The Problems Of Rural Tourism In Czech Republic
|
|
|
- Pamela Freeman
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Limiting factors in the field of business activities in rural tourism Faktory omezující podnikatelské aktivity ve venkovském cestovním ruchu K. RYGLOVÁ Mendel University of Agriculture and Forestry, Brno, Czech Republic Abstract: This paper deals with problems of rural tourism development. The works is focused on researching the situation in the area of rural tourism in the Czech Republic, on understanding the attitudes of entrepreneurial sphere and rural population to this entrepreneurship and mainly on the determination of limiting factors that prevent this form of tourism from a more distinctive development. Rural tourism in the Czech Republic is still in the initiating stage of its development and it is not as developed as in some countries in West Europe. This goal has been reached with the help of primary questionnaire inquiry among business and agricultural subjects in rural areas in the individual regions and the detail results of this questionnaire inquiry are enclosed to the following paper. These identified factors were mainly insufficient financial means and at the same time insufficient state assistance connected with this. Insufficient awareness of this support as well as its inaccessibility for small business appears to be a difficulty, too. From the other obstacles, we can mention the current legislation system, bureaucracy, the state of communication and tourist infrastructure, fears of neighbours intolerance and losing privacy and also unfamiliarity and little experience. Key words: rural tourism, agrotourism, entrepreneurship, limiting factors Abstrakt: Příspěvek se zabývá problematikou rozvoje venkovského cestovního ruchu. Práce je zaměřena na zjištění situace v oblasti venkovského cestovního ruchu v České republice, na pochopení postojů podnikatelské sféry a venkovských obyvatel k tomuto podnikání a zejména na určení limitujících faktorů, které brání výraznějšímu rozvoji této formy turistiky. Venkovská turistika je v České republice stále v počáteční fázi svého rozvoje a není rozvinuta tak, jako v některých zemích západní Evropy. Tohoto cíle bylo dosaženo pomocí primárního dotazníkového šetření mezi podnikatelskými a zemědělskými subjekty ve venkovských oblastech v jednotlivých krajích, jehož detailní výsledky jsou také součástí následujícího příspěvku. Identifikovanými faktory byly zejména nedostatečné peněžní prostředky a s nimi spojená nedostatečná státní podpora. Problémem je také nedostatečná informovanost o této podpoře a její nedosažitelnost pro drobné podnikatele. Dalšími překážkami je současná legislativa, byrokracie, stav komunikací a turistické infrastruktury, obavy z netolerance sousedů a ze ztráty soukromí a také neznalost a málo zkušeností. Klíčová slova: venkovský cestovní ruch, agroturistika, podnikání, omezující faktory INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE Tourism in our country as well as in the world is a segment of economy that is developing in a very dynamic way. With its volume of sales, it takes the third position in the world after petrochemical and car industries and at the same time, thanks to its scope of employment and creation of quality job opportunities, it falls into the group of the most important economic branches. The Czech Republic has significant preconditions for the development of tourism not only owing to Supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (Grant No. MSM ) and within the framework of the institutional research of the Faculty of Business and Economics, MUAF Brno. AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
2 its position in the centre of Europe but also thanks to its attractiveness in the form of nature beauties and cultural and historical amenities. Besides traditional products of tourism, there is also a new space which is opening for the development of tourism in the country. Structural changes, transformation and restitution of property legal proceedings after the year 1989 had a great impact on agriculture and the country area and they complicated the situation in employment, transportation and infrastructure. One of the possibilities that can at least partially contribute to the improvement of this oppressive situation is coming forward directly to country inhabitants themselves, and it is to provide what they dispose and what distinguishes them from cities countryside, calm, relaxation, traditions and customs, clean air and others. Rural tourism offers the solutions of utilizing all the treasures of the country in all its forms, such as agrotourism, ecoagrotourism, ecotourism etc. These alternative entrepreneurial activities are searched for directly by agricultural subjects themselves as another or additional financial source for obtaining and maintaining their main business activities, which is agricultural primary production, and also as the realization of a part of their own agricultural production directly on the farm. Rural tourism is not only a potential source of income for agricultural subjects and rural tourism facilities providers, but it also helps with creating new job opportunities and so it can also be beneficial for other rural inhabitants. They can contribute to the development of their village, urban area or region by offering accommodation services as well as mediating other activities in the area of trade, hospitality, handicraft, machinery maintenance etc. Activities connected with organizing the accompanying programmes for tourists (entertainment, sport, local attractions and others) are also of a high importance. The development of rural tourism and its specific products counts among very important tools for the economic recovery of regions, but there are also many other facts for which this area of tourism deserves more attention. Its other contribution can be seen in the stabilization of country population, landscaping, then also in the limited scope of ecological risks connected with it, mediating man s return back to nature and respecting natural environment. This work is aimed at determining the situation in the area of rural tourism in the Czech Republic, at understanding the attitudes of entrepreneurial sphere and country population to this kind of business and especially at determining limiting factors that hinder more distinctive development of this form of tourism. For reaching this goal, a primary questionnaire inquiry was used; it was conducted among the entrepreneurial and agricultural subjects in the country within the scope of the individual NUTS II regions in the Czech Republic. MATERIALS AND METHODS At present, tourism counts among the leading economic activities in most economically developed countries. Čertík (2001) states in his publication that according to the data of the WTO (World Tourism Organization) and the WTTC (World Travel and Tourism Council), tourism industry is the biggest employer in the world and one of the most profitable branches of world economy. According to the WTO estimations, tourism industry contributes to gross domestic product in the world with almost 11% and it employs approximately 11% active world population (in the Czech Republic 9 10%), and its following dynamic development is still expected. The significance of tourism, as Pourová (2000) states furthermore, is also given by the fact that it secondarily affects many other branches of national economy in a positive way, especially transportation, trade, building industry, agriculture (agrotourism), culture and sports and so on. Considering this secondary importance, we have to admit that tourism in global standards is on the first place in creating job opportunities (Figure 1). Tourism influences employment contributes to GD contributes to the balance of payment of a country creates incomes to the state budget influences the incomes to the budgets of regions positively influences investment activities Figure 1. Macroeconomic importance of tourism Source: Pourová 2002, p AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
3 Table 1. Latent potential of tourism and traveling for new member countries of the EU Country Change from current levels by moving to the EU 15 performance for each component of Travel & Tourism demand T&T Industry T&T Economy T&T Industry T&T Economy GDP ( milliard) Cyprus Czech Republic Estonia Hungary Latvia Lithuania Malta Poland Slovakia Slovenia Total Source: Welcoming the new EU member states with jobs and growth (2004) jobs According to Malá (1999), tourism also plays an important part in the revitalization of economically weak areas. The multiplication effect of tourism enables to keep, or as the case may be to create new job opportunities and financial sources for the development of such areas. Table 1 demonstrates the latent potential and increasing importance of tourism in new member countries including the Czech Republic as calculated by the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC). The estimations concerning increasing share in GDP and creating new job opportunities were calculated with the help of averages that are current in the former EU 15 countries and the following application of the established data on new member countries. The analysis reveals that ten of these accession countries can make other 46.9 milliard and this branch could create other 3 million new job positions. For the Czech Republic, such latent potential of tourism represents additional milliard and almost new job positions. In their works, many authors mention new products of tourism that have ideal conditions for their more striking development in the Czech Republic. Apart from traditional products of tourism, such as spa treatment, urban tourism, cultural cognitive tourism and so on, there is an opportunity for rural tourism in the Czech Republic, as mentioned in the publication Odvětví cestovního ruchu by Němčanský (1999). Rural tourism with its subproducts (agrotourism, ecotourism and others), as a product of sustainable development of tourism, can be applied more or less broadly even in nature reserves and national parks. Vaško (2002) discusses the whole range of new forms of tourism that are associated by thoughtfulness towards tourism destinations, consideration for nature as well as entire environment, for cultural and historical treasures and also consideration for relationships among people. These new forms of tourism are included in so-called green tourism. Green tourism is characterized by the desire of visitors to blend in with nature as well as human environment. It is a kind of tourism with mainly active content, respecting and protecting nature. It appears mainly in the form of ecotourism and rural tourism. Cottage and farmhouse stays are ranked among the repeated recreational stays and the other forms of rural tourism agrotourism, ecotourism, ecoagrotourism and others among one-time tourist and recreational stays (Figure 2). Similarly as determining appropriate goals for the realization of each business activity is very important, also the objectives of rural tourism are determined and defined in the way described by Čertík (2001): To stimulate the development of further business activities in the country To decongest the overloaded infrastructure of towns To reduce the migration of rural population to towns and to stabilize rural area AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
