TA 4862-VIE: Preparing the Ho Chi Minh City Metro Rail System - PPIAF Study -
|
|
|
- Myles Martin Hancock
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Asian Development Bank Public Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility TA 4862-VIE: Preparing the Ho Chi Minh City Metro Rail System - PPIAF Study - Completion Report August 2008
3 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Table of Contents Synopsis... i 1. Introduction Background Objectives of PPIAF Technical Assistance This Completion Report Study Team Activity 1: Framework for Considering Private Sector Participation (PSP) Options Development Activities 2 and 3: Financial Modeling Including Risk Financial Model Financing and Delivery Options Value for Money (VFM) Test Assumptions and contingencies Activity 4: Stakeholder Feedback and Implementation Arrangements Key Tasks Key Stakeholders Transport Agencies and Functions in HCMC Key Laws Institutional Options Fares and Ticketing Building Technical and Managerial Capacity Appendix A: Issues and Options for Private Sector Participation and Concession Template Working Paper Appendix B: Financial Modeling Working Paper Appendix C: Stakeholder Feedback and Implementation Arrangements: Institutional Options Working Paper Appendix D: Fares and Ticketing Working Paper References and Bibliography i
4 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Abbreviations ADB BOT DOPI Asian Development Bank Build-Operate-Transfer Department of Planning & Investment, HCMC PC DNRE Department of Natural Resources & DOF DTUPWS DUPA GVN HCMC HIFU IFI ODA PC PPI PPIAF PPP PSP SOE TA ToR MAUR Environment, HCMC PC Department of Finance, HCMC PC Department of Transport & Urban Public Works & Services, HCMC PC Department of Urban Planning & Architecture, HCMC PC Government of Viet Nam Ho Chi Minh City Ho Chi Minh City Infrastructure Fund for Urban Development International Financial Institution Official Development Assistance People s Committee Private Participation in Infrastructure Public Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility Public-Private Partnership Private Sector Participation State Owned Enterprise Technical Assistance Terms of Reference Management Authority for Urban Railways, HCMC PC ii
5 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Synopsis Rail based Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) is a key component of Ho Chi Minh City s urban transport strategy. But MRT is expensive. MRT therefore requires good integration with bus services and other modes, convenient access for pedestrians and coordinated land use intensification to optimize MRT s potential. Development of MRT of most benefit to the community requires a focus on the development of integrated network of services that are well integrated with bus, and that provide the fastest, most convenient and affordable journey possible between home and work and all the other origins and destinations in the city. A focus on how to secure the operation of efficient, high quality, and responsive MRT services, and integrated ticketing and fares, is therefore very important and is a necessary complement to the implementation of high quality MRT infrastructure. Recognizing the importance of efficient MRT operations and services ADB mobilized a grant from the Public Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility (PPIAF) to develop appropriate short term and longer term implementation and management arrangements for MRT in the context of wider urban transport, including options for how best to optimize private sector participation in MRT. The objectives of the PPIAF technical assistance (TA) therefore included developing (i) a framework for considering private sector participation in implementation and operation of the Project; (ii) a value-for-money analysis for implementation approaches that involve varying degrees of private sector participation, (iii) a detailed financial model reflecting the preferred approach and measuring the performance of the project from the points of view of the government and private sector participants; and (iv) a stakeholder feedback and a description of necessary institutional and contractual arrangements given the preferred implementation approach. A summary of the work undertaken is contained in the attached report along with copies of the key working papers produced by the TA. Si
6 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF 1. Introduction 1.1 Background With a population of approximately 6.1 million in 2004, HCMC is the largest city in Viet Nam and its economic hub. HCMC has a total administrative area of 2,095 km2 covering 19 urban and five suburban/rural districts. The average population density is about 2,900 inhabitants per square km with a central area density of around 45,000 inhabitants per square km (JICA 2004). Approximately 2.3 million people were estimated to live in the three adjoining provinces of Dong Nai, Binh Duong, and Long An which make up the Greater HCMC region. Population for the region was forecast to reach 13.5 million by 2020 with 10 million in HCMC by HOUTRANS (JICA 2004). Current trends are for continuing rapid growth in incomes and motorization, increased urbanization, and associated traffic congestion, and related pollution (local and global) and crashes, which will to some extent reduce the productivity of region s, and therefore, Viet Nam s economy. Addressing this considerable challenge requires as its foundation appropriate institutional and regulatory arrangements to coordinate land use and transport development management, formulation and implementation of transport policies and infrastructure, and the delivery of efficient integrated, multi-modal transport services. The People s Committee (PC) of Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC), Viet Nam has initiated studies to develop a rail mass rapid transit (MRT) system for the City based on the current MRT Master Plan (as approved in January 2007). Prior to early 2008, ttwo lines (MRT2 and MRT3) had been proposed for Asian Development Bank (ADB) funding with another line (MRT1) to be financed by the Government of Japan 1. The Government of China, is a developing a proposal for an MRT line, there are other proposals including one from China for MRT, Malaysian interests to develop a monorail, and for a French consortium to develop a tram route. ADB has mobilized a PPTA and selected a firm for the following components of the project preparation for MRT Lines 2 and 3. The PPTA study, which commenced in May 2007 and is to be completed in May 2008, is responsible for providing: An optimized MRT Master Plan which integrates the currently proposed MRT lines into a cohesive network with other modes, identifies required supporting policies, and develops design parameters for the two project lines. A feasibility assessment and preliminary engineering design for the two project lines. The PPTA must confirm the engineering feasibility, and identify social and environmental impacts for accurate cost estimation and financial appraisal. A plan to support project implementation, including institutional and staffing arrangements, capacity building, financing/funding options, and implementation program. In parallel, ADB mobilized a grant from the Public Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility (PPIAF) to optimize private sector participation in MRT 2 and 3, and to assist the HCMC PC to develop appropriate short term and longer term implementation and management arrangements for MRT in the context of wider urban transport 1 During 2007, the JBIC s role in funding increased with principal or sole involvement in the first three MRT lines. 1
7 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF 1.2 Objectives of PPIAF Technical Assistance The objectives of the PPIAF technical assistance (TA) therefore included developing (i) a framework for considering private sector participation in implementation and operation of the Project; (ii) a value-for-money analysis for implementation approaches that involve varying degrees of private sector participation, (iii) a detailed financial model reflecting the preferred approach and measuring the performance of the project from the points of view of the government and private sector participants; and (iv) a stakeholder feedback and a description of necessary institutional and contractual arrangements given the preferred implementation approach. This PPIAF TA draws on detailed information on project costs, patronage and revenue prepared by consultants undertaking the PPTA. The results of its work were presented in conjunction with the work of the PPTA to ensure an integrated and complete business case that the HCMC PC and ADB can use to direct implementation and ongoing operations. 1.3 This Completion Report This Completion Report summarizes the key findings and recommendations of the TA. In doing so, it draws upon the following reports, working papers or other outputs prepared by the TA: Table 1.1: Activities and Outputs Activity 1. Framework for Considering Private Sector Participation (PSP) Options Development Principal Outputs Issues and Options for Private Sector Participation & Concession Template Working Paper Vietnamese and English language versions (April 2008). Refer Appendix A for English Version. 2. Risk and Value-for-Money Analysis Financial Modeling Working Paper & Model Vietnamese and English language versions (June 2008). Refer Appendix B for English Version. 3. Financial Analysis: Financing Plan & Financial Model 4. Stakeholder Feedback and Implementation Arrangements Financial Modeling as above Inception Report English language version only (March 2008) Stakeholder Feedback and Implementation Arrangements: Institutional Options Working Paper Vietnamese and English language versions (March 2008). Refer Appendix C for English Version. Stakeholder Engagement Plan English language version only (March 2008) Informal document. Fares and Ticketing Working Paper Vietnamese and English language versions (June 2008). Refer Appendix D for English Version. The PPIAF TA mobilized on March 3, Work proceeded intermittently in HCMC and the consultants home offices over the period to July Subsequent sections of the report discuss identified key issues and priorities and the work program formulated to meet the 2
8 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF requirements of the TA. Several meetings with key agencies were held including the Management Authority for Urban Railways (MAUR) of the HCMC PC, other agencies of the PC, financial institutions, the PPTA team and the visiting supervising mission from ADB. 1.4 Study Team The PIAF consultant team responsible for preparing this report were greatly assisted by staff from the HCMC PC s: Management Authority for Urban Railways; Department of Planning and Investment; and Ho Chi Minh City Infrastructure Fund for Urban Development. Important guidance was also provided by several ADB staff who visited HCMC during the inception mission including: Dr Hubert Jenny, Senior Urban Development Specialist, Southeast Asia Department, Infrastructure Division; Dr Antoine Kunth, Infrastructure Specialist, Southeast Asia Infrastructure Division; Mr Le Dinh Thang, Program/Project Implementation Officer, Viet Nam Resident Mission; Mr Jamie Leather, Senior Transport Specialist, Energy, Transport and Water Division, Regional and Sustainable Development Department, and Yuji Tsujiki Financial Analysis Specialist Infrastructure Division, Southeast Asia Department. David Margonstern, PADDI (Centres de prospective et etudes urbaines of the Rhone Alpes Region, France), who worked closely with many departments in the HCMC PC provided valuable inputs. Close cooperation with the PPTA team was also facilitated by the PPIAF team making use of the PPTA team s office and day to day interaction. The consultant study team consisted of: Philip Sayeg, the Urban Transport Planning Specialist /Team Leader; David Bray, Urban Transport Institutional Specialist; and Dr Sudhisakdi Manibhandu, Private Sector Financing Specialist (Public Private Partnerships). 3
