ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS1 STUDENT RESOURCES
|
|
|
- Madeleine Atkins
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS1 STUDENT RESOURCES
2 PLANT OR ANIMAL? (Lesson 1:1) Card sort task: print out and get the students to sort them into: Plants or Animals. Get the students to explain why they have grouped them like that, how do they know?
3 ANIMAL GROUPING TASK (Lesson 1:2) Has legs Can fly Spider Donkey Snake Elephant Has fur or hair Cat Bird Group the animals into the correct areas in the Venn diagram. Fish Butterfly Sheep
4 ANIMAL GROUPING TASK (Lesson 1:2 alternative) Has legs Can fly Name the animal and then group them into the correct areas in the Venn diagram. Has fur or hair
5 ANIMAL GROUPING TASK (Lesson 1:3) Group the animals into the correct areas in the Carroll diagram
6 ANIMAL GROUPING TASK Group the animals into the correct areas in the Carroll diagram
7 ANIMAL GROUPING TASK Group the animals into the correct areas in the Venn diagram.
8 ANIMAL & PLANT CARDS (Lesson 1:4)
9 ANIMAL & PLANT CARDS (Lesson 1:4)
10 ANIMAL & PLANT CARDS (Lesson 1:4)
11 ANIMAL & PLANT CARDS (Lesson 1:4)
12 INDEPENDENT LEARNING (Lesson 1:5) Name the different parts of the animals and plants Name: Class:
13 POND DIPPING IDENTIFICATION (Lesson 2:1) Which of these have you seen or caught? Water Boatman Caddis larva in it s case Caddis fly larva Diving beetle Freshwater shrimp Damselfly Diving beetle larva Dragonfly Newt Rat tailed maggot Frog spawn Tadpole Froglet Frog Dragonfly nymph Water mite Pond skater Sticklepath Daphnia Water Louse
14 Where found Identified animal as Number of animals Where found Identified animal as Number of animals POND DIPPING IDENTIFICATION (Lesson 2:2) Identify and record your findings. Date of investigation: Name of pond: Drawing Drawing On top Top Middle Bottom On top Top Middle Bottom On top Top Middle Bottom On top Top Middle Bottom On top Top Middle Bottom On top Top Middle Bottom Name: Class:
15 TREE / LEAF IDENTIFICATION (Lesson 2:3)
16 dry hot damp cold HABITAT DESCRIPTIONS (Lesson 3:1) icy dark smooth wet bare
17 hard soft HABITAT DESCRIPTIONS (Lesson 3:1) sunny bumpy frozen plain colourful
18 BIG HABITATS: MOUNTAIN (Lesson 3:2)
19 BIG HABITATS: SEA (Lesson 3:2)
20 BIG HABITATS: FOREST (Lesson 3:2)
21 BIG HABITATS: DESERT (Lesson 3:2)
22 BIG HABITATS: POLAR (Lesson 3:2)
23 BIG HABITATS: RIVER (Lesson 3:2)
24 BIG HABITATS: BEACH (Lesson 3:2)
25 BIG HABITATS: JUNGLE (Lesson 3:2)
26 BIG HABITATS: SAVANNAH (Lesson 3:2)
27 BIG HABITATS (Lesson 3:3) Describe the habitats. Feel See Hear Weather Temperature Other Mountain River Jungle Sea Desert Beach Forest Polar Savannah Name: Class:
28 INDEPENDENT LEARNING (Lesson 3:4) List as many adjectives as you can that would describe three of the big habitats. Mountain Who in the team has done what tasks in this project? Name: Class:
29 HABITAT IN A BOX (Lesson 4:1)
30 Research Independent learning HABITAT RESEARCH (Lesson 4:2) Find out the animals, plants and colours for your habitat and sort them into types. Animals Plants Other things Colours Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Flowering Non flowering Name: Class:
31 DESIGN YOUR HABITAT (Lesson 4:3) Create 6 different ideas for your habitat in a box. My habitat is: Name: Class:
32 INDEPENDENT LEARNING (Lesson 7:1) Design the front edges of your habitat (Develop 3 ideas) Who in the team has done what tasks in this project? Name: Class:
33 STORY SEQUENCING (Lesson 8:1)
34 STORYBOARD (Lesson 8:2 alternative) Title of story: Name: Date:Class: Main characters:
35 STORYBOARD (Lesson 8:2 alternative) Title of story: Name: Date: Class: Main Characters:
36 (Lesson 8:2 alternative) What things happen? Build up the interest. The Problem Introduce the main characters and where the story is set. The Beginning What is said? The Build-Up Is there a mystery or problem? Do bad things happen? The Resolution How are things sorted out or solved? What makes it good? Happy or sad ending? What do people learn? Has anything changed? The Ending Name Date
37 (Lesson 8) savannah jungle forest wood mountain river sea desert arctic cold mild freezing clean dirty moist gritty hairy lumpy sandy slippery green light spiky smooth wet dry prickly heavy sharp red dull icy brown windy still blue quiet busy mushy frosty humid gentle tropical warm bright plant soft roaring hot leaf food wild tree bumpy wave surf grass vine flower seaweed snow climb shiny calm rock giant huge high bird rain misty cloudy sunny grow buzzing stream bent rough bush soil season brown black smelly
38 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: STORY SEQUENCING (Lesson 8:3) Create a set of story sequencing cards for your story. Name: Class:
39 ANIMAL ADAPTATIONS (Lesson 9:1) Create an animal suitable for the habitat. Label and explain why it is suitable. Name: Class:
40 ANIMAL ADAPTATIONS (Lesson 9:2) Create your own adapted animals. A parrot so it can hide in a palm tree A lamb so it can eat the fruit of the African sausage tree, the Kigelia africana Name: Class:
41 ANIMAL ADAPTATIONS: Tracing templates for animal adaptation drawings. (Lesson 9:2)
42 FOOD CHAIN CARDS (Lesson 10:1)
43 FOOD CHAIN CARDS (Lesson 10:1)
44 FOOD CHAIN CARDS (Lesson 10:1)
45 FOOD WEBS (Lesson 10:2) THE DONKEY SANCTUARY
46 FOOD CHAIN WORDSEARCH (Lesson 10:3) HABITAT ANIMAL PLANT OMNIVORE CARNIVORE PLANT CONSUMER PREDATOR PREY PRODUCER ENERGY HERBIVORE
47 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: FOOD CHAINS (Lesson 10:4) Explain the food chain terms below. Herbivore Producer Create a food web for the following animals. Frog Buzzard Consumer Dragonfly Ladybird Carnivore Predator Snake Grass Greenfly Omnivore Mouse Prey Rabbit Butterfly Fox Name: Class:
48 LOOKING AFTER PETS (Lesson 11:1) Explain what you need to do and the things you need to do them with for each of the pets and a pet of your own. Things I do Things I need Dog Donkey Guinea Pig Name: Class:
49 LOOKING AFTER PETS: THE FIVE FREEDOMS (Lesson 11:2) Explain how the five freedoms would apply to each of the pets and a pet of your own choice. Freedom from: Hunger and thirst Discomfort Pain, injury and Behaving Fear and stress Dog Donkey Guinea Pig Name: Class:
50 LOOKING AFTER PETS: HEALTHY PETS (Lesson 11:3) Match up the items up for each animal s care and well being. (Label whether they are for food, bedding, grooming, health care, water or fun) Name: Class:
Key Idea 2: Ecosystems
 Key Idea 2: Ecosystems Ecosystems An ecosystem is a living community of plants and animals sharing an environment with non-living elements such as climate and soil. An example of a small scale ecosystem
Key Idea 2: Ecosystems Ecosystems An ecosystem is a living community of plants and animals sharing an environment with non-living elements such as climate and soil. An example of a small scale ecosystem
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms
 Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
www.irishseedsavers.ie Natural surface water on earth includes lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries, seas and oceans.
