Fabrication of ITO thin films by filtered cathodic vacuum arc deposition
|
|
|
- Diane Alexander
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Materials Science and Engineering B 106 (2004) Fabrication of ITO thin films by filtered cathodic vacuum arc deposition B.J. Chen, X.W. Sun, B.K. Tay School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Nanyang Avenue, Singapore , Singapore Received 22 May 2003; accepted 30 September 2003 Abstract Polycrystalline indium tin-doped oxide (ITO) thin films have been fabricated on Si(1 1 1) and quartz substrates by filtered cathodic vacuum arc (FCVA) technique for the first time. The ITO thin films were deposited at different substrate temperature and oxygen gas flow rates into the reactor chamber. The films deposited at low temperature below 100 C are amorphous. The films grown between 200 and 350 C mainly oriented in the (2 2 2), (4 0 0), (4 4 0), and (6 2 2) directions both on silicon substrate and quartz substrate. The optimized ITO film has a high transmittance of about 95% in the wavelength range of nm, the volume resistivity is cm and the electron carrier concentration is as high as cm 3. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) images show that the surface of ITO film is very smooth both on silicon and quartz substrates, the RMS average roughness is 2.24 nm for silicon substrate and 2.43 nm for quartz substrate respectively Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: ITO thin films; Filtered cathodic vacuum arc; Electrical properties; Atomic force; microscopy; Transmittance 1. Introduction Indium tin-doped oxide (ITO) is an n-type wide band-gap oxide semiconductor. ITO is well known as the most widely applied transparent conducting oxides (TCOs), which have attracted a great deal of interest due to their prospective employment in the field of optoelectronics, such as optical windows and electrodes. ITO is ubiquitous in all kinds of flat panel displays, solar cells, photodetectors and electroluminescent devices [1 5]. Different techniques are used to prepare ITO thin films, including chemical-vapor deposition, evaporation, the sol gel process, magnetron sputtering, and pulsed-laser deposition (PLD) [6 10]. The commercially available ITO deposited by sputtering has low resistivity in the range of cm, and high transmittance of 85 90% in the visible region. The roughness of ITO surface is usually a few 10-folds angstroms. With the progress of flat panel display technology, much lower resistivity, higher transmittance and more smooth surface are needed to decrease the voltage drop and power consumption of ITO line and improve the performance of the display. The Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: exwsun@ntu.edu.sg (X.W. Sun). roughness of ITO thin film is especially important for organic light-emitting devices (OLEDs) [11]. In OLEDs, the organic layers are very thin, protrusions of as little as 30 nm in a 300 nm of ITO layer can cause shorts and dark spots formation [12]. Exploring new techniques and materials to produce a very planar layer (low roughness) of ITO thin film while maintaining or improving the sheet resistance and the transmittance becomes crucial for long life time organic light-emitting display. The filtered cathodic vacuum arc (FCVA) technique is an attractive thin film deposition method, which is one of the most promising techniques for high-quality hard coating and semiconductor applications [13]. The FCVA deposition system employs a magnetic filtering technique to remove unwanted macroparticles and neutral atoms. Only ions within a well-defined energy range and certain mass can reach the substrate, thus producing films with good quality, controllability and reproducibility. In this paper, we investigate ITO thin films deposited on Si(1 1 1) and quartz substrates by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technique. The ITO thin films were deposited at different substrate temperature and oxygen gas flow rates into the reactor chamber. The ITO thin films were characterized by surface profilometer (Alpha-step, TENCOR P-10), X-ray diffraction (XRD), optical transmittance, Hall effect /$ see front matter 2003 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /j.mseb
2 B.J. Chen et al. / Materials Science and Engineering B 106 (2004) measurement, and atomic force microscopy (AFM) at room temperature under ambient atmosphere. netic field around 40 mt was employed to produce the axial and curvilinear fields to steer the plasma. 2. Experimental A schematic of the FCVA system used in this study is shown in Fig. 1. A cylindrical tin-doped indium target was mounted on a water-cooled copper plate. A spiral heater with thermal couple was used for heating the substrate. Typically, the base vacuum of the chamber was Torr by a two-stage pumping system made of a mechanical roughening pump and a cryogenic pump. The pressure during the deposition was usually increased to about to Torr due to injection oxygen gas into the chamber. The oxygen gas was introduced into the chamber directly by a mass flow controller with constant flow rate. The substrates were (1 1 1) n-type silicon wafers with average thickness of 0.4 mm and quartz glasses of thickness of about 1 mm. Prior to loading into the chamber, the substrates were cleaned by ultrasonic bath in acetone, isopropyl alcohol, and rinsed in de-ionized water, and then dried by nitrogen gas. The arc current of 50 A was used for all the samples. A toroidal mag- 3. Results and discussion The thickness of all the ITO films obtained with surface profilometer ranged from 30 to 50 nm. The crystalline phase and crystal orientation were evaluated using X-ray diffractometer with Cu K radiation wavelength of nm at 40 kv and 40 ma. Fig. 2 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of ITO thin films on quartz glass substrate (a) and (1 1 1) silicon substrate (b) at different substrate temperatures of 200, 250, 300 and 350 C. The XRD patterns indicate that the films exhibit a polycrystalline body-centered cubic crystal structure (a = b = c = nm). Five peaks appear at 2θ = 30.6, 35.4, 50.9, 60.6, and 63.8, which correspond to the (2 2 2), (4 0 0), (4 4 0), (6 2 2), and (4 4 4) directions of the body-centered cubic crystal structure, respectively. The ITO films deposited at room temperature are almost amorphous as no preferred orientations peaks are observed. When the substrate temperature is increased to 200 C, the films tend to crystal. The crystalline peaks Fig. 1. A schematic of the filtered cathodic vacuum arc system.
