NORMAL CHEST X RAY. Dr Etienne Leroy Terquem Pr Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique Internationa / International Support for Pulmonology
|
|
|
- Morris Malone
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NORMAL CHEST X RAY Dr Etienne Leroy Terquem Pr Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique Internationa / International Support for Pulmonology
2 THE CHEST RADIOGRAPHY (CXR) The CXR, is very usefull for all lung problems, it extends the clinical examination and provides essential data for diagnosis Its technical realization, simple, uses X-rays Principle : 1. The rays emitted by the X-ray tube through the chest 2. They are absorbed or mitigated to varying degrees by the different structures crossings 3. The changes are recorded on X-ray film in a cassette lead, then visualized (developing hand or in a machine after opening the cassette in the darkroom)
3 Chest X ray Reproduce 1 volume (thorax) on 1 plan (film) On this flat reproduction, you must recognize normal anatomic structures of the thorax and find out what is abnormal X Rays
4 Calcium Water Oil Air Opacity Clarity Radiography of 4 identical tubes containing calcium, water, oil, air One containing Ca stop X-rays => its image is white Air is transparent to X-rays => its radiological picture is black Fat and water have an intermediate absorption => white - gray
5 The thorax is composed of: Bone (vertebrae, ribs, scapula ). The main component is calcium, which absorbs the x-ray considerably: the bone image is very opaque (white on the radiography) Blood and soft tissue (heart, mediastinum, vessels). The absorption of x-rays is less complete than bones: the image is less opaque (light grey) Fat tissue. the absorption of x-rays is lower: the image is dark grey Air (in lungs) which does not absorb the x-ray at all. The image of the lungs is black
6 calcium Fluid / soft tissu air Fat
7 The chest X ray 3 constants regulate its quality: the quantity of electrons which pass through the chest (milliampere) the speed of the electron (kilovoltage) the exposure time A chest X-ray of good quality requires : high voltage ( kv) => Contrast a short time of exposure deep inspiration 0.05 sec. Movement artefacts Difference of density levels of the different organs and tissues in the thorax A long distance between X-ray tube focus and film
8 How to obtain a good quality chest X-ray A long distance between X-ray tube focus and film improves picture clarity and reduces geometric blur
9 How to obtain a good quality chest X-ray Other criteria Good quality electrical power supply Effective & frequent maintenance of equipment Quality films and good storage conditions Good film processing (development, rinsing, fixing, washing, drying). If possible automatic developing machine Quality of the x-ray grid: the flat metallic plate with very narrow lead trips close to the film: increase in the image clarity and reduction of the scattered radiation from the patient
10 And digital radiography? The X-ray tube is identical the radiographic film is replaced by an X-ray receiver which enables scanning in numeric * The image display is done in grayscale high resolution on a powerful computer * For computed radiography (CR) a reusable cassette containing a luminescent screen memory ("phosphor plates") introduced in a reader connected to the computer For direct "digital Radiography (DR) direct scanning receiver that transmits the image directly on the computer
11 And digital radiography? The X-ray tube is identical the radiographic film is replaced by an X-ray receiver which enables scanning in numeric * The image display is done in grayscale high resolution on a powerful computer X-Ray Tube Analog Rx Film - Chemical Development CR Reusable plate with radio-luminescent memory screen + reader DR Electronic panel X-ray detector
12 Digital Radiography Advantages : Quick and easy image processing Adjusting the picture quality (Processing) No films, No chemicals No darkroom Data Storage Transfer remote to an expert "telemedicine Disadvantages: Expensive initial investment ( to U.S.). But prices decrease.. Need for training for operators of Radiology Need for maintenance
