The Influence of Coordinate Overexpression of Glutathione Phase II Detoxification Gene Products on Drug Resistance 1
|
|
|
- Rosaline Barrett
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /00/ $03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in U.S.A. JPET 294: , 2000 /2523/ The Influence of Coordinate Overexpression of Glutathione Phase II Detoxification Gene Products on Drug Resistance 1 MIECHELLE O BRIEN, 2 GARY D. KRUH, and KENNETH D. TEW Department of Pharmacology (M.O., K.D.T) and Division of Medical Sciences (G.D.K.), Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Accepted for publication April 17, 2000 This paper is available online at ABSTRACT Glutathione (GSH), glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), and the multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) have been independently studied for their contributions to drug resistance. Single cdna transfection experiments have provided inconsistent and disparate conclusions with respect to the importance of GSH and GST in conferring a resistant phenotype. Because these three proteins can act as a concerted coordinated pathway, we reasoned that equivalent increases may be required for enhanced resistance to be expressed. We have assembled these proteins together, or in various combinations, to determine whether they show cooperativity in determining drug response. Increased expression through single cdna transfection of GST, -glutamylcysteine synthetase ( -GCS) (regulatory plus catalytic subunits), or MRP1 enhanced resistance to a number of anticancer drugs. Cotransfection of GST and GCS, gave higher resistance to doxorubicin, etoposide, and vincristine than with either alone. Resistance toward chlorambucil and ethacrynic acid was similar in cells overexpressing either component or overexpressing GST alone. Coexpression of GST with MRP1 conferred significant resistance above that seen for MRP1 alone to chlorambucil, etoposide, ethacrynic acid, and vincristine. The combination of GCS and MRP1 did not afford additional resistance above MRP1 alone. When all three were transfected, significantly higher levels of resistance were found for doxorubicin and etoposide. These results support the concept that coordinate enhancement of focal thiol elements of detoxification pathways provides a more efficient protective phenotype than do single components alone. Resistance to chemotherapeutic agents has been a daunting problem to oncologists for decades. Major advances have been made in understanding drug metabolism and disposition, and how adaptive phase II metabolism can result in altered cytotoxicity to anticancer drugs. The glutathione S- transferase (GST) enzyme system has been implicated in the development of resistance to several anticancer drugs (O Brien and Tew, 1996). This family of isozymes can catalyze the conjugation of electrophilic compounds to the cellular tripeptide glutathione (GSH). A body of literature indicates that the levels of GST expression at the tissue or cellular level are important determinants for response to chemical insult. Often, increased GST expression is associated with a resistant phenotype in tumors, implicating GST as an adaptive response in cellular protection. Primary evidence for the role of GST and GSH in drug resistance comes from three sources: 1) analysis of tumor cells from patients before and after the onset of clinical drug Received for publication January 21, This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grants CA06927 and RR05539, by National Institutes of Health Grant CA53893 to K.D.T., and by an appropriation from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. 2 Present address: New York Medical College, Valhalla, NY resistance, where an increase in GSH and GST occurs after development of resistance (Schisselbauer et al., 1990); 2) an increase in GSH/GST after the selection of acquired resistance to anticancer agents in tumor cell lines (Tew, 1994; Hayes and Pulford, 1995); and 3) analysis of resistance expressed after transfection of particular GST genes into cell lines (Tew, 1994; Hayes and Pulford, 1995). Existing transfection data are not without variability in both results and interpretation. Much of the disparity may result from a baseline variability in expression of the GSH/GST components in the cell lines used for transfection. Although it is important to think of GST as contributory within the whole system, the efficiency of metabolism may rest with the homeostatic interactions among all members of the relevant detoxification pathway. For example, if there is a limit in the amount of GSH available for conjugation, the presence of increased GST may not result in increased detoxification. Furthermore, the ultimate removal of GSH conjugates from the cell will also provide a more rapid clearance of toxic chemicals. There is substantial evidence that one such protein is multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1), which functions to sequester and ultimately remove glutathione (GS)-conjugates or other products of phase II metabolism (Leier et al., 1994). ABBREVIATIONS: GST, glutathione S-transferase; GS-conjugate, glutathione conjugate; GSH, glutathione; MRP1, multidrug resistance-associated protein 1; -GCS, -glutamylcysteine sythetase; CDNB, 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; ROS, reactive oxygen species. 480
2 2000 Coordination of Glutathione Metabolism 481 MRP1 is a member of the ATP-binding cassette transporter gene family. Its capacity to confer resistance has been well described in transfection studies (Cole et al., 1994; Breuninger et al., 1995). MRP1 appears to exhibit broad substrate specificity and has been shown to confer resistance to various natural product drugs, including anthracyclines, vinca alkaloids, and epipodophyllotoxins. Resistant lines that overexpress MRP1 can be sensitized by pretreatment with buthionine sulfoximine, an agent which depletes cellular GSH levels (Zaman et al., 1995). Recent experiments indicate that buthionine sulfoximine sensitization is based on the requirement of GSH for MRP1-mediated cellular efflux of some natural product drugs (Rappa et al., 1997). Interestingly, many cell lines selected for resistance to drugs that are part of the MRP1 resistance profile also have increased GST (Tew, 1994; Hayes and Pulford, 1995). Thus, it is apparent that MRP1 serves as an integral component of thiol-based detoxification pathways. Because electrophilic drugs may be catalytically conjugated to GSH by GST and the resultant thioether product effluxed from a cell by MRP1, we rationalized that each of these components may contribute to resistance in a coordinate manner. In addition, although drugs that have classically been viewed as part of the multidrug resistant phenotype are not obvious candidates for GSH conjugation, some may be cotransported with GSH by MRP. Thus, this report elucidates the importance of coordinating the overexpression of phase II detoxification with enhanced efflux. The data support the general conclusion that cooperativity among GST, glutamylcysteine synthetase ( -GCS), and MRP1 exists. Materials and Methods Plasmids. Human GST cdna was polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-amplified from mrna prepared from an ethacrynic acid resistant human colon HT29 cell line. One microgram of RNA was reverse transcribed using a standard protocol. Two rounds of PCRamplified GSTP1 cdna were prepared, and a Kozak sequence added before the initiation codon (Kozak, 1978). The primers used in the PCRs were as follows: first PCR amplification: forward, 5 -ATG- CCG-CCC-TAC-ACC-GTC-3 ; reverse, 5 -TCA-CTG-TTT-CCC-GTT- GCC-3 ; second PCR amplification: forward, 5 -CGC-GGA-TCC- GCA-CCA-TGC-CGC-CCT-ACA-CCG-TG-3 ; reverse, 5 -GGG-CCA- GCA-CAG-TGG-TCA-CTG-TTT-CCC-GTT-GCC-3. PCR products were resolved on a 1% SeaKem gel (FMC, Rockland, ME), and the fragment was excised. cdna was purified by centrifugation through a Spin-X centrifuge tube filter (Corning Inc., Acton, MA) by standard procedures. The sequence of the GST cdna was confirmed by nucleotide sequence analysis. Cell Lines and Transfection. cdnas for -GCS heavy and -GCS light subunits were kindly provided by Dr. Tim Mulcahy (University of Wisconsin, Madison). The cdnas were cloned into the Not-1 site of pcdna3.1/hygro (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). NIH3T3 cells and 3T3/MRP cells (Breuninger et al., 1995) were transfected using the lipofectamine (Life Technologies, Rockville, MD) lipid transfection method. The various DNA plasmid constructs were added either alone (GST ) or in combination. 