3 302 B.J. Chen et al. / Materials Science and Engineering B 106 (2004) Fig. 2. X-ray diffraction patterns of ITO thin films on quartz glass substrate (a) and (1 1 1) silicon substrate (b) at different substrate temperatures. become sharper when the substrate temperature is increased to 350 C. Compared Fig. 2a and b, it can also be seen that there are similar XRD patterns at the same substrate temperature. The transmittance of the ITO films on quartz glass substrate was characterized by UV-Vis scanning spectrophotometer (UV-2501PC). Shown in Fig. 3 are the respective transmittances of the samples deposited under substrate temperatures of 200, 300 and 350 C with oxygen flow rates of 5 sccm (standard cubic centimeters per minute) and 15 sccm, Fig. 3. Optical transmittance of ITO films grown on quartz glass substrates at different substrate temperature and oxygen flow rates. respectively. The transmittance of the ITO films is dependent on grown temperature and oxygen flow rates. The films, deposited at lower temperature of 200 C and oxygen flow rates of 5 sccm, looks blackish as much less oxygen was incorporated in the film. The absorption edge of the ITO is at approximately 300 nm. The overall transmittance of the films deposited at higher temperature of 350 C and oxygen flow rates of 15 sccm is over 95% in the wavelength range of nm. Room temperature Hall effect measurements were performed for the samples based on quartz glass substrates grown at different temperature and oxygen flow rates. The results are given in Table 1. From the table, it can be seen that the volume resistivity is increased with the increase of the substrate temperature, when the oxygen flow rate is the same. While the volume resistivity is decreased with the increase of oxygen flow rate, when the substrate temperature is the same. The low volume resistivity is due to high carries concentrations in the ITO films. The sample, deposited at temperature of 300 C and oxygen flow rate of 15 sccm, has the lower volume resistivity of cm and higher carrier density of cm 3. The resistivity is comparable to the best reported results by other techniques [14]. The high carrier density in the order of cm 3 is close to that of ITO films derived by pulsed laser deposition and sputtering [7,8], where ions are involved in the deposition process. The low resistivity of ITO film is due to the large free carrier density. It is generally accepted that these free carriers are generated by two mechanisms: (1) tin atom substitution of indium atom and giving out one extra electron, and (2) oxygen vacancies acting as two electron donors [15]. The films deposited at room temperature appeared dark, indicating the incorporated oxygen of the films comes not only from the ionized oxygen because of ionization of oxygen at the arc source and the collision of indium and tin atoms with oxygen, but also from the reaction of the indium and tin with oxygen on the film surface. With fixed temperatures of 300 C, increasing the oxygen flow rate from 5 to 15 sccm helps to slow down the indium and tin ions towards the substrate, more oxygen can be incorporated into the film, thus resulting in a lowing of the resistivity. With fixed flow rate of 15 sccm, increasing the temperature facilitate more oxygen incorporation, but too much oxygen resulting in reduced oxygen vacancies. Thus the resistivity is increased. From the results mentioned above, the resistivity of ITO film is correlated with the free carrier density and the mobility of the free carriers. In general, the higher the free carrier density, the lower the resistivity [16,17]. On the other hand, the mobility of the free carriers are dependent on various scattering mechanisms in the film, for example, ionized impurity scattering and grain boundary scattering [16]. From Table 1, it can be seen that the mobility, in general, increases with the increase of the substrate temperature, indicating a reduced grain boundary scattering with the increase of temperature, which is consistent with XRD result that increasing
4 B.J. Chen et al. / Materials Science and Engineering B 106 (2004) Table 1 Summary of electrical properties of ITO thin films on quartz substrates grown at different temperature and oxygen flow rates Sample Substrate temperature ( C) Oxygen flow rate (sccm) Resistivity ( 10 4 cm) Hall mobility (cm 2 V 1 s 1 ) A B C D Carrier density ( cm 3 ) substrate temperature helps to improve crystallinity (Fig. 2). This result is in agreement with the result previously reported [8]. Also seen from Table 1, the increase of the flow rate, thus reducing the energy of ions reaching the substrate surface, also helps to increase the mobility. The reason is that there are less ionized impurities generated with smaller energy ions bombardment on the growing ITO film, hence, less ionized impurity scattering. The surface morphology of the ITO thin films deposited on silicon and quartz glass substrate was investigated by AFM technique. Fig. 4a and b show the AFM images of ITO films deposited on silicon and quartz glass substrates respectively. The top two figures of Fig. 4 show the 3D surface morphologies, while the bottom top figures show line scans of surfaces. The samples were deposited under the condition of 300 C substrate temperature and 15 sccm oxygen flow rates. For a scanning area of 1 1 m 2, Fig. 4 shows smooth surface morphologies for both silicon substrate and quartz glass substrate. For the silicon substrate in Fig. 4a, the width of the marked peaks is nm and the RMS value of the line scan is nm. The RMS average value is of nm for the whole area of the 1 1 m 2. For the quartz glass substrate in Fig. 4b, the width of the marked peaks is nm and the RMS value of the line scan is nm, while the RMS average value is of nm for the whole area of the 1 1 m 2. Overall, the surface morphology and roughness of the ITO films based on silicon substrate are similar to that of quartz substrate. The surface roughness is slightly better than commercial ITO glass that has a RMS roughness of around 2.8 nm from our own measurement. The smooth surface morphology of ITO films derived from FCVA technique is believed to come from the high energy and high density of ions involved in FCVA deposition [13]. Due to the bombarding of ions, the film becomes denser and amorphous, and etching of the growing film is also expected. The etching rate is higher for peaks on the films than for pits. Eventually the surface of the growing ITO thin film is smoothened. The smooth surface of ITO thin films can be used to fabricate highly reliable OLED for advanced applications [11]. Fig. 4. AFM images of ITO films based on different substrate: (a) on silicon substrate and (b) on quartz glass substrate.
5 304 B.J. Chen et al. / Materials Science and Engineering B 106 (2004) Conclusions ITO films have been successfully fabricated on Si (1 1 1) and quartz substrates by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technique. The properties of ITO thin films are dependent of the substrate temperature and oxygen gas flow rates. The optimized ITO film has a high transmittance of about 95% in the wavelength range of nm, the volume resistivity is cm and the electron carrier concentration is as high as cm 3. AFM images show that the surface of ITO film is very smooth both on silicon substrate and quartz substrate. These films are promising for OLED applications. Acknowledgements This project is supported by Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) Public Sector R&D Funding # and the Academic Research Fund RG 16/99 from the Ministry of Education of Singapore. References [1] B.G. Lewis, D.C. Paine, Mater. Res. Bull. 25 (2000) 45. [2] H. Ohta, M. Orita, M. Hirano, H. Tani, H. Kawazoe, H. Hosono, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76 (2000) [3] B. Thestrup, J. Schou, A. Nordskov, N.B. Larsen, Appl. Surf. Sci. 142 (1999) 248. [4] H. Kim, A. Piqué, J.S. Horwitz, H. Mattoussi, H. Murata, Z.H. Kafafi, D.B. Chrisey, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74 (1999) [5] B.J. Chen, X.Q. Lin, L.F. Cheng, C.S. Lee, W.A. Gambling, S.T. Lee, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 34 (2001) 30. [6] N. Aiko, K. Yoshizo, N. Hiroyuki, S. Takeshi, K. Naoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41 (2002) [7] X.W. Sun, H.C. Huang, H.S. Kwok, Appl. Phys. Lett. 68 (1996) [8] X.W. Sun, L.D. Wang, H.S. Kwok, Thin Solid Films 360 (2000) 75. [9] M.A. Morales-Paliza, R.F. Haglund Jr, L.C. Feldman, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 (2002) [10] R.B.H. Tahar, T. Ban, Y. Ohya, Y. Takahashi, J. Appl. Phys. 83 (1998) [11] B. Young, OLED Emitter 2 (2002) 4. [12] L. Ke, S.-J. Chua, K. Zhang, N. Yakovlev, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 (2002) [13] X. Shi, B.K. Tay, H.S. Tan, E. Liu, J. Shi, L.K. Cheah, X. Jin, Thin Solid Films 345 (1999) 1. [14] S. Maniv, C.J. Miner, W.D. Westwod, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1 (1983) [15] I. Hamberg, C.G. Granqvist, J. Appl. Phys. 60 (1986) R123. [16] X.W. Sun, D.H. Kim, H.S. Kwok, in: E. Jones, J. Kalejs, R. Noufi, B. Sopori (Eds.), Thin-Film Structures for Photovoltaics, Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, vol. 485, Boston, MA, 2 5 December 1997, p [17] H.S. Kwok, X.W. Sun, D.H. Kim, Thin Solid Films 335 (1998) 299.