9 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF 2. Activity 1: Framework for Considering Private Sector Participation (PSP) Options Development Under this Activity, in accordance with the ToR for the TA, various opportunities to use the private sector for implementing and operating rail mass rapid transit (MRT) in HCMC had to be considered. The English language version of the Working Paper prepared for the TA which is entitled Issues and Options for Private Sector Participation and Concession Template (contained in Appendix A) provides full details of the work carried out which is summarized below. Options for private sector participation were considered with a broader view than any individual MRT line in HCMC because the ultimate objective of the government is a substantial increase in the use of public transport in the city, which in turn requires an integrated public transport system. The use of the private sector is not addressed from an ideological perspective, but rather as a means for securing the delivery of high quality MRT at the lowest possible cost to the community. The Working Paper notes that the private sector has been involved in MRT in nearby countries in recent years: always for implementation of infrastructure; often for the operation of services; and to a lesser extent for investment in MRT assets. It also notes general experience that the cost of public sector operation of public transport is higher than with private sector operation, and that there is a general worldwide trend to make greater use of the private sector for the operation of public transport. Consideration was given to the range of factors that affect the manner in which the private sector could be involved. These factors have two broad influences. The first is the extent to which the private sector could provide finance for implementation of the MRT. In this respect, it appears that the current approach to MRT in HCMC is likely to result in fare and related revenue that will, at best, cover operating costs and make a small contribution to capital costs. Accordingly, the government will need to eventually pay the private sector for most of the cost of any capital that the private sector might provide in the first instance to implement the project. While the cost of capital to the private sector is generally more expensive than the cost of capital for the government, the report notes that this may be offset by lower costs that result from the transfer of manageable risk to the private sector and the incentive for the private sector to better integrate assets and operations to reduce life-cycle costs. The second influence is on the form of the agreement between the government and the organization that is to operate the MRT system (called the concessionaire). It is essential that such an agreement be in place, irrespective of whether the concessionaire is a government or a private organization. It is common for such agreements to have a term of around 30 years or so, especially where the concessionaire contributes capital investment. There is also a need for the agreement to include conditions that provide the operator with the incentive to undertake their tasks in a manner that meets the government s objectives for MRT in HCMC. There has been a tendency in the past to use a form of agreement wherein the concessionaire keeps fare and other revenue for the MRT line to which the contract pertains and uses the revenue to cover its costs. The government may need to provide supplementary financing if the revenue available to the concessionaire is insufficient to met the costs. This approach, called a Net Cost form of concession, has major limitations. In particular it does not facilitate operation of an integrated public transport system and reduces the flexibility of the government to develop the transport system and modify its urban transport policies over the term of the concession. An alternative approach, called a Gross Cost form of concession, is 4
10 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF strongly recommended. Under it, revenue from fares accrues to the government, which in turn pays the concessionaire for the services that the concessionaire provides. Refer Table 2.1 for a summary of the features of each approach. Infrastructure Risk sharing Table 2.1: Summary of Net Cost and Gross Cost Concession Models Net Cost Gross Cost Government provides civil infrastructure. Concessionaire provides trains and related items such as train control & communications systems and depot equipment. Concessionaire assumes all patronage risk, and shares extra profits (if any) with the Authority. Risk is shared between the Authority and concessionaire. Optimum sharing of risk will minimise the concession cost. Revenue Concessionaire keeps revenue Fare revenue is given to the Authority Services Concessionaire determines services to be provided on the basis of profitability. Authority sets service standards and the concessionaire determines services based on these standards. Payments Authority role Source: Consultant Concessionaire meets costs from its own revenue. Additional payments may be needed from the government if concessionaire s revenue is too low. Authority invites tenders & establishes a concession; has only a small role thereafter; difficult to vary contract conditions. Authority pays the concessionaire for services provided according to rates set on the basis of competitive tendering and quantity/quality of service provided. Authority invites tenders and establishes a concession; has a continuing major role in managing the concession agreement; can vary conditions when needed. The Working Paper describes how this form of concession can be implemented to give the concessionaire (or any other operator) the incentive to provide good quality services that meet the needs of passengers at the lowest possible cost and with the least need for detailed management of the concession contract by the government. Four possible implementation options were considered. All four were subject to value-formoney analysis as described in Section 3 of this report, to indicate the potential cost to the government of delivering Line 2 of the MRT system and the provision of services on the line over the long term. The results of this analysis will be presented in a separate report. The options are: Government financing, implementation and operation of the MRT. Government financing and implementation of all MRT assets, and engagement of a concessionaire to operate MRT services. Government financing and implementation of MRT civil infrastructure, and engagement of a concessionaire to finance and provide trains and related electrical and mechanical equipment and systems, and to operate MRT services. Private sector financing, implementation and operation of the MRT. Key features of each of these four options are shown in Table
11 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Delivery of: Civil Infrastructure and Fixed Equipment Trains, train control and communications, and depot equipment Train services and infrastructure maintenance Risk Transfer Finance Civil Infrastructure and Fixed Equipment Trains, train control and communications, and depot equipment Train services and infrastructure maintenance Fare revenue Source: Consultant Table 2.2: Features of Delivery and Financing Models Public Enterprise Public Implementation with Operating Concession (PIOC) Delivered through competitively tendered contracts to the government. Delivered through competitively tendered contracts to the government. Contract negotiated with an SOE. Transfer of risk from the government is limited to the extent allowed in construction and equipment supply contracts. The government retains risk associated with operations through its ownership of the operator. Competitively tendered Gross Cost contract. As for the Public Enterprise option but can transfer operating risk to the concessionaire. Some patronage risk can be transferred through the Gross Cost concession. The government retains operating risk related to mismatch between trains it provides and concessionaire needs. Capital provided by the government. Capital provided by the government. The government pays all costs incurred by the SOE, including working capital The government retains fare and other revenue (or pays SOE the difference between costs and revenue if the SOE retains the revenue). The government pays for operating and maintenance costs as specified in the contract. Train Supply and Operating Concession (TSOC) Delivered through a competitive tendered Gross Cost concession. The government transfers more risk to the concessionaire than in the PIOC option because the concessionaire purchases trains and can therefore bear more risk for operations because they have more control over service quality. Capital provided by the government. Capital provided by the concessionaire. The government pays for costs as specified in the contract (to cover both capital and O&M costs). Fare revenue accrues to the government. Build, Operate & Transfer (BOT) Delivered through competitively tendered Net Cost contract to the government. Transfers the greatest amount of risk from the government, but the government loses flexibility for change in policy and for public transport network integration. Capital provided by the concessionaire. The government will need to pay for costs as specified in the contract (to cover both capital and O&M costs net of fare revenue, where fare revenue will be much less than the costs). Concessionaire retains fare and other revenue. The Gross Cost form of concession is recommended for the first three options. A Net Cost form of concession is appropriate for the last option to allow the concessionaire to manage its greater financial exposure in a way that minimizes its risks. In all four cases, the government will eventually pay for the total cost of implementing and operating MRT. However, the total cost to the government will vary. This occurs because the four options involve different ways of allocating and managing MRT responsibilities, and hence the incentive and capacity for those involved to manage the associated financial, engineering, operational and patronage risks. 6
12 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF The report draws general conclusions about the relative merits of the four implementation/- financing options, but does not unequivocally recommend any particular approach. Rather, the intention of developing and assessing the options is to provide understanding that can help the government with its consideration of an arrangement that is appropriate for HCMC. Two other key recommendations are made. The first is that there should eventually be at least two companies involved in the operation of MRT in HCMC. This puts competitive pressure on each operator to improve its performance so that they are not seen to be inferior to the other operator(s). It also provides data that the government can use to benchmark the performance of the operators so that it can provide feedback to the operators on opportunities for improved performance. Finally, it provides the government with flexibility in the event that one operator fails to perform, with the capacity for another of the operators to take over in the short term if that should become necessary. The second recommendation is that international competitive tendering should be used to select the concessionaire, with the likelihood that a foreign party will form a consortium with a local enterprise. This will bring international experience and expertise to support the development of world class MRT in HCMC and provide a sound basis for developing domestic skills in MRT. Finally, the report presents an outline of a concession agreement and discusses the actions needed to select a concessionaire and establish and manage a contract. 7
13 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF 3. Activities 2 and 3: Financial Modeling Including Risk There were several strands to the financial modeling work that are summarized below. The English language version of the Working Paper prepared for the TA on this Activity is contained in Appendix B. 3.1 Financial Model Part of the PPIAF assignment has involved the development of a financial model capable of being used in MRT network planning and in project preparation of the HCMC Line 2. The model is used to perform two tasks: (i) a value-for-money (VfM) analysis of MRT project development options identified in the assignment issues and options analysis for private participation in the development of Line 2; and (ii) financial analysis of the HCMC Line 2. The second task, ie financial analysis of Line 2, is reported in the PPTA study documentation. A technical paper responding to the PPIAF terms of reference describes the financial model and the VfM analysis carried out of development options for Line 2. The VfM analysis is summarized in the following paragraphs. 3.2 Financing and Delivery Options The Issues and Options study identifies for detailed examination four alternative approaches including private sector participation and public private partnerships (PPP) to project development of Line 2: (i) the project is developed by a state-owned enterprise (SOE), with government taking maximum responsibility in project management, financing and service delivery; (ii) the service delivery is by a private sector concessionaire, with government retaining the remaining project responsibility; (iii) the operating concessionaire supplies (ie also finances) the required trains and signaling and communications, and government retains all other responsibility; and (iv) the project is developed as a build-operate-transfer (BOT) concession, where the private sector take the maximum project responsibility, allowing government to play only a monitoring and evaluation role, at least in theory. 3.3 Value for Money (VFM) Test The potential cost to the community of the four options is evaluated and compared in a quantitative value-for-money (VfM) test. It is common experience that government generally faces a lower financing cost compared to the private sector. At the same time, statistical analyses 1 of international transport projects provide well-founded evidence of substantial public sector optimism bias (a propensity for actual cost to exceed forecast or for actual revenue to fall short of forecast) in project capital cost estimates. Now, common experience suggests that, much more than the bureaucratic organization, a private sector enterprise is generally under strong motivation to manage uncertainly in project planning and implementation. Meanwhile, studies of privatized public transport 2, especially bus, indicate that the private sector can be expected to deliver service at a cost significantly lower than the public sector. Thus, in theory, an MRT project development with an appropriate assignment of responsibility and risk between government and the private sector concessionaire could yield a lower expected cost, risk taken into account, compared to a eg a pure government effort. 1 See references in Financial Model paper. 2 See Issues and Options paper, Section
