B. Dermatopathology. a. Epidermis. 1. Acanthosis (epidermal hyperplasia) 2. Epidermal atrophy (epidermal hypoplasia)
|
|
|
- Claud O’Connor’
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Fig..1- Procedure of skin biopsy. Incisional biopsy with a surgical knife. Table.1 Specific stains used in dermatology. B. Dermatopathology When observing a pathological specimen, it is necessary to identify the abnormality in the specimen by comparison with normal findings (Figs..-1 and.-). This section introduces fundamental terms for skin pathological changes and diseases. a. Epidermis a Fig..-1 Normal skin (hematoxylin and eosin staining). a: Normal skin of the forearm. A basket-weaved horny cell layer is seen. Gaps between the stained horny cell layers are lipids that dissolved during fixation. These gaps indicate that the skin is well protected by moisturizing lipids. 1. Acanthosis (epidermal hyperplasia) Acanthosis describes thickening of the epidermis. It is classified into flat (the entire site thickens moderately; e.g., in chronic eczema), proriasiform (epidermal protrusions are extended), papillomatous (the epidermis projects upwards; e.g., with viral warts or seborrheic keratosis), and pseudocarcinomatous (pseudosquamous cell carcinomas project irregularly downward; e.g., chronic ulcer margin, deep mycoses) (Figs..3 and.4).. Epidermal atrophy (epidermal hypoplasia) Epidermal atrophy (epidermal hypoplasia) is caused by reduction of keratinocytes (Fig..5). It leads to thinning of the epidermis. As a result, the papillary processes are diminished or lost. It
2 B. Dermatopathology 9 normal flat b psoriasiform papillomatous c pseudocarcinomatous Fig..3 Patterns of acanthosis. d Fig..- Normal skin (hematoxylin and eosin staining). b: Normal skin of the sole. A thick horny cell layer is seen. c: Scalp. Many follicles can be seen. d: Face. Sebaceous glands are abundant. Fig..4 Acanthosis. Chronic eczema. is often found in senile skin, discoid lupus erythematosus, lichen planus and actinic keratosis. 3. Hyperkeratosis The horny cell layer becomes abnormally thick. This is seen in psoriasis vulgaris, ichthyosis and callus (Fig..6). In ichthyosis, hyperkeratosis is due to detachment and exfoliation of the horny cell layer, a process called retention hyperkeratosis. Keratinization associated with hair follicles is called follicular keratosis. Fig..5 Epidermal atrophy. Dermatomyositis. 4. Parakeratosis Parakeratosis is caused by incomplete keratinization in which nuclei remain in the cells of the horny cell layer (Fig..7). In normal skin, keratinocytes denucleate when they reach the horny
3 30 Histopathology of the Skin cell layer; however, keratinocyte formation in inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis vulgaris or in tumorous diseases such as actinic keratosis and Bowen s disease takes place so quickly that most of the nuclei remain in the horny cell layer. It is frequently accompanied by hyperkeratosis and hypogranulosis. The nuclei remain physiologically in the mucous membranes. Wedge-shaped or columnar parakeratosis, called cornoid lamellae, is observed in porokeratosis (Chapter 1). Fig.6 Hyperkeratosis. Chronic eczema. Fig..7 Parakeratosis. Psoriasis vulgaris. Fig..8 Dyskeratosis. Bowen s disease. 5. Dyskeratosis Dyskeratosis occurs when some keratinocytes keratinize abnormally before they reach the horny cell layer (Fig..8). The keratinocytes become apoptotic and necrotic. The nuclei shrink and contain eosinophilic cytoplasm. Since intercellular bridges between the peripheral keratinocytes are lost, the cells become round. Dyskeratosis is often found with inflammatory diseases and malignant tumors. It is termed grains in Darier s disease and individual cell keratinization in Bowen s disease. 6. Hypergranulosis Hypergranulosis is a thickening of the granular cell layers to four or more layers from the normal one to three layers (Fig..9). It is often found in lichen planus, viral warts and congenital ichthyosis. 7. Granular degeneration, Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis In granular degeneration, numerous vacuolated cells containing large keratohyaline granules appear in the granular cell layer and suprabasal cell layer (Fig..10). It is characteristic of Vörner palmoplantar keratosis and bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (Chapter 15). It may also be found in epidermal nevus and even in normal skin. 8. Spongiosis, Intercellular edema Spongiosis occurs when the spaces between neighboring keratinocytes are enlarged by intense edema. As a result, the intercellular space becomes extended and distinct (Fig..11). When aggravated further, intradermal blisters (spongiotic bullae) form. It is found in eczemas and dermatitises such as contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis and acute eczema. Fig..9 Hypergranulosis. Parapsoriasis. 9. Intracellular edema (ballooning degeneration) Intracellular edema is the infiltration of cytoplasm into keratinocytes (Fig..1). As the swelling develops, the cells deform
4 B. Dermatopathology 31 and become spherical (ballooning degeneration). If the cytoplasm swells even further, the cells break and the membranes remain in a network pattern (reticular degeneration). It is found in eruptions caused by viral infections such as that of the herpes simplex virus. 10. Acantholysis Acantholysis is the dispersion of keratinocytes resulting from the dissociation of keratinocyte intercellular adhesion, particularly that of desmosomes. Intercellular spaces and blisters form, with acantholytic cells (spherical keratinocytes that have lost their intercellular adhesion) floating inside. Acantholytic cells have a tendency to become dyskeratotic (Fig..13). The phenomenon is found in pemphigus, Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier s disease, and it may also be found in part of the lesions of actinic keratosis, keratoacanthoma, warty dyskeratoma and squamous cell carcinoma. 11. Blister, Bulla Blisters, whose contents are cytoplasm and infiltrating cells, are divided into intraepidermal and subepidermal, according to the histological findings (Fig..14). Intraepidermal blisters are classified by formation mechanism into severe spongiosis (eczema/dermatitis group), prominent acantholysis (e.g., pemphigus vulgaris), reticular degeneration (e.g., herpes infection) and basal cell degeneration (e.g., burns, epidermolysis bullosa simplex). Causative diseases of subepidermal blistering are autoimmune bullous diseases such as bullous pemphigoid, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, dermatitis herpetiformis (Duhring) and epidermolysis bullosa, and burns (Chapter 4). 1. Pustule A pustule is a blister containing purulent components (mainly neutrophils). A small pustule below the horny cell layer is called Munro s micro-abscess, which characterizes psoriasis vulgaris (Fig..15). A multilocular pustule, also called a spongiform pustule, is caused by damage to keratinocytes from neutrophilic infiltration in which intercellular junctions are retained. It resembles the network formation that is found in pustular psoriasis (Kogoj s spongiform pustule) (Fig..16). Pautrier s microabscess is produced by infiltration of tumorous lymphocytes and is not a genuine pustule (refer to the following section). 13. Exocytosis (cell infiltration into the epidermis) Exocytosis is the infiltration of inflammatory cells and Fig..10 Granular degeneration. Bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma. Fig..11 Spongiosis. Acute eczema. Fig..1 Intracellular edema. Herpes simplex. Fig..13 Acantholysis. Pemphigus vulgaris.