 www.irishseedsavers.ie POND LIFE FACT SHEET Natural surface water on earth includes lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries, seas and oceans. A pond is a small body of fresh water shallow enough for sunlight
www.irishseedsavers.ie POND LIFE FACT SHEET Natural surface water on earth includes lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries, seas and oceans. A pond is a small body of fresh water shallow enough for sunlight
food chains reflect How are these organisms important to one another? organism: a living thing
 reflect Different plants and animals live together. Look at the picture of the garden. What organisms live there? Grass, trees, bugs, and birds live there. Fish and frogs live there, too. Can you think
reflect Different plants and animals live together. Look at the picture of the garden. What organisms live there? Grass, trees, bugs, and birds live there. Fish and frogs live there, too. Can you think
ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST
 4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2008 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2008 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
Lesson Plan Two - Ecosystems
 Lesson Plan Two - Ecosystems Summary Students discuss what living things need to survive. They identify the abiotic and biotic components of an ecosystem and describe the roles and interactions of producers
Lesson Plan Two - Ecosystems Summary Students discuss what living things need to survive. They identify the abiotic and biotic components of an ecosystem and describe the roles and interactions of producers
Wild About... Frogs and Frogspawn
 a Wild About... Rutland County Council Nature notes Frogs belong to a group of animals called amphibians, which also includes newts and toads. Amphibians live both on land and in water. Water is needed
a Wild About... Rutland County Council Nature notes Frogs belong to a group of animals called amphibians, which also includes newts and toads. Amphibians live both on land and in water. Water is needed
What is a food chain?
 3 What is a food chain? Learning Intention Understand that plants and animals in a habitat are dependent on each other. National Curriculum Skills Science Interdependence of living organisms in those 2
3 What is a food chain? Learning Intention Understand that plants and animals in a habitat are dependent on each other. National Curriculum Skills Science Interdependence of living organisms in those 2
Cycles of life. You will be visiting the museum to see some baby animals and their parents. Here are some of their stories.
 Cycles of life Some animals die of old age, some die of disease, some are killed and eaten by other animals. But the world does not run out of animals because more are being born or hatched all the time.
Cycles of life Some animals die of old age, some die of disease, some are killed and eaten by other animals. But the world does not run out of animals because more are being born or hatched all the time.
Region of Georgia : Mountains
 Region of Georgia : Mountains Northern most region of GA Cold weather in the winter Brasstown Bald is the highest point in Georgia Lots of creeks and streams High above sea level Poor soil for farming
Region of Georgia : Mountains Northern most region of GA Cold weather in the winter Brasstown Bald is the highest point in Georgia Lots of creeks and streams High above sea level Poor soil for farming
This hands-on activity incorporates observing, classifying, predicting, sequencing, formulating models, and drawing conclusions.
 SCIENCE Science and the Environment 4 th Grade FOOD CHAINS Overview: All organisms, or living things, depend on other organisms for nutrients. The movement of nutrients through an environment is visualized
SCIENCE Science and the Environment 4 th Grade FOOD CHAINS Overview: All organisms, or living things, depend on other organisms for nutrients. The movement of nutrients through an environment is visualized
Reptiles and Amphibians by Guy Belleranti
 Name: Take a look at the four animals pictures below. Do you know which ones are reptiles and which ones are amphibians? The chameleon is an unusual lizard that can change the color of its scaly body.
Name: Take a look at the four animals pictures below. Do you know which ones are reptiles and which ones are amphibians? The chameleon is an unusual lizard that can change the color of its scaly body.