4 Green tourism ecotourism rural tourism agrotourism rural tourism ecoagrotourism cottage and farmhouse stays Figure 2. The structure of green tourism Source: Pourová 2002, p. 43 To respect natural environment, maintain and develop it To contribute to landscape creation and general environmental care To popularize local beauties, uniqueness and traditions, contribute to their maintaining and development To return the man to nature Rural area 1, as it is defined, is connected with low population density, open space and settlements of not more than inhabitants. As far as soil utilization is concerned, agriculture and forestry are predominating, as well as nature reserves and national parks. The society living in these regions has strong tendencies to traditionalism the influence of traditional customs and past years is quite strong in most cases. For these reasons, rural tourism should have the following characteristics, as Janotka (1999) describes. It should be: Located in rural regions Functionally rural, established on the specific features of rural world small-scale production, open space, contact with nature, heritage of the past, traditional customs and manners Rural in its standard, i.e. small buildings, small settlements Traditional in its character slow and organic development in connection with local families Sustainable in the meaning that its development should help to maintain the rural character, should not liquidate local resources and specifics. The resource of rural tourism should be considered to be a tool for financing nature and landscape protection and sustainable development rather than a tool for further urbanization and fortune increase Rural tourism consists of many kinds and forms of activities and services which are a follow-up to the specific conditions of rural environment, village and family traditions and customs and specific initiatives of individuals and families in providing such services The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has conducted a study focusing on the problems of rural tourism and the contribution of this form of tourism to the development of the country 2. As it is stated in this source, tourist activities can be divided into typically rural ones or, on the contrary, typically urban ones, and also those that are on the boundary between rural and urban tourism. These types of activities can be seen in Table 2. Tourism does not include only accommodation or boarding for tourists, but also the care for their leisure time. Well-organized tourism should also contain interesting and attractive accompanying programmes that together with accommodation and boarding services act as the whole offered product. This does not only mean activities organized by the provider of the services, but mainly the activities in the connection with the surrounding environment. Stříbrná (2002) mentions the following: Boarding the offer should concentrate on food and customs connected with the village. For example bio-food in connection with organic agriculture or typical rural meals, regionally then at local specialities (wine-making areas) Agricultural activities recuperation activities linked with the help of tourists 1 For the classification of regions EU uses the methodology of the OECD based on the criterion of the recalculated population density. According to this methodology, NUTS 3 regions are divided into three types: predominantly rural regions more than 50%population live in rural settlements (for this purpose defined as villages with fewer than 150 inhabitants per 1 km 2), significantly rural regions 15 50% inhabitants live in rural settlements. In the CR, all regions except for the region of Vysočina predominantly rural region fall into the category of significantly rural regions (the programme for rural development for the period ). 2 Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Tourism strategy and rural development. Paris, AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
5 Table 2. The differentiation of typically rural and typically urban forms of tourism Typically rural holiday Holiday with the features of rural or urban holiday Hiking swimming sightseeing Mountaineering Adventure holiday holiday on little or medium frequented beaches downhill skiing in medium frequented places Typically urban holiday/in holiday resorts shopping holiday on the beach in highly frequented places Canoeing golf downhill skiing in highly frequented places Rafting holiday oriented at learning holiday oriented at urban traditions about traditions Cross-country skiing holiday oriented at nature protection zoological gardens Downhill skiing in little frequented places educational holiday spas Studying nature cultural shows industrial tourism Hunting holiday devoted to handicraft important conferences/meetings Cycling camping holiday in resorts Horse-riding sightseeing sports events Studies of rural traditions Chill-out holiday Conferences/meetings of lower importance Fishing conferences of lower or medium importance sailing/entertaining sails fishing at sea Source: Tourism strategy and rural development (1994) popular sports football, hockey Horse rides and horse-riding schools offering these services depends on the possibility of the farmer s agricultural subject to have or to keep horses. This can also be mediated by another business subject Hunting, fishing, mushrooming again depends on the complete background of the subject, its scope of property in terms of woods and ponds Summer and winter sports also the character of the surrounding countryside plays an important part. The offer can include hiking, cycling, swimming, mountaineering, in winter ice-skating, skiing etc. Local sights can be ranked among other accompanying programmes. The information about these attractions represents a certain packaging, as Pourová (2000) describes, in which the complete offer is presented. The same can also be applied to natural uniqueness, local customs, ethnographic traditions and others. For the accompanying programmes it is highly important to create a complex offer and the compact programme of the stay. Its specific form will always be dependant on the character of the village itself, its facilities and the character of wider environment (Malá 1999). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION First references concerning rural tourism and agrotourism in the Czech Republic come from 1993, when 15 farms begun to conduct their business in this field. A year later, there were already 51 of them and the attendance was represented by 800 tourists. Nowadays, approximately people spend their holiday at farms and one third of them are foreign tourists. According to the ECEAT organization, the length of their stay does not change and remains on the level of 3 4 days. When the guests come by the means of travel agencies, they stay for up to 7 days, which represents the length of programme packages. Among accommodation providers for rural tourism, we can find running farms, small campsites, country cottages, summer flats, boarding houses and also themed hotels. Nowadays approximately entrepreneurs work in the area of rural tourism services these estima- AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
6 Table 3. The structure of respondents according to the individual regions in the Czech Republic The structure of responders NUTS II Region SE SW MS SE SW CM CB The number of respondents % of respondents SE South-east, SW South-west, MS Moravian-Silesian region, SE South-east, SW South-west, CM Central Moravia, CB Central Bohemia, CR the Czech Republic CR tions come from the total number of subjects found in catalogues of various travel agencies and tourist information centres. However, in the Association of the Entrepreneurs of the Czech Republic (Svaz podnikatelů ČR), only subjects are registered. The most wellknown accommodation facilities for rural tourism can be found especially in Šumava, the South of Bohemia, in the Podkrkonošský region and in the Orlické mountains. However, the literature dealing with this form of tourism can see a big growth potential in other places, too, when the variety of the countryside, tourist attractiveness and rather good infrastructure are taken into account. At present times, there are programmes offering rural tourism in the Czech Republic that are covered by the Association of the Entrepreneurs of the Czech Republic in cooperation with the ECEAT organization (European Centre for Ecological and Agricultural Tourism) and the allowance organization of the Czech Centre of Tourism Czechtourism. These programmes represent a compact offer of services in the frame of projects Holiday in the Country (Prázdniny na venkově), Green Holiday (Zelené prázdniny) and Heritage Paths (Stezky dědictví). Below you can find the results of the conducted primary inquiry the main goal of which was to identify the factors that limit business activities in tourism in the rural areas. The partial goals were to assess the current conditions for the rural tourism development, to obtain information about tourist attendance and to analyse tourism clientele in the individual regions in the Czech Republic, then also to find out the attitudes and plans of business and agricultural subjects concerning rural tourism, to determine the most frequent areas of business in rural tourism and to detect the level of awareness of the supplementary state benefits for the area of rural tourism. The questionnaire survey was conducted in February and March An agricultural and business subject acting in the country was taken as the established basic unit of marketing research, so the basic set is represented by subjects carrying out agricultural activities or activities fitting into the area of rural tourism. A non-comprehensive inquiry was suggested for the marketing research, when only a certain sample of units was questioned, especially for financial and time reasons. The intentional selection was used for the research, when agricultural subjects and subjects working in the area of rural tourism services were selected intentionally. The inquiry concerns statistical regional units on the level of NUTS II and at the same time the research is limited to only seven out of eight regions in total, in other words all NUTS II regions apart from Prague. In total 309 questionnaires were distributed (154 to farmers, 106 to the ECEAT members and 49 to campsite providers), and 153 of these were then available for further processing. So the returnability was as high as 50%. The structure of respondents according to the individual NUTS II regions of the Czech Republic is shown in Table 3. Tourist attractiveness of monitored regions Respondents from individual regions mostly agreed on the attractiveness of living and natural environment from the point of view of rural tourism development. As a great advantage for tourism, they mentioned especially natural resources (87%), cycling and hiking paths were also assessed positively (60%) as well as the occurrence of traditional folk architecture and maintaining local traditions that could become a part of an interesting offer for tourists for their uniqueness. It is important not only to maintain such traditions, but also to offer them in an appropriate way and to benefit from their existence in favour of the area of their occurrence. On the other hand, the region representatives were not satisfied with tourist infrastructure (60%), transport accessibility (50%), and the occurrence of sports facilities (60%). 3 The data updated 1 st Jan 2006 were found on the ECEAT website. Available at AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
