AP1, Lab 8 - Central Nervous System The 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves
|
|
|
- Todd Fields
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP1, Lab 8 - Central Nervous System The 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves # Name Function I Olfactory Sensory impulses from nose for sense of smell II Optic Sensory impulses from eye for vision III Oculomotor Motor impulses to eye muscles for movements of the eyes IV Trochlear Motor impulses to eye muscles for movements of the eyes V Trigeminal Sensory impulses info from face, scalp, and teeth; Motor impulses to temporal and masseter muscles for closing the mandible as when chewing VI Abducens Motor impulses to eye muscles for abduction of the eyes VII Facial Sensory impulses from some taste buds of tongue; Motor impulses to muscles controlling facial expressions like frowning, smiling, etc. VIII Vestibulocochlear Sensory impulses from ear for senses of both sound and balance IX Glossopharyngeal Sensory impulses from throat and some taste buds at the back of the tongue (salty); Motor impulses to muscles of throat for swallowing and to salivary glands X Vagus Sensory impulses from throat, larynx, thoracic and abdominal organs; Motor impulses to stimulate digestive organs, to slow heart rate, to cough, and to swallow. XI Accessory Motor impulses to trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles of the neck and upper shoulder for shoulder movements and movements of the head. XII Hypoglossal Motor impulses to muscles of the tongue for most tongue movements. MNEMONIC DEVICES for Names of Cranial nerves: On occasion, our trusty truck acts funny - very good vehicle anyhow Or: Oh, Oh, Oh To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet, A-H! MNEMONIC DEVICE for Sensory, Motor, or Both: Some say Marry Money, but my brother says Big Business makes money Or: Some Say Marilyn Monroe, But My Brother Says Brigitte Bardot, My, My! Revised 8/20/14 1
2 Visual learning: The figure below is especially useful to visual learners: There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in humans. Their Roman numeral designations and names are: I Olfactory II Optic III Oculomotor IV Trochlear V Trigeminal VI Abducens VII Facial VIII Vestibulocochlear (auditory) IX Glossopharyngeal X Vagus XI Accessory (spinal accessory) XII Hypoglossal The cranial nerves mostly innervate structures in the head and neck. The cartoon codes for at least one major functional innervation of each cranial nerve. This drawing is based on one done by Beatrice Humphris, R.N. published in Nursing Revised 8/20/14 2
3 12 pairs of cranial nerves are associated with the ventral aspect of the brain. The first 2 pairs attach to the forebrain, the rest originate from the brainstem. **Note: The Intermediate nerve included in the diagram above is actually the smaller root of the facial nerve (VII). Most images do not illustrate it separately. This one just happens to do so. Revised 8/20/14 3
4 Test Your Cranial Nerves Now that you know the names and functions of the cranial nerves, let's test them. These tests will help you understand how the cranial nerves work. These tests are not meant to be a "clinical examination" of the cranial nerves. You will need to get a partner to help...both of you can serve as the experimenter (tester) and the subject. Record your observations of what your partner does and says. Olfactory Nerve (I): sensory for smell Gather some items with distinctive smells (for example, cloves, lemon, chocolate or coffee). Have your partner smell the items one at a time with each nostril. Have your partner record what the item is and the strength of the odor. Now you be the one who smells the items...have your partner use different smells for you. Optic Nerve (II): sensory for sight Use an eye chart (a "Snellen Chart") and have your partner try to read the lines at various distances away from the chart. Cranial nerves III, IV and VI are tested together. They each control muscles involved with eye movement. In addition, the oculomotor also functions in pupil dilation. Oculomotor Nerve (III), Trochlear Nerve (IV) and Abducens Nerve (VI): Motor These three nerves control eye movement and pupil diameter. Hold up a finger in front of your partner. Tell your partner to hold his or her head still and to follow your finger, then move your finger up and down, right and left. Do your partner's eyes follow your fingers? Check the pupillary response (oculomotor nerve): look at the diameter of your partner's eyes in dim light and also in bright light. Check for differences in the sizes of the right and left pupils. Trigeminal Nerve (V): sensory for touch/pain in face motor for chewing (mastication) The trigeminal nerve has both sensory and motor functions. To test the motor part of the nerve, tell your partner to close his or her jaws as if he or she was biting down on a piece of gum. Temporal and masseter muscles of the face should have equal strength To test the sensory part of the trigeminal nerve, lightly touch various parts of your partner's face with piece of cotton or a blunt object. Be careful not to touch your partner's eyes. Although much of the mouth and teeth are innervated by the trigeminal nerve, don't put anything into your subject's mouth. Revised 8/20/14 4