14 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF A VfM test carried out for the four options indicates that option (iii), private sector trains and train-related systems supply and service operation, incurs the lowest expected cost to the community; with option (ii) the next lowest. The BOT option shows a lower optimism bias than all the other options, but, since it uses the concessionaire s private sector financing for the full project investment, it incurs a maximum premium on the government s financing cost; this option turns out to have the highest expected cost to the community, the SOE option included. Evidently the BOT option is a doubly inappropriate approach to MRT project development. Details of the VfM test methodology, input data and parameters, as well as results can be found in the Financial Model paper Assumptions and contingencies It is important to understand what assumptions are necessary for, and what contingencies would invalidate, the VfM test results. These are summarized below. Market competition. VfM requires a competitive tender market for the concession and for related sub-contracting of the technology (eg design, construction, systems integration and installation, operation and maintenance in MRT service provision) and financing services to ensure that payment of concessionaires and sub-contractors is not in excess of a normal riskweighted remuneration for effort. This means that an option which has cleared a VfM test could at the procurement stage be facing a market failure (eg only one bidder), threatening its ability to deliver the anticipated VfM 1. Thus, transition and emerging countries in particular often cannot count on a reliable international supply of private sector financing. The threat of market failure in a specialized field such as MRT concessioning and sub-contracting should not be dismissed lightly. Financial and services market distortions. Here are some examples of distortions that can threaten or dilute VfM: Limited recourse financing of a PPP concession promotes VfM because the senior lenders, usually financial institutions regulated by a central bank, will for as long as the debt is outstanding have an interest in the project which is aligned with the authority granting the concession and bring professional skill to the monitoring of the concessionaire s performance. The lenders incentive to monitor the concessionaire performance is diluted with the lenders use of credit risk transfer (CRT) products. This practice dilutes the concession authority s effort to share an exposure to the concessionaire s performance level with the senior lenders, minimizing the monitoring cost in the process. Bilateral ODA financing can also introduce distortions in the sub-contracting markets. The tying of an ODA loan to supply of goods and services of a national origin restricts the competitive tendering for the procurement of MRT consulting and construction services and systems supply. An opportunity can be created for vendors to use the concessionary pricing of a loan to build in an additional margin on goods and services. In the long term, the practice can create a situation where, in a narrow field, the potential suppliers tacitly agree to live and let live instead of competing, with adverse effect on supply prices and therefore VfM. Partnering developed over time among financiers and sub-contractors while having a potential to be an effective project risk management tool for a concessionaire can be 1 The UK Treasury s answer to this problem, to give an illustration, is to require any candidate for a PPP development to have a back-up public sector option to be activated in the event of a market failure. 9
15 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF abused if allowed to develop into a collusive arrangement, which in the end threatens VfM. PPP procurement capability. Ability to procure well is important for realizing VfM. The balance of opinion, if not of evidence, is that a greater capability is required of the public sector in the procurement of a PPP concessionaire than in a conventional public works procurement. Ad hoc outsourcing for the required skills leads to limited results. For example, legal firms skilled in PPP contracting, forced to make a choice through conflict of interest rules, can tend to opt for working for the concessionaire side rather than government. Institutional capability building is required. 10
16 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF 4. Activity 4: Stakeholder Feedback and Implementation Arrangements 4.1 Key Tasks Key tasks carried out under this Activity were: Stakeholder analysis; Concession Template; Analysis of institutional options; and Fares and ticketing analysis and options. The outputs of these tasks are Stakeholder Feedback and Implementation Arrangements: Institutional Options Working Paper Vietnamese and English language versions (March 2008). Refer Appendix C for English Version. Stakeholder Engagement Plan English language version only (March 2008) Informal document; Concession Template refer Section 2 and Appendix A; Fares and Ticketing Working Paper Vietnamese and English language versions (June 2008). Refer Appendix D for English Version. Other capacity, likely legal and procurement requirements recognizing the PPIAF team did not have any legal resources available to them (covered variously in all outputs). 4.2 Key Stakeholders A list of identified core stakeholders 1 within HCMC is shown in Table 4.1. This list is based on the information contained in the Working Paper entitled Stakeholder Feedback and Implementation Arrangements: Institutional Options. While several stakeholders at national and HCMC levels have been identified the most important are shown in bold text in Table 4.1. IFIs or other bilateral donors have been excluded from the Table. Table 4.1: Identified Key Stakeholders Stakeholder National Level Ministry of Transport (MOT) Responsibility Through its different modal administrations and departments (a) plans, manages and maintains national infrastructure through its different departments and administrations; (b) assists local governments in developing transport plans and selecting transport projects; and (c) manages public bus transport plans by approving cities master plans 1 From now on in this paper core stakeholders will be referred to only as stakeholders. 11
17 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Stakeholder Vietnam Railways Administration (VNRA) under MOT Ministry of Finance (MOF) Transport Development Strategy Institute (TDSI)-under MOT Department of Planning and Investment (DPI)-under MOT The Ministry of Natural Resources and the Environment (MNRE) HCMC PC level People s Committee Transport and Urban Public Works Services (TUPWS) Transport and Industry Management Department (TIMD); and the Management and Operations Centre for Public Transport (MOCPT). HCMC Management Authority for Urban Railways HCMC Investment Fund (HIFU) Department of Finance (DOF) District Level and Commune Governments Urban Planning and Architecture Department (DUPA) Department of Planning and Investment (DPI) Traffic Police under the Public Security Department Responsibility Plans and manages the development of the sub sector Regulates the sub-sector including national and other rail systems including metro or MRT in cities and provinces. Provides oversight of City and Provincial rail and MRT Master Plans and is charged with approval of technical standards and safety of rail and MRT systems. Main functions of relevance to project: Informal MRT Master Plan approval MRT technical standards MRT safety standards & compliance Arranging of finance from external agencies including IFIs and provision of finance to local governments. Currently, financial planning aspects of future MRT development in Vietnam. Develops long and medium term transport sector strategies and plans (in collaboration with modal administrations) Integrates investment plans prepared by modal administrations for submission to MPI for inclusion in the PIP and to MOF for inclusion in the State Budget. Reviews and approves environmental impact assessments for transport projects. Approves key issues such as fares, opening and closing of routes, schedules and subsidies. Develops cities transport strategies; Plans and manages construction; Maintains urban transport infrastructure; Manages bus transport; Coordinates planning and implementation of traffic management with Police. Main functions of relevance to project: Transport Strategy Traffic management and parking Bus route planning & franchising incl bus-mrt integration Bus system ticketing Plans / implements rail-based mass transit plans and has responsibility for managing and arranging for operations and maintenance. Main functions of relevance to project: MRT civil infrastructure development incl land acquisition MRT rolling stock & E&M supply MRT ticketing MRT operations procurement and/or operations directly Arrangement of finance through bond issue for counterpart funds, coordination with private sector incl private financial institutions, possible shareholding role in a JV operating entity Treasury functions such as processing of project-related local expenditures including counterpart payments Relevant district governments through which a project passes will have a role in land acquisition & other facilitation Land Use Master Plan preparation and approval of developments. Land approvals are separately made by the Department of Natural Resources and Environment (DNRE) with little linkage to the Master Plan. Investment programming including one year annual budget and five year Public Investment Program (PIP) Enforces traffic management including the operation of traffic signals in coordination with TUPWS 12
18 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF 4.3 Transport Agencies and Functions in HCMC The HCMC PC is the key agency responsible for planning and delivery (ie here referring to regulation, purchasing of services and oversight, and construction of infrastructure) of public transport, such as bus, mass rapid transit and supporting land use and transport management functions. Within the PC the following agencies have key roles for urban transport: Transport and Urban Public Works Services (TUPWS) which is responsible for preparation of city transport strategies, the planning and management of construction, maintaining urban transport infrastructure, planning and managing bus transport; and coordinating planning and implementation of traffic management with Police. For planning and regulation of urban public transport (bus/ other) the Management and Operations Centre for Public Transport (MOCPT) of TUPWS is the most important agency; Management Authority for Urban Railways (MAUR) 1 plans and implements rail based mass transit infrastructure and responsible for operations; Urban Planning and Architecture Department (DUPA) Land Use Master Plan preparation and approval of developments. The process of planning is normative and appears not to reflect market preferences nor what is optimal in terms of infrastructure and social services provision. Land approvals are separately made by the Department of Natural Resources and Environment (DNRE) with little linkage to the Master Plan. Similarly infrastructure planning is made with little reference to the Master Plan. In addition, even for individual building and more major developments there are no specific standards or guidelines providing certainty to developers on how much Gross Floor Area (GFA) they can build or other conditions such as building set back and building form; Department of Planning and Investment investment promotion, coordination of investment including development of development assistance from IFIs and bilateral sources; and Department of Finance treasury, budget, investment planning and arrangement of sources of finance. 4.4 Key Laws National and city legislation governs the present provision of public transport services, currently mainly bus, in HCMC. The laws of most relevance to urban rail or urban MRT are: Railway Law 2005 (NA Order No. 35/2005/QH11); and HC PC Decree 119/ 2007/QD-UBND establishing the Management Authority for Urban Railways. Railway Law Within cities the Railway Law 2005 defines relevant types of urban railway as including metro or MRT using a wide variety of technologies. Authority for planning urban railway networks is given to People s Committees (Articles 14 and 15). Master Plans shall be prepared covering a detailed period of 10 years and less definitive further 10 year period. Fare setting is the responsibility of the PC. 1 Until September 2007, it was known as the Urban Railway Management Unit and was under TUPWS. 13