7 Investments in sports facilities downhill skiing, swimming pool areas are exactly the right way how to improve complete facilities of regions, but at the same time the places could become more attractive for tourist clientele. Tourist attendance in the individual regions has an increasing tendency according to approximately half of the responders. The Czechs are the most common visitors of these regions (27%), as to foreign visitors we can find the same nationalities as those mentioned in the national statistics, i.e. tourists from Germany (17%), the Netherlands (19%) and Poland (11%). Among the tourists, we can also find visitors from Austria, Slovakia, France, Belgium, but also from Lithuania, Estonia, Denmark, Switzerland or the USA. The respondents attitudes towards rural tourism This part of the work concludes and discusses the results concerning the respondents relationship towards entrepreneurial sphere in rural tourism. The level of awareness of rural tourism, planned expansion of current activities into rural tourism as well as the attitudes towards business in connection with demographic characteristics of respondents was determined in this part. Nearly 80% respondents are aware of the term agrotourism and they were able to define this term. There can be various reasons for the unawareness of this term the unawareness of problems or unwillingness or inability to explain it in their own words. At the same time, the existing connection between the awareness and the preferences of rural tourism was found. We can say that those who are informed incline to starting business in this area. Nevertheless, even the awareness can be a factor impeding starting the business. 87% respondents who were aware of this term said no to the possibility of expanding their enterprise into the area of rural tourism. Subjects from rural areas are open to business in rural tourism (approx. 60%) and they are considering the possibility to expand to this sphere (21%). In all the monitored regions, rural tourism sympathizers can be found. In most cases, the centre of entrepreneurs attention concerns accommodation in private facilities without boarding (over 40%). Other favourite activities include hiring sports equipment (over 35%), organizing picnics in the countryside (approx. 36%), leisure time activities for tourists (fishing, hunting), and also direct sale of agricultural products or horse-riding tourism. A very important fact is that respondents expressed positively for enterprise in several areas of rural tourism and so they try to provide a wider offer of their services with the aim to address more groups of tourists. Besides accommodation services, a facility can also ensure many other ways of spending free time, for instance in case of bad weather painting, weaving, clay modelling, making leather products, woodcarving and smithery workshops. This does not mean that business subjects themselves should dispose of all of these. Their task is rather to map their surroundings, gain information about opportunities and activities that might be interesting for tourists and with the help of which they could become even more attractive through the appropriate promotion. The concept of agrotourism farm in the form of sports grounds is also one of the European trends; then the offer includes for example combat games with blank shells or the Asian martial sports (aikido, sumo, karate). There is also a purely ladies entertainment fashion shows, aerobics, lectures about diets, health habits, make up and cosmetics, making decorations for household, such as flower arrangement, decalcomania, needlework, knotting and other ways of possible accompanying services. Another asset of the facility can be special services that add a certain exceptionality to the facility and help differentiate it from competitive services. These extra services also attract a specific target group of clients. Among popular services, mainly in West European countries, we can find for instance the offer of depositing valuables, saunas, laundries, babysitting, training facilities or possibilities to organize social events, equipment for disabled visitors, possibility to accommodate pets and so on. 70% respondents see rural tourism as beneficial for increasing businessmen or farmers income, and they find even a higher importance in the opportunity for self-realization. The responses for such benefits as, for example, possible stability of population or increasing living standards developed in rather an opposite way. Half of the respondents agreed with the positives of increasing the awareness about the village or creating new job positions. 61% men and 39% women participated in the survey. During the inquiry, it became evident that women are those who run the activities in rural tourism, but men rather incline to the idea of starting such business, while women keep more careful and hesitating attitudes. 51% respondents stated agriculture as their economic activity. The relationship of independently working farmers towards the enterprise in rural tourism was being found during the survey, and the AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
8 outcome showed that they are interested in the area of rural tourism (30% of them are interested and 32% already conduct such activities, 23% do not know and 15% farmers refused completely). Even the age of the respondent can play a certain role when deciding about the rural tourism business. It was shown that although the older generation has its representatives among the subjects working in rural tourism, younger people seem to be more open towards these activities. Concerning privately owned properties, an agricultural farm and then a family house were mentioned most often. More than half of all the business subjects working in rural tourism are owners of farmhouses, and 65% of the subjects planning to expand into rural tourism own farms. Then it was shown that the owners of family houses would rather not start to conduct business in rural tourism. The main reason are probably worries about losing privacy mentioned a few times before. Also reached education can have limiting effects on beginning activities in the area of rural tourism. University graduates or secondary educated people incline towards these activities more offer. The most significant factors limiting the development of business activities in rural tourism As presented in Table 4, the respondents consider the lack of financial means needed especially for reconstructing and constructing buildings used for rural tourism to be the greatest barrier. According to the results of the survey, it is difficult to obtain the financial means even despite the existence of state supporting programmes. Insufficient awareness of the possibilities of such state assistance is seen as another limiting factor 64% respondents are not informed about the programmes coming under the state assistance. Unavailability of this support due to strict conditions that have to be fulfilled appears to be a problem. Another difficulty is the fact that at first a project has to be financed from the entrepreneur s own means and only after that the grant can be asked for. It was also proved that the unawareness of the state support possibility can play a highly important part in making the decision. It is possible that in case of a higher knowledgeability, more responders would be interested in enterprise in rural tourism in comparison with the results of the survey (26%). One of the possibilities of making the state support available also for small businessmen is simplifying the conditions for gaining it, simplifying the administration and also a higher transparency of financial flows, so that the means are fairly distributed and they meet the objectives for which they were provided. Only after that the situation in tourism development can advance in a positive direction and not only will those who have an easy access to the means profit from it. 4 The current legislation is also seen as a barrier by 2/3 of the responders. Entrepreneurs registered according to the Agricultural Law cannot, according to this law, conduct their business in other areas such as rural tourism, for instance. It is inevitable to apply for a trade certificate in this area, for which in some cases the aforementioned subject has to have professional qualifications. Other difficulties are Table 4. The order of the most important factors limiting rural tourism business The shortage of financial means Missing accommodation capacity Unawareness of the problem. little experience Source: Bálková (2006) % Current legislation and bureaucracy % The state of communication and tourism infrastructure % Fears of misunderstanding from neighbors side % % Fears of losing privacy % % The shortage of time % Unattractive surroundings % 4 To give an example, one of the respondents mentioned a specific problem of the LEADER programme when one of the MAS selection boards approves projects and allocates funds particularly to the subjects that are the MAS members and therefore there are not enough financial means remaining for local farmers who are considering to provide accommodation services. 428 AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
9 complicated conditions and the enormous amount of bureaucratic acts connected with entrepreneurship, which is impossible to cope with during the standard operation. Poor state of communication is a real problem of the whole Czech Republic and this concerns unsatisfactory tourist infrastructure, too. On the other hand, tourist and cycling tracks as parts of this infrastructure were considered to be satisfactory. Despite the fact that individual regions dispose of rather a consistent network of cycling and hiking paths, not all of them achieve qualities high enough to attract larger numbers of tourists. Approximately half of the respondents assume that insufficient accommodation capacity as a part of tourist infrastructure is one of the factors that limit more considerable development of rural tourism. Intolerance and misunderstanding from neighbours side were also mentioned among the limiting factors, as well as a local board s envy. This problem can be caused by the villagers feeling of losing peace and rural comfort and so they can create obstacles for a business subject by complaining at the local authorities. This area is linked with another defined problem, and that is the fear of losing privacy. Such fears usually arise in case of the owners of family houses who do not have premises as sufficient as farmers to offer. Then there is a possibility to use the titles of subsidises and to construct an independent object to be used by tourists. The issue of unawareness and also insufficient experience can emerge from rural communities characteristics that are not prepared enough yet to diversify the existing activities. This problem could be solved by a suitable organizational structure of the village in the frame of which an association for supporting tourism could exist. Such associations are missing in villages as well as in regions. This unit could serve as a consultant and a coordinator of the country development including the area of rural tourism and it would have certain competences, for example selective procedures for development projects, monitoring correct and purposeful drawing of the EU funds for rural development and so on. It could also create new job opportunities and avert the outflow of young qualified inhabitants who could find their self-realization in this unit. Younger generation will bring new ideas and so it can change the traditionalistic tendencies that are inclined to by the older generation living mostly in these rural areas. The shortage of time needed for tourists and not very attractive surroundings are considered to be rather marginal issues by the responders, one third, respectively one fifth of them mentioned these matters. The support of tourism from the part of the village and the state, the promotion of facilities Nearly 60% respondents think that tourism is not supported in their village. As the most common ways of support, they mentioned investments in local infrastructure and the support of promotion via promotion materials. 8 respondents mentioned the support in the form of grants and 4 of them also stated the village s interest in educating their inhabitants in the area of tourism. The support of rural tourism is quite widespread in West European countries and it has many forms. One of them is the exemption from natural person income taxation depending on the number of beds to rent, which is undoubtedly a motivating factor. Another form of support is providing soft loans for reconstructions. Enterprise in agrotourism is permitted without a licence deed and there are trainings for tourist facilities providers starting their business. Then, there are organizations of country businessmen in agrotourism that represent the providers interests and coordinate the general development. Such organizations are mostly supported by the state and the additional amount of financial resources comes from the members fees. Despite the fact that in the Czech Republic the support of rural tourism exists in the form of financial support from the Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Local Development and also in the form of educational and consultant services (courses, seminars, conferences), it is not provided in such an extent and structure as in some EU countries. When promoting their facility, the respondents mostly rely on the effect of their websites (approx. 77%) and also satisfied customers references (73%). The ECEAT organization which offers the opportunity of promoting facilities on its web pages was mentioned by not more than 50% respondents. As an explanation to this fact, a few respondents stated increasing prices for the services provided. This fact can also be seen as one of the problematic areas. The organization originally created to support this area is too expensive for some providers. In case of lower prices, the organization could have more members than it has now 5 who with the help of a suitable promotion could have more clients and so higher profits and success organized members of the ECEAT organization. AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