AWESOME ADAPTATIONS WORKSHEETS. for. Rainforest Desert Mediterranean
 AWESOME ADAPTATIONS WORKSHEETS for Rainforest Desert Mediterranean IN THE RAINFOREST Write a sentence to record your experience in the Tropical House IT FEELS. IT SMELLS. THE TEMPERATURE is IT MAKES ME
AWESOME ADAPTATIONS WORKSHEETS for Rainforest Desert Mediterranean IN THE RAINFOREST Write a sentence to record your experience in the Tropical House IT FEELS. IT SMELLS. THE TEMPERATURE is IT MAKES ME
Structures of animals
 Structures of animals Name: All animals have been designed with different parts, which we call structures, that make up their bodies. Each of these structures is important as it is used to perform a specific
Structures of animals Name: All animals have been designed with different parts, which we call structures, that make up their bodies. Each of these structures is important as it is used to perform a specific
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK
 4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST JUNE 6, 2011 Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST JUNE 6, 2011 Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
Pond Vocabulary Words and Meanings
 Pond Vocabulary Words and Meanings Adapt: to adjust to a use or situation Aquatic: from or in the water Bacteria: tiny organisms, too small to be seen with the naked eye Carnivore: an animal that eats
Pond Vocabulary Words and Meanings Adapt: to adjust to a use or situation Aquatic: from or in the water Bacteria: tiny organisms, too small to be seen with the naked eye Carnivore: an animal that eats
Fry Phrases Set 1. TeacherHelpForParents.com help for all areas of your child s education
 Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
The Pond Pack. Background information and resources for teachers
 The Ecology Service 2010 Date published 02/03/10 Extended artwork area (REMOVE THIS TEXT) The Pond Pack Background information and resources for teachers For further information contact: Holland Park Ecology
The Ecology Service 2010 Date published 02/03/10 Extended artwork area (REMOVE THIS TEXT) The Pond Pack Background information and resources for teachers For further information contact: Holland Park Ecology
The Mountain Ecosystem by Kimberly M. Hutmacher
 A habitat is where a plant or animal lives and grows. A habitat is part of an ecosystem where lots of different plants and animals live. Mountains, with their many levels are an ecosystem containing many
A habitat is where a plant or animal lives and grows. A habitat is part of an ecosystem where lots of different plants and animals live. Mountains, with their many levels are an ecosystem containing many
KS1 Animal Habitats. Scheme of Learning
 KS1 Animal Habitats 1 Scheme of Learning KS1 Animal Habitats Scheme of Learning This scheme of learning has been put together by Marwell Wildlife for teachers to use with their KS1 pupils. It is a complete
KS1 Animal Habitats 1 Scheme of Learning KS1 Animal Habitats Scheme of Learning This scheme of learning has been put together by Marwell Wildlife for teachers to use with their KS1 pupils. It is a complete
World Oceans Day at ZSL Whipsnade Zoo
 World Oceans Day at ZSL Whipsnade Zoo Teachers notes KS 1 & KS 2 This booklet will help you to focus your self guided trail on ocean animals, looking at the adaptations of the species and focusing in on
World Oceans Day at ZSL Whipsnade Zoo Teachers notes KS 1 & KS 2 This booklet will help you to focus your self guided trail on ocean animals, looking at the adaptations of the species and focusing in on
Three Bears by Erin Ryan
 Three Bears by Erin Ryan Did you know that there are eight different kinds of bears found around the world? Three very different ones are polar bears, grizzly bears and Giant Pandas. Polar bears live in
Three Bears by Erin Ryan Did you know that there are eight different kinds of bears found around the world? Three very different ones are polar bears, grizzly bears and Giant Pandas. Polar bears live in
Exhibit Inquiry. Rainforest. Aug 11
 Exhibit Inquiry Exhibit Inquiry Have students look for the following exhibits related to living things during their visit to the Ontario Science Centre: Where to go: (Level 6) What it's about: Tropical
Exhibit Inquiry Exhibit Inquiry Have students look for the following exhibits related to living things during their visit to the Ontario Science Centre: Where to go: (Level 6) What it's about: Tropical
Who Eats What in the Woods?
 Who Eats What in the Woods? Developed with teachers at Tolworth Junior School in Kingston upon Thames in 2000. The webaddress for this activity is; Last updated 26th February 2008 This activity has now
Who Eats What in the Woods? Developed with teachers at Tolworth Junior School in Kingston upon Thames in 2000. The webaddress for this activity is; Last updated 26th February 2008 This activity has now
Habitats. A Wildwood KS2 Teachers Pack and Activity Sheets
 Habitats A Wildwood KS2 Teachers Pack and Activity Sheets Teachers Guidance Notes This teachers resource pack is designed to support the National Curriculum KS2 topic of animal homes and habitats (see
Habitats A Wildwood KS2 Teachers Pack and Activity Sheets Teachers Guidance Notes This teachers resource pack is designed to support the National Curriculum KS2 topic of animal homes and habitats (see
food webs reflect look out! what do you think?
 reflect Imagine for a moment that you stay after school one day to clean up the classroom. While cleaning, you move some plants away from the sunny windows. A week later, you remember to move the plants
reflect Imagine for a moment that you stay after school one day to clean up the classroom. While cleaning, you move some plants away from the sunny windows. A week later, you remember to move the plants
WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE
 7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
Food Chains (and webs) Flow of energy through an ecosystem Grade 5 Austin Carter, Dale Rucker, Allison Hursey
 Food Chains (and webs) Flow of energy through an ecosystem Grade 5 Austin Carter, Dale Rucker, Allison Hursey References: Columbus Public Schools Curriculum Guide- Grade 5 GK-12 Biological Science Lesson
Food Chains (and webs) Flow of energy through an ecosystem Grade 5 Austin Carter, Dale Rucker, Allison Hursey References: Columbus Public Schools Curriculum Guide- Grade 5 GK-12 Biological Science Lesson
4. Which choice below lists the biomes in order from lowest precipitation amounts to highest precipitation amounts?
 Ecosystems and Biomes 1. All of the living organisms in a forest plus their environment is an example of A. a biome. B. a community. C. a population. D. an ecosystem. 2. Which of the following best describes
Ecosystems and Biomes 1. All of the living organisms in a forest plus their environment is an example of A. a biome. B. a community. C. a population. D. an ecosystem. 2. Which of the following best describes
Use this diagram of a food web to answer questions 1 through 5.
