Computer Competency Test Preparation Workshop
|
|
|
- Nelson Morgan
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Competency Test Preparation Workshop Written Test Study Guide A. PC Components and Specifications The five primary components of a computer are: Input devices Output devices Central Processing Unit or CPU Memory Storage devices 1. Input Devices An input device is any hardware component that allows a user to enter data or instructions into a computer. Six commonly used input devices are the keyboard, mouse, microphone, scanner, digital camera and PC camera. A keyboard contains keys that allow a user to enter data and instructions into a computer. A mouse is a small handheld device that controls the movement of a symbol on the screen called a pointer. With the mouse, you can make choices, initiate a process and select objects. A microphone allows a user to speak to the computer to enter data and instructions into the computer. A scanner reads printed text and pictures and then translates the results into a form the computer can use. A digital camera allows a user to take pictures and transfer the photographed image to the computer, instead of storing on traditional film. A PC camera allows the users to have video telephone or conference calls where the participants can see each other while communicating. Reviewed June
2 2. Output Devices An output device is any hardware component that can convey information to a user. Three commonly used output devices are a printer, a monitor and speakers. A printer produces text and graphics on a physical medium such as paper or a transparency. This physical format is also referred to as a hard copy. A printer s resolution is measured in DPIs. A monitor, which looks like a small television screen, displays text, graphics, and video information. A monitor s viewable size is the diagonal measurement of the actual viewing area. Speakers allow the user to hear music, voice, and other sounds generated by the computer. Device Connectivity A serial port is the interface that connects devices to the system unit by transmitting data one bit at a time. Serial ports are mainly used for devices that do not require fast data transmission rates, such as a mouse, keyboard, or modem. A universal serial bus (USB) port can connect up to 127 different peripheral devices with a single connector type. The telephone system uses continuously-variable analog signals; your PC moves and stores data as digital signals using a series of 1 s and 0 s. Analog signals work over a continuous range (like the sound that comes from speakers); digital data is either on (1) or off(0) at any given time; never any in-between value. 3. Central Processing Unit or CPU The central processing unit (CPU) contains the electronic circuits that cause processing to occur. The CPU is made up of the control unit and the arithmetic/logic unit. The control unit interprets the instructions. The arithmetic/logic unit performs the logical and arithmetic processes. On personal computers, the CPU is designed into a chip called a processor. Manufacturers state clock speed (the speed at which a processor executes instructions) in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). 4. Memory Memory, also called random access memory, or RAM, consists of electronic components that store data including numbers, letters of the alphabet, graphics, and sound. Most RAM is volatile, meaning it loses its contents when the power is removed from the computer. Any data to be processed must be stored in memory. The amount of memory is typically measured in kilobytes or megabytes. One kilobyte (K or KB) equals approximately 1,000 memory locations and one megabyte (M or MB) equals approximately one million memory locations. A memory location, or byte, usually stores one character. Therefore, a computer with 512 MB of memory can store approximately 512 million characters. 2
3 Computer Competency Test Preparation Workshop Guide 5. Storage Devices Storage devices, also called auxiliary storage devices or secondary storage devices, are used to store instructions and data when they are not being used in memory. Four common types of auxiliary storage are floppy disks, hard disks, compact disks and zip disks. Floppy Disks A floppy disk, or diskette, is a portable, inexpensive storage medium that consists of a thin, circular, flexible plastic disk with magnetic coating enclosed in a square-shaped plastic shell. The most widely used floppy disk is 3.5 inches wide and typically stores up to 1.44 megabytes (1.44MB) of data. A floppy disk is a type of magnetic disk, which means it uses magnetic patterns to store items on the disks surface. Most floppy disks that you buy are already formatted if not the disk must be formatted before you can write to it. Formatting is the process of preparing a disk (floppy disk or hard disk) for reading and writing by organizing the disk into storage locations called tracks and sectors. A track is a narrow recording band that forms a full circle on the surface of the disk. The disk s storage locations then are divided into pie-shaped sections, which break the tracks into small arcs called sectors. A file that is stored in nonadjacent sectors is referred to as a fragmented file. If you leave a disk in the floppy disk drive, you will see a non-system disk error message when you try to boot the PC. Hard Disks A hard disk consists of one or more rigid metal