5 Facial Nerve (VII) Sensory for taste on anterior 2/3 of tongue and salivary glands. Sensory from external auditory meatus and ear drum but NOT sensory from inner ear for hearing. Motor for controlling muscles used in facial expression The motor part of the facial nerve can be tested by asking your partner to smile or frown or make funny faces. Lack of symmetry when smiling or frowning may indicate damage to this nerve or a portion of the motor cortex might indicate a stroke. The sensory part of the facial nerve is responsible for taste on the front part of the tongue. You could try a few drops of sweet or salty water on this part of the tongue and see if your partner can taste it. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII): Sensory for sound and balance The vestibulocochlear nerve is a branching nerve. The cochlear nerve is responsible for hearing and the vestibular controls balance. Hearing: Have your partner cover one ear and close his or her eyes. Stand about 2 feet from the subject and whisper a word with 2 distinct syllables, like mailman, or football and observe for difficulties distinguishing words. You may also determine the distance at which he or she can hear the ticking of a clock or stopwatch. Balance: Test for balance by having the subject stand with his feet close together and eyes closed. The subject may sway a little, but should not fall. Cranial nerves IX and X can be tested together since they both serve to innervate the pharynx. Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX): Sensory for taste on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue and conveying information from the tongue, tonsils and pharynx Motor for swallowing Have your partner drink some water and observe the swallowing reflex. Also the glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for taste on the back part of the tongue. You could try a few drops of salty (or sugar) water on this part of the tongue and see if your partner can taste it. Vagus Nerve (X): Sensory from throat, larynx, thoracic and abdominal organs Motor for swallowing, esophagus and to stimulate stomach and intestines (digestion). Motor to slow HR. Have the subject speak or cough. Her voice should be clear and strong. Cough should be strong. Subject should have a strong gag reflex. Spinal Accessory Nerve (XI): Motor to control the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles involved in head movement Put your hands on your partner s shoulders from the back. As you apply slight resistance, have him shrug his shoulders upward. Contraction should be symmetrical. Now place one hand on one side of your partner's jaw. Tell your partner to move his or her head toward your hand while you apply slight resistance. Repeat on the opposite side. Strength in the sternocleidomastoid should be symmetrical. Hypoglossal Nerve (XII): Motor for tongue movement Have your partner stick out his or her tongue and move it side to side. Check for symmetry. Revised 8/20/14 5
6 DO YOU KNOW? Which cranial nerve is the largest? Which cranial nerves are responsible for eye movements? What does "abducens" refer to? Which cranial nerves carry gustatory (taste) information? Which cranial nerve is the longest? Which nerve or nerves are involved in: Rotating the head? Smelling a flower? Raising the eyelids, pupillary constriction? Slowing the heart rate? Increasing motility of the digestive tract? Bell s Palsy? Chewing food? Listening to music? Seasickness? Secretion of saliva? Sensation of taste? Rolling the eyes? (3 nerves) Feeling a toothache? Reading a newspaper? Purely sensory in function? Revised 8/20/14 6
7 Revised 8/20/14 7
8 PAIN HOW THE BODY BLOCKS PAIN The Medical community has observed that a person can block or reduce the amount of perceived pain. Over time there have been many theories of the physiology of this phenomenon. The current theory states: the brain, in response to pain, will activate analgesic systems in the brainstem. These in turn will relay pain-suppressing signals to the spinal cord to release endogenous opioids such as ENDORPHINS and ENKEPHALINS. These create IPSPs to cancel out EPSPs (Substance P) produced by the pain receptors. HOW MEDICATIONS BLOCK PAIN: ASPIRIN and IBUPROFEN inhibit prostaglandin activity thereby reducing inflammation and pain. ACETAMINOPHEN (Tylenol) blocks pain but not inflammation by inhibiting activation of the COX enzyme. NSAIDS are anti-inflammatory in a variety of ways; often as COX2 inhibitors NARCOTICS such as morphine, Demerol, and heroin reduce pain by mimicking the effects of endorphins and enkephalins. HOW A T.E.N.S. UNIT BLOCKS PAIN TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Every day, ordinary afferent sensory impulses enter the spinal cord at the posterior horns of the gray matter. Here they must pass through synapses before traveling up to the brain via ascending tracts of the spinal cord. Pain messages follow the same pathway. Applying continuous or repetitive stimulation through the skin of an appropriate area using TENS annoys the brain with a flood of sensory input. In response, the brain increases the frequency of impulses down the spinal cord to create IPSPs to block both the incoming messages from the skin as well as the pain messages. Electrical stimulation of nerves using TENS also stimulates the release of endorphins so that fewer pain generating impulses reach the brain, so pain is not felt or at least is felt less. Revised 8/20/14 8
