Mobile Communication GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS and beyond
|
|
|
- Cora Stafford
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mobile Communication GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS and beyond Ralf Keller Ericsson Research, Corporate Unit Ericsson Eurolab Deutschland GmbH 1
2 Overview Services GSM GPRS & EDGE UMTS Beyond 2
3 Services 3
4 Personal and Secure Services Mobile Messaging Voic SMS/EMS + MMS Instant Message Mobile -WWW (Browsing/streaming) Information (news, sport, etc) Entertainment (Music, Games ) Location Services Mobile Commerce (Transactions) Banking Trading Ticketing Shopping UMTS GSM / EDGE / GPRS / HSCSD 4
5 GSM Global System for Mobile communication 5
6 GSM Evolution GSM P1 GSM P2 G2+ GPRS EDGE P1 EDGE P2 Basic CS domain: voice fax SMS data (9.6 kbps) Suppl Services: call waiting conf call Interw. with GSM 1800 GSM kbps HSCSD 57.6 kbps PS domain data 160 kbps 8PSK data 384 kbps EGPRS ECSD Voice over PS-domain all-ip 6
7 Key Terms LA-6 Location Area Roaming BSC-3 International Roaming LA-5 MSC Location Updating Paging Handover LA-1 LA-2 BSC-1 BSC-2 LA-3 LA-4 7
8 GSM900 Air Interface (TDMA) uplink frequencies 890 MHz F1-u TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 TS0 TS1 TS2 Time TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 915 MHz F124-u TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 downlink frequencies 935 MHz 960 MHz F1-d Frequency F124-d TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5TS6 TS7 8
9 GSM Frequency Bands GSM 900 egsm GSM 1800 GSM 1900 Uplink MHz MHz MHz MHz Downlink carrier separation 200 khz carrier pairs
10 Frequency Planning in GSM Cells Multiple Reuse Pattern Frequency Hopping Micro cell usage for further capacity increase Half rate calls for further capacity increase 10
11 GSM Network OSS BTS A-bis BSC BSS BTAP TRC A-ter BSSAP SC SMS-IWMSC SMS-GMSC A-IF MAP MAP MAP HLR MAP MAP EIR FNR MAP AUC CCN ILR ISUP GMSC SS PSTN BTS BSC BSS BSSAP A-IF MAP MSC/VLR ISUP CAP ISUP MSC/VLR Tigris PLMN A-bis SSP CAP SCP SDP MIN IP network 11
12 Most Important Traffic Cases Location Update with or without registration in HLR SMS-Mobile Terminating call SMS-Mobile Originating call Mobile Originating call Mobile Terminating call Handover (intra BSC, inter BSC, intra MSC, inter MSC) 12
13 SMS MT (Forw MT SM) SC SMS-GMSC HLR MSC Forward MT SM RR connection est Service request Authentication Ciphering mode set Data link est. Short message transfer RR connection rel Forward MT SM Send routing info for SM Result Forward SM 13
14 SMS MT (RR conn est) PCH MS BTS BSC MSC HLR Paging Paging Command Paging Request Forward MT SM RR connection est RACH Channel Request Channel Request cause, ref number Service request Channel Activation SDCCH #, MS-power Authentication Ciphering mode set Data link est. AGCH Immediate Assignment Channel Act Ack Imm Assignment Cmd Short message transfer SDCCH # RR connection rel 14
15 SMS MT (Data link est) MS BTS BSC MSC HLR Forward MT SM xyx SABM (SAPI=3) Est Req (SAPI=3) CP-Data(RP-Data) RR connection est Service request UA (SAPI=3) Est Conf (SAPI=3) Authentication Ciphering mode set Data link est. Short message transfer RR connection rel 15
16 SMS MT (SM transfer) MS BTS BSC MSC Forward MT SM xyx CP-Data(RP-Data) CP-Data (RP-Data) DTAP SMS- GMSC SC RR connection est Service request Authentication Ciphering mode set Data link est. CP-Ack CP-Ack(RP-Ack) CP-Ack CP-Ack(RP-Ack) CP-Ack CP-Ack(RP-Ack) RP-Ack Short message transfer RP-Ack RR connection rel 16
17 GSM Enhancements: GPRS and EDGE GPRS = General Packet Radio System EDGE = Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution 17
18 Why GPRS?? Packet-oriented services over circuit-switched bearers is often not resource-efficient New Services become possible Always Connected, Always On-line 18
19 GSM Enhancements GPRS BTS BSC BSS SC SMS-IWMSC SMS-GMSC BSSGP Gb -If MAP MAP MAP FNR HLR MAP MAP AUC MAP EIR CCN MAP CAP GTP SGSN ILR MAP GGSN PS-domain IP-network A-bis BSSAP A-If Gs-If MSC/VLR ISUP MSC/VLR CS-domain BSS 19
