SOLUTION OF BOUNDARY LAYER
|
|
|
- Cory Jacobs
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOUION OF BOUNDARY AYER EQUAIONS Prabal alkar Aociate Proeor Department o Mechanical Engineering II Delhi [email protected] P.alkar/Mech-IID
2 Bonar laer Approimation X momentm: ρ μ P Appling Newton n law in the -irection, we get -momentm eqation ρ μ P h,p P P P() Hence, For a late plate, ince U contant an otie the bonar laer, X- momentm eqation gie P P P.alkar/Mech-IID hereore, or low oer a lat plate, the prere remain contant oer the entire plate (both inie an otie the bonar laer).
3 Bonar laer oer a lat plate P.alkar/Mech-IID
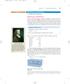
4 Pal Richar Heinrich Blai (88 97) wa a German Fli Dnamic Engineer. He wa one o the irt tent o Prantl. he continit an momentm eqation were irt ole in 98 b the German engineer H. Blai, a tent to. Prantl. Born Die Fiel Alma mater Doctoral aior 9 Agt 88 Berlin, German 4 April 97 (age 86) Hambrg, Wet German Fli mechanic an mechanical engineering Unierit o Göttingen wig Prantl hi wa one b tranorming the two partial ierential eqation into a ingle orinar ierential eqation b introcing a new inepenent ariable, calle the imilaritariable. he ining o ch a ariable, aming it eit, i more o an art than cience, an it reqire to hae a goo inight o the problem. P.alkar/Mech-IID
5 he hape o the elocit proile remain the ame along the plate. Blai reaone that the nonimenional elocit proile / hol remain nchange when plotte againt the nonimenional itance /δ, where δ i the thickne o the local elocit bonar laer at a gien. hat i, althogh both δ an at a gien ar with, the elocit at a ie / δ remain contant Blai wa alo aware rom the work o Stoke that δ i proportional to P.alkar/Mech-IID
6 Scale Anali Diiing b to epre the relt in imenionle orm gie P.alkar/Mech-IID
7 Similarit Variable he igniicant ariable i /δ, an we ame that the elocit ma be epree a a nction cto o othi aabe.wete ariable. then hae We hi eine make, / / δ Here, i calle the imilarit ariable, an g() i the nction we eek a a oltion P.alkar/Mech-IID
8 Variable ranormation A tream nction wa eine ch that: to get ri o continit eqation Ψ Ψ to get ri o continit eqation Ψ ( ) Ψ ) g( ) ( where ( ) ( ) Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ P.alkar/Mech-IID
9 Dierentiating the preio eqation with repect to an, Sbtitting thee relation into the momentm eqation an, Sbtitting thee relation into the momentm eqation an impliing, we obtain hi i a thir-orer nonlinear ierential eqation. hi wa the tem o two PDE i conerte to one ODE hi wa the tem o two PDE i conerte to one ODE. P.alkar/Mech-IID
10 Blai Soltion he ale o correponing to /.99 i 5. 5 δ P.alkar/Mech-IID δ Re Signiicance o,,
11 P.alkar/Mech-IID
12 he hear tre at the wall can be etermine rom: τ w μ μ τ w ρμ.. ρ Re ocal kin riction coeicient become C, τ ρv w ρ τ w.664re P.alkar/Mech-IID Note that nlike the bonar laer thickne, wall hear tre an the kin riction coeicient ecreae along the plate a -/.
13 Energ Eqation Introce a non-imenional temperatre θ(, ) (, ) Sbtittion gie an energ eqation o the orm: θ θ θ α emperatre proile or low oer an iothermal lat plate are imilar like the elocit proile. h, we epect a imilarit oltion or temperatre to eit. Frther, the thickne o the thermal bonar laer i proportional to / Uing the chain rle an btitting the an epreion into the energ eqation gie θ θ θ α P.alkar/Mech-IID
14 Uing the chain rle an btitting the an epreion into the energ eqation gie θ θ θ α / i replace b θ θ θ Pr Compare For Pr θ ( ) an θ ( ) an h we concle that the elocit an thermal bonar laer coincie, an the nonimenional elocit an temperatre proile (/ an θ) areientical or tea, incompreible, laminar low o a li with contant propertie an Pr oer an iothermal lat plate he ale o the temperatre graient at the race (Pr )?? θ P.alkar/Mech-IID.
15 θ θ Pr hi eq. i ole or nmero ale o Prantl nmber. For Pr >.6, the nonimenional temperatre graient at the race i on to be proportional to Pr / Pr >.6 θ. Pr θ(, ) (, ) δ he temperatre graient at the race i θ ( ) ( ) θ ( ). Pr P.alkar/Mech-IID
16 P.alkar/Mech-IID hi oltion i gien b Pohlhaen
17 he local conection coeicient can be epree a: k q h. Pr k ( ) ( ). Pr ( ) An the local Nelt nmber become h N k. Pr Re Pr >.6 Soling the thermal bonar laer eqation nmericall or the temperatre proile or ierent Prantl nmber, an ing the einition o the thermal bonar laer, it i etermine that δ δ t Pr P.alkar/Mech-IID δ t δ Pr Pr 5. Re
18 Non-imenionalization Non imenionalization p μ ρ μ ρ k ρ p k c an V p,p V, V,, ρ P.alkar/Mech-IID
19 p Continit: p Re Momentm: Pr Re Energ: With the bonar conition: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ),,,,,,,,,,,, P.alkar/Mech-IID
20 P.alkar/Mech-IID Geometricall Similar
21 Fnctional orm o Friction an Conection Coeicient i Momentm: p Re For a gien geometr, the oltion or can be epree a (,,Re ) hen the hear tre at the race become τ μ μ V μ V (, Re ) (, Re ) (, Re ) (, Re ) τ μv C, ρvv ρ V Re P.alkar/Mech-IID
22 Energ: he oltion or can be epree a Re Pr g (,,Re,Pr) Uing the einition o, the conection heat traner coeicient become h k k( ) ( ) k Nelt nmber: N h k g (, Re,Pr) Note that the Nelt nmber i eqialent to the imenionle temperatre graient at the race, an th it i properl reerre to a the imenionle heat traner coeicient P.alkar/Mech-IID
23 P.alkar/Mech-IID Aerage riction coeicient
24 Renol Analog Renol Analog When Pr (approimatel the cae or gae) an P/ (e g For lat Re or gae) an P / (e.g. For lat plate) Re h N k N N V V μ μ μ τ, N Re V N V V C ρ μ ρ τ, N Re C (Pr) Re V ρv ρ, St C (Pr) P.alkar/Mech-IID Pr Re N V c h St p ρ
25 Clinton-Colbrn Analog Alo calle moiie Renol analog C.664Re, N. Pr Re aking the ratio between C, an N Vali or.6<pr<6 P.alkar/Mech-IID C, Re C, N Pr Pr jh ρcpv h Colbrn j-actor Althogh thi relation i eelope ing relation or laminar low oer a lat plate (or which P/ ), eperimental tie how that it i alo applicable approimatel or trblent t low oer a race, een in the preence o prere graient. For laminar low, howeer, the analog i not applicable nle P/. hereore, it oe not appl to laminar low in a pipe
DIFFERENTIAL FORMULATION OF THE BASIC LAWS