platters that allow data to be recorded magnetically on the surface of the platters. Although some hard disks are available in a portable cartridge form, most are not removable. Like floppy disks the data is recorded on a series of tracks and the tracks are divided into sectors when the disk is formatted. Storage capacities of internally mounted hard disks for PCs range from one billion characters to more than seventy-five billion characters. One billion bytes are called a gigabyte (GB). Typical hard disk sizes range from 10 GB to 250 GB or more. A head crash can occur when a read/write head becomes misaligned, if the disk wobbles, or if the head runs into a stray bit of dust. Compact Disks and DVDs A compact disk (CD) is a flat, round, portable, metal storage medium. Compact discs are available in a variety of forms including CD-ROMs, CD-Rs, and CD-RWs,. DVDs (DVD-ROMs, DVD-Rs, DVD+Rs, DVD-RWs etc) are similar in form, but hold far more data. 3
4 Computer Competecy Test Preparation Workshop Guide CD-ROMs, DVD-ROMs, etc. A CD-ROM, or compact disc read-only memory, is a compact disc that uses the same laser technology as audio CDs for recording music. In addition to audio, a CD-ROM can contain text, graphics, and video. You can only read the contents of these discs; you cannot erase or modify the contents. A typical CD-ROM holds about 650 MB of data. This is about 450 times more than can be stored on a floppy disk. CD-R and CD-RWs A CD-R (compact disc-recordable) is a multisession compact disc onto which you can record you own data, such as text, graphics, and audio. A CD-RW (compact disc-rewritable) is an erasable disc you can write on multiple times. With CD-RWs, the disc acts like a floppy or hard disk allowing you to write and rewrite data onto to it multiple times. Note: CD- RW technology allows you to record data on special optical disks but many standard CD-ROM drives cannot read the data stored on these writable disks. DVD-ROMs To meet the tremendous storage requirements, some software companies have moved from CD-ROMs to the larger DVD-ROM format a technology that can be used to store large amounts of text and even videos. A DVD- ROM (digital video disc-rom) is a very high capacity compact disc capable of storing from 4.7 GB to 17 GB of data. DVDs are also available as Recordable (DVD-R, DVD+R) and Rewritable (DVD-RW, DVD+RW) Zip Disks A zip disk is a higher capacity disk that can store the equivalent of up to 170 standard floppy disks. For backup purposes, good choices of media for home users are higher-capacity Zip Disks, CD-Rs, or DVD-Rs. B. Network, Internet, and Software terms: Network A network is a collection of computers and devices connected via communications media and devices such as cables, telephone lines, modems or other means. A network that connects computers in a limited geographic area is called a local area network (LAN). A network that covers a large geographical area is called a wide area network (WAN). 4
5 Computer Competency Test Preparation Workshop Guide Internet The world s largest network is the Internet. The Internet is a worldwide collection of networks that link businesses, government agencies, educational institutions and individuals. Most users connect to the Internet one of two ways: through an Internet service provider or an Online service provider. An Internet service provider (ISP) is a business that has a permanent Internet connection and provides temporary connections to individuals and companies for free or for a fee. Like an ISP, an Online service provider (OSP) provides Internet access, but also provides a variety of other specialized content and services. A typical Internet connection consists of a computer, a phone line, a modem, and ISP or OSP and communications software. An increasing number of ISPs deliver broadband (high-speed) Internet connectivity via digital cable, DSL, or Fiber Optic service. These types of high-speed, always-on Internet connections can be far faster than dialup. One of the most popular segments of the Internet is the World Wide Web (also called the Web), which contains billions of documents called Web pages. A Web site is a related collection of Web pages. You can access and view Web pages using a software program called a Web browser. A Web page has a unique address, called a Uniform Resource Locator (URL). A browser retrieves a Web page by using its URL, or web address. Web page URLs begin with The http stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol, which is the communications standard used to transfer pages to the Web. Web pages are stored and retrieved upon request by Web servers. Netiquette, which is short for Internet etiquette, is the code of acceptable behaviors users should follow while online. is the transmission of messages and files via a computer network. server software provides an electronic mailbox for each person, sorts incoming messages into these mailboxes, and routes outgoing mail over the Internet to other servers. Software Freeware is software provided at no cost to a user by an individual or company. Freeware is copyrighted and cannot be resold. Public-domain software is also free, but it has been donated for public use and has no copyright restrictions. Shareware is copyrighted software that is distributed free for a trial period. A user would have to purchase the use of the shareware beyond the trial period. C. Application Menu Bars and Controls: Once started, an application displays in a window on the desktop. A window is the rectangular area of the screen that displays a program, data and/or information. The top of the window has a title bar, which is the horizontal space that contains the window s name. The title bar typically contains three control buttons, the Minimize button, the Maximize button and the Close button. A scroll bar on the side of the window helps you move a document or graphic up and down within the window. 5