10 Missing cooperation of business subjects that is common in the countries with developed tourism is another problem. In our conditions, we can rather meet the mutual jealousy and the unawareness of the importance and profitability of common operation in meeting tourists needs and requirements. The promotion of facilities, which is for example used by providers of rural tourism in Holland, can be a tourist attractive network with the help of which providers mutually support one another. Various ways of cooperation bring various advantages: Sharing clients higher occupancy rate (when the businessmen activities differ). Lower financial contribution form every entrepreneur (financially demanding promotion materials, participating at trade fairs of tourism as the entrepreneurs of one region). Creating sufficient unique sale qualities or a new product (e. g. cycling paths network, more accommodation facilities, refreshment facilities along the paths etc.). We can take a programme working in Austria as an example. It is called The Holiday at the Country Yard or Farm Holiday (Dovolená na selském dvoře) and it provides a sufficient income to farms in Austria but not a long time ago this kind of tourism was the weakest segment of Austrian tourist industry (problems in the area of marketing or creating a product of tourism). These imperfections were solved with the help of the institutional background and the state support. So called Host Associations (Sdružení hostitelů) were created in the individual regions of Austria whose members exchange their experience, hold collective seminars, trainings and many other events. Although rural tourism is considered to be one of the new forms of tourism in the Czech Republic, it is inevitable to see it as one of the tools that can help at least partially solve the problems of the Czech rural areas which have emerged after agriculture restructuring. For this, it is necessary to know the preconditions of the development of this form of tourism existing in the Czech Republic, but also to consider the difficulties that those interested in running tourist facilities meet. CONCLUSION This paper summarizes the results of the project the aim of which was to identify factors that limit business activities in rural tourism. This goal was achieved by a questionnaire survey of entrepreneurial and agricultural subjects in rural areas in individual NUTS II region of the Czech Republic. The work was aimed at several partial areas in which the conditions for rural tourism development were assessed and the attitudes and plans of the investigated subjects towards rural tourism business were found. Furthermore, the support of this form of tourism was assessed from the part of villages as well as the state, and the connections between the identification data of the responders and their attitudes towards rural tourism enterprise were followed. An independent area of the survey was devoted to the main goal of investigation and there the most significant factors limiting the development of this form of tourism were identified. These identified factors are mainly insufficient financial means and at the same time insufficient state assistance connected with this. Insufficient awareness of this support as well as its inaccessibility for small business appears to be a difficulty, too. From the other obstacles, we can mention the current legislation system, bureaucracy, the state of communication and tourist infrastructure, fears of neighbours intolerance and losing privacy and also unfamiliarity and little experience. Another problem is the ownership of the property, namely family houses, the conservatism of older generation and education. The results mentioned above are a part of the research project, id. code VZ: Czech economy in the process of integration and globalization and the development of agrarian sector and service sector in new conditions of the European integrated market, thematic complex 03 The development of business sphere relations in connection with the changes in lifestyle in the terms of purchasing behaviour of population and the changes of business environment in the processes of integration and globalization that was realized with the financial support of public funds via the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic MŠMT. REFERENCES Bálková E. (2006): Identifikace faktorů brzdící podnikatelské aktivity v cestovním ruchu na venkově (Identification of the factors limiting the business activities in the rural tourism sphere). [Diploma Thesis.] MZLU, Brno. Čertík M. (2001): Cestovní ruch vývoj, organizace a řízení (Tourism development, organization and management). OFF, Praha; ISBN Janotka K. (1999): Venkovská turistika a agroturistika specifické segmenty cestovního ruchu (Rural 430 AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
11 turism Specific segments in tourism). SOŠ CR Pardubice. Malá V. (1999): Cestovní ruch (Tourism). VŠE, Praha; ISBN Němčanský M. (1999): Odvětví cestovního ruchu (Tourism industry). Slezská universita, Karviná; ISBN Pourová M.(2000): Agroturistika (Agrotourism). ČZU, Praha; ISBN Stříbrná M. (2002): Venkovská turistika (Rural tourism). MMR, Praha; ISBN Vaško M. (2002): Cestovní ruch a regionální rozvoj (Tourism and rural development). VŠE, Praha; ISBN Welcoming the new EU member states with jobs and growth (2004): A practical manifesto from the travel and tourism private sector. World Travel & Tourism Council, London. Tourism strategy and rural development (1994). Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris. Arrived on 24 th May 2007 Contact address: Kateřina Ryglová, Mendel University of Agriculture and Forestry in Brno, Zemědělská 1, Brno, Czech Republic tel.: , katkag@mendelu.cz AGRIC. ECON. CZECH, 53, 2007 (9):
Human resources development in rural areas of the Czech Republic
 Human resources development in rural areas of the Czech Republic Vývoj lidských zdrojů ve venkovském prostoru ČR L. Svatošová Czech University of Life Sciences, Prague Czech Republic Abstract: al development
Human resources development in rural areas of the Czech Republic Vývoj lidských zdrojů ve venkovském prostoru ČR L. Svatošová Czech University of Life Sciences, Prague Czech Republic Abstract: al development
Statistical Data on Women Entrepreneurs in Europe
 Statistical Data on Women Entrepreneurs in Europe September 2014 Enterprise and Industry EUROPEAN COMMISSION Directorate-General for Enterprise and Industry Directorate D SMEs and Entrepreneurship Unit
Statistical Data on Women Entrepreneurs in Europe September 2014 Enterprise and Industry EUROPEAN COMMISSION Directorate-General for Enterprise and Industry Directorate D SMEs and Entrepreneurship Unit
RETAIL FINANCIAL SERVICES
 Special Eurobarometer 373 RETAIL FINANCIAL SERVICES REPORT Fieldwork: September 211 Publication: March 212 This survey has been requested by Directorate-General Internal Market and Services and co-ordinated
Special Eurobarometer 373 RETAIL FINANCIAL SERVICES REPORT Fieldwork: September 211 Publication: March 212 This survey has been requested by Directorate-General Internal Market and Services and co-ordinated
RETAIL FINANCIAL SERVICES
 Special Eurobarometer 373 RETAIL FINANCIAL SERVICES REPORT Fieldwork: September 211 Publication: April 212 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General Internal Market
Special Eurobarometer 373 RETAIL FINANCIAL SERVICES REPORT Fieldwork: September 211 Publication: April 212 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General Internal Market
Ferratum Group European Summer Barometer 2015
 page 1 Ferratum Group European Summer Barometer 2015 Summer holiday spending relative to disposable household income European Summer spending SPENDING IN RELATION TO OTHER COUNTRIES ESTONIA 60.2 % 17 %
page 1 Ferratum Group European Summer Barometer 2015 Summer holiday spending relative to disposable household income European Summer spending SPENDING IN RELATION TO OTHER COUNTRIES ESTONIA 60.2 % 17 %
World Tourism Organization RECOMMENDATIONS TO GOVERNMENTS FOR SUPPORTING AND/OR ESTABLISHING NATIONAL CERTIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR SUSTAINABLE TOURISM
 World Tourism Organization RECOMMENDATIONS TO GOVERNMENTS FOR SUPPORTING AND/OR ESTABLISHING NATIONAL CERTIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR SUSTAINABLE TOURISM Introduction Certification systems for sustainable tourism
World Tourism Organization RECOMMENDATIONS TO GOVERNMENTS FOR SUPPORTING AND/OR ESTABLISHING NATIONAL CERTIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR SUSTAINABLE TOURISM Introduction Certification systems for sustainable tourism
PREFERENCES OF EUROPEANS TOWARDS TOURISM
 Eurobarometer PREFERENCES OF EUROPEANS TOWARDS TOURISM REPORT Fieldwork: January 2014 Publication: February 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Enterprise
Eurobarometer PREFERENCES OF EUROPEANS TOWARDS TOURISM REPORT Fieldwork: January 2014 Publication: February 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Enterprise
ARE THE POINTS OF SINGLE CONTACT TRULY MAKING THINGS EASIER FOR EUROPEAN COMPANIES?
 ARE THE POINTS OF SINGLE CONTACT TRULY MAKING THINGS EASIER FOR EUROPEAN COMPANIES? SERVICES DIRECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION REPORT NOVEMBER 2011 EUROPEAN COMPANIES WANT WELL-FUNCTIONING POINTS OF SINGLE CONTACT
ARE THE POINTS OF SINGLE CONTACT TRULY MAKING THINGS EASIER FOR EUROPEAN COMPANIES? SERVICES DIRECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION REPORT NOVEMBER 2011 EUROPEAN COMPANIES WANT WELL-FUNCTIONING POINTS OF SINGLE CONTACT
Finland must take a leap towards new innovations
 Finland must take a leap towards new innovations Innovation Policy Guidelines up to 2015 Summary Finland must take a leap towards new innovations Innovation Policy Guidelines up to 2015 Summary 3 Foreword
Finland must take a leap towards new innovations Innovation Policy Guidelines up to 2015 Summary Finland must take a leap towards new innovations Innovation Policy Guidelines up to 2015 Summary 3 Foreword
THE EVOLUTION AND THE FUTURE ROLE OF THE BRANCH IN DISTRIBUTION OF THE BANKING PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
 Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 11(3), 2011, 15-22 15 THE EVOLUTION AND THE FUTURE ROLE OF THE BRANCH IN DISTRIBUTION OF THE BANKING PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CĂTĂLIN NICOLAE BULGĂREA * ABSTRACT:
Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 11(3), 2011, 15-22 15 THE EVOLUTION AND THE FUTURE ROLE OF THE BRANCH IN DISTRIBUTION OF THE BANKING PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CĂTĂLIN NICOLAE BULGĂREA * ABSTRACT:
187/2014-5 December 2014. EU28, euro area and United States GDP growth rates % change over the previous quarter
 187/2014-5 December 2014 This News Release has been revised following an error in the data for Gross Fixed Capital Formation. This affects both the growth of GFCF and its contribution to GDP growth. All
187/2014-5 December 2014 This News Release has been revised following an error in the data for Gross Fixed Capital Formation. This affects both the growth of GFCF and its contribution to GDP growth. All
IMPLEMENTATION OF MARKETING IN RURAL TOURISM Ciprian Pavel
 IMPLEMENTATION OF MARKETING IN RURAL TOURISM Ciprian Pavel Abstract: Because estimates of growth in the choice of Romanian and foreign tourists to rural pensions can be observed the growing need to ensure
IMPLEMENTATION OF MARKETING IN RURAL TOURISM Ciprian Pavel Abstract: Because estimates of growth in the choice of Romanian and foreign tourists to rural pensions can be observed the growing need to ensure
DEVELOPMENT PLAN AND POLICIES OF SLOVENE TOURISM 2007-2011 SUMMARY
 DEVELOPMENT PLAN AND POLICIES OF SLOVENE TOURISM 2007-2011 SUMMARY Introduction Pursuant to Article 5 of the Promotion of Tourism Development Act (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, No. 2/04
DEVELOPMENT PLAN AND POLICIES OF SLOVENE TOURISM 2007-2011 SUMMARY Introduction Pursuant to Article 5 of the Promotion of Tourism Development Act (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, No. 2/04
99/2015-9 June 2015. EU28, euro area and United States GDP growth rates % change over the previous quarter