 North arolina Testing Program EO iology Sample Items Goal 4 Use this diagram of a food web to answer questions 1 through 5. coyotes 3. If these organisms were arranged in a food pyramid, which organism
North arolina Testing Program EO iology Sample Items Goal 4 Use this diagram of a food web to answer questions 1 through 5. coyotes 3. If these organisms were arranged in a food pyramid, which organism
Class 4 Poetry 2008. Forever. Killer Lightning!! Lightning is dangerous so Keep Away!! By Gregory
 Class 4 Poetry 2008 Forever I went through A golden gate, A silver gate, A mother of pearl gate. Until I found a path, I followed it to I do not know where, But I ve followed it there, Through tangled
Class 4 Poetry 2008 Forever I went through A golden gate, A silver gate, A mother of pearl gate. Until I found a path, I followed it to I do not know where, But I ve followed it there, Through tangled
6. Which of the following is not a basic need off all animals a. food b. *friends c. water d. protection from predators. NAME SOL 4.
 NAME SOL 4.5 REVIEW - Revised Habitats, Niches and Adaptations POPULATION A group of the same species living in the same place at the same time. COMMUNITY-- All of the populations that live in the same
NAME SOL 4.5 REVIEW - Revised Habitats, Niches and Adaptations POPULATION A group of the same species living in the same place at the same time. COMMUNITY-- All of the populations that live in the same
NOTE TO TEACHER: It is appropriate to introduce the mitochondria (where energy is made) as a major structure common to all cells.
 5.2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
5.2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
REVIEW UNIT 10: ECOLOGY SAMPLE QUESTIONS
 Period Date REVIEW UNIT 10: ECOLOGY SAMPLE QUESTIONS A. Sample Multiple Choice Questions Complete the multiple choice questions to review this unit. 1. All of the following are density-dependent factors
Period Date REVIEW UNIT 10: ECOLOGY SAMPLE QUESTIONS A. Sample Multiple Choice Questions Complete the multiple choice questions to review this unit. 1. All of the following are density-dependent factors
Life Science Study Guide. Environment Everything that surrounds and influences (has an effect on) an organism.
 Life Science Study Guide Environment Everything that surrounds and influences (has an effect on) an organism. Organism Any living thing, including plants and animals. Environmental Factor An environmental
Life Science Study Guide Environment Everything that surrounds and influences (has an effect on) an organism. Organism Any living thing, including plants and animals. Environmental Factor An environmental
Caring for guinea pigs
 Caring for guinea pigs YOUR GUIDE TO KEEPING GUINEA PIGS HEALTHY AND HAPPY Animal Welfare Foundation www.bva-awf.org.uk AWF is the charity led by the veterinary profession Registered Charity No. 287118
Caring for guinea pigs YOUR GUIDE TO KEEPING GUINEA PIGS HEALTHY AND HAPPY Animal Welfare Foundation www.bva-awf.org.uk AWF is the charity led by the veterinary profession Registered Charity No. 287118
Get to Know Your Watershed. McMillan Creek
 Get to Know Your Watershed McMillan Creek Where is McMillan Creek? McMillan Creek is found in the northeastern portion of the City of Prince George, know as the Hart and Shady Valley. It is located entirely
Get to Know Your Watershed McMillan Creek Where is McMillan Creek? McMillan Creek is found in the northeastern portion of the City of Prince George, know as the Hart and Shady Valley. It is located entirely
First Grade Reading Street Unit 1.1: Sam, Come Back! - Taken from www.freidalewis.com
 Blend & Segment Phonemes Isolate Final Sounds Identify Position of Sounds Short a and Final ck Character Monitor & Fix Up 1. at 2. can 3. cat 4. back 5. dad 6. am First Grade Reading Street Unit 1.1: Sam,
Blend & Segment Phonemes Isolate Final Sounds Identify Position of Sounds Short a and Final ck Character Monitor & Fix Up 1. at 2. can 3. cat 4. back 5. dad 6. am First Grade Reading Street Unit 1.1: Sam,
One basic need of living things is energy. Living things use food and water to get energy. The bird is living. It eats fish for energy.
 reflect If you are cold, what can you do to get warm? You could put on a coat and hat. You can jump in place. These are ways you might react to the cold. Now think about a rock. What if a rock is somewhere
reflect If you are cold, what can you do to get warm? You could put on a coat and hat. You can jump in place. These are ways you might react to the cold. Now think about a rock. What if a rock is somewhere
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents?
 2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
My favourite animal is the cheetah. It lives in Africa in the savannah, It eats and gazel es. It is big and yel ow with black spots.
 The crocodile is big and green. It has got a long tail, a long body and a big mouth with big teeth. It has got four short legs. The crocodile eats fish and other animals. He lives in Africa and America,
The crocodile is big and green. It has got a long tail, a long body and a big mouth with big teeth. It has got four short legs. The crocodile eats fish and other animals. He lives in Africa and America,
Prairie Food Chains & Webs Producers, Consumers & Decomposers
 Kansas Prairies s, s & Decomposers Science, Life Science, Reading, Math Materials Vocabulary worksheet Food Chain worksheet Overview To explore the organisms found on a prairie and identify the various
Kansas Prairies s, s & Decomposers Science, Life Science, Reading, Math Materials Vocabulary worksheet Food Chain worksheet Overview To explore the organisms found on a prairie and identify the various
ZOOS GO BLUE. Your Trip to Zoo Atlanta! Sunday, April 6
 ZOOS GO BLUE Your Trip to Zoo Atlanta! Sunday, April 6 Autism Awareness Day at Zoo Atlanta! Going to the Zoo can be a lot of fun. Here are some things you can do to prepare for your exciting trip and make
ZOOS GO BLUE Your Trip to Zoo Atlanta! Sunday, April 6 Autism Awareness Day at Zoo Atlanta! Going to the Zoo can be a lot of fun. Here are some things you can do to prepare for your exciting trip and make
Food Webs and Food Chains Grade Five
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark B Analyze plant and animal structures and functions needed for survival and describe the flow of energy through a system that all organisms use to survive.
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark B Analyze plant and animal structures and functions needed for survival and describe the flow of energy through a system that all organisms use to survive.
