Perth Academy. Geography Department
|
|
|
- Rosa Cobb
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Perth Academy Geography Department Natural Hazards Tropical Storms
2 Natural Hazards Natural Hazards affect a large percentage of the world s population. Despite the damage and destruction caused, there are still many people living in areas affected by them. Unit Overview In this unit we will examine the main features of natural hazards, with a main focus on tropical storms. Over the coming weeks we will focus on the following aspects of tropical storms: What are natural hazards? Where are they found and why? How are they formed? Their effects. Contrasting case studies of a tropical storm in a developing and a developed country. Methods of predicting tropical storms. Preparing for tropical storms. 1 Unit Introduction What is a natural hazard? Where do they take place? In your groups, write down everything you know about natural hazards onto your section of the place mat, you have 2 minutes to do this. Watch the video clip on natural hazards and answer the following questions in your jotter: 1. Write down 3 types of natural hazard. 2. How do natural hazards affect humans? 3. What hazards can human activity contribute to? 4. In which area has the risk of flooding increased? 5. How can humans reduce the risk of hazards?
3 The exposure of an area to various natural hazards depends on its location in the world. Some areas are more prone to earthquakes than others, some are more at risk of hurricanes etc. Using your blank world map, shade in the world s natural hazards hotspots, from the diagram below and on the screen. 2 With the help of an atlas, use your shaded map to name 10 countries threatened by the risk of natural hazards. Throughout history, these hazards have caused many problems for societies, whether it be structural damage, loss of plant life, or indeed death. Read over the accompanying data sheet, showing some of the deadliest hazards in the world s history. Construct a bar graph, showing the 10 deadliest natural hazards in world history, using the information sheet. Your graph must have: A title Labelled axis Units of measurement An appropriate scale Colour A key
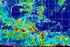
4 Tropical Storms What is a tropical storm? Tropical storms are large areas of intense low pressure and extreme depressions. On a satellite image (see picture above), a tropical storm will show as a huge, swirling mass of cloud. 3 A low pressure system, or "low", is an area where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of the area surrounding it. Lows are usually associated with high winds, warm air, and atmospheric lifting. Because of this, lows normally produce clouds, precipitation, and other bad weather such as hurricanes and cyclones. At the centre of a tropical storm, there is a calm area with no wind known as the eye of the storm. The route taken by a tropical storm is called its path. Does Scotland get Tropical Storms? Why do they not form everywhere? The Location of Tropical Storms
5 Using the blank map provided, shade in the areas where tropical storms form and glue this into your jotter under the heading, The Location of Tropical Storms. Under your map, write a paragraph describing the areas where these storms are found. Remember to include as much detail as possible, such as the names of countries, oceans and lines of latitude. What do you notice about the names of the tropical storms across the world? 4 The Formation of Tropical Storms Tropical storms use warm, moist air as fuel. That is why they form only over warm ocean waters near the equator. The warm, moist air over the ocean rises rapidly upward from near the surface and becomes saturated with evaporated moisture. This means that there is less air left at the surface (i.e. low pressure). Air from surrounding areas with higher air pressure rushes in to the low pressure area to try to equalise the pressure. Then that new air becomes warm and moist and rises, too. As the warm air continues to rise, the surrounding air swirls in to take its place. The rotation of the Earth encourages violent winds to rotate around the central eye of the storm. These winds are anti-clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere. In the central eye, the pressure is very low with descending winds, increasing temperatures, clear skies and calm, dry conditions. As the warmed, moist air rises and cools off, the water in the air forms towering cumulonimbus thunderclouds (because there is a huge amount of condensation). The whole system of clouds and wind spins and grows, fed by the ocean s heat and water evaporating from the surface.
6 : Pop-up tropical storms Complete this task in your jotter using templates, coloured pencils and instructions from the powerpoint. World Distribution of Tropical Storms As we have seen from our map, tropical storms are only found in certain areas of the world. These are the areas that have the necessary conditions for them to form. These are: Warm seas, which have a surface temperature of 27 C or more and water to a depth of at least 60 metres. A low air pressure, with the air beginning to rise. Damp moist air with a relative humidity of 60% or more. Between latitudes 5 and 20 north and south of the equator i.e. between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. 5 Copy the bullet points showing the necessary conditions for tropical storms to form into your jotter under the heading Necessary Conditions for Tropical Storms. As you will remember from your map showing the location of tropical storms, depending when you are in the world, a tropical storm will have a different name. For example: In America, the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico i.e. the Atlantic Ocean, these storms are called Hurricanes. In the Pacific Ocean they are known as Typhoons. In the Indian Ocean they are known as Cyclones. In Australia they are known as Willie-Willies. What do you notice about these tropical storms? Why does this happen?
