Transport Strategy. Transition, Reform, and Sustainable Management
|
|
|
- Paula Page
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transport Strategy Transition, Reform, and Sustainable Management
2 Vietnam s infrastructure challenge As Vietnam becomes richer it faces challenges in adapting its infrastructure policies and institutions. While the old challenges of providing basic services to all remain, new challenges are emerging, such as accessing new sources of finance, refining planning processes, preparing for rapid urbanization, improving the efficiency of infrastructure service providers, developing stronger institutions to encourage private finance of infrastructure or direct private provision of infrastructure, and developing more targeted approaches to poverty alleviation. This report on Transport Strategy - Transition, Reform, and Sustainable Management is one of six volumes dealing with Vietnam's Infrastructure Challenge. Other volumes deal with Infrastructure Cross Sectoral Issues, Water and Sanitation, Electricity, Telecommunications, and Urban Development. The work for these reports was carried out between 2004 and 2006 by World Bank staff and consultants. The reports have been revised to take account of comments made by the Government in workshops during May 15-17, The comments of numerous colleagues from the World Bank, the United Kingdom's Department for International Development Bank, the Asian Development Bank, and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation are gratefully acknowledged.
3 Abbreviations CAAV CIENCO CO CPC CPRGS DAF DPI DDoT DWT FDI GDP GMS GoV GRIPS GSO HDM4 HPC ICD ICOR IDA LDIF MARD MOF MOT MPI MTEF MTRR NLF NPTS NTSC NVOCC NWTC ODA PDoTs Civil Aviation Administration of Vietnam Civil Engineering Construction Corporation Carbon Monoxide Communes Peoples' Committees Comprehensive Poverty Reduction and Growth Strategy Development Assistance Fund Department of Planning and Investment District Departments of Transport Dead Weight Tonnage Foreign Direct Investment Gross Domestic Product Greater Mekong Sub-region Government of Vietnam The National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies (Japan) General Statistics Office of Vietnam Highway Development and Management System Hanoi People's Committee Inland Container Depot Incremental Capital-Output Ratio International Development Association (the World Bank) Local Development Investment Fund Ministry of Agriculture and Regional Development Ministry of Finance Ministry of Transport Ministry of Planning and Investment Medium Term Expenditure Framework Multimodal Transport Regulatory Review National Logistics Forum National Program on Traffic Safety National Transportation Safety Council Non Vessel-Operating Common Carrier Northern Waterway Transport Corporation Official Development Assistance Provincial Departments of Transport iii
4 PER-IFA PIP PMD PMU PDOT PPC PPI PTA RMMC RNIP RRMU SEDP SEDS SOCB SOE SWTC TD TDSI TEC TEU TRAMOC TRANSERCO TSDS TUPWS VAC VEC VHLSS VICT VLA VINALINES VITRANSS VIWA VND VNRA VRA VRC WTO Public Expenditure Review and Integrated Fiduciary Assessment Public Investment Program Prime Ministerial Decision Project Management Unit Provincial Department of Transport Provincial People's Committees Private Participation in Infrastructure Provincial Transport Authorities Road Management and Maintenance Company Road Network Improvement Project Regional Road Management Units Socio-Economic Development Plan Socio-Economic Development Strategy State-Owned Commercial Bank State-Owned Enterprise Southern Waterway Transport Corporation Transport Department (of MoT) Transport Development and Strategy Institute Transport Engineering Company Twenty Foot Equivalent Unit Traffic Management and Operation Center Transportation Cooperation Transport Sector Development Strategy Transport and Urban Public Works Services Vietnam Airlines Cooperation Vietnam Expressway Corporation Vietnam Household Living Standards Survey Vietnam International Container Terminal Vietnam Land Administration Vietnam National Shipping Lines Vietnam's Transport Strategy Study Vietnam Inland Waterway Administration Vietnamese Dong Vietnam Railway Administration Vietnam Road Administration Vietnamese Railway Corporation World Trade Organization iv
5 Table of Contents 1 OVERVIEW Introduction Transport Sector Goals Enhancing Efficiency in Resource Utilization and Service Delivery Establishing a sustainable financing framework for the sector Facilitating Sustainable Urban Growth Managing the negative impacts of transport Developing Institutional and Human Capacity to Respond to the Sectors Evolving Needs Two priorities POLICY AND INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK Sector Objectives Key Strategy and Policy Considerations Governing Sectoral Policies and Plans; and Laws and Regulations Planning and Programming SECTOR STRUCTURE AND OWNERSHIP Demand for Transport Services Transport Infrastructure and Services EXPENDITURES AND FINANCING High rate of growth in transport expenditures Local government expenditures growing fast Growth in recurrent expenditures not keeping up with capital expenditures Majority of spending is on roads: the sub sectoral expenditure distribution Sources of Financing Financing Local Government Transport Expenditures Future Expenditure Requirements Composition of Spending within Proposed Envelope Sustainable Financing for Transport Expenditures SECTOR PERFORMANCE Contribution to overall growth and poverty reduction Quality v
6 5.3 Safety Efficiency Access Affordability MAIN ISSUES Efficiency in Resource Utilization and Service Delivery Financial Sustainability of the Sector Urban Transport Issues Mitigating the Negative Impacts of Transport Institutional and Human Resource Capacity AN AGENDA FOR THE NEXT DECADE Enhance Efficiency in Resource Utilization and Service Delivery Financial Sustainability of the Sector Facilitating Sustainable Urban Growth Managing the Negative Impacts of Transport Institutional and Human Capacity Development Annex 1: Policy and Institutional Framework Annex 2: Sector Struãcture and Ownership Annex 3: Table A7 Capital and Recurrent Transport Expenditures Reference vi
7 Part I Overview 1.1 Introduction Solid contribution to growth and poverty reduction. The transport sector has contributed positively to the economic growth of Vietnam over the past decade and has helped reduce poverty directly through better linkages to markets, education and health facilities and indirectly through its contribution to growth. This is evident from surveys indicating that investment location in northern Vietnam, for example, was heavily influenced by transport improvements. The impact on poverty reduction is reflected in studies showing that investing 1% of provincial GDP in transport infrastructure could reduce poverty by % and that an investment of US$50 million in transport in the 15 poorest provinces could reduce poverty by 6-7%. Some old challenges remain; some new ones emerge. The rapid growth in transport infrastructure and services over the past decade has created new demands and challenges for the transport sector. Fast economic growth has contributed to high rates of urbanization, rising traffic accident rates, new capacity constraints, and a large increase in asset preservation requirements to meet the fast expansion of transport assets. Other impediments reside in the sector's policy, planning, budgeting, regulatory, and implementation frameworks. While these institutional issues have no doubt resulted in some inefficiency in resource allocation and service delivery in the past, they have not held back the progress of the sector whose primary objective was a massive rollout of infrastructure. The figure below summarizes the results of a recent review assessing the effectiveness of transport policies, legislation, regulations and their implementation, highlighting areas where attention is needed. Three issues stand out: the road sector, which typically receives 80-90% of national government funding for the transport sector, fairs poorly with respect to policy and policy implementation; the urban transport policy environment needs significant improvements; and implementation regulations in general are weak, a limitation that cuts across many sub sectors. 1
8 Market entry/licensing Competition/SOE role Basic Policies Safety/environment Planning/investment Pricing/cost recovery Legislation Policy Implementation Implementing regulations Implementing mechanisms Outcome/ overall performance Road Transport S ervices n.a. Road Infrastructure n.a. n.a. Ports and Related Infrastructure Railway Services & Infrastructure Urban Transport Inland Water Transport Services n.a. International Shipping n.a. Coastal Shipping n.a. Inland Waterway Infrastructure n.a. n.a. International Air Transport Services Domestic Air Transport Services Air Transport Infrastructure Multimodal Transport n.a. n.a. n.a. Good promising Fair In progress Poor n.a Not applicable/significant Sources Urban sub sector: assessment by World Bank staff; All other sub sectors: World Bank-Meyrick and Associates (2006); Vietnam Multimodal Transport Regulatory Review. 1.2 Transport Sector Goals To continue to support rapid economic growth and further contribute to poverty reduction during the next stage of Vietnam's economic development, the transport sector will need to overcome its challenges and work toward achieving five broad goals: (1) enhancing efficiency in both resource utilization and service delivery, (2) establishing a sustainable financing framework for the sector, (3) facilitating sustainable urban growth, (4) managing the negative impacts of transport; and (5) developing institutional and human capacity to respond to the sector's evolving needs Enhancing Efficiency in Resource Utilization and Service Delivery will require a number of actions by GoV: A results-oriented integrated planning process. There tends to be a gap between broad government strategies and detailed sectoral plans and little coordination between spatial and economic development plans. Moreover a 2
9 fragmentation of responsibilities for developing plans often results in long "wish lists" of projects many of which are not consistent, viable or funded. A results-oriented planning process at both national and provincial levels would help align sector and national goals towards desired outcomes. Under such a framework, MoT and other responsible agencies would define measurable outcomes reflecting sector goals and ultimately resulting in specific projects and reforms to achieve these goals. At present, the planning process at both national and provincial levels can also be characterized by suboptimal resource allocation. There is misallocation (i) between new investment and maintenance; (ii) among modes with the inland waterways receiving a significantly smaller share of funding than is commensurate with their important role; and (iii) in the selection of investments within each sub sector. The ongoing Medium Term Expenditure Framework (MTEF) pilots could help remedy many of the problems in the planning process by removing the rigidities in resource allocation and strengthening integrated planning. This would require the establishment of sound criteria for prioritization in the MTEF and the empowerment of the Inter-Ministerial Task Force established to oversee the implementation of the pilots. Investing in asset preservation. While government transport strategies and plans highlight maintenance as a priority, the amount of resources allocated to road maintenance indicate otherwise with at most 50% of the necessary maintenance expenditures being made at both national and local levels. The deferred maintenance coupled with the high rate of investment in new transport infrastructure over the past five years would suggest that expenditures on maintenance will have to grow faster than those on capital investment to ensure that the country's transport infrastructure is not run down. Simulations show that if expenditures on national road maintenance remained at their "current" levels over a 10 year period, the condition of the network would substantially deteriorate with about 34% being in poor condition including 55% of the high traffic volume network. Although a 10-year strategic plan for national road maintenance was developed using HDM4 models, and has been approved by the Prime Minister in 2004, it is still not being used in the preparation of annual maintenance work programs. While the MTEF can provide some flexibility in shifting resources from new investment to maintenance, this will not eliminate the need for developing an asset preservation framework and for implementing the strategic plan for national road maintenance. Asset preservation at the local level. Evidence from road condition surveys from 16 provinces suggests that shifting resources from road rehabilitation to periodic maintenance would result in a significant improvement in the overall condition of the local road network. Data from the surveys show that only 34% of the district road network is in good or fair condition. Estimates suggest that resources used for periodic maintenance should be 3