5 3 Histopathology of the Skin Fig..14 Bulla. Bullous pemphigoid. Fig..15 Munro s microabscess. Psoriasis vulgaris. Fig..16 Kogoj s spongiform pustule. Pustular psoriasis. erythrocytes into the dermis. It is mostly found in spongiotic space. Infiltration of lymphocytes is seen in epidermal inflammatory diseases such as contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis. Infiltration of multinucleated leukocytes is observed as a pustule in impetigo contagiosa, palmoplantar pustulosis and psoriasis. In cutaneous T-cell lymphomas such as mycosis fungoides, tumorous T cell may infiltrate into the epidermis forming a mass that does not become spongiform; it is called Pautrier s microabscess for its resemblance to an abscess (Fig..17). Langerhans cells infiltrate into the epidermis in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. b. Dermo-epidermal junction 1. Vacuolar degeneration (hydropic degeneration) Vacuolar degeneration occurs when the dermo-epidermal junctions become vacuolated and ill defined as a result of basal cell degeneration (Fig..18). It is often accompanied by edema and lymphocyte infiltration, and the basal membranes are lost at the site. It is an inflammation that mainly occurs at the dermo-epidermal junction. When further aggravated, subepidermal blisters form. Melanin granules contained in basal cells may permeate into the dermis, a condition called incontinentia pigmenti histologica. The macrophages phagocytose melanin granules. Dyskeratosis caused by necrotic keratinocytes is seen in erythema multiforme, lichen planus, lupus erythematosus and graft-versushost disease (GVHD). An eosinophilic Civatte body with a diameter of 10 mm may be found immediately beneath the dermis (Fig..9).. Melanin synthesis abnormality Production of melanin pigment in the basal epidermal layer is increased by exposure to ultraviolet radiation. When pigment is lost, leukoderma is observed. Generally, to diagnose melanin synthesis abnormality, a DOPA test or an immunohistological test is performed. Albinism: A congenital abnormality of melanin synthesis. Melanin loss can be identified by Fontana Masson staining, for example. Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis: Melanocytes experience functional reduction by aging. Nevus of Ota: Ectopic melanocytes are found in the dermis. Chloasma: Melanocytes and melanin pigments increase. Freckles: Melanocytes experience functional increase. Fig..17 Pautrier s microabscess. Mycosis fungoides. Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details
Spongiotic reaction pattern Spongiosis = Intercellular edema Elongation of bridges vesiculation, bullae?mechanism unclear Fluid comes from dermis Impo
 Spongiotic Reaction Pattern and review Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Spongiotic reaction pattern Spongiosis = Intercellular edema Elongation of bridges vesiculation, bullae?mechanism unclear Fluid comes from dermis
Spongiotic Reaction Pattern and review Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Spongiotic reaction pattern Spongiosis = Intercellular edema Elongation of bridges vesiculation, bullae?mechanism unclear Fluid comes from dermis
Chapter from BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline. Dermatology. 3rd edition. Edited by Hilary Jackson and Rosanna Marsella BSAVA 2012.
 Chapter from BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dermatology 3rd edition Edited by Hilary Jackson and Rosanna Marsella BSAVA 2012 www.bsava.com 4 Dermatopathology David H. Shearer Dogs and cats presented
Chapter from BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dermatology 3rd edition Edited by Hilary Jackson and Rosanna Marsella BSAVA 2012 www.bsava.com 4 Dermatopathology David H. Shearer Dogs and cats presented
Vesiculobullous reaction pattern. Dr. A. Theunis Dr. D. Creytens
 Vesiculobullous reaction pattern Dr. A. Theunis Dr. D. Creytens Vesiculobullous reaction pattern Early lesions should always be biopsied to ensure that a histopathological diagnosis can be made Once regeneration
Vesiculobullous reaction pattern Dr. A. Theunis Dr. D. Creytens Vesiculobullous reaction pattern Early lesions should always be biopsied to ensure that a histopathological diagnosis can be made Once regeneration
SKIN DISORDERS AND DISEASES Date:
 SKIN DISORDERS AND DISEASES Date: TOPIC 1: UNDERSTANDING SKIN DISORDERS 9 Rating: Text Pages: 184 205 1 Esthetics and dermatology are services that ideally complement one anotherthe esthetician should
SKIN DISORDERS AND DISEASES Date: TOPIC 1: UNDERSTANDING SKIN DISORDERS 9 Rating: Text Pages: 184 205 1 Esthetics and dermatology are services that ideally complement one anotherthe esthetician should
Highlights on Clinical Picture of Psoriasis
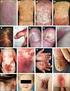 Highlights on Clinical Picture of Psoriasis PROF DR DOAA MAHGOUB CAIRO UNIVERSITY 1 Chronic Plaque Psoriasis Symmetric distribution of sharply defined, erythematous, scaly plaques. The scalp, elbows, knees
Highlights on Clinical Picture of Psoriasis PROF DR DOAA MAHGOUB CAIRO UNIVERSITY 1 Chronic Plaque Psoriasis Symmetric distribution of sharply defined, erythematous, scaly plaques. The scalp, elbows, knees
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Bacterial Infections Cutaneous bacterial infections are caused by resident or transient bacteria in the epidermis and mucosa.