Frog Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Frog Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Frog questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 frog fact cards (pages 4-8) Scissors and scotch tape Preparation: Print the frog fact cards and cut them apart. Make copies
Frog Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Frog questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 frog fact cards (pages 4-8) Scissors and scotch tape Preparation: Print the frog fact cards and cut them apart. Make copies
Weaving the Web. Overview Students construct food webs to learn how food chains are interconnected. Suggested Grade Level 2 5
 Weaving the Overview Students construct food webs to learn how food chains are interconnected. Suggested Grade Level 2 5 Estimated Time 30 40 minutes Objectives Students will be able to: 1. construct a
Weaving the Overview Students construct food webs to learn how food chains are interconnected. Suggested Grade Level 2 5 Estimated Time 30 40 minutes Objectives Students will be able to: 1. construct a
Prairie Food Chains & Webs Producers, Consumers, & Decomposers
 Kansas Prairies Prairie Food Chains & Webs Producers, s, & Decomposers Life Science, Math, Reading, Science Materials Student Worksheet A: Vocabulary Student Worksheet B: Food Chain Overview To explore
Kansas Prairies Prairie Food Chains & Webs Producers, s, & Decomposers Life Science, Math, Reading, Science Materials Student Worksheet A: Vocabulary Student Worksheet B: Food Chain Overview To explore
Grade 5 Standard 5 Unit Test Heredity. 1. In what way will a kitten always be like its parents? The kitten will...
 Grade 5 Standard 5 Unit Test Heredity Multiple Choice 1. In what way will a kitten always be like its parents? The kitten will... A. be the same color. B. learn the same things. C. have the same body structures.
Grade 5 Standard 5 Unit Test Heredity Multiple Choice 1. In what way will a kitten always be like its parents? The kitten will... A. be the same color. B. learn the same things. C. have the same body structures.
Animal Adaptations -- Vocabulary
 Section 1 Objectives o Children will understand what animal adaptations are. o Children will be able to explain why animal adaptations are important. o Children will be able to explain different types
Section 1 Objectives o Children will understand what animal adaptations are. o Children will be able to explain why animal adaptations are important. o Children will be able to explain different types
Rainforest Photo Sort Information Gap
 Rainforest Photo Sort Information Gap These activities form part of a sequence that can be used in a variety of ways and are very suitable for adaption to suit the children you are working with. The texts
Rainforest Photo Sort Information Gap These activities form part of a sequence that can be used in a variety of ways and are very suitable for adaption to suit the children you are working with. The texts
Unit: Plants & Animals (Grade 2)
 Unit: Plants & Animals (Grade 2) Content Area: Science Course(s): Science Time Period: 8 weeks Length: Weeks Status: Published Unit Overview Students will determine the life cycles of plants and animals
Unit: Plants & Animals (Grade 2) Content Area: Science Course(s): Science Time Period: 8 weeks Length: Weeks Status: Published Unit Overview Students will determine the life cycles of plants and animals
Third Grade Science Vocabulary Investigation Design & Safety
 recycle dispose reuse goggles data conclusion predict describe observe record identify investigate evidence analyze mass matter float sink attract force magnet magnetic magnetism pole pull push repel Third
recycle dispose reuse goggles data conclusion predict describe observe record identify investigate evidence analyze mass matter float sink attract force magnet magnetic magnetism pole pull push repel Third
Science. Year 7. Transition. Equipment allowed: calculator, pen, pencil, ruler, protractor or angle measurer, eraser. No other equipment allowed.
 Science Year 7 Transition Equipment allowed: calculator, pen, pencil, ruler, protractor or angle measurer, eraser. No other equipment allowed. Name Date WS: SA WS: ESI WS: AE 7 Year 7 1 The diagram below
Science Year 7 Transition Equipment allowed: calculator, pen, pencil, ruler, protractor or angle measurer, eraser. No other equipment allowed. Name Date WS: SA WS: ESI WS: AE 7 Year 7 1 The diagram below
Producers, Consumers, and Food Webs
 reflect Think about the last meal you ate. Where did the food come from? Maybe it came from the grocery store or a restaurant. Maybe it even came from your backyard. Now think of a lion living on the plains
reflect Think about the last meal you ate. Where did the food come from? Maybe it came from the grocery store or a restaurant. Maybe it even came from your backyard. Now think of a lion living on the plains
Rain Forests. America's. Web of Life. Rain Forest Ecology. Prince William Network's OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES SUBJECTS
 Rain Forest Ecology National Science Education Standards Standard C: Life Sciences Populations and ecosystems. Standard C: Life Sciences Diversity and adaptation of organisms. Standard F: Science in Personal
Rain Forest Ecology National Science Education Standards Standard C: Life Sciences Populations and ecosystems. Standard C: Life Sciences Diversity and adaptation of organisms. Standard F: Science in Personal
FIRST TERM ENGLISH WORKSHEET 2016-2017
 FIRST TERM ENGLISH WORKSHEET 2016-2017 Class -1 1& 11 GIRLS SECTION 1.Make sentences. Flower - Mother - Water - Butterfly - Lovely - Big - 1 2. Circle the correct word. a. It is [Mother s / Father s] birthday.
FIRST TERM ENGLISH WORKSHEET 2016-2017 Class -1 1& 11 GIRLS SECTION 1.Make sentences. Flower - Mother - Water - Butterfly - Lovely - Big - 1 2. Circle the correct word. a. It is [Mother s / Father s] birthday.
Let s Learn About Plants and Animals!
 Grade Two Pre-Visit Activities Let s Learn About Plants and Animals! i. Teacher Introduction ii. Standards Addressed iii. Pre-Visit Activities 1. Identifying Parts of a Plant 2. Plant a Seed 3. Life Cycles
Grade Two Pre-Visit Activities Let s Learn About Plants and Animals! i. Teacher Introduction ii. Standards Addressed iii. Pre-Visit Activities 1. Identifying Parts of a Plant 2. Plant a Seed 3. Life Cycles
Tropical rainforests grow in areas of high rainfall, they are found between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
 Tracking KS3 the Tropics In our Tropical Rainforest Biome you will discover how plants, animals and people of the Tropical Rainforest fit together. Let s Start! Look point 1 (Map on Left as you enter the
Tracking KS3 the Tropics In our Tropical Rainforest Biome you will discover how plants, animals and people of the Tropical Rainforest fit together. Let s Start! Look point 1 (Map on Left as you enter the
Principles of Ecology
 2 Principles of Ecology section 1 Organisms and Their Relationships Before You Read On the lines below, list the organisms that you have encountered today. You share the same environment with these organisms.