10 increased from their current level of about 10% of the overall budget to 50%. Multimodal transport and modern logistics for trade led growth and efficient distribution. Vietnam's economic growth requires efficient multimodal and logistics services to support both international trade and internal distribution. These services are currently at their infancy in Vietnam. Logistics costs, assessed to be roughly similar to China, are high at about 15%-20% of GDP, double the cost in industrialized countries. A significant proportion of this cost is associated with holding inventories, a result of under developed logistics systems. Reducing the logistics cost by 10% would result in resource savings equivalent to 1.5%-2.0% of GDP. A recently completed Multimodal Transport Regulatory Review (MTRR) in Vietnam indicates that new and revised laws and regulations provide a good facilitating environment but implementation mechanisms need to be strengthened and clarified. A common understanding between the Ministries of Transport, Trade, and Planning and Investment on the definition and coverage of logistics services as referred to in the 2005 Commerce Law is lacking. Coordination between the three ministries is necessary before the implementing regulations for the Commerce Law are finalized. The role of MoT's Transport Department in integrated multimodal transport planning needs to be clearly defined, and the department's capacity strengthened. To help increase the efficiency of the logistics industry, MoT may wish to encourage logistics providers to establish a National Logistics Forum (NLF) financed by its members to identify the industry's needs and to consult with the government on an appropriate course of action. One of the first tasks of the NLF could be the definition and estimation of a Logistics Index to be updated annually to better monitor logistics costs. As a counterpart to the Forum, an Inter-Ministerial Logistics Committee would help liase with the Forum as well as coordinate government policies affecting logistics and multimodal transport. The mandate of the GMS Transport Facilitation Committee could be broadened to enable it to play the role of the proposed Inter-Ministerial Committee. SOE reforms are key to an efficient sector. MoT's debt has been recently estimated at VND 19.5 trillion, about 1.5% of the country's GDP. This figure excludes the debt that has been accumulated at the provincial level. State banks have provided loan rollovers as in many cases the interest payments due are in excess of the borrowing enterprise's capitalization. The current debt situation of construction SOEs and their urgent and serious need for financing forces them to submit low "survival" bids to secure contracts, a practice which ultimately results in low quality works and delayed implementation. Moreover, current practices coupled with a lack of performance incentives do not foster a competitive, transparent or efficient operating environment. MoT has some elements of a phased equitization plan for its SOEs in place. The objective of equitization, the methodology for enterprise selection and the details need to be clear and transparent. It is essential to account for the debt situation of the SOEs accurately and for the government to explain the basis for bailing out some SOEs, as is likely to happen, and for letting others go bankrupt. A firm timetable for this process together with strict monitoring of its implementation by an interagency taskforce from MoT and MoF (and possibly others) increases the possibility of success of the SOE equitization and reform program and the chances of achieving the desired implementation efficiencies. The benefits of a sound regulatory framework will not be achieved without clear and transparent implementing regulations. 4
11 The recently completed regulatory review (MTRR) shows that the transport laws passed in the past few years provide a sound basis for the efficient operation of transport sub sectors. Nonetheless, the implementing regulations for these laws require strengthening to ensure that the principles of competition and transparency govern all business and investment licensing matters, and that private sector participation, both domestic and foreign, is encouraged to enhance operational and managerial efficiency and quality, and increase investment. Full efficiencies in the ports and maritime sub sector, in particular, are not being fully exploited as there is still no clear delineation between development, operations and regulation. While Cai Lan port is being operated under a concession, this was awarded to a state owned company on the basis of a negotiated contract without the benefit of competitive selection. Paving local roads An issue of significant financial and economic consequence is the paving of provincial and rural roads to avoid the annual financial burden of maintaining unpaved roads. The decision whether to pave a road or not should be based on a life cycle cost analysis of the different alternatives that would include investment costs, maintenance costs over the life of the road and the benefits to road users. The analysis would take into account the different topographic and climatic conditions of each location. Using this approach would ensure that the limited resources can be optimized and the appropriate surfacing option for each region used. The decision should not be influenced by the ability to secure one time State budgetary allocations from the national government Establishing a sustainable financing framework for the sector - Strict expenditure controls coupled with an increase in resource mobilization for the sector are essential for adequate and sustainable funding. A fiscally-constrained programming process. The Government of Vietnam made investment in transport infrastructure a key priority in its PIP and expenditures reached 4.5% of GDP in 2002, a relatively high figure by most regional and international standards. However, 35% of total central transport expenditures were approved by the Prime Minister but not allocated funding resulting in a critical and unsustainable debt situation for many state-owned construction companies. While such expenditure levels can be justified and indeed are necessary during periods of heavy rebuilding, programming needs to be fiscally constrained within the available resource envelope. Expenditure controls can be established by making the availability of financing a requirement for approving projects at both national and local levels and by replacing the current lax requirements for lending by some SOCBs by rigorous commercial criteria. The MTEF could play a role towards achieving these 5
12 objectives by ensuring that the proposed investment outlays fall within the available resource envelope. An agenda for resource mobilization. Nevertheless, it is highly unlikely that the recent expenditures levels can be sustained in the long run, not only because of the unsustainable SOE debt situation but also because 35% of central transport expenditures are being financed by concessional ODA that may no longer be available by the end of the decade and that will be, to some degree, replaced by competitively priced loans. In defining an agenda for resource mobilization, it is important to distinguish between two different levels in the financing framework: The first level involves the ultimate payers for the infrastructure and associated services. These are typically the direct beneficiaries, and the general public paying through government taxes and other revenues. A toll road provides an example where users may pay the full cost, or only a share with the government (general public) paying the shortfall. To this extent, increasing the share that is paid by the beneficiaries of a road, (or port or bus service) would reduce the share paid by the government. Mechanisms for mobilizing resources from beneficiaries in return for improvements to transport services and infrastructure include increasing user charges (by raising existing levels or reducing the fuel subsidy and using the savings). Another avenue would be to capture a proportion of the increase in land values associated with large transport improvements. The second level deals with the financiers of the infrastructure. Infrastructure can be financed by the government (central or local) or by the private sector. The central government has financed the vast majority of national-level infrastructure mostly through the budget but also by issuing a significant amount of bonds (30% of MoT's projects between 2001 and 2005 were financed by government bonds). Municipal finance, which includes government bonds and local development investment funds (LDIFs), is being utilized with some success in Vietnam's two largest cities. It is important to realize, however, that for most other cities and provinces, it will take several years before LDIFs can become an important contributor to the financing of infrastructure. It may be more practical and sustainable at this point to consider establishing local development funds at a regional level. The sustainable growth of this source of financing requires strong governance and an arms length relationship with the Provincial Peoples' Committees. For both national and municipal bonds, when financing extends beyond toll roads, or other assets that can generate sufficient revenues to cover their costs, a careful analysis of the fiscal capacity of the government is necessary. Another important source of finance is the private sector. The contribution of private capital to the financing of transport infrastructure in Vietnam remains low. This source of financing can play a more prominent role in financing highways and expressways, and the development and upgrading of ports and airports. There are two main advantages to involving the private sector. The first is that mobilizing resources relieves some of the pressure on the scare budgetary resources and reduces the need for additional government borrowing. The second is that the private sector is better positioned to bear certain risks. Key to tapping this source is the development of a framework for private participation. The framework needs to set the principles for efficient risk sharing, to define how contingent liabilities will be managed, and to identify appropriate institutional and regulatory structures. Within the parameters of the framework, the different models of private 6
13 participation can be considered and the most suitable used. It is recommended that the framework evolve gradually over time starting with a series of simple projects and building on the gained experience Facilitating Sustainable Urban Growth Ha Noi and Ho Chi Minh City alone contribute more than one quarter of the country's GDP. Consequently, it is essential that Vietnam's major cities have an efficient transport system to continue to support the country's economic growth. The predominant challenge for Vietnam's major cities in the coming decades will be facilitating spatial growth for future urbanization. Successful development of affordable and efficient, high capacity, public transport systems-bus based systems in the short term, with a role for urban rail in the longer term-that ensures high quality access to commercial areas and central business districts, will be critical to facilitate continued urban growth. An urban planning focus is essential to ensure that growth is coordinated along high density corridors and that the benefits of investments in public transport and road infrastructure are complementary. This would also help avoid the severe congestion that would result from unstructured peri-urban growth. However (a) rigidities in the planning process, (b) the lack of metropolitan/regional institutions that can coordinate between local governments to enhance development across jurisdictional boundaries, and (c) weaknesses in the regulatory capacity hamper a coordinated planning approach. Moreover, the absence of a well functioning land market, despite some progress in recent land reforms, distorts land prices and complicates the planning process. A resultsbased approach and a strategic review of the resource mobilization framework are as important for cities as they are at the national level. They provide incentives to identify incremental low-cost solutions given fiscal constraints and ways in which cities can develop revenue bases that reflect growth in the underlying economy A framework for the sustainable development and operation of a public transport system needs to be developed. At present, bus routes in Ha Noi, for example, are allocated to operators in an ad-hoc manner even though operators receive significant subsidies. Subsidies are based on regular detailed cost audits despite the limitations of such a system. A recommended alternative would be to award bus routes on the basis of fixed-term contracts established by competitive bidding. Municipal governments in both HCMC and Ha Noi subsidize both bus purchase and operations. The sustainability of these subsidies is in question. In 2003, revenues generated by public bus services in Ha Noi covered less than 50% of their operating costs and the gap is expected to further widen as ridership increases. There is some potential to reduce operating costs but it will be difficult to recover operating and investment costs without increasing fares. While, at present, there is a strong political will in both Ha Noi and HCMC 7