20 GSM Enhancements EDGE BTS A BSC A MSC/VLR Gr (MAP) HLR SOG Gb Gs SGSN GGSN Gi (IP) IP Network MS Gn Gn New HW New SW BGW Backbone Network IP Same core network and external interfaces Dimensioning and upgrades might be required 20
21 GSM Bit Rates Channel coding (error detection and correction) Interleaving Burst formation Modulation GMSK and 8PSK kb/s CS 57.6 kb/s HSCSD 115 kb/s GPRS 384 kb/s EDGE 21
22 Network Overview Abis BTS BSC A MSC/VLR SMS-GMSC Gd SMS-IWMSC (MAP) (MAP) HLR MS Gb Gs SGSN Gr (MAP) Gc GGSN Gi (IP) IP Network Gb Gb - - Interface Interface between between SGSN SGSN and and BSC BSC (Frame (Frame Relay) Relay) Gi Gi - - Reference Reference point point between between GPRS GPRS and and external external packet packet data data network network Gs Gs - - Interface Interface between between SGSN SGSN and and MSC MSC Gr Gr - - Home Home Location Location Register Register Gn Gn - - Interface Interface between between two two GSN GSN within within the the same same PLMN PLMN Gp Gp - - Interface Interface between between two two GSN GSN in in different different PLMN PLMN Gn Gn Backbone Network Gp (IP) PTM-SC Other PLMN 22
23 Gb Interface (BSS-SGSN) BTS BSC BSS BSS GPRS Protocol Network Service Frame Relay BSSGP NS FR E1/T1 BSC MS BSSGP NS FR E1/T1 SGSN Gb SGSN 23
24 Gs Interface (SGSN to MSC) BTS BSC MSC/VLR MS Gs SS7/BSSAP+ based Carries all all paging of of class A and and B terminals Combined attach/detach for for class A and and B terminals Combined routing/location area update SGSN 24
25 Gn and Gp Interfaces (SGSN to GGSN and SGSN to SGSN) SGSN Gn SGSN Gn GGSN Gp SGSN Other PLMN GGSN GTP protocol carries payload as as well well as as signalling (PDP context activation) SGSN to to SGSN transfer buffers in in case of of inter- SGSN routeing area update Gp Gpis is the the same as as Gn, Gn, but but inter-plmn 25
26 Gi Interface (GGSN to ISP/corporate network) IP Network Interfaces to to ISPs (and corporates) using standard IP-based protocols. Security functions Firewall (packet filtering) Authentication, integrity and and confidentiality (IPSEC, tunneling, key key exchange) Routing functions Static/dynamic routing supported GGSN Gi 26
27 PDP Context Activation How to Locate Correct GGSN BTS BSC ISP A MS DNS DNS GGSN (A) ISP B SGSN DNS Backbone GGSN (B) Corp. Network SGSN resolves an Access Point Name (APN) into the IP address for the GGSN connected to the target network 27
28 Fixed or Dynamic IP Address Allocation HLR ISP RADIUS BTS BSC SGSN Backbone GGSN MS Fixed: IP IP address stored in in the the HLR HLR Dynamic: A set set of of IP IP addresses are are allocated to to the the GGSN domain Dynamic: IP IP address can can be be allocated by by external RADIUS Corp. Network 28
29 Authentication in GPRS Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) ISP HLR RADIUS server BTS PAP/CHAP BSC SGSN Backbone GGSN RADIUS client Accept / Reject MS RADIUS server is is used primarily for for authentication IP IP address allocation is is optional RADIUS server validates PAP/CHAP sent sent from from MS MS and and returns Access -Accept/-Reject 29
30 Transmission Plane in GPRS Application IP / X.25 IP / X.25 SNDCP SNDCP GTP GTP LLC LLC UDP/ TCP UDP/ TCP RLC MAC RLC MAC BSSGP Frame Relay BSSGP Frame Relay IP L2 IP L2 GSM RF GSM RF L1bis L1bis L1 L1 MS BSS SGSN GGSN Um Gb Gn Gi 30
31 Interaction of GPRS services with CS connections Class A: A: Simultaneous usage of of Circuit- and Packet switched services (two TRX). Class B: B: Automatic choice of of service, Circuit- or or Packet switched, but but only one at at a time (one TRX). Suspension/resumption of of GPRS services at at setup/release of of CS CS connection. Class C: C: Manually selected use of of either Circuit- or or Packet switched service. Special case is is a packet only MS MS (one TRX). 31
32 GPRS High-Level Functions Network Access Control Functions Packet Routing and Transfer Mobility Management Logical Link Management Radio Resource Management Network Management 32
33 Packet Routing and Transfer Routing Address Translation Encapsulation and Tunneling Compression Ciphering 33
