Non-Colinear Pump-Probe Measurement: Pump pulse. Chopper. Lens. Probe pulse. Time delay between pump and probe pulse
|
|
|
- Allan Oliver
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 11 Ultrafast Measurement Techniques 11.1 Pump Probe Measurements Non-Colinear Pump-Probe Measurement: Mode-locked Laser Beam splitter Chopper Probe pulse Pump pulse Lens Test device Slow detector 1 fs <=> 0.15 µm t Time delay between pump and probe pulse Lock-In Amplifier translation stage t Computer screen Figure 11.1: Non-colinear pump-probe setup with co-polarized pump-probe beams. Adapted from U. Keller. Figure 11.1 shows a non-colinear pump-probe measurement setup. To suppress background light and low frequency noise of the probe beam the pump 371
2 372 CHAPTER 11. ULTRAFAST MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES beam is chopped. Typical chopper frequencies of regular mechanical choppers are f ch =100Hz 2kHz. Mechanical choppers up to 20kHz have been built. With acousto-optic modulators or electro-optic modulators chopper freuqencies up to several hundred MHz are possible. Lets denote S in = S 0 + δs astheprobepulseenergy,wheres 0 is the average value and δs a low frequency noise of the pulse source and is the probe signal transmitted through the test device. Then the detected signal transmitted through the test device can be written as = T (P (t))s in (11.1) = T 0 S in + dt dp (P 0m(t)) where T 0 is the transmission without pump pulse, P 0 is the pump pulse energy and m(t) the chopper modulation function. It is obvious that if the noise of the probe laser δs is of low freuqency, then the signal can be shifted away from this noise floor by chosing an appropriately large chopper frequency in m(t). Ideally, the chopper frequency is chosen large enough to enable shot noise limited detection. Sometimes the test devices or samples have a rough surface and pump light scattered from the surface might hit the detector. This can be partially suppressed by orthogonal pump and probe polarization This is a standard technique to understand relaxation dynamics in condensed matter, such as carrier relaxation processes in semiconductors for example Colinear Pump-Probe Measurement: Sometimes pump and probe pulses have to be collinear, for example when pump probe measurements of waveguide devices have to be performed. Then pump and probe pulse, which might both be at the same center wavelength have to be made separable. This can be achieved by using orthogonal pump and probe polarization as shown in Figure 11.2 or by chopping pump and probe at different frequencies and detecting at the difference frequency, see Figure 11.3.
3 11.1. PUMP PROBE MEASUREMENTS 373 Mode-Locked Laser Chopper PBS Probe pulse Pump pulse Lens Test device PBS λ/2-plate t Slow detector Lock-In Amplifier t Figure 11.2: Colinear pump-probe with orthogonally polarized pump and probe beams. Adapted from U. Keller. MLL Chopper f 1 Probe pulse Pump pulse Lens t Test device Slow detector Chopper f 2 Lock-In Amplifier at f - f 1 2 Figure 11.3: Colinear pump probe with chopping of pump and probe and lock-in detection at the difference frequency. Adapted from U. Keller.
4 374 CHAPTER 11. ULTRAFAST MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES Heterodyne Pump Probe The lock-in detection is greatly improved if the difference frequency at which the detection occurs can be chosen higher and the signal can be filtered much better using a heterodyne receiver. This is shown in Figure 11.4, where AOM s are used to prepare a probe and reference pulse shiftet by 39 and 40 MHz respectively. The pump beam is chopped at 1kHz. After the test device the probe and reference pulse are overlayed with each other by delaying the referencepulseinamichelson-interferometer. Thebeatnoteat1MHzis downconverted to base band with a receiver. MLL Chopper AOM Probe pulse Test device Pump pulse Reference t T>>t +39 Mhz Probe AOM +40 MHz Reference Slow detector 1 MHz Receiver Lock-In Amplifier t Figure 11.4: Colinear pump probe measurement with parallel polarization and large difference frequency. Adapted from U. Keller. If a AM or FM receiver is used and the interferometers generating the reference and probe pulse are interferometerically stable, both amplitude and phase nonlinearities can be detected with high signal to noise.
5 11.1. PUMP PROBE MEASUREMENTS 375 MLL Chopper AOM Probe pulse Test device Pump pulse Reference t T>>t PZT +39 Mhz Probe AOM +40 MHz Reference Slow detector 1 MHz Ham Radio Reciver AM or FM Lock-In Amplifier t Figure 11.5: Heterodyne pump probe using AM and FM receiver to detect amplitude and phase nonlinearities. Adapted from U. Keller.
6 376 CHAPTER 11. ULTRAFAST MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 11.2 Electro-Optic Sampling: Electro-Optic Sampling was invented by Valdmanis and Mourou in the early 1980 s [8][5]. Its is based on polarization rotation of a short laser pulse when propagating in a medium showing a linear electro-optic effect. The polarization rotation is due to an applied electric filed, i.e. the optical pulse samples the instantaneous electric field, see Fig.11.6 External Electro-Optic Sampling Scheme Probe beam in (arrive at delayed times of t+n. t) Probe Beam Out Excitation pulses (arrive at time t) Electro-Optic Probe Crystal Semiconductor Substrate Switch Bias Figure 11.6: Electro-optic sampling scheme according ot J. Whitaker, Univ. of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Figure by MIT OCW. In Fig a electic transient is generated with a photo-conductive switch activated by a femtosecond laser pulse. A delayed pulse samples the transient electronic pulse with an electro-optic probe as shown in Fig
7 11.2. ELECTRO-OPTIC SAMPLING: 377 Electro-Optic Probe Fused Silica Support Probe Beam LiTaO 3 Electro-Optic Crystal Figure 11.7: LiTaO 3 Electro-Otpic Probe according to J. Whitaker, Univ. Michigan. Figure by MIT OCW. Fig shows an overal version of an electro-optic sampling system according to J. Whitaker, Univ. of Michigan [6] Electro-Optic Sampling System Schematic To Lock-In Amplifier Detectors Eyepiece Fiber Analyzer Illumination Laser Lens Polarizer Dichroic Beam Splitter Delay Trigger Beam Bias Circuit Probe tip Figure 11.8: Electro-Otpic Sampling System according to J. Whitaker, Univ. Michigan. Figure by MIT OCW.
