EXERCISES. Ex Ex. 2 2
|
|
|
- Tiffany Washington
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXERCISES Ex. 2 1 Balance Sheet Accounts Assets Flight Equipment Purchase Deposits for Flight Equipment a Spare Parts and Supplies Liabilities Accounts Payable Air Traffic Liability b Stockholders Equity None Income Statement Accounts Revenue Cargo and Mail Revenue Passenger Revenue Expenses Aircraft Fuel Expense Commissions (Expense) c Landing Fees (Expense) d a Advance payments (deposits) on aircraft to be delivered in the future b Passenger ticket sales not yet recognized as revenue c Commissions paid to travel agents d Fees paid to airports for landing rights Ex. 2 2 Account Account Number Accounts Payable 21 Accounts Receivable 12 Cash 11 Fees Earned 41 Capital Stock 31 Retained Earnings 32 Dividends 33 Land 13 Miscellaneous Expense 53 Supplies Expense 52 Wages Expense 51 Note: Expense accounts are normally listed in order of magnitude from largest to smallest with Miscellaneous Expense always listed last. Since Wages Expense is normally larger than Supplies Expense, Wages Expense is listed as account 51 and Supplies Expense as account
2 Ex. 2 3 Balance Sheet Accounts 1. Assets 11 Cash 12 Accounts Receivable 13 Supplies 14 Prepaid Insurance 15 Equipment 2. Liabilities 21 Accounts Payable 22 Unearned Rent 3. Stockholders Equity 31 Capital Stock 32 Retained Earnings 33 Dividends Income Statement Accounts 4. Revenue 41 Fees Earned 5. Expenses 51 Wages Expense 52 Rent Expense 53 Supplies Expense 59 Miscellaneous Expense Note: The order of some of the accounts within the major classifications is somewhat arbitrary, as in accounts 13 14, accounts 21 22, and accounts In a new business, the order of magnitude of balances in such accounts is not determinable in advance. The magnitude may also vary from period to period. Ex. 2 4 a. debit g. credit b. debit h. credit c. debit i. debit d. credit j. debit e. debit k. credit f. credit l. debit Ex debit and credit (c) 2. debit and credit (c) 3. debit and credit (c) 4. debit only (a) 5. credit only (b) 6. debit only (a) 7. debit only (a) 60
3 Ex. 2 6 a. Liability credit f. Revenue credit b. Asset debit g. Asset debit c. Stockholders equity credit h. Expense debit d. Asset debit i. Asset debit e. Stockholders equity debit j. Expense debit Ex Oct. 1 Rent Expense... 2,000 Cash... 2,000 2 Advertising Expense Cash Supplies... 1,300 Cash... 1,300 6 Office Equipment... 16,000 Accounts Payable... 16, Cash... 6,700 Accounts Receivable... 6, Accounts Payable... 1,200 Cash... 1, Miscellaneous Expense Cash Utilities Expense Cash Accounts Receivable... 26,800 Fees Earned... 26, Utilities Expense Cash Dividends... 3,000 Cash... 3,000 61
4 Ex. 2 8 a. JOURNAL Page 19 Post. Date Description Ref. Debit Credit 2012 Feb. 3 Supplies ,250 Accounts Payable ,250 Purchased supplies on account. b., c., d. Supplies 15 Post. Balance Date Item Ref. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr Feb. 1 Balance , , Accounts Payable Feb. 1 Balance , , ,400 e. Yes, the rules of debit and credit apply to all companies. Ex. 2 9 a. (1) Accounts Receivable... 35,700 Fees Earned... 35,700 (2) Supplies... 2,000 Accounts Payable... 2,000 (3) Cash... 26,150 Accounts Receivable... 26,150 (4) Accounts Payable Cash
5 Ex. 2 9 (Concluded) b. Cash Accounts Payable (3) 26,150 (4) 800 (4) 800 (2) 2,000 Supplies Fees Earned (2) 2,000 (1) 35,700 Accounts Receivable (1) 35,700 (3) 26,150 c. No. A credit balance in Accounts Receivable could occur if a customer over paid his or her account. Regardless, the credit balance should be investigated to verify that an error has not occurred. Ex a. The increase of $110,000 ($400,000 $290,000) in the cash account does not indicate net income of that amount. Net income is the net change in all assets and liabilities from operating (revenue and expense) transactions. b. $75,000 ($185,000 $110,000) Ex a. Accounts Payable Oct. 1 X 90, ,000 Oct ,000 X + $125,000 $90,000 = $40,000 X = $40,000 + $90,000 $125,000 X = $5,000 63
6 Ex (Concluded) b. Accounts Receivable May 1 25, ,000 X May 31 36,000 $25,000 + X $240,000 = $36,000 X = $36,000 + $240,000 $25,000 X = $251,000 c. Cash Nov. 1 18,275 X 279,100 Nov ,200 $18,275 + $279,100 X = $13,200 X = $18,275 + $279,100 $13,200 X = $284,175 Ex a. Debit (negative) balance of $12,000 ($125,000 $7,000 $130,000). This negative balance means that the liabilities exceed the assets. b. Yes. The balance sheet prepared at December 31 will balance, with retained earnings being reported in the stockholders equity section as a debit (negative) balance of $12,