34 Mobility Management Attach Detach Location Management procedures Cell Update Routing Area Update Security functions 34
35 Mobility Management State Diagram IDLE Periodic Supervision Timer Expiration or Cancel Location GPRS Attach READY READY Timer Expiration or Force to STANDBY or Abnormal RLC condition STANDBY GPRS Detach or Cancel Location PDU Reception 35
36 EDGE - Enhanced Data Rate for GSM Evolution - 36
37 EDGE Modulation Principle Currently: GMSK Modulation Q EDGE: 8PSK Modulation (0,1,0) Q 1 I (0,0,0) (0,1,1) I 0 (0,0,1) (1,1,1) (1,0,1) (1,1,0) (1,0,0) 1 bit per symbol 3 bits per symbol 37
38 Comparison of Data Rates GPRS EGPRS CS4 = 20.0 kbps CS3 = 14.4 kbps CS2 = 12.0 kbps CS1 = 8.0 kbps 8PSK modulated Note: Both GMSK modulated but not the same! MCS9 = 59.2 kbps MCS8 = 54.4 kbps MCS7 = 44.8 kbps MCS6 = 29.6 kbps MCS5 = 22.4 kbps MCS4 = 16.8 kbps MCS3 = 14.8 kbps MCS2 = 11.2 kbps MCS1 = 8.4 kbps 38
39 EDGE Link Adaptation Data rates With EDGE Standard GSM Good Bad Signal quality 39
40 Universal Mobile Telecommunication System UMTS 40
41 Standardization Bodies 41
42 3G Systems CDMA technique IMT-2000 UMTS (WCDMA) Cdma2000 Two modes: FDD or TDD Europe - 3GPP (South Korea, Japan, USA) CDMA technique USA, South Korea 3GPP2 EDGE TDMA technique USA (Europe) TIA (ETSI) 42
43 UMTS Spectrum Division Europe Frequency Division Duplex; 2x60 MHz UTRA Paired Band: WCDMA Uplink: MHz Downlink: MHz TDD FDD MSS TDD FDD MSS f MHz Time Division Duplex UTRA Unpaired Band: TD-CDMA MHz and MHZ Mobile Satellite Service; 2x30 MHz Uplink: MHz Downlink: MHz 43
44 UMTS/GSM Reference model UE AN CN SIM SIM USIM USIM USIM USIM MT MT ME ME ME ME BTS BS BS UTRAN BSS RNS RNS BSC RNC Iur RNC A Iu Iu Gb MSC MSC MSC MSC EIR EIR SGSN SGSN SGSN SGSN SCF SCF HLR HLR SMS- SMS- GMSC GMSC SMS- SMS- IWMSC IWMSC GMSC GMSC AUC AUC GGSN GGSN Note: Not all interfaces shown and named External Networks ISDN PSTN PSPDN CSPDN PDN: -Intranet -Extranet -Internet 44
45 WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access High data rates in 5 MHz 384 kbps with wide-area coverage 2 Mbps with local coverage High service flexibility support for services with variable rate support for simultaneous services support of multiple parallel variable-rate services on one connection packet and circuit switched services Fast and efficient packet access Higher capacity 45
46 WCDMA Technical characteristics 5 MHz carriers Frequency Division Duplex, FDD 3.84 Mcps chip rate Variable spreading codes Optimised packet access on common or dedicated channel High spectrum effiency f P MHz t 10 ms frame 46
47 Why Spread Spectrum? Frequency selective fading - Frequency Diversity Interference Averaging Channel Quality Channel Quality f f 47
48 Bit-rate Flexibility WCDMA variability principle: Power is the common shared physical resource Bit rate Power level Spreading factor Varying user bit rate Translates into Varying power level Varying spreading factor 48
49 Power Control What? The Transmitter adapts the output power according to Path Loss Why? Mainly to solve the Near-Far problem Goal is that all users should experience the same SIR How? Open Loop Power control (Initially, No signaling) Inner Loop Power control (Signaling channel, continuously: 1500 times/s, relative changes: up or down) Outer loop Power control (Between BTS and RNC) 49
50 Uplink Power Control in Soft Handover BS1 BS2 P MS UP/DOWN Command UP/DOWN Command Outer loop: Down + Down Down + Up Up + Up Ul Eb/No target FER/ BER Adjust target QoS target Decrease power Increase power 50
51 Technical Vision Vertical vs Horizontal Integration Today s Solutions Services Future Solutions Services/Applications PLMN PSTN/ISDN Data/IP Networks CATV PLMN PSTN/ISDN Data/IP Networks CATV Connectivity Access Transport & Switching Networks 51
52 Connectivity Layer Services/ application layer Application Servers Service Capability Servers Application Servers MSC SGSN HLR/AuC/FNR GMSC/Transit Server Server Server SGW Control PSTN/ ISDN GSM EDGE MGW WCDMA Connectivity MGW Internet Intranets 52 Control User data
53 And beyond? 53