 2005Q1 2005Q2 2005Q3 2005Q4 2006Q1 2006Q2 2006Q3 2006Q4 2007Q1 2007Q2 2007Q3 2007Q4 2008Q1 2008Q2 2008Q3 2008Q4 2009Q1 2009Q2 2009Q3 2009Q4 2010Q1 2010Q2 2010Q3 2010Q4 2011Q1 2011Q2 2011Q3 2011Q4 2012Q1
2005Q1 2005Q2 2005Q3 2005Q4 2006Q1 2006Q2 2006Q3 2006Q4 2007Q1 2007Q2 2007Q3 2007Q4 2008Q1 2008Q2 2008Q3 2008Q4 2009Q1 2009Q2 2009Q3 2009Q4 2010Q1 2010Q2 2010Q3 2010Q4 2011Q1 2011Q2 2011Q3 2011Q4 2012Q1
The education system and lifelong learning in Finland. October 2015 Petri Haltia
 The education system and lifelong learning in Finland October 2015 Petri Haltia FINLAND Population: year 2012: 5,421,827 density: 16/km 2 Area: total 338,424 km 2 water 10 % GDP (nominal) 2011 estimate:
The education system and lifelong learning in Finland October 2015 Petri Haltia FINLAND Population: year 2012: 5,421,827 density: 16/km 2 Area: total 338,424 km 2 water 10 % GDP (nominal) 2011 estimate:
2012-2016 SLOVENIAN TOURISM DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY (summary) The 2012-2016 Partnership for the Sustainable Development of Tourism
 2012-2016 SLOVENIAN TOURISM DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY (summary) Introduction Pursuant to Article 5 of the Promotion of Tourism Development Act (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, No. 2/04), the Ministry
2012-2016 SLOVENIAN TOURISM DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY (summary) Introduction Pursuant to Article 5 of the Promotion of Tourism Development Act (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, No. 2/04), the Ministry
Consultation on the future of European Insolvency Law
 Consultation on the future of European Insolvency Law The Commission has put the revision of the Insolvency Regulation in its Work Programme for 2012. The revision is one of the measures in the field of
Consultation on the future of European Insolvency Law The Commission has put the revision of the Insolvency Regulation in its Work Programme for 2012. The revision is one of the measures in the field of
Ipsos / Europ Assistance barometer Europeans Plans and Concerns for the Holidays Summary Ipsos for the Europ Assistance Group May 24th 2012
 Ipsos / Europ Assistance barometer Europeans Plans and Concerns for the Holidays Summary Ipsos for the Europ Assistance Group May 24th 2012 Contacts Ipsos Public Affairs: Fabienne SIMON 01 41 98 92 15
Ipsos / Europ Assistance barometer Europeans Plans and Concerns for the Holidays Summary Ipsos for the Europ Assistance Group May 24th 2012 Contacts Ipsos Public Affairs: Fabienne SIMON 01 41 98 92 15
Tourism trends in Europe and in Mediterranean Partner Countries, 2000-2006
 Industry, trade and services Author: Ulrich SPÖREL, Volker TÄUBE Statistics in focus 95/28 Tourism trends in Europe and in Mediterranean Partner Countries, 2-26 Tourism is a growth industry in Europe and
Industry, trade and services Author: Ulrich SPÖREL, Volker TÄUBE Statistics in focus 95/28 Tourism trends in Europe and in Mediterranean Partner Countries, 2-26 Tourism is a growth industry in Europe and
Role of Agriculture in Strategic Planning of Regional Development in Regions of the Czech Republic
 Role of Agriculture in Strategic Planning of Regional Development in Regions of the Czech Republic PAVEL GREBENÍČEK Faculty of Management and Economics Tomas Bata University in Zlín Mostní 5139, 760 01
Role of Agriculture in Strategic Planning of Regional Development in Regions of the Czech Republic PAVEL GREBENÍČEK Faculty of Management and Economics Tomas Bata University in Zlín Mostní 5139, 760 01
ERASMUS FOR YOUNG ENTREPRENEURS : A NEW EXCHANGE PROGRAMME
 PRESS DOSSIER INDEX PRESS DOSSIER...1 INDEX...2 ERASMUS FOR YOUNG ENTREPRENEURS : A NEW EXCHANGE PROGRAMME...3 WHO CAN PARTICIPATE?...5 WHAT BENEFITS AND FOR WHOM?...6 HOW DOES IT WORK? STRUCTURE AND IMPLEMENTATION...7
PRESS DOSSIER INDEX PRESS DOSSIER...1 INDEX...2 ERASMUS FOR YOUNG ENTREPRENEURS : A NEW EXCHANGE PROGRAMME...3 WHO CAN PARTICIPATE?...5 WHAT BENEFITS AND FOR WHOM?...6 HOW DOES IT WORK? STRUCTURE AND IMPLEMENTATION...7
How To Understand Factoring
 EIF Project "Jeremie" General Report on Factoring 1 Market analysis on Factoring in EU 25+2 prepared by International Factors Group (IFG) for European Investment Fund (EIF) project JEREMIE Preliminary
EIF Project "Jeremie" General Report on Factoring 1 Market analysis on Factoring in EU 25+2 prepared by International Factors Group (IFG) for European Investment Fund (EIF) project JEREMIE Preliminary
Country specific notes on municipal waste data
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-2: Environmental Statistics and Accounts; Sustainable Development Country specific notes on municipal waste data Last
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-2: Environmental Statistics and Accounts; Sustainable Development Country specific notes on municipal waste data Last
SERVICES DIRECTIVE DOING BUSINESS MADE EASIER
 SERVICES DIRECTIVE DOING BUSINESS MADE EASIER Less red tape Faster procedures Easier market access ?WHAT IS THE SERVICES DIRECTIVE? The Services Directive is a European law that aims to make life easier
SERVICES DIRECTIVE DOING BUSINESS MADE EASIER Less red tape Faster procedures Easier market access ?WHAT IS THE SERVICES DIRECTIVE? The Services Directive is a European law that aims to make life easier
EUROPEAN AREA OF SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS
 EUROPEAN AREA OF SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS REPORT Fieldwork: April - May 2014 Publication: June 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Education and Culture
EUROPEAN AREA OF SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS REPORT Fieldwork: April - May 2014 Publication: June 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Education and Culture
THE ORGANISATION AND FINANCING OF HEALTH CARE SYSTEM IN LATVIA
 THE ORGANISATION AND FINANCING OF HEALTH CARE SYSTEM IN LATVIA Eriks Mikitis Ministry of Health of the Republic of Latvia Department of Health Care Director General facts, financial resources Ministry
THE ORGANISATION AND FINANCING OF HEALTH CARE SYSTEM IN LATVIA Eriks Mikitis Ministry of Health of the Republic of Latvia Department of Health Care Director General facts, financial resources Ministry
EUROPEAN CITIZENS DIGITAL HEALTH LITERACY
 Flash Eurobarometer EUROPEAN CITIZENS DIGITAL HEALTH LITERACY REPORT Fieldwork: September 2014 Publication: November 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General
Flash Eurobarometer EUROPEAN CITIZENS DIGITAL HEALTH LITERACY REPORT Fieldwork: September 2014 Publication: November 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General
PREFERENCES OF EUROPEANS TOWARDS TOURISM
 Flash Eurobarometer 414 PREFERENCES OF EUROPEANS TOWARDS TOURISM SUMMARY Fieldwork: January 2015 Publication: March 2015 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for
Flash Eurobarometer 414 PREFERENCES OF EUROPEANS TOWARDS TOURISM SUMMARY Fieldwork: January 2015 Publication: March 2015 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for
1. Perception of the Bancruptcy System... 2. 2. Perception of In-court Reorganisation... 4
 Bankruptcy Systems and In-court Reorganisation of Firms, 2010 Content: 1. Perception of the Bancruptcy System... 2 2. Perception of In-court Reorganisation... 4 3. Perception of Creditor Committees, Fast
Bankruptcy Systems and In-court Reorganisation of Firms, 2010 Content: 1. Perception of the Bancruptcy System... 2 2. Perception of In-court Reorganisation... 4 3. Perception of Creditor Committees, Fast
FLOOD DAMAGES AND TOOLS FOR THEIR MITIGATION Lenka Camrova, Jirina Jilkova
 FLOOD DAMAGES AND TOOLS FOR THEIR MITIGATION Lenka Camrova, Jirina Jilkova University of Economics, Prague, 2006, pp. 418. ISBN: 80-86684-35-0 English Summary In 1997 and 2002 the Czech Republic was heavily
FLOOD DAMAGES AND TOOLS FOR THEIR MITIGATION Lenka Camrova, Jirina Jilkova University of Economics, Prague, 2006, pp. 418. ISBN: 80-86684-35-0 English Summary In 1997 and 2002 the Czech Republic was heavily
IMMIGRATION TO AND EMIGRATION FROM GERMANY IN THE LAST FEW YEARS
 IMMIGRATION TO AND EMIGRATION FROM GERMANY IN THE LAST FEW YEARS Bernd Geiss* Germany, Destination for Migrants Germany is in the middle of Europe and has common borders with nine countries. Therefore,
IMMIGRATION TO AND EMIGRATION FROM GERMANY IN THE LAST FEW YEARS Bernd Geiss* Germany, Destination for Migrants Germany is in the middle of Europe and has common borders with nine countries. Therefore,
YOUNG PEOPLE AND DRUGS
 Eurobarometer YOUNG PEOPLE AND DRUGS REPORT Fieldwork: June 2014 Publication: August 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Justice and co-ordinated by
Eurobarometer YOUNG PEOPLE AND DRUGS REPORT Fieldwork: June 2014 Publication: August 2014 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Justice and co-ordinated by
Dutch hiking tourism. Terje Rakke/Nordic life - Visitnorway.com
 Dutch hiking tourism Terje Rakke/Nordic life - Visitnorway.com Index Chapter page Executive summary 3 1 Introduction 4 2 The Dutch hiking segment 5 3 Mapping Phase I 6 4 Survey Phase II: Selection and
Dutch hiking tourism Terje Rakke/Nordic life - Visitnorway.com Index Chapter page Executive summary 3 1 Introduction 4 2 The Dutch hiking segment 5 3 Mapping Phase I 6 4 Survey Phase II: Selection and
EUROPEAN YOUTH: PARTICIPATION IN DEMOCRATIC LIFE
 Flash Eurobarometer EUROPEAN YOUTH: PARTICIPATION IN DEMOCRATIC LIFE REPORT Fieldwork: April 2013 Publication: May 2013 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for
Flash Eurobarometer EUROPEAN YOUTH: PARTICIPATION IN DEMOCRATIC LIFE REPORT Fieldwork: April 2013 Publication: May 2013 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for
ERASMUS MOBILITY: STUDENTS MOTIVATION AND SATISFACTION
 ERASMUS MOBILITY: STUDENTS MOTIVATION AND SATISFACTION Mária Jašková*, Lenka Heczková** *Faculty of Economics, VŠB Technical University of Ostrava, Sokolská 33, Ostrava, Czech Republic, maria.jaskova@vsb.cz
ERASMUS MOBILITY: STUDENTS MOTIVATION AND SATISFACTION Mária Jašková*, Lenka Heczková** *Faculty of Economics, VŠB Technical University of Ostrava, Sokolská 33, Ostrava, Czech Republic, maria.jaskova@vsb.cz
The Future European Constitution
 Flash Eurobarometer European Commission The Future European Constitution Fieldwork : January 2004 Publication : February 2004 Flash Eurobarometer 159 - TNS Sofres / EOS Gallup Europe This survey was requested
Flash Eurobarometer European Commission The Future European Constitution Fieldwork : January 2004 Publication : February 2004 Flash Eurobarometer 159 - TNS Sofres / EOS Gallup Europe This survey was requested
Tourism in figures 2012
 Tourism in figures 2012 the Belgian market in Flanders July 2013 toerisme vlaanderen TABLE OF CONTENT A. THE BELGIAN MARKET IN FLANDERS 5 1. Key figures 5 2. Distribution within Flanders 5 3. Trends 8
Tourism in figures 2012 the Belgian market in Flanders July 2013 toerisme vlaanderen TABLE OF CONTENT A. THE BELGIAN MARKET IN FLANDERS 5 1. Key figures 5 2. Distribution within Flanders 5 3. Trends 8
Summary of the Research on the role of ICT related knowledge and women s labour market situation
 Summary of the Research on the role of ICT related knowledge and women s labour market situation Comparative anlysis of the situation in the five surveyed countries: Analysis of data about employment shows
Summary of the Research on the role of ICT related knowledge and women s labour market situation Comparative anlysis of the situation in the five surveyed countries: Analysis of data about employment shows
EU-10 AND THE CAP CONTENTS
 Agricultural Policy Perspectives Brief April 2014 EU-10 AND THE CAP 10 YEARS OF SUCCESS Thinkstockphotos.com CONTENTS 1. Structural Adjustment 2. Income 3. CAP expenditure 4. Land Tenure 5. Prices and
Agricultural Policy Perspectives Brief April 2014 EU-10 AND THE CAP 10 YEARS OF SUCCESS Thinkstockphotos.com CONTENTS 1. Structural Adjustment 2. Income 3. CAP expenditure 4. Land Tenure 5. Prices and
Small Scale Study ll. Managed Migration and the Labour Market the Health Sector
 1 Small Scale Study ll Managed Migration and the Labour Market the Health Sector Swedish NCP 2 1. Executive summary...3 2. Introduction to the healthcare sector in Sweden...4 2.1 County councils' main
1 Small Scale Study ll Managed Migration and the Labour Market the Health Sector Swedish NCP 2 1. Executive summary...3 2. Introduction to the healthcare sector in Sweden...4 2.1 County councils' main
Think Green, Act Green!