2 Principles of Ecology section 1 Organisms and Their Relationships Before You Read On the lines below, list the organisms that you have encountered today. You share the same environment with these organisms.
Name Class Date. Adapting to the Environment Adaptations and Survival
 CHAPTER 3 4 SECTIN Adapting to the Environment Adaptations and Survival EFRE YU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What adaptations help animals survive? What
CHAPTER 3 4 SECTIN Adapting to the Environment Adaptations and Survival EFRE YU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What adaptations help animals survive? What
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION
 Servicio de Inspección Educativa Hezkuntzako Ikuskapen Zerbitzua 2 0 1 1 / 1 2 DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION 4th YEAR of PRIMARY EDUCATION ENGLISH LITERACY Name / surname(s):... School:... Group:... City / Town:.
Servicio de Inspección Educativa Hezkuntzako Ikuskapen Zerbitzua 2 0 1 1 / 1 2 DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION 4th YEAR of PRIMARY EDUCATION ENGLISH LITERACY Name / surname(s):... School:... Group:... City / Town:.
Grade Level Content Expectations addressed: Activities: Schedule of Field Trip Activities at the Detroit Zoo 8:15 am Board Bus at School
 Title: Comparing and Contrasting Ecosystem Biodiversity Submitted by: Tracy Ortiz Email: [email protected] School: Coffey K-8 Educational Learning Community Date: May 12, 2010 Target Grade: 6 Duration:
Title: Comparing and Contrasting Ecosystem Biodiversity Submitted by: Tracy Ortiz Email: [email protected] School: Coffey K-8 Educational Learning Community Date: May 12, 2010 Target Grade: 6 Duration:
The Tiny Seed Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9
 Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
Name. A Walk in the Desert
 Grade 4 Unit 5 Week 1 Selection Test Name A Fill in the bubble next to the best answer. A Walk in the Desert 1. A desert gets little rain and has a very dry climate. Climate is. A. a kind of desert cactus
Grade 4 Unit 5 Week 1 Selection Test Name A Fill in the bubble next to the best answer. A Walk in the Desert 1. A desert gets little rain and has a very dry climate. Climate is. A. a kind of desert cactus
Wetlands by Leslie Cargile
 Name: by Leslie Cargile What do the bogs in Ireland, the marshes in South Carolina, and the swamps of Louisiana have in common? If you said they re all wetlands, you d be right! are any land that is flooded
Name: by Leslie Cargile What do the bogs in Ireland, the marshes in South Carolina, and the swamps of Louisiana have in common? If you said they re all wetlands, you d be right! are any land that is flooded
LESSON PLAN Toddler Room WEEK OF: January 31-February 4, 2011. THEME: Pets
 LESSON PLAN Toddler Room WEEK OF: January 31-February 4, 2011 THEME: Pets Cats, Cats, Cats Puppy and Me If You See A Kitten Skippy Jones Up and Down Barbie the Bunny Six Little Pets B-I-N-G-O Rags Hickory
LESSON PLAN Toddler Room WEEK OF: January 31-February 4, 2011 THEME: Pets Cats, Cats, Cats Puppy and Me If You See A Kitten Skippy Jones Up and Down Barbie the Bunny Six Little Pets B-I-N-G-O Rags Hickory
Kindergarten Science Unit B: Life Science Chapter 4: Plant and Animal Parts Lesson 1: What do plant parts do?
 Insert Photo or Graphic for Unit or Lesson Theme Kindergarten Science Unit B: Life Science Chapter 4: Plant and Animal Parts Lesson 1: What do plant parts do? Insert Photo/Graphic parts Insert Photo/Graphic
Insert Photo or Graphic for Unit or Lesson Theme Kindergarten Science Unit B: Life Science Chapter 4: Plant and Animal Parts Lesson 1: What do plant parts do? Insert Photo/Graphic parts Insert Photo/Graphic
How To Understand The Features And Behaviours Of Animals And Plants
 Childrenʼs Farmyard and Animal Nursery Teacher Resource Pack Curriculum linked worksheets and activities SACSA Band: Early Years Learning Area: Science Strand: Life systems Key Idea Children investigate
Childrenʼs Farmyard and Animal Nursery Teacher Resource Pack Curriculum linked worksheets and activities SACSA Band: Early Years Learning Area: Science Strand: Life systems Key Idea Children investigate
Animal Adaptations. Standards. Multiple Intelligences Utilized. Teaching First Step Nonfiction. Titles in this series: Reading.
 Teaching First Step Nonfiction Animal Adaptations K 2nd Grade Interest Level 1st Grade ing Level Titles in this series: What Can Live in a Desert? What Can Live in a Forest? What Can Live in a Grassland?
Teaching First Step Nonfiction Animal Adaptations K 2nd Grade Interest Level 1st Grade ing Level Titles in this series: What Can Live in a Desert? What Can Live in a Forest? What Can Live in a Grassland?
Grassland Food Webs: Teacher Notes
 Grassland Food Webs: Teacher Notes Alan Henderson ecosystem Objectives After completing this activity students will be able to: Create a food web and identify producers and consumers. Assign organisms
Grassland Food Webs: Teacher Notes Alan Henderson ecosystem Objectives After completing this activity students will be able to: Create a food web and identify producers and consumers. Assign organisms
Life processes. All animals have to carry out seven life processes. These are: 2. Respiration taking in one gas and getting rid of another
 Food chains Life processes All animals have to carry out seven life processes. These are: 1. Movement being able to move its body 2. Respiration taking in one gas and getting rid of another 3. Reproduction
Food chains Life processes All animals have to carry out seven life processes. These are: 1. Movement being able to move its body 2. Respiration taking in one gas and getting rid of another 3. Reproduction
A Most Colorful Mammal by Guy Belleranti
 Name: In the tropical rainforests of western Africa lives a mammal with a most colorful face and rump. This mammal is the mandrill, the world's largest monkey. The skin on a male mandrill's face has a
Name: In the tropical rainforests of western Africa lives a mammal with a most colorful face and rump. This mammal is the mandrill, the world's largest monkey. The skin on a male mandrill's face has a
MUNCH! CRUNCH! SLURP! SMACK!