The effect of film thickness on physical properties of fluorine-doped indium oxide thin films
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2004 The effect of film thickness on physical properties of fluorine-doped indium oxide thin films S. M. ROZATI *, T. GANJ Physics Department, University of Guilan,
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2004 The effect of film thickness on physical properties of fluorine-doped indium oxide thin films S. M. ROZATI *, T. GANJ Physics Department, University of Guilan,
Deposition of Conducting Oxide Thin Films as Anode for Solar Cell Device
 British Journal of Applied Science & Technology 4(5): 739-748, 2014 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Deposition of Conducting Oxide Thin Films as Anode for Solar Cell Device N. Mustapha
British Journal of Applied Science & Technology 4(5): 739-748, 2014 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Deposition of Conducting Oxide Thin Films as Anode for Solar Cell Device N. Mustapha
Impurity-doped ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Physical Deposition Methods Appropriate for
 Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience Impurity-doped ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Physical Deposition Methods Appropriate for Transparent Electrode Applications in Thin-film Solar
Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience Impurity-doped ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Physical Deposition Methods Appropriate for Transparent Electrode Applications in Thin-film Solar
Characterization of sputtered NiO thin films
 Surface & Coatings Technology 198 (2005) 138 142 www.elsevier.com/locate/surfcoat Characterization of sputtered NiO thin films Hao-Long Chen a, *, Yang-Ming Lu b, Weng-Sing Hwang a a Department of Materials
Surface & Coatings Technology 198 (2005) 138 142 www.elsevier.com/locate/surfcoat Characterization of sputtered NiO thin films Hao-Long Chen a, *, Yang-Ming Lu b, Weng-Sing Hwang a a Department of Materials
Titanium Doped ITO Thin Films Produced by Sputtering Method
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 3 (21) pp. 53 to 59 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Titanium Doped ITO Thin Films Produced by Sputtering Method Leandro Voisin 1, Makoto Ohtsuka 2; * and Takashi
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 3 (21) pp. 53 to 59 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Titanium Doped ITO Thin Films Produced by Sputtering Method Leandro Voisin 1, Makoto Ohtsuka 2; * and Takashi
Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering
 Satisloh Italy S.r.l. Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering Gianni Monaco, PhD R&D project manager, Satisloh Italy 04.04.2016 V1 The aim of this document is to provide basic technical information
Satisloh Italy S.r.l. Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering Gianni Monaco, PhD R&D project manager, Satisloh Italy 04.04.2016 V1 The aim of this document is to provide basic technical information
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Cells
 Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Cells A supplement topic to: Mi ti l S Micro-optical Sensors - A MEMS for electric power generation Science of Silicon PV Cells Scientific base for solar PV electric power generation
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Cells A supplement topic to: Mi ti l S Micro-optical Sensors - A MEMS for electric power generation Science of Silicon PV Cells Scientific base for solar PV electric power generation
NANOSTRUCTURED ZnO AND ZAO TRANSPARENT THIN FILMS BY SPUTTERING SURFACE CHARACTERIZATION
 Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Nanostructured ZnO 10 and (2005) ZAO 335-340 transparent thin films by sputtering surface characterization 335 NANOSTRUCTURED ZnO AND ZAO TRANSPARENT THIN FILMS BY SPUTTERING SURFACE
Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Nanostructured ZnO 10 and (2005) ZAO 335-340 transparent thin films by sputtering surface characterization 335 NANOSTRUCTURED ZnO AND ZAO TRANSPARENT THIN FILMS BY SPUTTERING SURFACE
2. Deposition process
 Properties of optical thin films produced by reactive low voltage ion plating (RLVIP) Antje Hallbauer Thin Film Technology Institute of Ion Physics & Applied Physics University of Innsbruck Investigations
Properties of optical thin films produced by reactive low voltage ion plating (RLVIP) Antje Hallbauer Thin Film Technology Institute of Ion Physics & Applied Physics University of Innsbruck Investigations
For Touch Panel and LCD Sputtering/PECVD/ Wet Processing
 production Systems For Touch Panel and LCD Sputtering/PECVD/ Wet Processing Pilot and Production Systems Process Solutions with over 20 Years of Know-how Process Technology at a Glance for Touch Panel,
production Systems For Touch Panel and LCD Sputtering/PECVD/ Wet Processing Pilot and Production Systems Process Solutions with over 20 Years of Know-how Process Technology at a Glance for Touch Panel,
Improved Contact Formation for Large Area Solar Cells Using the Alternative Seed Layer (ASL) Process
 Improved Contact Formation for Large Area Solar Cells Using the Alternative Seed Layer (ASL) Process Lynne Michaelson, Krystal Munoz, Jonathan C. Wang, Y.A. Xi*, Tom Tyson, Anthony Gallegos Technic Inc.,
Improved Contact Formation for Large Area Solar Cells Using the Alternative Seed Layer (ASL) Process Lynne Michaelson, Krystal Munoz, Jonathan C. Wang, Y.A. Xi*, Tom Tyson, Anthony Gallegos Technic Inc.,
Sputtered AlN Thin Films on Si and Electrodes for MEMS Resonators: Relationship Between Surface Quality Microstructure and Film Properties
 Sputtered AlN Thin Films on and Electrodes for MEMS Resonators: Relationship Between Surface Quality Microstructure and Film Properties S. Mishin, D. R. Marx and B. Sylvia, Advanced Modular Sputtering,
Sputtered AlN Thin Films on and Electrodes for MEMS Resonators: Relationship Between Surface Quality Microstructure and Film Properties S. Mishin, D. R. Marx and B. Sylvia, Advanced Modular Sputtering,
Conductivity of silicon can be changed several orders of magnitude by introducing impurity atoms in silicon crystal lattice.
 CMOS Processing Technology Silicon: a semiconductor with resistance between that of conductor and an insulator. Conductivity of silicon can be changed several orders of magnitude by introducing impurity
CMOS Processing Technology Silicon: a semiconductor with resistance between that of conductor and an insulator. Conductivity of silicon can be changed several orders of magnitude by introducing impurity
Exploring the deposition of oxides on silicon for photovoltaic cells by pulsed laser deposition
 Applied Surface Science 186 2002) 453±457 Exploring the deposition of oxides on silicon for photovoltaic cells by pulsed laser deposition Lianne M. Doeswijk a,*, Hugo H.C. de Moor b, Horst Rogalla a, Dave
Applied Surface Science 186 2002) 453±457 Exploring the deposition of oxides on silicon for photovoltaic cells by pulsed laser deposition Lianne M. Doeswijk a,*, Hugo H.C. de Moor b, Horst Rogalla a, Dave
OPTIMIZING OF THERMAL EVAPORATION PROCESS COMPARED TO MAGNETRON SPUTTERING FOR FABRICATION OF TITANIA QUANTUM DOTS
 OPTIMIZING OF THERMAL EVAPORATION PROCESS COMPARED TO MAGNETRON SPUTTERING FOR FABRICATION OF TITANIA QUANTUM DOTS Vojtěch SVATOŠ 1, Jana DRBOHLAVOVÁ 1, Marian MÁRIK 1, Jan PEKÁREK 1, Jana CHOMOCKÁ 1,
OPTIMIZING OF THERMAL EVAPORATION PROCESS COMPARED TO MAGNETRON SPUTTERING FOR FABRICATION OF TITANIA QUANTUM DOTS Vojtěch SVATOŠ 1, Jana DRBOHLAVOVÁ 1, Marian MÁRIK 1, Jan PEKÁREK 1, Jana CHOMOCKÁ 1,
Structure and properties of transparent conductive ZnO films grown by pulsed laser
 Structure and properties of transparent conductive ZnO films grown by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) by Yu Hsiu, Lin A dissertation submitted to the University of Birmingham for the degree of Master of
Structure and properties of transparent conductive ZnO films grown by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) by Yu Hsiu, Lin A dissertation submitted to the University of Birmingham for the degree of Master of
Optical Properties of Sputtered Tantalum Nitride Films Determined by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry
 Optical Properties of Sputtered Tantalum Nitride Films Determined by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Thomas Waechtler a, Bernd Gruska b, Sven Zimmermann a, Stefan E. Schulz a, Thomas Gessner a a Chemnitz University
Optical Properties of Sputtered Tantalum Nitride Films Determined by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Thomas Waechtler a, Bernd Gruska b, Sven Zimmermann a, Stefan E. Schulz a, Thomas Gessner a a Chemnitz University
Modification of Pd-H 2 and Pd-D 2 thin films processed by He-Ne laser
 Modification of Pd-H 2 and Pd-D 2 thin films processed by He-Ne laser V.Nassisi #, G.Caretto #, A. Lorusso #, D.Manno %, L.Famà %, G.Buccolieri %, A.Buccolieri %, U.Mastromatteo* # Laboratory of Applied
Modification of Pd-H 2 and Pd-D 2 thin films processed by He-Ne laser V.Nassisi #, G.Caretto #, A. Lorusso #, D.Manno %, L.Famà %, G.Buccolieri %, A.Buccolieri %, U.Mastromatteo* # Laboratory of Applied
Preparation of ZnS and SnS Nanopowders by Modified SILAR Technique
 Journal of Physical Sciences, Vol. 13, 009, 9-34 ISSN: 097-8791 : www.vidyasagar.ac.in/journal Preparation of ZnS and SnS Nanopowders by Modified SILAR Technique Department of Physics The University of
Journal of Physical Sciences, Vol. 13, 009, 9-34 ISSN: 097-8791 : www.vidyasagar.ac.in/journal Preparation of ZnS and SnS Nanopowders by Modified SILAR Technique Department of Physics The University of
High Rate Oxide Deposition onto Web by Reactive Sputtering from Rotatable Magnetrons
 High Rate Oxide Deposition onto Web by Reactive Sputtering from Rotatable Magnetrons D.Monaghan, V. Bellido-Gonzalez, M. Audronis. B. Daniel Gencoa, Physics Rd, Liverpool, L24 9HP, UK. www.gencoa.com,
High Rate Oxide Deposition onto Web by Reactive Sputtering from Rotatable Magnetrons D.Monaghan, V. Bellido-Gonzalez, M. Audronis. B. Daniel Gencoa, Physics Rd, Liverpool, L24 9HP, UK. www.gencoa.com,
Lecture 12. Physical Vapor Deposition: Evaporation and Sputtering Reading: Chapter 12. ECE 6450 - Dr. Alan Doolittle
 Lecture 12 Physical Vapor Deposition: Evaporation and Sputtering Reading: Chapter 12 Evaporation and Sputtering (Metalization) Evaporation For all devices, there is a need to go from semiconductor to metal.