3T3/pc and 3T3/ MRP/pc lines were made by transfecting NIH3T3 and 3T3/MRP cells with the parental pcdna3.1 vector. After a 20-h exposure of cells to DNA/lipidamine, cells were allowed to grow in drug-free media for 24 h before colony selection in media containing 175 ug/ml hygromycin (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO). Several colonies were isolated and characterized for each type of transfected cell line made. Cells were maintained in Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium containing 10% fetal calf serum, 100 g/ml streptomycin, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 2 mm L-glutamine at 5% CO 2 and 37 C. Immunoblot Analysis. Cytosolic fractions were used for the verification that the cytosolic enzymes GST, -GCS heavy, and -GCS light were overexpressed in the appropriate cell lines. Fifty micrograms of protein was separated by 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proteins were transferred to Immobilon-P membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA) for 4hat300mAinbuffer consisting of 0.38 M glycine, 50 mm Tris, 0.1% SDS, and 20% methanol. Gels were stained in Coomassie blue (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) to verify complete transfer. Blots were blocked overnight in 5% nonfat dry milk in Tris-buffered saline/tween 20, followed by a 1-h incubation in primary antisera diluted 1:1000. The GST antisera was provided by Biotrin (Dublin, Ireland), and the MRP1 antisera was previously described (Breuninger et al., 1995). Polyclonal antisera against -GCS heavy and -GCS light were generated against the peptides GLLSQGSPLSWEETK and LLTHNDPKELLSEAS, respectively, and were used at a 1:1000 dilution. Blots were washed three times for 10 min each before incubation with secondary antiserum. Anti-rabbit peroxidase-linked secondary antisera was purchased from Amersham (Piscataway, NJ) and used at a 1:5000 dilution. Blots were probed with antisera against actin (Amersham) to verify equivalent loading. After three washes for 30 min, blots were visualized using the enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit (NEN Life Science Products, Boston, MA) and quantified by scanning densitometry using NIH Image software. GSH Measurements. Intracellular GSH concentrations were measured using the GSH-400 assay kit from OXIS International Inc. (Portland, OR). Briefly, cells were grown to approximately 50 to 70% confluence in 80-cm 2 flasks before trypsinization and counting (Coulter Corp., Miami, FL). Approximately cells were pelleted and resuspended in freshly prepared 5% metaphosphoric acid. The suspension was sonicated for 30 s and spun at 3,000g for 10 min at 4 C. One hundred microliters of the supernatant was used in the assay for the detection at 400 nm of thione formed from the conjugation of GSH to 4-chloro-1-methyl-7-trifluoromethyl-quinolinium methylsulfate. Enzymatic Conjugation Assay. Conjugation of reduced GSH to 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) was stimulated by the addition of cellular protein as described previously (Habig and Jakoby, 1981). Briefly, 100 g of S-100 cellular fractions was added to cuvettes containing 1.0 mm CDNB and 1.0 mm GSH at a ph of 6.5 for a final volume of 1.0 ml. Change in absorbance (340 nm) was measured over a span of 3 min to calculate the rate of conjugation of CDNB. Cell Survival Assays. Drug sensitivities were determined by the Cell Titer 96 aqueous nonradioactive cell proliferation assay (Promega, Madison, WI). Cells were plated onto 96-well plates at a density of 1500 cells/well in 100 l of Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium plus 10% fetal calf serum. After cells were adherent, varying concentrations of drug were added, and the cells were maintained in drug for 72 h. After this period of drug exposure, 20 l of 2 mg/ml 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt, and 45.9 ug/ml phenazine methosulfate were added to each well and incubated at 37 C for approximately 1 h. Production of formazan was detected at 490 nm on a 7520 Microplate reader (Cambridge Technology Inc., Cambridge, MA). Statistical Analysis. Data from multiple biochemical or cytotoxicity assays were compared by ANOVA analysis followed by Dunnett s multiple comparison tests (GraphPad Prism; GraphPad, San Diego, CA) with statistical differences judged at P.01. Results Establishment of Cell Lines with Various Components of GSH/GST/MRP Detoxification Pathways. The cdnas for human GST, -GCS heavy, and -GCS light
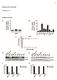
3 482 O Brien et al. Vol. 294 subunits were transfected into NIH3T3 fibroblasts or the previously described 3T3/MRP1 transfected fibroblasts (Breuninger et al., 1995). The cdnas were introduced alone or in combinations. After transfection of the fibroblasts with the various expression plasmids, cells were selected in hygromycin. After several weeks of colony expansion, immunoblots were used to determine which colonies expressed the requisite proteins. The cell lines generated are listed in Table 1. For all the transfectant lines, 4 to 6 separate clonal populations were established and characterized. Data for one clonal cell line was found to be representative of the others, and for reasons of clarity, one set of data is presented. For each culture, no significant differences were found for population doubling time and/or clonogenic potential. Analysis of Protein Expression. Figure 1A shows the immunoblot of GST in the cell lines in which only GST was added. Expression levels of GST increased approximately 5-fold over cells transfected with the parental vector (3T3/pc). Fig. 1B shows the expression of -GCS heavy and light subunits in the 3T3/GCS and 3T3/MRP/GCS lines. Levels of these proteins were increased 2- to 3-fold. Fig. 1C shows the increased expression of all three proteins, GST, -GCS heavy, and -GCS light. Once again, GST levels were elevated approximately 5-fold over the control 3T3/pc and 3T3/ MRP lines, and -GCS levels were raised approximately 2- to 3-fold. The MRP immunoblot (Fig. 1D) shows that single cdna transfectants had approximately 15-fold higher levels compared with 3T3/pc. This increase did not change in the multiple transfectants containing GST, -GCS, or the combination thereof. Expression of actin was determined in all lanes to control for equivalent loading. A summary of the quantitative increase in these blots is provided in Table 1. The activity of GST was determined by assaying the cell lysates for conjugation of CDNB with GSH. Figure 2A shows that compared with either 3T3/pc or 3T3/MRP cells, enzymatic activity increased significantly for each transfectant. These increases are lower than could be expected from the TABLE 