Chapter 8 Memory Units
 Chapter 8 Memory Units Contents: I. Introduction Basic units of Measurement II. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Storage versus Memory III. Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk IV.Optical
Chapter 8 Memory Units Contents: I. Introduction Basic units of Measurement II. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Storage versus Memory III. Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk IV.Optical
Discovering Computers 2008. Chapter 7 Storage
 Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 7 Storage Chapter 7 Objectives Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics of magnetic disks Describe the characteristics of
Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 7 Storage Chapter 7 Objectives Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics of magnetic disks Describe the characteristics of
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett
 Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Technical Product Specifications Model 3 PC Technical Diagrams Front Exterior Specifications
Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Technical Product Specifications Model 3 PC Technical Diagrams Front Exterior Specifications
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications. Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global
 CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
Primary Memory. Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit)
 Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O
 Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Tech Application Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE
 Name: Class: Date: Tech Application Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. This type of device retains data
Name: Class: Date: Tech Application Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. This type of device retains data
1 PERSONAL COMPUTERS
 PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
Chapter 8. Secondary Storage. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 8 Secondary Storage McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Distinguish between primary and secondary storage Describe
Chapter 8 Secondary Storage McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Distinguish between primary and secondary storage Describe
Computer Storage. Computer Technology. (S1 Obj 2-3 and S3 Obj 1-1)
 Computer Storage Computer Technology (S1 Obj 2-3 and S3 Obj 1-1) Storage The place in the computer where data is held while it is not needed for processing A storage device is device used to record (store)
Computer Storage Computer Technology (S1 Obj 2-3 and S3 Obj 1-1) Storage The place in the computer where data is held while it is not needed for processing A storage device is device used to record (store)
Management Challenge. Managing Hardware Assets. Central Processing Unit. What is a Computer System?
 Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Computer Hardware HARDWARE. Computer Hardware. Mainboard (Motherboard) Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN
 Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
Chapter 6. Inside the System Unit. What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future. What You Will Learn... Describing Hardware Performance
 What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System
 essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
Types Of Storage Device
 Types Of Storage Device by AA A POG D EE SRM U Outline Categorizing Storage Devices Magnetic Storage Devices Optical Storage Devices Categorizing Storage Devices Storage devices hold data, even when the
Types Of Storage Device by AA A POG D EE SRM U Outline Categorizing Storage Devices Magnetic Storage Devices Optical Storage Devices Categorizing Storage Devices Storage devices hold data, even when the
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
How To Store Data On A Computer (For A Computer)
 TH3. Data storage http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ A computer uses two types of storage. A main store consisting of ROM and RAM, and backing stores which can be internal, eg hard disk, or
TH3. Data storage http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ A computer uses two types of storage. A main store consisting of ROM and RAM, and backing stores which can be internal, eg hard disk, or
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS
 CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING. Chapter 5 Storage Devices
 CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 5 Storage Devices 1 1. Computer Data Storage 2. Types of Storage 3. Storage Device Features 4. Other Examples of Storage Device 2 Storage Devices A storage device
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 5 Storage Devices 1 1. Computer Data Storage 2. Types of Storage 3. Storage Device Features 4. Other Examples of Storage Device 2 Storage Devices A storage device