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Bacterial Infections Cutaneous bacterial infections are caused by resident or transient bacteria in the epidermis and mucosa.
PSORIASIS. -Multi factorial. -Papulosquamous disorder. -Genetically determined (few) -Chronic Scaly lesions. -Seasonal variations
 PSORIASIS -Multi factorial -Papulosquamous disorder -Genetically determined (few) -Chronic Scaly lesions -Seasonal variations -Recurrences & remissions Etiology & Pathogenesis T-cell mediated autoimmune
PSORIASIS -Multi factorial -Papulosquamous disorder -Genetically determined (few) -Chronic Scaly lesions -Seasonal variations -Recurrences & remissions Etiology & Pathogenesis T-cell mediated autoimmune
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
ICD-10 Code Analysis Dermotology
 Page 1 of 7 ICD-10 Code Analysis Dermotology 6.5% 5.6% 12.1% 15% 13.1% Filing Date Range: 5/1/14 to 5/1/15 17.8% 29.9% Ratio ICD-9 Codes Percentage 1:1 Exact 32 29.9% 1:3 19 17.8% 1:1 14 13.1% 1:2 13 12.1%
Page 1 of 7 ICD-10 Code Analysis Dermotology 6.5% 5.6% 12.1% 15% 13.1% Filing Date Range: 5/1/14 to 5/1/15 17.8% 29.9% Ratio ICD-9 Codes Percentage 1:1 Exact 32 29.9% 1:3 19 17.8% 1:1 14 13.1% 1:2 13 12.1%
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Psoriasis: an overview
 22 September/October 2012 SOUTH AFRICAN RHEUMATOLOGY JOURNAL ARTICLE Psoriasis: an overview Dr WH Fouche Dermatologist in private practice George Introduction The term psoriasis refers to a chronic inflammatory
22 September/October 2012 SOUTH AFRICAN RHEUMATOLOGY JOURNAL ARTICLE Psoriasis: an overview Dr WH Fouche Dermatologist in private practice George Introduction The term psoriasis refers to a chronic inflammatory
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
THE SKIN BIOPSY IS REALLY REQUIRED FOR CONFIRMATION OF A CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS OF PSORIASIS?
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 7 (56) No. 2-2014 THE SKIN BIOPSY IS REALLY REQUIRED FOR CONFIRMATION OF A CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS OF PSORIASIS? O.S. COTOI
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 7 (56) No. 2-2014 THE SKIN BIOPSY IS REALLY REQUIRED FOR CONFIRMATION OF A CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS OF PSORIASIS? O.S. COTOI
KERATINOCYTES AND KERATINIZATION
 KERATINOCYTES AND KERATINIZATION The human skin is a large organ comprising a sheetlike investment of the whole body that adapts admirably to its contours and neatly conforms to the movements of the organism
KERATINOCYTES AND KERATINIZATION The human skin is a large organ comprising a sheetlike investment of the whole body that adapts admirably to its contours and neatly conforms to the movements of the organism
Cutaneous Lymphoma FAST FACTS
 Cutaneous Lymphoma FAST FACTS What is Cutaneous Lymphoma? Cutaneous lymphomas are types of non-hodgkin s lymphomas (NHL) that originate in the lymphocytes (white blood cells). Unlike most other types of
Cutaneous Lymphoma FAST FACTS What is Cutaneous Lymphoma? Cutaneous lymphomas are types of non-hodgkin s lymphomas (NHL) that originate in the lymphocytes (white blood cells). Unlike most other types of
CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF PSORIASIS
 CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF PSORIASIS F. AYALA Division of Dermatology, Department of Systematic Pathology, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy SUMMARY Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory disease
CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF PSORIASIS F. AYALA Division of Dermatology, Department of Systematic Pathology, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy SUMMARY Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory disease
ROXBURGH S Common Skin Diseases
 ROXBURGH S Common Skin Diseases 17th Edition Ronald Marks Emeritus Professor of Dermatology and Former Head of Department of Dermatology University of Wales College of Medicine Cardiff, UK Clinical Professor
ROXBURGH S Common Skin Diseases 17th Edition Ronald Marks Emeritus Professor of Dermatology and Former Head of Department of Dermatology University of Wales College of Medicine Cardiff, UK Clinical Professor
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Protective Functions. Functions in Sensation. Functions in Excretion. Functions in Temperature Regulation
 Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Skin/Wound Referral Resource
 Skin/Wound Referral Resource This resource was designed by the University of Michigan Health System Multidisciplinary Pressure Ulcer Prevention Committee for nursing and physician use. This document s
Skin/Wound Referral Resource This resource was designed by the University of Michigan Health System Multidisciplinary Pressure Ulcer Prevention Committee for nursing and physician use. This document s
PathoBasic - Vulva, Vagina, Cervix. E.Obermann
 PathoBasic - Vulva, Vagina, Cervix E.Obermann Vulva Inflammatory Changes Non-neoplastic lesions «Skin type lesions» Lichen sclerosus Infection: HSV, Candida Fibroepithelial stroma polyp Cutaneous Neoplasia
PathoBasic - Vulva, Vagina, Cervix E.Obermann Vulva Inflammatory Changes Non-neoplastic lesions «Skin type lesions» Lichen sclerosus Infection: HSV, Candida Fibroepithelial stroma polyp Cutaneous Neoplasia
Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin
 Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
Psoriasis. Student's Name. Institution. Date of Submission
 Running head: PSORIASIS Psoriasis Student's Name Institution Date of Submission PSORIASIS 1 Abstract Psoriasis is a non-contagious chronic skin disease that is characterized by inflammatory and multiplying