7 A tropical storm is classified as a hurricane when wind speeds reach 74 miles per hour, though hurricane winds can be much faster. The centre of a hurricane is called an eye, where winds are light and cloud is broken. Since 1954, all tropical storms have been given names so they can be identified quickly and told apart. The first storm of the year will be given a name beginning with A' for example Alexandra, the next with B etc. Only women s names were used in the past, but from 1979 alternate male and female names have been used. There are six lists of names that are used in rotation and recycled every six years so the 2013 list will be used again in The names of powerful hurricanes, which caused a lot of damage, are never used again. 6 Effects of Tropical Storms
8 Tropical storms can have devastating effects on people, wildlife, plant life and infrastructure. Areas affected often take many years to recover from a single storm. The effects that areas experience can be divided into primary and secondary. Primary effects are the immediate physical effects which an area can experience. For example: High winds Torrential Rain Storm Surges Localised Tornadoes and Waterspouts 7 Secondary effects are the longer term impacts, which affect the area for an extended period of time. The length of time it takes for an area to recover is largely dependent upon its development, i.e. its wealth. This is something we will focus on in more detail during our case studies. These secondary effects can be social, economic or environmental: Social: effects on people and society Economic: effects on the wealth of the area Environmental: effects on the atmosphere, landscape, plant life, wildlife etc. In pairs, organise the cards showing effects of tropical storms under the correct heading - social, economic or environmental. Once you have decided where each of the cards should go, we will discuss as a class and then copy the final list into your jotters under the heading Effects of Tropical Storms.
9 Storm Surges Storm surges occur where the sea level along a shoreline rises as the result of a storm. This is shown in the diagram below: 8 There are two main causes of storm surges: 1. The Eye Pile: The low pressure draws the water beneath it upwards to form the eye pile. It gets dragged along with the eye. The eye pile grows in height as it is forced into shallower water. It splats onto the land as the storm makes landfall. 2. Wind-blown Water: Zonal winds push the water in the same direction that they are moving. If the wind blows long enough and hard enough, the water banks up and floods the land when the wind blows onshore. Copy the diagram and information on storm surges into your jotter. Measuring Tropical Storms You may have heard in some of the videos reference to a category of hurricane in reference to how severe it is. The strength of a tropical storm is measured using the Saffir- Simpson Scale:
10 Using the information from video, write down a named example of each category of hurricane and the year it hit. How many category 5 hurricanes have made landfall in the USA? Tropical storms usually weaken when they hit the land because they are no longer being fed by the energy from the warm ocean waters. When passing over the Caribbean, they can weaken as they pass over the islands before strengthening again as they pass over water and head towards the coast of the USA. 9 Developed Country Case Study Research a tropical storm of your choice and present your findings e.g. poster, powerpoint, written report, newspaper report, creative eyewitness account etc. Regardless, you will need to make sure that you include the following: The name and dates of the storm How the storm formed Where the storm formed The strength of the storm The path that the storm took from beginning to end Include the names of countries, oceans and/or US states that it passes though Describe the effects of the winds and heavy rainfall on people and the landscape including: Forests Farming Buildings Bridges Communications Describe the impact of the storm surge in coastal areas on people and the landscape The more detail you include, the better your work will be. Make sure that you include diagrams and pictures to prove what you have written.
11 Developed Country Case Study: Hurricane Katrina On the morning of August 23 rd 2005, Hurricane Katrina formed over the skies of Florida due to hot and humid weather conditions. As it worked its way across the state, it was still only classified as a category 1 hurricane but had already started taking lives and causing destruction. When she reached the Gulf of Mexico, she had grown to a category 3 hurricane, due to the warm water in the gulf. By the time she was in full flow, Katrina had reached a staggering category 5 status, making it the 6 th most powerful hurricane in history. This new surge and growth that she had gained caused death and destruction from Florida to Texas. The states affected most by the hurricane were Louisiana, Mississippi, Texas, Alabama and Florida. 10 Shade in the areas affected by Hurricane Katrina on your blank map of the USA and glue this into your jotter. Identify the following areas on your map: the Gulf of Mexico, New Orleans, Louisiana, Alabama, Mississippi, Florida. Of all the areas affected by Katrina however, New Orleans suffered by far the most in terms of the people and the landscape. These effects are still visible in the area today. In reflecting upon this great storm hitting the area, many scientists believe that more could have been done to limit the damage from the storm. Watch the documentary on Hurricane Katrina and take notes under the following headings: Effects on People, Effects on Landscape, Causes, Response to Storm. Using the information you have gathered, in pairs produce a story board, outlining the key stages in the storm s impact on New Orleans.