1 NIH3T3 cells were transfected, as detailed under Materials and Methods, with the vector pcdna3.1/hygromycin containing the cdnas for human MRP1, GST, -GCS heavy subunit, and -GCS light subunits to generate the cell lines indicated The increased protein expression was estimated from NIH Image software quantitation of immunoblots (average of three) using actin expression as standard control. Cell Line cdna Fold Increase in Protein Expression Level Compared with Mock Transfectants 3T3/pc pcdna3.1 3T3/ GST 5 3T3/GCS -GCS heavy subunit 2.5 -GCS light subunit 3 3T3/ /GCS GST 5 -GCS heavy subunit 2 -GCS light subunit 3 3T3/MRP MRP 15 3T3/MRP1/ MRP 15 GST 7 3T3/MRP/GCS MRP 15 -GCS heavy subunit 2 -GCS light subunit 3 3T3/MRP/GCS/ MRP 15 GST 5 -GCS heavy subunit 2 -GCS light subunit 2 Fig. 1. Immunoblot analysis of GST -, MRP-, and -GCS heavy- and -GCS light-transfected cell lines used in this study. Fifty micrograms of protein was separated by 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis before transfer and immunoblotting with antiserum, as detailed under Materials and Methods. Quantitative expression of protein levels was based on the immunostain intensity as a ratio of actin (NIH Image software). Representative blots from at least three experiments are shown. immunoblots. However, CDNB is a general GST substrate, and the specific GST effects may be muted by the other endogenous enzymes in NIH3T3 cells. As a functional measure of -GCS activity, intracellular GSH levels were assessed. Figure 2B shows that 3T3/GCS and 3T3/MRP/GCS cells have significantly higher intracellular GSH levels compared with 3T3/pc. MRP1-transfected cells had generally lower intracellular GSH concentrations, independent of the presence of -GCS, a finding that is consistent with the principle that elevated MRP levels may produce an increased efflux of GSH and/or conjugates (Schneider et al., 1995). This would have the net effect of counteracting the increased de novo synthesis enacted by -GCS. Analysis of Drug Sensitivity of Cell Lines Overexpressing GST. Figure 3 shows the survival curves for the
4 2000 Coordination of Glutathione Metabolism 483 Fig. 2. A, enzymatic conjugation of GSH to CDNB. Cytosolic protein extracts were prepared from each cell line and assessed for their ability to conjugate CDNB to GSH as described under Materials and Methods. Data are represented as mean S.D. of at least three independent experiments. ANOVA analysis followed by Dunnett s multiple comparison tests revealed statistical differences of *P.01. B, intracellular GSH concentrations in transfectant cells. Data were obtained using the GSH assay kit (OXIS International Inc.) and are represented as mean S.D. of at least three independent experiments. ANOVA analysis followed by Dunnett s multiple comparison tests revealed statistical differences of *P.01. various transfectant cell lines. To facilitate comparative analyses, the panels show either 3T3/pc or 3T3/MRP as controls. In each case, cell survival was determined after a 72-h exposure to drug. Figure 3 shows the survival curves toward chlorambucil, doxorubicin, ethacrynic acid, vincristine, and etoposide. For each drug, the addition of GST to NIH3T3 cells enhanced resistance, although the increase was not statistically significant for doxorubicin. The greatest change in drug sensitivity for 3T3/ cells was seen with etoposide (9-fold) and chlorambucil (3-fold). Transfection of MRP alone (3T3/MRP) caused a significant enhancement of resistance compared with 3T3/pc for all drugs tested. Addition of GST to MRP caused a further small increase in resistance for all drugs except doxorubicin. The most striking effect was with etoposide, where a further, approximate 4-fold, enhancement in resistance occurred. Transfection of the -GCS holoenzyme also resulted in significant changes in resistance. The cell line 3T3/GCS was generated by transfection of NIH3T3 cells with cdnas for both the -GCS heavy and light subunits. The forced expression of both subunits resulted in elevated levels of GSH (Fig. 2). Survival curves for 3T3/GCS cells indicate modest enhanced resistance to ethacrynic acid and etoposide ( 2-fold) and vincristine and chlorambucil ( 3-fold). When -GCS was cotransfected with MRP1, no enhancement in resistance above that associated with MRP1 was found. Enhanced resistance in 3T3/GCS/ cells was equal to or greater than that for 3T3/ or 3T3/GCS cells. For vincristine, the resistance factor associated with the addition of both proteins was additive when compared with either alone, whereas for doxorubicin a greater effect was found with the addition of both GST and GCS. Generally, 3T3/MRP/GCS/ cells did not display a greater resistance to ethacrynic acid, chlorambucil, or vincristine beyond that demonstrated in 3T3/MRP cells. However, more resistance was shown toward etoposide and doxorubicin. For etoposide, the resistance factor in the 3T3/ MRP/GCS/ lines was equivalent to that seen in the 3T3/ MRP/ line, approximately 4-fold more resistant than the 3T3/MRP cells. As in the 3T3/GCS/ line, the coexpression of GST, -GCS, and MRP1 resulted in a greater than additive resistance toward doxorubicin when compared with either GST or -GCS with MRP1. The resistance factor increased from approximately 13-fold in 3T3/MRP cells to an overall 100-fold in 3T3/MRP/GCS/ cells (see also Fig. 4). A quantitative comparison of the IC 50 values generated from the survival curves is shown in Fig. 4. For each of the five drugs, MRP transfection (3T3/MRP) resulted in a statistically significant enhancement in resistance. In many cases, this was further enhanced by cotransfection of -GCS and/or GST. For both doxorubicin and etoposide, 3T3/MRP/GCS/ cells expressed a resistance factor of approximately 100, the highest for any of the drugs tested. Discussion Information from drug-selected cell lines often gives the first indication that a particular protein has a role in resistance. However, when chronically exposed to drug insult, a pleiotropic response usually produces an up-regulation of multiple detoxification gene products, which can make evaluation of the contribution of any one protein difficult to assess. Single cdna transfection experiments offer a more defined system but will not always mimic the in vivo situation. In particular, single transfection of cdnas for members of the GST family has produced conflicting reports concerning the importance of this gene family (in particular GST )to drug resistance (reviewed in Tew, 1994 and in Hayes and Pulford, 1995). At least one plausible explanation for the earlier discrepancies could be the absence of a coordination of cellular metabolism and clearance required to enhance resistance. To demonstrate how coordinate expression influences anticancer drugs, we transfected components of the GSHbased detoxification system in various combinations in recipient cells. We selected a cross-section of anticancer drugs with some relevance to GSH-based metabolism that have been the subject of previous single cdna transfection analyses. For example, chlorambucil and ethacrynic acid are subject to GST-mediated conjugation with GSH and eventual
5 484 O Brien et al. Vol. 294 Fig. 3. Cytotoxicity of various drugs in transfectant cells. Cells were exposed to drug for 72 h as detailed under Materials and Methods. Data are from n 4 experiments, performed in triplicate and combined to generate the mean S.D. for each concentration. Survival curves are grouped based on the drug used. Individual transfectants are identified on the legend for each graph. Control survival is represented either by mock transfectants (3T3/pc, left panels) or by 3T3/MRP (right panels).