Running head: PSORIASIS Psoriasis Student's Name Institution Date of Submission PSORIASIS 1 Abstract Psoriasis is a non-contagious chronic skin disease that is characterized by inflammatory and multiplying
Melanoma The Skin Understanding Cancer
 Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Contents. Preface, xi Dedication, xii Abbreviations, xiii
 Contents Preface, xi Dedication, xii Abbreviations, xiii Part 1 General Dermatology Work-up Quick Reference, 3 Direct immunofl uorescence where to biopsy?, 3 False positive/negative DIFs, 4 Biopsy for
Contents Preface, xi Dedication, xii Abbreviations, xiii Part 1 General Dermatology Work-up Quick Reference, 3 Direct immunofl uorescence where to biopsy?, 3 False positive/negative DIFs, 4 Biopsy for
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
MANAGEMENT OF THE PATIENT WITH BLISTERS Dr Regina K Curley
 MANAGEMENT OF THE PATIENT WITH BLISTERS Dr Regina K Curley INTRODUCTION Blisters (definition: an elevated cutaneous lesion filled with clear fluid) have very many potential causes, and as always a good
MANAGEMENT OF THE PATIENT WITH BLISTERS Dr Regina K Curley INTRODUCTION Blisters (definition: an elevated cutaneous lesion filled with clear fluid) have very many potential causes, and as always a good
Removal of Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions (DRAFT POLICY)
 Removal of Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions (DRAFT POLICY) Search LCDs/LMRPs Effective: 3/1/2008 Status: Draft Final Revision Date: 12/3/2007 LCD Title Removal of Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions - 4S-140AB
Removal of Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions (DRAFT POLICY) Search LCDs/LMRPs Effective: 3/1/2008 Status: Draft Final Revision Date: 12/3/2007 LCD Title Removal of Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions - 4S-140AB
PPx System Comprehensive Treatment Options Including: Acne, Skin Rejuvenation & Permanent Hair Reduction
 The Technology The PPx System combines pneumatic energy and broadband light, hence Photopneumatic (PPx ). Photo meaning light and pneumatic meaning vacuum. Most conventional laser and light based systems
The Technology The PPx System combines pneumatic energy and broadband light, hence Photopneumatic (PPx ). Photo meaning light and pneumatic meaning vacuum. Most conventional laser and light based systems
Treating Psoriasis Naturally. Dr. Deborah Ardolf, ND
 Treating Psoriasis Naturally by Dr. Deborah Ardolf, ND Psoriasis is an extremely common, noncontagious skin disorder affecting between 2% to 4% of the United States population. Psoriasis affects men and
Treating Psoriasis Naturally by Dr. Deborah Ardolf, ND Psoriasis is an extremely common, noncontagious skin disorder affecting between 2% to 4% of the United States population. Psoriasis affects men and
The Integumentary System Chapter 6. Skin Functions Skin Layers Skin Color Hair Nails Cutaneous Glands Burns
 The Integumentary System Chapter 6 Skin Functions Skin Layers Skin Color Hair Nails Cutaneous Glands Burns Functions of the Skin Skin is a barrier to microbes, chemical irritants, water loss. Vitamin D
The Integumentary System Chapter 6 Skin Functions Skin Layers Skin Color Hair Nails Cutaneous Glands Burns Functions of the Skin Skin is a barrier to microbes, chemical irritants, water loss. Vitamin D
LICHEN PLANUS. Victor L. Perez, MD
 LICHEN PLANUS Victor L. Perez, MD CLINICAL CASE Referring Diagnosis "Cicatricial Pemphigoid involving the conjunctiva and the oral mucosa." History of Present Illness 42-year-old female with a 3 months
LICHEN PLANUS Victor L. Perez, MD CLINICAL CASE Referring Diagnosis "Cicatricial Pemphigoid involving the conjunctiva and the oral mucosa." History of Present Illness 42-year-old female with a 3 months
Skeletal System. Bone Cells. Elements of Bone Tissue
 Bio217: Pathophysiology Notes Professor Linda Falkow : Musculoskeletal System & Integumentary System Chapter 36: Musculoskeletal System Chapter 37: Alterations of Musculoskeletal Function Chapter 39: Structure,
Bio217: Pathophysiology Notes Professor Linda Falkow : Musculoskeletal System & Integumentary System Chapter 36: Musculoskeletal System Chapter 37: Alterations of Musculoskeletal Function Chapter 39: Structure,
The Integumentary System
 5 The Integumentary System FOCUS: The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and a variety of glands. The epidermis of the skin provides protection against abrasion, ultraviolet light,
5 The Integumentary System FOCUS: The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and a variety of glands. The epidermis of the skin provides protection against abrasion, ultraviolet light,
INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM
 INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM Inflammation is a response of a tissue to injury, often caused by invading microorganisms. The suffix which indicates inflammation is "-itis" (the
INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM Inflammation is a response of a tissue to injury, often caused by invading microorganisms. The suffix which indicates inflammation is "-itis" (the
Psoriasis. Background
 Psoriasis Plaque psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease with an unknown cause and no cure. Much research is based on the theory that psoriasis is a T cell mediated disorder. This review suggests that
Psoriasis Plaque psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease with an unknown cause and no cure. Much research is based on the theory that psoriasis is a T cell mediated disorder. This review suggests that
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System. What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system?
