The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection
|
|
|
- Evangeline Newman
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for the study of dentin infection R. Ordinola-Zapata 1, C. Monteiro Bramante 1, I. Gomes de Moraes 1, N. Bernardineli 1, V. Carvalho Porto 2, AP. Campanelli 3, RB Garcia 1 and M. Húngaro Duarte 1. 1 Department of Endodontics, University of São Paulo, Av. O. Pinheiro Brisola 9-75, , Bauru, SP, Brazil. 2 Department of Prosthodontics, University of São Paulo, Av. O. Pinheiro Brisola 9-75, , Bauru, SP, Brazil. 3 Department of Oral Biology, University of São Paulo, Av. O. Pinheiro Brisola 9-75, , Bauru, SP, Brazil. Bacteria and their products in the root canal system of necrotic teeth are the main etiological factor of apical periodontitis. One of the major advantages of confocal microscopy is the ability to analyze by thin optical sections the subsurface structure of biological samples. We describe the ability of the confocal microscopy to investigate the pattern of dentin infection provided by different infection models used in endodontic research that includes laboratory and in situ infected dentin. Confocal pictures of in vivo infected dentin from necrotic root canals are also presented. The ability to allow 3D observation of bacterial colonization may have the potential to significantly contribute to in situ morphological studies of endodontic infections as well as the ex vivo antibacterial effects of endodontic substances and procedures. Keywords: bacteria; dentin; confocal microscopy; pulp necrosis; biofilms; oral microbiology. 1. Introduction Bacteria and their products in the root canal system of necrotic teeth are the main etiological factor of apical periodontitis [1, 2]. The significance of root canal decontamination to achieve healing of apical periodontitis has been addressed by several studies [3-6]. These studies provide the basis for the study of root canal disinfections protocols that include the testing of instrumentation techniques, antibacterial compounds and root canal dressings Ideally, the evaluation of different antibacterial protocols should be performed under a clinical environment [7]. However, in vivo studies are time consuming and difficult to standardized. In addition, microscopic analyses and clinical protocols to test new devices as, instruments or antibacterial compounds could be difficult to perform in humans without preliminary laboratory studies or because ethical considerations. By these reasons, alternative models are commonly used. These models include: the bovine or human infection dentin model using extracted teeth [8], in situ models [9, 10], animal models [11] and ex vivo models [12]. Validation of dentin infection models includes microbiological and microscopic analyses [13, 14]. The development of confocal microscope (CLSM) and the improvement of direct viable staining methods have stimulated the study of bacteria s viability in the last years, especially in the biofilm area. The use of CLSM for the study of dentin infection and oral biofilms has been reported in some early studies [15-17]. Potential advantages of confocal microscopy for the study of dentin infection includes: observation of live bacteria in dentinal tubules and root canal walls by the use of vital staining techniques [15, 16, 18], identification of labeled bacteria by in situ hybridization [19] and 3D visualization of structural organization in biofilms [20]. Optical sectioning and the ability to study the subsurface of hydrated specimens could be useful to analyze samples that are performed by sectioning undecalcified dentin avoiding contaminants or artifacts situated at the surface layer. To date, there is only two published data [19, 21] about distribution of bacteria and biofilms in necrotic human root canals using the confocal microscopy, maybe, because of laboratory procedures to study clinical samples are limited or are not completely developed. The aims of this work are: 1. To describe the ability of a confocal microscopy technique to investigate the pattern of dentin infection provided by different models used in endodontic research that includes laboratory and in situ infected dentin; animal and human infected dentin from necrotic root canals were also evaluated. 2. Materials and Methods The sample of this study were: five bovine teeth infected with the bacteria Enterococcus faecalis under laboratory conditions, six bovine sterile dentin blocks used in an intraoral device by a volunteer to induce dentin infection of the specimens and two distal roots of mandibular molars and one extracted root of a maxillary pre-molar extracted by nonrestorable carious lesions and vertical fracture. 2.1 In vitro dentin infection Five bovine teeth with a length of about 7-8 mm were prepared by sectioning the root tip, and after the crowns were removed at below the cemento-enamel junction. Each root canal was enlarged to a size of a gates glidden bur # 5 583
2 A. Méndez-Vilas and J. Díaz (Eds.) (1.30mm). To create the bacterial inoculums, isolated colonies (24 h) of pure cultures of Enterococcus faecalis grown aerobically on BHI agar plates were suspended in 3.0 ml of BHI. For dentin infection, under laminar flow five blocks were transferred individually into 3 ml of BHI inoculated with 200µl of an overnight E. faecalis suspension for 21 days. BHI was changed every 48 hours, and the purity of the broth was verified to avoid contamination. A sterile sample was used as negative control. 2.2 In situ dentin infection This model includes the use of an intraoral appliance according to Zaura [22]. Six Dentin sections (3mmx3mmx2mm) were obtained from sterile bovine radicular dentin. The samples were treated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite for 15 minutes and 17% EDTA for 3 minutes. The dentin samples were fixed in an intraoral orthodontic device to allow the biofilm development. In order to standardize the microbiota and rate of biofilm development, one healthy single volunteer used the intraoral device for 36 hours. The ethical committee involving human research approved the use of the intraoral device (064/2009). Informed consent was also requested. At the end of the experiment the dentin specimens were carefully washed with 100µl of sterile distilled water prior to the staining procedure. Two sterile samples that were not in contact with the oral environment were used as negative control. 2.3 Human infected dentin Two non-vital distal roots of two mandibular first molars extracted by non-restorable carious lesions and one maxillary pre-molar extracted by a vertical fracture, were included. The mandibular first molars were part of a study that involves the evaluation of different root canal filling techniques. After the extraction a round bur was used to expose the pulp chamber to facilitate the fixation procedure. Then, the teeth were fixed in 10% formalin buffer for 72 hours. Prior to the sectioning and staining procedures the external surface of the teeth was cleaned and all the organic tissue attached to the root was eliminated carefully using a razor blade and alcohol. 