7 Ex a. and b. Account Debited Account Credited Transaction Type Effect Type Effect (1) asset + capital stock + (2) asset + asset (3) asset + asset liability + (4) expense + asset (5) asset + revenue + (6) liability asset (7) asset + asset (8) expense + asset (9) dividends + asset Ex (1) Cash... 40,000 Capital Stock... 40,000 (2) Supplies... 2,000 Cash... 2,000 (3) Equipment... 18,000 Accounts Payable... 14,400 Cash... 3,600 (4) Operating Expenses... 2,700 Cash... 2,700 (5) Accounts Receivable... 18,500 Service Revenue... 18,500 (6) Accounts Payable... 9,000 Cash... 9,000 (7) Cash... 10,000 Accounts Receivable... 10,000 (8) Operating Expenses... 1,050 Supplies... 1,050 (9) Dividends... 4,000 Cash... 4,000 65
8 Ex a. SOUTHWEST TOURS CO. Unadjusted Trial Balance May 31, 2012 Debit Credit Balances Balances Cash... 28,700 Accounts Receivable... 8,500 Supplies Equipment... 18,000 Accounts Payable... 5,400 Capital Stock... 40,000 Dividends... 4,000 Service Revenue... 18,500 Operating Expenses... 3,750 63,900 63,900 b. Net income, $14,750 ($18,500 $3,750) 66
9 Ex DIVA CO. Unadjusted Trial Balance July 31, 2012 Debit Credit Balances Balances Cash... 15,000 Accounts Receivable... 40,000 Supplies... 4,000 Prepaid Insurance... 6,400 Land ,000 Accounts Payable... 28,000 Unearned Rent... 13,500 Notes Payable... 50,000 Capital Stock... 20,000 Retained Earnings... 29,900 Dividends... 25,000 Fees Earned ,000 Wages Expense ,000 Rent Expense... 36,000 Utilities Expense... 18,000 Supplies Expense... 9,000 Insurance Expense... 6,000 Miscellaneous Expense... 12, , ,400 Ex Inequality of trial balance totals would be caused by errors described in (c) and (e). For (c), the debit total would exceed the credit total by $2,400 ($1,200 + $1,200). For (e), the credit total would exceed the debit total by $9,000 ($10,000 $1,000). Errors (b), (d), and (e) would require correcting entries. 67
10 Ex SEATS-FOR-YOU CO. Unadjusted Trial Balance March 31, 2012 Debit Credit Balances Balances Cash... 15,500 Accounts Receivable... 25,800 Prepaid Insurance... 9,000 Equipment... 75,000 Accounts Payable... 12,900 Unearned Rent... 5,400 Capital Stock... 30,000 Retained Earnings... 51,700 Dividends... 13,000 Service Revenue ,000 Wages Expense... 60,000 Advertising Expense... 11,300 Miscellaneous Expense... 15, , ,000 Ex (a) (b) (c) Error Out of Balance Difference Larger Total 1. yes $7,150 debit 2. no 3. yes 2,000 credit 4. yes 800 debit 5. no 6. yes 270 credit 7. yes 180 credit 68
11 Ex The Debit column total is added incorrectly. The sum is $583,500 rather than $916, The trial balance should be dated August 31, 2012, not For the Month Ending August 31, The Accounts Receivable balance should be in the Debit column. 4. The Accounts Payable balance should be in the Credit column. 5. Dividends balance should be in the Debit column. 6. The Advertising Expense balance should be in the Debit column. A corrected trial balance would be as follows: BLUEFIN CO. Unadjusted Trial Balance August 31, 2012 Debit Credit Balances Balances Cash... 45,000 Accounts Receivable... 98,400 Prepaid Insurance... 21,600 Equipment ,000 Accounts Payable... 11,100 Salaries Payable... 7,500 Capital Stock... 75,000 Retained Earnings ,200 Dividends... 36,000 Service Revenue ,200 Salary Expense ,860 Advertising Expense... 43,200 Miscellaneous Expense... 8, , ,000 Ex a. Prepaid Rent... 12,500 Cash... 12,500 b. Dividends... 7,500 Wages Expense... 7,500 69
12 Ex a. Cash... 25,950 Fees Earned... 12,975 Accounts Receivable... 12,975 b. Accounts Payable... 3,200* Supplies Expense... 3,200 Supplies... 3,200 Cash... 3,200 *The first entry reverses the original entry. The second entry is the entry that should have been made initially. Ex a. 1. Net sales: $1,581 million increase ($64,948 $63,367) 2.5% increase ($1,581 $63,367) 2. Total operating expenses: $2,451 million increase ($60,546 $58,095) 4.2% increase ($2,451 $58,095) b. During 2009, the percentage increase in total operating expenses (4.2%) is more than the percentage increase in net sales (2.5%), an unfavorable trend. Ex a. KMART CORPORATION Income Statement For the Years Ended January 31, 2000 and 1999 (in millions) Increase (Decrease) Amount Percent 1. Sales... $ 37,028 $ 35,925 $ 1, % 2. Cost of sales... (29,658) (28,111) 1, Selling, general, and administrative expenses... (7,415) (6,514) Operating income (loss) before taxes... $ (45) $ 1,300 $(1,345) (103.5) 70