Computers Are Your Future. 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
 Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
Main Memory & Backing Store. Main memory backing storage devices
 Main Memory & Backing Store Main memory backing storage devices 1 Introduction computers store programs & data in two different ways: nmain memory ntemporarily stores programs & data that are being processed
Main Memory & Backing Store Main memory backing storage devices 1 Introduction computers store programs & data in two different ways: nmain memory ntemporarily stores programs & data that are being processed
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX
 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
Tomorrow s Technology and You
 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Three steps to the best technology: 1. The Assessment 2. The Dialogue 3. The Recommendation
 Technology Assessment Checklist for Small Businesses A quick way to help your small-business customers get the best technology. Today's small-business owners want reliable technology that helps them do
Technology Assessment Checklist for Small Businesses A quick way to help your small-business customers get the best technology. Today's small-business owners want reliable technology that helps them do
Writing Assignment #2 due Today (5:00pm) - Post on your CSC101 webpage - Ask if you have questions! Lab #2 Today. Quiz #1 Tomorrow (Lectures 1-7)
 Overview of Computer Science CSC 101 Summer 2011 Main Memory vs. Auxiliary Storage Lecture 7 July 14, 2011 Announcements Writing Assignment #2 due Today (5:00pm) - Post on your CSC101 webpage - Ask if
Overview of Computer Science CSC 101 Summer 2011 Main Memory vs. Auxiliary Storage Lecture 7 July 14, 2011 Announcements Writing Assignment #2 due Today (5:00pm) - Post on your CSC101 webpage - Ask if
A Computer Glossary. For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses
 A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
Computers. Hardware. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer
 Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Chapter 7 Types of Storage. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 7 Types of Storage Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics
Chapter 7 Types of Storage Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate between storage devices and storage media Describe the characteristics
Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software
 What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2
 Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2 Definition of a Computer What does IPOS stand for? Input Process Output Storage Other types of Computers Name some examples of other types of computers, other than a typical
Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2 Definition of a Computer What does IPOS stand for? Input Process Output Storage Other types of Computers Name some examples of other types of computers, other than a typical
COMPUTER BASICS. Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre
 COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
Chap-02, Hardware and Software. Hardware Model
 Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
Week One Lecture Note 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER 1.1 WHAT IS COMPUTER?
 Week One Lecture Note 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER 1.1 WHAT IS COMPUTER? A Computer is a device or set of devices that work under the control of a stored program, automatically accepts and processes data
Week One Lecture Note 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER 1.1 WHAT IS COMPUTER? A Computer is a device or set of devices that work under the control of a stored program, automatically accepts and processes data
Block diagram of typical laptop/desktop
 What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS
 TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Changes that you make in virtual machines do not affect your physical computer. 2. The size of a bus
TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Changes that you make in virtual machines do not affect your physical computer. 2. The size of a bus
Parts of a Computer. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. 1 1999 Micron Technology Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Acceptable Use Policy (AUP): Policy which provides rules governing use of district technology.
 Glossary Acceptable Use Policy (AUP): Policy which provides rules governing use of district technology. Access Fees: Fee charged to user for usage of services. Application: A program written to perform
Glossary Acceptable Use Policy (AUP): Policy which provides rules governing use of district technology. Access Fees: Fee charged to user for usage of services. Application: A program written to perform
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT)
 Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies
 Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
McGraw-Hill Technology Education McGraw-Hill Technology Education
 McGraw-Hill Technology Education McGraw-Hill Technology Education Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
McGraw-Hill Technology Education McGraw-Hill Technology Education Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now
 1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
What's in a computer?
 What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
NCTE Advice Sheet Storage and Backup Advice Sheet 7
 Storage and Backup No matter how well you treat your system, no matter how much care you take, you cannot guarantee that your data will be safe if it exists in only one place. The risks are much greater
Storage and Backup No matter how well you treat your system, no matter how much care you take, you cannot guarantee that your data will be safe if it exists in only one place. The risks are much greater
Overview of MIS Professor Merrill Warkentin
 Management Systems (MIS) Mississippi State University Data raw numbers - not processed facts, lists, numbers, tables of value to an organization 1 2 Data Processing (DP) the restructuring of data to improve
Management Systems (MIS) Mississippi State University Data raw numbers - not processed facts, lists, numbers, tables of value to an organization 1 2 Data Processing (DP) the restructuring of data to improve
Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices. A PC in Every Home. Assembling a Computer System
 C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
Understanding Essential Computer Concepts
 UNIT A Understanding Essential Computer Files You Will Need: No files needed. Computers are essential tools in almost all kinds of activity in virtually every type of business. In this unit, you will learn
UNIT A Understanding Essential Computer Files You Will Need: No files needed. Computers are essential tools in almost all kinds of activity in virtually every type of business. In this unit, you will learn
Chapter 1. The largest computers, used mainly for research, are called a. microcomputers. b. maxicomputers. c. supercomputers. d. mainframe computers.
 Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT IMAGING
 AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
Understanding Digital Components
 Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
ICT THEORY 4 MAIN AREAS
 ICT THEORY RE- CAP & REVISION (SUMMARY OF THE THEORY HANDOUT) 4 MAIN AREAS 1. HARDWARE 2. SOFTWARE 3. NETWORKS, CONNECTIVITY, COMMUNICATION & THE INTERNET. 4. USE/MISUSE AND CARE OF COMPUTERS 1 Hardware
ICT THEORY RE- CAP & REVISION (SUMMARY OF THE THEORY HANDOUT) 4 MAIN AREAS 1. HARDWARE 2. SOFTWARE 3. NETWORKS, CONNECTIVITY, COMMUNICATION & THE INTERNET. 4. USE/MISUSE AND CARE OF COMPUTERS 1 Hardware
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal
 Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
Module 1 Concepts of Infor mation Technology (IT) Module Goals
 Module 1 Concepts of Infor mation Technology (IT) The following is the Syllabus for Module 1, Concepts of Information Technology (IT), which provides the basis for the theory-based test in this module
Module 1 Concepts of Infor mation Technology (IT) The following is the Syllabus for Module 1, Concepts of Information Technology (IT), which provides the basis for the theory-based test in this module
To understand how data is processed, by a computer, we can draw a simple analogy between computers and humans.
 UNIT 3 MEMORY SYSTEM Memory System Structure Page No. 3.0 Introduction 43 3.1 Objectives 46 3.2 Memory Types and Storage Devices 46 3.2.1 Semiconductor (Main) Memory 52 3.2.2 Magnetic Memory 56 3.2.3 Optical
UNIT 3 MEMORY SYSTEM Memory System Structure Page No. 3.0 Introduction 43 3.1 Objectives 46 3.2 Memory Types and Storage Devices 46 3.2.1 Semiconductor (Main) Memory 52 3.2.2 Magnetic Memory 56 3.2.3 Optical
Graphic Communication
 Graphic Communication St Pauls RC Academy Computer Hardware CDT Department Hardware Devices Hardware is the name given to any piece of equipment that is used along side a computer (including the main computer
Graphic Communication St Pauls RC Academy Computer Hardware CDT Department Hardware Devices Hardware is the name given to any piece of equipment that is used along side a computer (including the main computer
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module
 Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Computer Peripherals
 Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Fall 2009. Lecture 1. Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345. Introduction to Operating Systems. Mostafa Z. Ali. mzali@just.edu.
 Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali mzali@just.edu.jo 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali mzali@just.edu.jo 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
Today we will learn about:
 Storage Devices Today we will learn about: Storage Devices Ancient technology (from my days as a student) Floppies CD_ROM, DVDs Hard drives Magnetic tape Storage versus Memory Memory holds data, programs
Storage Devices Today we will learn about: Storage Devices Ancient technology (from my days as a student) Floppies CD_ROM, DVDs Hard drives Magnetic tape Storage versus Memory Memory holds data, programs
Communicating with devices
 Introduction to I/O Where does the data for our CPU and memory come from or go to? Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices. Input devices supply computers with data to operate on.
Introduction to I/O Where does the data for our CPU and memory come from or go to? Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices. Input devices supply computers with data to operate on.
Figure 1. Front and Back of a Computer Case
 Introduction Almost everyone uses a computer daily, but many don't know how a computer works or all the different individual pieces that make it up. In fact, many people erroneously look at a computer
Introduction Almost everyone uses a computer daily, but many don't know how a computer works or all the different individual pieces that make it up. In fact, many people erroneously look at a computer
File Management Backing up files
 What is Backup and why is it done? The word backup refers to making copies of data so that these additional copies may be used to restore the original data in the event of data loss. Basically backups
What is Backup and why is it done? The word backup refers to making copies of data so that these additional copies may be used to restore the original data in the event of data loss. Basically backups
Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 110 Course Title: Computer Literacy
 Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 11 Course Title: Computer Literacy Course Length: 3 credits 3 5-minute meetings per week or equivalent Course Description: An introduction to the
Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 11 Course Title: Computer Literacy Course Length: 3 credits 3 5-minute meetings per week or equivalent Course Description: An introduction to the
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
Assiut University, Administration Building, Room 210, Tel. 0882423110
 Assiut University Information and Communication Technology Training Project Concepts of Information Technology (102) Project Manager Prof. Mohamed Abo-Zahhad Abo-Zeid Professor of Communication Engineering,
Assiut University Information and Communication Technology Training Project Concepts of Information Technology (102) Project Manager Prof. Mohamed Abo-Zahhad Abo-Zeid Professor of Communication Engineering,
Discovering Computers 2011. Living in a Digital World
 Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
Chapter 4 System Unit Components. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Module A. Computing Fundamentals
 Module A Computing Fundamentals Module A Computing Fundamentals Computing Fundamentals The Computing Fundamentals examination covers subjects needed for a foundational understanding of computing, including
Module A Computing Fundamentals Module A Computing Fundamentals Computing Fundamentals The Computing Fundamentals examination covers subjects needed for a foundational understanding of computing, including
hp pavilion home pc hp dvd writer
 hp pavilion home pc hp dvd writer The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but
hp pavilion home pc hp dvd writer The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but
Practical Application How to Use a Flash Drive
 Practical Application How to Use a Flash Drive Practical application How to Use a Flash Drive Page 1 of 6 About this Practical Application Prerequisite Skills To use this Application you will need be comfortable
Practical Application How to Use a Flash Drive Practical application How to Use a Flash Drive Page 1 of 6 About this Practical Application Prerequisite Skills To use this Application you will need be comfortable
DMS-10101, Computer Equipment
 Overview Effective dates: September 2005 - August 2006. This Specification describes the procedures for providing desktop microcomputers, laptop microcomputers, printers, and internet service for use on
Overview Effective dates: September 2005 - August 2006. This Specification describes the procedures for providing desktop microcomputers, laptop microcomputers, printers, and internet service for use on
Lesson Plan. Preparation
 Lesson Plan Course Title: Computer Maintenance Session Title: Hard Drives Lesson Duration: 90 Minutes Performance Objective: Upon completion of this assignment, the student will be able to recognize a
Lesson Plan Course Title: Computer Maintenance Session Title: Hard Drives Lesson Duration: 90 Minutes Performance Objective: Upon completion of this assignment, the student will be able to recognize a
hp pavilion home pc hp dvd writer
 hp pavilion home pc hp dvd writer The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but
hp pavilion home pc hp dvd writer The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but
Student Edition Complete
 Computer Basics Student Edition Complete The Richard Stockton College of New Jersey Computer Courseware CustomGuide.com granted to Computer and Telecommunication Services a license agreement to print an
Computer Basics Student Edition Complete The Richard Stockton College of New Jersey Computer Courseware CustomGuide.com granted to Computer and Telecommunication Services a license agreement to print an
Computer Ha rdwa re CHAPTER 1. Introduction. Personal Computers. Input Devices
 CHAPTER 1 Computer Ha rdwa re 1 Introduction The term computer hardware refers to the physical components of a computer, namely Keyboard, Monitor, Mouse, and Printer, including the digital circuitry. Computer
CHAPTER 1 Computer Ha rdwa re 1 Introduction The term computer hardware refers to the physical components of a computer, namely Keyboard, Monitor, Mouse, and Printer, including the digital circuitry. Computer
How To Understand The Computer (For A Computer)
 Computer Fundamental Compiled by: Hemanta Baral Computer Fundamentals What is Computer? Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user and processes these data under
Computer Fundamental Compiled by: Hemanta Baral Computer Fundamentals What is Computer? Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user and processes these data under
Like millions of other computer users, you have probably used your
 435487389_ch0_CTP.qxd 7/6/09 9:00 PM Page CHAPTER Introducing Hardware In this chapter, you will learn: That a computer requires both hardware and software to work About the many different hardware components
435487389_ch0_CTP.qxd 7/6/09 9:00 PM Page CHAPTER Introducing Hardware In this chapter, you will learn: That a computer requires both hardware and software to work About the many different hardware components
ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. Backbone. Bandwidth. Bit. Bits Per Second or bps
 ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Backbone Bandwidth Bit Commonly called DSL. Technology and equipment that allow high-speed communication across standard copper telephone wires. This can include
ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Backbone Bandwidth Bit Commonly called DSL. Technology and equipment that allow high-speed communication across standard copper telephone wires. This can include
Chapter 5 Objectives. Chapter 5 Input
 Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
Tech Times. Back-up and Storage
 Tech Times Back-up and Storage Back-up and Storage Why? Avoid loss of personal information, settings and software. Save time, resources and sanity by storing data so it is easily retrievable. Be proactive.
Tech Times Back-up and Storage Back-up and Storage Why? Avoid loss of personal information, settings and software. Save time, resources and sanity by storing data so it is easily retrievable. Be proactive.
How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7
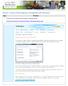 How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7 Enterprise Computing & Service Management 1 Follow this link to download the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-7/get/upgrade-advisor.aspx
How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7 Enterprise Computing & Service Management 1 Follow this link to download the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-7/get/upgrade-advisor.aspx
ICDL Module 1. David Varley
 ICDL Module 1 Concepts of Information Technology David Varley IMPORTANT NOTICE All candidates who follow an ICDL/ECDL course must have an official CDL/ECDL Skills Log Book or Skills Card. Without such
ICDL Module 1 Concepts of Information Technology David Varley IMPORTANT NOTICE All candidates who follow an ICDL/ECDL course must have an official CDL/ECDL Skills Log Book or Skills Card. Without such
Chapter 5 Busses, Ports and Connecting Peripherals
 Chapter 5 Busses, Ports and Connecting Peripherals 1 The Bus bus - groups of wires on a circuit board that carry information (bits - on s and off s) between computer components on a circuit board or within
Chapter 5 Busses, Ports and Connecting Peripherals 1 The Bus bus - groups of wires on a circuit board that carry information (bits - on s and off s) between computer components on a circuit board or within
Electronic Crime Scene Investigation: A Guide for First Responders, Second Edition
 APR. 08 Electronic Crime Scene Investigation: A Guide for First Responders, Second Edition Cover photographs copyright 2001 PhotoDisc, Inc. NCJ 219941 Chapter 1. Electronic Devices: Types, Description,
APR. 08 Electronic Crime Scene Investigation: A Guide for First Responders, Second Edition Cover photographs copyright 2001 PhotoDisc, Inc. NCJ 219941 Chapter 1. Electronic Devices: Types, Description,
HC-6950. Emission Protected Security Workstation
 Emission Protected Crypto AG / 6950-e-2.ppt / DA-HQ / 0004 / 1 PC and Workstation Risks Security Risks: Unauthorized change of data (Sabotage, Viruses) Unauthorized use of data Data loss (deletion) Physical
Emission Protected Crypto AG / 6950-e-2.ppt / DA-HQ / 0004 / 1 PC and Workstation Risks Security Risks: Unauthorized change of data (Sabotage, Viruses) Unauthorized use of data Data loss (deletion) Physical
Chapter One Introduction to Computer
 Chapter One Introduction to Computer Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according
Chapter One Introduction to Computer Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according
Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
 LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
Two main categories of storage technology used today are magnetic storage and optical storage.