8 378 CHAPTER 11. ULTRAFAST MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 11.3 THz Spectroscopy and Imaging Photo-conductive switches activated by sub-100 fs pulses or optical rectification with sub-100 fs pulses leads to the generation of THz electro-magnetic impulses, that can be received with similar photo-conductive receivers or by electro-optic sampling [8][9]. This technique was pioneered by Ch. Fattinger and D. Grischkowsky [7]. Delay Femtosecond Laser Ti:sapphire or Cr:LiSAF fs THz Transmitter THz Detector V Sample Laser Pulse LT-GaAs Substrate Dielectrics, Tissue, IC-Packaging etc. Current Figure 11.9: THz Time Domain Spectroscopy according to [8] Figure by MIT OCW.
9 11.3. THZ SPECTROSCOPY AND IMAGING 379 Delay GaInAs/GaAs/AlAs 12 fs Ti:sapphire Oscillator E 2 E 1 Optical Rectification in GaAs FIR - Probe: 15 fs ~ 5-15 µm 15 fs ~ 60 THz 6 fs > 100 THz QW THz -OPOs THz -OPAs Quantum-Cascade Laser Figure 11.10: THz Time Domain Spectroscopy using optical rectification in GaAs [9]. Figure by MIT OCW. Figure 11.11: Terahertz waveforms modified by passage through (a) a 10mm block of stycast and (b) a chinese fortune cookie. The dashed lines show the shape of the input waveform multiplied by 0.5 in (a) and by 0.1 in 9b). In *a( the transmitted plse exhibits a strong "chirp" due to frequency-dependent index, while in (b), pulse broadening indicates preferential absorption of high frequencies [8]. Figure shows typical generated THz waveforms and distortions due to propagation through materials.
10 380 CHAPTER 11. ULTRAFAST MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 11.4 Four-Wave Mixing A more advanced ultrafast spectroscopy technique than pump-probe is fourwave mixing (FWM). It enables to investigate not only energy relaxation processes, as is the case in pump-probe measurements, but also dephasing processes in homogenous as well as inhomogenously broadened materials. The typical set-up is shown in Fig t 23 t 12 Pulse 2 Sample k 1 Pulse 3 Pulse 1 k 3 k 2 k 3 + ( k 2 - k 1 ) Detector Figure 11.12: Typical Four-Wave-Mixing (FWM) beam geometry. Lets assume these pulses interact resonantely with a two-level system modelled by the Bloch Equations derived in chapter 2 ( ). µ 1 2 E (+) (z,t) c 2 0 t 2 = 2 µ 0 P t (+) (z, t), 2 (11.2) P (+) (z,t) = 2N M d(z,t) (11.3) d(z,t) = ( 1 jω eg )d + 1 M T 2 2j~ E (+) w, (11.4) ẇ(z,t) = w w 0 T j~ ( M E ( ) d M E (+) d )(11.5) The two-level system, located at z =0, will be in the ground state, i.e. d(t =0)=0and w(t =0)= 1, before arrival of the first pulses. That is, no polarization is yet present. Lets assume the pulse interacting with the two-level system are weak and we can apply perturbation theory. Then the arrival of the first pulse with the complex field E (+) ( x, t) = E (+) 0 δ(t)e j(ωegt j k 1 x) (11.6)
11 11.4. FOUR-WAVE MIXING 381 will generate a polarization wave according to the Bloch-equations M d( x, t) = E (+) 0 2j~ ej(ω eg 1/T 2 )t e j k 1 x δ(z), (11.7) which will decay with time. Once a polarization is created the second pulse will change the population and induce a weak population grating M E (+) 0 2 w( x, t) = e t 12/T 2 e j( k 1 k 2) x e (t t 2)/T 1 δ(z)+c.c., (11.8) ~ 2 When the third pulse comes, it will scatter of from this population grating, i.e. it will induce a polarization, that radiates a wave into the direction k3 + k 2 k 1 according to M d( x, t) = E (+) 0 2j~ M E (+) 0 2 ~ 2 e t 12/T 2 e t 32/T 1 e j ( k 3 + k 2 k 1) x δ(z) (11.9) Thus the signal detected in this direction, see Fig , which is proportional to the square of the radiating dipole layer d( x, t) 2 e 2t 12/T 2 e 2t 32/T 1 (11.10) will decay on two time scales. If the time delay between pulses 1 and 2, t 12, is only varied it will decay with the dephasing time T 2 /2. If the time delay betweenpulses2and3isvaried,t 32, the signal strength will decay with the energy relaxation time T 1 /2
12 382 CHAPTER 11. ULTRAFAST MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES
13 Bibliography [1] K. L. Hall, G. Lenz, E. P. Ippen, and G. Raybon, "Heterodyne pumpprobe technique for time-domain studies of optical nonlinearities in waveguides," Opt. Lett. 17, p , (1992). [2] K.L.Hall,A.M.Darwish,E.P.Ippen,U.KorenandG.Raybon,"Femtosecond index nonlinearities in InGaAsP optical amplifiers," App. Phys. Lett. 62, p , (1993). [3] K. L. Hall, G. Lenz, A. M. Darwish, E. P. Ippen, "Subpicosecond gain and index nonlinearities in InGaAsP diode lasers," Opt. Comm. 111, p (1994). [4] J. A. Valdmanis, G. Mourou, and C. W. Gabel, Picosecond electro-optic sampling system, Appl. Phys. Lett. 41, p (1982). [5] B. H. Kolner and D. M. Bloom, "Electrooptic Sampling in GaAs Integrated Circuits," IEEE J. Quantum Elect.22, (1986). [6] S.Gupta,M.Y.Frankel,J.A.Valdmanis,J.F.Whitaker,G.A.Mourou, F. W. Smith and A. R. Calaw, "Subpicosecond carrier lifetime in GaAs grown by molecular beam epitaxy at low temperatures," App. Phys. Lett. 59, pp ) [7] Ch. Fattinger, D. Grischkowsky, "Terahertz beams," Appl. Phys. Lett. 54, pp (1989) [8] D. M. Mittleman, R. H. Jacobsen, and M. Nuss, "T-Ray Imaging," IEEE JSTQE 2, (1996) [9] A. Bonvalet, J. Nagle, V. Berger, A. Migus, JL Martin, and M. Joffre, "Ultrafast Dynamic Control of Spin and Charge Density Oscillations in a GaAs Quantum Well," Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 4392 (1996). 383
14 384 BIBLIOGRAPHY
Broadband THz Generation from Photoconductive Antenna
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 331 Broadband THz Generation from Photoconductive Antenna Qing Chang 1, Dongxiao Yang 1,2, and Liang Wang 1 1 Zhejiang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 331 Broadband THz Generation from Photoconductive Antenna Qing Chang 1, Dongxiao Yang 1,2, and Liang Wang 1 1 Zhejiang
Pump-probe experiments with ultra-short temporal resolution
 Pump-probe experiments with ultra-short temporal resolution PhD candidate: Ferrante Carino Advisor:Tullio Scopigno Università di Roma ƒla Sapienza 22 February 2012 1 Pump-probe experiments: generalities
Pump-probe experiments with ultra-short temporal resolution PhD candidate: Ferrante Carino Advisor:Tullio Scopigno Università di Roma ƒla Sapienza 22 February 2012 1 Pump-probe experiments: generalities
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications
 Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators
 A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators D. J. McCarron December 7, 2007 1 Introduction Acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) are useful devices which allow the frequency, intensity and direction of a laser beam
A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators D. J. McCarron December 7, 2007 1 Introduction Acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) are useful devices which allow the frequency, intensity and direction of a laser beam
SPATIAL-TIME PATTERN OF ELECTRICAL FIELD OF TERAHERTZ PULSE IN THE FAR FIELD
 NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2013, 4 (2), P. 206 213 SPATIAL-TIME PATTERN OF ELECTRICAL FIELD OF TERAHERTZ PULSE IN THE FAR FIELD M. S. Kulya 1, Ya. V. Grachev 1, V. G. Bespalov 1, V.
NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2013, 4 (2), P. 206 213 SPATIAL-TIME PATTERN OF ELECTRICAL FIELD OF TERAHERTZ PULSE IN THE FAR FIELD M. S. Kulya 1, Ya. V. Grachev 1, V. G. Bespalov 1, V.
A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba +
 A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba + Abstract: Andrea Katz Trinity University UW REU 2010 In order to increase the efficiency and reliability of de-shelving barium ions, an infrared laser beam was
A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba + Abstract: Andrea Katz Trinity University UW REU 2010 In order to increase the efficiency and reliability of de-shelving barium ions, an infrared laser beam was
Limiting factors in fiber optic transmissions
 Limiting factors in fiber optic transmissions Sergiusz Patela, Dr Sc Room I/48, Th. 13:00-16:20, Fri. 9:20-10:50 sergiusz.patela@pwr.wroc.pl eportal.pwr.wroc.pl Copying and processing permitted for noncommercial
Limiting factors in fiber optic transmissions Sergiusz Patela, Dr Sc Room I/48, Th. 13:00-16:20, Fri. 9:20-10:50 sergiusz.patela@pwr.wroc.pl eportal.pwr.wroc.pl Copying and processing permitted for noncommercial
Acousto-optic modulator
 1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
ULTRAFAST LASERS: Free electron lasers thrive from synergy with ultrafast laser systems
 Page 1 of 6 ULTRAFAST LASERS: Free electron lasers thrive from synergy with ultrafast laser systems Free electron lasers support unique time-resolved experiments over a wide range of x-ray wavelengths,
Page 1 of 6 ULTRAFAST LASERS: Free electron lasers thrive from synergy with ultrafast laser systems Free electron lasers support unique time-resolved experiments over a wide range of x-ray wavelengths,
Numeric modeling of synchronous laser pulsing and voltage pulsing field evaporation
 Numeric modeling of synchronous laser pulsing and voltage pulsing field evaporation L. ZHAO 1, A. NORMAND, J. HOUARD, I. BLUM, F. DELAROCHE, F. VURPILLOT Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA Rouen, CNRS, GPM,
Numeric modeling of synchronous laser pulsing and voltage pulsing field evaporation L. ZHAO 1, A. NORMAND, J. HOUARD, I. BLUM, F. DELAROCHE, F. VURPILLOT Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA Rouen, CNRS, GPM,
Robert G. Hunsperger. Integrated Optics. Theory and Technology. Fourth Edition. With 195 Figures and 17 Tables. Springer
 Robert G. Hunsperger Integrated Optics Theory and Technology Fourth Edition With 195 Figures and 17 Tables Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Advantages of Integrated Optics 2 1.1.1 Comparison of
Robert G. Hunsperger Integrated Optics Theory and Technology Fourth Edition With 195 Figures and 17 Tables Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Advantages of Integrated Optics 2 1.1.1 Comparison of
Self-Mixing Laser Diode Vibrometer with Wide Dynamic Range
 Self-Mixing Laser Diode Vibrometer with Wide Dynamic Range G. Giuliani,, S. Donati, L. Monti -, Italy Outline Conventional Laser vibrometry (LDV) Self-mixing interferometry Self-mixing vibrometer Principle:
Self-Mixing Laser Diode Vibrometer with Wide Dynamic Range G. Giuliani,, S. Donati, L. Monti -, Italy Outline Conventional Laser vibrometry (LDV) Self-mixing interferometry Self-mixing vibrometer Principle:
Raman Spectroscopy Basics
 Raman Spectroscopy Basics Introduction Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on inelastic scattering of monochromatic light, usually from a laser source. Inelastic scattering means that
Raman Spectroscopy Basics Introduction Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on inelastic scattering of monochromatic light, usually from a laser source. Inelastic scattering means that
F en = mω 0 2 x. We should regard this as a model of the response of an atom, rather than a classical model of the atom itself.
 The Electron Oscillator/Lorentz Atom Consider a simple model of a classical atom, in which the electron is harmonically bound to the nucleus n x e F en = mω 0 2 x origin resonance frequency Note: We should
The Electron Oscillator/Lorentz Atom Consider a simple model of a classical atom, in which the electron is harmonically bound to the nucleus n x e F en = mω 0 2 x origin resonance frequency Note: We should
University of Pécs in ELI
 Dept. of Experimental Physics Institute of Physics 7624 Pécs, Ifjúság ú. 6. http://physics.ttk.pte.hu University of Pécs in ELI József Fülöp fulop@fizika.ttk.pte.hu Budapest, April 16, 2008 Outline ELI
Dept. of Experimental Physics Institute of Physics 7624 Pécs, Ifjúság ú. 6. http://physics.ttk.pte.hu University of Pécs in ELI József Fülöp fulop@fizika.ttk.pte.hu Budapest, April 16, 2008 Outline ELI
Suppression of Four Wave Mixing in 8 Channel DWDM System Using Hybrid Modulation Technique
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 97-108 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Suppression of Four
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 97-108 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Suppression of Four
PHYSICAL METHODS, INSTRUMENTS AND MEASUREMENTS Vol. IV Femtosecond Measurements Combined With Near-Field Optical Microscopy - Artyom A.