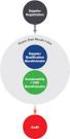
19 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Decree 119/ 2007/QD-UBND establishing Management Authority for Urban Railways, HCMC The Urban Railway Management Unit (known as the Management Authority for Urban Railways) was established in September 2007 by Decree 119. The Authority replaced the previous Urban Railway Management Division under TUPWS. MAUR is also under the guidance of Central Ministries branches and Departments branches of the city. The current MAUR structure is shown in Figure 4.1. With new responsibilities for management of operations and maintenance, the number of staff in MAUR is increasing. It is also understood that it is proposed to revise the current structure of MAUR in the near future to better reflect the management and operational functions. Figure 4.1: Current Structure of MAUR HCMC PC Director Nguyen Do Luong Vice Director Nguyen Van Quoc Vice Director Tran Thi Anh Nguyet Vice Director Le Hong Ha PMU Line 1 Planning and Investment Administration PMU Lines 2 & 3 Technical Quality Finance and Accounting Procurement Organization and Training Source: MAUR 4.5 Institutional Options Given the previous discussion, the alternative arrangements for an Authority relate primarily to the scope of its functions rather than to the underlying functions themselves. On this basis, four options for improved institutional arrangements for HCMC are identified: Option 1: Strengthen the Management Authority for Urban Railways (MAUR); Option 2: Interim Public Transport Authority using increased PC level coordination between bus and MRT; Option 3: Integrated Public Transport Authority. Refer Figure 4.2. In this option the proposed Integrated Public Transport Authority would be solely responsible for ensuring the delivery and operation of a fully integrated public transport system (MRT and bus) for HCMC; and Option 4: Integrated Transport Authority. In this option, a wholly integrated Authority would plan the multi-modal network, specify the services, program the investment (including roads, MRT and bus). 14
20 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF The options are capable of progressive implementation and a summary of their features is shown in Table 4.1. A worthwhile and practical option is Option 3 which is illustrated in Figure 4.2. In addition to developing integrated bus and MRT services this option would enable all public transport ticketing and fares to be integrated as long as MRT and bus operating arrangements are consistent. Table 4.1: Improvement Options Feature Option 1: Strengthen MAUR Option 2: Interim PT Authority Option 3: Integrated PT Authority Option 4: Integrated Transport Authority Integration of public transport in HCMC (1) Inc easing Inc easing Increasing integration Introduction Transport outcome Fairly good MRT integration possible Fairly good MRT integration more likely Fully integrated PT system more probable Fully integrated public transport system Description Minimum change to current institutional responsibilities. As for Option 1 but improved direction & coordination Strong direction and purpose for PT Strong direction and purpose for transport & land use Examples from other places Hong Kong & Singapore in the 1980s Bangkok in 1990s Melbourne and Brisbane, Australia Hong Kong, Singapore Benefits for customers Ease of use of MRT with integrated ticketing and easy interchanging where MRT lines intersect possible Ease of use of MRT with integrated ticketing and easy interchanging where MRT lines intersect. Integration with buses likely. Passengers able to use the PT system as though it was a single system, with fares, tickets, marketing and presentation integrated. Physical integration good. As for Option 3 but better integration with land use and road network. Agency responsibilities Transport policy & planning (2) Urban planning DUPA DUPA DUPA DUPA Transport policy TUPWS TUPWS TUPWS Integrated Transport Authority Strategic transport planning TUPWS TUPWS TUPWS Integrated Transport Authority Financing policies DPI & DOF DPI & DOF DPI, DOF with advice of Integrated PT Authority DPI, DOF with advice of Integrated Transport Authority Fares policy and service standards MAUR for MRT; TUPWS/ MOCPT for bus MAUR for rail; TUPWS/ MOCPT for bus Integrated PT Authority for MRT and bus Integrated Transport Authority for MRT and bus Regulation (3) Safety standards Independent regulator; TUPWS for bus Independent regulator; TUPWS for bus Independent regulator; Integrated PT Authority for bus Independent regulator; Integrated Transport Authority for bus Environmental standards DNRE DNRE DNRE DNRE Economic MAUR MAUR/ Interim PT regulation (5) Authority Integrated PT Authority Integrated Transport Authority 15
21 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Feature Option 1: Option 2: Option 3: Option 4: Strengthen MAUR Interim PT Authority Integrated PT Integrated Authority Transport Authority Public transport program management (4) Program coordination & direction Project planning & feasibility studies Investment programming & financing approval MAUR MAUR Integrated PT Authority MAUR MAUR Integrated PT Authority MAUR/ DPI/DOF/ PC MAUR/ DPI/DOF/ PC Integrated PT Authority / DPI/DOF/ PC Project design MAUR MAUR Integrated PT Authority Environmental & other approvals MAUR/ DNRE MAUR/ DNRE Integrated PT Authority/ DNRE Tendering MAUR MAUR Integrated PT Authority Contract management Infrastructure maintenance MRT service design Concession preparation and management Service delivery Rail services MAUR MAUR Integrated PT Authority MRT operators/ concessionaires (for operations) MRT operators/ concessionaires (for operations) MRT operators/ concessionaires (for operations) MAUR MAUR Integrated PT Authority MAUR MAUR Integrated PT Authority Operators/ Concessionaires Operators/ Concessionaires Operators/ Concessionaires Integrated Transport Authority Integrated Transport Authority Integrated Transport Authority / DPI/DOF/ PC Integrated Transport Authority Integrated Transport Authority/ DNRE Integrated Transport Authority Integrated Transport Authority MRT operators/ concessionaires (for operations) Integrated Transport Authority Integrated Transport Authority Operators/ Concessionaires Bus services Operators Operators Operators Operators Ticketing and fare collection Single contract under PC Single contract under PC Single contract under Integrated PT Authority Marketing Operators Operators Integrated PT Authority and operators Single contract under Integrated Transport Authority Integrated Transport Authority and operators (1) All options cover the provision of formal public transport in Greater HCMC. (2) Covers setting of policies within which agencies do detailed project planning & implementation & provision of services. (3) In the case of public transport, regulation relates primarily to safety. Vehicle registration and driver licensing, which are applicable for bus services, are not addressed because they are the same for all options. Economic regulation needs to be treated as an integral part of the Transport Policy and Planning function, though some aspects such as anti-monopoly regulation will be managed by other government agencies. (4) Includes activities to put strategies into practice strategies, including development and implementation of projects and arranging for the delivery of public transport and ancillary services. (5) Includes control over entry to the market (eg how many buses and companies are allowed) and control of fares. Source: Consultant 16
22 Preparing the HCMC Metro Rail System Completion Report Asian Development Bank and PPIAF Figure 4.2: Key lines of responsibility for Option 3 Integrated Public Transport Authority Source: Study Team 4.6 Fares and Ticketing An objective for rail mass rapid transit (MRT) in HCMC is that it be convenient to use and free of artificial barriers that could be imposed if MRT lines and their method of operations were to be done on a standalone basis. The Working Paper contained in Appendix D presents a discussion of the policy issues regarding fares and ticketing systems and recommends an approach to secure both integrated fares and an integrated ticketing system primarily for MRT, but also for other public transport, as MRT will rely on an integrated public transport system to maximize its performance. Fare policy and an associated ticketing system are essential to the success of MRT and the broader public transport system. Fare policy is vital because: financially, it affects the number of people who will use MRT, which in turn influences fare revenue, MRT operating costs and, ultimately, the viability of MRT lines; socially, the absolute level affects the affordability of public transport to people, while alternative fare structures have differential, and thus distributional, effects on the community; technically, it influences the form of operating concessions, and the design of the MRT system in general and the ticket system in particular; and for the remainder of transport system, the level and structure of MRT fares affects the use made of other public transport and the amount of private travel, with consequences for the transport system and community as a whole. A policy objective for HCMC, as it is in most cities that seek to provide an attractive public transport system, should be: 17
PROJECT PREPARATORY TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
 A. Justification PROJECT PREPARATORY TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE 1. The Government of Azerbaijan, the Ministry of Transport and Baku Metro Company requested ADB to help improving its urban transport system and
A. Justification PROJECT PREPARATORY TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE 1. The Government of Azerbaijan, the Ministry of Transport and Baku Metro Company requested ADB to help improving its urban transport system and
www.pwc.com/sg Delivering Rail Projects in Asia
 www.pwc.com/sg Delivering Rail Projects in Asia August 2014 2 Introduction Rail is an effective way to deliver mass transit to a large number of people. It provides fast, safe and comfortable transportation
www.pwc.com/sg Delivering Rail Projects in Asia August 2014 2 Introduction Rail is an effective way to deliver mass transit to a large number of people. It provides fast, safe and comfortable transportation
The Kingdom of Thailand: Capacity Building for the Neighbouring Countries Economic Development Cooperation Agency
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 40137 December 2006 The Kingdom of Thailand: Capacity Building for the Neighbouring Countries Economic Development Cooperation Agency The views expressed herein
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 40137 December 2006 The Kingdom of Thailand: Capacity Building for the Neighbouring Countries Economic Development Cooperation Agency The views expressed herein
Developing a Public-Private Partnership Framework: Policies and PPP Units
 Note 4 May 2012 Developing a Public-Private Partnership Framework: Policies and PPP Units This note is the fourth in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework
Note 4 May 2012 Developing a Public-Private Partnership Framework: Policies and PPP Units This note is the fourth in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework
INTRODUCTION TO PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS
 INTRODUCTION TO PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS WITH AVAILABILITY PAYMENTS Dr. Silviu Dochia, Senior Associate Michael Parker, Managing Director SUMMARY Public-private partnerships ( P3s ) can provide the
INTRODUCTION TO PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS WITH AVAILABILITY PAYMENTS Dr. Silviu Dochia, Senior Associate Michael Parker, Managing Director SUMMARY Public-private partnerships ( P3s ) can provide the
ii. Project Finance Specialist (national consultant; 9 person-months; intermittent).