14 to underwrite the promotion of public transport with public subsidy, if the subsidies continue to grow at the projected rates, it would be necessary to ensure that the deficits/subsidies can be sustained. The deficits need to be projected and sources for financing them identified Managing the negative impacts of transport is essential for the sustainability of the sector. Poor traffic organization remains a critical issue contributing to accidents, congestion and consequently air pollution, despite concerted efforts in both Ha Noi and HCMC focusing on safety and traffic management. Positive road safety management steps are being taken in Vietnam. Some performance targets have been set, a National Program on Traffic Safety (NPTS) was developed and a comprehensive program of work has been specified. Nevertheless, accidents and fatalities remain a problem, particularly the high levels of motorcycle-related accidents in Ha Noi and HCMC. While the death toll of 9.4 per 10,000 vehicles in 2003 compares favorably to other countries in Asia, data collection of traffic accidents is not yet adequate and the real number of casualties is likely to be much higher. About 80% of all accidents in 2003 were caused by poor driver behavior, and about one half of road accidents were on national roads particularly those passing through populated areas and one quarter occurred on urban roads. The "urbanization" of road space in Vietnam remains a major contributing factor to high accident rates as many people live within a few meters of the road side. Implementation of the NPTS remains weak and fragmented. There are gaps in the proposed NPTS and no clear articulation of priorities for action based on a strategic analysis of the problems. Proposed activities and interventions lack adequate finance, proper coordination and planning. In some cases they do not adequately reflect good practice. A statute in the law that provides a waiver to motorcycle users from an obligation to wear helmets inside city limits is inconsistent with the government policy in this regard, particularly when intra cerebral hemorrhage (common to motorcycle accident victims) was considered a major cause of hospital death in Vietnam in a study carried out a few years ago. There is a need to step up the implementation of the NPTS. There is a perception that international good practice in traffic management is not completely transferable. The situation is exacerbated by the lack of a culture of traffic management. Such a culture is currently inhibited by excessive fragmentation of responsibilities between different elements of the Public Works Department (responsible for planning, designing, implementation and some elements of enforcement) and the traffic police (responsible for operations and most enforcement). Efforts to control congestion by limiting motorcycle ownership in the urban districts of Ha Noi and HCMC by fiat are not equitable and have not proven to be effective. 8
15 Though Vietnam has successfully phased out lead from gasoline, both Ha Noi and HCMC have air quality problems. Analysis of available data from Ha Noi suggests that transport is a significant contributor to particulates (PM10 and PM2.5), Ozone formation and locally to Carbon Monoxide (CO) and old motorcycles and diesel trucks are the biggest polluters in aggregate. Though some policies are in place to inspect and control emissions from four-wheeled vehicles, motorcycle emissions are uncontrolled. To control pollution, both Ha Noi and Ho Chi Minh City need to develop a better understanding of transport's contribution to pollution and as appropriate develop control strategies including promotion of non-motorized modes for short trips and the development of inspection and maintenance programs Developing Institutional and Human Capacity to Respond to the Sector's Evolving Needs A long term capacity development framework to support the necessary reforms. The accomplishment of the transport sector's goals requires significant capacity development. To avoid ad hoc and incomplete institutional reform and capacity development initiatives that are often not very effective, a comprehensive capacity development framework with a realistic long term view for implementation needs to be built. This would address needs at three main levels: the enabling environment (policies and laws)-building on the findings from the recently completed regulatory review, organizational development, and human resource development. Strengthen implementation capacity. With some exceptions, implementation of works has often suffered from inefficiency and low quality. This can be attributed to the weak performance of PMUs, contractors and supervision consultants and the lack of a clear definition of accountability and oversight roles. There is no incentive system to encourage efficiency and timely implementation. Performance is not assessed against well defined targets and the criteria for selecting central and provincial PMUs to manage implementation of new projects are unclear. This issue, which has not received the necessary government attention, needs to be addressed with some urgency to avoid significant losses in resources. Even in the presence of a sound incentive system, the current system of project management through PMUs has a fundamental weakness when it comes to long term capacity development in MoT. While timely and satisfactory project implementation is an important goal for GoV and development partners alike, building capacity in the line ministry is even more important for the sector's development and projects' sustainability. The latest version of the construction law recommends moving PMUs under the modal administrations such as VRA and VIWA. A transition plan needs to be prepared and the process started as soon as possible. A major contributor to the low quality of infrastructure is the limited effectiveness of supervision consultants. PMUs do not typically empower them. They are often bypassed with SOE contractors reporting directly to PMUs and sometimes even to upper levels of management at MoT. To help ensure good quality of implementation, the roles of the PMU, as representative of the Client, the supervising engineer and the contractor should be clearly defined and adhered to. Resettlement is considered one of the largest contributors to implementation delays in transportation projects. Through various decrees and laws, however, GoV has considerably improved its resettlement policies and continues to work on remaining issues. 9
16 Better governance framework. The recent corruption incident surrounding PMU-18 has highlighted weaknesses in the current governance framework. It also shows the conflict of interest that can arise in the award of contracts to dependent agencies under the ministry or the province. Procurement within the sector suffers from collusion at many levels of the process. This contributes to both inefficiency in implementation and low quality of construction. Evidence from procurement associated with World Bank transport projects suggests that the fully competitive award of contracts has not been achieved yet. For example, evidence from ex-post procurement reviews highlights a trend towards collusion of bidders sometimes with the involvement of the contract-awarding authorities, and the artificial restriction of competition by limiting the sale of bidding documents. State control of prices is another area that limits truly competitive bidding. GoV needs to speed up measures to increase transparency in procurement as well as augment them by other policies. GoV is undertaking several measures to limit collusion. These include measures to increase transparency such as the publishing of all requests for proposals in MPI's gazette and on its website. A draft procurement law that provides a complaint mechanism is being discussed. Decree 80 requires community participation in, and supervision of, local decision making processes. There will be a need to develop the capacity of the relevant procurement authorities to strengthen their ability to identify collusion between contractors. Transparency can be further increased by making access to bidding documents freely available. Having a representative from the community sit on the bid evaluation panel is another way to reduce collusion. Without an effective sanction mechanism, it is unlikely that the complaints mechanism in the draft law will curb collusion. A centralized database needs to be established to support the black listing approach followed by GoV. At present, firms blacklisted due to collusion in one province can still be awarded contracts in other provinces due to a lack of such a database. 1.3 Two priorities The proposed recommendations for the sector are interlinked and the success of one component is often dependent on the success and progress of others. Moreover, the difficulty in implementation, the resource mobilization requirements and the time horizon for accomplishing the reforms vary from one component to another. Given the financial and, more importantly, the institutional capacity constraints, facing GoV and MoT, short run priorities need to be specified within a larger reform framework to ensure consistency in timeliness of implementation. As such, the two urgent priorities are (a) the SOE reforms that would enhance sector efficiency and financial sustainability, lead to better quality of works, and contribute to better governance; and (b) the development of an effective asset preservation framework to avoid the large losses of resources that Vietnam has invested in its transport infrastructure over the past decade. 10
17 Part II Policy and Institutional Framework Sector Objectives The government's objective for the sector is to develop a modern transport system that provides high quality, efficient and affordable transport services in a safe and environmentally sound manner Key Strategy and Policy Considerations The 2004 Transport Sector Development Strategy (TSDS) to 2020 supports Vietnam's various economic development plans, notably, the ten year ( ) Socio Economic Development Strategy (SEDS) and the Comprehensive Poverty Reduction and Growth Strategy (CPRGS). SEDS identifies the upgrading of Highway No. 1 and the construction of the Ho Chi Minh Highway as two priorities and strongly endorses the development of public transport services and long term transport planning in large cities. SEDS also cites the rising rate of traffic accidents as a concern. SEDS' emphasis and priorities differ within Vietnam's 3 focal economic zones and 8 regions. The main elements of TSDS are: A balanced approach to transport development capitalizing on the country's geographical shape. Prioritization of maintenance and upgrading of existing assets. Prioritization of rural transport infrastructure especially in mountainous and remote regions. Prioritization of new investments in the north-south backbone, important economic zones, large urban areas and key links to neighboring countries. Prioritization mass transit systems in the urban sector. Increasing the local content in ship and automobile construction and repair. Increasing the share of domestic enterprises in the international transportation of Vietnamese goods. TSDS highlights several policies to govern implementation. These include: Targeting domestic and foreign sources of finance, both private and public, and charging users for the construction and maintenance of infrastructure when possible. Encouraging private sector participation by speeding up the equitization of state-owned enterprises and separating state management from operations and business. Ensuring transport safety and environmental protection in transport related activities. 1. This section summarizes a few of the key aspects of the policy and institutional frameworks. The details of the frameworks are presented in Annex Adapted from Vietnam s Transport Development Orientation for the Next Decades on MOT s website: 11