 CHAPER DIFFERENIAL FORMULAION OF HE BASIC LAWS. Introdction Differential fmlation of basic las: Conseration of mass Conseration of momentm Conseration of energ. Flo Generation (i) Fced conection. Motion
CHAPER DIFFERENIAL FORMULAION OF HE BASIC LAWS. Introdction Differential fmlation of basic las: Conseration of mass Conseration of momentm Conseration of energ. Flo Generation (i) Fced conection. Motion
8. Forced Convection Heat Transfer
 8. Forced Convection Heat Transfer 8.1 Introdction The general definition for convection ma be smmarized to this definition "energ transfer between the srface and flid de to temperatre difference" and
8. Forced Convection Heat Transfer 8.1 Introdction The general definition for convection ma be smmarized to this definition "energ transfer between the srface and flid de to temperatre difference" and
Figure 2.1. a. Block diagram representation of a system; b. block diagram representation of an interconnection of subsystems
 Figure. a. Block diagram repreentation o a ytem; b. block diagram repreentation o an interconnection o ubytem REVIEW OF THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM Table. Laplace tranorm table Table. Laplace tranorm theorem
Figure. a. Block diagram repreentation o a ytem; b. block diagram repreentation o an interconnection o ubytem REVIEW OF THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM Table. Laplace tranorm table Table. Laplace tranorm theorem
Risk Management for Derivatives
 Risk Management or Derivatives he Greeks are coming the Greeks are coming! Managing risk is important to a large number o iniviuals an institutions he most unamental aspect o business is a process where
Risk Management or Derivatives he Greeks are coming the Greeks are coming! Managing risk is important to a large number o iniviuals an institutions he most unamental aspect o business is a process where
 α α λ α = = λ λ α ψ = = α α α λ λ ψ α = + β = > θ θ β > β β θ θ θ β θ β γ θ β = γ θ > β > γ θ β γ = θ β = θ β = θ β = β θ = β β θ = = = β β θ = + α α α α α = = λ λ λ λ λ λ λ = λ λ α α α α λ ψ + α =
α α λ α = = λ λ α ψ = = α α α λ λ ψ α = + β = > θ θ β > β β θ θ θ β θ β γ θ β = γ θ > β > γ θ β γ = θ β = θ β = θ β = β θ = β β θ = = = β β θ = + α α α α α = = λ λ λ λ λ λ λ = λ λ α α α α λ ψ + α =
Climate control of a bulk storage room for foodstuffs
 Climate control of a bulk storage room for foodstuffs S. an Mourik, H. Zwart, Twente Uniersity, K.J. Keesman*, Wageningen Uniersity, The Netherlands Corresponding author: S. an Mourik Department of Applied
Climate control of a bulk storage room for foodstuffs S. an Mourik, H. Zwart, Twente Uniersity, K.J. Keesman*, Wageningen Uniersity, The Netherlands Corresponding author: S. an Mourik Department of Applied
1D STEADY STATE HEAT
 D SEADY SAE HEA CONDUCION () Prabal alukdar Aociate Profeor Department of Mechanical Engineering II Delhi E-mail: [email protected] Convection Boundary Condition Heat conduction at the urface in a
D SEADY SAE HEA CONDUCION () Prabal alukdar Aociate Profeor Department of Mechanical Engineering II Delhi E-mail: [email protected] Convection Boundary Condition Heat conduction at the urface in a
Heat transfer to or from a fluid flowing through a tube
 Heat tranfer to or from a fluid flowing through a tube R. Shankar Subramanian A common ituation encountered by the chemical engineer i heat tranfer to fluid flowing through a tube. Thi can occur in heat
Heat tranfer to or from a fluid flowing through a tube R. Shankar Subramanian A common ituation encountered by the chemical engineer i heat tranfer to fluid flowing through a tube. Thi can occur in heat
Incline and Friction Examples
 Incline and riction Eample Phic 6A Prepared b Vince Zaccone riction i a force that oppoe the motion of urface that are in contact with each other. We will conider 2 tpe of friction in thi cla: KINETIC
Incline and riction Eample Phic 6A Prepared b Vince Zaccone riction i a force that oppoe the motion of urface that are in contact with each other. We will conider 2 tpe of friction in thi cla: KINETIC
Pipe Flow Calculations
 Pipe Flow Calculation R. Shankar Subramanian epartment o Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkon Univerity We begin with ome reult that we hall ue when making riction lo calculation or teady, ully
Pipe Flow Calculation R. Shankar Subramanian epartment o Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkon Univerity We begin with ome reult that we hall ue when making riction lo calculation or teady, ully
ME 24-221 THERMODYNAMICS I
 Solution to extra problem in chapter 8 Noember 9, 000 Fall 000 J. Murthy ME 4- HERMODYNAMICS I 8.5 Water i ued a the working fluid in a Carnot cycle heat engine, where it change from aturated liquid to
Solution to extra problem in chapter 8 Noember 9, 000 Fall 000 J. Murthy ME 4- HERMODYNAMICS I 8.5 Water i ued a the working fluid in a Carnot cycle heat engine, where it change from aturated liquid to
CIVE2400 Fluid Mechanics. Section 1: Fluid Flow in Pipes
 CIVE00 Flid Mechanics Section : Flid Flow in Pipes CIVE00 FLUID MECHNICS... SECTION : FLUID FLOW IN PIPES.... FLUID FLOW IN PIPES.... Pressre loss de to riction in a pipeline..... Pressre loss dring laminar
CIVE00 Flid Mechanics Section : Flid Flow in Pipes CIVE00 FLUID MECHNICS... SECTION : FLUID FLOW IN PIPES.... FLUID FLOW IN PIPES.... Pressre loss de to riction in a pipeline..... Pressre loss dring laminar
Heat and Mass Correlations
 Heat and Mass Correlations Alexander Rattner, Jonathan Bohren November 13, 008 Contents 1 Dimensionless Parameters Boundary ayer Analogies - Require Geometric Similarity 3 External Flow 3 3.1 External
Heat and Mass Correlations Alexander Rattner, Jonathan Bohren November 13, 008 Contents 1 Dimensionless Parameters Boundary ayer Analogies - Require Geometric Similarity 3 External Flow 3 3.1 External
A) When two objects slide against one another, the magnitude of the frictional force is always equal to μ
 Phyic 100 Homewor 5 Chapter 6 Contact Force Introduced ) When two object lide againt one another, the magnitude of the frictional force i alway equal to μ B) When two object are in contact with no relative