12 Predicting Tropical Storms With the increased use of and improvements in technology over the last 20 years, it has become easier for patterns of weather to be tracked in advance. The use of satellite communication has made this a much more simplistic exercise, giving forecasters an opportunity to produce detailed reports in advance, which can be broadcast via television and the internet. 11 Why Where are does tropical this information storms easier come to predict? from? Rich developed countries, such as the USA, can invest in technology to predict the general area in which hurricanes will strike. This technology is not so readily available to developing countries although many countries receive information from organisations such as the Joint Typhoon Warning Centre (Pacific) or National Hurricane Centre (Atlantic) to help them prepare for storms. The track of a tropical storm is affected by a great many factors, so they are very unpredictable. Forecasters have a 20-25% chance of knowing exactly where a tropical storm will hit 48 in advance of landfall. Forecasts are made available to residents on the internet so that they can make decisions about whether they need to evacuate. This is obviously a much more useful means of communication in a developed country where the percentage of residents with internet access is much higher than in developing countries. Indeed one of the major problems in preparing for a storm in a developing is communicating with the people in an area that is likely to be affected as the infrastructure may well be poorly developed. Watch the above clips showing some of the methods used to predict hurricanes and take notes in the form of a mind map.
13 Preparing for Tropical Storms 12 As a result of improved technology and communication systems governments are now better equipped to warn their residents about the onset of a tropical storm. Due to differing levels of risk for individual storms and the possibility of inaccurate predictions, full evacuations are not always possible or practical; citizens are informed by governments of the steps that can be taken in preparation for a hurricane. Brainstorm with the person sitting beside you the different ways that you think that both countries and individuals can predict that tropical storms will happen and ways of planning to reduce the damage that storms may cause. Share this information with your table and combine all of your thoughts. Create a spider diagram showing all of your ideas.
14 Hurricane Survival Kit Surviving the threat of a tropical storm can be made easier through the correct advice from governments and the owning of appropriate items. In this lesson you will work in pairs to examine the types of recommended items to include in a hurricane survival kit and think about why this is the case. You will then produce a hurricane safety information leaflet outlining the main information and advice you would give to people in order to survive a hurricane. 13 Read through the information guide provided in your pairs. Identify what you think are the 5 most important items for ensuring survival and give reasons why this is the case. Use the information from the survival guide to produce a leaflet outlining the key steps for hurricane survival. Ensure that your leaflet is well illustrated so that those who do not speak English would be able to make sense of it. Extension : Thinking Skills Why might such a document be less effective in developing countries? Summarise your answer in a paragraph.
15 Responding to Tropical Storms: The Role of Aid Agencies When responding to any natural hazard, aid can be provided in two forms, short term and long term. Short term aid comes in the form of aid that is immediately required by an affected area such as temporary shelter, canned food, clothing, bottled water and medicine. Long term aid comes in the form of things that an area requires to permanently repair damage and get back on its feet. This type of aid includes reconstructing roads, schools, hospitals and houses, repairing power lines and clearing debris. Long term aid can also include educating citizens of an area in basic healthcare and alternative farming methods in order to help citizens deal with any future problems. 14 Aid can also be classified depending upon who is providing it: Bilateral Aid is aid given from one country to another, e.g. from the USA to Bangladesh. Multilateral Aid is aid given by international organisations to a country e.g. The United Nations (UN) to Bangladesh. Voluntary Aid is aid given by non government organisations such as charities, to an affected area e.g. Oxfam, Red Cross, Christian Aid. Financial Aid is where banks give loans to a country to assist its development e.g. World Bank. While countries who suffer from natural hazards in particular rely upon aid given by various organisations, it is often argued that this aid can actually further disrupt their development. This is a huge issue, particularly for developing countries such as Bangladesh who have no choice but to accept aid regardless of who it is coming from. Read through the types of aid listed above. Which of these do you think could result in further problems for a developing country? Write a paragraph to explain and justify your answer.
16 Why do People Live in Areas Affected by Tropical Storms? Case Study: Florida 15 Florida, USA is one of the world s most desirable places to live and one the most popular holiday destinations for worldwide tourists. Situated just off the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico however, it is also prone to devastating tropical storms on a regular basis. So with this in mind, why do people continue to live here? : Watch the following video clips: Write down 3 things that make Florida an attractive place to live and work. Citizens of Florida as well as tourists are well aware of the risk of tropical storms in the area but continue to live and visit here. With preparation measures widely in place as well as information from the government readily available, the threat of tropical storms to human life in Florida is significantly reduced. In developing countries such as Bangladesh, however, people are less fortunate.
17 Case Study: Bangladesh 16 Situated on the coast of the Bay of Bengal, the warm waters of the Indian Ocean make perfect conditions for cyclones to form. With this in mind, once again we can ask, why do people live here? Alongside difficulties in forecasting and communicating the threat of cyclones, governments are limited in their ability to support citizens when a cyclone hits in Bangladesh. The citizens themselves also have great difficulty in knowing about the threat of cyclones and vacating areas affected by them. In developing countries the vast majority of people are forced to live in these affected areas for various reasons. : Thinking Skills In groups of 3, come up with 2 reasons why people in countries like Bangladesh are unable to move away from areas affected by cyclones. Try to imagine what life is like in these countries, the wealth that people have, the knowledge that people have and the types of job that they do. You may use the Bangladesh country factfile to help you.