54 The future Telecommunication Environment is Multi-Access Always Best Connected to Common Personal and Secure Services Mobile Nomadic Digital Broadcasting Fixed Wireless Fixed PAN 54
55 Capabilities of IMT-2000 and Systems Beyond Mobility Systems Beyond IMT-2000 will encompass the capabilities of previous systems New Capabilities Of Systems Beyond IMT-2000 High IMT-2000 Enhanced IMT-2000 New Mobile Access Dashed line indicates that the exact data rates associated with Systems Beyond are Enhancement not yet determined. Low New Nomadic / Local Area Wireless Access Peak Useful Data Rate (Mb/s) KEY: denotes interconnection between systems via networks or the like, which allows flexible use in any environments without making users aware of constituent systems. Nomadic / Local Area Access Systems Digital Broadcast Systems 55
56 Questions? 56
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
EDGE: The Introduction of High Speed Data in GSM / GPRS Networks
 10 September 2003 EDGE: The Introduction of High Speed Data in GSM / GPRS Networks Wendy Florence Ericsson South Africa Rev A 10 September 2003 1 Agenda What is EDGE? Implementing EDGE Network and transmission
10 September 2003 EDGE: The Introduction of High Speed Data in GSM / GPRS Networks Wendy Florence Ericsson South Africa Rev A 10 September 2003 1 Agenda What is EDGE? Implementing EDGE Network and transmission
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G
 CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
 General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
PDF vytvořeno zkušební verzí pdffactory www.fineprint.cz UMTS
 UMTS Generations of mobile systems Generation 1 (1980-1995) 2 (1992-2000) 2,5 (1999-2010) 3 (2004-20?) Names NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone); 450 MHz, 900 MHz AMPS (Advance Mobile Telephone System); USA
UMTS Generations of mobile systems Generation 1 (1980-1995) 2 (1992-2000) 2,5 (1999-2010) 3 (2004-20?) Names NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone); 450 MHz, 900 MHz AMPS (Advance Mobile Telephone System); USA
Wireless Access of GSM
 Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS
 Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
1G to 4G. Overview. Presentation By Rajeev Bansal Director(Mobile-1) Telecommunication Engineering Centre
 1G to 4G Overview Presentation By Rajeev Bansal Director(Mobile-1) Telecommunication Engineering Centre Mobile Networks differentiated from each other by the word Generation 1G, 2G, 2.5G, 2.75G, 3G milestones
1G to 4G Overview Presentation By Rajeev Bansal Director(Mobile-1) Telecommunication Engineering Centre Mobile Networks differentiated from each other by the word Generation 1G, 2G, 2.5G, 2.75G, 3G milestones
UMTS/GPRS system overview from an IP addressing perspective. David Kessens Jonne Soininen
 UMTS/GPRS system overview from an IP addressing perspective David Kessens Jonne Soininen Introduction 1) Introduction to 3GPP networks (GPRS, UMTS) Technical overview and concepts for 3GPP networks Mobility
UMTS/GPRS system overview from an IP addressing perspective David Kessens Jonne Soininen Introduction 1) Introduction to 3GPP networks (GPRS, UMTS) Technical overview and concepts for 3GPP networks Mobility
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks
 Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
3GPP Wireless Standard
 3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
LTE Overview October 6, 2011
 LTE Overview October 6, 2011 Robert Barringer Enterprise Architect AT&T Proprietary (Internal Use Only) Not for use or disclosure outside the AT&T companies except under written agreement LTE Long Term
LTE Overview October 6, 2011 Robert Barringer Enterprise Architect AT&T Proprietary (Internal Use Only) Not for use or disclosure outside the AT&T companies except under written agreement LTE Long Term
Wireless Cellular Networks: 3G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 3G Raj Jain Washington University Saint Louis, MO 63131 [email protected] These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-06/ 7-1 Overview Wireless
