Club Mosses, Ferns & Horsetails: the Seed-free Vascular Plants
|
|
|
- Tracey Merry Barnett
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Club Mosses, Ferns & Horsetails: the Seed-free Vascular Plants
2 Vascular Plants - a quick review Two unrelated groups within cryptogams seed free vascular plants are recognized as phyla: 1. Lycopodiophyta : lycopods 2. Polypodiophyta: ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns
3 Vascular Plants - a quick review Why were the seed-free plants grouped together? They produce free spores, the principal dispersal units, via meiosis. Spore: a reproductive cell, capable of developing into an adult without fusion with another cell. spores
4 Vascular Plants - a quick review Why were the seed-free plants grouped together? Spores develop within a sporangium (pl. sporangia) sporangium spores
5 Vascular Plants - a quick review Why were the seed-free plants grouped together? Spores germinate and develop into gametophytes that exist independently of the spore-producing plants. The gametophytes (haploid, n) tend to be inconspicuous and short-lived. sporangium gametophyte spores
6 Vascular Plants - a quick review Why were the seed-free plants grouped together? Like all plants, seed-free plants produce two kinds of gametes in their gametophytes: sperm and egg that unite to form a zygote (2n or diploid) via fertilization! sporangium zygote gametophyte spores
7 Vascular Plants - a quick review Why were the seed-free plants grouped together? The sporophyte (2n) develops from the zygote and is more conspicuous, usually perennial and lives for an indefinite period! sporophyte sporangium zygote gametophyte spores
8 Wisconsin Seed-free Plants The best website to identify and see images of Wisconsin s seedfree plants is Gary Fewless at UW-Green Bay; links provided below Key to Ferns and Fern Allies of Wisconsin List of Pteridophytes of Wisconsin Glossary of Fern Terminology also: Michigan Online Flora
9 Wisconsin Seed-free Plants The best manual to identify lycopods and ferns is Ferns of Northeastern and Central North America (2 nd ed.) in the Peterson Field Guides Warning: Families and genera (and thus species names) are changing quickly in the seed-free plants
10 Phylum Lycopodiophyta club mosses, spike mosses, quillworts! Leaves microphylls: generally small, simple, one-veined leaves. Microphylls evolved by the process of enation and vascularization. An enation is a veinless, lateral protrubence on the stem. When the enation becomes vascularized it is termed a microphyll.! Sporangia: the spore producers on the sporophytes are located singly on the upper surfaces or in axils of the bracts of a cone or of green leaves!
11 Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Carboniferous forest from Illinois This group arose in the Later Silurian about 420 million years ago and was dominant in the Carboniferous and used to be much more diverse.!
12 Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Lycopodiaceae - club mosses 15 genera and about 375 species Lycopodium now split into several genera cosmopolitan distribution, most diverse in tropics Evergreen, stems elongate and dichotomously branching. Leaves often densely covering the stem. Oily compounds in the cell walls ignite rapidly into a flash of light and were used by magicians and sorcerers in the Middle Ages. More recently they were used as a flash early in photography and in experimental photocopying machines. Many species over-collected for Christmas wreaths. Diphasiastrum complanatum Ground cedar, crowfoot
13 Lycopodiaceae - club mosses Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Homosporous: same spore - one kind of spore produced; cones terete (rounded)
14 Lycopodiaceae - club mosses other examples Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Dendrolycopodium obscurum Ground pine
15 Lycopodiaceae - club mosses other examples Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Lycopodiella inundata Bog club moss
16 Lycopodiaceae - club mosses other examples Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Huperzia lucidula Shiny club moss Alkaloid for Alzheimers?
17
18 Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Huperzia lucidula Shiny club moss Polytrichum forest mosses
19 Selaginellaceae - spike mosses 1 genus and about 750 species Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Mainly tropical family with some species extending into arctic regions of both hemispheres Leaves spirally arranged and often 4-ranked on the secondary and ultimate branches. Spores borne in or near the axils of well-differentiated sprophylls, usually on 4 sided stroboli.