2.4 General sectioning, staining and CLSM procedures The samples of the in vitro and the extracted human teeth were sectioned using a 0.3mm Isomet saw under constant cooling using sterile distilled water. The roots were fixed on an Isomet platform using a low fusion impression compound (Kerr, MI, USA). Two 1mm sections were taken form each root corresponding to the apical and middle third of each root. The dentin segments from the in situ experiment were not sectioned because they were flat before the infection being unnecessary the section for confocal analysis. The dentin sections corresponding to the in vitro and in situ experiments and the human sections were washed carefully with 100µl of sterile distilled water and stained with 100µl of 0.01% acridine orange in a dark environment for 30 minutes and then rinsed with 100µl of distilled water; such dye has the ability to bind with bacterial RNA emitting red fluorescence and to bind with bacterial DNA emitting green fluorescence. After the staining procedure, the corresponding specimens were immediately analyzed by the CLSM technique. The negative controls of the in situ and in vitro experiments were stained with the same protocol. For the human infected dentin study, an extracted vital tooth was used as negative control. All dentin samples were examined on an inverted Leica TCS-SPE confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) using a modified chamber device. For the acridine orange staining the excitation and emission for RNA was 460 and 650 nm; the excitation and emission for DNA was 500 and 526 nm respectively. The sequential frame scan mode was used in order to prevent crosstalk. The in vitro, human and animal infected dentin specimens were scanned at the subsurface level, 5-10µm inside the dentin structure. The dentin from the in situ experiment was scanned from the top of the biofilm to the dentin surface. All the samples were observed using the 5X lens, 10X lens, 40X oil lens, 63X oil lens and 63X oil lens with an additional zoom of 3X. The 40X pictures were obtained by using sections of 1 µm step size in a format of 1024 X 1024 pixels. The 63X zoom 3 pictures were taken by using a 0.3µm step size. The images were acquired using the Leica Application Suite-Advanced Fluorescence software (LAS AF, Leica Mannheim, Germany). Representative 3D reconstructions were performed from the confocal stacks using the open-source software OsiriX available at: running under Leopard Mac OSX software (Apple computer Inc., Cupertino CA, USA). 3. Results and discussion 3.1 In vitro dentin infection At 100X magnification all the root canals studied appear empty with no evidence of organic structures in root canal walls (Fig 2A). 40 X oil lens examination showed fluorescence in dentinal tubules that represented a clear dentin 584
3 infection in all the studied samples (Fig 1C). The more common finding was the presence of dentin infection with discrete colonization of the root canal walls, usually between 2-4 layers of cells (Fig 2B, D). Very sparse isolated bacterial colonies were also occasionally observed, bacteria in this structures appears to be coaggregated and were only visible using the 63X oil lens with zoom 3 (Fig 1E). Bacterial penetration in dentinal tubules was variable, usually 1 or 2 operative fields using the 40x oil lens ( µm). Fig. 1 (A) 100X picture of the root canal wall (*) of bovine dentin infected under laboratory conditions, despite the presence of dentin infection (detail) there is absence of visible organic structures in root canal walls using this magnification (B) root canal wall of in vitro infected specimen showed weak colonization of root canal walls (*), infection of dentinal tubules is present (detail). (C-D) infected dentinal tubules in almost absence of canal wall colonization, a thin layer of cells can be seen (arrow) (E) a Enterococcus faecalis colony can be seen attached to the dentin, bacteria appears to be coaggregated. 3.2 In situ model The experimental samples appeared intensely stained (Fig.2A). Confocal scanning was performed at this magnification; at least µm of scanning was required to acquire all the information in the Z-projection. This information showed that a high volume of labeled material (Biomass) was present on the dentin (Fig 2A-E). Carefully examination of these structures reveals the presence of complex biofilms with many morphological variations usually as heterogeneous forms, mushroom-like structures, or firmly compacted to the dentin structure. In very isolated areas, the process of initial colonization of the dentin was evident (Figure 2B). Initial stages of dentin infection in this model begin with a layer of bacteria of some micrometers (2-5µm) firmly adhered to the dentin. Initial colonization of dentinal tubules at this stage was visible using the 63X oil lens (Fig. 2B-C). Bacteria appear to be coaggregated in localized points forming a mass that was limited to some micrometers. These isolated biofilms spread forming a firm layer that has intense fluorescence and usually do not exceed from 10µm in the Z-plane (Fig 2C). More complex higher structures in the Zplane could also be found; these structures seem to be in relation with biomass growth usually seen as mushroom-like structures that exceeded 50µm in height. (Figure 2D). 585
4 A. Méndez-Vilas and J. Díaz (Eds.) Fig. 2 (A) 50X picture of in situ infected dentin after 72 hours in the oral environment; organic structures can be seen in orange/red at relative low magnification. Different stages of biofilm development can be seen in a single sample. A detail of the initial stage of dentin contamination can be seen in (B), there is a tendency of bacterial colonies to converge or coaggregate (arrows), and dentin infection is present. (C) The small bacterial colonies appear to converge into a firmly attached biofilm (*). Despite the dentin appears strongly cover by this structure, confocal data shows that this structure has 7µm in height (detail). A detail of a complex mushroomlike biofilm can be seen in (D) the biofilm is firmly attached to the dentin. (E) Intense dentin infection is showed in this sample at 100X the increment of the biomass difficult the identification of bacterial profiles in these structures maybe by an increment in the extracellular matrix. 