Phyic 100 Homewor 5 Chapter 6 Contact Force Introduced ) When two object lide againt one another, the magnitude of the frictional force i alway equal to μ B) When two object are in contact with no relative
Give a formula for the velocity as a function of the displacement given that when s = 1 metre, v = 2 m s 1. (7)
 . The acceleration of a bod is gien in terms of the displacement s metres as s a =. s (a) Gie a formula for the elocit as a function of the displacement gien that when s = metre, = m s. (7) (b) Hence find
. The acceleration of a bod is gien in terms of the displacement s metres as s a =. s (a) Gie a formula for the elocit as a function of the displacement gien that when s = metre, = m s. (7) (b) Hence find
Worked Examples. v max =?
 Exaple iction + Unifo Cicula Motion Cicula Hill A ca i diing oe a ei-cicula hill of adiu. What i the fatet the ca can die oe the top of the hill without it tie lifting off of the gound? ax? (1) Copehend
Exaple iction + Unifo Cicula Motion Cicula Hill A ca i diing oe a ei-cicula hill of adiu. What i the fatet the ca can die oe the top of the hill without it tie lifting off of the gound? ax? (1) Copehend
Darcy Friction Factor Formulae in Turbulent Pipe Flow
 Darcy Friction Factor Formulae in Turbulent Pipe Flow Jukka Kiijärvi Lunowa Fluid Mechanics Paper 110727 July 29, 2011 Abstract The Darcy riction actor in turbulent pipe low must be solved rom the Colebrook
Darcy Friction Factor Formulae in Turbulent Pipe Flow Jukka Kiijärvi Lunowa Fluid Mechanics Paper 110727 July 29, 2011 Abstract The Darcy riction actor in turbulent pipe low must be solved rom the Colebrook
Chapter 5: Applying Newton s Laws
 Chapter 5: Appling Newton s Laws Newton s 1 st Law he 1 st law defines what the natural states of motion: rest and constant velocit. Natural states of motion are and those states are when a = 0. In essence,
Chapter 5: Appling Newton s Laws Newton s 1 st Law he 1 st law defines what the natural states of motion: rest and constant velocit. Natural states of motion are and those states are when a = 0. In essence,
Empirical correlations of overconsolidation ratio, coefficient of earth pressure at rest and undrained strength
 Second Conference of Jnior Reearcher in Civil Engineering 88 Empirical correlation of overconolidation ratio, coefficient of earth prere at ret and ndrained trength Vendel Józa BME Department of Geotechnic,
Second Conference of Jnior Reearcher in Civil Engineering 88 Empirical correlation of overconolidation ratio, coefficient of earth prere at ret and ndrained trength Vendel Józa BME Department of Geotechnic,
Basic Principles in Microfluidics
 Basic Principles in Microfluidics 1 Newton s Second Law for Fluidics Newton s 2 nd Law (F= ma) : Time rate of change of momentum of a system equal to net force acting on system!f = dp dt Sum of forces
Basic Principles in Microfluidics 1 Newton s Second Law for Fluidics Newton s 2 nd Law (F= ma) : Time rate of change of momentum of a system equal to net force acting on system!f = dp dt Sum of forces
6. Friction, Experiment and Theory
 6. Friction, Experiment and Theory The lab thi wee invetigate the rictional orce and the phyical interpretation o the coeicient o riction. We will mae ue o the concept o the orce o gravity, the normal
6. Friction, Experiment and Theory The lab thi wee invetigate the rictional orce and the phyical interpretation o the coeicient o riction. We will mae ue o the concept o the orce o gravity, the normal
Tridiagonal Solvers on the GPU and Applications to Fluid Simulation. Nikolai Sakharnykh, NVIDIA [email protected]
 Tridiagonal Solvers on the GPU and Applications to Flid Simlation Nikolai Sakharnykh, NVIDIA [email protected] Agenda Introdction and Problem Statement Governing Eqations ADI Nmerical Method GPU Implementation
Tridiagonal Solvers on the GPU and Applications to Flid Simlation Nikolai Sakharnykh, NVIDIA [email protected] Agenda Introdction and Problem Statement Governing Eqations ADI Nmerical Method GPU Implementation
EXAMPLE: Water Flow in a Pipe
 EXAMPLE: Water Flow in a Pipe P 1 > P 2 Velocity profile is parabolic (we will learn why it is parabolic later, but since friction comes from walls the shape is intuitive) The pressure drops linearly along
EXAMPLE: Water Flow in a Pipe P 1 > P 2 Velocity profile is parabolic (we will learn why it is parabolic later, but since friction comes from walls the shape is intuitive) The pressure drops linearly along
Work, Energy & Power. AP Physics B
 ork, Energy & Power AP Physics B There are many dierent TYPES o Energy. Energy is expressed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calorie Energy can be expressed more speciically by using the term ORK() ork = The Scalar
ork, Energy & Power AP Physics B There are many dierent TYPES o Energy. Energy is expressed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calorie Energy can be expressed more speciically by using the term ORK() ork = The Scalar
THE EFFECTS OF DUCT SHAPE ON THE NUSSELT NUMBER
 Mathematical and Computational pplications, Vol, No, pp 79-88, 5 ssociation for Scientific Research THE EFFECTS OF DUCT SHPE ON THE NUSSELT NUMBER M Emin Erdoğan and C Erdem Imrak Faculty of Mechanical
Mathematical and Computational pplications, Vol, No, pp 79-88, 5 ssociation for Scientific Research THE EFFECTS OF DUCT SHPE ON THE NUSSELT NUMBER M Emin Erdoğan and C Erdem Imrak Faculty of Mechanical
Prediction of Pressure Drop in Chilled Water Piping System Using Theoretical and CFD Analysis
 Shirish P. Patil et.al / International Journal o Engineering and Technology (IJET) Prediction o Pressure Drop in Chilled Water Piping System Using Theoretical and CFD Analysis Shirish P. Patil #1, Abhijeet
Shirish P. Patil et.al / International Journal o Engineering and Technology (IJET) Prediction o Pressure Drop in Chilled Water Piping System Using Theoretical and CFD Analysis Shirish P. Patil #1, Abhijeet
Mannheim curves in the three-dimensional sphere
 Mannheim curves in the three-imensional sphere anju Kahraman, Mehmet Öner Manisa Celal Bayar University, Faculty of Arts an Sciences, Mathematics Department, Muraiye Campus, 5, Muraiye, Manisa, urkey.