 FEMTOSECOND MEASUREMENTS COMBINED WITH NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY Artyom A. Astafiev, Semyonov Institute of Chemical Physics, Moscow, Russian Federation. Keywords: diffraction limit nearfield scanning
FEMTOSECOND MEASUREMENTS COMBINED WITH NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY Artyom A. Astafiev, Semyonov Institute of Chemical Physics, Moscow, Russian Federation. Keywords: diffraction limit nearfield scanning
Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect
 Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect Incoming Laser Beam Travelling Acoustic Wave (longitudinal wave) O A 1st order diffracted laser beam A 1 Introduction qb d O 2qb rarefractions compressions Refer to Appendix
Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect Incoming Laser Beam Travelling Acoustic Wave (longitudinal wave) O A 1st order diffracted laser beam A 1 Introduction qb d O 2qb rarefractions compressions Refer to Appendix
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors
 Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
The front end of the receiver performs the frequency translation, channel selection and amplification of the signal.
 Many receivers must be capable of handling a very wide range of signal powers at the input while still producing the correct output. This must be done in the presence of noise and interference which occasionally
Many receivers must be capable of handling a very wide range of signal powers at the input while still producing the correct output. This must be done in the presence of noise and interference which occasionally
People screening using terahertz technology
 Invited Paper People screening using terahertz technology Colin Baker, William R. Tribe, Thomas Lo, Bryan E. Cole, Simon Chandler, Michael C. Kemp * TeraView Ltd, Platinum Building, St John s Innovation
Invited Paper People screening using terahertz technology Colin Baker, William R. Tribe, Thomas Lo, Bryan E. Cole, Simon Chandler, Michael C. Kemp * TeraView Ltd, Platinum Building, St John s Innovation
Study of Ultrafast Polarization and Carrier Dynamics in Semiconductor Nanostructures: a THz Spectroscopy Approach
 Study of Ultrafast Polarization and Carrier Dynamics in Semiconductor Nanostructures: a THz Spectroscopy Approach Inaugural-Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Fakultät für Mathematik und Physik
Study of Ultrafast Polarization and Carrier Dynamics in Semiconductor Nanostructures: a THz Spectroscopy Approach Inaugural-Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Fakultät für Mathematik und Physik
INTRODUCTION FIGURE 1 1. Cosmic Rays. Gamma Rays. X-Rays. Ultraviolet Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red Infrared. Ultraviolet.
 INTRODUCTION Fibre optics behave quite different to metal cables. The concept of information transmission is the same though. We need to take a "carrier" signal, identify a signal parameter we can modulate,
INTRODUCTION Fibre optics behave quite different to metal cables. The concept of information transmission is the same though. We need to take a "carrier" signal, identify a signal parameter we can modulate,
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Practical Course M I. Physikalisches Institut Universität zu Köln May 15, 2014 Abstract Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques are widely used in physics, chemistry, and
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Practical Course M I. Physikalisches Institut Universität zu Köln May 15, 2014 Abstract Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques are widely used in physics, chemistry, and
Millijoules high master-slave pulse ratio 532 nm picosecond laser
 Millijoules high master-slave pulse ratio 532 nm picosecond laser Zhao You Fan Zhongwei 1, Bai Zhenao 12, Zhang Guoxin 2, Lian Fuqiang 12, Zhao You 3, Shen Ming 3 1 Academy of Opto-Electronics, Chinese
Millijoules high master-slave pulse ratio 532 nm picosecond laser Zhao You Fan Zhongwei 1, Bai Zhenao 12, Zhang Guoxin 2, Lian Fuqiang 12, Zhao You 3, Shen Ming 3 1 Academy of Opto-Electronics, Chinese
Antennas & Propagation. CS 6710 Spring 2010 Rajmohan Rajaraman
 Antennas & Propagation CS 6710 Spring 2010 Rajmohan Rajaraman Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors o Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space o Reception
Antennas & Propagation CS 6710 Spring 2010 Rajmohan Rajaraman Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors o Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space o Reception
5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy
 5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy Resolution of optical microscope is limited by diffraction. Light going through an aperture makes diffraction
5. Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy 5.1. Resolution of conventional optical microscopy Resolution of optical microscope is limited by diffraction. Light going through an aperture makes diffraction
Projects. Objective To gain hands-on design and measurement experience with real-world applications. Contents
 Projects Contents 9-1 INTRODUCTION...................... 43 9-2 PROJECTS......................... 43 9-2.1 Alarm Radar Sensor................ 43 9-2.2 Microwave FM Communication Link....... 46 9-2.3 Optical
Projects Contents 9-1 INTRODUCTION...................... 43 9-2 PROJECTS......................... 43 9-2.1 Alarm Radar Sensor................ 43 9-2.2 Microwave FM Communication Link....... 46 9-2.3 Optical
Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure
 Northeastern University, PHYS5318 Spring 2014, 1 1. Introduction Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure The laser is a very important optical tool that has found widespread use in science and industry,
Northeastern University, PHYS5318 Spring 2014, 1 1. Introduction Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure The laser is a very important optical tool that has found widespread use in science and industry,
NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY WITH STM AND AFM PROBES
 Vol. 93 (1997) A CTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Scanning Probe Spectroscopy and Related Methods, Poznań 1997 NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY
Vol. 93 (1997) A CTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Scanning Probe Spectroscopy and Related Methods, Poznań 1997 NEAR FIELD OPTICAL MICROSCOPY AND SPECTROSCOPY
Ultrafast Optical Characterization of Novel Mid-Infrared Nanoscale Structures
 NSF ERC MIRTHE Summer Symposium, Princeton University, June 15-16, 2015 Ultrafast Optical Characterization of Novel Mid-Infrared Nanoscale Structures Dr. Anthony M. Johnson, Director* Center for Advanced
NSF ERC MIRTHE Summer Symposium, Princeton University, June 15-16, 2015 Ultrafast Optical Characterization of Novel Mid-Infrared Nanoscale Structures Dr. Anthony M. Johnson, Director* Center for Advanced
Ti:Sapphire Lasers. Tyler Bowman. April 23, 2015
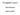 Ti:Sapphire Lasers Tyler Bowman April 23, 2015 Introduction Ti:Sapphire lasers are a solid state laser group based on using titanium-doped sapphire (Ti:Al 2O 3) plates as a gain medium. These lasers are
Ti:Sapphire Lasers Tyler Bowman April 23, 2015 Introduction Ti:Sapphire lasers are a solid state laser group based on using titanium-doped sapphire (Ti:Al 2O 3) plates as a gain medium. These lasers are
Specifying Plasma Deposited Hard Coated Optical Thin Film Filters. Alluxa Engineering Staff
 Specifying Plasma Deposited Hard Coated Optical Thin Film Filters. Alluxa Engineering Staff December 2012 Specifying Advanced Plasma Deposited Hard Coated Optical Bandpass and Dichroic Filters. Introduction
Specifying Plasma Deposited Hard Coated Optical Thin Film Filters. Alluxa Engineering Staff December 2012 Specifying Advanced Plasma Deposited Hard Coated Optical Bandpass and Dichroic Filters. Introduction
Scalable Frequency Generation from Single Optical Wave