9 REFERRED PAIN A painful sensation felt in a region of the body that is not the origin of the stimuli. Usually, it s a painful sensation of visceral origin felt in a somatic region of the body that is not the origin of the stimuli. Examples: 1. Heart attack the origin of the impulses is the heart muscle but the pain is often felt in the upper chest, left side of the mandible, and on the medial surface of L arm. 2. Gallbladder and Liver often felt at the top of the R shoulder. 3. Kidney, Ureters, and Urinary Bladder often felt in the lower back, groin, or scrotum. 4. Appendix often felt near the umbilicus Happens because the visceral sensory neurons and somatic sensory neurons converge on the same ascending tracts of the spinal cord. When messages arrive on these tracts the brain can t always distinguish between the two points of origin. PHANTOM LIMB PAIN and HYPERALGESIA The sensation of pain experienced in a body part you no longer have a missing foot, leg, arm, etc. The brain receives no sensory information from the missing limb to inhibit pain sensations. If an action potential is initiated anywhere along the neuronal pathway from the severed limb, the idea of pain will be projected back to the missing limb even though the limb is not there. Hyperalgesia is pain amplification and is common in amputations. In order to reduce this hyperalgesia during amputations, epidural anesthetics (in addition to general anesthesia) are used to block neurotransmission in the spinal cord and thus prevent the spinal cord from learning hyperalgesia. Revised 8/20/14 9
10 Dissection of Cow Brain with Dura Mater Use images from the dissection manuals in lab and your knowledge of the brain to identify the following. Recall the functions of those with an *. Your group will be evaluated on the quality of your dissection. FOLLOW INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. 1. Glove up your choice of latex or polyethylene. 2. Safety practice caution with the knives and other implements. 3. Housekeeping (Your mother does not work here, kindly clean up after yourself) Don t put pieces of tissue in the sink. If you notice, there is no garbage disposal. At the end of lab, we will put brains back in the bag. Don t get slime on the brain models. When you are finished, wash everything and return it where you found it. 4. Open your bag and rinse away as much preservative as possible. Observe the dull white DURA MATER covering the surface of the brain. 5. The two, large fatty masses dangling from the anterior and inferior surface are the tissues that were behind the eyes. Find the two OPTIC NERVES in these and then cut the fatty mass off. 6. Use scissors to cut away the superior 90% of the DURA MATER. Leave the bottom portion intact as it will contain the pituitary gland. The ARACHNOID LAYER will come off with the dura mater leaving only the PIA MATER on the surface of the brain. 7. Observe the LONGITUDINAL and TRANSVERSE FISSURES containing DURAL SINUSES as you remove the dura mater. What occurs at your dural sinuses? 1. Identify the following externally visible structures while the brain is still whole. No cutting necessary. CEREBRUM L and R CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES Various SULCI & GYRI OLFACTORY BULBS and OLFACTORY TRACTS. This is CRANIAL NERVE #1 carrying sensory messages to the brain for the sense of smell. Observe the delicate PIA MATER anchoring blood vessels to the cerebrum mostly in the sulci. These vessels are dark brown/black in color. CEREBELLUM OPTIC NERVES and OPTIC CHIASMA. Cut the optic nerves (cranial nerve #2) and other motor nerves as far out as you can clearly see them to get rid of those dangling lumps of fatty tissue that were located behind the eyes. Pituitary gland - usually appears as a nodule or lump approximately ¼ inch in diameter on the ventral side of the brain.) TRIGEMINAL NERVES - The lateral edges of the dura mater containing the pituitary gland also contain the large trigeminal nerves (cranial nerve #5). Cut the nerves near the dura mater to leave stumps on the lateral walls of the pons. Remove the dura mater containing any branches of this nerve but do not remove the pituitary gland. Revised 8/20/14 10