 MUNCH! CRUNCH! SLURP! SMACK! A Mini Unit on What and How Animals Eat By Nancy VandenBerge Firstgradewow.blogspot.com Graphics by thistle girl, scrappin doodles, dj inkers and melonheadz This little unit
MUNCH! CRUNCH! SLURP! SMACK! A Mini Unit on What and How Animals Eat By Nancy VandenBerge Firstgradewow.blogspot.com Graphics by thistle girl, scrappin doodles, dj inkers and melonheadz This little unit
2. What kind of energy is stored in food? A. chemical energy B. heat energy C. kinetic energy D. light energy
 Assessment Bank Matter and Energy in Living Things SC.8.L.18.4 1. What is energy? A. anything that takes up space B. anything that has mass C. the ability to conduct current D. the ability to do work 2.
Assessment Bank Matter and Energy in Living Things SC.8.L.18.4 1. What is energy? A. anything that takes up space B. anything that has mass C. the ability to conduct current D. the ability to do work 2.
Desert Communities Third Grade Core: Standard 2 Objective 2 Describe the interactions between living and nonliving things in a small environment.
 Desert Communities Third Grade Core: Standard 2 Objective 2 Describe the interactions between living and nonliving things in a small environment. (Discovering Deserts NatureScope: page 40, 43, 44) Objective:
Desert Communities Third Grade Core: Standard 2 Objective 2 Describe the interactions between living and nonliving things in a small environment. (Discovering Deserts NatureScope: page 40, 43, 44) Objective:
Zoo Connections Curriculum
 Zoo Connections Curriculum We Like to Move It, Move It: Classifying animals by features 1 st grade Curriculum is aligned with the Mississippi Academic Framework. Lessons and support material are provided
Zoo Connections Curriculum We Like to Move It, Move It: Classifying animals by features 1 st grade Curriculum is aligned with the Mississippi Academic Framework. Lessons and support material are provided
Lesson 1. Objectives: ocus: Subjects:
 Lesson 1 The Web of Life Objectives: 1. Understand the concept of an ecosystem. 2. Understand the interdependence of members of an ecosystem. Subjects: 1. Ecology 2. Language 3. Art MATERIALS: Copies of
Lesson 1 The Web of Life Objectives: 1. Understand the concept of an ecosystem. 2. Understand the interdependence of members of an ecosystem. Subjects: 1. Ecology 2. Language 3. Art MATERIALS: Copies of
Year 3 Reading optional SAT mark scheme 2003
 Year 3 Reading optional SAT mark scheme 2003 1. The Sand Horse Multiple choice questions 1 7. Award for each correctly identified option. Do not award a mark if a child has circled more than one option.
Year 3 Reading optional SAT mark scheme 2003 1. The Sand Horse Multiple choice questions 1 7. Award for each correctly identified option. Do not award a mark if a child has circled more than one option.
Unit 2, lesson 1. 1. Listen! 2. Listen and answer. (You can check with the sentences above.) 3. Draw your pet or the pet you would like.
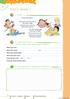 S é q u e n c e Unit, lesson. Listen! Do you like pets? Peter s got a pet. It s a he-cat. His name is Billy. Dorothea s got a she-dog. Her name is Beauty. Sue s got a guinea-pig. His name is Fluffy. Bruce
S é q u e n c e Unit, lesson. Listen! Do you like pets? Peter s got a pet. It s a he-cat. His name is Billy. Dorothea s got a she-dog. Her name is Beauty. Sue s got a guinea-pig. His name is Fluffy. Bruce
Effects of Water Classroom Activity
 Effects of Water Classroom Activity The Classroom Activity introduces students to the context of a performance task, so they are not disadvantaged in demonstrating the skills the task intends to assess.
Effects of Water Classroom Activity The Classroom Activity introduces students to the context of a performance task, so they are not disadvantaged in demonstrating the skills the task intends to assess.
DOG Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster - rabbit - fish
 CAT Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster - rabbit - fish DOG Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster - rabbit - fish HORSE Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster - rabbit - fish HAMSTER Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster
CAT Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster - rabbit - fish DOG Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster - rabbit - fish HORSE Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster - rabbit - fish HAMSTER Pets cat - dog - horse - hamster
God, the Great Creator
 Pre-Session Warm Up God, the Great Creator (Genesis 1: 2:3) Today we re going to start a new series of lessons all about God s attributes. An attribute is a character trait or quality about someone. For
Pre-Session Warm Up God, the Great Creator (Genesis 1: 2:3) Today we re going to start a new series of lessons all about God s attributes. An attribute is a character trait or quality about someone. For
Bountiful Beetles Lesson Plan
 Bountiful Beetles Lesson Plan Lesson Title: Bountiful Beetles Objectives: Students will identify the life cycle, anatomy and other characteristics of beetles. Students will conduct a simple research using
Bountiful Beetles Lesson Plan Lesson Title: Bountiful Beetles Objectives: Students will identify the life cycle, anatomy and other characteristics of beetles. Students will conduct a simple research using
Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes
 Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes Objective & Overview: Using measurement and books, students will gain a better understanding of animal size, diversity, and diet through the fun study of wildlife.
Activity 1 Exploring Animal Diets and Sizes Objective & Overview: Using measurement and books, students will gain a better understanding of animal size, diversity, and diet through the fun study of wildlife.
Box 1 - Article Noun - Blue
 the floor a basket the people a broom the igloo the rocks a dog an eagle a bats the leaves a dolphin a triangle the tusks the shoes the book the sky an elephant the ocean a tiger a donkey the shark a cage
the floor a basket the people a broom the igloo the rocks a dog an eagle a bats the leaves a dolphin a triangle the tusks the shoes the book the sky an elephant the ocean a tiger a donkey the shark a cage
Ecology 1 Star. 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the
 Name: ate: 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the 5. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.. biotic factors and decomposers.