 Scalable Frequency Generation from Single Optical Wave S. Radic Jacobs School Of Engineering Qualcomm Institute University of California San Diego - Motivation - Bandwidth Engineering - Noise Inhibition
Scalable Frequency Generation from Single Optical Wave S. Radic Jacobs School Of Engineering Qualcomm Institute University of California San Diego - Motivation - Bandwidth Engineering - Noise Inhibition
Fiber optic communication
 Fiber optic communication Fiber optic communication Outline Introduction Properties of single- and multi-mode fiber Optical fiber manufacture Optical network concepts Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado
Fiber optic communication Fiber optic communication Outline Introduction Properties of single- and multi-mode fiber Optical fiber manufacture Optical network concepts Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado
Analysis and Improvement of Mach Zehnder Modulator Linearity Performance for Chirped and Tunable Optical Carriers
 886 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 5, MAY 2002 Analysis and Improvement of Mach Zehnder Modulator Linearity Performance for Chirped and Tunable Optical Carriers S. Dubovitsky, Member, IEEE,
886 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 5, MAY 2002 Analysis and Improvement of Mach Zehnder Modulator Linearity Performance for Chirped and Tunable Optical Carriers S. Dubovitsky, Member, IEEE,
AM TRANSMITTERS & RECEIVERS
 Reading 30 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com AM TRANSMITTERS & RECEIVERS Revision: our definition of amplitude modulation. Amplitude modulation is when the modulating audio is combined
Reading 30 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com AM TRANSMITTERS & RECEIVERS Revision: our definition of amplitude modulation. Amplitude modulation is when the modulating audio is combined
Optical Fibres. Introduction. Safety precautions. For your safety. For the safety of the apparatus
 Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Introduction Optical fibres are widely used for transmitting data at high speeds. In this experiment,
Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Introduction Optical fibres are widely used for transmitting data at high speeds. In this experiment,
Development of an intense THz source using tilted pulse front method in LiNbO 3 crystal and its application in non-linear THz spectroscopy
 UNIVERSITÉ DU QUÉBEC INRS- ÉNERGIE, MATÉRIAUX ET TÉLÉCOMMUNICATIONS Development of an intense THz source using tilted pulse front method in LiNbO 3 crystal and its application in non-linear THz spectroscopy
UNIVERSITÉ DU QUÉBEC INRS- ÉNERGIE, MATÉRIAUX ET TÉLÉCOMMUNICATIONS Development of an intense THz source using tilted pulse front method in LiNbO 3 crystal and its application in non-linear THz spectroscopy
Keywords: Slot antenna, ultra wideband (UWB), Microstrip line feeding, HFSS Simulation software.
 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Design of Compact UWB Printed Slot Antenna for GPS, GSM &Bluetooth Applications S.P.Shinde *1, M. M. Jadhav 2 *1, 2 Electronics
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Design of Compact UWB Printed Slot Antenna for GPS, GSM &Bluetooth Applications S.P.Shinde *1, M. M. Jadhav 2 *1, 2 Electronics
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
T = 1 f. Phase. Measure of relative position in time within a single period of a signal For a periodic signal f(t), phase is fractional part t p
 Data Transmission Concepts and terminology Transmission terminology Transmission from transmitter to receiver goes over some transmission medium using electromagnetic waves Guided media. Waves are guided
Data Transmission Concepts and terminology Transmission terminology Transmission from transmitter to receiver goes over some transmission medium using electromagnetic waves Guided media. Waves are guided
Self-Guided Intense Laser Pulse Propagation in Air
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2000, v.6, No, 2-26 Self-Guided Intense Laser Pulse Propagation in Air R. Danielius, D. Mikalauskas, A. Dubietis and A. Piskarskas Department of Quantum Electronics,
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2000, v.6, No, 2-26 Self-Guided Intense Laser Pulse Propagation in Air R. Danielius, D. Mikalauskas, A. Dubietis and A. Piskarskas Department of Quantum Electronics,
Laser-induced surface phonons and their excitation of nanostructures
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 49, NO. 1 FEBRUARY 2011 Laser-induced surface phonons and their excitation of nanostructures Markus Schmotz, 1, Dominik Gollmer, 1 Florian Habel, 1 Stephen Riedel, 1 and
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 49, NO. 1 FEBRUARY 2011 Laser-induced surface phonons and their excitation of nanostructures Markus Schmotz, 1, Dominik Gollmer, 1 Florian Habel, 1 Stephen Riedel, 1 and
Copyright 2000 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000
 Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
PUMPED Nd:YAG LASER. Last Revision: August 21, 2007
 PUMPED Nd:YAG LASER Last Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: How can an efficient atomic transition laser be constructed and characterized? INTRODUCTION: This lab exercise will allow
PUMPED Nd:YAG LASER Last Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: How can an efficient atomic transition laser be constructed and characterized? INTRODUCTION: This lab exercise will allow
Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
Optical Communications Research Group Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering University of Limerick, Ireland b
 Numerical Analysis of Pulse Pedestal and Dynamic Chirp Formation on Picosecond Modelocked Laser Pulses after Propaation throuh a Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Michael J. Connelly a Aislin M. Clarke b
Numerical Analysis of Pulse Pedestal and Dynamic Chirp Formation on Picosecond Modelocked Laser Pulses after Propaation throuh a Semiconductor Optical Amplifier Michael J. Connelly a Aislin M. Clarke b
It has long been a goal to achieve higher spatial resolution in optical imaging and
 Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy Fehmi Yasin, Advisor: Dr. Markus Raschke, Post-doc: Dr. Gregory Andreev, Graduate Student: Benjamin Pollard Department of Physics,
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy Fehmi Yasin, Advisor: Dr. Markus Raschke, Post-doc: Dr. Gregory Andreev, Graduate Student: Benjamin Pollard Department of Physics,
Various Technics of Liquids and Solids Level Measurements. (Part 3)
 (Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
(Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
DIAGNOSTICS OF HETEROGENEOUS POLYMER MATERIALS USING NOISE-LIKE MM-WAVE RADIATION
 DIAGNOSTICS OF HETEROGENEOUS POLYMER MATERIALS USING NOISE-LIKE MM-WAVE RADIATION B. Kapilevich, B. Litvak, T. Ben Yehuda and O. Shotman The College of J&S, Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Eng. The
DIAGNOSTICS OF HETEROGENEOUS POLYMER MATERIALS USING NOISE-LIKE MM-WAVE RADIATION B. Kapilevich, B. Litvak, T. Ben Yehuda and O. Shotman The College of J&S, Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Eng. The
Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy for Measuring Materials Properties at the Nanoscale
 Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy for Measuring Materials Properties at the Nanoscale Outline Background Research Design Detection of Near-Field Signal Submonolayer Chemical Sensitivity Conclusions
Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy for Measuring Materials Properties at the Nanoscale Outline Background Research Design Detection of Near-Field Signal Submonolayer Chemical Sensitivity Conclusions
Avalanche Photodiodes: A User's Guide
 !"#$%& Abstract Avalanche Photodiodes: A User's Guide Avalanche photodiode detectors have and will continue to be used in many diverse applications such as laser range finders and photon correlation studies.