3.2 Human infected root canals The presence of organic structures in root canal walls discernible at relative low magnifications (100X) was the common characteristic (Figure 3B). In spite of the presence of a firmly attached layer of bacteria in form of biofilm could be seen in some samples (Figure 3B, D), another sections showed the presence of amorphous organic structures attached to the canal walls. Dentin infection appears to be highly correlated with the presence of these amorphous structures (Figure 4B-C). In limited area bacteria appears to be enclosed inside these structures (Figure. 3D). Observation of the 3D pictures showed irregular and mushroom-like surfaces morphologies on root canal walls (Fig. 3D-E, 4B). Negative controls evidenced stained peritubular dentin without bacteria (Fig. 5A-B). Dentinal tubules of vital teeth appeared stained, maybe by the presence of odontoblastic prolongations. No bacterial profiles were evident. Clear differences between the infected and non-infected dentin were evident (Fig. 5C). Sawing undecalcified dentin and pulp tissue for microscopically purposes have been performed by previous studies. Lan et al. [23] used an Isomet saw machine to slice tooth specimens for histological purposes, he describe that this method has a low risk of laceration of the pulp. Gonçalves et al. [24] sliced extracted vital mandibular molars using an Isomet saw for implantation purposes in mices to study pulp angiogenesis; the pulp vitality appeared not be affected by the cutting process and the histological sections not revealed artifacts product of the cutting process. In this context, we verified that an interesting confocal microscopy property is the ability to perform scanning at the sub-surface level avoiding the smear layer and contamination created by the sectioning procedure on in vitro and in vivo samples. This procedure appears to be important to future studies that include fresh extracted teeth to study metabolic activity of microorganisms in root canals, since the inclusion of the teeth in paraffin or resin for sectioning can eliminate the bacteria s viability. Advantages of the sawing technique are that specimen processing and analyzes of the samples can be performed in a reasonable time. However, one disadvantage of this technique is that is impossible to get thin slices. The use of thin slices (2-5µm) is critical to show bacterial contamination at the apical third level for example. Another limitation is that bacteria suspended in a fluid phase in root canal walls are lost during the section procedure, limiting the analyzes only to the bacteria and organic structures attached to root canal walls and bacteria situated in dentinal tubules. We think that many problems can be solved combining other microscopical techniques in the same sample as correlative optical and transmission electron microscopy where thin sections can be performed and compared with the confocal images or using a hard-tissue microtome [25, 26]. 586
5 Fig. 3 (A) Detail of carious infected dentinal tubules of the cervical third of a necrotic root canal. The lumen of dentinal tubules appears enlarged and infected. (B) 400X 3D reconstruction of middle third section of the same specimen shows infected dentinal tubules (square), organic structures attached to root canal walls (*) and tertiary dentin (#). A detail of the square is shown in (C). Dentinal tubules appear stained but no bacterial profiles are seen. A section from the confocal stack shows the presence of coccoidal cells in the dentinal tubules (arrow in detail). (D) Apical section shows less tubular density in the dentin and bacterial profiles are clearly seen attached to the root canal walls (area in the square is shown in detail in E). A 3D projection of the attached structure (detail in D) shows an evident compact biofilm with visible bacterial profiles and smooth surface. 587
6 A. Méndez-Vilas and J. Díaz (Eds.) Fig. 4 Maxillary pre-molar extracted by non-restaurable fracture is shown in (A). A 100X transversal apical section can be seen in the detail in (B). Intense colonization of the root canal wall by diverse attached mushroom-like biofilms structures is evident. 3D reconstruction showing clearly the source of bacterial cells in dentinal tubules, that is the biofilm in root canal wall (B). A 630X magnification with zoom 3 shows intense dentinal tubule infection. The bacterial profiles are restricted to dentinal tubules and not in the intertubular dentin (C). Fig. 5 Negative controls from in vitro and in situ experiments are shown in (A-B). Dentin structure of a non-infected teeth is shown in (C). Dentinal tubules appear stained maybe by the presence of odontoblastic prolongations, no bacterial profiles are evident in any sample. In summary, this work showed that high-resolution images of necrotic root canals and biofilms developed on dentin can be achieved using confocal microscopy, the fact that the slicing technique described in this study allows the capture of high-resolution images showed that research about biofilms and distribution of bacterial DNA in root canals in situ is promissory. Future refinements of this technique including the use of the fluorescence in situ hybridization and the use 588
7 of other staining protocols as the Live/Dead technique will allow to show the description of the tridimensional distribution of bacteria in endodontic biofilms and most important, the establishment of the metabolic activity and vitality of bacteria in infected root canals from fresh non-dehydrated samples. Discrepancies between the different infections models used in endodontic research should be taken into account for a more reliable interpretation of microbiological laboratory studies and their application to the clinical practice. This detail needs to be addressed in future studies. Acknowledgements The support by FAPESP (2007/ ) is gratefully acknowledged. References [1] Kakehashi S, Stanley HR, Fitzgerald RJ. The Effects of Surgical Exposures of Dental Pulps in Germ-Free and Conventional Laboratory Rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1965;20: [2] Silva LA, Leonardo MR, Assed S, Tanomaru Filho M. Histological study of the effect of some irrigating solutions on bacterial endotoxin in dogs. Braz Dent J 2004;15: [3] Sjogren U, Figdor D, Persson S, Sundqvist G. Influence of infection at the time of root filling on the outcome of endodontic treatment of teeth with apical periodontitis. Int Endod J 1997;30: [4] Molander A, Warfvinge J, Reit C, Kvist T. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of one- and two-visit endodontic treatment of asymptomatic necrotic teeth with apical periodontitis: a randomized clinical trial. J Endod 2007;33: [5] Bystrom A, Happonen RP, Sjogren U, Sundqvist G. Healing of periapical lesions of pulpless teeth after endodontic treatment with controlled asepsis. Endod Dent Traumatol 1987;3: [6] Bergenholtz G, Lekholm U, Milthon R, Heden G, Odesjo B, Engstrom B. Retreatment of endodontic fillings. Scand J Dent Res 1979;87: [7] McGurkin-Smith R, Trope M, Caplan D, Sigurdsson A. Reduction of intracanal bacteria using GT rotary instrumentation, 5.25% NaOCl, EDTA, and Ca(OH)2. J Endod 2005;31: [8] Haapasalo M, Orstavik D. In vitro infection and disinfection of dentinal tubules. J Dent Res 1987;66: [9] Barthel CR, Zimmer S, Zilliges S, Schiller R, Gobel UB, Roulet JF. In situ antimicrobial effectiveness of chlorhexidine and calcium hydroxide: gel and paste versus gutta-percha points. J Endod 2002;28: [10] Virtej A, MacKenzie CR, Raab WH, Pfeffer K, Barthel CR. Determination of the performance of various root canal disinfection methods after in situ carriage. J Endod 2007;33: [11] Tanomaru Filho M, Leonardo MR, da Silva LA. Effect of irrigating solution and calcium hydroxide root canal dressing on the repair of apical and periapical tissues of teeth with periapical lesion. J Endod 2002;28: [12] Villette G, Manek S, Legner M, Fillery ED, Torneck CD, Basrani BR, et al. Characterization of an ex vivo model for the assessment of root canal disinfection. J Endod 2008;34: [13] Siqueira JF, Jr., Rocas IN, Lopes HP, Elias CN, de Uzeda M. Fungal infection of the radicular dentin. J Endod 2002;28: [14] Sedgley CM. The influence of root canal sealer on extended intracanal survival of Enterococcus faecalis with and without gelatinase production ability in obturated root canals. J Endod 2007;33: [15] George S, Kishen A, Song KP. The role of environmental changes on monospecies biofilm formation on root canal wall by Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod 2005;31: [16] Kishen A, George S, Kumar R. Enterococcus faecalis-mediated biomineralized biofilm formation on root canal dentine in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A 2006;77: [17] Distel JW, Hatton JF, Gillespie MJ. Biofilm formation in medicated root canals. J Endod 2002;28: [18] Zapata RO, Bramante CM, de Moraes IG, Bernardineli N, Gasparoto TH, Graeff MS, et al. Confocal laser scanning microscopy is appropriate to detect viability of Enterococcus faecalis in infected dentin. J Endod 2008;34: [19] Schaudinn C, Carr G, Gorur A, Jaramillo D, Costerton JW, Webster P. Imaging of endodontic biofilms by combined microscopy (FISH/cLSM - SEM). J Microsc 2009;235: [20] Shen Y, Qian W, Chung C, Olsen I, Haapasalo M. Evaluation of the effect of two chlorhexidine preparations on biofilm bacteria in vitro: a three-dimensional quantitative analysis. J Endod 2009;35: [21] Lacovidou A NM, J. A. P. Figueiredo, K. Gulabivala. Utility of the FISH technique in conjunction with confocal microscopy to study the intraradicular microflora of teeth associated with apical periodontitis. Int Endod J 2008;41(9). Abstract. [22] Zaura-Arite E, van Marle J, ten Cate JM. Conofocal microscopy study of undisturbed and chlorhexidine-treated dental biofilm. J Dent Res 2001;80: [23] Lan WH, Kwan HW, Sunada I. Slicing technique for tooth specimens in histological preparation. Bull Tokyo Med Dent Univ 1986;33: [24] Goncalves SB, Dong Z, Bramante CM, Holland GR, Smith AJ, Nor JE. Tooth slice-based models for the study of human dental pulp angiogenesis. J Endod 2007;33: [25] Nair PN, Henry S, Cano V, Vera J. Microbial status of apical root canal system of human mandibular first molars with primary apical periodontitis after "one-visit" endodontic treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2005;99: [26] Richardson N, Mordan NJ, Figueiredo JA, Ng YL, Gulabivala K. Microflora in teeth associated with apical periodontitis: a methodological observational study comparing two protocols and three microscopy techniques. Int Endod J 2009;42:
Instruction manual. Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system. Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics
 Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
Instruction manual Safe and efficient NiTi rotary system Fulfilling the biological requirement for successful endodontics FKG REF. - 99.7AA.50.04B.AN - 06/2010 BioRaCe kit 1 Educational CD 1 Endo Stand
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures
 Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility
 Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: 135-140. www.ijos.org.cn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tooth anatomy risk factors influencing root canal working length accessibility Lu Tang 1,2, Tuo-qi Sun 1,2, Xiao-jie Gao 1, Xue-dong Zhou
original article Keywords: Sodium hypochlorite. Chlorhexidine. Calcium hydroxide. Endodontic infection. Root canal medication.
 original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
original article Efficacy of chemo-mechanical preparation with different substances and the use of a root canal medication in dog s teeth with induced periapical lesion Frederico C. Martinho, DDS, MSc
Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical Periodontitis: New Treatment Protocol?
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin
 Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Eliminating effect of Er, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation on the smear layer of dentin Jingtao Yu, MD, DDS, and Lu Yan, MD, DDS College of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang, P. R. China Purpose:
Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):463-7 Case Report Article Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):463-7 Case Report Article Persistent infection in root-filled tooth: an SEM morphological analysis after apical microsurgery
Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size
 original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
original article Location of the apical foramen and its relationship with foraminal file size Ronaldo Araújo Souza, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Suely Colombo, DDS 1
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research
 BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
BioPure MTAD Antibacterial Root Canal Cleanser Research ANTIBACTERIAL 1. Torabinejad M, Shabahang S, Aprecio RM, Kettering JD. The antimicrobial effect of MTAD: An in vitro investigation. J Endodon 2003;
Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report
 325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
325 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 325-329, 2007 Case Report Endodontic treatment with MTA apical plugs: a case report Pari Ghaziani 1), Navid Aghasizadeh 2) and Mahshid Sheikh-Nezami 1) 1) Department
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental
 EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
EndoActivator from Tulsa Dental Irrigation-EndoActivator http://endoactivator.com/video3.html EndoActivator System did not enhance the removal of smear layer as compared with conventional Max-I-Probe irrigation
endodontic therapy combined to photo-disinfection on patients with periapical lesion. A 6-month follows up.