Hurricanes: Nature's Wildest Storms by Erin Ryan
 Name: : Nature's Wildest Storms by Erin Ryan You may already know that hurricanes are major tropical storms that can cause devastating waves, wind, and rain. They happen during Hurricane Season, which
Name: : Nature's Wildest Storms by Erin Ryan You may already know that hurricanes are major tropical storms that can cause devastating waves, wind, and rain. They happen during Hurricane Season, which
CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate
 Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Storms Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Hurricanes. Characteristics of a Hurricane
 Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
2. The map below shows high-pressure and low-pressure weather systems in the United States.
 1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
Using a Concept Definition Map
 Lesson Plan Using a Concept Definition Map 1. Set Expectations Print Disaster on the board. Tell students, You are going to come up with as many words as you can that are related to the word disaster,
Lesson Plan Using a Concept Definition Map 1. Set Expectations Print Disaster on the board. Tell students, You are going to come up with as many words as you can that are related to the word disaster,
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6
 Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
FOURTH GRADE WEATHER
 FOURTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different reservoirs of water. LAB: Experimenting with surface tension and capillary
FOURTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different reservoirs of water. LAB: Experimenting with surface tension and capillary
THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen
THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen
7613-1 - Page 1. Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions
 Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Evaluating components of the water cycle. LAB: Experimenting with porosity and permeability.
SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Evaluating components of the water cycle. LAB: Experimenting with porosity and permeability.
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: WEATHER BASICS: STATION MODELS: MOISTURE: PRESSURE AND WIND: Weather
 Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration
Follow That Hurricane!
 Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Discover Your World With NOAA Follow That Hurricane! What You Will Do Devastating damage expected A most Track a hurricane on the same powerful hurricane with unprecedented type of chart used at the strength
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
YEAR 1: Seasons and Weather
 YEAR 1: Seasons and Weather Contents Include: The four seasons Tools to record the weather Making graphs Clouds Weather forecasts Weather around the world Please Note: The activities included in this pack
YEAR 1: Seasons and Weather Contents Include: The four seasons Tools to record the weather Making graphs Clouds Weather forecasts Weather around the world Please Note: The activities included in this pack
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS THINGS
 CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
Severe Weather. www.readinga-z.com. Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
 Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,801 LEVELED READER T Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrations by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,801 LEVELED READER T Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrations by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
6. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows the average monthly temperature of two cities A and B.
 1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
Advice For the multiple-choice questions, completely fill in the circle alongside the appropriate answer(s).
 SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL GCSE GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Living with the physical environment Specimen Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a ruler. Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions
SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL GCSE GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Living with the physical environment Specimen Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a ruler. Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions
Chapter Overview. Seasons. Earth s Seasons. Distribution of Solar Energy. Solar Energy on Earth. CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer!
 Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test
 WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
Damage Potential of Tropical Cyclone
 Damage Potential of Tropical Cyclone Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre (RSMC)- Tropical Cyclone, New Delhi Cyclone Warning Division India Meteorological Department Mausam Bhavan, Lodi Road, New
Damage Potential of Tropical Cyclone Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre (RSMC)- Tropical Cyclone, New Delhi Cyclone Warning Division India Meteorological Department Mausam Bhavan, Lodi Road, New
Storm tide is the water level rise during a storm due to the combination of storm surge and the astronomical tide.
 INTRODUCTION TO STORM SURGE Introduction to Storm Surge BOLIVAR PENINSULA IN TEXAS AFTER HURRICANE IKE (2008) What is Storm Surge? Inland Extent Storm surge can penetrate well inland from the coastline.
INTRODUCTION TO STORM SURGE Introduction to Storm Surge BOLIVAR PENINSULA IN TEXAS AFTER HURRICANE IKE (2008) What is Storm Surge? Inland Extent Storm surge can penetrate well inland from the coastline.
WeatherBug Vocabulary Bingo
 Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
Storm tide is the water level rise during a storm due to the combination of storm surge and the astronomical tide.
 INTRODUCTION TO STORM SURGE Introduction to Storm Surge National Hurricane Center Storm Surge Unit BOLIVAR PENINSULA IN TEXAS AFTER HURRICANE IKE (2008) What is Storm Surge? Inland Extent Storm surge can
INTRODUCTION TO STORM SURGE Introduction to Storm Surge National Hurricane Center Storm Surge Unit BOLIVAR PENINSULA IN TEXAS AFTER HURRICANE IKE (2008) What is Storm Surge? Inland Extent Storm surge can
7) Coastal Storms: Multi-Hazard Analysis for New York City
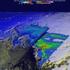 7) Coastal Storms: Multi-Hazard Analysis for New York City a) Hazard Profile i) Hazard Description Coastal storms, including nor'easters, tropical storms, and hurricanes, can and do affect New York City.