18 Utilizing new technologies and processes in transport-related construction and operations. 2.3 Governing Sectoral Policies and Plans; and Laws and Regulations Road Infrastructure and Transport Services Prime Ministerial Decision (PMD) 162/2002, which sets out the government's policy for national, provincial, urban and rural roads, contains some general statements on the aim to enhance maintenance capacity, but the focus is on new infrastructure needs, particularly for national roads. The Decision set as targets the sealing of all national and provincial roads by 2005 and 2010 respectively, and the upgrading of 90% of all rural roads to all-weather roads by The Decision also lists over 1,400 kms of 4/6 lane expressways to be built by 2010 but contains relatively little about sources of finance. It foresees the use of tolls and an additional fuel tax and identifies a number of steps to attract further ODA and FDI. The Decision directs the government to consider establishing a Road Maintenance Fund. The Fund proposed by MoT was opposed by the Ministry of Finance as it appeared to be more broadly defined in scope as a Transport Sector Fund. the short, medium and long term. For Vietnam's two largest cities, the strategic foci are to promote and develop public transport, and to develop road infrastructure to alleviate congestion and open up new areas for urbanization. Maritime and Shipping The government's strategy is to rehabilitate existing key facilities, focus on the construction of deepwater ports in the focal economic zones to serve vessels over 30,000 DWT while also developing small scale satellite ports to serve the local economy. Two of the government's key port projects are Van Phong, a transshipment port in Khanh Hoa in central Vietnam and Cai Mep, a deep sea port in Vung Tau to serve southern Vietnam. The rehabilitation and construction of a total of 114 ports in 8 port Urban Transport Developing policy for urban transport is the responsibility of the cities subject to central government approval for major plans and investments. Urban transport policies are devised to support cities accommodate the significant increases in population particularly in HCMC and Ha Noi which are forecast to triple their populations between 2000 and PMD 162/2002 sets some targets for urban roads for Ha Noi, Ho Chi Minh City and medium size cities for 12
19 complexes is planned by As a matter of government policy, the construction of new ports or berths that would compete with existing national ports is prohibited. The Government also plans to develop its fleet of container vessels and tankers, and ship building facilities. A new maritime code was approved by the National Assembly in 2005 and came into effect in January Inland Waterways The government's main objectives for the sector are modernizing inland waterway navigation to meet international standards and further developing its fleet of vessels. The Government's master plan for developing Vietnam's inland waterway system though 2020 lists landing stages and ports to be upgraded and equipped with modern loading equipment (targeting at least one port/landing stage per province, mostly in the south) and identifies several waterway channels for improvement. The sector is governed by the 2005 Law on inland waterway navigation. The implementing regulations for this law have not been finalized yet. Railways Prime Ministerial Decision 34/2003/QÐ-TTg (March 2003) established the state-owned Vietnamese Railway Corporation (VRC) to operate the railways. Decree 34/2003/ND-CP (April 2003) placed the policy and regulatory functions within the Vietnam Railway Administration (VNRA), a modal administration under MoT. VNRA is responsible for the development of the rail sector and also oversees the performance of VNC. The new railway law that was passed by parliament in June 2005 provides a framework for separating infrastructure and operations, and for the possible operation of trains by third parties. The implementing regulations have not been finalized yet. Civil Aviation PMD No. 206/2004/QD-Ttg identifies the upgrading and expansion of existing international and domestic airports, and the building of new ones as objectives for the sector. Specific airports throughout the country are mentioned in the Decision. The construction of Long Thanh International airport in Dong Nai province to replace Tan Son Nhat airport in Ho Chi Minh City at the estimated cost of US $3 billion for the first phase ( ) is the largest airport project currently under consideration. Multi Modal Transport MoT stresses the goal of achieving optimum transport conditions on the entire network through the efficient use of different transport modes of transport and the utilization of advanced technologies, especially multi-modal transport technology in cargo handling. 3 Government Decree No. 125/2003/ND-CP defines the scope and regulations for international multi-modal activities carried out by national and foreign entities. Certain articles of the Commerce Law also sets rules for commercial activities relating to logistics services; and a number of government decisions define customs procedures relating to the movement of goods and vessels by international multi modal transporters. 3. Vietnam s Transport Development Orientation for the Next Decades on MOT s website: 13
20 Table A1 in Annex 1 provides the main legal and regulatory provisions governing the transport sector in Vietnam. 2.4 Planning and Programming The Ministry of Transport (MoT) has the responsibility for planning, managing and maintaining national transport infrastructure, and for assisting local governments in project selection. MoT prepares long term transport strategies, 5 year plans for inclusion in the Public Investment Program and one year plans for inclusion in the annual State Budget. While transport strategies generally transcend local government boundaries, the 5-year and annual plans prepared by MoT are limited to national infrastructure. The details for planning and programming are presented in Annex 1. Figure A1 and Table A2 in the annex respectively present key transportrelated government institutions; and the sector's main players and their roles. 14
21 Part III Sector Structure and Ownership Demand for Transport Services The demand for transport grew slightly faster than GDP between 1999 and Over this period, annual growth rates in freight and passenger demand measured in ton/passenger km were 12% and 10% respectively (see Table 1). Road remains a dominant mode, accounting for 67% of tons moved but coastal shipping accounts for 71% of all ton-km due to its dominance in long-distance movements. Reflecting Vietnam's rapid growth in trade, annual throughput of sea ports doubled from 56 million tons in 1998 to 114 million tons in 2003; and cargo flows through southern ports in 2000 exceeded forecasts made two years earlier in the National Transport Development Strategy (VITRANSS) by 50%. 5 The increase in market share of coastal shipping between 1999 and 2005 came at the expense of roads and inland waterways. Nevertheless, the freight task (ton-kilometers) for both modes increased during that period although the growth rate for waterways was Table 1: Domestic Transportation Volume Mode Mode Goods G oods 1000 tons % M iltonkm tons km km tons km % % Milton- % Miltonkm Transport 1000 tons % Milton % % - Transport km % Annual increase in ton-km (%(%) ) Railways 5, , , , , , Roads 132, , , , , , Waterways 39, , , , , , Coastal 13, , , , , , Aviation Total 190, , , , , , Passenger Transport Mil pass. % Mil pass-km % Mil pass. % Mil passkm % Mil pass. % Mil pass-km % Annual increase in pass-km (%)) Railways , , , Road , , , , Waterways , , , Aviation , , Other Total , , , , , Sources: 99 and 03 data from Statistical Year Book 2004, 05 data from General Statistical Office website. 4. This section provides a summary of the sector structure. For more details see Annex Vietnam, Managing Public Expenditure for Poverty Reduction and Growth, Public Expenditure Review and Integrated Fiduciary Assessment, Volume II Sectoral Issues, Page
Planning and Design for Sustainable Urban Mobility
 1 Planning and Design for Sustainable Urban Mobility 2 1 UrbanizationUrbanization Rapid pace, largely uncontrolled growth, taking place mainly in developing countries 3 Global Urbanization Trends World
1 Planning and Design for Sustainable Urban Mobility 2 1 UrbanizationUrbanization Rapid pace, largely uncontrolled growth, taking place mainly in developing countries 3 Global Urbanization Trends World
TRANSPORT SECTOR ROADMAP AND THE INVESTMENT PROGRAM I. Roadmap
 TRANSPORT SECTOR ROADMAP AND THE INVESTMENT PROGRAM I. Roadmap 1. Launched in 2008, the government s Afghanistan National Strategy (ANDS) is a Millennium Goals (MDGs) based action plan and road map for
TRANSPORT SECTOR ROADMAP AND THE INVESTMENT PROGRAM I. Roadmap 1. Launched in 2008, the government s Afghanistan National Strategy (ANDS) is a Millennium Goals (MDGs) based action plan and road map for
Thailand s Logistics
 Thailand s Logistics Over the past fourteen years, overall international trade with Thailand has grown 340% and manufacturing trade 370%; this growth, aided in part by the nation s bilateral trade agreements
Thailand s Logistics Over the past fourteen years, overall international trade with Thailand has grown 340% and manufacturing trade 370%; this growth, aided in part by the nation s bilateral trade agreements
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): PUBLIC RESOURCE MANAGEMENT. 1. Public Resource Management Sector Issues and Opportunities
 Country Partnership Strategy: SRI, 2012 2016 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): PUBLIC RESOURCE MANAGEMENT 1. Public Resource Management Sector Issues and Opportunities 1. The problems in Sri Lanka are multifaceted
Country Partnership Strategy: SRI, 2012 2016 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): PUBLIC RESOURCE MANAGEMENT 1. Public Resource Management Sector Issues and Opportunities 1. The problems in Sri Lanka are multifaceted
GMS Economic Cooperation Program
 GMS Economic Cooperation Program In 1992, six countries bordering the Mekong River Cambodia, People s Republic of China (specifically, Yunnan province and later, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region), Lao
GMS Economic Cooperation Program In 1992, six countries bordering the Mekong River Cambodia, People s Republic of China (specifically, Yunnan province and later, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region), Lao
The Positive Role of Audit in Public Debt Management in China
 The Positive Role of Audit in Public Debt Management in China (for the 1 st ASOSAI-EUROSAI Joint Conference) September 2011, Turkey By Dr. DONG Dasheng, the first Deputy Auditor Introduction Since 2008,
The Positive Role of Audit in Public Debt Management in China (for the 1 st ASOSAI-EUROSAI Joint Conference) September 2011, Turkey By Dr. DONG Dasheng, the first Deputy Auditor Introduction Since 2008,
Mexico Shipments Made Simple. Third-party logistics providers help streamline the U.S. Mexico cross-border process WHITE PAPER
 Mexico Shipments Made Simple Third-party logistics providers help streamline the U.S. Mexico cross-border process WHITE PAPER Introduction With the cost of manufacturing rising in Asia, many companies
Mexico Shipments Made Simple Third-party logistics providers help streamline the U.S. Mexico cross-border process WHITE PAPER Introduction With the cost of manufacturing rising in Asia, many companies
Building Capacity to Make Transport Work for Women and Men in Vietnam
 EAST ASIA AND PACIFIC REGION Social Development Notes INNOVATIONS, LESSONS, AND BEST PRACTICE Building Capacity to Make Transport Work for Women and Men in Vietnam Gender and Transport Challenges Women
EAST ASIA AND PACIFIC REGION Social Development Notes INNOVATIONS, LESSONS, AND BEST PRACTICE Building Capacity to Make Transport Work for Women and Men in Vietnam Gender and Transport Challenges Women
LAW ON PUBLIC DEBT MANAGEMENT
 LAW ON PUBLIC DEBT MANAGEMENT THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY - SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIET NAM Independence Freedom Happiness - No. 29/2009/QH12 Hanoi, June 17, 2009 LAW ON PUBLIC DEBT MANAGEMENT Pursuant to the
LAW ON PUBLIC DEBT MANAGEMENT THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY - SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIET NAM Independence Freedom Happiness - No. 29/2009/QH12 Hanoi, June 17, 2009 LAW ON PUBLIC DEBT MANAGEMENT Pursuant to the
Development of Shanghai Integrated Transport (2010-2015) XIAO Hui and GU Yu
 Development of Shanghai Integrated Transport (2010-2015) XIAO Hui and GU Yu Abstract This article summarises the general situation of Shanghai s integrated transport system and then determines the trends
Development of Shanghai Integrated Transport (2010-2015) XIAO Hui and GU Yu Abstract This article summarises the general situation of Shanghai s integrated transport system and then determines the trends
Thailand focus 2014 Competencies & Growth potentials. Arkhom Termpittayapaisith
 Thailand Focus 2014 What s new in Thailand s Economic Development Strategy Thailand focus 2014 Competencies & Growth potentials Arkhom Termpittayapaisith Secretary-General Office of the National Economic
Thailand Focus 2014 What s new in Thailand s Economic Development Strategy Thailand focus 2014 Competencies & Growth potentials Arkhom Termpittayapaisith Secretary-General Office of the National Economic