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
MEDICAL POLICY No. 91456-R13 SKIN CONDITIONS I. POLICY/CRITERIA
 SKIN CONDITIONS MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: June 2, 2014 Review Dates: 8/02, 2/03, 8/03, 7/04, 7/05, 6/06, 2/07, 8/07, 2/08, 2/09, 10/09, 4/10, 4/11, 4/12, 4/13, 5/14, 5/15 Date Of Origin: August 28,
SKIN CONDITIONS MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: June 2, 2014 Review Dates: 8/02, 2/03, 8/03, 7/04, 7/05, 6/06, 2/07, 8/07, 2/08, 2/09, 10/09, 4/10, 4/11, 4/12, 4/13, 5/14, 5/15 Date Of Origin: August 28,
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Skin Lesion (Non-Melanoma) Removal (L28300)
 Search Home Medicare Medicaid CHIP About CMS Regulations & Guidance Research, Statistics, Data & Systems Outreach & Education People with Medicare & Medicaid Questions Careers Newsroom Contact CMS Acronyms
Search Home Medicare Medicaid CHIP About CMS Regulations & Guidance Research, Statistics, Data & Systems Outreach & Education People with Medicare & Medicaid Questions Careers Newsroom Contact CMS Acronyms
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist
 Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Measurement of epidermal thickness in a patient with psoriasis by computer-supported image analysis
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2004) 37: 111-117 Measurement of epidermal thickness in psoriasis ISSN 0100-879X 111 Measurement of epidermal thickness in a patient with psoriasis
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2004) 37: 111-117 Measurement of epidermal thickness in psoriasis ISSN 0100-879X 111 Measurement of epidermal thickness in a patient with psoriasis
B. Disorders of sebaceous glands
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details B. Disorders of sebaceous glands 1. Acne vulgaris It most frequently occurs on the face of adolescent men and women. Comedones, folliculitis,
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details B. Disorders of sebaceous glands 1. Acne vulgaris It most frequently occurs on the face of adolescent men and women. Comedones, folliculitis,
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
 SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. It tells you what they are, what causes
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. It tells you what they are, what causes
Anatomy and Functions of Skin
 3 The Anatomy and Functions of Skin 3.1 Introduction Skin is considered to be the largest organ of the human body with an average surface area of 1.6 2 m 2 and accounts for about 15% of the total body
3 The Anatomy and Functions of Skin 3.1 Introduction Skin is considered to be the largest organ of the human body with an average surface area of 1.6 2 m 2 and accounts for about 15% of the total body
CANINE & FELINE AUTOIMMUNE & IMMUNE MEDIATED DISEASES: AN UPDATE PART 2 Rod A.W. Rosychuk DVM, DACVIM
 CANINE & FELINE AUTOIMMUNE & IMMUNE MEDIATED DISEASES: AN UPDATE PART 2 Rod A.W. Rosychuk DVM, DACVIM DERMATOLOGY Selected Lupus and Lupus-like Diseases Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) DLE in dogs is
CANINE & FELINE AUTOIMMUNE & IMMUNE MEDIATED DISEASES: AN UPDATE PART 2 Rod A.W. Rosychuk DVM, DACVIM DERMATOLOGY Selected Lupus and Lupus-like Diseases Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) DLE in dogs is
12/7/2014. Dr.Mohammad Alshami associate professor of dermatology Sana a university Yemen
 Dr.Mohammad Alshami associate professor of dermatology Sana a university Yemen 1 2 Types of resurfacing lasers A. Classical ablative lasers -CO2 10600nm -Erbium-YAG 2400nm B. Non ablative lasers -Nd-YAG
Dr.Mohammad Alshami associate professor of dermatology Sana a university Yemen 1 2 Types of resurfacing lasers A. Classical ablative lasers -CO2 10600nm -Erbium-YAG 2400nm B. Non ablative lasers -Nd-YAG
Cytology of Lymph Nodes
 Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
LCD for Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
 LCD for Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Applicable CPT Code(s): 85651 Sedimentation Rate, Erythrocyte; Non-Automated 85652 Sedimentation Rate, Erythrocyte; Automated ICD-9 Codes that Support Medical
LCD for Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Applicable CPT Code(s): 85651 Sedimentation Rate, Erythrocyte; Non-Automated 85652 Sedimentation Rate, Erythrocyte; Automated ICD-9 Codes that Support Medical
5 Dermatology. 1 Summary. HC Williams. Introduction. Increase in future demand
 5 Dermatology HC Williams 1 Summary Introduction This chapter sets out the major issues which health service purchasers need to consider in specifying services for people with skin problems. Skin disease
5 Dermatology HC Williams 1 Summary Introduction This chapter sets out the major issues which health service purchasers need to consider in specifying services for people with skin problems. Skin disease
Oral Vesicular Bullous disorders O R A L B L I S T E R I N G D I S O R D E R S
 Oral Vesicular Bullous disorders O R A L B L I S T E R I N G D I S O R D E R S Definitions Blister: Accumulation of fluid either within or below the epidermis and mucous membrane Vesicle: Elevated blister
Oral Vesicular Bullous disorders O R A L B L I S T E R I N G D I S O R D E R S Definitions Blister: Accumulation of fluid either within or below the epidermis and mucous membrane Vesicle: Elevated blister
Rosacea under the microscope: characteristic histological findings
 DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12121 JEADV REVIEW ARTICLE Rosacea under the microscope: characteristic histological findings B. Cribier* Clinique Dermatologique, University Hospital, Strasbourg, France *Correspondence:
DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12121 JEADV REVIEW ARTICLE Rosacea under the microscope: characteristic histological findings B. Cribier* Clinique Dermatologique, University Hospital, Strasbourg, France *Correspondence:
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN
 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
Topical Tacrolimus or Pimecrolimus for the treatment of mild, moderate or severe atopic eczema. Effective Shared Care Agreement
 Topical Tacrolimus or Pimecrolimus for the treatment of mild, moderate or severe atopic eczema. Effective Shared Care Agreement A Copy of this page signed by all three parties should be retained in the