11 OCULOMOTOR NERVES Gently lift the pituitary gland from its anterior edge while looking for the oculomotor nerves (cranial nerve #3) to be raised with the dura mater and the pituitary gland. Go ahead and remove the dura mater and pituitary gland. The stumps of the oculomotor nerves will either be lying on the midbrain, projecting forward or they will have torn loose and be attached to the dura mater above the pituitary gland. BRAIN STEM Spinal cord function? Medulla Oblongata functions? Pons functions? **Confirm identifications of everything up to this point with your instructor. 2. Bisect the brain on the mid-sagittal plane along the longitudinal fissure all the way through the brain stem. Make one clean, straight cut all the way through. Try to cut as precisely in the middle as possible. Identify the following. Corpus Callosum and Fornix recall function? Thalamus recall functions? Hypothalamus recall functions? Lateral ventricles - Use your metal probe to separate the corpus callosum and the fornix in order to see better into the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum will be the roof and the fornix will be the floor of each ventricle. Third ventricle Look above the thalamus but below the fornix. Choroid plexus - specialized capillaries for production of CSF. They are delicate and dark brown in color similar to the vessels on the surface of the cerebrum. Use your forceps to gently reach deep into the posterior portion of a lateral ventricle and pull some of this out. You might also find some in the 3 rd and 4 th ventricles. Cerebral aqueduct passageway for CSF to flow from 3 rd to 4 th ventricle. Fourth ventricle space between the cerebellum and spinal cord. 3. Locate your thalamus again. Put the two hemispheres back together and perform a coronal section such that your cut passes through the thalamus. Hold the two posterior portions together and view them from the anterior side. Identify the following: Cerebral white matter Cerebral cortex - The term cortex refers to the outer layer of any structure. On the cow brain it s the darker, more superficial layer that borders the white matter and follows the contour of the sulci. The majority of the synapses of the brain are found in the cortex. Corpus callosum Lateral ventricles Fornix Third ventricle Thalamus Revised 8/20/14 11
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
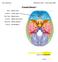 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
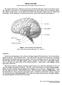 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Frog Dissection. Procedure
 Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Frog Dissection Amphibians, such as frogs, are examples of animals that have structural adaptations for living in or near water and for living on land. As tadpoles,
Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Frog Dissection Amphibians, such as frogs, are examples of animals that have structural adaptations for living in or near water and for living on land. As tadpoles,
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
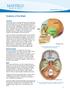 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
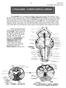 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Cranial Nerves. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve
 Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain
 Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd.
 About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
 Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
Stress Psychophysiology. Introduction. The Brain. Chapter 2
 Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28
 The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus
 Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Vestibular Assessment
 Oculomotor Examination A. Tests performed in room light Vestibular Assessment 1. Spontaneous nystagmus 2. Gaze holding nystagmus 3. Skew deviation 4. Vergence 5. Decreased vestibular ocular reflex i. Head
Oculomotor Examination A. Tests performed in room light Vestibular Assessment 1. Spontaneous nystagmus 2. Gaze holding nystagmus 3. Skew deviation 4. Vergence 5. Decreased vestibular ocular reflex i. Head
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system
 Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services
 Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Session 1. Body Systems and Structures. Teacher Notes. Body Systems and Organs: Descriptions and Functions. Intermediate ENGLISH FOR YOUR HEALTH
 Session 1 Body Systems and Structures Teacher Notes Body Systems and Organs: Descriptions and Functions Heart The heart is a muscle that pumps blood to all parts of the body by contracting and releasing
Session 1 Body Systems and Structures Teacher Notes Body Systems and Organs: Descriptions and Functions Heart The heart is a muscle that pumps blood to all parts of the body by contracting and releasing
CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD
 1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab. Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