13 Ex (Concluded) b. The horizontal analysis of Kmart Corporation reveals deteriorating operating results from 1999 to While sales increased by $1,103 million, a 3.1% increase, cost of sales increased by $1,547 million, a 5.5% increase. Selling, general, and administrative expenses also increased by $901 million, a 13.8% increase. The end result was that operating income decreased by $1,345 million, over a 100% decrease, and created a $45 million loss in Little over a year later, Kmart filed for bankruptcy protection. It has now emerged from bankruptcy and was merged into Sears to form the company Sears Holding Corporation. 71
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
CHAPTER 3 THE ADJUSTING PROCESS
 1. a. Under cash-basis accounting, revenues are reported in the period in which cash is received and expenses are reported in the period in which cash is paid. b. Under accrual-basis accounting, revenues
1. a. Under cash-basis accounting, revenues are reported in the period in which cash is received and expenses are reported in the period in which cash is paid. b. Under accrual-basis accounting, revenues
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET
 Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
Supplement to CHAPTER 3 CLOSING ENTRIES AND THE WORK SHEET Answers to Review Questions 1. No, the work sheet cannot be used as a substitute for the financial statements. It is a tool used in preparing
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
Accumulated Depreciation Equipment
 Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle > DO IT! Worksheet Balance sheet: Extend assets to debit column. Extend liabilities to credit column. Extend contra assets to credit column. Extend drawings account
The Statement of Cash Flows Direct Method
 23 The Statement of Cash Flows Direct Method DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM The financial statements of Bolero Corporation follow. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 1 Bolero Corporation Income
23 The Statement of Cash Flows Direct Method DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM The financial statements of Bolero Corporation follow. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 1 Bolero Corporation Income
Chapter 2. Analyzing transactions
 1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 16
 Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
Learning Goal 16: Prepare Closing Entries S1 Learning Goal 16 Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. b 4. d Because drawing is closed directly into the capital account, not into income summary. 5. c 6. b This a
Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and
 Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
PROFESSOR S NAME ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8)
 COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) Page 137 NAME ANSWER KEY PROFESSOR S NAME SECTION SCORE ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) INSTRUCTIONS: COMPLETE ALL
COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) Page 137 NAME ANSWER KEY PROFESSOR S NAME SECTION SCORE ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) INSTRUCTIONS: COMPLETE ALL
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings
 Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process
 The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process o b j e c t i v e s After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 4 Explain how the matching concept relates to the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process o b j e c t i v e s After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 4 Explain how the matching concept relates to the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
Chapter 1. Introduction to Accounting and Business
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
CHAPTER 5 ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING BUSINESSES