 Antimicrobial comparison on effectiveness of endodontic therapy and endodontic therapy combined to photo-disinfection on patients with periapical lesion. A 6-month follows up. Aguinaldo S Garcez a, Silvia
Antimicrobial comparison on effectiveness of endodontic therapy and endodontic therapy combined to photo-disinfection on patients with periapical lesion. A 6-month follows up. Aguinaldo S Garcez a, Silvia
Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases
 Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
Clinical Removal of a fractured instrument with a new extractor: clinical cases Dominique Martin 1 Introduction The fracture of a root canal instrument during endodontic treatment is a surgical accident
The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of
 Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
Murat AYDIN *, The antibacterial effect of silver anode in root canals Oral Microbiol Immunol Abstract The present study reports on the application of silver anode in root canals for disinfection of infected
Endodontic treatment outcome is related to treatment expectations of the operator
 Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
Endodontic Treatment Outcome: Survey of Oral Health Care Professionals Ilan Rotstein, DDS,* Robert Salehrabi, DDS,* and Jane L. Forrest, BSDH, MS, EdD Abstract This study assessed the opinion of oral health
Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2011 Winter 2011 Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork:
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Winter 2011 Winter 2011 Root Canal Irrigants and Disinfectants Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork:
Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report
 original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
original article Removal of a silver cone by using clinical microscope and ultrasound: Case report Maíra do Prado 1 Marcos Cesar Pimenta de Araújo 2 Heloísa Carla Gusman 3 abstract Introduction: The retreatment
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of. the procedure.
 Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
protocol handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel
 handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
How To Train To Be A Dentist
 Bilaga 1. Sökstrategier Abbreviations * Wildcard indicating a variable number of characters (including none) /AE adverse effects (MeSH Subheading) /CL classification (MeSH Subheading) /CO complications
Bilaga 1. Sökstrategier Abbreviations * Wildcard indicating a variable number of characters (including none) /AE adverse effects (MeSH Subheading) /CL classification (MeSH Subheading) /CO complications
Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation
 Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
Clinical Histologic comparison of biologic width around teeth versus implants: The effect on bone preservation Kazuto Makigusa 1 Abstract Histological analysis of the biological width surrounding primate
BACTERIAL ENUMERATION
 BACTERIAL ENUMERATION In the study of microbiology, there are numerous occasions when it is necessary to either estimate or determine the number of bacterial cells in a broth culture or liquid medium.
BACTERIAL ENUMERATION In the study of microbiology, there are numerous occasions when it is necessary to either estimate or determine the number of bacterial cells in a broth culture or liquid medium.
Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01719.x CASE REPORT Non-surgical management of a large periapical lesion using a simple aspiration technique: a case report M. Fernandes & I. De Ataide Goa Dental College &
Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA. For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.
 METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Pulp reactions to exposure after experimental crown fractures or grinding in adult monkeys
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Pulp reactions to exposure after experimental crown fractures or grinding in adult monkeys 9 Miomir Cvek, DMS, PhD; Peter E. Cleaton-Jones, BDS, PhD; John C. Austin, 8VSc; and Jens
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Pulp reactions to exposure after experimental crown fractures or grinding in adult monkeys 9 Miomir Cvek, DMS, PhD; Peter E. Cleaton-Jones, BDS, PhD; John C. Austin, 8VSc; and Jens
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES
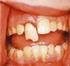 DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
Factors Affecting the Long-term Results of Endodontic Treatment
 0099-2399/90/1610-0498/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1990 Factors Affecting the Long-term Results
0099-2399/90/1610-0498/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1990 Factors Affecting the Long-term Results
Crown Dilaceration in Permanent Teeth after Trauma to the Primary Predecessors: Report of Three Cases
 Braz Dent J (2012) 23(5): 591-596 Crown dilaceration after trauma to the predecessors ISSN 0103-6440 591 Crown Dilaceration in Permanent Teeth after Trauma to the Primary Predecessors: Report of Three
Braz Dent J (2012) 23(5): 591-596 Crown dilaceration after trauma to the predecessors ISSN 0103-6440 591 Crown Dilaceration in Permanent Teeth after Trauma to the Primary Predecessors: Report of Three
Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators
 original article Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators Maria Rosa Felix de Sousa G. GUIMARÃES, DDS, MSc 1 Henner Alberto GOMIDE, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Maria Antonieta
original article Analysis of forces developed during root canal filling by different operators Maria Rosa Felix de Sousa G. GUIMARÃES, DDS, MSc 1 Henner Alberto GOMIDE, DDS, MSc, PhD 2 Maria Antonieta
Endodontics. Colleagues for Excellence. Access Opening and Canal Location
 Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
Endodontics Colleagues for Excellence Spring 2010 Access Opening and Canal Location Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists Cover artwork: Rusty Jones,
Dental caries is an infectious disease caused
 Emerging Methods of Caries Diagnosis George K. Stookey, Ph.D.; Carlos González-Cabezas, D.D.S., Ph.D. Abstract: Current diagnostic tools used in dental caries detection are not sensitive enough to diagnose
Emerging Methods of Caries Diagnosis George K. Stookey, Ph.D.; Carlos González-Cabezas, D.D.S., Ph.D. Abstract: Current diagnostic tools used in dental caries detection are not sensitive enough to diagnose
Jamia Millia Islamia: Performa for CV of Faculty/ Staff Members
 Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
Curriculum Vitae Brief Profile: 1-2 paragraphs (not exceeding 500 words) 1. Name: Vivek Aggarwal 2. Designation: Assistant Professor 3. Office Address: Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics,
Test Method for the Continuous Reduction of Bacterial Contamination on Copper Alloy Surfaces
 Test Method for the Continuous Reduction of Bacterial Contamination on Copper Alloy Surfaces Test Organisms: Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) Enterobacter aerogenes (ATCC 13048) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Test Method for the Continuous Reduction of Bacterial Contamination on Copper Alloy Surfaces Test Organisms: Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) Enterobacter aerogenes (ATCC 13048) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
CDT 2015 Code Change Summary New codes effective 1/1/2015
 CDT 2015 Code Change Summary New codes effective 1/1/2015 Code Nomenclature Delta Dental Policy D0171 Re-Evaluation Post Operative Office Visit Not a Covered Benefit D0351 3D Photographic Image Not a Covered
CDT 2015 Code Change Summary New codes effective 1/1/2015 Code Nomenclature Delta Dental Policy D0171 Re-Evaluation Post Operative Office Visit Not a Covered Benefit D0351 3D Photographic Image Not a Covered
Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction
 1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
Develop a specialist who is capable of correlation of basic sciences and clinical sciences, and challenge the requirements for certification.
 Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 05 Page 5590-5594 May 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Nanoparticles in Irrigation and Disinfection of the Root Canal System A Review Authors Rucheet Purba 1, Snehal Sonarkar 2, Vidya Mokhade
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Nanoparticles in Irrigation and Disinfection of the Root Canal System A Review Authors Rucheet Purba 1, Snehal Sonarkar 2, Vidya Mokhade
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Cracked Teeth Iowa Dental Association Annual Session May 6, 2011 Dr. Bruce C. Justman
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Cracked Teeth Iowa Dental Association Annual Session May 6, 2011 Dr. Bruce C. Justman Longitudinal Fractures Types of Longitudinal Fractures Craze Lines Cusp Fracture
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis of Cracked Teeth Iowa Dental Association Annual Session May 6, 2011 Dr. Bruce C. Justman Longitudinal Fractures Types of Longitudinal Fractures Craze Lines Cusp Fracture
Confocal Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) A very brief primer...
 Confocal Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) of biofilms A very brief primer... Fundamentals of Confocal Microscopy Based on a conventional fluorescence microscope Fluorescent Microscope Confocal
Confocal Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) of biofilms A very brief primer... Fundamentals of Confocal Microscopy Based on a conventional fluorescence microscope Fluorescent Microscope Confocal
Wound healing of apical tissues after root canal therapy: a long-term clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic observation study
 Vol. 108 No. 4 October 2009 ENDODONTOLOGY Editor: Larz S.W. Spångberg Wound healing of apical tissues after therapy: a long-term clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic observation study Domenico Ricucci,
Vol. 108 No. 4 October 2009 ENDODONTOLOGY Editor: Larz S.W. Spångberg Wound healing of apical tissues after therapy: a long-term clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic observation study Domenico Ricucci,
Dental-based Injuries
 Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND PREPARATIONS. 4. Serve as a reference point for evaluating the fit of the framework to the teeth.
 CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND DEFINITIONS A REST is any rigid part of an RPD framework which contacts a properly prepared surface of a tooth. A REST PREPARATION or REST SEAT is any portion of a tooth or restoration
CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND DEFINITIONS A REST is any rigid part of an RPD framework which contacts a properly prepared surface of a tooth. A REST PREPARATION or REST SEAT is any portion of a tooth or restoration
Root canal treatment by means of electronic conductometry without radiographic transoperative verification: a report of five cases
 original article Root canal treatment by means of electronic conductometry without radiographic transoperative verification: a report of five cases Norberto J. BROON 1 Alvaro CRUZ 2 Claudia A. PALAFOX-SÁNCHEZ
original article Root canal treatment by means of electronic conductometry without radiographic transoperative verification: a report of five cases Norberto J. BROON 1 Alvaro CRUZ 2 Claudia A. PALAFOX-SÁNCHEZ
4-1-2005. Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements
 4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
The persistence of different calcium hydroxide paste medications in root canals: an SEM study
 original article The persistence of different calcium hydroxide paste medications in root canals: an SEM study Hélio Katsuya Onoda, DDS 1 Gerson Hiroshi Yoshinari, MSc, PhD 2 Key Fabiano Souza Pereira,
original article The persistence of different calcium hydroxide paste medications in root canals: an SEM study Hélio Katsuya Onoda, DDS 1 Gerson Hiroshi Yoshinari, MSc, PhD 2 Key Fabiano Souza Pereira,
Transferring a Broth Culture to Fresh Broth
 Sterile Technique It is very important in microbiology to work with pure cultures. Unfortunately this is difficult. The world around us is covered with microorganisms. Microorganisms are even carried on
Sterile Technique It is very important in microbiology to work with pure cultures. Unfortunately this is difficult. The world around us is covered with microorganisms. Microorganisms are even carried on
Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1
 The use of ozone in dentistry a case study Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1 Ozone gas is a
The use of ozone in dentistry a case study Svea Baumgarten, Dr. med. dent., M Sc, accredited implantologist as per the criteria of the DGZI (German Association of Dental Implantology) 1 Ozone gas is a
The use of the erbium, chromium:yttriumscandium-gallium-garnet ABSTRACT
 The use of the erbium, chromium:yttriumscandium-gallium-garnet laser in endodontic treatment The results of an in vitro study Ulrich Schoop, DDS, MD; Kawe Goharkhay, DMD, MD; Johannes Klimscha, DMD, MD;
The use of the erbium, chromium:yttriumscandium-gallium-garnet laser in endodontic treatment The results of an in vitro study Ulrich Schoop, DDS, MD; Kawe Goharkhay, DMD, MD; Johannes Klimscha, DMD, MD;
Histology of Irreversible Pulpitis Premolars Treated with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Pulpotomy
 Operative Dentistry, 2010, 35-3, 370-374 Clinical Technique/Case Report Histology of Irreversible Pulpitis Premolars Treated with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Pulpotomy L-H Chueh C-P Chiang Clinical Relevance
Operative Dentistry, 2010, 35-3, 370-374 Clinical Technique/Case Report Histology of Irreversible Pulpitis Premolars Treated with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Pulpotomy L-H Chueh C-P Chiang Clinical Relevance
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function!
 Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
Foundation Revolutionary Bone Augmentation Material. Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Regional Partner
 Foundation Revolutionary Bone Augmentation Material Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Regional Partner Stimulates New Bone Growth Foundation is a collagen-based, bone filling augmentation material for use
Foundation Revolutionary Bone Augmentation Material Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Regional Partner Stimulates New Bone Growth Foundation is a collagen-based, bone filling augmentation material for use
Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines
 Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines Albadri S, Zaitoun H, Kinirons MJ Introduction Traumatic intrusion is a luxation injury where the tooth
Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines Albadri S, Zaitoun H, Kinirons MJ Introduction Traumatic intrusion is a luxation injury where the tooth
Influence of Biomechanical Factors on Restoration of Devitalized Teeth
 Influence of Biomechanical Factors on Restoration of Devitalized Teeth Adnan atoviê 1 Davor Seifert 1 Renata Poljak-Guberina 1 Boris KvasniËka 2 1 Department of Fixed Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine
Influence of Biomechanical Factors on Restoration of Devitalized Teeth Adnan atoviê 1 Davor Seifert 1 Renata Poljak-Guberina 1 Boris KvasniËka 2 1 Department of Fixed Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine
Replacement of the upper left central incisor with a Straumann Bone Level Implant and a Straumann Customized Ceramic Abutment
 Replacement of the upper left central incisor with a Straumann Bone Level Implant and a Straumann Customized Ceramic Abutment by Dr. Ronald Jung and Master Dental Technician Xavier Zahno Initial situation
Replacement of the upper left central incisor with a Straumann Bone Level Implant and a Straumann Customized Ceramic Abutment by Dr. Ronald Jung and Master Dental Technician Xavier Zahno Initial situation
Properties and applications of calcium hydroxide in endodontics and dental traumatology
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01886.x Review Properties and applications of calcium hydroxide in endodontics and dental traumatology Z. Mohammadi 1 & P. M. H. Dummer 2 1 Department of Endodontics, Hamedan
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01886.x Review Properties and applications of calcium hydroxide in endodontics and dental traumatology Z. Mohammadi 1 & P. M. H. Dummer 2 1 Department of Endodontics, Hamedan
Immediate Molar Implant Placement: A Private Practice Clinical Investigation. Abstract
 Immediate Molar Implant Placement: A Private Practice Clinical Investigation Gargiulo et al Alphonse Gargiulo, DDS, MS 1 Thomas Manos, DDS, MS 2 Mark Kolozenski, DDS, MS 3 Alex Tzanos, DDS, MSD 3 Michael
Immediate Molar Implant Placement: A Private Practice Clinical Investigation Gargiulo et al Alphonse Gargiulo, DDS, MS 1 Thomas Manos, DDS, MS 2 Mark Kolozenski, DDS, MS 3 Alex Tzanos, DDS, MSD 3 Michael
Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated)
 Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Product Manual Radius 24-Well Cell Migration Assay (Laminin Coated) Catalog Number CBA-125-LN 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cell migration is a highly
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Humoral response to therapeutic low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) treatment of rat maxillary socket after the removal of a molar tooth
 Humoral response to therapeutic low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) treatment of rat maxillary socket after the removal of a molar tooth Kouki Hidaka *1, Chihiro Miyamoto *2, Satoko Wada-Takahashi
Humoral response to therapeutic low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) treatment of rat maxillary socket after the removal of a molar tooth Kouki Hidaka *1, Chihiro Miyamoto *2, Satoko Wada-Takahashi
Development of Teeth
 Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES
 E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
E N D O D O N T I CE SN D O D O N T I C S Root Canal Retreatment: 2. Practical Solutions T.R. PITT FORD AND J.S. RHODES Abstract: Root canal retreatment is often the preferred method of treating a tooth
Course Descriptions. I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students)
 Course Descriptions I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students) This course is offered during the first semester of the second year of the MD Program. It
Course Descriptions I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students) This course is offered during the first semester of the second year of the MD Program. It
Longitudinal tooth fractures: findings that contribute to complex endodontic diagnoses
 Endodontic Topics 2009, 16, 82 111 All rights reserved 2009 r John Wiley & Sons A/S ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2009 1601-1538 Longitudinal tooth fractures: findings that contribute to complex endodontic diagnoses
Endodontic Topics 2009, 16, 82 111 All rights reserved 2009 r John Wiley & Sons A/S ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2009 1601-1538 Longitudinal tooth fractures: findings that contribute to complex endodontic diagnoses
Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01180.x QUALITY GUIDELINES Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology Abstract. Quality guidelines for endodontic
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01180.x QUALITY GUIDELINES Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology Abstract. Quality guidelines for endodontic
Chart 1. Chart 2. How to Use the Following Charts. Be sure to follow the legal requirements to perform dental radiographic procedures.
 These data are presented for informational purposes only and are not intended as a legal opinion regarding dental practice in any state. DANB confers with each state s dental board at least annually regarding
These data are presented for informational purposes only and are not intended as a legal opinion regarding dental practice in any state. DANB confers with each state s dental board at least annually regarding
Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report. Abu-Hussein Muhamad 1 *, Watted Nezar 2, and Abdulgani Azzaldeen 3. 1 Department of Pediatric
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report. Abu-Hussein Muhamad 1 *, Watted Nezar 2, and Abdulgani Azzaldeen 3. 1 Department of Pediatric
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells
 METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT
 RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT 1. Dr. Yadav Chakravarthy, MDS* Professor and Head of The Department. Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
RICHMOND CROWN - FOR RESTORATION OF BADLY MUTILATED POSTERIOR TEETH - A CASE REPORT 1. Dr. Yadav Chakravarthy, MDS* Professor and Head of The Department. Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
Propionibacterium Acnes Cause Delayed Surgical Site Infection Only In The Presence Of Implant
 Propionibacterium Acnes Cause Delayed Surgical Site Infection Only In The Presence Of Implant Yuta Shiono 1,2, Ken Ishii 1, Shigenori Nagai 3, Hiroaki Kakinuma 4, Aya Sasaki 5, Mamoru Aizawa 4, Yasunori
Propionibacterium Acnes Cause Delayed Surgical Site Infection Only In The Presence Of Implant Yuta Shiono 1,2, Ken Ishii 1, Shigenori Nagai 3, Hiroaki Kakinuma 4, Aya Sasaki 5, Mamoru Aizawa 4, Yasunori
Counting and imaging bacteria using fluorescent microscopy & Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
 Counting and imaging bacteria using fluorescent microscopy & Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Bruce E. Logan Kappe Professor of Environmental Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental
Counting and imaging bacteria using fluorescent microscopy & Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Bruce E. Logan Kappe Professor of Environmental Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental
ABSTRACT. CFU/ml in case of air water syringe, 6.181 log 10 CFU/ml in case of high speed air turbine hand-piece and 2.828 log 10
 Original Research Waterline contamination and role of flushing dental water unit lines in private dental clinics of Mangalore ROSHAN SHETTY*# B. SURESHCHANDRA**## VIJAYA HEGDE***# ABSTRACT Aim: To determine
Original Research Waterline contamination and role of flushing dental water unit lines in private dental clinics of Mangalore ROSHAN SHETTY*# B. SURESHCHANDRA**## VIJAYA HEGDE***# ABSTRACT Aim: To determine
Richmond Crown- A Conventional Approach for Restoration of Badly Broken Posterior Teeth
 Richmond Crown- A Conventional Approach for Restoration of Badly Broken Posterior Teeth Abhinav Agarwal 1, Manish Chadha 2, D.R.V.Kumar 3, Prakash Somani 4, Preet Jain 5 Abstract: Restoration of badly
Richmond Crown- A Conventional Approach for Restoration of Badly Broken Posterior Teeth Abhinav Agarwal 1, Manish Chadha 2, D.R.V.Kumar 3, Prakash Somani 4, Preet Jain 5 Abstract: Restoration of badly
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity
 Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein. Table of Contents Fall 2012
 Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers
 Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers Dubravka KnezoviÊ-ZlatariÊ Asja»elebiÊ Biserka LaziÊ Department of Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine University
Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers Dubravka KnezoviÊ-ZlatariÊ Asja»elebiÊ Biserka LaziÊ Department of Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine University
CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME
 CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME Dr Vijay Salvi We all come across apparently healthy teeth eliciting complex and often bizarre symptoms. The patient will give a long history of undiagnosed but severe pain, and
CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME Dr Vijay Salvi We all come across apparently healthy teeth eliciting complex and often bizarre symptoms. The patient will give a long history of undiagnosed but severe pain, and
MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES
 EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth
 Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth Dr. Zuhair Al-Khatib Traumatic injuries to the teeth are so common among any community; trauma to the face especially to the oral region occurs frequently and comprises
Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth Dr. Zuhair Al-Khatib Traumatic injuries to the teeth are so common among any community; trauma to the face especially to the oral region occurs frequently and comprises
ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF SECRETORY GRANULES FROM RAT ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. II. Ultrastructure of the Beta Granule
 ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF SECRETORY GRANULES FROM RAT ISLETS OF LANGERHANS II Ultrastructure of the Beta Granule MARIE H GREIDER, S L HOWELL, and P E LACY From the Department of Pathology, Washington
ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF SECRETORY GRANULES FROM RAT ISLETS OF LANGERHANS II Ultrastructure of the Beta Granule MARIE H GREIDER, S L HOWELL, and P E LACY From the Department of Pathology, Washington
Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Apr-Jun;11(2):199-203 Case Report Article Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report Bernardo Almeida Aguiar 1 Fábio
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Apr-Jun;11(2):199-203 Case Report Article Hypochlorite-induced severe cellulitis during endodontic treatment: case report Bernardo Almeida Aguiar 1 Fábio
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION
 MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
Page 1 of 11 BDS FINAL PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2007 OPERATIVE DENTISTRY (MCQs) Model Paper
 Page 1 of 11 Marks 45 Time 45 minutes Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each 01. Hand cutting instruments are composed of: A. Handle and neck. B. Handle and blade only. C. Handle, shank and blade. D. Handle,
Page 1 of 11 Marks 45 Time 45 minutes Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each 01. Hand cutting instruments are composed of: A. Handle and neck. B. Handle and blade only. C. Handle, shank and blade. D. Handle,
Nd:YAG Laser Irradiation Effect on Apical Intracanal Dentin - A Microleakage and SEM Evaluation
 Braz Dent J (2011) 22(5): 377-381 Apical dentin evaluation after laser irradiation ISSN 0103-6440 377 Nd:YAG Laser Irradiation Effect on Apical Intracanal Dentin - A Microleakage and SEM Evaluation Cacio
Braz Dent J (2011) 22(5): 377-381 Apical dentin evaluation after laser irradiation ISSN 0103-6440 377 Nd:YAG Laser Irradiation Effect on Apical Intracanal Dentin - A Microleakage and SEM Evaluation Cacio
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY. To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques.
 DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques. To observe flagella in prepared slides stained by specific flagellar stains. II.
DETECTION OF BACTERIAL MOTILITY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate bacterial motility by microscopic and macroscopic techniques. To observe flagella in prepared slides stained by specific flagellar stains. II.
The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy
 The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy Dr. Katalin Déri Semmelweis Egyetem Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Risk Angle II/1 Predisposing factor: overjet insufficient lip
The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy Dr. Katalin Déri Semmelweis Egyetem Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Risk Angle II/1 Predisposing factor: overjet insufficient lip
3D Cell Culture mimsys G
 3D Cell Culture mimsys G xeno-free & nutrient permeable hydrogel for 3D cell culture mimsys G is a xeno-free and non-immunogenic, easy to handle hydrogel for cell encapsulation in 3D experiments in vitro
3D Cell Culture mimsys G xeno-free & nutrient permeable hydrogel for 3D cell culture mimsys G is a xeno-free and non-immunogenic, easy to handle hydrogel for cell encapsulation in 3D experiments in vitro
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology
 Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Lab Exercise 3: Media, incubation, and aseptic technique
 Lab Exercise 3: Media, incubation, and aseptic technique Objectives 1. Compare the different types of media. 2. Describe the different formats of media, plate, tube etc. 3. Explain how to sterilize it,
Lab Exercise 3: Media, incubation, and aseptic technique Objectives 1. Compare the different types of media. 2. Describe the different formats of media, plate, tube etc. 3. Explain how to sterilize it,
CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating solutions
 Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17621 Review of ultrasonic irrigation in endodontics: increasing action of irrigating
In the past decade, there has been a remarkable
 TECHNO BYTES Principles of cosmetic dentistry in orthodontics: Part 1. Shape and proportionality of anterior teeth David M. Sarver, DMD, MS Vestavia Hills, Ala In the past decade, there has been a remarkable
TECHNO BYTES Principles of cosmetic dentistry in orthodontics: Part 1. Shape and proportionality of anterior teeth David M. Sarver, DMD, MS Vestavia Hills, Ala In the past decade, there has been a remarkable