Road Transport Charging ~ Road Pricing. Jani Saarinen Financial Director, Finnish Road Administration
 1 Road Transport Charging ~ Road Pricing Jani Saarinen Financial Director, Finnish Road Administration General taxes Earmarked road transport taxes Loans, bonds etc. Funding sources 2 State tax revenue
1 Road Transport Charging ~ Road Pricing Jani Saarinen Financial Director, Finnish Road Administration General taxes Earmarked road transport taxes Loans, bonds etc. Funding sources 2 State tax revenue
SOUTH EAST EUROPE TRANSNATIONAL CO-OPERATION PROGRAMME. Terms of reference
 SOUTH EAST EUROPE TRANSNATIONAL CO-OPERATION PROGRAMME 3 rd Call for Proposals Terms of reference Efficient access to a SEE coordinated multimodal freight network between ports and landlocked countries
SOUTH EAST EUROPE TRANSNATIONAL CO-OPERATION PROGRAMME 3 rd Call for Proposals Terms of reference Efficient access to a SEE coordinated multimodal freight network between ports and landlocked countries
Meeting Urban Development Challenges
 Discussion Draft Meeting Urban Development Challenges Its importance for both growth and poverty calls for a coherent national framework toward urbanization. The objective of such a framework should be
Discussion Draft Meeting Urban Development Challenges Its importance for both growth and poverty calls for a coherent national framework toward urbanization. The objective of such a framework should be
SECTOR ASSESMENT (SUMMARY): EDUCATION 1
 Country Partnership Strategy: Viet Nam, 2012 2015 SECTOR ASSESMENT (SUMMARY): EDUCATION 1 Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Country context. In Viet Nam, education is
Country Partnership Strategy: Viet Nam, 2012 2015 SECTOR ASSESMENT (SUMMARY): EDUCATION 1 Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Country context. In Viet Nam, education is
 CONTENTS TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY POLICIES INTRODUCTION 1. Traffic Accidents in General 1 2. Promotion of Traffic Safety and Accident Trends 3 3. The Future Direction of Traffic Safety Measures 6 BOOK
CONTENTS TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY POLICIES INTRODUCTION 1. Traffic Accidents in General 1 2. Promotion of Traffic Safety and Accident Trends 3 3. The Future Direction of Traffic Safety Measures 6 BOOK
PPP Basics and Principles of a PPP Framework
 Note 1 May 2012 PPP Basics and Principles of a PPP Framework This note is the first in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework for public-private partnership
Note 1 May 2012 PPP Basics and Principles of a PPP Framework This note is the first in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework for public-private partnership
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): TRANSPORT, and INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ROAD TRANSPORT SUBSECTOR) 1
 Country Partnership Strategy: Kazakhstan 2012 2016 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): TRANSPORT, and INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ROAD TRANSPORT SUBSECTOR) 1 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and
Country Partnership Strategy: Kazakhstan 2012 2016 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): TRANSPORT, and INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ROAD TRANSPORT SUBSECTOR) 1 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and
Analysis of the Obama Administration s FY 2017 Budget Proposal for Transportation
 Analysis of the Obama Administration s FY 2017 Budget Proposal for Transportation FY 2017 Budget Summary The Obama s Administration s proposed budget for FY 2017, which was submitted to Congress February
Analysis of the Obama Administration s FY 2017 Budget Proposal for Transportation FY 2017 Budget Summary The Obama s Administration s proposed budget for FY 2017, which was submitted to Congress February
Ministerie van Toerisme, Economische Zaken, Verkeer en Telecommunicatie Ministry of Tourism, Economic Affairs, Transport and Telecommunication
 SME Policy Framework for St. Maarten May, 2014 Department of Economic Affairs, Transportation & P. 1 of 16 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. SME Developments in St. Maarten 2.1 Definition 2.2 Government
SME Policy Framework for St. Maarten May, 2014 Department of Economic Affairs, Transportation & P. 1 of 16 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. SME Developments in St. Maarten 2.1 Definition 2.2 Government
main type of locomotive in use, but over half of those had surpassed their durable lifespan. China Afghanistan Project Sites Nepal
 Pakistan Diesel Electric Locomotives Rehabilitation Project (1) and Diesel Electric Locomotives Production Project (2) External Evaluator: Hajime Sonoda Field Survey: September 2004 1 Project Profile and
Pakistan Diesel Electric Locomotives Rehabilitation Project (1) and Diesel Electric Locomotives Production Project (2) External Evaluator: Hajime Sonoda Field Survey: September 2004 1 Project Profile and
Sustainable Freight Transport Systems: Opportunities for Developing Countries
 Multi-year Expert Meeting on Transport, Trade Logistics and Trade Facilitation: Sustainable Freight Transport Systems: Opportunities for Developing Countries 14-16 October 2015 NATIONAL EXPERIENCE PAKISTAN
Multi-year Expert Meeting on Transport, Trade Logistics and Trade Facilitation: Sustainable Freight Transport Systems: Opportunities for Developing Countries 14-16 October 2015 NATIONAL EXPERIENCE PAKISTAN
India s Infrastructure - Trends, Projections, Requirements
 India s Infrastructure - Trends, Projections, Requirements Werner Heesen Consulting GmbH Werner Heesen Consulting GmbH LOGISTICS FORUM»MORE THAN CURRY« Index Key Areas A Snapshot Projections by 2020 Mega
India s Infrastructure - Trends, Projections, Requirements Werner Heesen Consulting GmbH Werner Heesen Consulting GmbH LOGISTICS FORUM»MORE THAN CURRY« Index Key Areas A Snapshot Projections by 2020 Mega
DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION
 DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION UNITED STATES OF AMERICA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION Funding Highlights: Invests a total of $74 billion in discretionary and mandatory budgetary resources for the Department
DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION UNITED STATES OF AMERICA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION Funding Highlights: Invests a total of $74 billion in discretionary and mandatory budgetary resources for the Department
Examples of Transportation Plan Goals, Objectives and Performance Measures
 Examples of Transportation Plan Goals, Objectives and Performance Measures The next step in the Long Range Transportation Plan (LRTP) process is to develop goals, objectives, and performance measures.
Examples of Transportation Plan Goals, Objectives and Performance Measures The next step in the Long Range Transportation Plan (LRTP) process is to develop goals, objectives, and performance measures.
GOOD GOVERNANCE FRAMEWORK
 Provincial Roads Improvement (RRP CAM 43309) GOOD GOVERNANCE FRAMEWORK In all instances, the Loan Agreement shall be the overriding legal document. Asian Development Bank () Procurement Guidelines (2010,
Provincial Roads Improvement (RRP CAM 43309) GOOD GOVERNANCE FRAMEWORK In all instances, the Loan Agreement shall be the overriding legal document. Asian Development Bank () Procurement Guidelines (2010,
PROJECT PREPARATORY TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
 A. Justification PROJECT PREPARATORY TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE 1. The Government of Azerbaijan, the Ministry of Transport and Baku Metro Company requested ADB to help improving its urban transport system and
A. Justification PROJECT PREPARATORY TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE 1. The Government of Azerbaijan, the Ministry of Transport and Baku Metro Company requested ADB to help improving its urban transport system and
IN DEFENSE OF THE JONES ACT
 IN DEFENSE OF THE JONES ACT ASBA Annual Cargo Conference Miami, FL September 26-28, 2012 Background of the Jones Act Section 27 of the Merchant Marine Act of 1920 (46 U.S.C. 883), commonly referred to
IN DEFENSE OF THE JONES ACT ASBA Annual Cargo Conference Miami, FL September 26-28, 2012 Background of the Jones Act Section 27 of the Merchant Marine Act of 1920 (46 U.S.C. 883), commonly referred to
Infrastructure Development Funding and Financing
 Infrastructure Development Funding and Financing 09 December 2013 2 Presentation outline 1. Role of infrastructure development 2. Public sector infrastructure investment 3. Funding options i. Recent airport
Infrastructure Development Funding and Financing 09 December 2013 2 Presentation outline 1. Role of infrastructure development 2. Public sector infrastructure investment 3. Funding options i. Recent airport
United States House Committee on Transportation and Infrastructure. Subcommittee on Highways and Transit
 United States House Committee on Transportation and Infrastructure Subcommittee on Highways and Transit Improving the Nation s Highway Freight Network Testimony of Henry J. Maier President and Chief Executive
United States House Committee on Transportation and Infrastructure Subcommittee on Highways and Transit Improving the Nation s Highway Freight Network Testimony of Henry J. Maier President and Chief Executive
TRADE FACILITATION, VALUE CREATION, AND COMPETITIVENESS: A CASE STUDY OF VIETNAM. Duc Minh Pham World Bank Vietnam GDLN, April 9, 2014
 0 TRADE FACILITATION, VALUE CREATION, AND COMPETITIVENESS: A CASE STUDY OF VIETNAM Duc Minh Pham World Bank Vietnam GDLN, April 9, 2014 1 CONTENT 1. ANALYTICAL FRAMEWORK 2. TRADE FACILITATION AND LOGISTICS
0 TRADE FACILITATION, VALUE CREATION, AND COMPETITIVENESS: A CASE STUDY OF VIETNAM Duc Minh Pham World Bank Vietnam GDLN, April 9, 2014 1 CONTENT 1. ANALYTICAL FRAMEWORK 2. TRADE FACILITATION AND LOGISTICS
2 Integrated planning. Chapter 2. Integrated Planning. 2.4 State highway categorisation and integrated planning
 2 Integrated planning Chapter 2 Integrated Planning This chapter contains the following sections: Section No. Topic 2.1 Introduction to integrated planning 2.2 Transit s Integrated Planning Policy 2.3
2 Integrated planning Chapter 2 Integrated Planning This chapter contains the following sections: Section No. Topic 2.1 Introduction to integrated planning 2.2 Transit s Integrated Planning Policy 2.3
Plan on establishment of National Committee on Geographical Names and Spatial Data Infrastructure in Viet Nam *
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.104/IP.23 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Twentieth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Jeju, 6-9 October 2015 Item 7(b) of the provisional agenda
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.104/IP.23 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Twentieth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Jeju, 6-9 October 2015 Item 7(b) of the provisional agenda
How to Become a Green Farmer in China
 Detailed Recommendations 4: Strengthen Discounted Green Loans 4 This is a background paper to the report: Establishing China s Green Financial System published by the Research Bureau of the People s Bank
Detailed Recommendations 4: Strengthen Discounted Green Loans 4 This is a background paper to the report: Establishing China s Green Financial System published by the Research Bureau of the People s Bank
OUTPUT: RURAL ROAD ASSET MANAGEMENT
 Rural Roads Improvement Project II (RRP CAM 42334) OUTPUT: RURAL ROAD ASSET MANAGEMENT A. Introduction 1. The Project. The Royal Government of Cambodia (the Government) has requested for a loan from Asian
Rural Roads Improvement Project II (RRP CAM 42334) OUTPUT: RURAL ROAD ASSET MANAGEMENT A. Introduction 1. The Project. The Royal Government of Cambodia (the Government) has requested for a loan from Asian
Vietnam: A Comprehensive Strategy for Growth and Poverty Reduction
 44 Part 2. Examples of MfDR at the National Level Vietnam: A Comprehensive Strategy for Growth and Poverty Reduction Author: Carolyn Turk, Sr. Poverty Specialist, World Bank Executive Summary V ietnam
44 Part 2. Examples of MfDR at the National Level Vietnam: A Comprehensive Strategy for Growth and Poverty Reduction Author: Carolyn Turk, Sr. Poverty Specialist, World Bank Executive Summary V ietnam
PUBLIC WORKS DEPARTMENT STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2020
 PUBLIC WORKS DEPARTMENT STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2020 1 Purpose of Strategic Plan This document serves as the road map for the Public Works Department. It identifies where we are going and how we are going
PUBLIC WORKS DEPARTMENT STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2020 1 Purpose of Strategic Plan This document serves as the road map for the Public Works Department. It identifies where we are going and how we are going
THE PROCESS OF PLANNING AND INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK FOR POVERTY REDUCTION STRATEGY: THE CASE OF UGANDA.