7) Coastal Storms: Multi-Hazard Analysis for New York City a) Hazard Profile i) Hazard Description Coastal storms, including nor'easters, tropical storms, and hurricanes, can and do affect New York City.
Response and Recovery
 LESSON PLAN 3 Response and Recovery Hurricanes When young people see what individuals and communities can do before, during and after a hurricane, they will begin to understand the importance of people
LESSON PLAN 3 Response and Recovery Hurricanes When young people see what individuals and communities can do before, during and after a hurricane, they will begin to understand the importance of people
6 th Grade Science Assessment: Weather & Water Select the best answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this test.
 Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
Tropical Cyclones. This document last updated on 17-Nov-2014
 Page 1 of 14 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tropical Cyclones This document last updated on 17-Nov-2014 We have already discussed the factors involved in the circulation
Page 1 of 14 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tropical Cyclones This document last updated on 17-Nov-2014 We have already discussed the factors involved in the circulation
EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters
 EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters Language & Literacy Objectives: 1. Identify what constitutes an emergency or disaster,
EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters Language & Literacy Objectives: 1. Identify what constitutes an emergency or disaster,
Humidity the story for teachers
 Humidity the story for teachers As we have learned earlier, water may exist as a gas (water vapour). Even in the driest desert there is some water vapour in the air. Water vapour is the most important
Humidity the story for teachers As we have learned earlier, water may exist as a gas (water vapour). Even in the driest desert there is some water vapour in the air. Water vapour is the most important
List 10 different words to describe the weather in the box, below.
 Weather and Climate Lesson 1 Web Quest: What is the Weather? List 10 different words to describe the weather in the box, below. How do we measure the weather? Use this web link to help you: http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/weatherwise/activities/weatherstation/
Weather and Climate Lesson 1 Web Quest: What is the Weather? List 10 different words to describe the weather in the box, below. How do we measure the weather? Use this web link to help you: http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/weatherwise/activities/weatherstation/
Climate Change: A Local Focus on a Global Issue Newfoundland and Labrador Curriculum Links 2010-2011
 Climate Change: A Local Focus on a Global Issue Newfoundland and Labrador Curriculum Links 2010-2011 HEALTH Kindergarten: Grade 1: Grade 2: Know that litter can spoil the environment. Grade 3: Grade 4:
Climate Change: A Local Focus on a Global Issue Newfoundland and Labrador Curriculum Links 2010-2011 HEALTH Kindergarten: Grade 1: Grade 2: Know that litter can spoil the environment. Grade 3: Grade 4:
8.5 Comparing Canadian Climates (Lab)
 These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air
 LESSON 4 Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air INTRODUCTION How can a hang glider stay up in the air for hours without a motor? How can a bird soar over an open field without flapping its wings? They can
LESSON 4 Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air INTRODUCTION How can a hang glider stay up in the air for hours without a motor? How can a bird soar over an open field without flapping its wings? They can
1/2/3. Finding out about the Water Cycle
 The Water Cycle 1/2/3. Finding out about the Water Cycle Aims: To enable pupils to learn and understand what happens at each stage of the Water Cycle To introduce specific vocabulary related to the Water
The Water Cycle 1/2/3. Finding out about the Water Cycle Aims: To enable pupils to learn and understand what happens at each stage of the Water Cycle To introduce specific vocabulary related to the Water
MiSP WEATHER WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION Teacher Guide, L1 L3. Introduction
 MiSP WEATHER WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION Teacher Guide, L1 L3 Introduction This MiSP unit can be included in a standard weather and climate unit. Some teachers may like it as part of the introduction. Others
MiSP WEATHER WIND SPEED AND DIRECTION Teacher Guide, L1 L3 Introduction This MiSP unit can be included in a standard weather and climate unit. Some teachers may like it as part of the introduction. Others
Preparation / Background Information:
 Aim / Learning Objective: Looking at the world through science, students can learn about the marine elements of our natural environment and the importance of the water cycle. Students can look at and compare
Aim / Learning Objective: Looking at the world through science, students can learn about the marine elements of our natural environment and the importance of the water cycle. Students can look at and compare
Air Masses and Fronts
 Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Hurricanes and Storm Surge www.hcfcd.org/tropicalweather
 Hurricanes and Storm Surge www.hcfcd.org High-level winds fl ow outward Strong surface winds spiral inward EYE Calm, sometimes cloudfree, sinking air Air sinks in calm area at the storm s eye THUNDERSTORMS
Hurricanes and Storm Surge www.hcfcd.org High-level winds fl ow outward Strong surface winds spiral inward EYE Calm, sometimes cloudfree, sinking air Air sinks in calm area at the storm s eye THUNDERSTORMS
Answer Keys to Unit Tests
 Reading Geography Series Answer Keys to Unit Tests Unit 1 The Five Themes of Geography Unit 2 Patterns in Physical Geography Unit 3 Natural Resources 7 Portage & Main Press Unit Test for The Five Themes
Reading Geography Series Answer Keys to Unit Tests Unit 1 The Five Themes of Geography Unit 2 Patterns in Physical Geography Unit 3 Natural Resources 7 Portage & Main Press Unit Test for The Five Themes
Emergency Management is responsible for coordinating the City of Houston s preparation for and response to emergency situations.