 1 ADDITIONAL CONSULTANTS FOR THE PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP CENTER AND THE DEPARTMENT OF FINANCE 1. Expansion of the PPP Center s consultant pool is proposed to strengthen PPP Center s capacity in thematic
1 ADDITIONAL CONSULTANTS FOR THE PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP CENTER AND THE DEPARTMENT OF FINANCE 1. Expansion of the PPP Center s consultant pool is proposed to strengthen PPP Center s capacity in thematic
Seoul Metro line 9 O&M Contract
 Seoul Metro line 9 O&M Contract 1 1 Veolia Transport Veolia Transport is a leading operator of public transportation in Europe More than 3000 public clients 2007 annual turnover: 5.6 billion 82 000 employees
Seoul Metro line 9 O&M Contract 1 1 Veolia Transport Veolia Transport is a leading operator of public transportation in Europe More than 3000 public clients 2007 annual turnover: 5.6 billion 82 000 employees
Consolidated I&T Data Centre - P3 Canada Fund
 STAFF REPORT ACTION REQUIRED Consolidated I&T Data Centre - P3 Canada Fund Date: January 16, 2012 To: From: Wards: Reference Number: Government Management Committee Deputy City Manager & Chief Financial
STAFF REPORT ACTION REQUIRED Consolidated I&T Data Centre - P3 Canada Fund Date: January 16, 2012 To: From: Wards: Reference Number: Government Management Committee Deputy City Manager & Chief Financial
Best Practice in Design of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) for Social Infrastructure, particularly in Health Care and Education
 EMAIL contact@fosterinfrastructure.com WEB www.fosterinfrastructure.com Best Practice in Design of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) for Social Infrastructure, particularly in Health Care and Education
EMAIL contact@fosterinfrastructure.com WEB www.fosterinfrastructure.com Best Practice in Design of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) for Social Infrastructure, particularly in Health Care and Education
T o o l k i t f o r P u b l i c - P r i v a t e P a r t n e r s h i p s i n r o a d s & H i g h w a y s. PPP Modalities
 PPP Modalities Types and characteristics of PPP are presented in several sections of the Toolkit: refer Types of PPP in Key Issues. This section provides some consideration of which modality, or which
PPP Modalities Types and characteristics of PPP are presented in several sections of the Toolkit: refer Types of PPP in Key Issues. This section provides some consideration of which modality, or which
Republic of the Union of Myanmar: Support for Strengthening Public Debt Management
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 47225 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) December 2013 Republic of the Union of Myanmar: Support for Strengthening Public Debt Management The views
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 47225 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) December 2013 Republic of the Union of Myanmar: Support for Strengthening Public Debt Management The views
PPP Basics and Principles of a PPP Framework
 Note 1 May 2012 PPP Basics and Principles of a PPP Framework This note is the first in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework for public-private partnership
Note 1 May 2012 PPP Basics and Principles of a PPP Framework This note is the first in a series of notes on developing a comprehensive policy, legal, and institution framework for public-private partnership
立 法 會 Legislative Council
 立 法 會 Legislative Council LC Paper No. CB(3) 801/10-11 Ref : CB(3)/M/MM Tel : 2869 9205 Date : 26 May 2011 From : Clerk to the Legislative Council To : All Members of the Legislative Council Council meeting
立 法 會 Legislative Council LC Paper No. CB(3) 801/10-11 Ref : CB(3)/M/MM Tel : 2869 9205 Date : 26 May 2011 From : Clerk to the Legislative Council To : All Members of the Legislative Council Council meeting
Cost Management Guidelines for. 1 September 2010
 Cost Management Guidelines for Public Transport Investment Projects 1 September 2010 Table of Contents Foreword iv 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Purpose Of The Guidelines 1 1.2 Applicability 1 1.2.1 Conventionally
Cost Management Guidelines for Public Transport Investment Projects 1 September 2010 Table of Contents Foreword iv 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Purpose Of The Guidelines 1 1.2 Applicability 1 1.2.1 Conventionally
Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan)
 Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan) 1.Name of the Project Country: Socialist Republic of Viet Nam Project: Regional and Provincial Hospital Development Project (II). Loan Agreement:
Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan) 1.Name of the Project Country: Socialist Republic of Viet Nam Project: Regional and Provincial Hospital Development Project (II). Loan Agreement:
Papua New Guinea: Supporting Public Financial Management, Phase 2
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 44379 012 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) November 2012 Papua New Guinea: Supporting Public Financial Management, Phase 2 The views expressed
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 44379 012 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) November 2012 Papua New Guinea: Supporting Public Financial Management, Phase 2 The views expressed
Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Vietnamese Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2104740/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Vietnamese Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2104740/ Industry Dynamics and Competitive Landscape in the Vietnamese Non-Life Insurance Industry to 2016: Market Profile Description:
Capital Works Management Framework
 POLICY DOCUMENT Capital Works Management Framework Policy for managing risks in the planning and delivery of Queensland Government building projects Department of Public Works The concept of the asset
POLICY DOCUMENT Capital Works Management Framework Policy for managing risks in the planning and delivery of Queensland Government building projects Department of Public Works The concept of the asset
TEC Capital Asset Management Standard January 2011
 TEC Capital Asset Management Standard January 2011 TEC Capital Asset Management Standard Tertiary Education Commission January 2011 0 Table of contents Introduction 2 Capital Asset Management 3 Defining
TEC Capital Asset Management Standard January 2011 TEC Capital Asset Management Standard Tertiary Education Commission January 2011 0 Table of contents Introduction 2 Capital Asset Management 3 Defining
How To Help The Republic Of The Maldives
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 47150 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) December 2013 Republic of the Maldives: Enhancing Tax Administration Capacity (Financed by the Japan Fund
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 47150 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) December 2013 Republic of the Maldives: Enhancing Tax Administration Capacity (Financed by the Japan Fund
reliable essential service, an affordable public good and a vital ingredient in the city s quest for liveability and sustainability.
 SMRT CORPORATION CEO SPEAKS ON IMPROVING RAIL NETWORK PERFORMANCE FOR GREATER PASSENGER CONVENIENCE AND MOBILITY DURING THE ASIA PACIFIC RAIL 2014 IN HONG KONG ON 19 MARCH 2014 When we think about rail
SMRT CORPORATION CEO SPEAKS ON IMPROVING RAIL NETWORK PERFORMANCE FOR GREATER PASSENGER CONVENIENCE AND MOBILITY DURING THE ASIA PACIFIC RAIL 2014 IN HONG KONG ON 19 MARCH 2014 When we think about rail
PROGRAM EXPENDITURE AND FINANCING ASSESSMENT
 Electricity Grid Strengthening Sumatra Program (RRP INO 49080) PROGRAM EXPENDITURE AND FINANCING ASSESSMENT 1. The program expenditure and financing assessment reviews the extent to which the Electricity
Electricity Grid Strengthening Sumatra Program (RRP INO 49080) PROGRAM EXPENDITURE AND FINANCING ASSESSMENT 1. The program expenditure and financing assessment reviews the extent to which the Electricity
Planning and Design for Sustainable Urban Mobility
 1 Planning and Design for Sustainable Urban Mobility 2 1 UrbanizationUrbanization Rapid pace, largely uncontrolled growth, taking place mainly in developing countries 3 Global Urbanization Trends World
1 Planning and Design for Sustainable Urban Mobility 2 1 UrbanizationUrbanization Rapid pace, largely uncontrolled growth, taking place mainly in developing countries 3 Global Urbanization Trends World
Vietnam's Experiences in Strengthening. Procurement and Public Financial Management Systems. in Harmonization, Alignment and Capacity Development
 Vietnam's Experiences in Strengthening Procurement and Public Financial Management Systems in Harmonization, Alignment and Capacity Development Mr. Chairman, Ladies and gentlemen, Dr. Duong Duc Ung Director
Vietnam's Experiences in Strengthening Procurement and Public Financial Management Systems in Harmonization, Alignment and Capacity Development Mr. Chairman, Ladies and gentlemen, Dr. Duong Duc Ung Director
Part B1: Business case developing the business case
 Overview Part A: Strategic assessment Part B1: Business case developing the business case Part B2: Business case procurement options Part B3: Business case funding and financing options Part C: Project
Overview Part A: Strategic assessment Part B1: Business case developing the business case Part B2: Business case procurement options Part B3: Business case funding and financing options Part C: Project
List of Consulting Service Experiences:
 List of Consulting Service Experiences: Name of assignment or project: Local Partner of IXE Group for Various Projects in Indonesia Year: October 2011 October 2013 Client: Mr. Walter Bizzarri IXE Group,
List of Consulting Service Experiences: Name of assignment or project: Local Partner of IXE Group for Various Projects in Indonesia Year: October 2011 October 2013 Client: Mr. Walter Bizzarri IXE Group,
Preliminary Draft JOB DESCRIPTIONS AND QUALIFICATIONS OF KEY PERSONNEL. XXXXX PPP Unit
 Preliminary Draft JOB DESCRIPTIONS AND QUALIFICATIONS OF KEY PERSONNEL XXXXX PPP Unit Chief Executive Officer Job Description: The CEO is tasked with the establishment of a PPP Unit for the Government
Preliminary Draft JOB DESCRIPTIONS AND QUALIFICATIONS OF KEY PERSONNEL XXXXX PPP Unit Chief Executive Officer Job Description: The CEO is tasked with the establishment of a PPP Unit for the Government
DRAFT PLANNING THE OPENING OF A ROAD PROJECT GUIDELINE 1
 DRAFT PLANNING THE OPENING OF A ROAD PROJECT GUIDELINE 1 Guideline: DRAFT Planning the opening of a road project guideline Version: 1.1 Issue: September 2009 Approved By: Phil Margison General Manager,
DRAFT PLANNING THE OPENING OF A ROAD PROJECT GUIDELINE 1 Guideline: DRAFT Planning the opening of a road project guideline Version: 1.1 Issue: September 2009 Approved By: Phil Margison General Manager,
GUIDELINES FOR TOTAL PROJECT COST MANAGEMENT
 GUIDELINES FOR TOTAL PROJECT COST MANAGEMENT March 2013 MINISTRY OF STRATEGY AND FINANCE TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER Ⅰ GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 (Purpose)... 1 Article 2 (Definition of Total Project Cost)...
GUIDELINES FOR TOTAL PROJECT COST MANAGEMENT March 2013 MINISTRY OF STRATEGY AND FINANCE TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER Ⅰ GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 (Purpose)... 1 Article 2 (Definition of Total Project Cost)...
Law of Mongolia on Concessions
 Economic Policy Reform and Competitiveness Project April 2005 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development The views expressed
Economic Policy Reform and Competitiveness Project April 2005 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development The views expressed
Technical Assistance Report. Project Number: 42532 December 2008. Public Debt and Risk Management Forum
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 42532 December 2008 Public Debt and Risk Management Forum ABBREVIATIONS ADB ADF Asian Development Bank Asian Development Fund DMC PDRM SDR developing member
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 42532 December 2008 Public Debt and Risk Management Forum ABBREVIATIONS ADB ADF Asian Development Bank Asian Development Fund DMC PDRM SDR developing member
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN URBAN PLANNING (MSc[UrbanPlanning])
![REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN URBAN PLANNING (MSc[UrbanPlanning]) REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN URBAN PLANNING (MSc[UrbanPlanning])](/thumbs/27/9938136.jpg) REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN URBAN PLANNING (MSc[UrbanPlanning]) To be applicable to all students enrolled for 2012-13 academic year and thereafter. (See also General Regulations)
REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN URBAN PLANNING (MSc[UrbanPlanning]) To be applicable to all students enrolled for 2012-13 academic year and thereafter. (See also General Regulations)
Risk Management in the Development of a Penta-P Project
 Risk Management in the Development of a Penta-P Project Bill Van Meter Regional Transportation District Denver, CO Julie Skeen Jacobs Engineering Denver, CO Damian Carey Jacobs Engineering Denver, CO Don
Risk Management in the Development of a Penta-P Project Bill Van Meter Regional Transportation District Denver, CO Julie Skeen Jacobs Engineering Denver, CO Damian Carey Jacobs Engineering Denver, CO Don
A Review of Melbourne s Rail Franchising Reforms
 A Review of Melbourne s Rail Franchising Reforms Graham CURRIE Abstract This paper reviews Melbourne s rail franchising to identify lessons learned. The first franchising model sought cost efficiencies
A Review of Melbourne s Rail Franchising Reforms Graham CURRIE Abstract This paper reviews Melbourne s rail franchising to identify lessons learned. The first franchising model sought cost efficiencies
Technical Assistance Report. Project Number: 38281 December 2005. Technical Assistance Republic of the Philippines: Debt and Risk Management Project
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 38281 December 2005 Technical Assistance Republic of the Philippines: Debt and Risk Management Project CURRENCY EQUIVALENTS (as of 24 November 2005) Currency
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 38281 December 2005 Technical Assistance Republic of the Philippines: Debt and Risk Management Project CURRENCY EQUIVALENTS (as of 24 November 2005) Currency
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR:PRC 34096-02
 ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR:PRC 34096-02 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE TO THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA FOR POLICY AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT FOR SOCIAL INSURANCE ADMINISTRATION October 2003 CURRENCY EQUIVALENTS
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR:PRC 34096-02 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE TO THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA FOR POLICY AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT FOR SOCIAL INSURANCE ADMINISTRATION October 2003 CURRENCY EQUIVALENTS
GUIDE FOR EVALUATION PROCEDURES FOR EMPLOYMENT OF CONSULTANTS UNDER JAPANESE ODA LOANS
 GUIDE FOR EVALUATION PROCEDURES FOR EMPLOYMENT OF CONSULTANTS UNDER JAPANESE ODA LOANS Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) December 2006 (Amended December 2009) version 1.0 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...