 1. Merchandising businesses acquire merchandise for resale to customers. It is the selling of merchandise, instead of a service, that makes the activities of a merchandising business different from the
1. Merchandising businesses acquire merchandise for resale to customers. It is the selling of merchandise, instead of a service, that makes the activities of a merchandising business different from the
CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME
 CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME Chapter 3, SE 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. c b d a Chapter 3, SE 2. Dec. 31 Insurance Expense 800 Prepaid Insurance To record insurance expired during the year $460 + $1,040
CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME Chapter 3, SE 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. c b d a Chapter 3, SE 2. Dec. 31 Insurance Expense 800 Prepaid Insurance To record insurance expired during the year $460 + $1,040
Financial Statements Tutorial
 Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
The Adjusting Process
 Chapter 03.qxd 5/21/08 7:07 PM Page 99 C H A P T E R 3 AP Photo/Jeff Kravitz Fo r Sa le The Adjusting Process M A R V E L D E N T E R T A I N M E N T, N ot o you subscribe to any magazines? Most of us
Chapter 03.qxd 5/21/08 7:07 PM Page 99 C H A P T E R 3 AP Photo/Jeff Kravitz Fo r Sa le The Adjusting Process M A R V E L D E N T E R T A I N M E N T, N ot o you subscribe to any magazines? Most of us
COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE
 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Review the seven basic steps of the accounting cycle. Prepare a work sheet. Prepare financial statements
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
 Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
EXERCISES. The cash from operating activities detail is provided as follows for class discussion:
 EXERCISES Ex. 14 1 There were net additions, such as depreciation and amortization of intangible assets of $389 million, to the net loss reported on the income statement to convert the net loss from the
EXERCISES Ex. 14 1 There were net additions, such as depreciation and amortization of intangible assets of $389 million, to the net loss reported on the income statement to convert the net loss from the
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations
 Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
Chapter 5 Accounting for Merchandising Operations Purchase Transactions Purchaser records goods at cost. When goods are returned, purchaser reduces Inventory. On September 5, De La Hoya Company buys merchandise
The worksheet for Hancock Company shows the following in the financial statement
 Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
Chapter 4 Do it! Susan Elbe is preparing a worksheet. Explain to Susan how she should extend the following adjusted trial balance accounts to the financial statement columns of the worksheet. Cash Accumulated
BUS312A/612A Financial Reporting I. Homework 9.10.2014 & 9.15.2014 The Accounting Cycle Review Chapter 3
 BUS312A/612A Financial Reporting I Homework 9.10.2014 & 9.15.2014 The Accounting Cycle Review Chapter 3 E3-1 (Transaction Analysis-Service Company) During the first month of operations of her business
BUS312A/612A Financial Reporting I Homework 9.10.2014 & 9.15.2014 The Accounting Cycle Review Chapter 3 E3-1 (Transaction Analysis-Service Company) During the first month of operations of her business
> DO IT! Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts. Timing Concepts. Adjusting Entries for Deferrals D-12. Solution
 Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University, Boone, NC 28608, pollardwb@appstate.edu INTRODUCTION
 TEACHING PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING: HELPING STUDENTS IDENTIFY TEN DIFFERENCES WHEN COMPARING A TRIAL BALANCE, AN ADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE AND A BALANCE SHEET William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University,
TEACHING PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING: HELPING STUDENTS IDENTIFY TEN DIFFERENCES WHEN COMPARING A TRIAL BALANCE, AN ADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE AND A BALANCE SHEET William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University,