Wireless Cellular Networks: 3G Raj Jain Washington University Saint Louis, MO 63131 [email protected] These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-06/ 7-1 Overview Wireless
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS
 Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS Anthony Lo [email protected] 1 Wiskunde end Informatica Outline UMTS Overview TCP and MPEG-4 Performance Summary 2 1 Universal Mobile Telecommunications
Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS Anthony Lo [email protected] 1 Wiskunde end Informatica Outline UMTS Overview TCP and MPEG-4 Performance Summary 2 1 Universal Mobile Telecommunications
GPRS Overview. GPRS = General Packet Radio Service. GPRS Network
 GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
Copyright. GSM - Phase 2+ From GSM to GPRS. From GSM to GPRS. Motivations. General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) HSCSD EDGE GPRS
 Copyright HSCSD EDGE GPRS GSM - Phase 2+ Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs-NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/nd-nc/1.0/
Copyright HSCSD EDGE GPRS GSM - Phase 2+ Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs-NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/nd-nc/1.0/
2G Cellular Data Networks
 1 2 General Mobility Issues 2G Cellular Data Networks Registration and Authentication User Locate local service provider access point Obtain network access Service provider Locate mobile user within network
1 2 General Mobility Issues 2G Cellular Data Networks Registration and Authentication User Locate local service provider access point Obtain network access Service provider Locate mobile user within network
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed Radio Access Network Architecture. [email protected]
 IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed Radio Access Network Architecture [email protected] Outline - Definition IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed RAN Architecture Page 2 Siemens
IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed Radio Access Network Architecture [email protected] Outline - Definition IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed RAN Architecture Page 2 Siemens
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Mobility and cellular networks
 Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility Management in UMTS
 Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Otto Spaniol Mobility Management in UMTS Seminar: Datacommunication & Distributed Systems WS 2003/2004
Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Otto Spaniol Mobility Management in UMTS Seminar: Datacommunication & Distributed Systems WS 2003/2004
Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ABSTRACT W-CDMA (Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access), an ITU standard derived
Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ABSTRACT W-CDMA (Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access), an ITU standard derived
Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517
 Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517 Some slides are adapted from Dr. Dave Johnson Notes Dr. Sumi Helal, Ph.D. Professor Computer & Information Science & Engineering Department University
Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517 Some slides are adapted from Dr. Dave Johnson Notes Dr. Sumi Helal, Ph.D. Professor Computer & Information Science & Engineering Department University
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Long-Term Evolution. Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab
 Long-Term Evolution Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab Background Long-Term Evolution Define a new packet-only wideband radio with flat architecture as part of 3GPP radio technology family 2004:
Long-Term Evolution Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab Background Long-Term Evolution Define a new packet-only wideband radio with flat architecture as part of 3GPP radio technology family 2004:
GPRS Systems Performance Analysis