 THE PROCESS OF PLANNING AND INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK FOR POVERTY REDUCTION STRATEGY: THE CASE OF UGANDA. By Margaret Kakande Poverty Analyst Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, Government
THE PROCESS OF PLANNING AND INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK FOR POVERTY REDUCTION STRATEGY: THE CASE OF UGANDA. By Margaret Kakande Poverty Analyst Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, Government
How To Improve Road Infrastructure In The Germany
 Financing of rural infrastructure and services trends, achievements and challenges Peter O Neill World Bank The recently published World Bank Transport Business strategy (2008-2012) advises: 1.2 billion
Financing of rural infrastructure and services trends, achievements and challenges Peter O Neill World Bank The recently published World Bank Transport Business strategy (2008-2012) advises: 1.2 billion
Lao PDR Public-Private Partnership Policy
 Lao PDR Public-Private Partnership Policy Supported by the Asian Development Bank GRANT-0309 LAO Governance and Capacity Development in Public Sector Management Program (Public Private Partnerships) Table
Lao PDR Public-Private Partnership Policy Supported by the Asian Development Bank GRANT-0309 LAO Governance and Capacity Development in Public Sector Management Program (Public Private Partnerships) Table
Index. D Domestic logistics enterprises direct financing, 30 economic recovery, 29 network placement, 30 31
 A Agricultural products logistics acceleration, infrastructure construction, 115 116 circulation modes direct distribution, 110 111 processing & sales, 111 self-marketing, 109 wholesale market, 109 110
A Agricultural products logistics acceleration, infrastructure construction, 115 116 circulation modes direct distribution, 110 111 processing & sales, 111 self-marketing, 109 wholesale market, 109 110
ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises. I. Introduction
 ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises I. Introduction I.1 Current Challenge: Most countries in the region are undergoing reforms that are opening their economies to greater
ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises I. Introduction I.1 Current Challenge: Most countries in the region are undergoing reforms that are opening their economies to greater
CONTENTS TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY POLICIES INTRODUCTION BOOK 1 TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS
 CONTENTS TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY POLICIES INTRODUCTION 1. General Accident Statistics 3 2. Promotion of Traffic Safety Policy and Accident Trends 3 3. The Future Direction of Traffic Safety Measures
CONTENTS TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS AND SAFETY POLICIES INTRODUCTION 1. General Accident Statistics 3 2. Promotion of Traffic Safety Policy and Accident Trends 3 3. The Future Direction of Traffic Safety Measures
Current challenges in delivering social security health insurance
 International Social Security Association Afric ISSA Meeting of Directors of Social Security Organizations in Asia and the Pacific Seoul, Republic of Korea, 9-11 November 2005 Current challenges in delivering
International Social Security Association Afric ISSA Meeting of Directors of Social Security Organizations in Asia and the Pacific Seoul, Republic of Korea, 9-11 November 2005 Current challenges in delivering
MACROECONOMIC AND FISCAL ASSESSMENT
 Public Sector Financial Management Program (RRP SAM 46384) A. BACKGROUND MACROECONOMIC AND FISCAL ASSESSMENT 1. Samoa is composed of about 10 islands, 4 inhabited, and several uninhabited islets situated
Public Sector Financial Management Program (RRP SAM 46384) A. BACKGROUND MACROECONOMIC AND FISCAL ASSESSMENT 1. Samoa is composed of about 10 islands, 4 inhabited, and several uninhabited islets situated
The Hospital Strategy Project in South Africa
 8 The Hospital Strategy Project in South Africa Monitor Company, Health Partners International, Center for Health Policy, and National Labor and Economic Development Institute, South Africa This chapter
8 The Hospital Strategy Project in South Africa Monitor Company, Health Partners International, Center for Health Policy, and National Labor and Economic Development Institute, South Africa This chapter
SUMMARY OF THE FORUM Vietnam: Readiness for WTO Accession Hanoi, June 3-4, 2003 and Ho Chi Minh City, June 6-7, 2003
 SUMMARY OF THE FORUM Vietnam: Readiness for WTO Accession Hanoi, June 3-4, 2003 and Ho Chi Minh City, June 6-7, 2003 Forum as the most comprehensive event on WTO accession to date. The international forum
SUMMARY OF THE FORUM Vietnam: Readiness for WTO Accession Hanoi, June 3-4, 2003 and Ho Chi Minh City, June 6-7, 2003 Forum as the most comprehensive event on WTO accession to date. The international forum
3.06. Infrastructure Asset Management at Colleges. Chapter 3 Section. Background. Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities
 Chapter 3 Section 3.06 Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities Infrastructure Asset Management at Colleges Chapter 3 VFM Section 3.06 Background The Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities
Chapter 3 Section 3.06 Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities Infrastructure Asset Management at Colleges Chapter 3 VFM Section 3.06 Background The Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities
Chapter 2 ASSET MANAGEMENT PLANNING AND PROGRAMMING FRAMEWORK CHAPTER 2 ASSET MANAGEMENT PLANNING AND PROGRAMMING FRAMEWORK PAGE 11
 Chapter 2 ASSET MANAGEMENT PLANNING AND PROGRAMMING FRAMEWORK CHAPTER 2 ASSET MANAGEMENT PLANNING AND PROGRAMMING FRAMEWORK PAGE 11 This page intentionally left blank. PAGE 12 MINNESOTA GO MNDOT TRANSPORTATION
Chapter 2 ASSET MANAGEMENT PLANNING AND PROGRAMMING FRAMEWORK CHAPTER 2 ASSET MANAGEMENT PLANNING AND PROGRAMMING FRAMEWORK PAGE 11 This page intentionally left blank. PAGE 12 MINNESOTA GO MNDOT TRANSPORTATION
South Carolina Multimodal Transportation Plan Vision, Goals, Objectives, and Performance Measures
 South Carolina Multimodal Transportation Plan Vision, Goals, Objectives, and Performance Measures Prepared for: Prepared by: June 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Baseline Understanding...
South Carolina Multimodal Transportation Plan Vision, Goals, Objectives, and Performance Measures Prepared for: Prepared by: June 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Baseline Understanding...
Traffic accidents in Hanoi: data collection and analysis
 Traffic accidents in Hanoi: data collection and analysis Nguyen Hoang Hai Vietnam, Hanoi Department of Transport, haitups@yahoo.com.au 1. Introduction Hanoi, the capital and administrative center of Vietnam,
Traffic accidents in Hanoi: data collection and analysis Nguyen Hoang Hai Vietnam, Hanoi Department of Transport, haitups@yahoo.com.au 1. Introduction Hanoi, the capital and administrative center of Vietnam,
Sustainable urban mobility: visions beyond Europe. Brest. Udo Mbeche, UN-Habitat
 Sustainable urban mobility: visions beyond Europe 2 nd October 2013 Brest Udo Mbeche, UN-Habitat The Global Report for Human Settlements Published every two years under a UN General Assembly mandate. Aims
Sustainable urban mobility: visions beyond Europe 2 nd October 2013 Brest Udo Mbeche, UN-Habitat The Global Report for Human Settlements Published every two years under a UN General Assembly mandate. Aims
Papua New Guinea: Supporting Public Financial Management, Phase 2
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 44379 012 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) November 2012 Papua New Guinea: Supporting Public Financial Management, Phase 2 The views expressed
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 44379 012 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) November 2012 Papua New Guinea: Supporting Public Financial Management, Phase 2 The views expressed
Transport Canada s Departmental Sustainable Development Strategy 2012 2013 Reporting Update
 Transport Canada s Departmental Sustainable Development Strategy 2012 2013 Reporting Update 1 For more information, please visit Transport Canada s website at http://www.tc.gc.ca/eng/policy/acs-sd-dsds-2615.htm
Transport Canada s Departmental Sustainable Development Strategy 2012 2013 Reporting Update 1 For more information, please visit Transport Canada s website at http://www.tc.gc.ca/eng/policy/acs-sd-dsds-2615.htm
THE COST OF ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENT IN VIETNAM
 THE COST OF ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENT IN VIETNAM Trinh Thuy ANH Lecturer. University of Transport and Communication. Department of Transport - Economics Address: Caugiay, Ha Noi, Vietnam Tel: 84 4 8674702
THE COST OF ROAD TRAFFIC ACCIDENT IN VIETNAM Trinh Thuy ANH Lecturer. University of Transport and Communication. Department of Transport - Economics Address: Caugiay, Ha Noi, Vietnam Tel: 84 4 8674702
Response to questionnaire for: Assessment of strategic plans and policy measures on Investment and Maintenance in Transport Infrastructure.