Name: ate: 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the 5. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.. biotic factors and decomposers.
DESCRIBING DESERT, TAIGA, AND TUNDRA BIOMES
 Lesson B5 1 DESCRIBING DESERT, TAIGA, AND TUNDRA BIOMES Unit B. Science and Technology in Wildlife Management Problem Area 5. Desert, Taiga, and Tundra Biomes National Academic Standard. NS.9-12.1 Science
Lesson B5 1 DESCRIBING DESERT, TAIGA, AND TUNDRA BIOMES Unit B. Science and Technology in Wildlife Management Problem Area 5. Desert, Taiga, and Tundra Biomes National Academic Standard. NS.9-12.1 Science
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Ecology - (BIO.B.4.1.1 ) Ecological Organization, (BIO.B.4.1.2 ) Ecosystem Characteristics, (BIO.B.4.2.
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Ecology - (BIO.B.4.1.1 ) Ecological Organization, (BIO.B.4.1.2 ) Ecosystem Characteristics, (BIO.B.4.2.1 ) Energy Flow 1) Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George Date:
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Ecology - (BIO.B.4.1.1 ) Ecological Organization, (BIO.B.4.1.2 ) Ecosystem Characteristics, (BIO.B.4.2.1 ) Energy Flow 1) Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George Date:
Animals of the Desert
 Animals of the Desert (NatureScope Discovering Deserts page 26-27) Third Grade Core: Standard 2 Objective 2 Describe the interactions between living and nonliving things in a small environment. Teach a
Animals of the Desert (NatureScope Discovering Deserts page 26-27) Third Grade Core: Standard 2 Objective 2 Describe the interactions between living and nonliving things in a small environment. Teach a
Silent, Nighttime Hunters By Guy Belleranti
 By Guy Belleranti Owls are raptors, or birds of prey. They are carnivores who quickly and silently swoop down on their prey from above. Most raptors such as eagles, hawks and falcons are day hunters. They
By Guy Belleranti Owls are raptors, or birds of prey. They are carnivores who quickly and silently swoop down on their prey from above. Most raptors such as eagles, hawks and falcons are day hunters. They
Pond Water Web Lesson Plan
 Pond Water Web Lesson Plan Purpose: As a result of this lesson, students will become familiar with common organisms found in a pond and discover their importance in a balanced aquatic habitat as they create
Pond Water Web Lesson Plan Purpose: As a result of this lesson, students will become familiar with common organisms found in a pond and discover their importance in a balanced aquatic habitat as they create
Tracks of a Panda by Nick Dowson, Illustrated by Yu Rong Scripted for Readers Theater by Karen Antikajian
 Tracks of a Panda by Nick Dowson, Illustrated by Yu Rong Scripted for Readers Theater by Karen Antikajian Narrator 1: Narrator 6: Narrator 2: Narrator 7: Narrator 3: Narrator 8: Narrator 4: Fact Announcer
Tracks of a Panda by Nick Dowson, Illustrated by Yu Rong Scripted for Readers Theater by Karen Antikajian Narrator 1: Narrator 6: Narrator 2: Narrator 7: Narrator 3: Narrator 8: Narrator 4: Fact Announcer
Our Earth, Our Resources
 UNIT 4 Essential Question: How can we take the best care of our Earth? Objectives Our Earth, Our Resources Unit Resource Guide Social Studies Resources Identify and describe the physical characteristics
UNIT 4 Essential Question: How can we take the best care of our Earth? Objectives Our Earth, Our Resources Unit Resource Guide Social Studies Resources Identify and describe the physical characteristics
Tropical Tracks. Tropical rainforests are located along the Equator. Look at the map in the Biome. Draw the Equator on your map and label it.
 Tropical Tracks KS2 In Eden s Rainforest Biome you will discover how plants, animals and people of the Tropical Rainforest fit together. Let s Start! Look Point 1 (The Map, grid reference 175 482) Tropical
Tropical Tracks KS2 In Eden s Rainforest Biome you will discover how plants, animals and people of the Tropical Rainforest fit together. Let s Start! Look Point 1 (The Map, grid reference 175 482) Tropical
First Grade Spelling Words
 First Grade Spelling Words The Hat 1. at 2. hat 3. cat 4. can 5. cap 6. tap 7. map 8. mad 9. a 10. the I tap the can. Sam and the Bag 1. am 2. ham 3. had 4. bad 5. bag 6. rag 7. cap 8. mad 9. up 10. go
First Grade Spelling Words The Hat 1. at 2. hat 3. cat 4. can 5. cap 6. tap 7. map 8. mad 9. a 10. the I tap the can. Sam and the Bag 1. am 2. ham 3. had 4. bad 5. bag 6. rag 7. cap 8. mad 9. up 10. go
Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Food Chains and Food Webs
 Program Support Notes by: Spiro Liacos B.Ed. Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. Executive Producers: Edwina Baden-Powell B.A, CVP. Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. You
Program Support Notes by: Spiro Liacos B.Ed. Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. Executive Producers: Edwina Baden-Powell B.A, CVP. Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. You
PLANET EARTH: Seasonal Forests
 PLANET EARTH: Seasonal Forests Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Running Time: 42 minutes Program Description Investigate temperate forests and find some of the most elusive creatures and welladapted plant
PLANET EARTH: Seasonal Forests Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Running Time: 42 minutes Program Description Investigate temperate forests and find some of the most elusive creatures and welladapted plant
Is That Mammal a Carnivore, Herbivore or Omnivore?
 Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
ESL 3 8 8 + 1 62 QUESTION 62 ANSWER 8 LUCKY CARDS
 Speaking Cards ESL Card Game For 3 8 players Age: 8 + Level of English: High Beginners or False Beginners (at least 1 year of learning English) 62 QUESTION cards, 62 ANSWER cards, 8 LUCKY CARDS (together:
Speaking Cards ESL Card Game For 3 8 players Age: 8 + Level of English: High Beginners or False Beginners (at least 1 year of learning English) 62 QUESTION cards, 62 ANSWER cards, 8 LUCKY CARDS (together:
