on offspring development. Alcohol Health and Research World, 18(1), Cicero, T. J., Nock, B., O'Connor, L. H., Sewing, B. N., Adams, M. L., & Meyer, E. R. (1994). Acute paternal alcohol exposure impairs fertility and fetal outcome. Life Sciences, 55(2), PL Encyclopedia Britannica and Fine, C. (2008). The Britannica Guide to the Brain: A guided tour of the brain mind, memory, and intelligence. Philadelphia. Running Press Book Publishers. Fryer, S. L., Schweinsburg, B. C., Bjorkquist, O. A., Frank, L. R., Mattson, S. N., Spadoni, A. D. & Riley, E. P. (2009). Characterization of white matter microstructure in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 33 (3), 1-8. Gearing, R. B., McNeill, T., & Fernand, A. L. (2005). Father involvement and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: Developing best practices. Journal of FAS International, 3(e14), Ledig, M., Misslin, R., Vogel, E., Holownia, A., Copin, J. C., & Tholey, G. (1998). Paternal alcohol exposure: Developmental and behavioral effects on the offspring of rats. Neuropharmacology, 37(1), Parker, S. (2007). The Human Body Book. New York. Dorling Kindersley Limited. Passaro, K. T., Little, R. E., Savitz, D. A., & Noss, J. (1998). Effect of paternal alcohol consumption before conception on infant birth weight. Teratology, 57(6), Society for Neuroscience. (2008). Brain Facts: A Primer on the Brain and Nervous System. Washington, DC. Spadoni, A. D., McGee, C. L., Fryer, S. L. & Riley, E. P. (2006). Neuroimaging and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Review, 31, Page 11
13 Stratton, K., Howe, C., Battaglia, F. C. (1996). Fetal alcohol syndrome: Diagnosis, epidemiology, prevention, and treatment. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine and National Academy Press. Tanaka, H., Suzuki, N., & Arima, M. (1982). Experimental studies on the influence of male alcoholism on fetal development. Brain & Development, 4(1), 1-6. University of Virginia. (2006). Medical genetics: Teratogens. Retrieved February 20, 2009, from Page 12
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo
 Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Developing Human Fetus
 Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
Period Date LAB. DEVELOPMENT OF A HUMAN FETUS After a human egg is fertilized with human sperm, the most amazing changes happen that allow a baby to develop. This amazing process, called development, normally
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Human Embryonic Development. Human fetal development
 Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse
 Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 4 Prenatal Development and Birth PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 4 Prenatal Development and Birth PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
 STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
STAGES OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT College of William and Mary Students for Life 2013 Germinal Period From conception to implantation Terms to Know Conception: the first stage in human development in which
Chapter Fourteen. Emotion, Reward, Aggression, and Stress
 Chapter Fourteen Emotion, Reward, Aggression, and Stress EMOTIONS! Emotions generally include a Physical component, and a Subjective component or quality, and a Valence Emotions a product of Evolution?
Chapter Fourteen Emotion, Reward, Aggression, and Stress EMOTIONS! Emotions generally include a Physical component, and a Subjective component or quality, and a Valence Emotions a product of Evolution?
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Table of Contents. Neurotra nsmission F act Sh eet Page 2. Neurotransmission Scavenger Hunt Page 4. Brain Parts Fact Sheet Page 6
 Table of Contents Neurotra nsmission F act Sh eet Page 2 Neurotransmission Scavenger Hunt Page 4 Brain Parts Fact Sheet Page 6 Nicotine and the Brain Page 8 Alcohol and the Brain Page 10 Puzzle Pieces
Table of Contents Neurotra nsmission F act Sh eet Page 2 Neurotransmission Scavenger Hunt Page 4 Brain Parts Fact Sheet Page 6 Nicotine and the Brain Page 8 Alcohol and the Brain Page 10 Puzzle Pieces
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Embryology. From Conception through Birth. From Conception through Death
 Embryology From Conception through Birth From Conception through Death - Immune system 18 months after birth - Lungs 3-8 years after birth - Nervous 12 years after birth - Reproductive Puberty - Skeletal
Embryology From Conception through Birth From Conception through Death - Immune system 18 months after birth - Lungs 3-8 years after birth - Nervous 12 years after birth - Reproductive Puberty - Skeletal
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function?
 How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Brain Development. Genetic make-up... is not the major determiner
 Brain Development Presented by: Linda Alsop SKI-HI Institute Utah State University Genetic make-up... is not the major determiner Early experiences are so powerful that they can completely change the way
Brain Development Presented by: Linda Alsop SKI-HI Institute Utah State University Genetic make-up... is not the major determiner Early experiences are so powerful that they can completely change the way
ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE
 ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and the Action of Nicotine, Cocaine, and Marijuana in the Brain Te a c h e r s G u i d e Films for the Humanities & Sciences Background Information This program, made entirely of
ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and the Action of Nicotine, Cocaine, and Marijuana in the Brain Te a c h e r s G u i d e Films for the Humanities & Sciences Background Information This program, made entirely of
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics
 Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cells. Part 1: What is a Stem Cell?
 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become
It s All in the Brain!