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Vol. 1, Chapter 4 Corporate Accounting
 Vol. 1, Chapter 4 Corporate Accounting Problem 1 The high and low prices for McDonald s stock over the last 52 weeks were $35.91 and $27.36 respectively. The annual cash dividend yield is 1.9% of that
Vol. 1, Chapter 4 Corporate Accounting Problem 1 The high and low prices for McDonald s stock over the last 52 weeks were $35.91 and $27.36 respectively. The annual cash dividend yield is 1.9% of that
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries
 Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
Authored for ENMU Tutoring Services. By Jessica Huff
 By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
CHAPTER 4. Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
CHAPTER 4 Adjusting the accounts and preparing financial statements CONTENTS Demonstration problem 4.1 Adjusting entries and corrections 4.2 Adjusting centries and effect on financial statements 4.3 Adjusting
HERE'S A TIP. Double Entry Accounting. Debits and Credits
 Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca)
 Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
Periodicity Assumption... Time Period Assumption... Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts
 Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 4th Ed. CHAPTER 4 Kimmel, Weygandt, Kieso Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts KEY THINGS WE LL DO: Refresh and expand Ch.3 concepts. Differentiate
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 4th Ed. CHAPTER 4 Kimmel, Weygandt, Kieso Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts KEY THINGS WE LL DO: Refresh and expand Ch.3 concepts. Differentiate
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
TRADING ACCOUNT (Horizontal Format) for the year ended. Particulars. Rs.
 Dr. To Opening Stock To Purchases Less: Returns outwards () To Frieght & Carriage To Customs & Insurance To Wages To Gas, Water & Fuel To Factory Expenses To Royalty on Production To Cargo Expenses To
Dr. To Opening Stock To Purchases Less: Returns outwards () To Frieght & Carriage To Customs & Insurance To Wages To Gas, Water & Fuel To Factory Expenses To Royalty on Production To Cargo Expenses To
Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures
 Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
Chapter 13 - Financial Statements and Closing Procedures Chapter 13 Financial Statements and Closing Procedures TEACHING OBJECTIVES 13-1) Prepare a classified income statement from the worksheet. 13-2)
The Accounting Process
 GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
Adjusting and Closing Entries
 Adjusting and Closing Entries Adjusting and Closing entries tend to be difficult to grasp at first. A reason for this might be due to the type of transactions requiring adjustment, which tend to be unfamiliar.
Adjusting and Closing Entries Adjusting and Closing entries tend to be difficult to grasp at first. A reason for this might be due to the type of transactions requiring adjustment, which tend to be unfamiliar.
1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000.
 Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance
 6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
6-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Closing Entries and the Postclosing Trial Balance 6 Section 1: Closing Entries Section Objectives 1. Journalize and post
CHAPTER 3. BE3-2 Advertising. Dec. 31 Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 to adjust. BE3-3 Bere Co.
 CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
The Work Sheet and the Closing Process
 C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
SOLUTIONS TO BRIEF EXERCISES
 SOLUTIONS TO BRIEF EXERCISES B. Ex. 2.1 Walters Company's assets (machinery) will increase by $20,000. The company's liabilities will also increase by $20,000 to include the new obligation the company
SOLUTIONS TO BRIEF EXERCISES B. Ex. 2.1 Walters Company's assets (machinery) will increase by $20,000. The company's liabilities will also increase by $20,000 to include the new obligation the company
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows
 Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS
 CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises Topic Learning Objectives Skills B. Ex. 5.1 B. Ex.
CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises Topic Learning Objectives Skills B. Ex. 5.1 B. Ex.
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements
 CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
CHAPTER 4 COMPLETING THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 4
Baseline Assessment. Date Accounting 1
 Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Name Baseline Assessment Date Accounting 1 Part 1: Instructions: Place a check mark under the column for each account to determine which Financial the accounts belongs on. Financial Information 1. Cash
Time Period Assumption
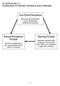 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J
 Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3
 Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3 The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic Events Peter Rivera August 2011 Disclaimer This Quiz Prep is provided as an outline of the key
Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3 The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic Events Peter Rivera August 2011 Disclaimer This Quiz Prep is provided as an outline of the key
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 15
 Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
How To Account For Revenue Under Accrual Accounting
 BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Shari Mann Professor Donna Psutka Professor Mindy Wolfe Mid-Term Examination Fall 2010 Date and Time: October 21, 2010, 6:30 8:00pm
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Shari Mann Professor Donna Psutka Professor Mindy Wolfe Mid-Term Examination Fall 2010 Date and Time: October 21, 2010, 6:30 8:00pm
ACCOUNTING 105 CONCEPTS REVIEW
 ACCOUNTING 105 CONCEPTS REVIEW A note from the tutors: This handout is designed to help you review important information as you study for your cumulative final exam. While it does cover many important
ACCOUNTING 105 CONCEPTS REVIEW A note from the tutors: This handout is designed to help you review important information as you study for your cumulative final exam. While it does cover many important
A Simple Model. The Accounting Equation
 An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
國 立 體 育 學 院 九 十 六 學 年 度 學 士 班 轉 學 考 試 試 題
 國 立 體 育 學 院 九 十 六 學 年 度 學 士 班 轉 學 考 試 試 題 會 計 學 ( 本 試 題 共 8 頁 ) 注 意 :1 答 案 一 律 寫 在 答 案 卷 上, 否 則 不 予 計 分 2 請 核 對 試 卷 准 考 證 號 碼 與 座 位 號 碼 三 者 是 否 相 符 3 試 卷 彌 封 處 不 得 汚 損 破 壞 4 行 動 電 話 或 呼 叫 器 等 通 訊 器 材 不
國 立 體 育 學 院 九 十 六 學 年 度 學 士 班 轉 學 考 試 試 題 會 計 學 ( 本 試 題 共 8 頁 ) 注 意 :1 答 案 一 律 寫 在 答 案 卷 上, 否 則 不 予 計 分 2 請 核 對 試 卷 准 考 證 號 碼 與 座 位 號 碼 三 者 是 否 相 符 3 試 卷 彌 封 處 不 得 汚 損 破 壞 4 行 動 電 話 或 呼 叫 器 等 通 訊 器 材 不
GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich
 GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich Multiple Choice (3 points for each question) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Wynn Corp. Wynn Corp. reported
GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich Multiple Choice (3 points for each question) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Wynn Corp. Wynn Corp. reported
MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com. Fall 2009
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping
 Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report
 Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
Consolidated Interim Earnings Report For the Six Months Ended 30th September, 2003 23th Octorber, 2003 Hitachi Capital Corporation These financial statements were prepared for the interim earnings release
Chapter 4: Accounting Records
 Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Accounting II Second Semester Final
 Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs
 ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
ACC 211/212: Double Entry Logs Journal Entries: o Credits are always indented (account name and value). o The sum of debits will always equal the sum of credits. o The month name is required only for the
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
Student s name: SSN s: (Last, First Name) (Last 4#) Comprehensive Problem Fall 03
 Student s name: SSN s: (Last, First Name) (Last 4#) Comprehensive Problem Fall 03 Ken Harper, Master Chef A.k.a., Ken Harper Cooking School Company Profile and Background: For the past several months,
Student s name: SSN s: (Last, First Name) (Last 4#) Comprehensive Problem Fall 03 Ken Harper, Master Chef A.k.a., Ken Harper Cooking School Company Profile and Background: For the past several months,
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II
 Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Gold Run Snowmobile. Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31. Final Project Evaluation. 5 th Edition.