 CITY OF HOUSTON Office of Emergency Management October 2004 Emergency Management is responsible for coordinating the City of Houston s preparation for and response to emergency situations. Houston is exposed
CITY OF HOUSTON Office of Emergency Management October 2004 Emergency Management is responsible for coordinating the City of Houston s preparation for and response to emergency situations. Houston is exposed
Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe
 58 The Causes of Climate R E A D I N G Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe weather, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind. You now know that oceans have an important effect
58 The Causes of Climate R E A D I N G Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe weather, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind. You now know that oceans have an important effect
Texas Department of Public Safety Texas Division of Emergency Management. Texas State Operations Center
 Texas Department of Public Safety Texas Division of Emergency Management Texas State Operations Center Situation Awareness Brief Saturday, July 20 th 2013 As of 0900 CDT Tropical Weather Outlook For the
Texas Department of Public Safety Texas Division of Emergency Management Texas State Operations Center Situation Awareness Brief Saturday, July 20 th 2013 As of 0900 CDT Tropical Weather Outlook For the
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY. Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in
 ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
Fry Phrases Set 1. TeacherHelpForParents.com help for all areas of your child s education
 Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
The Tornado Diaries. Tornadoes K-2. Tornado Science LESSON PLAN 2. Key Terms and Concepts. Purposes. Objectives
 LESSON PLAN 2 The Tornado Diaries Tornadoes K-2 A tornado is a violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm to the ground. Tornadoes have been reported in every state and, though they
LESSON PLAN 2 The Tornado Diaries Tornadoes K-2 A tornado is a violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm to the ground. Tornadoes have been reported in every state and, though they
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation
 The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775
 Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775 LEVELED BOOK T SEVERE WEATHER Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrated by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775 LEVELED BOOK T SEVERE WEATHER Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrated by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and
1. Incredible India. Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India
 1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow
 AS/A2-Level Geography Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow Learning Objectives: To describe and explain the weather associated with high and low pressure systems and their links to extreme
AS/A2-Level Geography Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow Learning Objectives: To describe and explain the weather associated with high and low pressure systems and their links to extreme
RISD Hurricane Preparedness
 RISD Hurricane Preparedness Hurricane It is the policy of RISD to view each hurricane threat as an extremely hazardous condition. As such, our goal is to minimize the risk to personnel consistent with
RISD Hurricane Preparedness Hurricane It is the policy of RISD to view each hurricane threat as an extremely hazardous condition. As such, our goal is to minimize the risk to personnel consistent with
Temperature affects water in the air.
 KEY CONCEPT Most clouds form as air rises and cools. BEFORE, you learned Water vapor circulates from Earth to the atmosphere Warm air is less dense than cool air and tends to rise NOW, you will learn How
KEY CONCEPT Most clouds form as air rises and cools. BEFORE, you learned Water vapor circulates from Earth to the atmosphere Warm air is less dense than cool air and tends to rise NOW, you will learn How
Natural Hazards 1.1. Natural Hazards. Objective: Natural Hazards in Western Australia Are we at risk? Page 1. Natural Hazards Years 5-7
 Natural Hazards 1.1 Engage Natural Hazards To introduce students to the natural hazards which occur in Western Australia and their risk. Western Australia experiences a range of natural hazards each year,
Natural Hazards 1.1 Engage Natural Hazards To introduce students to the natural hazards which occur in Western Australia and their risk. Western Australia experiences a range of natural hazards each year,
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage
 Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Rainforest Concern Module 2 Why do we need rainforests?