13 But prices decreases,especially for DDR.
14 Clearly WHO recommands X-ray D DR and Xpert See Internet
15 See Internet
16 In summary Digital X ray system (Direct Digitalised System) composed with: Electronic flat-panel X ray detector High resolution grayscale diagnostic display High performance computer The top!,expansive but prices decreases
17 Direct digital radiography (DR) comprises: A flat panel electronic X-ray detector Display high resolution grayscale A high performance computer
18 Transportable DR unit
19 Possible compromise with computed radiography (CR system) Digital radiography using a Photo stimulable Phosphor plate (PSP, also called Imaging Plate, IP) enclosed in a cassette as a detector, instead of a film screen. The IP is then introduced into a CR Reader which reads the film and converts the recorded signal into a digital grey scale image Same avantages than digitalised system Lower cost than DR system, because can be used with the existing X ray equipment. Only a CR reader and CR cassette (with Imaging Plates) need to be purchased
20 Computed Radiograpy (CR) CENAT Phnom Penh Cambodge Dr Peou Satha
21 IMIS Hospital Port-au-Prince Haïti CMETE Paris
22 Dosage of x-rays type of investigation Equivalent of chest x-ray Equivalent of natural radiation chest x-ray 1 3 days CT-Scan month-1year NMR: no radiation
23 CXR - Basic radiographic views: Front view : Postero - anterior view Lateral view Other views : Expiration Radiography CXR in suppine position Radiography in suppine and lateral position Back view Antero-posterior view
24 CXR - Quality Criteria Deep inspiration Adequate density / contrast Good position of the patient (strictly front) X-ray beam in postero-anterior incidence (patient standing)
25
26 Poor inspiration False opacity of the inferior lobes Same patient with deep inspiration Adequate inspiration if you can count 9 posterior or 6 anterior parts of ribs over the diaphragm
27 posterior arches or 6 anterior arches above the diaphragm
28 AP versus PA view False cardiomegaly clavicles are high and horizontal The x-ray beam is antero posterior Same patient with correct postero-anterior x-ray beam incidence PA is the correct view The technician should specify the position of the patient if AP view
29 The heart outline is bigger on D2 PA AP D1 D2 D1 D2 ( bird s-eye view of the patient)
30 Correct standing or sitting Postero Anterior position for chest radiography
31 Standing or sitting position not always easy to obtain
32 If the patient is in supine position (too ill to stand up), the cardiac outline and Mediastinum is enlarged. The scapula may be on the lung field. The chest x-ray has poor quality for analysis
33 Patient in supine position Standing patient with postero-anterior X ray beam The technician should specify the patient position if supine
34 Light film Under penetration No detail visible in the mediastinum area. Dark film no detail visible in the lung area
35 OFCP Correct density and good contrast: - Pulmonary vessels visible in the lungs, below the diaphragm and behind the heart -Para-aortic line visible - Vertebra visible behind the mediastinum
36 Conditions for adequate contrast / density Correct x-ray factor (Kv, Mas, exposure time) Good conditions of developing and good quality of processing chemicals Correct temperature of developer Correct quality of film In case of digitalised or computerised system, imaging quality is adjusted by computer processing and the 3 last conditions are no more needed.
37 Exact front view : the vertical line connecting the spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae is in the middle of the two sterno-clavicular joints
38 Front View l a o r a o D1 D2 D3 D3> D1>D2
39 exact PA view left anterior oblique position cardiac silhouette is smaller
40 right anterior oblique position ( false enlargment of cardiac silhouette)
41 Chest x-ray: to ensure top quality Deep inspiration Adequate contrast / density Correct position of the patient (exact front view) X-ray beam in postero anterior view (the patient is standing)
42
43 Normal chest radiography and some pitfalls ( trouble-shooting)
44 What do you read in this triangle? Courtesy Martina Martins, Charles Perrot and Nigel Howarth (Radiology depatment university hospital Geneva
45
46 Did you notice that «the» was written twice? Courtesy Martina Martins, Charles Perrot and Nigel Howarth (Radiology depatment univerity hospital Geneva
47 Unstructured gaze leads to no results (exemple: the watch that we watch dozens of times) Color and shape of the dial? Arabic or Roman numerals? Form of needles? Location of brand name? Where is the date stamp? Look at your watch: How many mistakes have you done Probably a lot. And yet... this is the subject most frequently watched in the day!!!