20 Selaginellaceae - spike mosses 1 genus and about 750 species Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Mainly tropical family with some species extending into arctic regions of both hemispheres Leaves spirally arranged and often 4-ranked on the secondary and ultimate branches. Spores borne in or near the axils of well-differentiated sprophylls, usually on 4 sided stroboli. Heterosporous: different spores!! Unlike Lycopodiaceae, Selaginellaceae are heterosporous with different types of spores: microspores and megaspore (not related to size) the micro give rise to male gametophytes and the mega give rise to the female gametophytes.
21 Selaginellaceae - spike mosses Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Heterosporous: different spores!! Unlike Lycopodiaceae, Selaginellaceae are heterosporous with different types of spores: microspores and megaspore (not related to size) the micro give rise to male gametophytes and the mega give rise to the female gametophytes.
22 Selaginellaceae - spike mosses Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Selaginella eclipes meadow spike moss
23 Selaginellaceae - spike mosses Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Selaginella ruprestis Rock spike moss Selaginella selaginoides Northern spike moss Endangered!
24 Isoetaceae - quillworts Phylum Lycopodiophyta! 1 genus and about 150 species; worldwide; 2 spp. in WI - Isoetes echinospora most common Aquatic or semi-aquatic plants with corm-like stems with secondary growth. Absorb carbon through their roots. Leaves with ligules and quite long (15+ cm) for microphylls. I. butleri - not native Isoetes echinospora
25 Isoetaceae - quillworts Phylum Lycopodiophyta! Heterosporous plants with sporangia borne at the base of sporophylls which are similar to vegetative leaves. Megasporangia + microsporangia
26 Phylum Polypodiophyta - ferns & horsetails! Equisetaceae - horsetails, scouring rushes [previously placed in own phylum - Equisetophyta] 1 genus, Equisetum, 15 species with a cosmopolitan distribution except for Australia or New Zealand [9 species in Wisconsin] Plants are primarily colonizers of unforested areas, lake margins and wetlands Shoots monomorphic or dimorphic (see right). Often highly branched (horsetails) appearing like leaves. Others not branched (scouring rushes). Internodes with conspicuous vertical ridges; jointed stems; stems hollow (both important taxonomic features for keying species)
27 Equisetaceae - horsetails, scouring rushes Phylum Polypodiophyta! Leaves in whorls; leaves one veined, verticillate, united to form a sheath around the stem; these leaves are probably reduced megaphylls: Megaphylls are larger than microphylls have a blade that has a complex system of veins. megaphyll sheath branch Megaphyll theory is supported by placement of Equisetum among primitive ferns using DNA.
28 Equisetaceae - horsetails, scouring rushes Phylum Polypodiophyta! Sporangia clustered terminally in cones composed of polygonal, umbrella-like structures with sporangia beneath.
29 Equisetaceae - horsetails, scouring rushes Phylum Polypodiophyta! Horsetails are homosporous, have green spores with hygroscopic elators, and form conspicuous green gametophytes
30 Phylum Polypodiophyta! Equisetaceae - some examples of native horsetails & scouring rushes Equisetum arvense Field horsetail Equisetum sylvaticum Woodland horsetail
31 Phylum Polypodiophyta! Equisetaceae - some examples of native horsetails & scouring rushes Equisetum laevigatum Smooth scouring rush Equisetum scirpoides Dwarf horsetail
32 Phylum Polypodiophyta the true ferns! Most diverse of the vascular cryptogams, both in species number (ca. 11,000 worldwide) and form (small aquatics to trees). Like the horsetails (which may be thought of as specialized ferns), leaves are megaphylls; blade is called a frond and the petioles as stipes.
33 Phylum Polypodiophyta ferns! Circinate vernation: vernation is the arrangement of folded leaves in a bud, forming a crozier or fiddlehead, i.e. coiled or rolled up at the tip and unfolding lengthwise when emerging - due to auxin and differential growth of tissue. Protects young bud.