 GPRS Systems Performance Analysis Fátima de Lima Procópio Duarte, Antonio A.F. Loureiro, Leonardo Barbosa e Oliveira, Cláudio Márcio de Souza Vicente Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte,
GPRS Systems Performance Analysis Fátima de Lima Procópio Duarte, Antonio A.F. Loureiro, Leonardo Barbosa e Oliveira, Cláudio Márcio de Souza Vicente Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte,
EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1
 EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1 1 Circuit-Switched Systems In a circuit-switched system, each traffic channel is dedicated to a user until its cell is terminated. Circuit
EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1 1 Circuit-Switched Systems In a circuit-switched system, each traffic channel is dedicated to a user until its cell is terminated. Circuit
Data Services in GSM HSCSD GPRS. GPRS Infrastructure Components
 4 4 Data Services in Data transmission in with only 9.6 kbit/s Advanced channel coding allows 14.4 kbit/s Still not enough for Internet access or even multimedia applications Thus: UMTS as 3G network :
4 4 Data Services in Data transmission in with only 9.6 kbit/s Advanced channel coding allows 14.4 kbit/s Still not enough for Internet access or even multimedia applications Thus: UMTS as 3G network :
How To Improve Data Rates For Global Evolution (Edge)
 EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
Private DNS for Mobile Operators
 Private for James Yu Senior Director - Strategic Technical Initiatives NeuStar, Inc. [email protected] +1-571-434-5572 (B) +1-703-622-5187 (M) Richard Xu Chief Architect Aicent, Inc [email protected]
Private for James Yu Senior Director - Strategic Technical Initiatives NeuStar, Inc. [email protected] +1-571-434-5572 (B) +1-703-622-5187 (M) Richard Xu Chief Architect Aicent, Inc [email protected]
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 2: Mobile Networks Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 2 Mobile Networks 2.1 Infrastructure
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 2: Mobile Networks Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 2 Mobile Networks 2.1 Infrastructure
Index. Common Packet Channel (CPCH) 25 Compression 265, 279 82, 288 header compression 284
 bindex.fm Page 296 Tuesday, March 22, 2005 7:17 AM Index 2G, 2.5G, 3G 13 3GPP 118 Release 5 (Rel 5) 124 Release 6 (Rel 6) 125 Release 97/98 (Rel 97/98) 119 Release 99 (Rel 99) 120 4 3GPP2 129 4G 13, 44
bindex.fm Page 296 Tuesday, March 22, 2005 7:17 AM Index 2G, 2.5G, 3G 13 3GPP 118 Release 5 (Rel 5) 124 Release 6 (Rel 6) 125 Release 97/98 (Rel 97/98) 119 Release 99 (Rel 99) 120 4 3GPP2 129 4G 13, 44
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
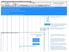 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Mobile Communications TCS 455
 Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong [email protected] Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong [email protected] Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
STAR-GATE TM. Annex: Intercepting Packet Data Compliance with CALEA and ETSI Delivery and Administration Standards.
 STAR-GATE TM Annex: Intercepting Packet Data Compliance with CALEA and ETSI Delivery and Administration Standards. In this document USA Tel: +1-703-818-2130 Fax: +1-703-818-2131 E-mail: [email protected]
STAR-GATE TM Annex: Intercepting Packet Data Compliance with CALEA and ETSI Delivery and Administration Standards. In this document USA Tel: +1-703-818-2130 Fax: +1-703-818-2131 E-mail: [email protected]
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Mobile@Home GSM services over wireless LAN
 Mobile@Home GSM services over wireless LAN Martin Bäckström, Andreas Havdrup, Tomas Nylander, Jari Vikberg and Peter Öhman What do you get when you combine mobile telephony with voice over IP (VoIP)? Mobile@Home.
Mobile@Home GSM services over wireless LAN Martin Bäckström, Andreas Havdrup, Tomas Nylander, Jari Vikberg and Peter Öhman What do you get when you combine mobile telephony with voice over IP (VoIP)? Mobile@Home.
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
Introduction to EDGE. 2.1 What Is EDGE?