 Rainforest Concern Module 2 Why do we need rainforests? Rainforest Concern Module 2: Why do we need Rainforest? Before we go any further, there are some words you may not understand, and these words and
Rainforest Concern Module 2 Why do we need rainforests? Rainforest Concern Module 2: Why do we need Rainforest? Before we go any further, there are some words you may not understand, and these words and
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum. Lesson title: Weather Maps. Grade level: 4-6. Subject area: Earth Science. Duration: Two class periods
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: Weather Maps Grade level: 4-6 Subject area: Earth Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students will do the following: Understand basic information
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: Weather Maps Grade level: 4-6 Subject area: Earth Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students will do the following: Understand basic information
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind
 Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
SESSION TWO: MID-LATITUDE AND TROPICAL CYCLONES
 SESSION TWO: MID-LATITUDE AND TROPICAL CYCLONES TOPIC 1: MID-LATITUDE CYLONES KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Mid-Latitude Cyclones: - Introduction
SESSION TWO: MID-LATITUDE AND TROPICAL CYCLONES TOPIC 1: MID-LATITUDE CYLONES KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Mid-Latitude Cyclones: - Introduction
Basics of weather interpretation
 Basics of weather interpretation Safety at Sea Seminar, April 2 nd 2016 Dr. Gina Henderson Oceanography Dept., USNA [email protected] Image source: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/naturalhazards/view.php?id=80399,
Basics of weather interpretation Safety at Sea Seminar, April 2 nd 2016 Dr. Gina Henderson Oceanography Dept., USNA [email protected] Image source: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/naturalhazards/view.php?id=80399,
barometer 1 of 5 For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.com/encyclopedia/barometer/
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry For the complete
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry For the complete
Understanding the altimeter
 Understanding the altimeter What you see isn't always what you have by Jack Willams Flying is an adventure for most pilots--sometimes more adventure than they really want. A pilot's report to Canada's
Understanding the altimeter What you see isn't always what you have by Jack Willams Flying is an adventure for most pilots--sometimes more adventure than they really want. A pilot's report to Canada's
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
climate science A SHORT GUIDE TO This is a short summary of a detailed discussion of climate change science.
 A SHORT GUIDE TO climate science This is a short summary of a detailed discussion of climate change science. For more information and to view the full report, visit royalsociety.org/policy/climate-change
A SHORT GUIDE TO climate science This is a short summary of a detailed discussion of climate change science. For more information and to view the full report, visit royalsociety.org/policy/climate-change
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
5. Why does the weather near cities tend to be cloudier and wetter than in rural areas?
 Name: Date: 1. Today weather forecasting is better because of the use of A. barometers. B. telescopes. C. satellites. D. anemometers. 2. The letter H is the weather symbol for A. hail storms. B. humidity.
Name: Date: 1. Today weather forecasting is better because of the use of A. barometers. B. telescopes. C. satellites. D. anemometers. 2. The letter H is the weather symbol for A. hail storms. B. humidity.
Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds
 Name: Pd: Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a large collection of very tiny droplets of water or ice crystals. The
Name: Pd: Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a large collection of very tiny droplets of water or ice crystals. The
Expository Essay. 8 th Grade Writing
 Expository Essay 8 th Grade Writing Purpose (definition) to inform about or explain a topic Expository essays explain, interpret, or describe something based on prior knowledge, background experiences,
Expository Essay 8 th Grade Writing Purpose (definition) to inform about or explain a topic Expository essays explain, interpret, or describe something based on prior knowledge, background experiences,
sample The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation
 sample The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 Impacts
sample The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 Impacts
In the Caribbean, August and September are peak months during the hurricane season that lasts from June 1 through November 30.
 Hurricane Fact sheet What is a hurricane? A hurricane is a tropical storm with winds that have reached a constant speed of 74 miles per hour more. Hurricane winds blow in a large spiral around a relative
Hurricane Fact sheet What is a hurricane? A hurricane is a tropical storm with winds that have reached a constant speed of 74 miles per hour more. Hurricane winds blow in a large spiral around a relative
Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011
 Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011 Overview A significant amount of existing research indicates that the world s climate is changing. Emergency
Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011 Overview A significant amount of existing research indicates that the world s climate is changing. Emergency
Glossary. ambulance: a vehicle equipped for transportation of sick and injured persons. believe: to accept as true or real
 act: the process of doing or performing something ambulance: a vehicle equipped for transportation of sick and injured persons believe: to accept as true or real cascading disaster: the effects of one
act: the process of doing or performing something ambulance: a vehicle equipped for transportation of sick and injured persons believe: to accept as true or real cascading disaster: the effects of one
EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON PACIFIC ISLANDS by Imogen P. Ingram
 EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON PACIFIC ISLANDS by Imogen P. Ingram Map courtesy of University of South Pacific LOCATION OF THE COOK ISLANDS I come from the Cook Islands group, which is in the South-West
EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON PACIFIC ISLANDS by Imogen P. Ingram Map courtesy of University of South Pacific LOCATION OF THE COOK ISLANDS I come from the Cook Islands group, which is in the South-West
Fighting Fire with Fire: Can Fire Positively Impact an Ecosystem?