34 Phylum Polypodiophyta ferns! Sporangia borne on the margin or the lower surface of the leaf; often grouped in sori (pl.) sorus (sing.); a sorus may be protected by a flap-like structure called the indusium - an important feature for identification of ferns due to its remarkable variation in size, shape, and position.
35 Phylum Polypodiophyta ferns! The sprorangium is often associated with an annulus a cluster or row of cells with thick walls that open the sporangium and catapult the spores into the air. Ferns can be either homosporous or heterosporous. annulus
36 Phylum Polypodiophyta ferns!
37 Phylum Polypodiophyta! There is major disagreement on what are the fern families, but 30 are generally recognized worldwide. In Wisconsin there are 9 families. Characters used to circumscribe families often relate to cryptic features such as the presence or absence of annulus and its orientation, the length and diameter (number of cells) of the sporangial stalk, spore shape, stem and petiole crosssection anatomy. The primitive ferns include horsetails and whiskferns.
38 Phylum Polypodiophyta! Ophioglossaceae - adder s tongue family Primitive ferns; 2 genera in Wisconsin: Ophioglossum and Botrychium (now 3 genera) Sporangia are on an erect axis with a green blade attached below the sporangia bearing part Ophioglossum pusillum Adder s tongue fern
39 Ophioglossaceae - adder s tongue family Primitive ferns; 4 genera in Wisconsin: Ophioglossum and Botrychium (now 3 genera) Phylum Polypodiophyta! Botrychium mormo Goblin fern Botrychium lunaria Moonwort fern Botrypus virginianum Rattlesnake fern
40 Osmundaceae - royal fern family Primitive ferns; 1 genus in Wisconsin: Osmunda Fertile and sterile leaves dimorphic and the fertile portion is non-green at maturity. Sporangia not clustered in sori, but naked. Phylum Polypodiophyta!
41 Osmundaceae - royal fern family Phylum Polypodiophyta! 3 species of Osmunda in Wisconsin; easily separated by position of fertile portions All wide-spread & Bot 401 exam plant! Osmunda cinnamomea Cinnamon fern Osmunda claytoniana Interrupted fern Osmunda regalis Royal fern
42 Dennstaedtiaceae - bracken family Phylum Polypodiophyta! 2 genera in Wisconsin. Includes one of the most widespread of all vascular plants. Clonal with rhizome; large compound leaves. Ubiquitous in Wisconsin. Marginal sori with no indusia but with revolute (rolled over) leaf edge protecting sori. Pteridium aquilinum Bracken fern
43 Phylum Polypodiophyta! Pteridaceae - maidenhair fern family 4 genera in Wisconsin Sori that lack indusia or are protected by a reflexed or revolute margins Distinctively compound frond with dark purple stipe and rachis Adiatum pedatum Maidenhair fern
44 Aspleniaceae - spleenwort family 1 genus in Wisconsin. Defined by linear or kidney shaped sori. Phylum Polypodiophyta! Asplenium viride (A. trichomanes-ramosum) Green spleenwort Asplenium platyneuron Ebony spleenwort
45 Onocleaceae- sensitive fern family Phylum Polypodiophyta! 2 genera in Wisconsin (also Matteuccia ostrich fern). Sensitive ferns has dimorphic fronds. Sterile frond pinnately lobed. Fertile frond turning black. Onoclea sensibilis Sensitive fern
46 Dryopteridaceae - woodfern family Phylum Polypodiophyta! Large and diverse group of ferns; often broadly defined to include other smaller families. 2 genera and 13 species in Wisconsin. Polystichum acrostichoides Christmas fern Dryopteris intermedia Shield fern
47 Polypodiaceae - rockcap family Phylum Polypodiophyta! 40 genera and over 500 species in tropics and subtropics, but a single species in Wisconsin. Distinctive fronds: simple, pinnately lobed; leathery. Colonizes bare rock. Sori in two rows on each lobe. Polypodium virginianum Rockcap fern
48 Phylum Polypodiophyta! Salviniaceae (Azollaceae) - mosquito fern family 2 species in Wisconsin. Floating aquatic, reduced ferns with 2 ranked leaves, each 2 lobed. Symbiotic relationship with N2 fixing blue green bacteria Anabaena azollae. Heterosporous! Western & SE coastal elements Azolla mexicana & A. caroliniana Floating fern
BIOL 1030 TOPIC 5 LECTURE NOTES TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29)
 TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants
 The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants Laboratory 4 Introduction Members of kingdom Plantae are all multicellular organisms exhibiting cellulose cell walls, an alternation of generations life