 It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Chapter 3 The Brain and Behavior
 Chapter 3 The Brain and Behavior Learning Goals 1. Discuss the nature and basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain what neurons are and how they process information. 3. Identify the brain s levels
Chapter 3 The Brain and Behavior Learning Goals 1. Discuss the nature and basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain what neurons are and how they process information. 3. Identify the brain s levels
the puzzle packet! Brought to you by
 the puzzle packet! Brought to you by It s Mindboggling! word search The following brain-related words all appear in It s Mindboggling! How many can you find? Words may appear in all directions, including
the puzzle packet! Brought to you by It s Mindboggling! word search The following brain-related words all appear in It s Mindboggling! How many can you find? Words may appear in all directions, including
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Stress Psychophysiology. Introduction. The Brain. Chapter 2
 Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Abortion and Stem Cell Debate Background Information
 Abortion and Stem Cell Debate Background Information 1 Fetal Development 2 Terms Syngamy: fusion of two gametes in fertilization Zygote: name of the cell resulting from fertilization until it implants
Abortion and Stem Cell Debate Background Information 1 Fetal Development 2 Terms Syngamy: fusion of two gametes in fertilization Zygote: name of the cell resulting from fertilization until it implants
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT
 PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Alcohol and Reproduction
 The facts about... Alcohol and Reproduction Five key things you need to know Even small amounts of alcohol can interfere with our reproductive systems. The more you drink, the greater the effect it can
The facts about... Alcohol and Reproduction Five key things you need to know Even small amounts of alcohol can interfere with our reproductive systems. The more you drink, the greater the effect it can
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
What Alcohol Does to the Body. Chapter 25 Lesson 2
 What Alcohol Does to the Body Chapter 25 Lesson 2 Short-Term Effects of Drinking The short-term term effects of alcohol on the body depend on several factors including: amount of alcohol consumed, gender,
What Alcohol Does to the Body Chapter 25 Lesson 2 Short-Term Effects of Drinking The short-term term effects of alcohol on the body depend on several factors including: amount of alcohol consumed, gender,
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Alcohol and the Adolescent Brain. Ruth Bowles. BS, CPP Executive Director The Rockland Council on Alcoholism and other Drug Dependence, Inc.
 Alcohol and the Adolescent Brain Ruth Bowles. BS, CPP Executive Director The Rockland Council on Alcoholism and other Drug Dependence, Inc. Freedom is that instant between when someone tells you to do
Alcohol and the Adolescent Brain Ruth Bowles. BS, CPP Executive Director The Rockland Council on Alcoholism and other Drug Dependence, Inc. Freedom is that instant between when someone tells you to do
Alcohol and drugs Be proactive
 Alcohol and drugs Be proactive PREGNANCY: a critical time to take care of yourself and your future baby Pregnant women must often change certain daily habits and are bombarded with recommendations from
Alcohol and drugs Be proactive PREGNANCY: a critical time to take care of yourself and your future baby Pregnant women must often change certain daily habits and are bombarded with recommendations from
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
 Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Overview of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Natalie Novick Brown, PhD. University of Washington [email protected]
 Overview of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Natalie Novick Brown, PhD University of Washington [email protected] Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)
Overview of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Natalie Novick Brown, PhD University of Washington [email protected] Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT
 PURDUE UNIVERSITY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Crawford County A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Developed by Carol Judd Description: Brain architecture is a process that begins early in life and continues
PURDUE UNIVERSITY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Crawford County A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Developed by Carol Judd Description: Brain architecture is a process that begins early in life and continues
Changes to Your Baby and Your Body During Pregnancy
 Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs
 Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
Neural Tube Defects - NTDs Introduction Neural tube defects are also known as NTDs. They happen when the spine and brain do not fully develop while the fetus is forming in the uterus. Worldwide, there
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR
 ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
BRAIN storming Copyright, Poliakoff and Bee, 2000
 by Ellen Poliakoff and Sally Bee Illustrations by Serena Korda BRAIN storming The 1990 s was hailed as the decade of the brain. We ask, what do we really know about the elusive workings of the grey matter
by Ellen Poliakoff and Sally Bee Illustrations by Serena Korda BRAIN storming The 1990 s was hailed as the decade of the brain. We ask, what do we really know about the elusive workings of the grey matter
Homework Help Stroke
 The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
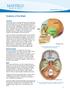 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
CLASS OBJECTIVE: What factors influence prenatal development? Test Your Knowledge! True or False? Is the prenatal environment that important??
 Life Span Development I Chapter 9 CLASS OBJECTIVE: What factors influence prenatal development? 1 Test Your Knowledge! True or False? Most babies are born healthy and most hazards can be avoided. TRUE!
Life Span Development I Chapter 9 CLASS OBJECTIVE: What factors influence prenatal development? 1 Test Your Knowledge! True or False? Most babies are born healthy and most hazards can be avoided. TRUE!
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
STEM CELL FACTS. The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine.
 STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
STEM CELL FACTS The ISSCR is an independent, nonproft organization providing a global forum for stem cell research and regenerative medicine. WHAT ARE STEM CELLS? Stem cells are the foundation cells for
Prenatal Testing Special tests for your baby during pregnancy
 English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
Functions of the Brain
 Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
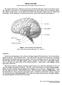 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