Topical Tacrolimus or Pimecrolimus for the treatment of mild, moderate or severe atopic eczema. Effective Shared Care Agreement A Copy of this page signed by all three parties should be retained in the
Inflammation and Healing. Review of Normal Defenses. Review of Normal Capillary Exchange. BIO 375 Pathophysiology
 Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Emerging Applications
 Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE
 DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE Scottsdale, Arizona The Phoenician February 13 15, 2015 Participating Faculty Jennifer Krejci-Manwaring, MD Assistant Professor, University of Texas Health Science Center Staff
DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE Scottsdale, Arizona The Phoenician February 13 15, 2015 Participating Faculty Jennifer Krejci-Manwaring, MD Assistant Professor, University of Texas Health Science Center Staff
2014 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament
 2014 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Neurons and Reflex Arc Diagram 1 Diagram 2 Use the Diagram 1 in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A
2014 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Neurons and Reflex Arc Diagram 1 Diagram 2 Use the Diagram 1 in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Consists of the skin and its accessory organs; hair, nails, and cutaneous glands Inspection of the skin, hair, and nails is significant part of a physical exam Skin is the most
The Integumentary System Consists of the skin and its accessory organs; hair, nails, and cutaneous glands Inspection of the skin, hair, and nails is significant part of a physical exam Skin is the most
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Skin (Integumentary System)
 Skin (Integumentary System) considered an organ or an organ system body s largest organ organ of greatest surface area:15-20 sq ft. (1.5-2 m 2 ) General Functions: 1. protection mechanical chemical bacterial
Skin (Integumentary System) considered an organ or an organ system body s largest organ organ of greatest surface area:15-20 sq ft. (1.5-2 m 2 ) General Functions: 1. protection mechanical chemical bacterial
Nurse Practitioner, Dermatology
 Melissa O Neill, O MS, APRN Nurse Practitioner, Dermatology Three Types of Skin Cancer > Basal Cell Carcinoma > Squamous Cell Carcinoma > Malignant Melanoma Basal Cell Carcinoma > Most common skin cancer
Melissa O Neill, O MS, APRN Nurse Practitioner, Dermatology Three Types of Skin Cancer > Basal Cell Carcinoma > Squamous Cell Carcinoma > Malignant Melanoma Basal Cell Carcinoma > Most common skin cancer
EBMT Education Day for Nurses and AHPs April 2012 Skin care: not every rash is GVHD
 EBMT Education Day for Nurses and AHPs April 2012 Skin care: not every rash is GVHD Eileen Parry Consultant Dermatologist Tameside Hospital Foundation Trust Overview How to assess a patient with a rash
EBMT Education Day for Nurses and AHPs April 2012 Skin care: not every rash is GVHD Eileen Parry Consultant Dermatologist Tameside Hospital Foundation Trust Overview How to assess a patient with a rash
ACNE. Nisakorn Saewan, Ph.D.
 ACNE, Ph.D. Contents Definition Cause of acne Type of acne Acne grades Acne treatments Objectives To explain the definition of acne To elucidate cause of acne To identify type and grade of acne To explain
ACNE, Ph.D. Contents Definition Cause of acne Type of acne Acne grades Acne treatments Objectives To explain the definition of acne To elucidate cause of acne To identify type and grade of acne To explain
Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium
 Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium Introduction 3 cavities with the same embryologic origin the mesoderme Pleura Exudates Pleura Peritoneum Pericardium 22%
Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium Introduction 3 cavities with the same embryologic origin the mesoderme Pleura Exudates Pleura Peritoneum Pericardium 22%
Coding Dermatology Procedures. Presented by: Betty A Hovey Director, ICD-10 Development and Training AAPC
 Coding Dermatology Procedures Presented by: Betty A Hovey Director, ICD-10 Development and Training AAPC 1 No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically,
Coding Dermatology Procedures Presented by: Betty A Hovey Director, ICD-10 Development and Training AAPC 1 No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically,
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Department of Dermatology, Mugla Sitki Kocman University Training and Research Hospital, Mugla, Turkey
 Case Report Dermatology North Clin Istanbul 2015;2(3):231 235 doi: 10.14744/nci.2015.95914 Pustular eruption induced by etanercept in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis: a rare side effect Asude Kara,
Case Report Dermatology North Clin Istanbul 2015;2(3):231 235 doi: 10.14744/nci.2015.95914 Pustular eruption induced by etanercept in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis: a rare side effect Asude Kara,
Diagnostic Challenge. Department of Pathology,
 Cytology of Pleural Fluid as a Diagnostic Challenge Paavo Pääkkö,, MD, PhD Chief Physician and Head of the Department Department of Pathology, Oulu University Hospital,, Finland Oulu University Hospital
Cytology of Pleural Fluid as a Diagnostic Challenge Paavo Pääkkö,, MD, PhD Chief Physician and Head of the Department Department of Pathology, Oulu University Hospital,, Finland Oulu University Hospital
Gateway Health SM Non-Formulary Prior Authorization Criteria Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG)
 Gateway Health SM Non-Formulary Prior Authorization Criteria Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG) Coverage is provided in the following situations: PARP Approved 6/2015 Coverage is provided for Primary Immunodeficiency
Gateway Health SM Non-Formulary Prior Authorization Criteria Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG) Coverage is provided in the following situations: PARP Approved 6/2015 Coverage is provided for Primary Immunodeficiency
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis and Stasis Dermatitis With Id Reaction
 Id Reaction December 01, 2007 By David L. Kaplan, MD [1] A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills Case 1: A slightly pruritic eruption developed on the lower legs of a 39-year-old woman after she had an
Id Reaction December 01, 2007 By David L. Kaplan, MD [1] A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills Case 1: A slightly pruritic eruption developed on the lower legs of a 39-year-old woman after she had an