 Gold Run Snowmobile 5 th Edition Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31 and the Final Project Evaluation Page 1 ADJUSTING ENTRIES FOR THE QUARTER Using a copy of the December
Gold Run Snowmobile 5 th Edition Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31 and the Final Project Evaluation Page 1 ADJUSTING ENTRIES FOR THE QUARTER Using a copy of the December
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed
 Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
Statement of Change in Working Capital & Inflows/Outflows of Working Capital
 HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Change in Working Capital & Inflows/Outflows of Working Capital The statement of changes in working capital shows the net change in working capital
HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Change in Working Capital & Inflows/Outflows of Working Capital The statement of changes in working capital shows the net change in working capital
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201
 The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
Delta Air Lines, Inc. David Pruchno BUS 210-00A-Su13 - M/W 6-9
 Delta Air Lines, Inc. David Pruchno BUS 210-00A-Su13 - M/W 6-9 http://www.delta.com/content/dam/delta-www/pdfs/about-financial/deltaairlines_10k_2012.pdf Introduction Richard H Anderson, CEO Former UnitedHealth
Delta Air Lines, Inc. David Pruchno BUS 210-00A-Su13 - M/W 6-9 http://www.delta.com/content/dam/delta-www/pdfs/about-financial/deltaairlines_10k_2012.pdf Introduction Richard H Anderson, CEO Former UnitedHealth
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow:
 Problems 2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow: Increase in accounts receivable Increase in notes payable Depreciation expense Increase in investments Decrease
Problems 2-8. Identify whether each of the following items increases or decreases cash flow: Increase in accounts receivable Increase in notes payable Depreciation expense Increase in investments Decrease
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 3 The General Journal and the General Ledger DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM G. Bell, a fitness enthusiast, buys an existing exercise center, Body Firm. The following chart of accounts now applies: Assets Revenue
3 The General Journal and the General Ledger DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM G. Bell, a fitness enthusiast, buys an existing exercise center, Body Firm. The following chart of accounts now applies: Assets Revenue
How To Calculate A Book Value Of A Stock
 CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET As of Assets Current assets Cash $ 32,736 Loan Receivables - Related Parties 15,285 Total current assets 48,021 Investment 55,000 Total assets $ 103,021 Current liabilities Liabilities
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET As of Assets Current assets Cash $ 32,736 Loan Receivables - Related Parties 15,285 Total current assets 48,021 Investment 55,000 Total assets $ 103,021 Current liabilities Liabilities
Accounting 300A-10A The Operating Cycle: Worksheet/Closing Entries Page 1
 Accounting 3A-1A The Operating Cycle: Worksheet/Closing Entries Page 1 THE WORKSHEET and CLOSING ENTRIES I. Review of Key Concepts and Terms: A. The purpose of the worksheet 1. To show that the accounts
Accounting 3A-1A The Operating Cycle: Worksheet/Closing Entries Page 1 THE WORKSHEET and CLOSING ENTRIES I. Review of Key Concepts and Terms: A. The purpose of the worksheet 1. To show that the accounts
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives
 CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
CHAPTER 4 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: ACCRUALS AND DEFERRALS
 CHAPTER 4 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: ACCRUALS AND DEFERRALS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS, AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises B. Ex. 4.1 B. Ex. 4.2 B. Ex. 4.3 B. Ex. 4.4 Topic Deferred
CHAPTER 4 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: ACCRUALS AND DEFERRALS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS, AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises B. Ex. 4.1 B. Ex. 4.2 B. Ex. 4.3 B. Ex. 4.4 Topic Deferred
Statement of Cash Flows
 HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows (or cash flow statement) is one of the main financial statements used by investors. It shows the cash generated
HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows (or cash flow statement) is one of the main financial statements used by investors. It shows the cash generated