The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants Laboratory 4 Introduction Members of kingdom Plantae are all multicellular organisms exhibiting cellulose cell walls, an alternation of generations life
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Ferns of the National Forests in Alaska
 Ferns of the National Forests in Alaska United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Alaska Region R10-RG-182 June 2010 Ferns abound in Alaska s two national forests, the Chugach and the Tongass,
Ferns of the National Forests in Alaska United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Alaska Region R10-RG-182 June 2010 Ferns abound in Alaska s two national forests, the Chugach and the Tongass,
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout
 PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns
 Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
PLANT DIVERSITY. EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae
 PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
FERNS AND SIMILAR PLANTS (PTERIDOPHYTES)
 FERNS AND SIMILAR PLANTS (PTERIDOPHYTES) AAlthough ferns and similar seedless vascular plants (reproducing by spores) were formerly lumped together as Division Pteridophyta, they are currently segregated
FERNS AND SIMILAR PLANTS (PTERIDOPHYTES) AAlthough ferns and similar seedless vascular plants (reproducing by spores) were formerly lumped together as Division Pteridophyta, they are currently segregated
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones
 Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers
 Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Plant Form and Function
 Part X Plant Form and Function Part Opener Title Text to come. Part opener figure 1 title. Figure legend. 733 Part opener figure 2 title. Figure legend. 734 Part X Plant Form and Function 37 Evolutionary
Part X Plant Form and Function Part Opener Title Text to come. Part opener figure 1 title. Figure legend. 733 Part opener figure 2 title. Figure legend. 734 Part X Plant Form and Function 37 Evolutionary
Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification
 1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
1 Tips for Identifying Broadleaf Weeds Laboratory Broadleaf Weed Identification The cotyledon is an important identifying characteristic for broadleaf weeds. Shape and position of leaves, presence of pubescence
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification
 Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
Pocket Guide to Common Ferns for Delineating Bordering Vegetated Wetlands in Massachusetts 2012
 Credits: Special thanks to Arieh Tal who developed the Quick Guide and is the major contributor of photos and text to the Pocket Guide. Arieh Tal is a nature photographer living in western Massachusetts.
Credits: Special thanks to Arieh Tal who developed the Quick Guide and is the major contributor of photos and text to the Pocket Guide. Arieh Tal is a nature photographer living in western Massachusetts.
Dichotomous Keys for the Arboretum Walk. Plant List
 1 Dichotomous Keys for the Arboretum Walk Plant List Common name 1. Pin oak 2. Sweet gum 3. Red maple 4. Bur oak 5. River birch 6. Black cherry 7. Tulip poplar 8. Kentucky coffeetree 9. Catalpa 10. Honeylocust
1 Dichotomous Keys for the Arboretum Walk Plant List Common name 1. Pin oak 2. Sweet gum 3. Red maple 4. Bur oak 5. River birch 6. Black cherry 7. Tulip poplar 8. Kentucky coffeetree 9. Catalpa 10. Honeylocust
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All. Evolution of Plants
 And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey)
 Araştırma Makalesi/Research Article A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey) Ömer KILIÇ 1 Abstract- In this study morphological characters of Malabaila
Araştırma Makalesi/Research Article A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey) Ömer KILIÇ 1 Abstract- In this study morphological characters of Malabaila
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Czhobadze A. B. [email protected]
 SOZOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF LYCOPODIOPHYTA OF THE VOLOGDA REGION Czhobadze A. B. [email protected] METHODS OF ASSESSMENT OF STATUS OF THE THREATENED SPECIES FOR THE BARENTS-REGION RED DATA BOOKS
SOZOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF LYCOPODIOPHYTA OF THE VOLOGDA REGION Czhobadze A. B. [email protected] METHODS OF ASSESSMENT OF STATUS OF THE THREATENED SPECIES FOR THE BARENTS-REGION RED DATA BOOKS
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY. Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller. Other Commonly Used Names: none. Previously Used Scientific Names: none
 Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
KEY TO GENERA AND FAMILIES
 KEY TO GENERA AND FAMILIES Identification notes: The key is highly artificial and unabashedly pragmatic. One can get to the sub-keys (Key A, Key B, Key A7, etc.) by proceeding through the general key,
KEY TO GENERA AND FAMILIES Identification notes: The key is highly artificial and unabashedly pragmatic. One can get to the sub-keys (Key A, Key B, Key A7, etc.) by proceeding through the general key,
Table 3. List of descritors for maize
 Table 3. List of descritors for maize Descriptor Descriptor Descriptor state Recording stage Remarks number 1 Accession number 2 Total no. of leaves Record the total number of At flowering leaves per plant
Table 3. List of descritors for maize Descriptor Descriptor Descriptor state Recording stage Remarks number 1 Accession number 2 Total no. of leaves Record the total number of At flowering leaves per plant
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Chapter 3. Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction. Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY
 Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
 Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta The Importance of Plant Collections Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta The Importance of Plant Collections Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants
Laboratory. Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs
 Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Meiosis is a special form of cell division.
 Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Germination is the process in which a
 The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt [email protected] Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt [email protected] Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function. I. Background
 Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types
 Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Plant Parts and Their Function
 Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Protists and Fungi. What color are the cells in the living culture?
 Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
Unit 1: What is Biology? Unit 2: Ecology Unit 3: The Life of a Cell Unit 4: Genetics Unit 5: Change Through Time Unit 6: Viruses, Bacteria, Protists,
 Unit 1: What is Biology? Unit 2: Ecology Unit 3: The Life of a Cell Unit 4: Genetics Unit 5: Change Through Time Unit 6: Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Unit 7: Plants Unit 8: Invertebrates Unit
Unit 1: What is Biology? Unit 2: Ecology Unit 3: The Life of a Cell Unit 4: Genetics Unit 5: Change Through Time Unit 6: Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Unit 7: Plants Unit 8: Invertebrates Unit
IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions. Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9. Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
 1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
AQUATIC AND WETLAND PLANTS OF PUERTO RICO. I. PTERIDOPHYTA
 AQUATIC AND WETLAND PLANTS OF PUERTO RICO. I. PTERIDOPHYTA by RODULIO CAUDALES', EFREN VEGA HERNANDEZ 2, ANTONIO SANCHEZ-PEREZ' & HENRY ALAIN LIOGIER 3 Resumen CAUDALES, R., E. VEGA HERNANDEZ, A. SANCHEZ-PEREZ
AQUATIC AND WETLAND PLANTS OF PUERTO RICO. I. PTERIDOPHYTA by RODULIO CAUDALES', EFREN VEGA HERNANDEZ 2, ANTONIO SANCHEZ-PEREZ' & HENRY ALAIN LIOGIER 3 Resumen CAUDALES, R., E. VEGA HERNANDEZ, A. SANCHEZ-PEREZ
Figure 1: Seagrass structural detail. Differences in leaf shapes, leaf sheaths etc. are characteristics for taxonomic distinction.
 Marine Angiosperms There are a wide variety of marine angiosperms some, such an the mangals, saltmarsh grasses and seagrasses that will either partly or entirely submerged (or submerged dependent on the
Marine Angiosperms There are a wide variety of marine angiosperms some, such an the mangals, saltmarsh grasses and seagrasses that will either partly or entirely submerged (or submerged dependent on the
1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes?