 Response to questionnaire for: Assessment of strategic plans and policy measures on Investment and Maintenance in Transport Infrastructure. Country: Iceland 1 INTRODUCTION In the National Transport Plan
Response to questionnaire for: Assessment of strategic plans and policy measures on Investment and Maintenance in Transport Infrastructure. Country: Iceland 1 INTRODUCTION In the National Transport Plan
Infrastructure & Growth Leadership Pillar Strategy Statements from Existing Plans Developing Florida s Strategic 5-Year Direction, 29 November 2011
 Infrastructure & Growth Leadership Pillar Strategy Statements from Existing Plans Developing Florida s Strategic 5-Year Direction, 29 November 2011 Key Themes Global trade infrastructure seaports, airports,
Infrastructure & Growth Leadership Pillar Strategy Statements from Existing Plans Developing Florida s Strategic 5-Year Direction, 29 November 2011 Key Themes Global trade infrastructure seaports, airports,
Texas Freight Advisory Committee A PRIMER ON PUBLIC SECTOR FREIGHT PERFORMANCE MEASURES
 Texas Freight Advisory Committee A PRIMER ON PUBLIC SECTOR FREIGHT PERFORMANCE MEASURES October 1, 2013 A PRIMER ON PUBLIC SECTOR FREIGHT PERFORMANCE MEASURES How Do Performance Measures Assist the Public
Texas Freight Advisory Committee A PRIMER ON PUBLIC SECTOR FREIGHT PERFORMANCE MEASURES October 1, 2013 A PRIMER ON PUBLIC SECTOR FREIGHT PERFORMANCE MEASURES How Do Performance Measures Assist the Public
How To Fund A Rail Bank
 Appendix 2. State Rail s in Neighboring States and Peer Review Inventory 118 P age 1. Rail Line Rehabilitation 1. Rail Industrial Access 1. Ohio Rail Assistance ConnectOregon 2. Rail Preservation s Rail
Appendix 2. State Rail s in Neighboring States and Peer Review Inventory 118 P age 1. Rail Line Rehabilitation 1. Rail Industrial Access 1. Ohio Rail Assistance ConnectOregon 2. Rail Preservation s Rail
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS I. FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY. 1. Counterpart Funds
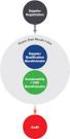 Health Human Resources Sector Development Program (RRP VIE 40354-01) I. FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY 1. Counterpart Funds FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 1. The proposed program loan is for $30 million and the project
Health Human Resources Sector Development Program (RRP VIE 40354-01) I. FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY 1. Counterpart Funds FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 1. The proposed program loan is for $30 million and the project
Chapter 9: Transportation
 Chapter 9: Transportation What is this chapter about? The goals and policies in this chapter convey the City s intent to: Create a coordinated, efficient, and more affordable multimodal transportation
Chapter 9: Transportation What is this chapter about? The goals and policies in this chapter convey the City s intent to: Create a coordinated, efficient, and more affordable multimodal transportation
NATIONAL TREASURY STRATEGIC PLAN 2011/14
 NATIONAL TREASURY STRATEGIC PLAN 2011/14 PRESENTATION TO PARLIAMENTARY FINANCE COMMITTEES Presenter: Lungisa Fuzile Director General, National Treasury 31 May 2011 TREASURY AIMS AND OBJECTIVES Chapter
NATIONAL TREASURY STRATEGIC PLAN 2011/14 PRESENTATION TO PARLIAMENTARY FINANCE COMMITTEES Presenter: Lungisa Fuzile Director General, National Treasury 31 May 2011 TREASURY AIMS AND OBJECTIVES Chapter
2 nd National Workshop on Global Fuel Economy Initiative (GFEI) in Mauritius. Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development 27 th November 2014
 2 nd National Workshop on Global Fuel Economy Initiative (GFEI) in Mauritius Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development 27 th November 2014 1 Global Fuel Economy Initiative Background Estimated
2 nd National Workshop on Global Fuel Economy Initiative (GFEI) in Mauritius Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development 27 th November 2014 1 Global Fuel Economy Initiative Background Estimated
PRRIA PASSENGER RAIL REFORM AND INVESTMENT ACT OF 2014 TRANSPORTATION & INFRASTRUCTURE COMMITTEE
 PRRIA PASSENGER RAIL REFORM AND INVESTMENT ACT OF 2014 TRANSPORTATION & INFRASTRUCTURE COMMITTEE The Importance of Reforming and Improving Our Intercity Passenger Rail PHOTO COURTESY OF AMTRAK For nearly
PRRIA PASSENGER RAIL REFORM AND INVESTMENT ACT OF 2014 TRANSPORTATION & INFRASTRUCTURE COMMITTEE The Importance of Reforming and Improving Our Intercity Passenger Rail PHOTO COURTESY OF AMTRAK For nearly
Mid-Coast Corridor Transit Project San Diego, California New Starts Project Development (Rating Assigned November 2014)
 Mid-Coast Corridor Transit Project San Diego, California New Starts Project Development (Rating Assigned November 2014) Summary Description Proposed Project: Light Rail Transit 10.9 Miles, 9 Stations Total
Mid-Coast Corridor Transit Project San Diego, California New Starts Project Development (Rating Assigned November 2014) Summary Description Proposed Project: Light Rail Transit 10.9 Miles, 9 Stations Total
Ne w J e r s e y Tr a f f i c Co n g e s t i o n :
 Ne w J e r s e y Tr a f f i c Co n g e s t i o n : A Growing Crisis January 2008 Cover photo : Route 3, Passaic County introduction A rising tide of traffic congestion threatens to increase roadway gridlock,
Ne w J e r s e y Tr a f f i c Co n g e s t i o n : A Growing Crisis January 2008 Cover photo : Route 3, Passaic County introduction A rising tide of traffic congestion threatens to increase roadway gridlock,
INSURANCE VIETNAM 22 DECEMBER 2014
 client alert INSURANCE VIETNAM 22 DECEMBER 2014 OVERVIEW OF INSURANCE REGULATIONS The Vietnamese insurance market is one of the most dynamic in South East Asia and by many different measures is seen to
client alert INSURANCE VIETNAM 22 DECEMBER 2014 OVERVIEW OF INSURANCE REGULATIONS The Vietnamese insurance market is one of the most dynamic in South East Asia and by many different measures is seen to
Road Safety ROAD SAFETY
 Road Safety 1 ROAD SAFETY Our staff and contractors drive around 1.1 billion kilometres each year: to deliver products to our customers or keep our operations running. That s equivalent to driving about
Road Safety 1 ROAD SAFETY Our staff and contractors drive around 1.1 billion kilometres each year: to deliver products to our customers or keep our operations running. That s equivalent to driving about
1. Transport challenges in subnational entities and related GHG emissions
 MOBILITY and TRANSPORTS CODATU and FRANCE NATURE ENVIRONNEMENT 1. Transport challenges in subnational entities and related GHG emissions Mobility for people as well as goods is at the heart of issues related
MOBILITY and TRANSPORTS CODATU and FRANCE NATURE ENVIRONNEMENT 1. Transport challenges in subnational entities and related GHG emissions Mobility for people as well as goods is at the heart of issues related
Florida Transportation Commission: A Meeting of the Modes
 Florida Transportation Commission: A Meeting of the Modes Corridors of the Future: A National and I-95 Corridor Perspective George Schoener, Executive Director I-95 Corridor Coalition February 12, 2007
Florida Transportation Commission: A Meeting of the Modes Corridors of the Future: A National and I-95 Corridor Perspective George Schoener, Executive Director I-95 Corridor Coalition February 12, 2007
18.1 million people 1 billion tons of goods moved 2.5 billion dollars of trucking congestion costs
 G-MAP A COMPREHENSIVE GOODS MOVEMENT ACTION PROGRAM FOR THE NEW YORK-NEW JERSEY METROPOLITAN REGION FALL 2014 A Joint Initiative of: The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey The New Jersey Department
G-MAP A COMPREHENSIVE GOODS MOVEMENT ACTION PROGRAM FOR THE NEW YORK-NEW JERSEY METROPOLITAN REGION FALL 2014 A Joint Initiative of: The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey The New Jersey Department
Prepared April 2004. Source: Draft originally prepared for Ministry of Finance, Lesotho.
 CONTRACTING OUT DAY-TO-DAY MANAGEMENT OF THE ROAD FUND ADMINISTRATION Prepared April 2004. Source: Draft originally prepared for Ministry of Finance, Lesotho. Some countries have decided that they could
CONTRACTING OUT DAY-TO-DAY MANAGEMENT OF THE ROAD FUND ADMINISTRATION Prepared April 2004. Source: Draft originally prepared for Ministry of Finance, Lesotho. Some countries have decided that they could
Recommendation for a COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION. on the 2015 National Reform Programme of Portugal
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 13.5.2015 COM(2015) 271 final Recommendation for a COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION on the 2015 National Reform Programme of Portugal and delivering a Council opinion on the 2015 Stability
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 13.5.2015 COM(2015) 271 final Recommendation for a COUNCIL RECOMMENDATION on the 2015 National Reform Programme of Portugal and delivering a Council opinion on the 2015 Stability
PROGRAM EXPENDITURE AND FINANCING ASSESSMENT
 Electricity Grid Strengthening Sumatra Program (RRP INO 49080) PROGRAM EXPENDITURE AND FINANCING ASSESSMENT 1. The program expenditure and financing assessment reviews the extent to which the Electricity
Electricity Grid Strengthening Sumatra Program (RRP INO 49080) PROGRAM EXPENDITURE AND FINANCING ASSESSMENT 1. The program expenditure and financing assessment reviews the extent to which the Electricity
Progress of Water Environmental Governance/Management and Future Challenges in Vietnam
 Progress of Water Environmental Governance/Management and Future Challenges in Vietnam The Second International Workshop and the Sixth Annual Meeting for Water Environmental Partnership in Asia (WEPA)
Progress of Water Environmental Governance/Management and Future Challenges in Vietnam The Second International Workshop and the Sixth Annual Meeting for Water Environmental Partnership in Asia (WEPA)
COUNTRY EXPERIENCE ON EMISSION MEASUREMENT AND MITIGATION POLICIES. Republic of the Fiji Islands
 COUNTRY EXPERIENCE ON EMISSION MEASUREMENT AND MITIGATION POLICIES Republic of the Fiji Islands Major Exports (i)sugar $120m (ii) Tourism F$500m (iii) Fisheries F$30m (iv) Minerals F$40m Populated Islands
COUNTRY EXPERIENCE ON EMISSION MEASUREMENT AND MITIGATION POLICIES Republic of the Fiji Islands Major Exports (i)sugar $120m (ii) Tourism F$500m (iii) Fisheries F$30m (iv) Minerals F$40m Populated Islands
NEWSFLASH October 2009
 NEWSFLASH October 2009 INVESTING IN INFRASTRUCTURE IN VIETNAM Vietnam's need for investment in infrastructure to keep pace with and to sustain economic growth has been voiced loudly. To date, the State
NEWSFLASH October 2009 INVESTING IN INFRASTRUCTURE IN VIETNAM Vietnam's need for investment in infrastructure to keep pace with and to sustain economic growth has been voiced loudly. To date, the State
Overview of East Asia Infrastructure Trends and Challenges
 Overview of East Asia Infrastructure Trends and Challenges Christian Delvoie. Director, Knowledge Strategy Group, The World Bank Until September 28: Director, Sustainable Development, East Asia and Pacific
Overview of East Asia Infrastructure Trends and Challenges Christian Delvoie. Director, Knowledge Strategy Group, The World Bank Until September 28: Director, Sustainable Development, East Asia and Pacific