48 To enjoy reading the chest radiograph, the gase should be disciplined To discipline the gase one must have resort to a method of examination
49 Young man with a right chest pain and shortness of breath with sudden onset Le syndrome de New York
50 You had of course noticed the large right pneumothorax
51 Did you see that he also had a small left pneumothorax? L imagerie thoracique pour l ECN Pr C. H. Marquette- Pr B. Padovanni
52 Process for analysis of the chest radiography: the check list Verification of name and date Clinical history and findings Verification of the factors for good quality Assess - Thoracic wall and thoracic skeleton («first circle») - Each lung field, one after the other («2 nd circle») - Mediastinum («third circle») Do not skip any item in the checklist!
53 First Circle: Soft part of the chest wall diaphragmatic areas bony thorax
54 Second Circle: Lung tissue Reading from top to bottom Comparing left and right side
55 Third circle: Mediastinum: The container (= edges) The content (= behind the heart Hilus areas
56 The hidden area There are some areas that need special attention, because pathology in these areas can easily be overlooked: Apical zones Hilar zones Retrocardial zone Zone below the dome of diaphragm
57 OFCP Thoracic wall And skeleton
58 Thoracic wall Clavicles External side of Sterno cleido-mastoid muscle
59 Thoracic wall 1 The clavicles are projected on the level of the 3rd or 4th posterior part of ribs 3 4
60 Cervical ribs Minor malformation
61 RUL TB infiltrate?
62 Be aware of foreign body or artefacts on the chest x-ray trap picture: opacity of the superior part of right lung due to a hair braid
63 Breast implant
64 Woman, cough but no fever, no woresening condition. Diagnosis: Right inferior lobe pneumonia
65 Breast prosthesis superposition! (past history of breast cancer )
66 The retro-clavicular fields are always difficult to analyse, because of bone superposition: - Clavicles - Anterior part of first rib - Posterior part of third and fourth rib, - Sterno-clavicular joint
67 There are 2 ways to correctly analyse the retro-clavicular fields: Always compare right and left Ask for a chest x-ray with the patient s back against the film (AP view, lordotic position)
68 Always compare left and right RUL TB infiltrate
69 Patient with fever, cough, AFB sputum positive
70 You have not CT scan. So use your eyes and Compare right and left! If any doubt, request AP/ lordotic chest X ray
71 Special incidence for apex view Courtezy DR Nay Wunn Linn NTP Myanmar
72 Normal chest x-ray, front close to the film Normal AP chest x-ray, back close to the film
73 Chest x-ray, front close to the film Chest x-ray, back close to the film And clavicles out of the field by raising hands
74 Fever and weight loss. No respiratory symptoms
75 Small infiltrate in the right apex well visible on PA view. Notice the difference between right and left apex.
76 Chest x-ray back close to the film
77 Thoracic wall physiological blur of the inferior side of the ribs Rib view section
78 Is this CXR normal?
79 6th and 9th ribs missing on this CXR You must always read a chest x-ray with methodology: For the chest wall, you must look at every rib, one after the other
80 Chest wall Top of the axillar hole Big pectoral muscle
81 Scapula thoracic wall
82 What is wrong with this chest x-ray?
83 What is wrong with this chest x-ray? Congenital clavicles agenesy
84
85 Thoracic wall Breast silhouette
86 Be careful with false opacities in the inferior lobes, consequences of breast superposition.
87 Chest x-ray. Before and after right mastectomy
88 Carefull with the nipples. (not only in women CXR)
89 Thoracic wall Diaphragm The right side is usually higher than the left side (3cm )
90
91 Component elements of lungs
92 On a normal chest x-ray, bronchi are not visible except trachea and proximal part of main right and left bronchi (opacification with iodin hydrosoluble solution)
93 The grey part of this diagrammis visible on the CXR
94 Only trachea and proximal part of main left and right bronchi are visible on the chest X ray
95 but pulmonary arteries are visible.
96 but pulmonary arteries are visible.