Mannheim curves in the three-imensional sphere anju Kahraman, Mehmet Öner Manisa Celal Bayar University, Faculty of Arts an Sciences, Mathematics Department, Muraiye Campus, 5, Muraiye, Manisa, urkey.
Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Ale Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Ale Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Convective Heat Transfer Lecture No. # 03 Heat Transfer Correlation
Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Ale Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Convective Heat Transfer Lecture No. # 03 Heat Transfer Correlation
Solution of the Heat Equation for transient conduction by LaPlace Transform
 Solution of the Heat Equation for tranient conduction by LaPlace Tranform Thi notebook ha been written in Mathematica by Mark J. McCready Profeor and Chair of Chemical Engineering Univerity of Notre Dame
Solution of the Heat Equation for tranient conduction by LaPlace Tranform Thi notebook ha been written in Mathematica by Mark J. McCready Profeor and Chair of Chemical Engineering Univerity of Notre Dame
U = x 1 2. 1 x 1 4. 2 x 1 4. What are the equilibrium relative prices of the three goods? traders has members who are best off?
 Chapter 7 General Equilibrium Exercise 7. Suppose there are 00 traders in a market all of whom behave as price takers. Suppose there are three goods and the traders own initially the following quantities:
Chapter 7 General Equilibrium Exercise 7. Suppose there are 00 traders in a market all of whom behave as price takers. Suppose there are three goods and the traders own initially the following quantities:
Rotated Ellipses. And Their Intersections With Lines. Mark C. Hendricks, Ph.D. Copyright March 8, 2012
 Rotated Ellipses And Their Intersections With Lines b Mark C. Hendricks, Ph.D. Copright March 8, 0 Abstract: This paper addresses the mathematical equations for ellipses rotated at an angle and how to
Rotated Ellipses And Their Intersections With Lines b Mark C. Hendricks, Ph.D. Copright March 8, 0 Abstract: This paper addresses the mathematical equations for ellipses rotated at an angle and how to
Graph-based Simplex Method for Pairwise Energy Minimization with Binary Variables
 Graph-based Simplex Method for Pairwise Energy Minimization with Binary Variables Daniel Průša Center for Machine Perception, Faclty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical Uniersity Karloo náměstí
Graph-based Simplex Method for Pairwise Energy Minimization with Binary Variables Daniel Průša Center for Machine Perception, Faclty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical Uniersity Karloo náměstí
MECH 2110 - Statics & Dynamics
 Chapter D Problem 3 Solution 1/7/8 1:8 PM MECH 11 - Static & Dynamic Chapter D Problem 3 Solution Page 7, Engineering Mechanic - Dynamic, 4th Edition, Meriam and Kraige Given: Particle moving along a traight
Chapter D Problem 3 Solution 1/7/8 1:8 PM MECH 11 - Static & Dynamic Chapter D Problem 3 Solution Page 7, Engineering Mechanic - Dynamic, 4th Edition, Meriam and Kraige Given: Particle moving along a traight
Chapter 11 Relative Velocity
 Chapter 11 Relatie Velocity 11 Relatie Velocity Vector add like ector, not like nuber. Except in that ery pecial cae in which the ector you are adding lie along one and the ae line, you can t jut add the
Chapter 11 Relatie Velocity 11 Relatie Velocity Vector add like ector, not like nuber. Except in that ery pecial cae in which the ector you are adding lie along one and the ae line, you can t jut add the
4 Impulse and Impact. Table of contents:
 4 Impulse and Impact At the end of this section you should be able to: a. define momentum and impulse b. state principles of conseration of linear momentum c. sole problems inoling change and conseration
4 Impulse and Impact At the end of this section you should be able to: a. define momentum and impulse b. state principles of conseration of linear momentum c. sole problems inoling change and conseration
CHAPTER ONE VECTOR GEOMETRY
 CHAPTER ONE VECTOR GEOMETRY. INTRODUCTION In this chapter ectors are first introdced as geometric objects, namely as directed line segments, or arrows. The operations of addition, sbtraction, and mltiplication
CHAPTER ONE VECTOR GEOMETRY. INTRODUCTION In this chapter ectors are first introdced as geometric objects, namely as directed line segments, or arrows. The operations of addition, sbtraction, and mltiplication
Basic Equations, Boundary Conditions and Dimensionless Parameters
 Chapter 2 Basic Equations, Boundary Conditions and Dimensionless Parameters In the foregoing chapter, many basic concepts related to the present investigation and the associated literature survey were
Chapter 2 Basic Equations, Boundary Conditions and Dimensionless Parameters In the foregoing chapter, many basic concepts related to the present investigation and the associated literature survey were
ES240 Solid Mechanics Fall 2007. Stress field and momentum balance. Imagine the three-dimensional body again. At time t, the material particle ( x, y,
 S40 Solid Mechanics Fall 007 Stress field and momentum balance. Imagine the three-dimensional bod again. At time t, the material particle,, ) is under a state of stress ij,,, force per unit volume b b,,,.