 2 Introduction to EDGE This chapter is the first of a series dedicated to EDGE. It introduces the different EDGE concepts from a global point of view, explaining how they have been introduced into the
2 Introduction to EDGE This chapter is the first of a series dedicated to EDGE. It introduces the different EDGE concepts from a global point of view, explaining how they have been introduced into the
Cellular Phone Systems
 Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies
 GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP
 Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been selected as the main signaling protocol of the Third Generation Partnership Projects IP Multimedia
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been selected as the main signaling protocol of the Third Generation Partnership Projects IP Multimedia
A Performance Evaluation of Internet Access via the General Packet Radio Service of GSM
 A Performance Evaluation of Internet Access via the General Packet Radio Service of GSM Simon Hoff, Michael Meyer, Andreas Schieder Ericsson Eurolab Deutschland Ericsson Allee 1, 52134 Herzogenrath, Germany
A Performance Evaluation of Internet Access via the General Packet Radio Service of GSM Simon Hoff, Michael Meyer, Andreas Schieder Ericsson Eurolab Deutschland Ericsson Allee 1, 52134 Herzogenrath, Germany
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013
 EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude [email protected] Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude [email protected] Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
Product Description. HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Issue 01. Date 2013-6-13
 HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 Issue 01 Date 2013-6-13 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support and service. Please feel
HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 Issue 01 Date 2013-6-13 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support and service. Please feel
operation, and their architectures.
 Chapter 1 ireless communications have become very pervasive. The number of mobile phones and wireless Internet users has increased significantly in recent years. Traditionally, first-generation wireless
Chapter 1 ireless communications have become very pervasive. The number of mobile phones and wireless Internet users has increased significantly in recent years. Traditionally, first-generation wireless
CDMA Network Planning
 CDMA Network Planning by AWE Communications GmbH www.awe-com.com Contents Motivation Overview Network Planning Module Air Interface Cell Load Interference Network Simulation Simulation Results by AWE Communications
CDMA Network Planning by AWE Communications GmbH www.awe-com.com Contents Motivation Overview Network Planning Module Air Interface Cell Load Interference Network Simulation Simulation Results by AWE Communications
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao Zhang IP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. January 2004 This material is protected under all Copyright Laws as
Chapter 1: Introduction Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao Zhang IP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. January 2004 This material is protected under all Copyright Laws as
ETSI TS 129 119 V9.0.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification
 TS 129 119 V9.0.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) specification for Gateway Location Register (GLR) (3GPP TS 29.119
TS 129 119 V9.0.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) specification for Gateway Location Register (GLR) (3GPP TS 29.119
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE
 Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS! 2. Third Party Voice over IP! 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem! 4. Circuit Switched Fallback! 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS! 2. Third Party Voice over IP! 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem! 4. Circuit Switched Fallback! 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Siemens GERAN Troubleshooting Using Signaling Analyzer
 Application Note Siemens GERAN Troubleshooting Using Signaling Analyzer Introduction................................................................................ 2 Scope of this Document.....................................................................
Application Note Siemens GERAN Troubleshooting Using Signaling Analyzer Introduction................................................................................ 2 Scope of this Document.....................................................................