 Types of Storage Devices Physical components or materials on which data is stored are called storage media. Hardware components that read/write to storage media are called storage devices. Two main categories
Types of Storage Devices Physical components or materials on which data is stored are called storage media. Hardware components that read/write to storage media are called storage devices. Two main categories
Understanding P2 Workflow. Technology Update: USING P2 HD WITH FINAL CUT PRO. when it counts
 Technology Update: Understanding P2 Workflow USING P2 HD WITH FINAL CUT PRO when it counts Computer / OS specs A Macintosh computer with a 500 megahertz (MHz) or faster PowerPC G4 or G5 processor (550
Technology Update: Understanding P2 Workflow USING P2 HD WITH FINAL CUT PRO when it counts Computer / OS specs A Macintosh computer with a 500 megahertz (MHz) or faster PowerPC G4 or G5 processor (550
Obj: Sec 1.0, to describe the relationship between hardware and software HW: Read p.2 9. Do Now: Name 3 parts of the computer.
 C1 D1 Obj: Sec 1.0, to describe the relationship between hardware and software HW: Read p.2 9 Do Now: Name 3 parts of the computer. 1 Hardware and Software Hardware the physical, tangible parts of a computer
C1 D1 Obj: Sec 1.0, to describe the relationship between hardware and software HW: Read p.2 9 Do Now: Name 3 parts of the computer. 1 Hardware and Software Hardware the physical, tangible parts of a computer
File Management Windows XP Word 2007. What is File Management?
 File Management Windows XP Word 2007 What is File Management? As you use your computer and create files you may need some help in storing and retrieving those files. File management shows you how to create,
File Management Windows XP Word 2007 What is File Management? As you use your computer and create files you may need some help in storing and retrieving those files. File management shows you how to create,
Computer Logic (2.2.3)
 Computer Logic (2.2.3) Distinction between analogue and discrete processes and quantities. Conversion of analogue quantities to digital form. Using sampling techniques, use of 2-state electronic devices
Computer Logic (2.2.3) Distinction between analogue and discrete processes and quantities. Conversion of analogue quantities to digital form. Using sampling techniques, use of 2-state electronic devices
Computer & Information Systems (22:198:604) Fall 2008 Homework 2 Solution
 Computer & Information Systems (22:198:604) Fall 2008 Homework 2 Solution 1. Chapter 3. Review Question 2 (Page 66) Comment on the statement, "The CPU is the brain of the computer." The CPU selects instructions,
Computer & Information Systems (22:198:604) Fall 2008 Homework 2 Solution 1. Chapter 3. Review Question 2 (Page 66) Comment on the statement, "The CPU is the brain of the computer." The CPU selects instructions,
Examine Your Strategy, Weigh Your Options in Choosing Removable Storage. Dave Holmstrom Associate Director of New Products Verbatim Corporation
 Examine Your Strategy, Weigh Your Options in Choosing Removable Storage Dave Holmstrom Associate Director of New Products Verbatim Corporation Evaluating Storage Solutions What type of data is being stored?
Examine Your Strategy, Weigh Your Options in Choosing Removable Storage Dave Holmstrom Associate Director of New Products Verbatim Corporation Evaluating Storage Solutions What type of data is being stored?
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Computer Literacy. Hardware & Software Classification
 Computer Literacy Hardware & Software Classification Hardware Classification Hardware is just another word for computer equipment; it is the physical parts of the computer that we can see and touch. All
Computer Literacy Hardware & Software Classification Hardware Classification Hardware is just another word for computer equipment; it is the physical parts of the computer that we can see and touch. All
Chapter 5 Input. Chapter 5 Objectives. What Is Input? What Is Input? The Keyboard. The Keyboard
 Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Input Define input List characteristics of of a keyboard Describe different mouse types and how they work Summarize how pointing devices work Explain how a digital camera
Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Input Define input List characteristics of of a keyboard Describe different mouse types and how they work Summarize how pointing devices work Explain how a digital camera