S40 Solid Mechanics Fall 007 Stress field and momentum balance. Imagine the three-dimensional bod again. At time t, the material particle,, ) is under a state of stress ij,,, force per unit volume b b,,,.
Open channel flow Basic principle
 Open channel flow Basic principle INTRODUCTION Flow in rivers, irrigation canals, drainage ditches and aqueducts are some examples for open channel flow. These flows occur with a free surface and the pressure
Open channel flow Basic principle INTRODUCTION Flow in rivers, irrigation canals, drainage ditches and aqueducts are some examples for open channel flow. These flows occur with a free surface and the pressure
11 CHAPTER 11: FOOTINGS
 CHAPTER ELEVEN FOOTINGS 1 11 CHAPTER 11: FOOTINGS 11.1 Introuction Footings are structural elements that transmit column or wall loas to the unerlying soil below the structure. Footings are esigne to transmit
CHAPTER ELEVEN FOOTINGS 1 11 CHAPTER 11: FOOTINGS 11.1 Introuction Footings are structural elements that transmit column or wall loas to the unerlying soil below the structure. Footings are esigne to transmit
Accurate Calibration of Stereo Cameras for Machine Vision
 JCS&T Vol. 4 No. 3 Otober 004 Aurate Calibration o Stereo Camera or Mahine Viion Liangu Li, Zuren Feng, Yuanjing Feng Intitute o Stem Engineering, Xi an Jiaotong Unierit Xi an, ShanXi Proine, China ABSTRACT
JCS&T Vol. 4 No. 3 Otober 004 Aurate Calibration o Stereo Camera or Mahine Viion Liangu Li, Zuren Feng, Yuanjing Feng Intitute o Stem Engineering, Xi an Jiaotong Unierit Xi an, ShanXi Proine, China ABSTRACT
Section 1.4. Difference Equations
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 1.4 Difference Equations At this point almost all of our sequences have had explicit formulas for their terms. That is, we have looked mainly at sequences
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 1.4 Difference Equations At this point almost all of our sequences have had explicit formulas for their terms. That is, we have looked mainly at sequences
Fluid Pressure and Fluid Force
 0_0707.q //0 : PM Page 07 SECTION 7.7 Section 7.7 Flui Pressure an Flui Force 07 Flui Pressure an Flui Force Fin flui pressure an flui force. Flui Pressure an Flui Force Swimmers know that the eeper an
0_0707.q //0 : PM Page 07 SECTION 7.7 Section 7.7 Flui Pressure an Flui Force 07 Flui Pressure an Flui Force Fin flui pressure an flui force. Flui Pressure an Flui Force Swimmers know that the eeper an
The Concept of the Effective Mass Tensor in GR. The Equation of Motion
 The Concept of the Effective Mass Tensor in GR The Equation of Motion Mirosław J. Kubiak Zespół Szkół Technicznych, Gruziąz, Polan Abstract: In the papers [, ] we presente the concept of the effective
The Concept of the Effective Mass Tensor in GR The Equation of Motion Mirosław J. Kubiak Zespół Szkół Technicznych, Gruziąz, Polan Abstract: In the papers [, ] we presente the concept of the effective
Scalar Transport. Introduction. T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41. Eddy-Diffusivity Modelling. TPFE MSc Advanced Turbulence Modelling
 School of Mechanical Aerospace and Civil Engineering TPFE MSc Advanced Turbulence Modelling Scalar Transport T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41 Reading: S. Pope, Turbulent Flows D. Wilco, Turbulence
School of Mechanical Aerospace and Civil Engineering TPFE MSc Advanced Turbulence Modelling Scalar Transport T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41 Reading: S. Pope, Turbulent Flows D. Wilco, Turbulence
and that of the outgoing water is mv f
 Week 6 hoework IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT WEBASSIGN: In the WebAssign ersions of these probles, arious details hae been changed, so that the answers will coe out differently. The ethod to find the solution is
Week 6 hoework IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT WEBASSIGN: In the WebAssign ersions of these probles, arious details hae been changed, so that the answers will coe out differently. The ethod to find the solution is
LINES AND PLANES IN R 3
 LINES AND PLANES IN R 3 In this handout we will summarize the properties of the dot product and cross product and use them to present arious descriptions of lines and planes in three dimensional space.
LINES AND PLANES IN R 3 In this handout we will summarize the properties of the dot product and cross product and use them to present arious descriptions of lines and planes in three dimensional space.