Lecture 12 Physical Vapor Deposition: Evaporation and Sputtering Reading: Chapter 12 Evaporation and Sputtering (Metalization) Evaporation For all devices, there is a need to go from semiconductor to metal.
Ion Beam Sputtering: Practical Applications to Electron Microscopy
 Ion Beam Sputtering: Practical Applications to Electron Microscopy Applications Laboratory Report Introduction Electron microscope specimens, both scanning (SEM) and transmission (TEM), often require a
Ion Beam Sputtering: Practical Applications to Electron Microscopy Applications Laboratory Report Introduction Electron microscope specimens, both scanning (SEM) and transmission (TEM), often require a
Effect of the oxide film formed on the electrical properties of Cu-Zn alloy electric contact material
 Effect of the oxide film formed on the electrical properties of Cu-Zn alloy electric contact material Hao-Long Chen *, Ke-Cheng Tseng and Yao-Sheng Yang Department of Electronic Engineering, Kao Yuan University,
Effect of the oxide film formed on the electrical properties of Cu-Zn alloy electric contact material Hao-Long Chen *, Ke-Cheng Tseng and Yao-Sheng Yang Department of Electronic Engineering, Kao Yuan University,
Chapter 4 Indium Tin Oxide Films Deposited by d.c. Sputtering
 Chapter 4 Indium Tin Oxide Films Deposited by d.c. Sputtering 4.1. Introduction Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) thin films are widely used in optoelectronics devices, flat panel display and electrochromic (EC)
Chapter 4 Indium Tin Oxide Films Deposited by d.c. Sputtering 4.1. Introduction Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) thin films are widely used in optoelectronics devices, flat panel display and electrochromic (EC)
A Remote Plasma Sputter Process for High Rate Web Coating of Low Temperature Plastic Film with High Quality Thin Film Metals and Insulators
 A Remote Plasma Sputter Process for High Rate Web Coating of Low Temperature Plastic Film with High Quality Thin Film Metals and Insulators Dr Peter Hockley and Professor Mike Thwaites, Plasma Quest Limited
A Remote Plasma Sputter Process for High Rate Web Coating of Low Temperature Plastic Film with High Quality Thin Film Metals and Insulators Dr Peter Hockley and Professor Mike Thwaites, Plasma Quest Limited
The study of structural and optical properties of TiO 2 :Tb thin films
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXVII, No. 4, 2007 The study of structural and optical properties of TiO 2 :Tb thin films AGNIESZKA BORKOWSKA, JAROSLAW DOMARADZKI, DANUTA KACZMAREK, DAMIAN WOJCIESZAK Faculty of
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXVII, No. 4, 2007 The study of structural and optical properties of TiO 2 :Tb thin films AGNIESZKA BORKOWSKA, JAROSLAW DOMARADZKI, DANUTA KACZMAREK, DAMIAN WOJCIESZAK Faculty of
Introduction OLEDs OTFTs OPVC Summary. Organic Electronics. Felix Buth. Walter Schottky Institut, TU München. Joint Advanced Student School 2008
 Felix Buth Joint Advanced Student School 2008 Outline 1 Introduction Difference organic/inorganic semiconductors From molecular orbitals to the molecular crystal 2 Organic Light Emitting Diodes Basic Principals
Felix Buth Joint Advanced Student School 2008 Outline 1 Introduction Difference organic/inorganic semiconductors From molecular orbitals to the molecular crystal 2 Organic Light Emitting Diodes Basic Principals
histaris Inline Sputtering Systems
 vistaris histaris Inline Sputtering Systems Inline Sputtering Systems with Vertical Substrate Transport Modular System for Different Applications VISTARIS Sputtering Systems The system with the brand name
vistaris histaris Inline Sputtering Systems Inline Sputtering Systems with Vertical Substrate Transport Modular System for Different Applications VISTARIS Sputtering Systems The system with the brand name
Reactive Sputtering Using a Dual-Anode Magnetron System
 Reactive Sputtering Using a Dual-Anode Magnetron System A. Belkind and Z. Zhao, Stevens Institute of Technology, Hoboken, NJ; and D. Carter, G. McDonough, G. Roche, and R. Scholl, Advanced Energy Industries,
Reactive Sputtering Using a Dual-Anode Magnetron System A. Belkind and Z. Zhao, Stevens Institute of Technology, Hoboken, NJ; and D. Carter, G. McDonough, G. Roche, and R. Scholl, Advanced Energy Industries,
State of the art in reactive magnetron sputtering
 State of the art in reactive magnetron sputtering T. Nyberg, O. Kappertz, T. Kubart and S. Berg Solid State Electronics, The Ångström Laboratory, Uppsala University, Box 534, S-751 21 Uppsala, Sweden D.
State of the art in reactive magnetron sputtering T. Nyberg, O. Kappertz, T. Kubart and S. Berg Solid State Electronics, The Ångström Laboratory, Uppsala University, Box 534, S-751 21 Uppsala, Sweden D.
Transparent conducting sol gel ATO coatings for display applications by an improved dip coating technique
 Transparent conducting sol gel ATO coatings for display applications by an improved dip coating technique G. Guzman a, *, B. Dahmani b, J. Puetz c, M.A. Aegerter c a Corning S.A., Centre Européen de Recherche
Transparent conducting sol gel ATO coatings for display applications by an improved dip coating technique G. Guzman a, *, B. Dahmani b, J. Puetz c, M.A. Aegerter c a Corning S.A., Centre Européen de Recherche
Vacuum Evaporation Recap
 Sputtering Vacuum Evaporation Recap Use high temperatures at high vacuum to evaporate (eject) atoms or molecules off a material surface. Use ballistic flow to transport them to a substrate and deposit.
Sputtering Vacuum Evaporation Recap Use high temperatures at high vacuum to evaporate (eject) atoms or molecules off a material surface. Use ballistic flow to transport them to a substrate and deposit.