GUIDE FOR EVALUATION PROCEDURES FOR EMPLOYMENT OF CONSULTANTS UNDER JAPANESE ODA LOANS Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) December 2006 (Amended December 2009) version 1.0 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...
CONCEPT AND BACKGROUND TO PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP (PPP) / PRIVATE FINANCE INITIATIVE (PFI) UK EXPERIENCE
 CONCEPT AND BACKGROUND TO PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP (PPP) / PRIVATE FINANCE INITIATIVE (PFI) UK EXPERIENCE Professor Mustafa Alshawi 11/20/2009 Chairman Iraq Institute for Economic Reforms (IIER) Baghdad,
CONCEPT AND BACKGROUND TO PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP (PPP) / PRIVATE FINANCE INITIATIVE (PFI) UK EXPERIENCE Professor Mustafa Alshawi 11/20/2009 Chairman Iraq Institute for Economic Reforms (IIER) Baghdad,
With offices in the UK, Canada and France, MDT has developed a reputation for structuring and arranging financial solutions for clients worldwide.
 MDT is a financial services and investment firm specialising in arranging equity, debt, lease and structured finance for a broad range of clients involved in capital intensive projects and industries.
MDT is a financial services and investment firm specialising in arranging equity, debt, lease and structured finance for a broad range of clients involved in capital intensive projects and industries.
GOOD GOVERNANCE FRAMEWORK
 Provincial Roads Improvement (RRP CAM 43309) GOOD GOVERNANCE FRAMEWORK In all instances, the Loan Agreement shall be the overriding legal document. Asian Development Bank () Procurement Guidelines (2010,
Provincial Roads Improvement (RRP CAM 43309) GOOD GOVERNANCE FRAMEWORK In all instances, the Loan Agreement shall be the overriding legal document. Asian Development Bank () Procurement Guidelines (2010,
SECURITIES TRADING ACCOUNT OPENING CONTRACT
 For Individual CONTRACT No:. SECURITIES TRADING ACCOUNT OPENING CONTRACT Acount No - 0 5 7 C Today DD..MM..YY at KIS VN Securities Joint Stock Company, We are : From one side A : Customer: Gender: Male
For Individual CONTRACT No:. SECURITIES TRADING ACCOUNT OPENING CONTRACT Acount No - 0 5 7 C Today DD..MM..YY at KIS VN Securities Joint Stock Company, We are : From one side A : Customer: Gender: Male
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK
 ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR: TAJ 37040 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE (Financed by the Japan Special Fund) TO THE REPUBLIC OF TAJIKISTAN FOR IMPROVING THE ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OF THE SUBSIDIARIES
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR: TAJ 37040 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE (Financed by the Japan Special Fund) TO THE REPUBLIC OF TAJIKISTAN FOR IMPROVING THE ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OF THE SUBSIDIARIES
Availability Payment Mechanisms For Transit Projects ADVISORY
 Availability Payment Mechanisms For Transit Projects ADVISORY Agenda Availability Payments Overview Structure Financial Implications Case Study Additional Considerations KPMG Infrastructure 2 What is an
Availability Payment Mechanisms For Transit Projects ADVISORY Agenda Availability Payments Overview Structure Financial Implications Case Study Additional Considerations KPMG Infrastructure 2 What is an
Capital Metro Business Case in Brief. Prepared by: CAPITAL METRO AGENCY ACT Government, GPO Box 158, Canberra ACT 2601. capitalmetro.act.gov.
 Capital Metro Business Case in Brief Prepared by: CAPITAL METRO AGENCY ACT Government, GPO Box 158, Canberra ACT 2601 capitalmetro.act.gov.au 1.0 Chief Minister s Foreword Light rail is part of a long
Capital Metro Business Case in Brief Prepared by: CAPITAL METRO AGENCY ACT Government, GPO Box 158, Canberra ACT 2601 capitalmetro.act.gov.au 1.0 Chief Minister s Foreword Light rail is part of a long
REPORT BY THE COMPTROLLER AND AUDITOR GENERAL HC 535 SESSION 2013-14 5 JULY 2013. Department for Culture, Media & Sport. The rural broadband programme
 REPORT BY THE COMPTROLLER AND AUDITOR GENERAL HC 535 SESSION 2013-14 5 JULY 2013 Department for Culture, Media & Sport The rural broadband programme 4 Key facts The rural broadband programme Key facts
REPORT BY THE COMPTROLLER AND AUDITOR GENERAL HC 535 SESSION 2013-14 5 JULY 2013 Department for Culture, Media & Sport The rural broadband programme 4 Key facts The rural broadband programme Key facts
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS I. FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY. 1. Counterpart Funds
 Health Human Resources Sector Development Program (RRP VIE 40354-01) I. FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY 1. Counterpart Funds FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 1. The proposed program loan is for $30 million and the project
Health Human Resources Sector Development Program (RRP VIE 40354-01) I. FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY 1. Counterpart Funds FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 1. The proposed program loan is for $30 million and the project
Government to Government (G2G) Implementing and Funding Mechanisms Cost Reimbursement Projects
 Government to Government (G2G) Implementing and Funding Mechanisms Cost Reimbursement Projects A Mandatory Reference for ADS Chapter 220 New Edition Date: 07/28/2014 Responsible Office: M/CFO File Name:
Government to Government (G2G) Implementing and Funding Mechanisms Cost Reimbursement Projects A Mandatory Reference for ADS Chapter 220 New Edition Date: 07/28/2014 Responsible Office: M/CFO File Name:
People s Republic of China: Strategy and Transport Policy Study on Promoting Logistics Development in Rural Areas
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 48022 Policy and Advisory Technical Assistance (PATA) August 2014 People s Republic of China: Strategy and Transport Policy Study on Promoting Logistics Development
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 48022 Policy and Advisory Technical Assistance (PATA) August 2014 People s Republic of China: Strategy and Transport Policy Study on Promoting Logistics Development
arrangements typified by joint working between the public and private sectors covering all types of collaboration across the private-public sector
 20//204 PUBLIC PARTNERSHIP PRIVATE on Institutional Arrangement and Policy Implications Case Studies from the Republic of Korea November 8, 204 Seung-Jin Baek Economic Development Division UN ECLAC What
20//204 PUBLIC PARTNERSHIP PRIVATE on Institutional Arrangement and Policy Implications Case Studies from the Republic of Korea November 8, 204 Seung-Jin Baek Economic Development Division UN ECLAC What
Integrated Fares and Ticketing Programme - update
 Report 14.630 Date 26 November 2014 File TD/11/01/02 Committee Author Council Annika Lane, Project Manager, Integrated Fares and Ticketing Integrated Fares and Ticketing Programme - update 1. Purpose The
Report 14.630 Date 26 November 2014 File TD/11/01/02 Committee Author Council Annika Lane, Project Manager, Integrated Fares and Ticketing Integrated Fares and Ticketing Programme - update 1. Purpose The
Introduction from the Chair - Michael Burnett
 OECD International Transport Forum Roundtable: Public-Private Partnerships for Transport Infrastructure Renegotiations - How to approach them and economic outcomes, George Mason University, Washington
OECD International Transport Forum Roundtable: Public-Private Partnerships for Transport Infrastructure Renegotiations - How to approach them and economic outcomes, George Mason University, Washington
Governments implement PPP programmes in the healthcare sector for one or more of a number of reasons:
 UNECE Healthcare PPP Project Team Project Brief Introduction This is a very active time globally for the healthcare sector as demand for services continues to grow exponentially, driven by rising life
UNECE Healthcare PPP Project Team Project Brief Introduction This is a very active time globally for the healthcare sector as demand for services continues to grow exponentially, driven by rising life
Interim Guidelines for the Provision of Infrastructure and Capital Investments through Public Private Partnerships:
 Interim Guidelines for the Provision of Infrastructure and Capital Investments through Public Private Partnerships: Procedures for the Assessment, Approval, Audit and Procurement of Projects Table of Contents
Interim Guidelines for the Provision of Infrastructure and Capital Investments through Public Private Partnerships: Procedures for the Assessment, Approval, Audit and Procurement of Projects Table of Contents
Integrated Public Transport. Planning. National workshop on promoting sustainable transport solutions for East Africa
 Integrated Public Transport National workshop on promoting sustainable transport solutions for East Africa Carly Koinange, GEF Sustran Consultant UN-HABITAT Urban Mobility Unit Urban Basic Services Branch
Integrated Public Transport National workshop on promoting sustainable transport solutions for East Africa Carly Koinange, GEF Sustran Consultant UN-HABITAT Urban Mobility Unit Urban Basic Services Branch
REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL SPECTATOR FACILITY FEASIBILITY STUDY ADDENDUM NO. 1
 Financial Management Services Purchasing Division Request for Proposal Spectator Facility Feasibility Study REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL FOR A SPECTATOR FACILITY FEASIBILITY STUDY ADDENDUM NO. 1 This addendum
Financial Management Services Purchasing Division Request for Proposal Spectator Facility Feasibility Study REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL FOR A SPECTATOR FACILITY FEASIBILITY STUDY ADDENDUM NO. 1 This addendum
PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP IN INFRASTRUCTURE
 A GUIDEBOOK ON PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP IN INFRASTRUCTURE ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMISSION FOR ASIA AND THE PACIFIC This Guidebook was developed by Mr. Abdul Quium of the Transport Division of ESCAP. Its
A GUIDEBOOK ON PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP IN INFRASTRUCTURE ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMISSION FOR ASIA AND THE PACIFIC This Guidebook was developed by Mr. Abdul Quium of the Transport Division of ESCAP. Its
Mai Thi Hoang Minh, Nguyen Thi Ngoc Bich. University of Economics of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
 Journal of Modern Accounting and Auditing, April 2015, Vol. 11, No. 4, 223-232 doi: 10.17265/1548-6583/2015.04.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Compliance of Documentation Transfer Pricing Requirements in Foreign
Journal of Modern Accounting and Auditing, April 2015, Vol. 11, No. 4, 223-232 doi: 10.17265/1548-6583/2015.04.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Compliance of Documentation Transfer Pricing Requirements in Foreign
UNECE PPP Healthcare Standard
 INTERNATIONAL SPECIALIST CENTRE OF EXCELLENCE ON PPPs IN HEALTH MANILA, PHILIPPINES UNECE PPP Healthcare Standard Questions on lessons learned in the development of Public-Private Partnership ( PPP ) programmes