3GPP TS 27.060 V3.8.0 (2003-06)
 TS 27.060 V3.8.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Packet Domain; Mobile Station (MS) supporting Packet Switched Services
TS 27.060 V3.8.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Packet Domain; Mobile Station (MS) supporting Packet Switched Services
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
5.0 Network Architecture. 5.1 Internet vs. Intranet 5.2 NAT 5.3 Mobile Network
 5.0 Network Architecture 5.1 Internet vs. Intranet 5.2 NAT 5.3 Mobile Network 1 5.1The Internet Worldwide connectivity ISPs connect private and business users Private: mostly dial-up connections Business:
5.0 Network Architecture 5.1 Internet vs. Intranet 5.2 NAT 5.3 Mobile Network 1 5.1The Internet Worldwide connectivity ISPs connect private and business users Private: mostly dial-up connections Business:
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks
 Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
NTT DOCOMO Technical Journal. Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications
 M2M 3GPP Standardization Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications The number
M2M 3GPP Standardization Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications The number
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;
GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
Role and Evolution of Radio Network Controllers
 01001000100000110000001000001100 010010001000 Role and Evolution of Radio Network Controllers Pekka Varis SPRP501 Senior R&D Manager / Senior Specialist Nokia [email protected] Agenda Radio Network
01001000100000110000001000001100 010010001000 Role and Evolution of Radio Network Controllers Pekka Varis SPRP501 Senior R&D Manager / Senior Specialist Nokia [email protected] Agenda Radio Network
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
RBS 6000 Training Programs. Catalog of Course Descriptions
 RBS 6000 Training Programs Catalog of Course Descriptions Page 2 2 Telephone: +46 8 757 0000 Page 3 Catalog of Course Descriptions INTRODUCTION... 5 GSM RADIO NETWORK OVERVIEW... 7 WCDMA RADIO ACCESS NETWORK
RBS 6000 Training Programs Catalog of Course Descriptions Page 2 2 Telephone: +46 8 757 0000 Page 3 Catalog of Course Descriptions INTRODUCTION... 5 GSM RADIO NETWORK OVERVIEW... 7 WCDMA RADIO ACCESS NETWORK
IP Multimedia System: general aspects and migration perspectives
 IMS TPC EPC IP Multimedia System: general aspects and migration perspectives Dr. Leo Lehmann Federal Office of Communication, Switzerland ITU Workshop on Developments regarding telecommunication network
IMS TPC EPC IP Multimedia System: general aspects and migration perspectives Dr. Leo Lehmann Federal Office of Communication, Switzerland ITU Workshop on Developments regarding telecommunication network
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
Introduction to Cellular Networks: 1G/2G/3G
 Introduction to Cellular Networks: 1G/2G/3G Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 [email protected] Audio/Video recordings of this class lecture are available at: 14-1 Overview
Introduction to Cellular Networks: 1G/2G/3G Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 [email protected] Audio/Video recordings of this class lecture are available at: 14-1 Overview
Mobile Packet Backbone Network Training Programs. Catalog of Course Descriptions
 Mobile Packet Backbone Network Training Programs Catalog of Course Descriptions Page 2 Catalog of Course Descriptions INTRODUCTION... 6 MOBILE PACKET BACKBONE NETWORK (M-PBN) R5.1 DELTA... 7 MOBILE PACKET
Mobile Packet Backbone Network Training Programs Catalog of Course Descriptions Page 2 Catalog of Course Descriptions INTRODUCTION... 6 MOBILE PACKET BACKBONE NETWORK (M-PBN) R5.1 DELTA... 7 MOBILE PACKET
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Nokia Networks Oy 1 (48)
 1 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols Training Document GPRS System Course 2 (48) 3 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols The information in this document is subject to change without
1 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols Training Document GPRS System Course 2 (48) 3 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols The information in this document is subject to change without
Mobile Data Transfer
 Mobile Data Transfer -Access Technologies for 3G Services- Bonn, April 8, 2003 Presented by: Vice President Training Telecommunication Networks Klingenhofstrasse 58, 90411 Nuremberg / Germany About TOP
Mobile Data Transfer -Access Technologies for 3G Services- Bonn, April 8, 2003 Presented by: Vice President Training Telecommunication Networks Klingenhofstrasse 58, 90411 Nuremberg / Germany About TOP
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP Operations
 Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
The future of mobile networking. David Kessens <[email protected]>
 The future of mobile networking David Kessens Introduction Current technologies Some real world measurements LTE New wireless technologies Conclusion 2 The future of mobile networking
The future of mobile networking David Kessens Introduction Current technologies Some real world measurements LTE New wireless technologies Conclusion 2 The future of mobile networking
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
IMT-2000 Network Architecture
 IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
Nokia Siemens Networks LTE 1800 MHz Introducing LTE with maximum reuse of GSM assets
 Nokia Siemens Networks LTE 1800 MHz Introducing LTE with maximum reuse of GSM assets White paper Table of contents 1. Overview... 3 2. 1800 MHz spectrum... 3 3. Traffic Migration... 5 4. Deploying LTE-GSM
Nokia Siemens Networks LTE 1800 MHz Introducing LTE with maximum reuse of GSM assets White paper Table of contents 1. Overview... 3 2. 1800 MHz spectrum... 3 3. Traffic Migration... 5 4. Deploying LTE-GSM