 Think Green, Act Green! March November 2015 Lastours, France Starting date: 1st March 2015 Ending date: 30th November 2015 Number of volunteers: 4 Venue: Lastours, France Hosting organization: Initiative
Think Green, Act Green! March November 2015 Lastours, France Starting date: 1st March 2015 Ending date: 30th November 2015 Number of volunteers: 4 Venue: Lastours, France Hosting organization: Initiative
RED BANK REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL CURRICULUM MAP Course Title: Hospitality & Entertainment Marketing Grade Levels: 11, 12
 What is Hospitality Marketing Marketing Basics Hotel Marketing: A competitive Industry The Importance of Hospitality Marketing Types of Hospitality Markets Key Players in Hospitality Operations Selling
What is Hospitality Marketing Marketing Basics Hotel Marketing: A competitive Industry The Importance of Hospitality Marketing Types of Hospitality Markets Key Players in Hospitality Operations Selling
YOUNG GENERATION: BARRIERS TO SETTING UP A BUSINESS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC
 YOUNG GENERATION: BARRIERS TO SETTING UP A BUSINESS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. SURVEY RESULTS... 1 3. ANALYSES OF VARIOUS BARRIERS TO SETTING UP A BUSINESS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC...
YOUNG GENERATION: BARRIERS TO SETTING UP A BUSINESS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. SURVEY RESULTS... 1 3. ANALYSES OF VARIOUS BARRIERS TO SETTING UP A BUSINESS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC...
UK hiking tourism. CH - Visitnorway.com
 UK hiking tourism CH - Visitnorway.com Contents 1. Executive Summary 3 2. Introduction 4 3. Research on the Internet: Phase 1 5 3.01: Tour operators: 5 3.02: Websites/forums: 5 3.03: Hiking/Outdoor magazines
UK hiking tourism CH - Visitnorway.com Contents 1. Executive Summary 3 2. Introduction 4 3. Research on the Internet: Phase 1 5 3.01: Tour operators: 5 3.02: Websites/forums: 5 3.03: Hiking/Outdoor magazines
Sale of agricultural land in the Czech Republic after accession to the EU
 Sale of agricultural land in the Czech Republic after accession to the EU Prodej zemědělské půdy v České republice po vstupu do EU J. NĚMEC Research Institute of Agricultural Economics, Prague, Czech Republic
Sale of agricultural land in the Czech Republic after accession to the EU Prodej zemědělské půdy v České republice po vstupu do EU J. NĚMEC Research Institute of Agricultural Economics, Prague, Czech Republic
ANNUAL TOURISM REPORT 2013 Czech Republic
 ANNUAL TOURISM REPORT 2013 Czech Republic Article 3 of Council Decision 86/664/EEC 1 of 22 December 1986 establishing a consultation and cooperation procedure in the field of tourism stipulates that: "...each
ANNUAL TOURISM REPORT 2013 Czech Republic Article 3 of Council Decision 86/664/EEC 1 of 22 December 1986 establishing a consultation and cooperation procedure in the field of tourism stipulates that: "...each
Country note China. More than 255 million people in OECD and G20 countries have now attained tertiary education (Table A1.3a).
 Education at a Glance 2011 OECD Indicators DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/eag-2011-en OECD 2011 Under embargo until 13 September, at 11:00 Paris time Education at a Glance 2011 Country note China Questions
Education at a Glance 2011 OECD Indicators DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/eag-2011-en OECD 2011 Under embargo until 13 September, at 11:00 Paris time Education at a Glance 2011 Country note China Questions
Research Briefing. The Best and the Brightest EU students at UK universities and as highly skilled graduate workers in the UK
 Research Briefing The Best and the Brightest EU students at UK universities and as highly skilled graduate workers in the UK Academic performance and labour market outcomes of EU domiciled students in
Research Briefing The Best and the Brightest EU students at UK universities and as highly skilled graduate workers in the UK Academic performance and labour market outcomes of EU domiciled students in
Operational Companies VAT Indirect Taxes. Why Luxembourg: VAT advantages for commercial companies*
 Operational Companies VAT Indirect Taxes Why : VAT advantages for commercial companies* Why : VAT advantages for commercial companies as an international decision-making, financing or distribution hub:
Operational Companies VAT Indirect Taxes Why : VAT advantages for commercial companies* Why : VAT advantages for commercial companies as an international decision-making, financing or distribution hub:
Chalet Larchie sits in a small village development
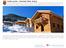 Chalet Larchie Dachstein West, Austria Ski-in ski-out Three double bedroom chalet with wonderful views Fully furnished including fitted kitchen, appliances, bedding and garden furniture Development includes
Chalet Larchie Dachstein West, Austria Ski-in ski-out Three double bedroom chalet with wonderful views Fully furnished including fitted kitchen, appliances, bedding and garden furniture Development includes
Household Finance and Consumption Survey
 An Phríomh-Oifig Staidrimh Central Statistics Office Household Finance and Consumption Survey 2013 Published by the Stationery Office, Dublin, Ireland. Available from: Central Statistics Office, Information
An Phríomh-Oifig Staidrimh Central Statistics Office Household Finance and Consumption Survey 2013 Published by the Stationery Office, Dublin, Ireland. Available from: Central Statistics Office, Information
Alcohol Consumption in Ireland 1986-2006 A Report for the Health Service Executive
 Alcohol Consumption in Ireland 1986-2006 A Report for the Health Service Executive Prepared by Dr. Ann Hope This report should be referenced: Hope, A. (2007). Alcohol consumption in Ireland 1986-2006.
Alcohol Consumption in Ireland 1986-2006 A Report for the Health Service Executive Prepared by Dr. Ann Hope This report should be referenced: Hope, A. (2007). Alcohol consumption in Ireland 1986-2006.
WJEC GCSE Modern Foreign Languages Controlled Assessment Writing Task Bank
 For further guidance, we have added bullet points to the existing 2013 task bank for use by centres if they so wish. Expanded tasks are denoted by an * Please note that we have renumbered the tasks and
For further guidance, we have added bullet points to the existing 2013 task bank for use by centres if they so wish. Expanded tasks are denoted by an * Please note that we have renumbered the tasks and
TPI: Traffic Psychology International on a common European curriculum for postgraduate education in traffic psychology
 TPI: Traffic Psychology International on a common European curriculum for postgraduate education in traffic psychology Sucha, M.*, Sramkova, L.** DeVol, D.* * TPI - Traffic Psychology International **
TPI: Traffic Psychology International on a common European curriculum for postgraduate education in traffic psychology Sucha, M.*, Sramkova, L.** DeVol, D.* * TPI - Traffic Psychology International **
User language preferences online. Analytical report
 Flash Eurobarometer 313 The Gallup Organization Flash Eurobarometer European Commission User language preferences online Analytical report Fieldwork: January 2011 Publication: May 2011 This survey was
Flash Eurobarometer 313 The Gallup Organization Flash Eurobarometer European Commission User language preferences online Analytical report Fieldwork: January 2011 Publication: May 2011 This survey was
Monitoring the social impact of the crisis: public perceptions in the European Union (wave 6) REPORT
 Eurobarometer Monitoring the social impact of the crisis: public perceptions in the European Union (wave 6) REPORT Fieldwork: December 2011 Publication: April 2012 This survey has been requested by Directorate-General
Eurobarometer Monitoring the social impact of the crisis: public perceptions in the European Union (wave 6) REPORT Fieldwork: December 2011 Publication: April 2012 This survey has been requested by Directorate-General
How To Find Out What Young People Do In The European Union
 Flash Eurobarometer 319a The Gallup Organization Flash Eurobarometer European Commission Youth on the move Fieldwork: February 211 Publication: May 211 Flash Eurobarometer 319a YOUTH PARTICIPION This survey
Flash Eurobarometer 319a The Gallup Organization Flash Eurobarometer European Commission Youth on the move Fieldwork: February 211 Publication: May 211 Flash Eurobarometer 319a YOUTH PARTICIPION This survey
Transport demands in suburbanized locations
 Agronomy Research 12(2), 351 358, 2014 Transport demands in suburbanized locations M. Lukeš *, M. Kotek and M. Růžička Faculty of Engineering, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, 165 21 Prague 6
Agronomy Research 12(2), 351 358, 2014 Transport demands in suburbanized locations M. Lukeš *, M. Kotek and M. Růžička Faculty of Engineering, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, 165 21 Prague 6
Management of agricultural production in the conditions of information society
 Management of agricultural production in the conditions of information society Riadenie poľnohospodárskej výroby v podmienkach informačnej spoločnosti A. LÁTEČKOVÁ, M. KUČERA Slovak University of Agriculture,
Management of agricultural production in the conditions of information society Riadenie poľnohospodárskej výroby v podmienkach informačnej spoločnosti A. LÁTEČKOVÁ, M. KUČERA Slovak University of Agriculture,
Dossier documentaire
 DCL AG 04/11 02 Dossier documentaire Page 1 sur 6 DCL ANGLAIS Diplôme de Compétence en Langue Session du vendredi 1 avril 2011 Dossier documentaire Phase 1: Document 1 Internal memo Document 2 Document
DCL AG 04/11 02 Dossier documentaire Page 1 sur 6 DCL ANGLAIS Diplôme de Compétence en Langue Session du vendredi 1 avril 2011 Dossier documentaire Phase 1: Document 1 Internal memo Document 2 Document
CZECH REPUBLIC. Similarities of the good practice with the experience of the Czech Republic
 Promoting social inclusion of children in a disadvantaged rural environment Tomas Habart People in Need Viktor Piorecky Agency for Social Inclusion in Excluded Roma Localities A brief assessment of the
Promoting social inclusion of children in a disadvantaged rural environment Tomas Habart People in Need Viktor Piorecky Agency for Social Inclusion in Excluded Roma Localities A brief assessment of the
INVITATION TO. the youth exchange Youth Entrepreneurship Cefalu, Italy. Please, confirm your arrival/departure dates before booking the tickets!