6 2000 Coordination of Glutathione Metabolism 485 Fig. 3. Continued. efflux by MRP (Ciaccio et al., 1991, 1996). Doxorubicin, vincristine, and etoposide are component drugs of the multidrug resistant phenotype, and their detoxification/efflux has been linked with GSH/GST and MRP, although the nature of the association is not completely defined. Ethacrynic acid has a -unsaturated carbonyl group that provides Michael addition properties. It can react either spontaneously or catalytically (GST) with GSH, and the thioether conjugate is a substrate for MRP. Only low degrees of resistance can be achieved in acquired resistant cells ( 5- fold), and the phenotype is characterized by an increased expression of -GCS, GST, and MRP (Ciaccio et al., 1996). The transfection data are consistent with these adaptive changes, where GST, -GCS, or MRP as single transfectants give a modest, but significant, increase in resistance. The multiple transfectants show some degree of additivity with an approximate 5-fold resistance achieved for 3T3/ MRP/ and 3T3/MRP/GCS/. Thus, there is a direct relationship between the transfectant data and the acquired resistant phenotype. A similar response pattern was shown for chlorambucil. GST can catalyze the formation of GS-conjugates with the aziridinium-alkylating species of chlorambucil (Ciaccio et al., 1991). 3T3/ cells had a 2.6-fold increase in GST activity over the control 3T3/pc cells, which gave a 3-fold increase in resistance to chlorambucil. Although GSH levels are typically 1 to 10 mm in most cells (Anderson, 1989), 3T3/GCS cells achieved a 2-fold increase in intracellular GSH that translated to a 3-fold increase in resistance. The combination of GST and -GCS produced equivalent resistance to GST or -GCS alone. MRP1 alone conferred resistance when compared with 3T3/pc, whereas the combination in 3T3/MRP/ cells showed further enhancement. This finding is the first to demonstrate MRP1 conferred resistance to an alkylating agent and is consistent with previous reports citing MRP1 as a transporter of chlorambucil only when conjugated to GSH (Barnouin et al., 1998; Morrow et al., 1998). Overall, the data suggest that GSH conjugation may be sufficient for decreasing chlorambucil toxicity and that the presence of the MRP1 impacts on cell survival only marginally. As for ethacrynic acid, the maximal degree of resistance reflected the concordance of transfection and acquired resistance data (Tew, 1994; Hayes and Pulford, 1995; O Brien and Tew, 1996). The production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxides is one mechanism by which anthracyclines such as doxorubicin are thought to exert toxicity (Sinha et al., 1987; Poot et al., 1988). Products of oxidative stress, such as acrolein and base propenals, are documented substrates for GST catalysis to GS-conjugates (Berhane et al., 1994). Previous reports have shown that transfection of GST (Nakagawa et al., 1990) or the light subunit of GCS (Tipnis et al., 1999) alone can produce an approximate 2-fold resistance to doxorubicin. In other cases, GST transfection had no impact on survival, particularly when compared with cotransfection of P-glycoprotein (Fairchild et al., 1990). Although the P- glycoprotein can transport a broad range of natural product drugs, there was no indication that transfection conditions altered its expression in any of the cell lines used (data not shown). GS-conjugates of doxorubicin are transported by MRP1, but although it has been suggested that their in vivo occurrence may be possible (Koch et al., 1994), such conjugates have not been identified in cells. Although quantitatively less significant than MRP, incremental increases in resistance are found when GST or -GCS are transfected individually or together, implying that thiols affect doxorubicin response. Interestingly, the 3T3/MRP/GCS/ cells show a significant 3-fold increase in resistance compared with 3T3/MRP, a value similar to that for 3T3/GCS/ compared with 3T3/pc. Thus, MRP confers significant resistance, perhaps as a result of direct efflux of doxorubicin ( / GSH). The additional 3-fold increment provided by -GCS and GST may be a function of detoxification of ROS as by-products of doxorubicin metabolism. Resistance to vincristine was enhanced by each of the component cdnas as individual transfectants. GS-conjugates of vincristine have not been described and in the absence of anthracycline quinone cycling, it is less likely that ROS will play a large role in vincristine toxicity. There is evidence that vinca alkaloids are subject to oxidation by monoamine oxidases and P-450 microsomal preparations (Rosazza et al., 1992). Clearance of oxidized metabolites of vincristine may in part explain why the addition of GST renders cells less sensitive to cytotoxicity associated with the drug. Increased expression of -GCS in 3T3/MRP/GCS cells imparted only a slight increase in resistance to vincristine compared with 3T3/MRP. Although intracellular GSH levels are doubled in 3T3/MRP/ GCS cells compared with 3T3/MRP cells, there may be sufficient GSH in the latter to accommodate efficient efflux of vincristine, with further increase in GSH having no additional impact. Consistent with this possibility, bio-
7 486 O Brien et al. Vol. 294 Fig. 4. Comparison of IC 50 values for various drugs. IC 50 values were determined individually from each cytotoxicity experiment performed. A minimum of four values was used in the determination of mean S.D. ANOVA analysis followed by Dunnett s multiple comparison tests revealed statistical differences of *P.01. In all cases, 3T3/MRP cells had statistically significant increased IC 50 values compared with 3T3/pc. Therefore, the asterisk ( ) for the dark histogram bars shows P.01 significance when multitransfectant cells are compared with 3T3/MRP. chemical experiments suggest that MRP1-mediated vincristine transport reaches steady state when the GSH concentrations approximate 5 mm (Loe et al., 1998). Etoposide is another drug for which GS-conjugates have not been described, yet many resistant lines selected in the drug have elevated GST (Tew, 1994). Etoposide also increases GSH export from cells expressing MRP1, suggesting cotransport of etoposide and GSH in a manner similar to that of vincristine (Rappa et al., 1997). We found, once again, that each of the single transfections significantly influenced resistance to etoposide, whether expressed alone or in combination with other members of the GSH detoxification pathway ( 8-fold in 3T3/, 14-fold in 3T3/GCS/, escalating to 20-fold in 3T3/MRP, and 100-fold in 3T3/MRP/GCS/ ). There is evidence for quinone and semiquinone metabolites of etoposide, and the latter can form conjugates with GSH. Hydroxyl radicals are generated from this metabolism, and as with anthracyclines, it is possible that GST and MRP1 serve protective roles. For most of the natural product drugs tested, coordinate forced overexpression of MRP1 with GST and the holoenzyme of GCS provided the highest resistance factors. Precise correlations between extent of expression and degree of resistance would be of only limited value because cellular homeostasis of both the endogenous and introduced gene products will complicate any direct stoichiometric assessment. Perhaps of more importance, the general patterns of response support the principle that -GCS, GST, and MRP1 function in series for the detoxification of anticancer drugs or products of oxidative stress. The data generated support the concept that a coordinated increase in expression of gene products, which participate in a concerted step-wise detoxification of a drug, provide a generally more effective means of cellular protection. It should be recognized that GSH and thiols in general have a broad role in controlling kinase pathways that lead to cell survival or apoptosis. Many transcription factors are regulated by redox conditions, and recent studies have shown