Fluid Mechanics: Static s Kinematics Dynamics Fluid
 Fluid Mechanics: Fluid mechanics may be defined as that branch of engineering science that deals with the behavior of fluid under the condition of rest and motion Fluid mechanics may be divided into three
Fluid Mechanics: Fluid mechanics may be defined as that branch of engineering science that deals with the behavior of fluid under the condition of rest and motion Fluid mechanics may be divided into three
SIMULATION OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROLLED PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR DRIVE
 SIMULATION OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROLLED PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR DRIVE Selin Özçıra Nur Bekiroğlu Engin Ayçiçek e-mail: [email protected] e-mail: [email protected] e-mail: [email protected]
SIMULATION OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROLLED PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR DRIVE Selin Özçıra Nur Bekiroğlu Engin Ayçiçek e-mail: [email protected] e-mail: [email protected] e-mail: [email protected]
Numerical investigation of heat transfer process form with constant heat flux in exothermic board by natural convection inside a closed cavity
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECANICS Numerical inestigation of heat transfer process form with constant heat flux in exothermic board by natural conection inside a closed caity Behnaz Arjoman Kermani,Islamic
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECANICS Numerical inestigation of heat transfer process form with constant heat flux in exothermic board by natural conection inside a closed caity Behnaz Arjoman Kermani,Islamic
Lecture 7 Force and Motion. Practice with Free-body Diagrams and Newton s Laws
 Lecture 7 Force and Motion Practice with Free-body Diagrams and Newton s Laws oday we ll just work through as many examples as we can utilizing Newton s Laws and free-body diagrams. Example 1: An eleator
Lecture 7 Force and Motion Practice with Free-body Diagrams and Newton s Laws oday we ll just work through as many examples as we can utilizing Newton s Laws and free-body diagrams. Example 1: An eleator
FLUID DYNAMICS. Intrinsic properties of fluids. Fluids behavior under various conditions
 FLUID DYNAMICS Intrinsic properties of fluids Fluids behavior under various conditions Methods by which we can manipulate and utilize the fluids to produce desired results TYPES OF FLUID FLOW Laminar or
FLUID DYNAMICS Intrinsic properties of fluids Fluids behavior under various conditions Methods by which we can manipulate and utilize the fluids to produce desired results TYPES OF FLUID FLOW Laminar or
CSI:FLORIDA. Section 4.4: Logistic Regression
 SI:FLORIDA Section 4.4: Logistic Regression SI:FLORIDA Reisit Masked lass Problem.5.5 2 -.5 - -.5 -.5 - -.5.5.5 We can generalize this roblem to two class roblem as well! SI:FLORIDA Reisit Masked lass
SI:FLORIDA Section 4.4: Logistic Regression SI:FLORIDA Reisit Masked lass Problem.5.5 2 -.5 - -.5 -.5 - -.5.5.5 We can generalize this roblem to two class roblem as well! SI:FLORIDA Reisit Masked lass
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter
 Kinetic Molecular Theor of Matter Heat capacit of gases and metals Pressure of gas Average speed of electrons in semiconductors Electron noise in resistors Positive metal ion cores Free valence electrons
Kinetic Molecular Theor of Matter Heat capacit of gases and metals Pressure of gas Average speed of electrons in semiconductors Electron noise in resistors Positive metal ion cores Free valence electrons
The FitzHugh-Nagumo Model
 Lecture 6 The FitzHugh-Nagumo Model 6.1 The Nature of Excitable Cell Models Classically, it as knon that the cell membrane carries a potential across the inner and outer surfaces, hence a basic model for
Lecture 6 The FitzHugh-Nagumo Model 6.1 The Nature of Excitable Cell Models Classically, it as knon that the cell membrane carries a potential across the inner and outer surfaces, hence a basic model for
On Secure Network Coding with Unequal Link Capacities and Restricted Wiretapping Sets
 On Secure Network Coing with Unequal Link Capacitie an Retricte Wiretapping Set Tao Cui an Tracey Ho Department of Electrical Engineering California Intitute of Technology Paaena, CA 9115, USA Email: {taocui,
On Secure Network Coing with Unequal Link Capacitie an Retricte Wiretapping Set Tao Cui an Tracey Ho Department of Electrical Engineering California Intitute of Technology Paaena, CA 9115, USA Email: {taocui,
Heat Transfer From A Heated Vertical Plate
 Heat Transfer From A Heated Vertical Plate Mechanical and Environmental Engineering Laboratory Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California at San Diego La Jolla, California
Heat Transfer From A Heated Vertical Plate Mechanical and Environmental Engineering Laboratory Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California at San Diego La Jolla, California
MHD effects on natural convection laminar flow from a horizontal circular cylinder in presence of radiation
 RESEARCH Revista Mexicana de Física 61 (2015) 450 457 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 2015 MHD effects on natural convection laminar flow from a horizontal circular cylinder in presence of radiation Tariq Javed, Abid
RESEARCH Revista Mexicana de Física 61 (2015) 450 457 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 2015 MHD effects on natural convection laminar flow from a horizontal circular cylinder in presence of radiation Tariq Javed, Abid
Chapter 8: Flow in Pipes
 Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of laminar and turbulent flow in pipes and the analysis of fully developed flow 2. Calculate the major and minor losses associated with pipe flow in piping networks
Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of laminar and turbulent flow in pipes and the analysis of fully developed flow 2. Calculate the major and minor losses associated with pipe flow in piping networks
Bob York. Simple FET DC Bias Circuits
 Bob York Simple FET DC Bia Circuit Loa-Line an Q-point Conier the effect of a rain reitor in the comnon-ource configuration: Smaller + g D out KL: Thi i the equation of a line that can be uperimpoe on
Bob York Simple FET DC Bia Circuit Loa-Line an Q-point Conier the effect of a rain reitor in the comnon-ource configuration: Smaller + g D out KL: Thi i the equation of a line that can be uperimpoe on
σ m using Equation 8.1 given that σ
 8. Etimate the theoretical fracture trength of a brittle material if it i known that fracture occur by the propagation of an elliptically haped urface crack of length 0.8 mm and having a tip radiu of curvature
8. Etimate the theoretical fracture trength of a brittle material if it i known that fracture occur by the propagation of an elliptically haped urface crack of length 0.8 mm and having a tip radiu of curvature
Reading: Ryden chs. 3 & 4, Shu chs. 15 & 16. For the enthusiasts, Shu chs. 13 & 14.
 7 Shocks Reaing: Ryen chs 3 & 4, Shu chs 5 & 6 For the enthusiasts, Shu chs 3 & 4 A goo article for further reaing: Shull & Draine, The physics of interstellar shock waves, in Interstellar processes; Proceeings
7 Shocks Reaing: Ryen chs 3 & 4, Shu chs 5 & 6 For the enthusiasts, Shu chs 3 & 4 A goo article for further reaing: Shull & Draine, The physics of interstellar shock waves, in Interstellar processes; Proceeings
Practice Problems on the Navier-Stokes Equations
 ns_0 A viscous, incompressible, Newtonian liquid flows in stead, laminar, planar flow down a vertical wall. The thickness,, of the liquid film remains constant. Since the liquid free surface is eposed
ns_0 A viscous, incompressible, Newtonian liquid flows in stead, laminar, planar flow down a vertical wall. The thickness,, of the liquid film remains constant. Since the liquid free surface is eposed
Precision Mass Flow Metering For CVD Applications.