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Making and using keys Teacher Guidance
 Teacher Guidance Activities in earlier sections should have laid foundations that lead children to these more complex activities, in which they apply their observation and sorting skills to the practical
Teacher Guidance Activities in earlier sections should have laid foundations that lead children to these more complex activities, in which they apply their observation and sorting skills to the practical
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Stages. Differences in the Developmental Mechanisms of Plants and Animals. Development
 Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones
 Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Plantae: Bryophytes & Vascular Plants
 EXERCISE 9 Plantae: Bryophytes & Vascular Plants The Kingdom Plantae represents an extremely large group of mostly terrestrial organisms that are photosynthetic. Hence they provide the base of the food
EXERCISE 9 Plantae: Bryophytes & Vascular Plants The Kingdom Plantae represents an extremely large group of mostly terrestrial organisms that are photosynthetic. Hence they provide the base of the food
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions Sepals Anther Stamens (male) Filament Stigma Pistil Style (female) Ovary Petals sepals petals stamens pistil
 Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
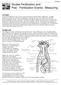 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
What's in a Flower. Ages: 8 to 12. Contributor: Susan Jaquette, Cornell Plantations volunteer
 Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Pinus Life Cycle. Name
 Name Pinus Life Cycle You have observed some gymnosperm diversity last week; today you will observe the details of the life cycle of Pinus, one of the most common conifers (Coniferophyta). This life history
Name Pinus Life Cycle You have observed some gymnosperm diversity last week; today you will observe the details of the life cycle of Pinus, one of the most common conifers (Coniferophyta). This life history
Chapter 3. Cell Division. Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.
 Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Sexual Reproduction. and Meiosis. Sexual Reproduction
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. 1. Write an A if you agree with the statement. 2. Write a D if you disagree with the statement.
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. 1. Write an A if you agree with the statement. 2. Write a D if you disagree with the statement.
Exhibit Inquiry. Rainforest. Aug 11
 Exhibit Inquiry Exhibit Inquiry Have students look for the following exhibits related to living things during their visit to the Ontario Science Centre: Where to go: (Level 6) What it's about: Tropical
Exhibit Inquiry Exhibit Inquiry Have students look for the following exhibits related to living things during their visit to the Ontario Science Centre: Where to go: (Level 6) What it's about: Tropical
Geraniaceae geranium family
 Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
2. Fill in the blank. The of a cell is like a leader, directing and telling the different parts of the cell what to do.
 1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
 CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
Tropical Tracks. Tropical rainforests are located along the Equator. Look at the map in the Biome. Draw the Equator on your map and label it.
 Tropical Tracks KS2 In Eden s Rainforest Biome you will discover how plants, animals and people of the Tropical Rainforest fit together. Let s Start! Look Point 1 (The Map, grid reference 175 482) Tropical
Tropical Tracks KS2 In Eden s Rainforest Biome you will discover how plants, animals and people of the Tropical Rainforest fit together. Let s Start! Look Point 1 (The Map, grid reference 175 482) Tropical
AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Note: At least 1 point must be earned from each of parts (a), (b), (c), and (d) in order to earn a maximum score of 10. The ability to reproduce is a characteristic
AP BIOLOGY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Note: At least 1 point must be earned from each of parts (a), (b), (c), and (d) in order to earn a maximum score of 10. The ability to reproduce is a characteristic
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Asexual Reproduction Grade Six
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark B Describe the characteristics of an organism in terms of a combination of inherited traits and recognize reproduction as a characteristic of living organisms
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark B Describe the characteristics of an organism in terms of a combination of inherited traits and recognize reproduction as a characteristic of living organisms
PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES
 PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES Compiled by HOLLY BROWN and MARTIN WILKINSON, School of Life Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland Although
PICTURES TO HELP WITH IDENTIFICATION OF FUCUS SPECIES FROM THE BRITISH ISLES Compiled by HOLLY BROWN and MARTIN WILKINSON, School of Life Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland Although
How To Understand Plant Biology
 SECOND GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics of
SECOND GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics of
Strawberry Leaf Spot
 Strawberry Leaf Spot Cathy Heidenreich and Bill Turechek Introduction - Leaf spot is one of the most common and widespread diseases of strawberry. Mycosphaerella fragariae is also the cause of black seed
Strawberry Leaf Spot Cathy Heidenreich and Bill Turechek Introduction - Leaf spot is one of the most common and widespread diseases of strawberry. Mycosphaerella fragariae is also the cause of black seed
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE BEGINNING! YOU MAY WORK WITH A PARTNER ON THIS ACTIVITY, BUT YOU MUST COMPLETE YOUR OWN LAB SHEET! Plants are incredible organisms!