 INVITATION TO the youth exchange Youth Entrepreneurship Cefalu, Italy DATE: 19.09-27.09.2015 (7 activity days) (19 th is arrival day, 26 rd evening or 27 th morning is departure) Please, confirm your arrival/departure
INVITATION TO the youth exchange Youth Entrepreneurship Cefalu, Italy DATE: 19.09-27.09.2015 (7 activity days) (19 th is arrival day, 26 rd evening or 27 th morning is departure) Please, confirm your arrival/departure
Development of Spa and Wellness Tourism in Hungary; Business Results
 Development of Spa and Wellness Tourism in Hungary; Business Results Dr. Ákos NIKLAI Chairman, Hungarian National Tourist Office Past President of the Hotel Association of Hungary Brussels, 6 June 2007
Development of Spa and Wellness Tourism in Hungary; Business Results Dr. Ákos NIKLAI Chairman, Hungarian National Tourist Office Past President of the Hotel Association of Hungary Brussels, 6 June 2007
Višja strokovna šola Šolski center Nova Gorica Higher Vocational College of School Centre Nova Gorica
 Višja strokovna šola Šolski center Nova Gorica Higher Vocational College of School Centre Nova Gorica Who are we and what do we do? Higher Vocational College of School Centre Nova Gorica means: short-cycle,
Višja strokovna šola Šolski center Nova Gorica Higher Vocational College of School Centre Nova Gorica Who are we and what do we do? Higher Vocational College of School Centre Nova Gorica means: short-cycle,
The energy industry and energy price issues in Slovakia during recent years 1
 The energy industry and energy price issues in Slovakia during recent years 1 Ing. Mikulá Cár, PhD. National Bank of Slovakia The energy industry and energy prices are becoming a subject of political decisions
The energy industry and energy price issues in Slovakia during recent years 1 Ing. Mikulá Cár, PhD. National Bank of Slovakia The energy industry and energy prices are becoming a subject of political decisions
EUROPE 2020 TARGET: TERTIARY EDUCATION ATTAINMENT
 EUROPE 2020 TARGET: TERTIARY EDUCATION ATTAINMENT Low tertiary or equivalent education attainment levels create skills bottlenecks in knowledgeintensive economic sectors and hamper productivity, innovation
EUROPE 2020 TARGET: TERTIARY EDUCATION ATTAINMENT Low tertiary or equivalent education attainment levels create skills bottlenecks in knowledgeintensive economic sectors and hamper productivity, innovation
The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU 27 2013 Edition
 (Cover page) The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU 27 2013 Edition James Rogers & Cécile Philippe May 2013 Data provided by NEW DIRECTION Page 1 of 16 The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU
(Cover page) The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU 27 2013 Edition James Rogers & Cécile Philippe May 2013 Data provided by NEW DIRECTION Page 1 of 16 The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU
EUROPE 2020 TARGETS: RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
 EUROPE 2020 TARGETS: RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT Research, development and innovation are key policy components of the EU strategy for economic growth: Europe 2020. By fostering market take-up of new, innovative
EUROPE 2020 TARGETS: RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT Research, development and innovation are key policy components of the EU strategy for economic growth: Europe 2020. By fostering market take-up of new, innovative
CYPRUS TOURISM ORGANISATION OBLIGATIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF ENTREPRENEURS/ MANAGERS OF HOTEL & OTHER TOURIST ESTABLISHMENTS
 CYPRUS TOURISM ORGANISATION OBLIGATIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF ENTREPRENEURS/ MANAGERS OF HOTEL & OTHER TOURIST ESTABLISHMENTS A General Information 1. The establishment, operation and supervision of
CYPRUS TOURISM ORGANISATION OBLIGATIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF ENTREPRENEURS/ MANAGERS OF HOTEL & OTHER TOURIST ESTABLISHMENTS A General Information 1. The establishment, operation and supervision of
LONDON BOROUGH OF HAVERING
 LONDON BOROUGH OF HAVERING CORPORATE ASSET MANAGEMENT PLAN 2015-2019 Sections LONDON BOROUGH OF HAVERING CORPORATE ASSET MANAGEMENT PLAN CONTENTS 1 Introduction and Context 2 Corporate Vision 3 Policy
LONDON BOROUGH OF HAVERING CORPORATE ASSET MANAGEMENT PLAN 2015-2019 Sections LONDON BOROUGH OF HAVERING CORPORATE ASSET MANAGEMENT PLAN CONTENTS 1 Introduction and Context 2 Corporate Vision 3 Policy
The International Master Double Degree Program in Business Economics
 The International Master Double Degree Program in Business Economics organized by SLOVAK UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE IN NITRA Faculty of Economics and Management and UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE IN KRAKOW Faculty
The International Master Double Degree Program in Business Economics organized by SLOVAK UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE IN NITRA Faculty of Economics and Management and UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE IN KRAKOW Faculty
Destination Management Company
 Destination Management Company Message from Chairman of the Board BORIS ŽGOMBA Since it was founded in 1996, travel agency Uniline has reached the status of one of the leading destination management companies
Destination Management Company Message from Chairman of the Board BORIS ŽGOMBA Since it was founded in 1996, travel agency Uniline has reached the status of one of the leading destination management companies
Size and Development of the Shadow Economy of 31 European and 5 other OECD Countries from 2003 to 2015: Different Developments
 January 20, 2015 ShadEcEurope31_January2015.doc Size and Development of the Shadow Economy of 31 European and 5 other OECD Countries from 2003 to 2015: Different Developments by Friedrich Schneider *)
January 20, 2015 ShadEcEurope31_January2015.doc Size and Development of the Shadow Economy of 31 European and 5 other OECD Countries from 2003 to 2015: Different Developments by Friedrich Schneider *)
LAPLAND VITALITY FOR LIFE
 LAPLAND VITALITY FOR LIFE An Abstract of Lapland Tourism Strategy 2007-2010 1. GOOD RESULTS THROUGH STRATEGIC PLANNING The earlier tourism strategy for Lapland set the guidelines for regional tourism development
LAPLAND VITALITY FOR LIFE An Abstract of Lapland Tourism Strategy 2007-2010 1. GOOD RESULTS THROUGH STRATEGIC PLANNING The earlier tourism strategy for Lapland set the guidelines for regional tourism development
Consumer Price Index
 An Phríomh-Oifig Staidrimh Central Statistics Office 19 January 2012 CPI/HICP - all items Annual Percentage Change CPI HICP % 4.0 2.0 0.0-2.0-4.0 Consumer Price Index December 2011 Aug 2011 Sep 2011 Oct
An Phríomh-Oifig Staidrimh Central Statistics Office 19 January 2012 CPI/HICP - all items Annual Percentage Change CPI HICP % 4.0 2.0 0.0-2.0-4.0 Consumer Price Index December 2011 Aug 2011 Sep 2011 Oct
EVS project description Sunnahof Tufers
 EVS project description Sunnahof Tufers EVS Project: Sunnahof Tufers (PIC 946094739) Number of volunteers: 4 Looking for volunteers from: - Belgium - Bosnia and Herzegovina - Bulgaria - Denmark - Germany
EVS project description Sunnahof Tufers EVS Project: Sunnahof Tufers (PIC 946094739) Number of volunteers: 4 Looking for volunteers from: - Belgium - Bosnia and Herzegovina - Bulgaria - Denmark - Germany
Characteristics of Private Farms and Family Farm Labour in Hungary by Settlement Size
 Characteristics of Private Farms and Family Farm Labour in Hungary by Settlement Size Zsolt Andrási Drafter, HCSO E-mail: Zsolt.Andrasi@ksh.hu Pál Bóday Head of Section, HCSO E-mail: Pal.Boday@ksh.hu The
Characteristics of Private Farms and Family Farm Labour in Hungary by Settlement Size Zsolt Andrási Drafter, HCSO E-mail: Zsolt.Andrasi@ksh.hu Pál Bóday Head of Section, HCSO E-mail: Pal.Boday@ksh.hu The
Definition of Public Interest Entities (PIEs) in Europe
 Definition of Public Interest Entities (PIEs) in Europe FEE Survey October 2014 This document has been prepared by FEE to the best of its knowledge and ability to ensure that it is accurate and complete.
Definition of Public Interest Entities (PIEs) in Europe FEE Survey October 2014 This document has been prepared by FEE to the best of its knowledge and ability to ensure that it is accurate and complete.