 Fighting Fire with Fire: Can Fire Positively Impact an Ecosystem? Science Topic: Fire Ecology Grades: 6 th 8 th Essential Questions: What role does fire play in maintaining healthy ecosystems? How does
Fighting Fire with Fire: Can Fire Positively Impact an Ecosystem? Science Topic: Fire Ecology Grades: 6 th 8 th Essential Questions: What role does fire play in maintaining healthy ecosystems? How does
Mangrove loss faster than land-based forests
 ESL ENGLISH LESSON (60-120 mins) 10 th August 2010 Mangrove loss faster than land-based forests Mangrove forests are disappearing faster than land-based forests according to a new United Nations report
ESL ENGLISH LESSON (60-120 mins) 10 th August 2010 Mangrove loss faster than land-based forests Mangrove forests are disappearing faster than land-based forests according to a new United Nations report
Preparing for A Flood
 Preparing for A Flood 1. Know if you are in a flood prone area. 2. Each year, update flood procedures to be followed by your company, employees and tenants: Including Emergency Contacts Evacuation Plans
Preparing for A Flood 1. Know if you are in a flood prone area. 2. Each year, update flood procedures to be followed by your company, employees and tenants: Including Emergency Contacts Evacuation Plans
Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain
 Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain Terminal Learning Objective Action: Analyze weather of cold regions and mountainous terrain Condition: Given a training mission that involves a specified
Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain Terminal Learning Objective Action: Analyze weather of cold regions and mountainous terrain Condition: Given a training mission that involves a specified
Noon Sun Angle = 90 Zenith Angle
 Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
Seasonal Temperature Variations
 Seasonal and Daily Temperatures Fig. 3-CO, p. 54 Seasonal Temperature Variations What causes the seasons What governs the seasons is the amount of solar radiation reaching the ground What two primary factors
Seasonal and Daily Temperatures Fig. 3-CO, p. 54 Seasonal Temperature Variations What causes the seasons What governs the seasons is the amount of solar radiation reaching the ground What two primary factors
The Polar Climate Zones
 The Polar Climate Zones How cold is it in the polar climate? Polar areas are the coldest of all the major climate zones The Sun is hardly ever high enough in the sky to cause the plentiful ice to melt,
The Polar Climate Zones How cold is it in the polar climate? Polar areas are the coldest of all the major climate zones The Sun is hardly ever high enough in the sky to cause the plentiful ice to melt,
How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms?
 How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms? Objective In the summer, over the Great Plains, weather predictions often call for afternoon thunderstorms. While most of us use weather forecasts to help pick
How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms? Objective In the summer, over the Great Plains, weather predictions often call for afternoon thunderstorms. While most of us use weather forecasts to help pick
WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE
 7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
HURRICANE EVACUATION GUIDE
 booklet-final 6/30/00 9:41 AM Page 1 E M E R G E N C Y P R E P A R E D N E S S HURRICANE EVACUATION GUIDE Vital information you need to know in case of a hurricane evacuation. Information brought to you
booklet-final 6/30/00 9:41 AM Page 1 E M E R G E N C Y P R E P A R E D N E S S HURRICANE EVACUATION GUIDE Vital information you need to know in case of a hurricane evacuation. Information brought to you
Climate Change is Underway Lesson Plan
 Climate Change is Underway Lesson Plan For Teachers: The following is a lesson plan designed to be used with section of the Climate Change material entitled Climate Change is Underway from the After Earth
Climate Change is Underway Lesson Plan For Teachers: The following is a lesson plan designed to be used with section of the Climate Change material entitled Climate Change is Underway from the After Earth
Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze: Routing Considerations Table of Contents
 Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze: Routing Considerations Table of Contents Introduction Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze Description 2 3 Introduction Four Sea Breeze Quadrants (Figure 1) When considering a sea breeze and its
Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze: Routing Considerations Table of Contents Introduction Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze Description 2 3 Introduction Four Sea Breeze Quadrants (Figure 1) When considering a sea breeze and its
Unit: Plants & Animals (Grade 2)
 Unit: Plants & Animals (Grade 2) Content Area: Science Course(s): Science Time Period: 8 weeks Length: Weeks Status: Published Unit Overview Students will determine the life cycles of plants and animals
Unit: Plants & Animals (Grade 2) Content Area: Science Course(s): Science Time Period: 8 weeks Length: Weeks Status: Published Unit Overview Students will determine the life cycles of plants and animals
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE!
 FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
Stage 4. Geography. Blackline Masters. By Karen Devine
 1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
defined largely by regional variations in climate
 1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives
 Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
Impacts of Global Warming on Hurricane-related Flooding in Corpus Christi,Texas
 Impacts of Global Warming on Hurricane-related Flooding in Corpus Christi,Texas Sea-level Rise and Flood Elevation A one-foot rise in flood elevation due to both sea-level rise and hurricane intensification
Impacts of Global Warming on Hurricane-related Flooding in Corpus Christi,Texas Sea-level Rise and Flood Elevation A one-foot rise in flood elevation due to both sea-level rise and hurricane intensification