!"#$%& Abstract Avalanche Photodiodes: A User's Guide Avalanche photodiode detectors have and will continue to be used in many diverse applications such as laser range finders and photon correlation studies.
Characteristic and use
 . Basic principle A PSD basically consists of a uniform resistive layer formed on one or both surfaces of a high-resistivity semiconductor substrate, and a pair of electrodes formed on both ends of the
. Basic principle A PSD basically consists of a uniform resistive layer formed on one or both surfaces of a high-resistivity semiconductor substrate, and a pair of electrodes formed on both ends of the
Different Types of Dispersions in an Optical Fiber
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 12, December 2012 1 Different Types of Dispersions in an Optical Fiber N.Ravi Teja, M.Aneesh Babu, T.R.S.Prasad, T.Ravi B.tech
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 12, December 2012 1 Different Types of Dispersions in an Optical Fiber N.Ravi Teja, M.Aneesh Babu, T.R.S.Prasad, T.Ravi B.tech
THz Imaging: Biomedical Applications
 THz Imaging: Biomedical Applications Mark Stringer Institute of Microwaves and Photonics School of Electronic + Electrical Engineering University of Leeds imp The TeraHertz Gap Technology Review (MIT)
THz Imaging: Biomedical Applications Mark Stringer Institute of Microwaves and Photonics School of Electronic + Electrical Engineering University of Leeds imp The TeraHertz Gap Technology Review (MIT)
Real-world applications of intense light matter interaction beyond the scope of classical micromachining.
 Dr. Lukas Krainer lk@onefive.com CEO Real-world applications of intense light matter interaction beyond the scope of classical micromachining. 1 Management & Company Company Based in Zürich, Switzerland
Dr. Lukas Krainer lk@onefive.com CEO Real-world applications of intense light matter interaction beyond the scope of classical micromachining. 1 Management & Company Company Based in Zürich, Switzerland
Finite Difference Time Domain and BPM: Flexible Algorithm Selection Technology
 Finite Difference Time Domain and BPM: Flexible Algorithm Selection Technology 1. Introduction This application note shows the use of the Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) module in the calculation
Finite Difference Time Domain and BPM: Flexible Algorithm Selection Technology 1. Introduction This application note shows the use of the Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) module in the calculation
Sampling Theorem Notes. Recall: That a time sampled signal is like taking a snap shot or picture of signal periodically.
 Sampling Theorem We will show that a band limited signal can be reconstructed exactly from its discrete time samples. Recall: That a time sampled signal is like taking a snap shot or picture of signal
Sampling Theorem We will show that a band limited signal can be reconstructed exactly from its discrete time samples. Recall: That a time sampled signal is like taking a snap shot or picture of signal
Diode Applications. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008. This note illustrates some common applications of diodes.
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008 This note illustrates some common applications of diodes. Power supply applications A common application for diodes is converting AC to DC. Although half-wave rectification
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008 This note illustrates some common applications of diodes. Power supply applications A common application for diodes is converting AC to DC. Although half-wave rectification
High-Frequency Engineering / Photonics
 Technische Universität Berlin High-Frequency Engineering / Photonics K. Petermann petermann@tu-berlin.de Main campus High-Frequency Engineering. Electrical Engineering. Technical Acoustics High Voltage
Technische Universität Berlin High-Frequency Engineering / Photonics K. Petermann petermann@tu-berlin.de Main campus High-Frequency Engineering. Electrical Engineering. Technical Acoustics High Voltage
Precision Diode Rectifiers
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn March 21, 2013 Precision half-wave rectifiers An operational amplifier can be used to linearize a non-linear function such as the transfer function of a semiconductor diode. The classic
by Kenneth A. Kuhn March 21, 2013 Precision half-wave rectifiers An operational amplifier can be used to linearize a non-linear function such as the transfer function of a semiconductor diode. The classic
Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics
 Photonics Technical Note # 21 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric wave-guides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded
Photonics Technical Note # 21 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric wave-guides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded
PIPELINE LEAKAGE DETECTION USING FIBER-OPTIC DISTRIBUTED STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSORS WHITE PAPER
 PIPELINE LEAKAGE DETECTION USING FIBER-OPTIC DISTRIBUTED STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSORS WHITE PAPER Lufan Zou and Taha Landolsi OZ Optics Limited, 219 Westbrook Road, Ottawa, ON, Canada, K0A 1L0 E-mail:
PIPELINE LEAKAGE DETECTION USING FIBER-OPTIC DISTRIBUTED STRAIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSORS WHITE PAPER Lufan Zou and Taha Landolsi OZ Optics Limited, 219 Westbrook Road, Ottawa, ON, Canada, K0A 1L0 E-mail:
Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation
 Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering s.h.gerez@utwente.nl Version 4 (February 7, 2013)
Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering s.h.gerez@utwente.nl Version 4 (February 7, 2013)
Timing Errors and Jitter
 Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems
 Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Lecture : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Attenuation (Loss)
Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Lecture : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Attenuation (Loss)
Engineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99
 Engineering Sciences 151 Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99 WAVE PROPAGATION II: HIGH FREQUENCY SLOTTED LINE AND REFLECTOMETER MEASUREMENTS OBJECTIVES: To build greater
Engineering Sciences 151 Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99 WAVE PROPAGATION II: HIGH FREQUENCY SLOTTED LINE AND REFLECTOMETER MEASUREMENTS OBJECTIVES: To build greater
Scientific Exchange Program
 Scientific Exchange Program Electrical characterization of photon detectors based on acoustic charge transport Dr. Paulo Santos, Paul Drude Institute, Berlin,Germany Dr. Pablo Diniz Batista, Brazilian
Scientific Exchange Program Electrical characterization of photon detectors based on acoustic charge transport Dr. Paulo Santos, Paul Drude Institute, Berlin,Germany Dr. Pablo Diniz Batista, Brazilian
Master Degree Program
 SAINT PETERSBURG STATE ELECTROTECHNICAL UNIVERSITY LETI Laser Measurement and Navigation Systems department Master Degree Program ETU LETI TRADITIONS AND INNOVATIONS ETU LETI is the oldest Electrotechnical
SAINT PETERSBURG STATE ELECTROTECHNICAL UNIVERSITY LETI Laser Measurement and Navigation Systems department Master Degree Program ETU LETI TRADITIONS AND INNOVATIONS ETU LETI is the oldest Electrotechnical
SFG spectrometers. Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy. More than 20 years experience
 Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy More than 20 years experience Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy (SFG-VS) is powerful
Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy More than 20 years experience Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy (SFG-VS) is powerful
Experimental results for the focal waveform and beam width in the focusing lens with a 100 ps filter
 EM Implosion Memos Memo 51 July, 2010 Experimental results for the focal waveform and beam width in the focusing lens with a 100 ps filter Prashanth Kumar, Carl E. Baum, Serhat Altunc, Christos G. Christodoulou
EM Implosion Memos Memo 51 July, 2010 Experimental results for the focal waveform and beam width in the focusing lens with a 100 ps filter Prashanth Kumar, Carl E. Baum, Serhat Altunc, Christos G. Christodoulou
The Role of Electric Polarization in Nonlinear optics
 The Role of Electric Polarization in Nonlinear optics Sumith Doluweera Department of Physics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio 45221 Abstract Nonlinear optics became a very active field of research
The Role of Electric Polarization in Nonlinear optics Sumith Doluweera Department of Physics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio 45221 Abstract Nonlinear optics became a very active field of research
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP - 1-1 Introduction In this lab you will use software reconfigurable RF hardware from National
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP - 1-1 Introduction In this lab you will use software reconfigurable RF hardware from National
Amplifier for Small Magnetic and Electric Wideband Receiving Antennas (model AAA-1B)
 Amplifier for Small Magnetic and Electric Wideband Receiving Antennas (model AAA-1B) 1. Description and Specifications Contents 1.1 Description 1.2 1.2 Specifications 1.3 1.3 Tested parameters in production
Amplifier for Small Magnetic and Electric Wideband Receiving Antennas (model AAA-1B) 1. Description and Specifications Contents 1.1 Description 1.2 1.2 Specifications 1.3 1.3 Tested parameters in production
Preview of Period 3: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II
 Preview of Period 3: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Radiant Energy from the Sun How is light reflected and transmitted? What is polarized light? 3.2 Energy Transfer with Radiant Energy How
Preview of Period 3: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Radiant Energy from the Sun How is light reflected and transmitted? What is polarized light? 3.2 Energy Transfer with Radiant Energy How
Self-Mixing Differential Laser Vibrometer
 Self-Mixing Differential Laser Vibrometer Michele Norgia e Informazione, Politecnico di Milano, Italy Guido Giuliani,, Silvano Donati -,, Italy guido.giuliani@unipv.it Outline Conventional Laser Doppler
Self-Mixing Differential Laser Vibrometer Michele Norgia e Informazione, Politecnico di Milano, Italy Guido Giuliani,, Silvano Donati -,, Italy guido.giuliani@unipv.it Outline Conventional Laser Doppler
Optical nutation at a Raman-active transition
 JETP LETTERS VOLUME 70, NUMBER 1 10 JULY 1999 Optical nutation at a Raman-active transition S. V. Anikeev, V. B. Morozov,* ) A. N. Olenin, and V. G. Tunkin M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119899
JETP LETTERS VOLUME 70, NUMBER 1 10 JULY 1999 Optical nutation at a Raman-active transition S. V. Anikeev, V. B. Morozov,* ) A. N. Olenin, and V. G. Tunkin M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119899
Interferometric Measurement of Dispersion in Optical Components
 Interferometric Measurement of Dispersion in Optical Components Mark Froggatt, Eric Moore, and Matthew Wolfe Luna Technologies, Incorporated, 293-A Commerce Street, Blacksburg, Virginia 246 froggattm@lunatechnologies.com.
Interferometric Measurement of Dispersion in Optical Components Mark Froggatt, Eric Moore, and Matthew Wolfe Luna Technologies, Incorporated, 293-A Commerce Street, Blacksburg, Virginia 246 froggattm@lunatechnologies.com.
PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory I Notes on Noise Reduction
 PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory I Notes on Noise Reduction When setting out to make a measurement one often finds that the signal, the quantity we want to see, is masked by noise, which is anything
PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory I Notes on Noise Reduction When setting out to make a measurement one often finds that the signal, the quantity we want to see, is masked by noise, which is anything
SEMICONDUCTOR lasers with optical feedback have
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 34, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1979 Dynamics and Linear Stability Analysis in Semiconductor Lasers with Phase-Conjugate Feedback Atsushi Murakami and Junji Ohtsubo,
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 34, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1979 Dynamics and Linear Stability Analysis in Semiconductor Lasers with Phase-Conjugate Feedback Atsushi Murakami and Junji Ohtsubo,
RAY TRACING UNIFIED FIELD TRACING
 RAY TRACING Start to investigate the performance of your optical system using 3D ray distributions, dot diagrams of ray positions and directions, and optical path length. GEOMETRIC FIELD TRACING Switch
RAY TRACING Start to investigate the performance of your optical system using 3D ray distributions, dot diagrams of ray positions and directions, and optical path length. GEOMETRIC FIELD TRACING Switch
Optical Communications
 Optical Communications Telecommunication Engineering School of Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2005-2006 Lecture #2, May 2 2006 The Optical Communication System BLOCK DIAGRAM OF
Optical Communications Telecommunication Engineering School of Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2005-2006 Lecture #2, May 2 2006 The Optical Communication System BLOCK DIAGRAM OF
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference (selectivity, images and distortion) Large dynamic range
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference (selectivity, images and distortion) Large dynamic range
Laser Based Micro and Nanoscale Manufacturing and Materials Processing
 Laser Based Micro and Nanoscale Manufacturing and Materials Processing Faculty: Prof. Xianfan Xu Email: xxu@ecn.purdue.edu Phone: (765) 494-5639 http://widget.ecn.purdue.edu/~xxu Research Areas: Development
Laser Based Micro and Nanoscale Manufacturing and Materials Processing Faculty: Prof. Xianfan Xu Email: xxu@ecn.purdue.edu Phone: (765) 494-5639 http://widget.ecn.purdue.edu/~xxu Research Areas: Development
Time out states and transitions
 Time out states and transitions Spectroscopy transitions between energy states of a molecule excited by absorption or emission of a photon hn = DE = E i - E f Energy levels due to interactions between
Time out states and transitions Spectroscopy transitions between energy states of a molecule excited by absorption or emission of a photon hn = DE = E i - E f Energy levels due to interactions between
Selected Radio Frequency Exposure Limits
 ENVIRONMENT, SAFETY & HEALTH DIVISION Chapter 50: Non-ionizing Radiation Selected Radio Frequency Exposure Limits Product ID: 94 Revision ID: 1736 Date published: 30 June 2015 Date effective: 30 June 2015
ENVIRONMENT, SAFETY & HEALTH DIVISION Chapter 50: Non-ionizing Radiation Selected Radio Frequency Exposure Limits Product ID: 94 Revision ID: 1736 Date published: 30 June 2015 Date effective: 30 June 2015
Germanium Diode AM Radio
 Germanium Diode AM Radio LAB 3 3.1 Introduction In this laboratory exercise you will build a germanium diode based AM (Medium Wave) radio. Earliest radios used simple diode detector circuits. The diodes
Germanium Diode AM Radio LAB 3 3.1 Introduction In this laboratory exercise you will build a germanium diode based AM (Medium Wave) radio. Earliest radios used simple diode detector circuits. The diodes
OPTICAL FIBERS INTRODUCTION
 OPTICAL FIBERS References: J. Hecht: Understanding Fiber Optics, Ch. 1-3, Prentice Hall N.J. 1999 D. R. Goff: Fiber Optic Reference Guide (2 nd ed.) Focal Press 1999 Projects in Fiber Optics (Applications
OPTICAL FIBERS References: J. Hecht: Understanding Fiber Optics, Ch. 1-3, Prentice Hall N.J. 1999 D. R. Goff: Fiber Optic Reference Guide (2 nd ed.) Focal Press 1999 Projects in Fiber Optics (Applications
NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE. Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407, University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706
 (revised 4/21/03) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407, University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract This experiment studies the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of protons
(revised 4/21/03) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407, University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract This experiment studies the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of protons
LM1596 LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator
 LM1596 LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator General Description The LM1596 LM1496 are doubled balanced modulator-demodulators which produce an output voltage proportional to the product of an input (signal)
LM1596 LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator General Description The LM1596 LM1496 are doubled balanced modulator-demodulators which produce an output voltage proportional to the product of an input (signal)
Concept 2. A. Description of light-matter interaction B. Quantitatities in spectroscopy
 Concept 2 A. Description of light-matter interaction B. Quantitatities in spectroscopy Dipole approximation Rabi oscillations Einstein kinetics in two-level system B. Absorption: quantitative description
Concept 2 A. Description of light-matter interaction B. Quantitatities in spectroscopy Dipole approximation Rabi oscillations Einstein kinetics in two-level system B. Absorption: quantitative description
An optical pump-probe technique for measuring the thermal conductivity of liquids
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 79, 064902 2008 An optical pump-probe technique for measuring the thermal conductivity of liquids Aaron Schmidt, a Matteo Chiesa, Xiaoyuan Chen, and Gang Chen Department
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 79, 064902 2008 An optical pump-probe technique for measuring the thermal conductivity of liquids Aaron Schmidt, a Matteo Chiesa, Xiaoyuan Chen, and Gang Chen Department
AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Amplified High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the
AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Amplified High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING See beginning of Section H for abbreviations, course numbers and coding. The * denotes labs which are held on alternate weeks. A minimum grade of C is required for all prerequisite
Four Wave Mixing in Closely Spaced DWDM Optical Channels
 544 VOL. 1, NO. 2, AUGUST 2006 Four Wave Mixing in Closely Spaced DWDM Optical Channels Moncef Tayahi *, Sivakumar Lanka, and Banmali Rawat Advanced Photonics Research lab, Department of Electrical Engineering
544 VOL. 1, NO. 2, AUGUST 2006 Four Wave Mixing in Closely Spaced DWDM Optical Channels Moncef Tayahi *, Sivakumar Lanka, and Banmali Rawat Advanced Photonics Research lab, Department of Electrical Engineering
GLOBAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY: YSR DIST. Unit VII Fiber Optics Engineering Physics
 Introduction Fiber optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibers. Fiber optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Introduction Fiber optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibers. Fiber optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Nexus Technology Review -- Exhibit A
 Nexus Technology Review -- Exhibit A Background A. Types of DSL Lines DSL comes in many flavors: ADSL, ADSL2, ADSL2+, VDSL and VDSL2. Each DSL variant respectively operates up a higher frequency level.
Nexus Technology Review -- Exhibit A Background A. Types of DSL Lines DSL comes in many flavors: ADSL, ADSL2, ADSL2+, VDSL and VDSL2. Each DSL variant respectively operates up a higher frequency level.
- thus, the total number of atoms per second that absorb a photon is
 Stimulated Emission of Radiation - stimulated emission is referring to the emission of radiation (a photon) from one quantum system at its transition frequency induced by the presence of other photons
Stimulated Emission of Radiation - stimulated emission is referring to the emission of radiation (a photon) from one quantum system at its transition frequency induced by the presence of other photons
THE FIBRE-OPTICS TRAINER MANUAL
 THE FIBRE-OPTICS TRAINER MANUAL THE FIBRE-OPTICS TRAINER MANUAL THE FIBRE-OPTICS TRAINER CONTAINS: TRANSMITTER UNIT RECEIVER UNIT 5m. LENGTH OF TERMINATED OPTICAL CABLE INSTRUCTION MANUAL (THIS BOOK) CARRYING
THE FIBRE-OPTICS TRAINER MANUAL THE FIBRE-OPTICS TRAINER MANUAL THE FIBRE-OPTICS TRAINER CONTAINS: TRANSMITTER UNIT RECEIVER UNIT 5m. LENGTH OF TERMINATED OPTICAL CABLE INSTRUCTION MANUAL (THIS BOOK) CARRYING