Brief on Climate Change Finance
 Brief on Climate Change Finance Introduction Climate change is a complex policy issue with major implications in terms of finance. All actions to address climate change ultimately involve costs. Funding
Brief on Climate Change Finance Introduction Climate change is a complex policy issue with major implications in terms of finance. All actions to address climate change ultimately involve costs. Funding
DECISION APPROVAL OF THE NATIONAL MASTER PLAN FOR POWER DEVELOPMENT FOR THE 2011-2020 PERIOD WITH THE VISION TO 2030
 THE PRIME MINISTER ------- THE SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Independence - Freedom - Happiness No. 1208/QD-TTg --------------- Hanoi, 21 July 2011 DECISION APPROVAL OF THE NATIONAL MASTER PLAN FOR POWER
THE PRIME MINISTER ------- THE SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Independence - Freedom - Happiness No. 1208/QD-TTg --------------- Hanoi, 21 July 2011 DECISION APPROVAL OF THE NATIONAL MASTER PLAN FOR POWER
Job Code Job Title Function Sub Function EEO 4. TRM011 Sr Mgr, Air Transport Admin Front Line Mgr Senior Manager Professionals N
 TRM010 Mgr, Air Transport Admin Front Line Mgr Manager (1,2,3) Professionals M Manages the operation of an aviation program or air transportation office. Develops and implements flight safety and maintenance
TRM010 Mgr, Air Transport Admin Front Line Mgr Manager (1,2,3) Professionals M Manages the operation of an aviation program or air transportation office. Develops and implements flight safety and maintenance
China Railways Development, Financing and Challenges
 China Railways Development, Financing and Challenges Zhang, Jianping Depart. of Development & Planning Ministry of Railway, P. R. China March 31, 2006 Transport Forum, World Bank 1. Current Situation of
China Railways Development, Financing and Challenges Zhang, Jianping Depart. of Development & Planning Ministry of Railway, P. R. China March 31, 2006 Transport Forum, World Bank 1. Current Situation of
04of 2012. Income Shocks and Household Risk-Coping Strategies: The Role of Formal Insurance in Rural Vietnam POLICY BRIEF: Background
 POLICY BRIEF: 04of 2012 This policy brief is written based on the study entitled Income Shocks and Household Risk- Coping Strategies: The Role of Formal Insurance in Rural Vietnam written by researchers
POLICY BRIEF: 04of 2012 This policy brief is written based on the study entitled Income Shocks and Household Risk- Coping Strategies: The Role of Formal Insurance in Rural Vietnam written by researchers
2009-3. The Preservation of Local Truck Routes: A Primary Connection between Commerce and the Regional Freight Network
 2009-3 The Preservation of Local Truck Routes: A Primary Connection between Commerce and the Regional Freight Network July 2009 This Goods Movement Challenges and Opportunities Report was prepared jointly
2009-3 The Preservation of Local Truck Routes: A Primary Connection between Commerce and the Regional Freight Network July 2009 This Goods Movement Challenges and Opportunities Report was prepared jointly
People s Republic of China: Strategy and Transport Policy Study on Promoting Logistics Development in Rural Areas
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 48022 Policy and Advisory Technical Assistance (PATA) August 2014 People s Republic of China: Strategy and Transport Policy Study on Promoting Logistics Development
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 48022 Policy and Advisory Technical Assistance (PATA) August 2014 People s Republic of China: Strategy and Transport Policy Study on Promoting Logistics Development
Prefeasibility Study for the High Speed Line HU-RO Border Bucharest - Constanta Description and Objectives
 Prefeasibility Study for the High Speed Line HU-RO Border Bucharest - Constanta Description and Objectives Timisoara - 13 th of September 2012 1 The European Vision for Railway Transport The European Commission's
Prefeasibility Study for the High Speed Line HU-RO Border Bucharest - Constanta Description and Objectives Timisoara - 13 th of September 2012 1 The European Vision for Railway Transport The European Commission's
TA 4862-VIE: Preparing the Ho Chi Minh City Metro Rail System - PPIAF Study -
 Asian Development Bank Public Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility TA 4862-VIE: Preparing the Ho Chi Minh City Metro Rail System - PPIAF Study - Completion Report August 2008 Preparing the HCMC Metro
Asian Development Bank Public Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility TA 4862-VIE: Preparing the Ho Chi Minh City Metro Rail System - PPIAF Study - Completion Report August 2008 Preparing the HCMC Metro
INDONESIA - LAW ON WATER RESOURCES,
 Environment and Development Journal Law LEAD INDONESIA - LAW ON WATER RESOURCES, 2004 VOLUME 2/1 LEAD Journal (Law, Environment and Development Journal) is a peer-reviewed academic publication based in
Environment and Development Journal Law LEAD INDONESIA - LAW ON WATER RESOURCES, 2004 VOLUME 2/1 LEAD Journal (Law, Environment and Development Journal) is a peer-reviewed academic publication based in
foundations for success québec infrastructures plan
 foundations for success québec infrastructures plan The content of this publication was drafted by the Secrétariat du Conseil du trésor. This edition was produced by the Direction des communications. Legal
foundations for success québec infrastructures plan The content of this publication was drafted by the Secrétariat du Conseil du trésor. This edition was produced by the Direction des communications. Legal
Mid-Coast Corridor Transit Project San Diego, California New Starts Engineering (Rating Assigned November 2015)
 Mid-Coast Corridor Transit Project San Diego, California New Starts Engineering (Rating Assigned November 2015) Summary Description Proposed Project: Light Rail Transit 10.9 Miles, 9 Stations Total Capital
Mid-Coast Corridor Transit Project San Diego, California New Starts Engineering (Rating Assigned November 2015) Summary Description Proposed Project: Light Rail Transit 10.9 Miles, 9 Stations Total Capital
S.B. NO. JAN 2 2 2016
 THE SENATE TWENTY-EIGHTH LEGISLATURE, 0 STATE OF HAWAII S.B. NO. JAN 0 A BILL FOR AN ACT RELATING TO STATEWIDE INFRASTRUCTURE CAPACITY BUILDING CONSTRUCTION FINANCING. BE IT ENACTED BY THE LEGISLATURE
THE SENATE TWENTY-EIGHTH LEGISLATURE, 0 STATE OF HAWAII S.B. NO. JAN 0 A BILL FOR AN ACT RELATING TO STATEWIDE INFRASTRUCTURE CAPACITY BUILDING CONSTRUCTION FINANCING. BE IT ENACTED BY THE LEGISLATURE
arrangements typified by joint working between the public and private sectors covering all types of collaboration across the private-public sector
 20//204 PUBLIC PARTNERSHIP PRIVATE on Institutional Arrangement and Policy Implications Case Studies from the Republic of Korea November 8, 204 Seung-Jin Baek Economic Development Division UN ECLAC What
20//204 PUBLIC PARTNERSHIP PRIVATE on Institutional Arrangement and Policy Implications Case Studies from the Republic of Korea November 8, 204 Seung-Jin Baek Economic Development Division UN ECLAC What
Why infrastructure is so important
 Maersk in Brazil Brazil is a key growth market for Maersk. We share a common interest with Brazil in promoting economic development, national competitiveness and prosperity for Brazil s population. Since
Maersk in Brazil Brazil is a key growth market for Maersk. We share a common interest with Brazil in promoting economic development, national competitiveness and prosperity for Brazil s population. Since
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): WATER SUPPLY AND OTHER MUNICIPAL INFRASTRUCTURE AND SERVICES 1. 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
 Country Partnership Strategy: Kyrgyz Republic, 2013 2017 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): WATER SUPPLY AND OTHER MUNICIPAL INFRASTRUCTURE AND SERVICES 1 Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and
Country Partnership Strategy: Kyrgyz Republic, 2013 2017 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): WATER SUPPLY AND OTHER MUNICIPAL INFRASTRUCTURE AND SERVICES 1 Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and
GAO U.S. INFRASTRUCTURE. Funding Trends and Federal Agencies Investment Estimates. Testimony
 GAO For Release on Delivery Expected at 3:00 p.m. EST Monday July 23, 2001 United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Subcommittee on Transportation and Infrastructure, Committee on Environment
GAO For Release on Delivery Expected at 3:00 p.m. EST Monday July 23, 2001 United States General Accounting Office Testimony Before the Subcommittee on Transportation and Infrastructure, Committee on Environment
Railway Reform in South East Europe and Turkey: On the Right Track?
 KOSOVO RAILWAYS 329. Kosovo Railways (Hekurudhat e Kosovës; KR) is a joint stock company created in December 25 and previously known as UNMIK Railways. It was originally formed as the United Nations Interim
KOSOVO RAILWAYS 329. Kosovo Railways (Hekurudhat e Kosovës; KR) is a joint stock company created in December 25 and previously known as UNMIK Railways. It was originally formed as the United Nations Interim
STRATEGIC PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS PROGRAM
 DOCUMENT OF THE INTER-AMERICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK COLOMBIA STRATEGIC PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS PROGRAM (CO-L1091) This document was prepared by the program team consisting of: Miroslava de Nevo, Program
DOCUMENT OF THE INTER-AMERICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK COLOMBIA STRATEGIC PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS PROGRAM (CO-L1091) This document was prepared by the program team consisting of: Miroslava de Nevo, Program
Audit Results by Transport Sector
 Regulatory Audit Results by Transport Sector As part of the Government s Red Tape Reduction Programme the Infrastructure and Regional Development portfolio (the portfolio) has undertaken an Audit of its
Regulatory Audit Results by Transport Sector As part of the Government s Red Tape Reduction Programme the Infrastructure and Regional Development portfolio (the portfolio) has undertaken an Audit of its
Vietnam's Experiences in Strengthening. Procurement and Public Financial Management Systems. in Harmonization, Alignment and Capacity Development
 Vietnam's Experiences in Strengthening Procurement and Public Financial Management Systems in Harmonization, Alignment and Capacity Development Mr. Chairman, Ladies and gentlemen, Dr. Duong Duc Ung Director
Vietnam's Experiences in Strengthening Procurement and Public Financial Management Systems in Harmonization, Alignment and Capacity Development Mr. Chairman, Ladies and gentlemen, Dr. Duong Duc Ung Director
Transportation and Public Works. Business Plan 2002-2003
 Business Plan 2002-2003 March 27, 2002 Mission Transportation and Public Works Construct, maintain and manage provincial highways, buildings and related infrastructure, and provide accommodation, property
Business Plan 2002-2003 March 27, 2002 Mission Transportation and Public Works Construct, maintain and manage provincial highways, buildings and related infrastructure, and provide accommodation, property