Survey of young person s perception and ideas on Baltic Sea Region tourism products
 Survey of young person s perception and ideas on Baltic Sea Region tourism products Lise Lyck 1 Survey of young person s perception and ideas on Baltic Sea Region tourism products Copenhagen Business School
Survey of young person s perception and ideas on Baltic Sea Region tourism products Lise Lyck 1 Survey of young person s perception and ideas on Baltic Sea Region tourism products Copenhagen Business School
Fostering Entrepreneurship among young people through education: a EU perspective. Simone Baldassarri Unit Entrepreneurship
 Fostering Entrepreneurship among young people through education: a EU perspective Simone Baldassarri Unit Entrepreneurship Definition of Entrepreneurship Entrepreneurship refers to an individual s ability
Fostering Entrepreneurship among young people through education: a EU perspective Simone Baldassarri Unit Entrepreneurship Definition of Entrepreneurship Entrepreneurship refers to an individual s ability
University of Lleida. UdL the best university for teaching quality. (Report of the Fundación Conocimiento y Desarrollo 2008)
 University of Lleida UdL the best university for teaching quality (Report of the Fundación Conocimiento y Desarrollo 2008) Iceland Ireland United Kingtom Norway Denmark Sweden Finland Lithuania Belarus
University of Lleida UdL the best university for teaching quality (Report of the Fundación Conocimiento y Desarrollo 2008) Iceland Ireland United Kingtom Norway Denmark Sweden Finland Lithuania Belarus
T wo EA-M - Enhancing Attractiveness of Environmental Assessment and Management Higher Education
 T wo EA-M - Enhancing Attractiveness of Environmental Assessment and Management Higher Education 1. Introduction Thomas Fischer, Urmila Jha-Thakur, Ingrid Belcakova, Ralf Aschemann The European Commission
T wo EA-M - Enhancing Attractiveness of Environmental Assessment and Management Higher Education 1. Introduction Thomas Fischer, Urmila Jha-Thakur, Ingrid Belcakova, Ralf Aschemann The European Commission
The Community Innovation Survey 2010 (CIS 2010)
 The Community Innovation Survey 2010 (CIS 2010) THE HARMONISED SURVEY QUESTIONNAIRE The Community Innovation Survey 2010 FINAL VERSION July 9, 2010 This survey collects information on your enterprise s
The Community Innovation Survey 2010 (CIS 2010) THE HARMONISED SURVEY QUESTIONNAIRE The Community Innovation Survey 2010 FINAL VERSION July 9, 2010 This survey collects information on your enterprise s
Marketing Authorisation Of A Product In Czech Republic
 MARKETING AUTHORISATION APPLICATION FOR NEW PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS VIA THE MUTUAL RECOGNITION PROCEDURE AS SPECIFIED UNDER REGULATION (EC) No 1107/2009 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
MARKETING AUTHORISATION APPLICATION FOR NEW PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS VIA THE MUTUAL RECOGNITION PROCEDURE AS SPECIFIED UNDER REGULATION (EC) No 1107/2009 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
Special Eurobarometer 398 INTERNAL MARKET REPORT
 Special Eurobarometer 398 INTERNAL MARKET REPORT Fieldwork: April - May 2013 Publication: October 2013 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General Internal Market and
Special Eurobarometer 398 INTERNAL MARKET REPORT Fieldwork: April - May 2013 Publication: October 2013 This survey has been requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General Internal Market and
VAT Refunds Irrecoverable Tax A Country by Country Detailed Guide
 VAT Refunds Irrecoverable Tax A Country by Country Detailed Guide EC VAT refunds Irrecoverable Tax VAT incurred in other EC Member States may be recovered in certain circumstances. However, some claims
VAT Refunds Irrecoverable Tax A Country by Country Detailed Guide EC VAT refunds Irrecoverable Tax VAT incurred in other EC Member States may be recovered in certain circumstances. However, some claims
10.1 WILL HEY FARM WATFORD LANE NEW MILLS RETENSION OF NEW STABLE BLOCK, SAND PADDOCK AND ASSOCIATED EARTHWORKS AND LANDSCAPING (FULL - MINOR)
 HPK/2012/0207 03/04/2012 WILL HEY FARM WATFORD LANE NEW MILLS MR & MRS M WILSON KIRSTY WILSON EQUINE AND WILL HEY FARM BED & BREAKFAST RETENSION OF NEW STABLE BLOCK, SAND PADDOCK AND ASSOCIATED EARTHWORKS
HPK/2012/0207 03/04/2012 WILL HEY FARM WATFORD LANE NEW MILLS MR & MRS M WILSON KIRSTY WILSON EQUINE AND WILL HEY FARM BED & BREAKFAST RETENSION OF NEW STABLE BLOCK, SAND PADDOCK AND ASSOCIATED EARTHWORKS
Education and training in Denmark Facts and Key Figures
 Education and training in Denmark Facts and Key Figures Education and training in Denmark The Danish education and training system is composed of two parallel systems: the mainstream education and training
Education and training in Denmark Facts and Key Figures Education and training in Denmark The Danish education and training system is composed of two parallel systems: the mainstream education and training
RULES FOR THE REIMBURSEMENT OF TRAVEL AND SUBSISTENCE EXPENSES FOR EXCHANGE OF OFFICIALS
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION CONSUMERS, HEALTH AND FOOD EXECUTIVE AGENCY Consumers and Food Safety Unit RULES FOR THE REIMBURSEMENT OF TRAVEL AND SUBSISTENCE EXPENSES FOR EXCHANGE OF OFFICIALS CONSUMER PROGRAMME
EUROPEAN COMMISSION CONSUMERS, HEALTH AND FOOD EXECUTIVE AGENCY Consumers and Food Safety Unit RULES FOR THE REIMBURSEMENT OF TRAVEL AND SUBSISTENCE EXPENSES FOR EXCHANGE OF OFFICIALS CONSUMER PROGRAMME
Family benefits Information about health insurance country. Udbetaling Danmark Kongens Vænge 8 3400 Hillerød. A. Personal data
 Mail to Udbetaling Danmark Kongens Vænge 8 3400 Hillerød Family benefits Information about health insurance country A. Personal data Name Danish civil registration (CPR) number Address Telephone number
Mail to Udbetaling Danmark Kongens Vænge 8 3400 Hillerød Family benefits Information about health insurance country A. Personal data Name Danish civil registration (CPR) number Address Telephone number
Automatic Recognition of Full Degrees. Erasmus Student Network AISBL *1. Emanuel Alfranseder #2. February 2014
 Automatic Recognition of Full Degrees *1 Emanuel Alfranseder #2 February 2014 * 1 ESN AISBL, Rue Hydraulique / Waterkrachtstraat, 15B, 1210 Saint-Josse-Ten-Noode / Sint-Jost-ten-Node, Brussels BELGIUM,
Automatic Recognition of Full Degrees *1 Emanuel Alfranseder #2 February 2014 * 1 ESN AISBL, Rue Hydraulique / Waterkrachtstraat, 15B, 1210 Saint-Josse-Ten-Noode / Sint-Jost-ten-Node, Brussels BELGIUM,
Online gambling: Finnish and French models. Virve Pöysti University of Helsinki Department of Social Research 12.1.2 012.
 Online gambling: Finnish and French models 12.1.2 012 1 Online gambling in Europe - Three models of online gambling in Europe (www.senat.fr) No online gambling markets Finland, Sweden, Portugal, Slovenia,
Online gambling: Finnish and French models 12.1.2 012 1 Online gambling in Europe - Three models of online gambling in Europe (www.senat.fr) No online gambling markets Finland, Sweden, Portugal, Slovenia,
Guidance on Sponsorship
 Guidance on Sponsorship (Recruiting and Employing Non-EEA Nationals under Tier 2 of the UK s Points Based System) Human Resources 1 Introduction 1.1 These guidance notes set out the requirements in place
Guidance on Sponsorship (Recruiting and Employing Non-EEA Nationals under Tier 2 of the UK s Points Based System) Human Resources 1 Introduction 1.1 These guidance notes set out the requirements in place
The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU 28 2014 Edition. James Rogers & Cécile Philippe May 2014. (Cover page) Data provided by
 (Cover page) The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU 28 2014 Edition NEW DIRECTION Page 1 of 17 James Rogers & Cécile Philippe May 2014 New Direction aims to help shift the EU onto a different course
(Cover page) The Tax Burden of Typical Workers in the EU 28 2014 Edition NEW DIRECTION Page 1 of 17 James Rogers & Cécile Philippe May 2014 New Direction aims to help shift the EU onto a different course
Netherlands. Croatia. Malta. Slovenia. Greece. Czech Republic. Portugal. Compulsory. households actual. social contributions.
 Structure and development of tax revenues Table EL.: Revenue (% of GDP) 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 200 20 202 203 I. Indirect taxes : : 2.3 2.7 2.7.8 2.6 3.5 3. 3.4 VAT : : 6.8 7. 7.0 6.3 7. 7.2 7.
Structure and development of tax revenues Table EL.: Revenue (% of GDP) 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 200 20 202 203 I. Indirect taxes : : 2.3 2.7 2.7.8 2.6 3.5 3. 3.4 VAT : : 6.8 7. 7.0 6.3 7. 7.2 7.
Look at Leisure. Participation. No. 50. Introduction
 No. 50 Look at Leisure Participation Inside this issue: Introduction 1 Overview of Participation Participation by Category A Closer Look at Walking and Cycling 1 3 9 Introduction This bulletin examines
No. 50 Look at Leisure Participation Inside this issue: Introduction 1 Overview of Participation Participation by Category A Closer Look at Walking and Cycling 1 3 9 Introduction This bulletin examines
The Development of Self-Employment in Russia
 The Development of Self-Employment in Russia Theodore February 2001 PONARS Policy Memo 186 University of Arizona Despite the important economic, social, and political roles the self-employed can potentially
The Development of Self-Employment in Russia Theodore February 2001 PONARS Policy Memo 186 University of Arizona Despite the important economic, social, and political roles the self-employed can potentially
Labour Market, Social Policy, Social Security System and Migration Policy - Current State and Problems Which Bulgaria Faces
 Labour Market, Social Policy, Social Security System and Migration Policy - Current State and Problems Which Bulgaria Faces February 21, 2003, Bratislava I. Labour market- current state, problems and undertaken
Labour Market, Social Policy, Social Security System and Migration Policy - Current State and Problems Which Bulgaria Faces February 21, 2003, Bratislava I. Labour market- current state, problems and undertaken
ABOUT DIRECT SALES IN THE WORLD, EUROPE AND ROMANIA
 Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 11(4), 2011, 151-158 151 ABOUT DIRECT SALES IN THE WORLD, EUROPE AND ROMANIA CLAUDIA ISAC, ALIN ISAC * ABSTRACT: Direct sale represents a modern product
Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 11(4), 2011, 151-158 151 ABOUT DIRECT SALES IN THE WORLD, EUROPE AND ROMANIA CLAUDIA ISAC, ALIN ISAC * ABSTRACT: Direct sale represents a modern product
How To Study At Mikkeli University Of Applied Sciences
 UPDATE YOURSELF Study in English we make it easy, so take it easy. Your life your degree It is our pleasure to invite you to study in the stimulating environment of Mikkeli University of Applied Sciences
UPDATE YOURSELF Study in English we make it easy, so take it easy. Your life your degree It is our pleasure to invite you to study in the stimulating environment of Mikkeli University of Applied Sciences