8 2000 Coordination of Glutathione Metabolism 487 that a NH 2 -terminal c-jun kinase (JNK) is directly regulated by GST (Adler et al., 1999). Because the multiple transfections significantly influence intracellular redox balance, future experiments will consider how survival may be influenced by more general stress response pathways leading to survival or apoptosis. References Adler V, Yin Z, Fuchs SY, Benezra M, Rosario L, Tew KD, Pincus MR, Sardana M, Henderson CJ, Wolf CR, Davis R and Ronai Z (1999) Regulation of JNK signaling by GSTp. EMBO J 18: Anderson ME (1989) Enzymatic and chemical methods for the determination of glutathione, in Glutathione: Chemical, Biochemical and Medical Aspects, Volume A (Dolphin D, Poulson R and Avramovic O eds) pp , John Wiley and Sons, New York. Barnouin K, Leier I, Jedlitschky G, Pourtier-Manzanedo A, Konig J, Lehmann W-D and Keppler D (1998) Multidrug resistance protein-mediated transport of chlorambucil and melphalan conjugated to glutathione. Br J Cancer 77: Berhane K, Widersten M, Engstrom A, Kozarich JW and Mannervik B (1994) Detoxication of base propenals and other alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehyde products of radical reactions and lipid peroxidation by human glutathione transferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: Breuninger LM, Paul S, Gaughan K, Miki T, Chan A, Aaronson SA and Kruh GD (1995) Expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein in NIH/3T3 cells confers multidrug resistance associated with increased drug efflux and altered intracellular drug distribution. Cancer Res 55: Ciaccio PJ, Shen H, Kruh GD and Tew KD (1996) Effects of chronic ethacrynic acid exposure on glutathione conjugation and MRP expression in human colon tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 222: Ciaccio PJ, Tew KD and LaCreta FP (1991) Enzymatic conjugation of chlorambucil with glutathione is catalyzed by human glutathione S-transferases and inhibited by ethacrynic acid. Biochem Pharmacol 42: Cole SPC, Sparks KE, Fraser K, Loe DW, Grant CE, Wilson GM and Deeley RG (1994) Pharmacological characterization of multidrug resistant MRP-transfected human tumor cells. Cancer Res 54: Fairchild CR, Moscow JA, O Brien EE and Cowan KH (1990) Multidrug resistance in cells transfected with human genes encoding a variant P-glycoprotein and glutathione S-transferase-pi. Mol Pharmacol 37: Habig WH and Jakoby WB (1981) Assays for differentiation of glutathione S- transferases. Methods Enzymol 77: Hayes JD and Pulford DJ (1995) The glutathione S-transferase supergene family: Regulation of GST and the contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 30: Koch TH, Gaudiano G and Resing K (1994) Reaction of anthracycline antitumor drugs with reduced glutathione. Formation of aglycon conjugates. J Am Chem Soc 116: Kozak M (1978) How do eukaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell 15: Leier I, Jedlitschky G, Buchholz U, Cole SP, Deeley RG and Keppler D (1994) The MRP gene encodes an ATP-dependent export pump for leukotriene C4 and structurally related conjugates. J Biol Chem 269: Loe DW, Deeley RG and Cole SPC (1998) Characterization of vincristine transport by the M r 190,000 multidrug resistance protein (MRP): Evidence for cotransport with reduced glutathione. Cancer Res 58: Morrow CS, Smitherman PK, Diah SK, Schneider E and Townsend AJ (1998) Coordinated action of glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) and multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) in antineoplastic drug detoxification. J Biol Chem 273: Nakagawa K, Saijo N, Tsuchida S, Sakai M, Tsunokawa M, Yokota J, Murumatsu M, Sato K, Terada M and Tew KD (1990) Glutathione S-transferase p as a determinant of drug resistance in transfectant cell lines. J Biol Chem 265: O Brien ML and Tew KD (1996) Glutathione and related enzymes in multidrug resistance. Eur J Cancer 32A: Poot M, Esterbauer H, Rabinovitch PS and Hoehn H (1988) Disturbance of cell proliferation by two model compounds of lipid peroxidation contradicts causative role in proliferative senescence. J Cell Physiol 137: Rappa G, Lorico A, Flavell RA and Sartorelli AC (1997) Evidence that the multidrug resistance protein (MRP) functions as a co-transporter of glutathione and natural product toxins. Cancer Res 57: Rosazza JP, Duffel MW, el-marakby S and Ahn SH (1992) Metabolism of the catharanthus alkaloids: From streptomyces griseus to monoamine oxidase B. J Nat Prod 55: Schisselbauer J, Silber R, Papadopoulous E, LaCreata FP and Tew KD (1990) Characterization of glutathione S-transferase isozymes in lymphocytes from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Cancer Res 50: Schneider E, Yamazaki H, Sinha BK and Cowan KH (1995) Buthionine sulphoximine-mediated sensitisation of etoposide-resistant human breast cancer MCF7 cells overexpressing the multidrug resistance-associated protein involves increased drug accumulation. Br J Cancer 71: Sinha BK, Katki AG, Batist G, Cowan KH and Myers CE (1987) Differential formation of hydroxyl radicals by adriamycin in sensitive and resistant MCF-7 human breast tumor cells: Implications for the mechanism of action. Biochemistry 26: Tew KD (1994) Glutathione-associated enzymes in anticancer drug resistance. Perspectives in Cancer Research. Cancer Res 54: Tipnis SR, Blake DG, Shepherd AG and McLellan LI (1999) Overexpression of the regulatory subunit of g-glutamylcysteine synthetase in HeLa cells increases -glutamylcysteine synthetase activity and confers drug resistance. Biochem J 337: Zaman GJR, Lankelma J, van Tellingen O, Beunen J, Dekker H, Paulusma CP, Elferink RPJO, Baas F and Borst P (1995) Role of glutathione in the export of compounds from cells by the multidrug-resistance-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: Send reprint requests to: Dr. Kenneth D. Tew, Department of Pharmacology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, 7701 Burholme Ave., Philadelphia, PA kd_tew@fccc.edu
Chapter 8. Summary and Perspectives
 Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
BIOMARKERS AND TOXICITY MECHANISMS 06 Mechanisms Metabolism & Detoxification. Luděk Bláha, PřF MU, RECETOX www.recetox.cz
 BIOMARKERS AND TOXICITY MECHANISMS 06 Mechanisms Metabolism & Detoxification Luděk Bláha, PřF MU, RECETOX www.recetox.cz Metabolism and detoxification Chemicals enter body... mostly via food Pass directly
BIOMARKERS AND TOXICITY MECHANISMS 06 Mechanisms Metabolism & Detoxification Luděk Bláha, PřF MU, RECETOX www.recetox.cz Metabolism and detoxification Chemicals enter body... mostly via food Pass directly
Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer
 Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer Referees: PD Dr. Tobias Dick Prof. Dr. Wilfried Roth http://d-nb.info/1057851272 CONTENTS Summary 1 Zusammenfassung 2 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1
Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer Referees: PD Dr. Tobias Dick Prof. Dr. Wilfried Roth http://d-nb.info/1057851272 CONTENTS Summary 1 Zusammenfassung 2 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1
Methionine Sulfoxide Immunoblotting Kit
 Methionine Sulfoxide Immunoblotting Kit Item No. 600160 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
Methionine Sulfoxide Immunoblotting Kit Item No. 600160 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
The cell lines used in this study were obtained from the American Type Culture
 Supplementary materials and methods Cell culture and drug treatments The cell lines used in this study were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and grown as previously described.
Supplementary materials and methods Cell culture and drug treatments The cell lines used in this study were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and grown as previously described.
CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Supplemental Information. McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data
 1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
Induction of Enzyme Activity in Bacteria:The Lac Operon. Preparation for Laboratory: Web Tutorial - Lac Operon - submit questions
 Induction of Enzyme Activity in Bacteria:The Lac Operon Preparation for Laboratory: Web Tutorial - Lac Operon - submit questions I. Background: For the last week you explored the functioning of the enzyme
Induction of Enzyme Activity in Bacteria:The Lac Operon Preparation for Laboratory: Web Tutorial - Lac Operon - submit questions I. Background: For the last week you explored the functioning of the enzyme
Running protein gels and detection of proteins
 Running protein gels and detection of proteins 1. Protein concentration determination using the BIO RAD reagent This assay uses a colour change reaction to give a direct measurement of protein concentration.
Running protein gels and detection of proteins 1. Protein concentration determination using the BIO RAD reagent This assay uses a colour change reaction to give a direct measurement of protein concentration.
Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION
 Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION Susan Carson Heather B. Miller D.Scott Witherow ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN
Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION Susan Carson Heather B. Miller D.Scott Witherow ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN
Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit
 Product Manual Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit Catalog Number PRB-5002 20 blots FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The technique of immunoprecipitation (IP) is used
Product Manual Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit Catalog Number PRB-5002 20 blots FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The technique of immunoprecipitation (IP) is used
TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides
 Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and subsequent analyses are common tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. This Application
Western Blot Analysis with Cell Samples Grown in Channel-µ-Slides Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and subsequent analyses are common tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. This Application
First Strand cdna Synthesis
 380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay
 Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
RNA & Protein Synthesis
 RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
hydrocortisone (5 mg/ml), EGF (10 µg/ml) and Heparin (5000 U/ml). Antibodies against the N-terminal peptide of MEK1 (MEK1-N) and against Flotillin 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Cells HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells) were grown in complete Medium 199 (Gibco) supplemented with glutamax, 10% foetal calf serum, BBE (9 mg/ml), hydrocortisone (5
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Cells HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells) were grown in complete Medium 199 (Gibco) supplemented with glutamax, 10% foetal calf serum, BBE (9 mg/ml), hydrocortisone (5
Classic Immunoprecipitation
 292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
Protocol for Western Blotting
 Protocol for Western Blotting Materials Materials used on Day 3 Protease inhibitor stock: 1 μg/μl pepstatin A in DMSO 200 μm leupeptin in OG Buffer 200 mm PMSF: Freshly made. Ex) 34.8 mg PMSF in 1 ml isopropanol
Protocol for Western Blotting Materials Materials used on Day 3 Protease inhibitor stock: 1 μg/μl pepstatin A in DMSO 200 μm leupeptin in OG Buffer 200 mm PMSF: Freshly made. Ex) 34.8 mg PMSF in 1 ml isopropanol
Western Blotting. USA: proteintech@ptglab.com UK & Europe: europe@ptglab.com China: service@ptglab.com. www.ptglab.com
 Western Blotting All steps are carried out at room temperature unless otherwise indicated. Recipes for all solutions highlighted bold are included at the end of the protocol. SDS-PAGE 1. Construct an SDS-PAGE
Western Blotting All steps are carried out at room temperature unless otherwise indicated. Recipes for all solutions highlighted bold are included at the end of the protocol. SDS-PAGE 1. Construct an SDS-PAGE
STUDIES ON SEED STORAGE PROTEINS OF SOME ECONOMICALLY MINOR PLANTS
 STUDIES ON SEED STORAGE PROTEINS OF SOME ECONOMICALLY MINOR PLANTS THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREB OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY (SCIENCE) OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CALCUTTA 1996 NRISINHA DE, M.Sc DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY
STUDIES ON SEED STORAGE PROTEINS OF SOME ECONOMICALLY MINOR PLANTS THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREB OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY (SCIENCE) OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CALCUTTA 1996 NRISINHA DE, M.Sc DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS
 EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus
 Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus Introduction Protein extraction from tissues and cultured cells is the first step for many biochemical and analytical
Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus Introduction Protein extraction from tissues and cultured cells is the first step for many biochemical and analytical
Anti-ATF6 α antibody, mouse monoclonal (1-7)
 Anti-ATF6 α antibody, mouse monoclonal (1-7) 73-500 50 ug ATF6 (activating transcription factor 6) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane-bound transcription factor activated in response to ER stress.
Anti-ATF6 α antibody, mouse monoclonal (1-7) 73-500 50 ug ATF6 (activating transcription factor 6) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane-bound transcription factor activated in response to ER stress.
Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual
 Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual I. Purpose...1 II. Introduction...1 III. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth Protocol...2 IV. Inhibition of in vitro
Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual I. Purpose...1 II. Introduction...1 III. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth Protocol...2 IV. Inhibition of in vitro
PRODUCT INFORMATION...
 VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
Western Blotting: Mini-gels
 Western Blotting: Mini-gels Materials a Protein Extraction Buffer (for callus or kernel), Solution Stock Final Volume Tris-HCl ph 80 1 M 200 mm 20 ml NaCl 4 M 100 mm 25 ml Sucrose 2 M 400 mm 20 ml EDTA
Western Blotting: Mini-gels Materials a Protein Extraction Buffer (for callus or kernel), Solution Stock Final Volume Tris-HCl ph 80 1 M 200 mm 20 ml NaCl 4 M 100 mm 25 ml Sucrose 2 M 400 mm 20 ml EDTA
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit
 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
In vitro analysis of pri-mirna processing. by Drosha-DGCR8 complex. (Narry Kim s lab)
 In vitro analysis of pri-mirna processing by Drosha-DGCR8 complex (Narry Kim s lab) 1-1. Preparation of radiolabeled pri-mirna transcript The RNA substrate for a cropping reaction can be prepared by in
In vitro analysis of pri-mirna processing by Drosha-DGCR8 complex (Narry Kim s lab) 1-1. Preparation of radiolabeled pri-mirna transcript The RNA substrate for a cropping reaction can be prepared by in
Overexpression of Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein (MRP) Increases Resistance to Natural Product Drugs I
 [CANCER RESEARCH 54, 357-361, January 15, 1994] Advances in Brief Overexpression of Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein (MRP) Increases Resistance to Natural Product Drugs I Caroline E. Grant, Gunnar
[CANCER RESEARCH 54, 357-361, January 15, 1994] Advances in Brief Overexpression of Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein (MRP) Increases Resistance to Natural Product Drugs I Caroline E. Grant, Gunnar
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a
 Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Over Expression of IPTG inducible GST protein in E.coli BL21
 ISSN:0975-542X Over Expression of IPTG inducible GST protein in E.coli BL21 1 Sugantha priya S, 1 Gowri Shankar J, 1 Thirumalaisamy R, 1 Kavitha P, 1 Prakash B 2 Arunachalam G, 3 S.Selvamuthukumar 1 Department
ISSN:0975-542X Over Expression of IPTG inducible GST protein in E.coli BL21 1 Sugantha priya S, 1 Gowri Shankar J, 1 Thirumalaisamy R, 1 Kavitha P, 1 Prakash B 2 Arunachalam G, 3 S.Selvamuthukumar 1 Department
Clonal Analysis of Cancer Cells that Survived Anticancer Drug Treatment
 Osaka City Medical Journal Vol. 43, No.2 259-265, 1997 Clonal Analysis of Cancer Cells that Survived Anticancer Drug Treatment TETSUJI TANAKA, LING CHANG, NAOHIKO UMESAKI and SACHIO OGITA Department of
Osaka City Medical Journal Vol. 43, No.2 259-265, 1997 Clonal Analysis of Cancer Cells that Survived Anticancer Drug Treatment TETSUJI TANAKA, LING CHANG, NAOHIKO UMESAKI and SACHIO OGITA Department of
pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing
 pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing Tagging HSP60 with HA tag genome editing The latest tool in genome editing CRISPR/Cas9 allows for specific genome disruption and replacement in a flexible
pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing Tagging HSP60 with HA tag genome editing The latest tool in genome editing CRISPR/Cas9 allows for specific genome disruption and replacement in a flexible
2.1.2 Characterization of antiviral effect of cytokine expression on HBV replication in transduced mouse hepatocytes line
 i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small
 The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
Protein transfer from SDS-PAGE to nitrocellulose membrane using the Trans-Blot SD cell (Western).
 Western Blot SOP Protein transfer from SDS-PAGE to nitrocellulose membrane using the Trans-Blot SD cell (Western). Date: 8/16/05, 10/31/05, 2/6/06 Author: N.Oganesyan, R. Kim Edited by: R. Kim Summary:
Western Blot SOP Protein transfer from SDS-PAGE to nitrocellulose membrane using the Trans-Blot SD cell (Western). Date: 8/16/05, 10/31/05, 2/6/06 Author: N.Oganesyan, R. Kim Edited by: R. Kim Summary:
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation A) Prepare a yeast culture (see the Galactose Induction Protocol for details). 1) Start a small culture (e.g. 2 ml) in YEPD or selective media from a single colony. 2) Spin
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation A) Prepare a yeast culture (see the Galactose Induction Protocol for details). 1) Start a small culture (e.g. 2 ml) in YEPD or selective media from a single colony. 2) Spin
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit
 Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Just the Facts: A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
 1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
How To Make A Tri Reagent
 TRI Reagent For processing tissues, cells cultured in monolayer or cell pellets Catalog Number T9424 Store at room temperature. TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description TRI Reagent is a quick and convenient
TRI Reagent For processing tissues, cells cultured in monolayer or cell pellets Catalog Number T9424 Store at room temperature. TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description TRI Reagent is a quick and convenient
Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles stabilized with. intermolecular disulfide bonds. Supporting Information
 Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles stabilized with intermolecular disulfide bonds Wentan Wang, Yanbin Huang*, Shufang Zhao, Ting Shao and Yi Cheng* Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University,
Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles stabilized with intermolecular disulfide bonds Wentan Wang, Yanbin Huang*, Shufang Zhao, Ting Shao and Yi Cheng* Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University,
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity
 Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit
 Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600450 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600450 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
CypExpress 3A4 Catalyzed Conversion of Testosterone (TE) to 6β- Hydroxytestosterone (HT)
 TM CASE STUDY CypExpress 3A4 Catalyzed Conversion of to Shuvendu Das, 1 Enrique Martez, 2 and Mani Subramanian 1 1 Center for Biocatalysis and Bioprocessg, University of Iowa 2 Oxford Biomedical Research,
TM CASE STUDY CypExpress 3A4 Catalyzed Conversion of to Shuvendu Das, 1 Enrique Martez, 2 and Mani Subramanian 1 1 Center for Biocatalysis and Bioprocessg, University of Iowa 2 Oxford Biomedical Research,
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse
 THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
THE His Tag Antibody, mab, Mouse Cat. No. A00186 Technical Manual No. TM0243 Update date 01052011 I Description.... 1 II Key Features. 2 III Storage 2 IV Applications.... 2 V Examples - ELISA..... 2 VI
Phosphate Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Product Manual Phosphate Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-685 1000 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphorus exists as a soluble free phosphate
Product Manual Phosphate Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-685 1000 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphorus exists as a soluble free phosphate
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
CLINICAL STUDY OF MARKETED AYURVEDIC PREPARATION IN THYROID INDUCED STRESS A. A. ROY* 1, K. R. KAKADE 2, R.P. BHOLE 1, V. B.
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 870-874, July-Sept 2009 CLINICAL STUDY OF MARKETED AYURVEDIC PREPARATION IN THYROID INDUCED STRESS A. A.
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 870-874, July-Sept 2009 CLINICAL STUDY OF MARKETED AYURVEDIC PREPARATION IN THYROID INDUCED STRESS A. A.
Nucleic Acid Purity Assessment using A 260 /A 280 Ratios
 Nucleic Acid Purity Assessment using A 260 /A 280 Ratios A common practice in molecular biology is to perform a quick assessment of the purity of nucleic acid samples by determining the ratio of spectrophotometric
Nucleic Acid Purity Assessment using A 260 /A 280 Ratios A common practice in molecular biology is to perform a quick assessment of the purity of nucleic acid samples by determining the ratio of spectrophotometric
MAB Solut. MABSolys Génopole Campus 1 5 rue Henri Desbruères 91030 Evry Cedex. www.mabsolut.com. is involved at each stage of your project
 Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Ubiquitin Interact Kit
 Ubiquitin Interact Kit Item No. 15978 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Precautions 4 If You
Ubiquitin Interact Kit Item No. 15978 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Precautions 4 If You
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
Rapid GST Inclusion Body Solubilization and Renaturation Kit
 Product Manual Rapid GST Inclusion Body Solubilization and Renaturation Kit Catalog Number AKR-110 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Bacteria are widely used for His
Product Manual Rapid GST Inclusion Body Solubilization and Renaturation Kit Catalog Number AKR-110 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Bacteria are widely used for His
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
 INTRODUCTION Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity The chemical reactions occurring in living things are controlled by enzymes. An enzyme is a protein in the cell which lowers the activation energy of a catalyzed
INTRODUCTION Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity The chemical reactions occurring in living things are controlled by enzymes. An enzyme is a protein in the cell which lowers the activation energy of a catalyzed
MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2
 page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit
 PAGE 1 UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit Catalog # 12800-50 50 preps New improved PCR inhibitor removal solution (IRS) included Instruction Manual (New Alternative Protocol maximizes yields) Introduction
PAGE 1 UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit Catalog # 12800-50 50 preps New improved PCR inhibitor removal solution (IRS) included Instruction Manual (New Alternative Protocol maximizes yields) Introduction
PROTOCOL. Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry. Background. Materials and equipment required.
 PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
PCR was carried out in a reaction volume of 20 µl using the ABI AmpliTaq GOLD kit (ABI,
 Supplemental Text/Tables PCR Amplification and Sequencing PCR was carried out in a reaction volume of 20 µl using the ABI AmpliTaq GOLD kit (ABI, Foster City, CA). Each PCR reaction contained 20 ng genomic
Supplemental Text/Tables PCR Amplification and Sequencing PCR was carried out in a reaction volume of 20 µl using the ABI AmpliTaq GOLD kit (ABI, Foster City, CA). Each PCR reaction contained 20 ng genomic
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit
 Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit Part # 103015-100 User Guide For use with Seahorse XF e and XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers For Research Use Only 1 Table of Contents Product Description... 2 Introduction...
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit. Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C
 FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit is suitable for the conjugation of polyclonal and
FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit is suitable for the conjugation of polyclonal and
Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr. 1 Introduction. Gene Expression Application Note No. 4
 Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
Animal Cell Culture. Third Edition. A Practical Approach OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS
 Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Using TaqMan Endogenous Control Assays to select an endogenous control for experimental studies
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Using TaqMan Endogenous Control Assays to select an endogenous control for experimental studies Introduction Quantitative real-time PCR (qpcr) allows for
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Using TaqMan Endogenous Control Assays to select an endogenous control for experimental studies Introduction Quantitative real-time PCR (qpcr) allows for
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay. Introduction
 Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million deaths
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million deaths
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL. 1 Standard sirna transfection of adherent cells... 2
 INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
Bacterial Transformation and Plasmid Purification. Chapter 5: Background
 Bacterial Transformation and Plasmid Purification Chapter 5: Background History of Transformation and Plasmids Bacterial methods of DNA transfer Transformation: when bacteria take up DNA from their environment
Bacterial Transformation and Plasmid Purification Chapter 5: Background History of Transformation and Plasmids Bacterial methods of DNA transfer Transformation: when bacteria take up DNA from their environment
Ann.wellhouse@TouchStoneScience.net 1. Enzyme Function
 Ann.wellhouse@TouchStoneScience.net 1 Enzyme Function National Science Standards Science as Inquiry: Content Standard A: As a result of activities in grades 9-12, all students should develop: Abilities
Ann.wellhouse@TouchStoneScience.net 1 Enzyme Function National Science Standards Science as Inquiry: Content Standard A: As a result of activities in grades 9-12, all students should develop: Abilities
TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0010 TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael W. Fannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0010 TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael W. Fannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
RayBio Creatine Kinase (CK) Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit
 RayBio Creatine Kinase (CK) Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 28, 2014 RayBio Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay (Cat#: 68CL-CK-S100) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You
RayBio Creatine Kinase (CK) Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 28, 2014 RayBio Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay (Cat#: 68CL-CK-S100) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Determination of specificity of intracellular detection of IL-7Rα by flow cytometry
 CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
Basic Science in Medicine
 Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
Product Datasheet. Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase Reporter Kit NBP2-25285. Unit Size: 1 Kit. Storage is content dependent.
 Product Datasheet Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase Reporter Kit NBP2-25285 Unit Size: 1 Kit is content dependent. Publications: 6 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images
Product Datasheet Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase Reporter Kit NBP2-25285 Unit Size: 1 Kit is content dependent. Publications: 6 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images
Product name Company Cat # PowerPac Basic Power supply Bio Rad 165-6019 Mini Protean electrophoresis system Mini trans blot cell Bio Rad 170-3930
 SDS-PAGE and western blot for low molecular weight proteins (2-20kDa) Merav Marom Shamur, Smart Assays Aim: Analysis of low molecular weight proteins by SDS-PAGE and western blot under reducing conditions.
SDS-PAGE and western blot for low molecular weight proteins (2-20kDa) Merav Marom Shamur, Smart Assays Aim: Analysis of low molecular weight proteins by SDS-PAGE and western blot under reducing conditions.
Custom Antibody Services
 prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method)
 Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
Immune Tolerance Network RPCI 004 v.002 Staining Procedure For all Directly Conjugated Reagents (Whole Blood Method) Author: Paul Wallace, Director, RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry Approved by: Paul
OxiSelect Advanced Glycation End Product (AGE) Competitive ELISA Kit
 Product Manual OxiSelect Advanced Glycation End Product (AGE) Competitive ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-817 STA-817-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
Product Manual OxiSelect Advanced Glycation End Product (AGE) Competitive ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-817 STA-817-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
Classical drug resistance in the molecular age
 Classical drug resistance in the molecular age Robert O Connor, Ph.D. Senior Programme Leader, Translational Cancer Pharmacology Lecturer in Biological Sciences, School of Nursing Chair ICORG Translational
Classical drug resistance in the molecular age Robert O Connor, Ph.D. Senior Programme Leader, Translational Cancer Pharmacology Lecturer in Biological Sciences, School of Nursing Chair ICORG Translational
to 370C in a matter of seconds. Materials and Methods.-Yeast spheroplasts were prepared, resuspended to a concentration
 A MUTANT OF YEAST APPARENTLY DEFECTIVE IN THE INITIATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS* BT LELAND H. HARTWELLt AND CALVIN S. MCLAUGHLIN DEPARTMENT OF MOLECULAR AND CELL BIOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA (IRVINE)
A MUTANT OF YEAST APPARENTLY DEFECTIVE IN THE INITIATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS* BT LELAND H. HARTWELLt AND CALVIN S. MCLAUGHLIN DEPARTMENT OF MOLECULAR AND CELL BIOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA (IRVINE)
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
From DNA to Protein. Proteins. Chapter 13. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. The Path From Genes to Proteins. All proteins consist of polypeptide chains
 Proteins From DNA to Protein Chapter 13 All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequence of a gene The Path From Genes
Proteins From DNA to Protein Chapter 13 All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequence of a gene The Path From Genes
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay. Introduction
 Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note 2 Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note 2 Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million
Protein Precipitation Protocols
 Protein Precipitation Protocols Notes: All reagents need to high purity/hplc quality. All tubes used should be new or hand cleaned thoroughly with Micro90 detergent. High quality water needs to be used
Protein Precipitation Protocols Notes: All reagents need to high purity/hplc quality. All tubes used should be new or hand cleaned thoroughly with Micro90 detergent. High quality water needs to be used
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary GeneBLAzer RAR alpha DA Assay Kit GeneBLAzer RAR alpha-uas-bla GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1387, K1685 Target Description The retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha)
Validation & Assay Performance Summary GeneBLAzer RAR alpha DA Assay Kit GeneBLAzer RAR alpha-uas-bla GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1387, K1685 Target Description The retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha)
Supplementary Figure 1.
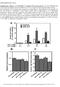 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) MicroRNA 212 enhances IS from pancreatic β-cells. INS-1 832/3 β-cells were transfected with precursors for mirnas 212, 375, or negative control oligonucleotides. 48 hrs after
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) MicroRNA 212 enhances IS from pancreatic β-cells. INS-1 832/3 β-cells were transfected with precursors for mirnas 212, 375, or negative control oligonucleotides. 48 hrs after
Bottlenecks in Clinical Source Material Acquisition. Aby J. Mathew, PhD May 5, 2009 ISCT Annual Meeting San Diego, CA amathew@biolifesolutions.
 Bottlenecks in Clinical Source Material Acquisition Aby J. Mathew, PhD May 5, 2009 ISCT Annual Meeting San Diego, CA amathew@biolifesolutions.com Biopreservation What s the issue? Biopreservation considerations
Bottlenecks in Clinical Source Material Acquisition Aby J. Mathew, PhD May 5, 2009 ISCT Annual Meeting San Diego, CA amathew@biolifesolutions.com Biopreservation What s the issue? Biopreservation considerations
LESSON 3.5 WORKBOOK. How do cancer cells evolve? Workbook Lesson 3.5
 LESSON 3.5 WORKBOOK How do cancer cells evolve? In this unit we have learned how normal cells can be transformed so that they stop behaving as part of a tissue community and become unresponsive to regulation.
LESSON 3.5 WORKBOOK How do cancer cells evolve? In this unit we have learned how normal cells can be transformed so that they stop behaving as part of a tissue community and become unresponsive to regulation.
STOP. Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below:
 STOP Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below: Important Limited Use License information for pdrive5lucia-rgfap The purchase of the pdrive5lucia-rgfap vector conveys
STOP Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below: Important Limited Use License information for pdrive5lucia-rgfap The purchase of the pdrive5lucia-rgfap vector conveys
Liver Disease and Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus Infections
 Liver Disease and Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus Infections University of Adelaide Catherine Scougall Arend Grosse Huey-Chi Low Allison Jilbert Fox Chase Cancer Center Chunxiao Xu Carol Aldrich Sam Litwin
Liver Disease and Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus Infections University of Adelaide Catherine Scougall Arend Grosse Huey-Chi Low Allison Jilbert Fox Chase Cancer Center Chunxiao Xu Carol Aldrich Sam Litwin
Methods for Protein Analysis
 Methods for Protein Analysis 1. Protein Separation Methods The following is a quick review of some common methods used for protein separation: SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) separates
Methods for Protein Analysis 1. Protein Separation Methods The following is a quick review of some common methods used for protein separation: SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) separates
TOOLS sirna and mirna. User guide
 TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
DP419 RNAsimple Total RNA Kit. RNAprep pure Series. DP501 mircute mirna Isolation Kit. DP438 MagGene Viral DNA / RNA Kit. DP405 TRNzol Reagent
 Overview of TIANGEN Products DP419 RNAsimple Total RNA Kit DP430 RNAprep pure Kit(For Cell/Bacteria) DP315/DP315-R TIANamp Virus DNA/RNA Kit DP431 RNAprep pure Kit (For Tissue) Silica-membrane Technology
Overview of TIANGEN Products DP419 RNAsimple Total RNA Kit DP430 RNAprep pure Kit(For Cell/Bacteria) DP315/DP315-R TIANamp Virus DNA/RNA Kit DP431 RNAprep pure Kit (For Tissue) Silica-membrane Technology
User Manual. CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit. Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube
 User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit
 ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE Q5B
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