 Precision Mass Flow Metering For CVD Applications. Ir. H.J. Boer Research Department of Bronkhorst High-Tech B.V. Nijverheidsstraat 1A, 7261 AK Ruurlo The Netherlands. Tel: +31 (0)573 458800 Fax: +31 (0)573
Precision Mass Flow Metering For CVD Applications. Ir. H.J. Boer Research Department of Bronkhorst High-Tech B.V. Nijverheidsstraat 1A, 7261 AK Ruurlo The Netherlands. Tel: +31 (0)573 458800 Fax: +31 (0)573
Iterative calculation of the heat transfer coefficient
 Iterative calculation of the heat transfer coefficient D.Roncati Progettazione Ottica Roncati, via Panfilio, 17 44121 Ferrara Aim The plate temperature of a cooling heat sink is an important parameter
Iterative calculation of the heat transfer coefficient D.Roncati Progettazione Ottica Roncati, via Panfilio, 17 44121 Ferrara Aim The plate temperature of a cooling heat sink is an important parameter
HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER
 MEL242 HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Prabal Talukdar Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering g IIT Delhi [email protected] MECH/IITD Course Coordinator: Dr. Prabal Talukdar Room No: III,
MEL242 HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Prabal Talukdar Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering g IIT Delhi [email protected] MECH/IITD Course Coordinator: Dr. Prabal Talukdar Room No: III,
A technical guide to 2014 key stage 2 to key stage 4 value added measures
 A technical guide to 2014 key tage 2 to key tage 4 value added meaure CONTENTS Introduction: PAGE NO. What i value added? 2 Change to value added methodology in 2014 4 Interpretation: Interpreting chool
A technical guide to 2014 key tage 2 to key tage 4 value added meaure CONTENTS Introduction: PAGE NO. What i value added? 2 Change to value added methodology in 2014 4 Interpretation: Interpreting chool
Turbulent Mixing and Chemical Reaction in Stirred Tanks
 Turbulent Mixing and Chemical Reaction in Stirred Tank André Bakker Julian B. Faano Blend time and chemical product ditribution in turbulent agitated veel can be predicted with the aid of Computational
Turbulent Mixing and Chemical Reaction in Stirred Tank André Bakker Julian B. Faano Blend time and chemical product ditribution in turbulent agitated veel can be predicted with the aid of Computational
Black-Scholes model under Arithmetic Brownian Motion
 Black-Scholes model under Arithmetic Brownian Motion Marek Kolman Uniersity of Economics Prague December 22 23 Abstract Usually in the Black-Scholes world it is assumed that a stock follows a Geometric
Black-Scholes model under Arithmetic Brownian Motion Marek Kolman Uniersity of Economics Prague December 22 23 Abstract Usually in the Black-Scholes world it is assumed that a stock follows a Geometric
On sediment transport under dam-break flow
 J. Fluid Mech. (2002), vol. 473, pp. 265 274. c 2002 Cambridge Univerity Pre DOI: 10.1017/S0022112002002550 Printed in the United Kingdom 265 On ediment tranport under dam-break flow By DAVID PRITCHARD
J. Fluid Mech. (2002), vol. 473, pp. 265 274. c 2002 Cambridge Univerity Pre DOI: 10.1017/S0022112002002550 Printed in the United Kingdom 265 On ediment tranport under dam-break flow By DAVID PRITCHARD
Lecture 6 Black-Scholes PDE
 Lecture 6 Black-Scholes PDE Lecture Notes by Andrzej Palczewski Computational Finance p. 1 Pricing function Let the dynamics of underlining S t be given in the risk-neutral measure Q by If the contingent
Lecture 6 Black-Scholes PDE Lecture Notes by Andrzej Palczewski Computational Finance p. 1 Pricing function Let the dynamics of underlining S t be given in the risk-neutral measure Q by If the contingent
Ross Recovery Empirical Project
 Jens Carsten Jackwert Marco Menner University of Konstanz [email protected] ttp://www.wiwi.ni-konstanz.e/jackwert/ 2 Motivation State prices q pricing kernel m pysical probabilities f Normally
Jens Carsten Jackwert Marco Menner University of Konstanz [email protected] ttp://www.wiwi.ni-konstanz.e/jackwert/ 2 Motivation State prices q pricing kernel m pysical probabilities f Normally
Pipe flow with friction losses solutions using HP and TI calculators By Gilberto E. Urroz, October 2005
 Pipe low with riction losses solutions using HP and TI calculators By Gilberto E. Urroz, October 005 1. arcy-weisbach Equation and riction actor The basic equation governing riction losses in a pipeline
Pipe low with riction losses solutions using HP and TI calculators By Gilberto E. Urroz, October 005 1. arcy-weisbach Equation and riction actor The basic equation governing riction losses in a pipeline
240EQ014 - Transportation Science
 Coordinating unit: 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering Teaching unit: 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2015 MASTER'S DEGREE IN CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Coordinating unit: 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering Teaching unit: 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2015 MASTER'S DEGREE IN CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
LAB1 2D and 3D step-index waveguides. TE and TM modes.