97 Pulmonary arteries and bronchial tree are parallelic ( it is not the case for pulmonary veni )
98
99 Small fissura Big fissura Right view
100 Left fissura Left view
101 minor fissure Right superior lobe pneumonia Large oblique fissure posterior part minor fissure
102
103 Right inferior pneumonia Large oblique fissure
104
105 minor fissure Large fissure (anterior part) Small pleural effusion Middle lobe pneumonia
106
107 External segment of middle lobe pneumonia
108 External segment of middle lobe pneumonia
109 Left upper lobe pneumonia
110
111 Left inferior pneumonia Left fissure
112
113
114 Component elements of Mediatinum and hilus
115 AO AO PA PA LA RV RA RV LV LV
116 SVC AO PA AO RA LV RV PA LA LV Front view SVC: superor vena cava AO : aortic vessel PA: pulmonary artery RA: right atrium LV; left ventricle LA: left atrium RV: right ventricle Lateral view LA RA LV RV
117
118
119 Left pulmonary artery Right pulmonary artery
120
121 RSPV LPSV RIPV L A L V The pulmonary vena are not physiologiccally visible
122 RSPV LPSV RIPV L A L V The pulmonary vena are not physiologiccally visible
123 Mediastinum lines X ray beam crossing thorax and mediastinum meets in some places pleural thickness, producing images on the CXR like lines defining mediastinum lines
124 Mediastinum lines 1. Sub clavicle arterial line 2. Posterior mediastinum line 3. Brachio cepahalic vena line 4. para-azygos line Too complicated And not so usefull 5. Anterior mediastinum line 6. Descending aortic line 7. Right and left paravertébral line 8. Inferior veina cava line 9. para-œsophageal line 10. para-trachéal line 6
125 Right paratracheal line Aorto pulmonary line Para-aortic line 3 of them are really important.
126 Para tracheal line Aorto- pulmonary line Para aortic line
127 Mediastinum enlargment due to fat tissu
128 Mediastinum enlargment due to fat tissu
129 Be aware of false enlargment of mediastinum if obesity, poor inspiration, oblique view or supine position
130 Trap: false mediastinum enlargment in the case of this older woman with cyphoscoliosis, in supine position
131
132 Normal lateral view
133 Lateral view
134 AO PA LA RV LV
135 SVC AO PA AO RA LV RV PA LA LV Front view SVC: superor vena cava AO : aortic vessel PA: pulmonary artery RA: right auricle LV; left ventricle LA: left auricle RV: right venticle Lateral view LA RA LV RV
136 Superior vena cava area Ascending Aorta Pulmonary arteria Right ventricle Descending aorta Heart and mediastinum vessels
137 Heart and Mediastinum vessels Left ventricle Inferior vena cava
138 Mediastinum vessels Aortic arch
139 mediastinum vessels Descending aorta
140 Mediastinum vessels Right pulmonary artery Left pulmonary artery
141 normal CXR Lateral view is very useful for diagnosis of mediastinal adenopathies
142 Lateral view is very useful for diagnosis of mediastinal adenopathies
143 trachea 20 mm
144 Right superior lobe bronchus Left superior lobe bronchus
145
146 The «clear spaces» Retro sternal clear space Retro cardiac clear space
147 The «clear spaces» Retro tracheal space
148 enlargment of the clear spaces: Emphysema
149 Emphysema ( notice clear space enlargment and flattened diaphragm ) Normal lateral view
150 The retro sternal space is filled: thymoma
151 The retro sternal space is filled: thymoma. Normal view on the right
152 Diaphragm Right diaphragm Left diaphragm
153 Summary normal CXR
154 Normal frontal chest view Aortic arch (AA) Descending aorta (DA) Proximal left pulmonary artery (PLPA) Left interlobar pulmonary artery (LPA) Aortopulmonary window (AW) Left main bronchus (LB) Left atrial appendage (LAA) Left ventricle (LV) Superior vena cava (SVC) Right paratracheal stripe (RPS) Azygos vein (AV) Aortic arch (AA) Right interlobar pulmonary artery (RIPA) Right atrium (RA) Trachea (T) RD SVC RPTS AV RIPA RA T A A A W DA LPA LB LV LD
155 Normal lateral chest view Posteriorly: vertebral bodies (V) and intervertebral disc spaces (*) Anteriorly: retrosternal clear space (RSCS) Trachea (T) Orifice of Right Upper Lobe bronchus (RUL) appears as circular lucency projecting over the continuation of the tracheal air column Left pulmonary artery (LPA) Right pulmonary artery (RPA) Left auricle (LA) Left ventricle (LV) Right ventricle (RV) Aortic arch (AA) Postero costo phrenic angle (PCPA) Right diphragm (RD) Left diaphragm (LD) Inferior vena cava (IVC) Scapula (Sc) Retro cardiac clear space (RCCS) RD RSCS RPA RUL RV LV T AA LA RCCS IVC LD Sc LPA V * PCPA
NORMAL CHEST RADIOGRAPHY. Front and lateral view
 NORMAL CHEST RADIOGRAPHY Front and lateral view Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) OFCP How to obtain a good quality
NORMAL CHEST RADIOGRAPHY Front and lateral view Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) OFCP How to obtain a good quality
Administrative. Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality
 CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
The silhouette sign. Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP)
 The silhouette sign Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) The silhouette sign When 2 opacities of the same density
The silhouette sign Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) The silhouette sign When 2 opacities of the same density
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chest X-ray STUDY GUIDE 2014-2015
 Internal Medicine Clerkship Chest X-ray STUDY GUIDE 2014-2015 10 Steps/ABC s for Reading Chest X-Rays & Table of Contents to be used with CXR CD-ROM #1 10 Steps / ABC s for Reading Chest X-Rays 0 Normal
Internal Medicine Clerkship Chest X-ray STUDY GUIDE 2014-2015 10 Steps/ABC s for Reading Chest X-Rays & Table of Contents to be used with CXR CD-ROM #1 10 Steps / ABC s for Reading Chest X-Rays 0 Normal
Computed tomographic atlas for the new international lymph node map for lung cancer: A radiation oncologist perspective
 Practical Radiation Oncology (2013) 3, 54 66 www.practicalradonc.org Special Article Computed tomographic atlas for the new international lymph node map for lung cancer: A radiation oncologist perspective
Practical Radiation Oncology (2013) 3, 54 66 www.practicalradonc.org Special Article Computed tomographic atlas for the new international lymph node map for lung cancer: A radiation oncologist perspective
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging. Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the chest and the pulmonary System
 The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the chest and the pulmonary System The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the Chest
The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the chest and the pulmonary System The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the Chest
6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant 8. Blood supply of lungs 9. Lymphatics of Lungs 10. Nerve supply of Lungs 11. Pleura 12.
 ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen
 RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
R/F. Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening. 3. Utility of Chest Tomosynthesis. 1.
 R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Linfoma maligno pulmonar tratado com Nerium oleander. http://www.drozel.org/eng/diagnosis_malignant_mg.htm CASE REPORT
 Linfoma maligno pulmonar tratado com Nerium oleander http://www.drozel.org/eng/diagnosis_malignant_mg.htm CASE REPORT Diagnosis: Malignant lymphoma, lung cancer A 60-year-old woman experienced pain in
Linfoma maligno pulmonar tratado com Nerium oleander http://www.drozel.org/eng/diagnosis_malignant_mg.htm CASE REPORT Diagnosis: Malignant lymphoma, lung cancer A 60-year-old woman experienced pain in
Digital radiography conquers the veterinary world
 Digital radiography conquers the veterinary world Author: Dirk De Langhe Increasingly, veterinarians are using medical imaging to diagnose their patients. There is a corresponding tendency towards replacing
Digital radiography conquers the veterinary world Author: Dirk De Langhe Increasingly, veterinarians are using medical imaging to diagnose their patients. There is a corresponding tendency towards replacing
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Dental Radiography collimator Ionising radiation image radiolucent area radiopaque area controlled zone scatter radiation intraoral
 Dental Radiography X-rays for dental radiography are produced by high voltages of electricity within an x-ray head and come out through a metal tube called a collimator. This ensures the x-rays only come
Dental Radiography X-rays for dental radiography are produced by high voltages of electricity within an x-ray head and come out through a metal tube called a collimator. This ensures the x-rays only come
Normal CT scan of the chest
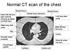 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Case 2. 30 year old involved in a MVA complaining of chest pain. Bruising over the right upper chest. Your Diagnosis
 Case 2 30 year old involved in a MVA complaining of chest pain. Bruising over the right upper chest. Your Diagnosis Diagnosis: Posterior Sterno-clavicular dislocation [PSCD] A posterior sterno-clavicular
Case 2 30 year old involved in a MVA complaining of chest pain. Bruising over the right upper chest. Your Diagnosis Diagnosis: Posterior Sterno-clavicular dislocation [PSCD] A posterior sterno-clavicular
Contents. Acknowledgments...ⅱ
 HANDBOOK Contents Acknowledgments...ⅱ Abbreviations and Units... ⅲ Glossary... ⅳ Introduction...1 I. Why we need quality assurance of chest radiography... 2 Roles of X-ray examination...2 Contribution
HANDBOOK Contents Acknowledgments...ⅱ Abbreviations and Units... ⅲ Glossary... ⅳ Introduction...1 I. Why we need quality assurance of chest radiography... 2 Roles of X-ray examination...2 Contribution
Pulmonary Patterns VMA 976
 Pulmonary Patterns VMA 976 PULMONARY PATTERNS Which pulmonary patterns are commonly described in veterinary medicine? PULMONARY PATTERNS Normal Alveolar Interstitial Structured/Nodular Unstructured Bronchial
Pulmonary Patterns VMA 976 PULMONARY PATTERNS Which pulmonary patterns are commonly described in veterinary medicine? PULMONARY PATTERNS Normal Alveolar Interstitial Structured/Nodular Unstructured Bronchial
Lung & Thorax Exams. Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM cggoldberg@ucsd.edu
 Lung & Thorax Exams Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM cggoldberg@ucsd.edu Lung Exam Includes Vital Signs & Cardiac Exam 4 Elements (cardiac & abdominal too) Observation Palpation Percussion
Lung & Thorax Exams Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM cggoldberg@ucsd.edu Lung Exam Includes Vital Signs & Cardiac Exam 4 Elements (cardiac & abdominal too) Observation Palpation Percussion
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest
 Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Standards for Chest Radiography
 Standards for Chest Radiography First adopted in 1994 and revised in June 2000 These standards were prepared by the Chest Expert Advisory Panel of the CAR: Craig L. Coblentz, M.D., Chair, Frederick Matzinger,
Standards for Chest Radiography First adopted in 1994 and revised in June 2000 These standards were prepared by the Chest Expert Advisory Panel of the CAR: Craig L. Coblentz, M.D., Chair, Frederick Matzinger,
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Chest radiography is the most
 ... Chest Radiography for Radiologic Technologists DAN L. HOBBS, M.S.R.S., R.T.(R)(CT)(MR) The chest exam is performed more frequently than any other exam in the imaging department. It is important for
... Chest Radiography for Radiologic Technologists DAN L. HOBBS, M.S.R.S., R.T.(R)(CT)(MR) The chest exam is performed more frequently than any other exam in the imaging department. It is important for
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System
 Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect
 Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Congestive Heart Failure
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Congestive Heart Failure In Slide Show mode, to advance slides, press spacebar or click left mouse button Congestive Heart Failure Causes of Coronary artery disease Hypertension
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Congestive Heart Failure In Slide Show mode, to advance slides, press spacebar or click left mouse button Congestive Heart Failure Causes of Coronary artery disease Hypertension
The heart walls and coronary circulation
 CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
PRACTICAL TIPS IN ENSURING RADIATION SAFETY IN THE USE OF MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY EQUIPMENT
 PRACTICAL TIPS IN ENSURING RADIATION SAFETY IN THE USE OF MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY EQUIPMENT Although the medical uses of X-rays to examine a patient without surgery became an amazing medical breakthrough,
PRACTICAL TIPS IN ENSURING RADIATION SAFETY IN THE USE OF MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY EQUIPMENT Although the medical uses of X-rays to examine a patient without surgery became an amazing medical breakthrough,
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Page: 1 of 6 Page: 1 of 6
 Page: 1 of 6 Page: 1 of 6 CR Basics and FAQ Overview Computed Radiography is a term used to describe a system that electronically records a radiographic image. Computed Radiographic systems use unique
Page: 1 of 6 Page: 1 of 6 CR Basics and FAQ Overview Computed Radiography is a term used to describe a system that electronically records a radiographic image. Computed Radiographic systems use unique
Resection of Lung Cancer Invading the Mediastinum
 Resection of Lung Cancer Invading the Mediastinum Philippe G. Dartevelle MARIE-LANNELONGUE HOSPITAL GUSTAVE ROUSSY INSTITUTE INSTITUTE OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY PARIS SUD UNIVERSITY Mediastinal Invasion Superior
Resection of Lung Cancer Invading the Mediastinum Philippe G. Dartevelle MARIE-LANNELONGUE HOSPITAL GUSTAVE ROUSSY INSTITUTE INSTITUTE OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY PARIS SUD UNIVERSITY Mediastinal Invasion Superior
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen. Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate Patient information: Breast cancer screening (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is breast cancer screening? Breast
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate Patient information: Breast cancer screening (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is breast cancer screening? Breast
Handbook of radiographic positions and projections in the dog
 THE VETERINARY PUBLISHING COMPANY COMPANION ANIMALS Handbook of radiographic positions and projections in the dog Aimed at veterinary surgeons, students, teachers and other professionals in the veterinary
THE VETERINARY PUBLISHING COMPANY COMPANION ANIMALS Handbook of radiographic positions and projections in the dog Aimed at veterinary surgeons, students, teachers and other professionals in the veterinary
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Radiation-Induced Lung Injury
 May 2001 Radiation-Induced Lung Injury Warren Phipps, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient D.C. is a 50 year-old woman with a 30-pack year history of smoking who presented to the ED because she
May 2001 Radiation-Induced Lung Injury Warren Phipps, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient D.C. is a 50 year-old woman with a 30-pack year history of smoking who presented to the ED because she
Diseases. Inflammations Non-inflammatory pleural effusions Pneumothorax Tumours
 Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects
 Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects This document lists sample learning objectives by subject matter The numerical ranking in parenthesis following
Sample Learning Objectives for a Medical School Radiology Curriculum: Listed by Subjects This document lists sample learning objectives by subject matter The numerical ranking in parenthesis following
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
General Thoracic Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks. C34.11 Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe, right bronchus or lung
 ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
Management of Chest Tubes and Air Leaks after Lung Resection
 Management of Chest Tubes and Air Leaks after Lung Resection Emily Kluck PA-C The Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore, MD AATS 2014, Toronto, CAN April 2014 Management of Chest Tubes 1 Overview Review the
Management of Chest Tubes and Air Leaks after Lung Resection Emily Kluck PA-C The Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore, MD AATS 2014, Toronto, CAN April 2014 Management of Chest Tubes 1 Overview Review the
Doppler. Doppler. Doppler shift. Doppler Frequency. Doppler shift. Doppler shift. Chapter 19
 Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
MEDICAL REPORT MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONS
 MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONS PAGE 1 OF 7 IF YOUR ANSWER IS YES TO ANY OF THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS, PLEASE PROVIDE ADDITIONAL INFORMATION INCLUDING: DIAGNOSIS, DATE, AND TREATMENT (INCLUDING MEDICATIONS AND/OR
MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONS PAGE 1 OF 7 IF YOUR ANSWER IS YES TO ANY OF THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS, PLEASE PROVIDE ADDITIONAL INFORMATION INCLUDING: DIAGNOSIS, DATE, AND TREATMENT (INCLUDING MEDICATIONS AND/OR
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
ANTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION (ALIF) Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Lumbar Spine
 (ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
(ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24
 Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Chest Pain. Acute Myocardial Infarction: Differential Diagnosis and Patient Management. Common complaint in ED. Wide range of etiologies
 Acute Myocardial Infarction: Differential Diagnosis and Patient Management Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Chest Pain
Acute Myocardial Infarction: Differential Diagnosis and Patient Management Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Chest Pain
ENT Emergencies. Injuries of the Neck. Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital
 ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
CHEST TUBES AND CHEST DRAINAGE SYSTEMS
 CHEST TUBES AND CHEST DRAINAGE SYSTEMS Central Nursing Orientation April 2008 Revised September 2011 OBJECTIVES Describe common tubes and indications for use at LHSC Review indications and contraindications,
CHEST TUBES AND CHEST DRAINAGE SYSTEMS Central Nursing Orientation April 2008 Revised September 2011 OBJECTIVES Describe common tubes and indications for use at LHSC Review indications and contraindications,
Radiographic Grid. Principles of Imaging Science II (RAD 120) Image-Forming X-Rays. Radiographic Grids
 Principles of Imaging Science II (RAD 120) Radiographic Grids 1 Image-Forming X-Rays Four X-ray paths a. X-rays interact with patient and scatter away from the receptor b. X-rays interact and are absorbed
Principles of Imaging Science II (RAD 120) Radiographic Grids 1 Image-Forming X-Rays Four X-ray paths a. X-rays interact with patient and scatter away from the receptor b. X-rays interact and are absorbed
Horizon Blue Cross Blue Shield of NJ Radiology Rules Bank
 Horizon Blue Cross Blue Shield of NJ Radiology Rules Bank * Rule added 05/30/13 Code Pay Code Do Not Pay Source 70010 Myelography, posterior fossa, radiological supervision and 76000 Fluoroscopy, up to
Horizon Blue Cross Blue Shield of NJ Radiology Rules Bank * Rule added 05/30/13 Code Pay Code Do Not Pay Source 70010 Myelography, posterior fossa, radiological supervision and 76000 Fluoroscopy, up to
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
 Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Emergency Ultrasound Course
 Emergency Ultrasound Course Dr Justin Bowra ED Course Manual 2: EFAST Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma JUSTIN BOWRA 1 The Questions: 1. Is there free fluid (FF) a. In the pleural space?
Emergency Ultrasound Course Dr Justin Bowra ED Course Manual 2: EFAST Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma JUSTIN BOWRA 1 The Questions: 1. Is there free fluid (FF) a. In the pleural space?
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
IGRT. IGRT can increase the accuracy by locating the target volume before and during the treatment.
 DERYA ÇÖNE RADIOTHERAPY THERAPIST ACIBADEM KOZYATAGI HOSPITAL RADIATION ONCOLOGY DEPARTMENT IGRT IGRT (image-guided radiation therapy) is a technique that reduces geometric uncertainties by considering
DERYA ÇÖNE RADIOTHERAPY THERAPIST ACIBADEM KOZYATAGI HOSPITAL RADIATION ONCOLOGY DEPARTMENT IGRT IGRT (image-guided radiation therapy) is a technique that reduces geometric uncertainties by considering
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients
 Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011
 Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
Common Regional Nerve Blocks Quick Guide developed by UWHC Acute Pain Service Jan 2011 A single shot nerve block is the injection of local anesthetic to block a specific nerve distribution. It can be placed
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax
 NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
How To Treat A Single Ventricle And Fontan
 COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
Production of X-rays. Radiation Safety Training for Analytical X-Ray Devices Module 9
 Module 9 This module presents information on what X-rays are and how they are produced. Introduction Module 9, Page 2 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Other types of electromagnetic radiation
Module 9 This module presents information on what X-rays are and how they are produced. Introduction Module 9, Page 2 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Other types of electromagnetic radiation
Patient Exposure Doses During Diagnostic Radiography
 Patient Exposure Doses During Diagnostic Radiography JMAJ 44(11): 473 479, 2001 Shoichi SUZUKI Associated Professor, Faculty of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Fujita Health University
Patient Exposure Doses During Diagnostic Radiography JMAJ 44(11): 473 479, 2001 Shoichi SUZUKI Associated Professor, Faculty of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Fujita Health University
INTRODUCTION. A. Purpose
 New York State Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Radiation Protection Guide for Radiation Safety/Quality Assurance Programs Computed Radiography INTRODUCTION A. Purpose This guide describes
New York State Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Radiation Protection Guide for Radiation Safety/Quality Assurance Programs Computed Radiography INTRODUCTION A. Purpose This guide describes
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