Skin Deep. Revised Version 2013
 Skin Deep Revised Version 2013 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION Dermatology Does it Matter? SECTION 1 - Conditions Acne vulgaris Actinic keratosis (solar keratosis) Alopecia Basal cell papillomas (seborrhoeic keratoses/warts)
Skin Deep Revised Version 2013 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION Dermatology Does it Matter? SECTION 1 - Conditions Acne vulgaris Actinic keratosis (solar keratosis) Alopecia Basal cell papillomas (seborrhoeic keratoses/warts)
Newborn Skin Rashes. References
 Newborn Skin Rashes COMPETENCIES: The resident should be able to: Recognize presenting signs and symptoms of a neonatal herpes simplex virus infection Recognize erythema toxicum and characteristics of
Newborn Skin Rashes COMPETENCIES: The resident should be able to: Recognize presenting signs and symptoms of a neonatal herpes simplex virus infection Recognize erythema toxicum and characteristics of
lå Blåsdermatoser Bo Nilsson
 lå Blåsdermatoser Bo Nilsson Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (LE) Pemphigus Pemphigoid Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) Samples 1.Biopsy 2.Serum The biopsy 1H 1. How should ldthe biopsy be taken? tk Lesional
lå Blåsdermatoser Bo Nilsson Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (LE) Pemphigus Pemphigoid Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) Samples 1.Biopsy 2.Serum The biopsy 1H 1. How should ldthe biopsy be taken? tk Lesional
Melanoma. Edward Buckingham, M.D. Combined Plastics & Otolaryngology Conference The University of Texas Medical Branch September 6, 2000
 Melanoma Edward Buckingham, M.D. Combined Plastics & Otolaryngology Conference The University of Texas Medical Branch September 6, 2000 Melanoma - Outline General statistics and development Risk factors
Melanoma Edward Buckingham, M.D. Combined Plastics & Otolaryngology Conference The University of Texas Medical Branch September 6, 2000 Melanoma - Outline General statistics and development Risk factors
Cervical lymphadenopathy
 Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Melanoma: some useful facts
 Melanoma: some useful facts Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Contents
Melanoma: some useful facts Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Contents
VITILIGO Charles Camisa, MD 1/24/12. Vitiligo is a common autoimmune skin disease that causes gradual loss of the natural
 VITILIGO Charles Camisa, MD 1/24/12 What is vitiligo? Vitiligo is a common autoimmune skin disease that causes gradual loss of the natural brown pigment in the skin called melanin. It affects about 1%
VITILIGO Charles Camisa, MD 1/24/12 What is vitiligo? Vitiligo is a common autoimmune skin disease that causes gradual loss of the natural brown pigment in the skin called melanin. It affects about 1%
BOWEN S DISEASE (SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA IN SITU)
 BOWEN S DISEASE (SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA IN SITU) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen s disease). It
BOWEN S DISEASE (SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA IN SITU) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen s disease). It
Neonatal Eruptions Not to Miss!
 Neonatal Eruptions Not to Miss! Rash neonatales poco communes, para tener en cuenta Miriam Weinstein MD FRCPC University of Toronto Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Disclosure No Disclosures
Neonatal Eruptions Not to Miss! Rash neonatales poco communes, para tener en cuenta Miriam Weinstein MD FRCPC University of Toronto Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Disclosure No Disclosures
Climatotherapy at the Dead Sea is a remittive therapy for psoriasis: Combined effects on epidermal and immunologic activation
 Climatotherapy at the Dead Sea is a remittive therapy for psoriasis: Combined effects on epidermal and immunologic activation Emmilia Hodak, MD, a Alice B. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, c Tsvi Segal, MD, a Yael Politi,
Climatotherapy at the Dead Sea is a remittive therapy for psoriasis: Combined effects on epidermal and immunologic activation Emmilia Hodak, MD, a Alice B. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, c Tsvi Segal, MD, a Yael Politi,
Common Skin Conditions in Children. Liz Moore and Emma King Dermatology Nurse Consultants
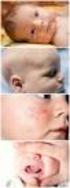 Common Skin Conditions in Children Liz Moore and Emma King Dermatology Nurse Consultants Diagnosis? Nummular Dermatitis Disc pattern rash (discoid eczema) Clearly demarcated edges Occurs at any age Can
Common Skin Conditions in Children Liz Moore and Emma King Dermatology Nurse Consultants Diagnosis? Nummular Dermatitis Disc pattern rash (discoid eczema) Clearly demarcated edges Occurs at any age Can
Pathology Update. Introduction
 Pathology Update This regular feature presents special issues in oncologic pathology. HISTOLOGIC VARIANTS OF SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA OF THE SKIN Margaret H. Rinker, MD, Neil A. Fenske, MD, Leigh Ann Scalf,
Pathology Update This regular feature presents special issues in oncologic pathology. HISTOLOGIC VARIANTS OF SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA OF THE SKIN Margaret H. Rinker, MD, Neil A. Fenske, MD, Leigh Ann Scalf,
FastTest. You ve read the book... ... now test yourself
 FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. Please refer back to relevant sections
FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. Please refer back to relevant sections
Disorders of the Vulva
 Disorders of the Vulva WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Certain health problems can affect the vulva (the outer part of the female genital area). Some problems are minor. Others
Disorders of the Vulva WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Certain health problems can affect the vulva (the outer part of the female genital area). Some problems are minor. Others
The Epidermis. Provides mechanical protection. Helps keep micoorganisms out of the body. Consists of stratified squamous epithelium
 Components of the Integumentary System include 1. cutaneous membrane (skin) a. epidermis (superficial epithelium) b. dermis (under lying connective tissue layer) 2. hair 3. nails } 2,3,4 accessory structures