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
The Wonderful World of Wetlands BINGO
 The Wonderful World of Wetlands BINGO Time: 10-15 minutes to create Bingo board; 5-10 minutes to play one-round of Bingo Scituate Reservoir Watershed Education Program 17 Smith Ave Greenville, RI 02828
The Wonderful World of Wetlands BINGO Time: 10-15 minutes to create Bingo board; 5-10 minutes to play one-round of Bingo Scituate Reservoir Watershed Education Program 17 Smith Ave Greenville, RI 02828
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GENERAL BIOLOGY II BIO4135 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GENERAL BIOLOGY II BIO4135 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
Cheilanthes distans. bristly rockfern
 Cheilanthes distans Listing Statement for Cheilanthes distans (bristly rockfern) bristly rockfern T A S M A N I A N T H R E A T E N E D F L O R A L I S T I N G S T A T E M E N T Image by Richard Schahinger
Cheilanthes distans Listing Statement for Cheilanthes distans (bristly rockfern) bristly rockfern T A S M A N I A N T H R E A T E N E D F L O R A L I S T I N G S T A T E M E N T Image by Richard Schahinger
Anatomical study on Vaccinium arctostaphylos L.
 Department of Pharmacognosy 1, School of Pharmacy, Shaheed Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, and Faculty of Pharmacy 2, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Anatomical study on Vaccinium
Department of Pharmacognosy 1, School of Pharmacy, Shaheed Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, and Faculty of Pharmacy 2, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Anatomical study on Vaccinium
Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land,
 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
Matoniaceae (Pteridophyta) - a new family record for Thailand
 THAI FOR. BULL. (BOT.) 31: 47 52. 2003. Matoniaceae (Pteridophyta) - a new family record for Thailand STUART LINDSAY*, SOMRAN SUDDEE**, DAVID J. MIDDLETON* & RACHUN POOMA** ABSTRACT. The fern species Matonia
THAI FOR. BULL. (BOT.) 31: 47 52. 2003. Matoniaceae (Pteridophyta) - a new family record for Thailand STUART LINDSAY*, SOMRAN SUDDEE**, DAVID J. MIDDLETON* & RACHUN POOMA** ABSTRACT. The fern species Matonia
The content assessed by the examination papers and the type of questions are unchanged.
 www.xtremepapers.com Location Entry Codes From the June 2007 session, as part of CIE s continual commitment to maintaining best practice in assessment, CIE has begun to use different variants of some question
www.xtremepapers.com Location Entry Codes From the June 2007 session, as part of CIE s continual commitment to maintaining best practice in assessment, CIE has begun to use different variants of some question
IDENTIFICATION OF ORGANISMS
 reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
North Shore Community Garden Society Plants to Avoid
 North Shore Community Garden Society - Plants to Avoid Page 1 North Shore Community Garden Society Plants to Avoid Japanese Polygonum Kno tw eed Cuspidatum Rhizomatous, semi-woody, herbaceous perennial
North Shore Community Garden Society - Plants to Avoid Page 1 North Shore Community Garden Society Plants to Avoid Japanese Polygonum Kno tw eed Cuspidatum Rhizomatous, semi-woody, herbaceous perennial
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms
 Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
Chapter 14: Page 181
 Chapter 14: Page 181 Chapter 14: Page 182 The plant kingdom contains organisms that can be divided into two separate groups: nonvascular plants (like mosses) that absorb water through their entire body
Chapter 14: Page 181 Chapter 14: Page 182 The plant kingdom contains organisms that can be divided into two separate groups: nonvascular plants (like mosses) that absorb water through their entire body
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis
 Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