Electron Beam and Sputter Deposition Choosing Process Parameters
 Electron Beam and Sputter Deposition Choosing Process Parameters General Introduction The choice of process parameters for any process is determined not only by the physics and/or chemistry of the process,
Electron Beam and Sputter Deposition Choosing Process Parameters General Introduction The choice of process parameters for any process is determined not only by the physics and/or chemistry of the process,
Cathodic Arc Deposition of superconducting thin films of MgB 2 for RF cavities*
 Alameda Applied Sciences Corporation Cathodic Arc Deposition of superconducting thin films of MgB 2 for RF cavities* Mahadevan Krishnan, Andrew Gerhan, Kristi Wilson and Brian Bures Alameda Applied Sciences
Alameda Applied Sciences Corporation Cathodic Arc Deposition of superconducting thin films of MgB 2 for RF cavities* Mahadevan Krishnan, Andrew Gerhan, Kristi Wilson and Brian Bures Alameda Applied Sciences
High performance. Architectural glazings utilise thin. low-emissivity coating. Coating technology
 Coating technology High performance low-emissivity coating Growing concern with energy efficiency has sparked the development of double low-emissivity coatings in architectural glass. BOC Coating has designed
Coating technology High performance low-emissivity coating Growing concern with energy efficiency has sparked the development of double low-emissivity coatings in architectural glass. BOC Coating has designed
Microhardness study of Ti(C, N) films deposited on S-316 by the Hallow Cathode Discharge Gun
 of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering VOLUME 14 ISSUE 1-2 January-February 2006 Microhardness study of Ti(C, N) films deposited on S-316 by the Hallow Cathode Discharge Gun A.J. Novinrooz*,
of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering VOLUME 14 ISSUE 1-2 January-February 2006 Microhardness study of Ti(C, N) films deposited on S-316 by the Hallow Cathode Discharge Gun A.J. Novinrooz*,
Neuere Entwicklungen zur Herstellung optischer Schichten durch reaktive. Wolfgang Hentsch, Dr. Reinhard Fendler. FHR Anlagenbau GmbH
 Neuere Entwicklungen zur Herstellung optischer Schichten durch reaktive Sputtertechnologien Wolfgang Hentsch, Dr. Reinhard Fendler FHR Anlagenbau GmbH Germany Contents: 1. FHR Anlagenbau GmbH in Brief
Neuere Entwicklungen zur Herstellung optischer Schichten durch reaktive Sputtertechnologien Wolfgang Hentsch, Dr. Reinhard Fendler FHR Anlagenbau GmbH Germany Contents: 1. FHR Anlagenbau GmbH in Brief
Introduction to VLSI Fabrication Technologies. Emanuele Baravelli
 Introduction to VLSI Fabrication Technologies Emanuele Baravelli 27/09/2005 Organization Materials Used in VLSI Fabrication VLSI Fabrication Technologies Overview of Fabrication Methods Device simulation
Introduction to VLSI Fabrication Technologies Emanuele Baravelli 27/09/2005 Organization Materials Used in VLSI Fabrication VLSI Fabrication Technologies Overview of Fabrication Methods Device simulation
Chemical vapor deposition of novel carbon materials
 Thin Solid Films 368 (2000) 193±197 www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Chemical vapor deposition of novel carbon materials L. Chow a, b, *, D. Zhou b, c, A. Hussain b, c, S. Kleckley a, K. Zollinger a, A. Schulte
Thin Solid Films 368 (2000) 193±197 www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Chemical vapor deposition of novel carbon materials L. Chow a, b, *, D. Zhou b, c, A. Hussain b, c, S. Kleckley a, K. Zollinger a, A. Schulte
International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Modern Education (IJMRME) ISSN (Online): 2454-6119 (www.rdmodernresearch.org) Volume I, Issue
 STUDIES ON OPTICAL AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES OF Ag2S FILMS PREPARED BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION METHOD Goverdhan Yadu*, K. K. Pathak**, Kusumanjali Deshmukh*** & Mini A. Pateria*** * Govt. Rajeev Lochan
STUDIES ON OPTICAL AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES OF Ag2S FILMS PREPARED BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION METHOD Goverdhan Yadu*, K. K. Pathak**, Kusumanjali Deshmukh*** & Mini A. Pateria*** * Govt. Rajeev Lochan
Coating Thickness and Composition Analysis by Micro-EDXRF
 Application Note: XRF Coating Thickness and Composition Analysis by Micro-EDXRF www.edax.com Coating Thickness and Composition Analysis by Micro-EDXRF Introduction: The use of coatings in the modern manufacturing
Application Note: XRF Coating Thickness and Composition Analysis by Micro-EDXRF www.edax.com Coating Thickness and Composition Analysis by Micro-EDXRF Introduction: The use of coatings in the modern manufacturing
Femtosecond laser-induced silicon surface morphology in water confinement
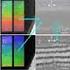 Microsyst Technol (2009) 15:1045 1049 DOI 10.1007/s00542-009-0880-8 TECHNICAL PAPER Femtosecond laser-induced silicon surface morphology in water confinement Yukun Han Æ Cheng-Hsiang Lin Æ Hai Xiao Æ Hai-Lung
Microsyst Technol (2009) 15:1045 1049 DOI 10.1007/s00542-009-0880-8 TECHNICAL PAPER Femtosecond laser-induced silicon surface morphology in water confinement Yukun Han Æ Cheng-Hsiang Lin Æ Hai Xiao Æ Hai-Lung
X-ray thin-film measurement techniques
 Technical articles X-ray thin-film measurement techniques II. Out-of-plane diffraction measurements Toru Mitsunaga* 1. Introduction A thin-film sample is two-dimensionally formed on the surface of a substrate,
Technical articles X-ray thin-film measurement techniques II. Out-of-plane diffraction measurements Toru Mitsunaga* 1. Introduction A thin-film sample is two-dimensionally formed on the surface of a substrate,
COMPARISON OF TEXTURE IN COPPER AND ALUMINUM THIN FILMS DETERMINED BY XRD AND EBSD *
 201 COMPARISON OF TEXTURE IN COPPER AND ALUMINUM THIN FILMS DETERMINED BY XRD AND EBSD * J. Müller 1, D. Balzar 1,2, R.H. Geiss 1, D.T. Read 1, and R.R. Keller 1 1 Materials Reliability Division, National
201 COMPARISON OF TEXTURE IN COPPER AND ALUMINUM THIN FILMS DETERMINED BY XRD AND EBSD * J. Müller 1, D. Balzar 1,2, R.H. Geiss 1, D.T. Read 1, and R.R. Keller 1 1 Materials Reliability Division, National
DIEGO TONINI MORPHOLOGY OF NIOBIUM FILMS SPUTTERED AT DIFFERENT TARGET SUBSTRATE ANGLE
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA SCIENCE FACULTY MATERIAL SCIENCE DEGREE INFN LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI LEGNARO DIEGO TONINI MORPHOLOGY OF NIOBIUM FILMS SPUTTERED AT DIFFERENT TARGET SUBSTRATE ANGLE 2 QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA SCIENCE FACULTY MATERIAL SCIENCE DEGREE INFN LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI LEGNARO DIEGO TONINI MORPHOLOGY OF NIOBIUM FILMS SPUTTERED AT DIFFERENT TARGET SUBSTRATE ANGLE 2 QUESTIONS
Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014
 Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014 Introduction Following our previous lab exercises, you now have the skills and understanding to control
Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014 Introduction Following our previous lab exercises, you now have the skills and understanding to control
Thin Is In, But Not Too Thin!
 Thin Is In, But Not Too Thin! K.V. Ravi Crystal Solar, Inc. Abstract The trade-off between thick (~170 microns) silicon-based PV and thin (a few microns) film non-silicon and amorphous silicon PV is addressed
Thin Is In, But Not Too Thin! K.V. Ravi Crystal Solar, Inc. Abstract The trade-off between thick (~170 microns) silicon-based PV and thin (a few microns) film non-silicon and amorphous silicon PV is addressed
The study of deep-level emission center in ZnO films grown on c-al 2 O 3 substrates
 The study of deep-level emission center in ZnO films grown on c-al 2 O 3 substrates Guotong Du Yuantao Zhang, Jinzhong Wang, Yongguo Cui (College of Electronic Science and Engineering, State Key Laboratory
The study of deep-level emission center in ZnO films grown on c-al 2 O 3 substrates Guotong Du Yuantao Zhang, Jinzhong Wang, Yongguo Cui (College of Electronic Science and Engineering, State Key Laboratory
Effect of Deposition Time on ZnS Thin Films Properties by Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) Techinique
 World Applied Sciences Journal 19 (8): 1087-1091, 01 ISSN 1818-495 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.wasj.01.19.08.591 Effect of Deposition Time on ZnS Thin Films Properties by Chemical Bath Deposition
World Applied Sciences Journal 19 (8): 1087-1091, 01 ISSN 1818-495 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.wasj.01.19.08.591 Effect of Deposition Time on ZnS Thin Films Properties by Chemical Bath Deposition
Improvement of surface porosity and properties of alumina films by incorporation of Fe micrograins in micro-arc oxidation
 Applied Surface Science 253 (2006) 863 868 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Improvement of surface porosity and properties of alumina films by incorporation of Fe micrograins in micro-arc oxidation Fanya
Applied Surface Science 253 (2006) 863 868 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Improvement of surface porosity and properties of alumina films by incorporation of Fe micrograins in micro-arc oxidation Fanya
Solid State Detectors = Semi-Conductor based Detectors
 Solid State Detectors = Semi-Conductor based Detectors Materials and their properties Energy bands and electronic structure Charge transport and conductivity Boundaries: the p-n junction Charge collection
Solid State Detectors = Semi-Conductor based Detectors Materials and their properties Energy bands and electronic structure Charge transport and conductivity Boundaries: the p-n junction Charge collection
Light management for photovoltaics. Ando Kuypers, TNO Program manager Solar
 Light management for photovoltaics Ando Kuypers, TNO Program manager Solar Global energy consumption: 500 ExaJoule/Year Solar irradiation on earth sphere: 5.000.000 ExaJoule/year 2 Capturing 0,01% covers
Light management for photovoltaics Ando Kuypers, TNO Program manager Solar Global energy consumption: 500 ExaJoule/Year Solar irradiation on earth sphere: 5.000.000 ExaJoule/year 2 Capturing 0,01% covers
Ultra-High Density Phase-Change Storage and Memory
 Ultra-High Density Phase-Change Storage and Memory by Egill Skúlason Heated AFM Probe used to Change the Phase Presentation for Oral Examination 30 th of May 2006 Modern Physics, DTU Phase-Change Material
Ultra-High Density Phase-Change Storage and Memory by Egill Skúlason Heated AFM Probe used to Change the Phase Presentation for Oral Examination 30 th of May 2006 Modern Physics, DTU Phase-Change Material
Module 7 Wet and Dry Etching. Class Notes
 Module 7 Wet and Dry Etching Class Notes 1. Introduction Etching techniques are commonly used in the fabrication processes of semiconductor devices to remove selected layers for the purposes of pattern
Module 7 Wet and Dry Etching Class Notes 1. Introduction Etching techniques are commonly used in the fabrication processes of semiconductor devices to remove selected layers for the purposes of pattern
ELG4126: Photovoltaic Materials. Based Partially on Renewable and Efficient Electric Power System, Gilbert M. Masters, Wiely
 ELG4126: Photovoltaic Materials Based Partially on Renewable and Efficient Electric Power System, Gilbert M. Masters, Wiely Introduction A material or device that is capable of converting the energy contained
ELG4126: Photovoltaic Materials Based Partially on Renewable and Efficient Electric Power System, Gilbert M. Masters, Wiely Introduction A material or device that is capable of converting the energy contained
SALES SPECIFICATION. SC7640 Auto/Manual High Resolution Sputter Coater
 SALES SPECIFICATION SC7640 Auto/Manual High Resolution Sputter Coater Document Number SS-SC7640 Issue 1 (01/02) Disclaimer The components and packages described in this document are mutually compatible
SALES SPECIFICATION SC7640 Auto/Manual High Resolution Sputter Coater Document Number SS-SC7640 Issue 1 (01/02) Disclaimer The components and packages described in this document are mutually compatible
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope
 Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
Sn-Cu Intermetallic Grain Morphology Related to Sn Layer Thickness
 Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 36, No. 11, 2007 DOI: 10.1007/s11664-007-0270-x Ó 2007 TMS Special Issue Paper -Cu Intermetallic Grain Morphology Related to Layer Thickness MIN-HSIEN LU 1 and KER-CHANG
Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 36, No. 11, 2007 DOI: 10.1007/s11664-007-0270-x Ó 2007 TMS Special Issue Paper -Cu Intermetallic Grain Morphology Related to Layer Thickness MIN-HSIEN LU 1 and KER-CHANG
Types of Epitaxy. Homoepitaxy. Heteroepitaxy
 Epitaxy Epitaxial Growth Epitaxy means the growth of a single crystal film on top of a crystalline substrate. For most thin film applications (hard and soft coatings, optical coatings, protective coatings)
Epitaxy Epitaxial Growth Epitaxy means the growth of a single crystal film on top of a crystalline substrate. For most thin film applications (hard and soft coatings, optical coatings, protective coatings)
Observation of Long Transients in the Electrical Characterization of Thin Film BST Capacitors
 Integrated Ferroelectrics, 53: 503 511, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390258651 Observation of Long Transients in the Electrical Characterization
Integrated Ferroelectrics, 53: 503 511, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390258651 Observation of Long Transients in the Electrical Characterization
Photovoltaic Power: Science and Technology Fundamentals
 Photovoltaic Power: Science and Technology Fundamentals Bob Clark-Phelps, Ph.D. Evergreen Solar, Inc. Renewable Energy Seminar, Nov. 2, 2006 Photovoltaic Principle Energy Conduction Band electron Energy
Photovoltaic Power: Science and Technology Fundamentals Bob Clark-Phelps, Ph.D. Evergreen Solar, Inc. Renewable Energy Seminar, Nov. 2, 2006 Photovoltaic Principle Energy Conduction Band electron Energy
Fabrication and photoelectrical properties of a novel violet and blue enhanced SINP silicon photovoltaic device
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 3, 2009 Fabrication and photoelectrical properties of a novel violet and blue enhanced SINP silicon photovoltaic device HEBO 1, ZHONGQUANMA 1, XUJING 2, ZHAOLEI 1, ZHANGNANSHENG
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 3, 2009 Fabrication and photoelectrical properties of a novel violet and blue enhanced SINP silicon photovoltaic device HEBO 1, ZHONGQUANMA 1, XUJING 2, ZHAOLEI 1, ZHANGNANSHENG
Fundamentals of Photovoltaic Materials
 Fundamentals of Photovoltaic Materials National Solar Power Reasearch Institute, Inc. 12/21/98-1 - 12/21/98 Introduction Photovoltaics (PV) comprises the technology to convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Fundamentals of Photovoltaic Materials National Solar Power Reasearch Institute, Inc. 12/21/98-1 - 12/21/98 Introduction Photovoltaics (PV) comprises the technology to convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Chapter 4 COATINGS Full Reflective Coatings:
 Chapter 4 COATINGS Technical developments in coatings for plastic optics have resulted in optical and durability characteristics once believed possible only with glass. These advances in coating technology
Chapter 4 COATINGS Technical developments in coatings for plastic optics have resulted in optical and durability characteristics once believed possible only with glass. These advances in coating technology
Crystallization of Amorphous Silicon Using Xenon Flash Lamp Annealing
 Crystallization of Amorphous Silicon Using Xenon Flash Lamp Annealing Henry Hellbusch 2/5/2016 RIT - Corning - Crystallization of A-Si with FLA 1 Purpose Thin Film Transistors (TFT) on glass are utilized
Crystallization of Amorphous Silicon Using Xenon Flash Lamp Annealing Henry Hellbusch 2/5/2016 RIT - Corning - Crystallization of A-Si with FLA 1 Purpose Thin Film Transistors (TFT) on glass are utilized
High quality superconducting niobium films produced by Ultra High Vacuum
 High quality superconducting niobium films produced by Ultra High Vacuum Cathodic Arc R. Russo a Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli studi di Roma Tor Vergata, 00133 Roma, Italy and Istituto di Cibernetica
High quality superconducting niobium films produced by Ultra High Vacuum Cathodic Arc R. Russo a Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli studi di Roma Tor Vergata, 00133 Roma, Italy and Istituto di Cibernetica
h e l p s y o u C O N T R O L
 contamination analysis for compound semiconductors ANALYTICAL SERVICES B u r i e d d e f e c t s, E v a n s A n a l y t i c a l g r o u p h e l p s y o u C O N T R O L C O N T A M I N A T I O N Contamination
contamination analysis for compound semiconductors ANALYTICAL SERVICES B u r i e d d e f e c t s, E v a n s A n a l y t i c a l g r o u p h e l p s y o u C O N T R O L C O N T A M I N A T I O N Contamination
Silicon, the test mass substrate of tomorrow? Jerome Degallaix The Next Detectors for Gravitational Wave Astronomy Beijing - 2015
 Silicon, the test mass substrate of tomorrow? Jerome Degallaix The Next Detectors for Gravitational Wave Astronomy Beijing - 2015 Program of the talk... What we have now What we know about silicon What
Silicon, the test mass substrate of tomorrow? Jerome Degallaix The Next Detectors for Gravitational Wave Astronomy Beijing - 2015 Program of the talk... What we have now What we know about silicon What
Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials
 Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials PhD theses Gabriella Kecskeméti Department of Optics and Quantum Electronics University of Szeged Supervisor: Dr. Béla Hopp senior research fellow Department
Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials PhD theses Gabriella Kecskeméti Department of Optics and Quantum Electronics University of Szeged Supervisor: Dr. Béla Hopp senior research fellow Department
Pressure effect on diamond nucleation in a hot-filament CVD system
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 23 15 JUNE 1997-I Pressure effect on diamond nucleation in a hot-filament CVD system S. T. Lee and Y. W. Lam Department of Physics & Materials Science, City University
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 23 15 JUNE 1997-I Pressure effect on diamond nucleation in a hot-filament CVD system S. T. Lee and Y. W. Lam Department of Physics & Materials Science, City University
OLED display. Ying Cao
 OLED display Ying Cao Outline OLED basics OLED display A novel method of fabrication of flexible OLED display Potentials of OLED Suitable for thin, lightweight, printable displays Broad color range Good
OLED display Ying Cao Outline OLED basics OLED display A novel method of fabrication of flexible OLED display Potentials of OLED Suitable for thin, lightweight, printable displays Broad color range Good
CVD SILICON CARBIDE. CVD SILICON CARBIDE s attributes include:
 CVD SILICON CARBIDE CVD SILICON CARBIDE is the ideal performance material for design engineers. It outperforms conventional forms of silicon carbide, as well as other ceramics, quartz, and metals in chemical
CVD SILICON CARBIDE CVD SILICON CARBIDE is the ideal performance material for design engineers. It outperforms conventional forms of silicon carbide, as well as other ceramics, quartz, and metals in chemical
3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
 3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Introduction Atomic-absorption (AA) spectroscopy uses the absorption of light to measure the concentration of gas-phase atoms. Since samples are usually liquids or solids,
3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Introduction Atomic-absorption (AA) spectroscopy uses the absorption of light to measure the concentration of gas-phase atoms. Since samples are usually liquids or solids,
Surface characterization of oxygen deficient SrTiO 3
 U. Scotti di Uccio Surface characterization of oxygen deficient SrTiO 3 films and single crystals Coherentia-CNR-INFM Napoli, Italy Prof. R. Vaglio R. Di Capua, G. De Luca, M. Radovic, N. Lampis, P. Perna,
U. Scotti di Uccio Surface characterization of oxygen deficient SrTiO 3 films and single crystals Coherentia-CNR-INFM Napoli, Italy Prof. R. Vaglio R. Di Capua, G. De Luca, M. Radovic, N. Lampis, P. Perna,
WHITEPAPER ENHANCED REACTIVELY SPUTTERED AL 2 O 3 DEPOSITION BY ADDITION OF ACTIVATED REACTIVE OXYGEN
 WHITEPAPER By D. Carter and G. McDonough of Advanced Energy Industries, Inc. ENHANCED REACTIVELY The impact of preactivation of oxygen in the reactive sputter deposition of Al 2 O 3 is investigated. Oxygen,
WHITEPAPER By D. Carter and G. McDonough of Advanced Energy Industries, Inc. ENHANCED REACTIVELY The impact of preactivation of oxygen in the reactive sputter deposition of Al 2 O 3 is investigated. Oxygen,
Study of tungsten oxidation in O 2 /H 2 /N 2 downstream plasma
 Study of tungsten oxidation in O 2 /H 2 /N 2 downstream plasma Songlin Xu a and Li Diao Mattson Technology, Inc., Fremont, California 94538 Received 17 September 2007; accepted 21 February 2008; published
Study of tungsten oxidation in O 2 /H 2 /N 2 downstream plasma Songlin Xu a and Li Diao Mattson Technology, Inc., Fremont, California 94538 Received 17 September 2007; accepted 21 February 2008; published
Chapter 6 Metal Films and Filters
 Chapter 6 Metal Films and Filters 6.1 Mirrors The first films produced by vacuum deposition as we know it were aluminum films for mirrors made by John Strong in the 1930s; he coated mirrors for astronomical
Chapter 6 Metal Films and Filters 6.1 Mirrors The first films produced by vacuum deposition as we know it were aluminum films for mirrors made by John Strong in the 1930s; he coated mirrors for astronomical
Chapter 2 The Study on Polycrystalline Pentacene Thin Film Transistors
 Chapter 2 The Study on Polycrystalline Pentacene Thin Film Transistors 2.1 Introduction Recent focus and attention on organic thin film transistors (TFTs) resulted in dramatic performance improvements
Chapter 2 The Study on Polycrystalline Pentacene Thin Film Transistors 2.1 Introduction Recent focus and attention on organic thin film transistors (TFTs) resulted in dramatic performance improvements
How compact discs are made
 How compact discs are made Explained by a layman for the laymen By Kevin McCormick For Science project at the Mountain View Los Altos High School Abstract As the major media for music distribution for
How compact discs are made Explained by a layman for the laymen By Kevin McCormick For Science project at the Mountain View Los Altos High School Abstract As the major media for music distribution for
Photovoltaics photo volt Photovoltaic Cells Crystalline Silicon Cells Photovoltaic Systems
 1 Photovoltaics Photovoltaic (PV) materials and devices convert sunlight into electrical energy, and PV cells are commonly known as solar cells. Photovoltaics can literally be translated as light-electricity.
1 Photovoltaics Photovoltaic (PV) materials and devices convert sunlight into electrical energy, and PV cells are commonly known as solar cells. Photovoltaics can literally be translated as light-electricity.
Robert G. Hunsperger. Integrated Optics. Theory and Technology. Fourth Edition. With 195 Figures and 17 Tables. Springer
 Robert G. Hunsperger Integrated Optics Theory and Technology Fourth Edition With 195 Figures and 17 Tables Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Advantages of Integrated Optics 2 1.1.1 Comparison of
Robert G. Hunsperger Integrated Optics Theory and Technology Fourth Edition With 195 Figures and 17 Tables Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Advantages of Integrated Optics 2 1.1.1 Comparison of
Luminescence study of structural changes induced by laser cutting in diamond films
 Luminescence study of structural changes induced by laser cutting in diamond films A. Cremades and J. Piqueras Departamento de Fisica de Materiales, Facultad de Fisicas, Universidad Complutense, 28040
Luminescence study of structural changes induced by laser cutting in diamond films A. Cremades and J. Piqueras Departamento de Fisica de Materiales, Facultad de Fisicas, Universidad Complutense, 28040
Molecular Beam Epitaxy
 Molecular Beam Epitaxy Klaus Ploog Paul Drude Institut Tutorial Session #1 Epitaxial Growth 27 th International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors Flagstaff, AZ, 2004 Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE)
Molecular Beam Epitaxy Klaus Ploog Paul Drude Institut Tutorial Session #1 Epitaxial Growth 27 th International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors Flagstaff, AZ, 2004 Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE)
High Open Circuit Voltage of MQW Amorphous Silicon Photovoltaic Structures
 High Open Circuit Voltage of MQW Amorphous Silicon Photovoltaic Structures ARGYRIOS C. VARONIDES Physics and EE Department University of Scranton 800 Linden Street, Scranton PA, 18510 United States Abstract:
High Open Circuit Voltage of MQW Amorphous Silicon Photovoltaic Structures ARGYRIOS C. VARONIDES Physics and EE Department University of Scranton 800 Linden Street, Scranton PA, 18510 United States Abstract:
Damage-free, All-dry Via Etch Resist and Residue Removal Processes
 Damage-free, All-dry Via Etch Resist and Residue Removal Processes Nirmal Chaudhary Siemens Components East Fishkill, 1580 Route 52, Bldg. 630-1, Hopewell Junction, NY 12533 Tel: (914)892-9053, Fax: (914)892-9068
Damage-free, All-dry Via Etch Resist and Residue Removal Processes Nirmal Chaudhary Siemens Components East Fishkill, 1580 Route 52, Bldg. 630-1, Hopewell Junction, NY 12533 Tel: (914)892-9053, Fax: (914)892-9068
Micro-Power Generation
 Micro-Power Generation Elizabeth K. Reilly February 21, 2007 TAC-meeting 1 Energy Scavenging for Wireless Sensors Enabling Wireless Sensor Networks: Ambient energy source Piezoelectric transducer technology
Micro-Power Generation Elizabeth K. Reilly February 21, 2007 TAC-meeting 1 Energy Scavenging for Wireless Sensors Enabling Wireless Sensor Networks: Ambient energy source Piezoelectric transducer technology
Phase Characterization of TiO 2 Powder by XRD and TEM
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 357-361 (28) Phase Characterization of TiO 2 Powder by XRD and TEM Kheamrutai Thamaphat 1 *, Pichet Limsuwan 1 and Boonlaer Ngotawornchai 2 ABSTRACT In this study, the commercial
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 357-361 (28) Phase Characterization of TiO 2 Powder by XRD and TEM Kheamrutai Thamaphat 1 *, Pichet Limsuwan 1 and Boonlaer Ngotawornchai 2 ABSTRACT In this study, the commercial
Supporting information
 Supporting information Ultrafast room-temperature NH 3 sensing with positively-gated reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistors Ganhua Lu 1, Kehan Yu 1, Leonidas E. Ocola 2, and Junhong Chen 1 * 1
Supporting information Ultrafast room-temperature NH 3 sensing with positively-gated reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistors Ganhua Lu 1, Kehan Yu 1, Leonidas E. Ocola 2, and Junhong Chen 1 * 1
Deposition of Silicon Oxide, Silicon Nitride and Silicon Carbide Thin Films by New Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Source Technology
 General Plasma, Inc. 546 East 25th Street Tucson, Arizona 85713 tel. 520-882-5100 fax. 520-882-5165 and Silicon Carbide Thin Films by New Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Source Technology M.