Components of the Integumentary System include 1. cutaneous membrane (skin) a. epidermis (superficial epithelium) b. dermis (under lying connective tissue layer) 2. hair 3. nails } 2,3,4 accessory structures
Proceeding of the NAVC North American Veterinary Conference Jan. 8-12, 2005, Orlando, Florida
 Proceeding of the NAVC North American Veterinary Conference Jan. 8-12, 2005, Orlando, Florida Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the NAVC http:/// Small Animal - Dermatology CLINICAL
Proceeding of the NAVC North American Veterinary Conference Jan. 8-12, 2005, Orlando, Florida Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the NAVC http:/// Small Animal - Dermatology CLINICAL
Vesiculobullous Diseases Non-Infectious Etiology. Vesiculobullous Diseases. Infectious Etiology
 Vesicles and Pustules in the Newborn Julian Trevino, M.D. Associate Professor Boonshoft School of Medicine Department of Dermatology Vesicles and Pustules in the Newborn Represent wide spectrum of disorders
Vesicles and Pustules in the Newborn Julian Trevino, M.D. Associate Professor Boonshoft School of Medicine Department of Dermatology Vesicles and Pustules in the Newborn Represent wide spectrum of disorders
Histopathology of Major Salivary Gland Neoplasms
 Histopathology of Major Salivary Gland Neoplasms Sam J. Cunningham, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: Shawn D. Newlands, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: David C. Teller, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch, Department
Histopathology of Major Salivary Gland Neoplasms Sam J. Cunningham, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: Shawn D. Newlands, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: David C. Teller, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch, Department
Informed Consent for Cosmetic Laser Skin Resurfacing with the DOT laser
 Informed Consent for Cosmetic Laser Skin Resurfacing with the DOT laser INSTRUCTIONS This informed-consent document has been prepared to help inform you about laser procedure, its risks, as well as alternative
Informed Consent for Cosmetic Laser Skin Resurfacing with the DOT laser INSTRUCTIONS This informed-consent document has been prepared to help inform you about laser procedure, its risks, as well as alternative
ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY THYROID PAPILLARY CARCINOMA
 Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Guideline on management and referral for cryotherapy. Professional Development & Quality Assurance. Department of Health
 Guideline on management and referral for cryotherapy Professional Development & Quality Assurance Department of Health CONTENT 1. Introduction 2. Indication 3. Contraindication 4. Role of staff in cryotherapy
Guideline on management and referral for cryotherapy Professional Development & Quality Assurance Department of Health CONTENT 1. Introduction 2. Indication 3. Contraindication 4. Role of staff in cryotherapy
X-Plain Psoriasis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Psoriasis Reference Summary Introduction Psoriasis is a long-lasting skin disease that causes the skin to become inflamed. Patches of thick, red skin are covered with silvery scales. It affects
X-Plain Psoriasis Reference Summary Introduction Psoriasis is a long-lasting skin disease that causes the skin to become inflamed. Patches of thick, red skin are covered with silvery scales. It affects
Accurate diagnosis of the generalized
 The Generalized Rash: Part II. Diagnostic Approach JOHN W. ELY, MD, MSPH, and MARY SEABURY STONE, MD University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine, Iowa City, Iowa Although it is important to begin the
The Generalized Rash: Part II. Diagnostic Approach JOHN W. ELY, MD, MSPH, and MARY SEABURY STONE, MD University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine, Iowa City, Iowa Although it is important to begin the
Nail Psoriasis. 1. Introduction
 9 Nail Eckart Haneke 1 Dept Dermatol, Inselspital, Univ Bern, Bern, 2 Practice of Dermatology Dermaticum, Freiburg, 3 Centro de Dermatología Epidermis, Instituto CUF, Porto, 4 Dept Dermatol, Acad Hosp,
9 Nail Eckart Haneke 1 Dept Dermatol, Inselspital, Univ Bern, Bern, 2 Practice of Dermatology Dermaticum, Freiburg, 3 Centro de Dermatología Epidermis, Instituto CUF, Porto, 4 Dept Dermatol, Acad Hosp,
9/25/2012. Composed of three layers. Glands. Basic skin care Acne How to recognize How to treat. I have no conflict of interest
 By Theresa M. Schimmels, PA-C WAPA Fall CME 2012 Basic skin care Acne How to recognize How to treat I have no conflict of interest Composed of three layers epidermis dermis hypodermis or subcutaneous Glands
By Theresa M. Schimmels, PA-C WAPA Fall CME 2012 Basic skin care Acne How to recognize How to treat I have no conflict of interest Composed of three layers epidermis dermis hypodermis or subcutaneous Glands
Psoriasis. Psoriasis. Mark A. Bechtel, M.D. Director of Dermatology The Ohio State University College of Medicine
 Psoriasis Mark A. Bechtel, M.D. Director of Dermatology The Ohio State University College of Medicine Psoriasis Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder resulting from a polygenic predisposition combined with
Psoriasis Mark A. Bechtel, M.D. Director of Dermatology The Ohio State University College of Medicine Psoriasis Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder resulting from a polygenic predisposition combined with
EVALUATING THE PATIENT WITH AN ACUTE, GENERALIZED VESICULAR OR PUSTULAR RASH ILLNESS AND DETERMINING THE RISK OF SMALLPOX
 EVALUATING THE PATIENT WITH AN ACUTE, GENERALIZED VESICULAR OR PUSTULAR RASH ILLNESS AND DETERMINING THE RISK OF SMALLPOX Many rash illnesses can present with vesicles and pustules. The purpose of this
EVALUATING THE PATIENT WITH AN ACUTE, GENERALIZED VESICULAR OR PUSTULAR RASH ILLNESS AND DETERMINING THE RISK OF SMALLPOX Many rash illnesses can present with vesicles and pustules. The purpose of this
THE SKIN PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
 INTRODUCTION THE SKIN PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Among the many aspects of the physical examination, the diagnosis of skin disorders requires a unique approach. It demands the diagnostician s ability not only
INTRODUCTION THE SKIN PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Among the many aspects of the physical examination, the diagnosis of skin disorders requires a unique approach. It demands the diagnostician s ability not only