 LAB1 2D and 3D tep-index waveguide. T and TM mode. 1. Getting tarted 1.1. The purpoe o thi laboratory are: - T/TM mode propagation in 2D (lab waveguide) tep-index waveguide a a unction o guide peciic parameter
LAB1 2D and 3D tep-index waveguide. T and TM mode. 1. Getting tarted 1.1. The purpoe o thi laboratory are: - T/TM mode propagation in 2D (lab waveguide) tep-index waveguide a a unction o guide peciic parameter
Flow Calculations for the V-Cone and Wafer-Cone Flowmeters
 Basic low equation: Flow alculations or the V-one an Waer-one Floweters π g c ΔPps ρ 1 Volue lowrate π lb g c ρ ΔPps s 1 Δ Pps ΔPwc 5. 197 1 Mass lowrate 60 600 ac ach 7.805 7. 805 gp ac gph ach π Δ PPa
Basic low equation: Flow alculations or the V-one an Waer-one Floweters π g c ΔPps ρ 1 Volue lowrate π lb g c ρ ΔPps s 1 Δ Pps ΔPwc 5. 197 1 Mass lowrate 60 600 ac ach 7.805 7. 805 gp ac gph ach π Δ PPa
Optimal Digital Content Distribution Strategy in the Presence of the Consumer-to-Consumer Channel
 Optimal Digital Content Ditribution Strategy in the Preence o the Conumer-to-Conumer Channel Yunang Feng, Zhiling Guo, and Wei-yu Kevin Chiang Yu n a n g Fe n g received hi PhD in Inormation Sytem rom
Optimal Digital Content Ditribution Strategy in the Preence o the Conumer-to-Conumer Channel Yunang Feng, Zhiling Guo, and Wei-yu Kevin Chiang Yu n a n g Fe n g received hi PhD in Inormation Sytem rom
Dimensionless versus Dimensional Analysis in CFD and Heat Transfer
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2 Boston Dimensionless versus Dimensional Analysis in CFD and Heat Transfer Heather E Dillon,, Ashley Emery, RJ Cochran 2, and Ann Mescher University
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2 Boston Dimensionless versus Dimensional Analysis in CFD and Heat Transfer Heather E Dillon,, Ashley Emery, RJ Cochran 2, and Ann Mescher University
Heat transfer in Flow Through Conduits
 Heat transfer in Flow Through Conduits R. Shankar Suramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University A common situation encountered y the chemical engineer is heat transfer
Heat transfer in Flow Through Conduits R. Shankar Suramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University A common situation encountered y the chemical engineer is heat transfer
FLUID FLOW STREAMLINE LAMINAR FLOW TURBULENT FLOW REYNOLDS NUMBER
 VISUAL PHYSICS School of Physics University of Sydney Australia FLUID FLOW STREAMLINE LAMINAR FLOW TURBULENT FLOW REYNOLDS NUMBER? What type of fluid flow is observed? The above pictures show how the effect
VISUAL PHYSICS School of Physics University of Sydney Australia FLUID FLOW STREAMLINE LAMINAR FLOW TURBULENT FLOW REYNOLDS NUMBER? What type of fluid flow is observed? The above pictures show how the effect
THE FLEXURE AND SHEAR DESIGN OF CORBEL (BRACKET)
 http://silsipil96.blogspot.com/ [email protected] CHPTER 11 THE FLEXURE ND SHER DESIGN OF CORBEL (BRCKET 11.1 INTRODUCTION Corbel or brcket is reinorce concrete member is short-hnche cntilever se to spport
http://silsipil96.blogspot.com/ [email protected] CHPTER 11 THE FLEXURE ND SHER DESIGN OF CORBEL (BRCKET 11.1 INTRODUCTION Corbel or brcket is reinorce concrete member is short-hnche cntilever se to spport
Poiseuille and Nusselt Numbers for Laminar Flow in Microchannels with Rounded Corners
 iseuille and sselt mbers for Laminar Flow in Microchannels with Rounded Corners Marco LORENZINI 1,, Gian Luca MORINI 1, Corresponding author: Tel.: ++39 051 2093293; Fax: ++39 051 2090544; Email: [email protected]
iseuille and sselt mbers for Laminar Flow in Microchannels with Rounded Corners Marco LORENZINI 1,, Gian Luca MORINI 1, Corresponding author: Tel.: ++39 051 2093293; Fax: ++39 051 2090544; Email: [email protected]
3 The boundary layer equations
 3 The boundar laer equations Having introduced the concept of the boundar laer (BL), we now turn to the task of deriving the equations that govern the flow inside it. We focus throughout on the case of
3 The boundar laer equations Having introduced the concept of the boundar laer (BL), we now turn to the task of deriving the equations that govern the flow inside it. We focus throughout on the case of
Viscous flow in pipe
 Viscous flow in pipe Henryk Kudela Contents 1 Laminar or turbulent flow 1 2 Balance of Momentum - Navier-Stokes Equation 2 3 Laminar flow in pipe 2 3.1 Friction factor for laminar flow...........................
Viscous flow in pipe Henryk Kudela Contents 1 Laminar or turbulent flow 1 2 Balance of Momentum - Navier-Stokes Equation 2 3 Laminar flow in pipe 2 3.1 Friction factor for laminar flow...........................
CE 3500 Fluid Mechanics / Fall 2014 / City College of New York
 1 Drag Coefficient The force ( F ) of the wind blowing against a building is given by F=C D ρu 2 A/2, where U is the wind speed, ρ is density of the air, A the cross-sectional area of the building, and
1 Drag Coefficient The force ( F ) of the wind blowing against a building is given by F=C D ρu 2 A/2, where U is the wind speed, ρ is density of the air, A the cross-sectional area of the building, and
Advanced Multiphase Modeling of Solidification
 Advanced Multiphae Modeling o Solidiication with OpenFOAM A. Vakhruhev 1, A. Ludwig 2, M. Wu 1, Y. Tang 3, G. Hackl 3, G. Nitzl 4 1 Chritian Doppler Laboratory or Advanced roce Simulation o Solidiication
Advanced Multiphae Modeling o Solidiication with OpenFOAM A. Vakhruhev 1, A. Ludwig 2, M. Wu 1, Y. Tang 3, G. Hackl 3, G. Nitzl 4 1 Chritian Doppler Laboratory or Advanced roce Simulation o Solidiication
University of Maryland Fraternity & Sorority Life Spring 2015 Academic Report
 University of Maryland Fraternity & Sorority Life Academic Report Academic and Population Statistics Population: # of Students: # of New Members: Avg. Size: Avg. GPA: % of the Undergraduate Population
University of Maryland Fraternity & Sorority Life Academic Report Academic and Population Statistics Population: # of Students: # of New Members: Avg. Size: Avg. GPA: % of the Undergraduate Population
Acceleration due to Gravity
 Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
Ch 2 Properties of Fluids - II. Ideal Fluids. Real Fluids. Viscosity (1) Viscosity (3) Viscosity (2)
 Ch 2 Properties of Fluids - II Ideal Fluids 1 Prepared for CEE 3500 CEE Fluid Mechanics by Gilberto E. Urroz, August 2005 2 Ideal fluid: a fluid with no friction Also referred to as an inviscid (zero viscosity)
Ch 2 Properties of Fluids - II Ideal Fluids 1 Prepared for CEE 3500 CEE Fluid Mechanics by Gilberto E. Urroz, August 2005 2 Ideal fluid: a fluid with no friction Also referred to as an inviscid (zero viscosity)
Two Dimensional FEM Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Isotropic Solid Media using COMSOL
 Excerpt from the Proceeding of the COMSO Conference 0 India Two Dimenional FEM Simulation of Ultraonic Wave Propagation in Iotropic Solid Media uing COMSO Bikah Ghoe *, Krihnan Balaubramaniam *, C V Krihnamurthy
Excerpt from the Proceeding of the COMSO Conference 0 India Two Dimenional FEM Simulation of Ultraonic Wave Propagation in Iotropic Solid Media uing COMSO Bikah Ghoe *, Krihnan Balaubramaniam *, C V Krihnamurthy