INTERNATIONAL SPECIALIST CENTRE OF EXCELLENCE ON PPPs IN HEALTH MANILA, PHILIPPINES UNECE PPP Healthcare Standard Questions on lessons learned in the development of Public-Private Partnership ( PPP ) programmes
SUMMARY PROGRAM IMPACT ASSESSMENT
 Third Financial Sector Program, Subprogram 2 (RRP VIE 37577) SUMMARY PROGRAM IMPACT ASSESSMENT I. Introduction 1. This program impact analysis (PIA) documents the formulation of the Financial Sector Program
Third Financial Sector Program, Subprogram 2 (RRP VIE 37577) SUMMARY PROGRAM IMPACT ASSESSMENT I. Introduction 1. This program impact analysis (PIA) documents the formulation of the Financial Sector Program
Principal risks and uncertainties
 Principal risks and uncertainties Our risk management approach We have a well-established risk management methodology which we use throughout the business to allow us to identify and manage the principal
Principal risks and uncertainties Our risk management approach We have a well-established risk management methodology which we use throughout the business to allow us to identify and manage the principal
NEWSFLASH October 2009
 NEWSFLASH October 2009 INVESTING IN INFRASTRUCTURE IN VIETNAM Vietnam's need for investment in infrastructure to keep pace with and to sustain economic growth has been voiced loudly. To date, the State
NEWSFLASH October 2009 INVESTING IN INFRASTRUCTURE IN VIETNAM Vietnam's need for investment in infrastructure to keep pace with and to sustain economic growth has been voiced loudly. To date, the State
CONTRACT FOR OPENING A SECURITIES TRADING ACCOUNT
 CONTRACT FOR OPENING A SECURITIES TRADING ACCOUNT No. :. This contract is entered into on./.2013 in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, by and between: 1..Ltd (hereinafter referred as to the Client ) - Registered
CONTRACT FOR OPENING A SECURITIES TRADING ACCOUNT No. :. This contract is entered into on./.2013 in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, by and between: 1..Ltd (hereinafter referred as to the Client ) - Registered
PPP Models. Ownership of capital assets Responsibility for investment Assumption of risks, and Duration of contract.
 PPP Models The PPP models vary from short-term simple management contracts (with or without investment requirements) to long-term and very complex BOT form, to divestiture. These models vary mainly by:
PPP Models The PPP models vary from short-term simple management contracts (with or without investment requirements) to long-term and very complex BOT form, to divestiture. These models vary mainly by:
Data Communications Company (DCC) price control guidance: process and procedures
 Guidance document Contact: Tricia Quinn, Senior Economist Publication date: 27 July 2015 Team: Smarter Metering Email: tricia.quinn@ofgem.gov.uk Overview: The Data and Communications Company (DCC) is required
Guidance document Contact: Tricia Quinn, Senior Economist Publication date: 27 July 2015 Team: Smarter Metering Email: tricia.quinn@ofgem.gov.uk Overview: The Data and Communications Company (DCC) is required
Acquisition of SAIT Communications. 28 July 2015
 Acquisition of SAIT Communications 28 July 2015 Conference call details SpeedCast acquires SAIT Communications The company has scheduled a conference call as follows: Time: 11.00am (Sydney time), 28 th
Acquisition of SAIT Communications 28 July 2015 Conference call details SpeedCast acquires SAIT Communications The company has scheduled a conference call as follows: Time: 11.00am (Sydney time), 28 th
Guidance on the template contract for social impact bonds and payment by results
 Guidance on the template contract for social impact bonds and payment by results Introduction These guidance notes have been prepared to assist users of the Cabinet Office template contract. The guidance
Guidance on the template contract for social impact bonds and payment by results Introduction These guidance notes have been prepared to assist users of the Cabinet Office template contract. The guidance
Re: Accessible Transport Strategy Draft Action Plan 2012 2015
 Mobility Inclusion Unit Strategic Policy and Co-ordination Division Department for Regional Development Room 301, Clarence Court 10-18 Adelaide Street BELFAST BT28GB 5 April 2012 TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN
Mobility Inclusion Unit Strategic Policy and Co-ordination Division Department for Regional Development Room 301, Clarence Court 10-18 Adelaide Street BELFAST BT28GB 5 April 2012 TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN
Asset Management Policy March 2014
 Asset Management Policy March 2014 In February 2011, we published our current Asset Management Policy. This is the first update incorporating further developments in our thinking on capacity planning and
Asset Management Policy March 2014 In February 2011, we published our current Asset Management Policy. This is the first update incorporating further developments in our thinking on capacity planning and
Kingdom of Thailand: Strengthening Integrated Water and Flood Management Implementation
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 46231 Policy and Advisory Technical Assistance (PATA) December 2012 Kingdom of Thailand: Strengthening Integrated Water and Flood Management Implementation (Financed
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: 46231 Policy and Advisory Technical Assistance (PATA) December 2012 Kingdom of Thailand: Strengthening Integrated Water and Flood Management Implementation (Financed
Policy for the Exploitation of University Intellectual property - Formation of New Companies
 Policy for the Exploitation of University Intellectual property - Formation of New Companies 1. Introduction By law, the University owns the Intellectual property (IP) generated by its employees in the
Policy for the Exploitation of University Intellectual property - Formation of New Companies 1. Introduction By law, the University owns the Intellectual property (IP) generated by its employees in the
6.0 Procurement procedure 1 Infrastructure
 Page 6-1 6.0 Procurement procedure 1 Infrastructure 6.1 Overview Introduction Procurement procedure 1 Infrastructure consists of four parts: guidelines for understanding the strategic context for the procurement
Page 6-1 6.0 Procurement procedure 1 Infrastructure 6.1 Overview Introduction Procurement procedure 1 Infrastructure consists of four parts: guidelines for understanding the strategic context for the procurement
A Systematic Approach for the use of Climate Finance in Sustainable Transport
 A Systematic Approach for the use of Climate Finance in Sustainable Transport Stacy A. Swann (consultant with GIZ) Transport Day, Paris December 6, 2015 Page 1 Why is Financing Low-Carbon Transport Important?
A Systematic Approach for the use of Climate Finance in Sustainable Transport Stacy A. Swann (consultant with GIZ) Transport Day, Paris December 6, 2015 Page 1 Why is Financing Low-Carbon Transport Important?
Facilitating Local Hiring on Transportation Projects: A Recommendation for the Surface Transportation Authorization. Overview
 Facilitating Local Hiring on Transportation Projects: A Recommendation for the Surface Transportation Authorization Prepared by: Center for Community Change, Gamaliel Foundation, Green for All, Partnership
Facilitating Local Hiring on Transportation Projects: A Recommendation for the Surface Transportation Authorization Prepared by: Center for Community Change, Gamaliel Foundation, Green for All, Partnership
Financial Analysis, Traffic Forecast and Analysis of Railway Payment
 FIXED LINK ACROSS FEHMARNBELT Trafikministeriet, København Bundesministerium für Verkehr, Bau- und Wohnungswesen, Berlin Financial Analysis, Traffic Forecast and Analysis of Railway Payment Summary Report
FIXED LINK ACROSS FEHMARNBELT Trafikministeriet, København Bundesministerium für Verkehr, Bau- und Wohnungswesen, Berlin Financial Analysis, Traffic Forecast and Analysis of Railway Payment Summary Report
Lao PDR Public-Private Partnership Policy
 Lao PDR Public-Private Partnership Policy Supported by the Asian Development Bank GRANT-0309 LAO Governance and Capacity Development in Public Sector Management Program (Public Private Partnerships) Table
Lao PDR Public-Private Partnership Policy Supported by the Asian Development Bank GRANT-0309 LAO Governance and Capacity Development in Public Sector Management Program (Public Private Partnerships) Table
Public Sector Comparator for Highway PPP Projects. Henry Kerali Lead Transport Specialist
 Public Sector Comparator for Highway PPP Projects Henry Kerali Lead Transport Specialist Presentation Outline Purpose and Definition of PSC Basis for comparison between Public v. Private Valuing risk Characteristics
Public Sector Comparator for Highway PPP Projects Henry Kerali Lead Transport Specialist Presentation Outline Purpose and Definition of PSC Basis for comparison between Public v. Private Valuing risk Characteristics
GUIDANCE NOTE ON OUTSOURCING
 GN 14 GUIDANCE NOTE ON OUTSOURCING Office of the Commissioner of Insurance Contents Page I. Introduction.. 1 II. Application...... 1 III. Interpretation.... 2 IV. Legal and Regulatory Obligations... 3
GN 14 GUIDANCE NOTE ON OUTSOURCING Office of the Commissioner of Insurance Contents Page I. Introduction.. 1 II. Application...... 1 III. Interpretation.... 2 IV. Legal and Regulatory Obligations... 3
Cost and Financial Analysis
 Chapter 19: Cost and Financial Analysis A. INTRODUCTION The purpose of this chapter is to present examples of financial resources available to the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA), which may
Chapter 19: Cost and Financial Analysis A. INTRODUCTION The purpose of this chapter is to present examples of financial resources available to the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA), which may
Consultancy Services to re-engineer the public transport industry in Mauritius
 REPUBLIC OF MAURITIUS Ministry of Public Infrastructure and Land Transport (Land Transport Division) Request for Expression of Interest (EOI) for Consultancy Services (Authorised under Section 24 (2)(a)
REPUBLIC OF MAURITIUS Ministry of Public Infrastructure and Land Transport (Land Transport Division) Request for Expression of Interest (EOI) for Consultancy Services (Authorised under Section 24 (2)(a)
Risk Management. Risk Identification
 Management This part provides guidance on the treatment of risks on a PPP project, and; Identifies the major risks common to many PPP projects across all sectors; Allocates the identified risks between
Management This part provides guidance on the treatment of risks on a PPP project, and; Identifies the major risks common to many PPP projects across all sectors; Allocates the identified risks between
PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP HANDBOOK
 PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP HANDBOOK VERSION 2 March 2012 1 CONTENTS Section 1: Introduction to Public Private Partnerships... 3 1.1 What is Public Private Partnership?... 4 1.2 Typical PPP Delivery Models...
PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP HANDBOOK VERSION 2 March 2012 1 CONTENTS Section 1: Introduction to Public Private Partnerships... 3 1.1 What is Public Private Partnership?... 4 1.2 Typical PPP Delivery Models...
Growth of Addis Ababa
 Growth of Addis Ababa Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa Annual growth rate is 3.8% By 2020 population growth would reach to eight million.
Growth of Addis Ababa Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa Annual growth rate is 3.8% By 2020 population growth would reach to eight million.
Technical Assistance for Socioeconomic Impact of Road Crashes (Financed by the Poverty Reduction Cooperation Fund)
 Technical Assistance TAR: STU 38081 Technical Assistance for Socioeconomic Impact of Road Crashes (Financed by the Poverty Reduction Cooperation Fund) October 2005 ABBREVIATIONS ADB Asian Development Bank
Technical Assistance TAR: STU 38081 Technical Assistance for Socioeconomic Impact of Road Crashes (Financed by the Poverty Reduction Cooperation Fund) October 2005 ABBREVIATIONS ADB Asian Development Bank
Position Description
 To apply for this position, please provide an up to date resume, covering letter, and statement addressing the Key Selection Criteria in section 6 of this Position Description. Your application will not
To apply for this position, please provide an up to date resume, covering letter, and statement addressing the Key Selection Criteria in section 6 of this Position Description. Your application will not
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT
 Power Transmission Rehabilitation Project (RRP ARM 46416-002) A. Introduction FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT 1. An assessment on the financial management capacity and financial performance
Power Transmission Rehabilitation Project (RRP ARM 46416-002) A. Introduction FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT 1. An assessment on the financial management capacity and financial performance
Annex II: Terms of Reference for Management and Implementation Support Consultant (Firm)
 Annex II: Terms of Reference for Management and Implementation Support Consultant (Firm) a. Background: 1. The GoB in accordance with its Public Financial Management (PFM) Strategy & Vision and Medium
Annex II: Terms of Reference for Management and Implementation Support Consultant (Firm) a. Background: 1. The GoB in accordance with its Public Financial Management (PFM) Strategy & Vision and Medium
Position Classification Standard for Traffic Management Series, GS-2130. Table of Contents
 Position Classification Standard for Traffic Management Series, GS-2130 Table of Contents SERIES DEFINITION... 2 EXCLUSIONS... 2 OCCUPATIONAL INFORMATION... 2 TITLES... 5 EVALUATING POSITIONS... 5 GRADE
Position Classification Standard for Traffic Management Series, GS-2130 Table of Contents SERIES DEFINITION... 2 EXCLUSIONS... 2 OCCUPATIONAL INFORMATION... 2 TITLES... 5 EVALUATING POSITIONS... 5 GRADE
Department of the Environment and Local Government. Project Management. Public Private Partnership Guidance Note 7. 14 April 2000
 Project Management Project Management Public Private Partnership Guidance Note 7 14 April 2000 Guidance Note 7 14 April 2000 Project Management Contents Section Page I INTRODUCTION...1 SCOPE AND PURPOSE
Project Management Project Management Public Private Partnership Guidance Note 7 14 April 2000 Guidance Note 7 14 April 2000 Project Management Contents Section Page I INTRODUCTION...1 SCOPE AND PURPOSE
STAG Technical Database Section 13
 Risk and Uncertainty May 2014 Transport Scotland Once printed or downloaded this document is considered to be uncontrolled. For the current version refer to the Scot-TAG section of the Transport Scotland
Risk and Uncertainty May 2014 Transport Scotland Once printed or downloaded this document is considered to be uncontrolled. For the current version refer to the Scot-TAG section of the Transport Scotland
COUNTRY REPORT ON INFRASTRUCTURE AND FINANCE TAJIKISTAN TABLE OF CONTENT
 COUNTRY REPORT ON INFRASTRUCTURE AND FINANCE TABLE OF CONTENT I. COUNTRY INFRASTRUCTURE AND POLICY DIRECTIONS... 2 II. 1.1 IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS... 3 1.2 LEGAL AND REGULATORY FRAMEWORK FOR INFRASTRUCTURE...
COUNTRY REPORT ON INFRASTRUCTURE AND FINANCE TABLE OF CONTENT I. COUNTRY INFRASTRUCTURE AND POLICY DIRECTIONS... 2 II. 1.1 IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS... 3 1.2 LEGAL AND REGULATORY FRAMEWORK FOR INFRASTRUCTURE...
PROCUREMENT PROGRAMME PROCUREMENT OF CONSULTANTS HEAD OF WASTE STRATEGY AND CONTRACTS
 NORTH LONDON WASTE AUTHORITY Agenda Item No: REPORT TITLE: PROCUREMENT PROGRAMME PROCUREMENT OF CONSULTANTS REPORT OF: HEAD OF WASTE STRATEGY AND CONTRACTS FOR SUBMISSION TO: DATE: AUTHORITY MEETING 11
NORTH LONDON WASTE AUTHORITY Agenda Item No: REPORT TITLE: PROCUREMENT PROGRAMME PROCUREMENT OF CONSULTANTS REPORT OF: HEAD OF WASTE STRATEGY AND CONTRACTS FOR SUBMISSION TO: DATE: AUTHORITY MEETING 11
Pakse Urban Environmental Improvement Project (RRP LAO 43316)
 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 1. Financial viability was assessed for solid waste management (SWM) improvements, which is the project s only revenue-earning subcomponent. 1 A financial sustainability analysis was
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 1. Financial viability was assessed for solid waste management (SWM) improvements, which is the project s only revenue-earning subcomponent. 1 A financial sustainability analysis was
Programme Manager/Procurement Specialist. Suva. Capital Works Manager. As soon as possible. As follows
 JOB DESCRIPTION Position: Location of position: Reporting to: Special functional relationships: Term of Appointment: Programme Manager/Procurement Specialist Suva Capital Works Manager Capital Works Programme
JOB DESCRIPTION Position: Location of position: Reporting to: Special functional relationships: Term of Appointment: Programme Manager/Procurement Specialist Suva Capital Works Manager Capital Works Programme
Urban Road Transport in Asia s Developing Countries : Strategy for Safety and Efficiency
 Urban Road Transport in Asia s Developing Countries : Strategy for Safety and Efficiency Submission Data : 7 November 2002 Word Count : Author s Name : 3981 (2981 + 4 figure/table) Kim Jraiw Transport
Urban Road Transport in Asia s Developing Countries : Strategy for Safety and Efficiency Submission Data : 7 November 2002 Word Count : Author s Name : 3981 (2981 + 4 figure/table) Kim Jraiw Transport
UNSOLICITED PROPOSALS
 UNSOLICITED PROPOSALS GUIDE FOR SUBMISSION AND ASSESSMENT January 2012 CONTENTS 1 PREMIER S STATEMENT 3 2 INTRODUCTION 3 3 GUIDING PRINCIPLES 5 3.1 OPTIMISE OUTCOMES 5 3.2 ASSESSMENT CRITERIA 5 3.3 PROBITY
UNSOLICITED PROPOSALS GUIDE FOR SUBMISSION AND ASSESSMENT January 2012 CONTENTS 1 PREMIER S STATEMENT 3 2 INTRODUCTION 3 3 GUIDING PRINCIPLES 5 3.1 OPTIMISE OUTCOMES 5 3.2 ASSESSMENT CRITERIA 5 3.3 PROBITY
Mary Immaculate College. Travel and Expenses Policy
 1. Introduction Mary Immaculate College Travel and Expenses Policy Adopted by ABR Pro Tem on 17 Dec. 2014 Updated to comply with Circular 05/2015 from 1 st July 2015 The M.I.C. Travel & Expenses Policy
1. Introduction Mary Immaculate College Travel and Expenses Policy Adopted by ABR Pro Tem on 17 Dec. 2014 Updated to comply with Circular 05/2015 from 1 st July 2015 The M.I.C. Travel & Expenses Policy
Procurement Policy Review Feedback Summary
 The World Bank Procurement Policy Review Feedback Summary Date: NOVEMBER 10, 2014 (afternoon session with Government agencies and PMUs) Location (City, Country): HANOI, VIETNAM Total Number of Participants:
The World Bank Procurement Policy Review Feedback Summary Date: NOVEMBER 10, 2014 (afternoon session with Government agencies and PMUs) Location (City, Country): HANOI, VIETNAM Total Number of Participants:
Capital Expenditure Guidelines
 Division of Local Government Department of Premier and Cabinet Capital Expenditure Guidelines December 2010 These are Director General s Guidelines issued pursuant to section 23A of the Local Government
Division of Local Government Department of Premier and Cabinet Capital Expenditure Guidelines December 2010 These are Director General s Guidelines issued pursuant to section 23A of the Local Government
Ministry Of Health Registration of Interest
 Ministry Of Health Registration of Interest Intermediaries Social Bond Pilot(s) Part 1 Instructions and Supporting Information What s inside? Introduction to Social Bonds Purpose of the ROI Instructions
Ministry Of Health Registration of Interest Intermediaries Social Bond Pilot(s) Part 1 Instructions and Supporting Information What s inside? Introduction to Social Bonds Purpose of the ROI Instructions
VALUE ADDED TAX in GREATER CHINA Risks and Opportunities
 VALUE ADDED TAX in GREATER CHINA Risks and Opportunities Mr. Michael Lorenz German Attorney at Law, Registered Foreign Lawyer in Hong Kong and Vietnam Lorenz & Partners Page 1 About Lorenz & Partners We
VALUE ADDED TAX in GREATER CHINA Risks and Opportunities Mr. Michael Lorenz German Attorney at Law, Registered Foreign Lawyer in Hong Kong and Vietnam Lorenz & Partners Page 1 About Lorenz & Partners We