General Plasma, Inc. 546 East 25th Street Tucson, Arizona 85713 tel. 520-882-5100 fax. 520-882-5165 and Silicon Carbide Thin Films by New Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Source Technology M.
Electrochromism of amorphous ruthenium oxide thin films
 Solid State Ionics 165 (2003) 217 221 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssi Electrochromism of amorphous ruthenium oxide thin films Se-Hee Lee a, *, Ping Liu a, Hyeonsik M. Cheong b, C. Edwin Tracy a, Satyen K.
Solid State Ionics 165 (2003) 217 221 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssi Electrochromism of amorphous ruthenium oxide thin films Se-Hee Lee a, *, Ping Liu a, Hyeonsik M. Cheong b, C. Edwin Tracy a, Satyen K.
Effect of Ambient Conditions on Thermal Properties of Photovoltaic Cells: Crystalline and Amorphous Silicon
 Effect of Ambient Conditions on Thermal Properties of Photovoltaic Cells: Crystalline and Amorphous Silicon Latifa Sabri 1, Mohammed Benzirar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences
Effect of Ambient Conditions on Thermal Properties of Photovoltaic Cells: Crystalline and Amorphous Silicon Latifa Sabri 1, Mohammed Benzirar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences
SOLAR ELECTRICITY: PROBLEM, CONSTRAINTS AND SOLUTIONS
 SOLAR ELECTRICITY: PROBLEM, CONSTRAINTS AND SOLUTIONS The United States generates over 4,110 TWh of electricity each year, costing $400 billion and emitting 2.5 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide (Yildiz,
SOLAR ELECTRICITY: PROBLEM, CONSTRAINTS AND SOLUTIONS The United States generates over 4,110 TWh of electricity each year, costing $400 billion and emitting 2.5 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide (Yildiz,
Characteristics of blocking voltage for power 4H-SiC BJTs with mesa edge termination
 Vol. 31, No. 7 Journal of Semiconductors July 2010 Characteristics of blocking voltage for power 4H-SiC BJTs with mesa edge termination Zhang Qian( 张 倩 ), Zhang Yuming( 张 玉 明 ), and Zhang Yimen( 张 义 门
Vol. 31, No. 7 Journal of Semiconductors July 2010 Characteristics of blocking voltage for power 4H-SiC BJTs with mesa edge termination Zhang Qian( 张 倩 ), Zhang Yuming( 张 玉 明 ), and Zhang Yimen( 张 义 门
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 101, 114301 2007
 Optimization of open circuit voltage in amorphous silicon solar cells with mixed-phase amorphous+ nanocrystalline p-type contacts of low nanocrystalline content J. M. Pearce a Physics Department, Clarion
Optimization of open circuit voltage in amorphous silicon solar cells with mixed-phase amorphous+ nanocrystalline p-type contacts of low nanocrystalline content J. M. Pearce a Physics Department, Clarion
High Density Ceramic TCO Sputtering Targets. Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) for deposition of transparent conductive oxide layers
 High Density Ceramic TCO Sputtering Targets Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) for deposition of transparent conductive oxide layers High Density Ceramic TCO Sputtering Targets: Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Rotary ceramic
High Density Ceramic TCO Sputtering Targets Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) for deposition of transparent conductive oxide layers High Density Ceramic TCO Sputtering Targets: Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Rotary ceramic
Chapter 5. Second Edition ( 2001 McGraw-Hill) 5.6 Doped GaAs. Solution
 Chapter 5 5.6 Doped GaAs Consider the GaAs crystal at 300 K. a. Calculate the intrinsic conductivity and resistivity. Second Edition ( 2001 McGraw-Hill) b. In a sample containing only 10 15 cm -3 ionized
Chapter 5 5.6 Doped GaAs Consider the GaAs crystal at 300 K. a. Calculate the intrinsic conductivity and resistivity. Second Edition ( 2001 McGraw-Hill) b. In a sample containing only 10 15 cm -3 ionized
Optical Hyperdoping: Transforming Semiconductor Band Structure for Solar Energy Harvesting
 Optical Hyperdoping: Transforming Semiconductor Band Structure for Solar Energy Harvesting 3G Solar Technologies Multidisciplinary Workshop MRS Spring Meeting San Francisco, CA, 5 April 2010 Michael P.
Optical Hyperdoping: Transforming Semiconductor Band Structure for Solar Energy Harvesting 3G Solar Technologies Multidisciplinary Workshop MRS Spring Meeting San Francisco, CA, 5 April 2010 Michael P.
Balzers Sputter Coater SCD 050
 Balzers Sputter Coater SCD 050 The SCD 050 is a bench top, sputter deposition system designed for thin films on substrates up to 6 inches. Morphology and thickness is user controlled using power, pressure,
Balzers Sputter Coater SCD 050 The SCD 050 is a bench top, sputter deposition system designed for thin films on substrates up to 6 inches. Morphology and thickness is user controlled using power, pressure,
NANO SILICON DOTS EMBEDDED SIO 2 /SIO 2 MULTILAYERS FOR PV HIGH EFFICIENCY APPLICATION
 NANO SILICON DOTS EMBEDDED SIO 2 /SIO 2 MULTILAYERS FOR PV HIGH EFFICIENCY APPLICATION Olivier Palais, Damien Barakel, David Maestre, Fabrice Gourbilleau and Marcel Pasquinelli 1 Outline Photovoltaic today
NANO SILICON DOTS EMBEDDED SIO 2 /SIO 2 MULTILAYERS FOR PV HIGH EFFICIENCY APPLICATION Olivier Palais, Damien Barakel, David Maestre, Fabrice Gourbilleau and Marcel Pasquinelli 1 Outline Photovoltaic today
Lapping and Polishing Basics
 Lapping and Polishing Basics Applications Laboratory Report 54 Lapping and Polishing 1.0: Introduction Lapping and polishing is a process by which material is precisely removed from a workpiece (or specimen)
Lapping and Polishing Basics Applications Laboratory Report 54 Lapping and Polishing 1.0: Introduction Lapping and polishing is a process by which material is precisely removed from a workpiece (or specimen)
