Electrolyte Physiology. Something in the way she moves
|
|
|
- Annabel Simpson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me
2 Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small ions PORES: medium-sized molecules (sweat) TRANSPORT PROTEINS
3 Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small ions PORES: medium-sized molecules (sweat) TRANSPORT PROTEINS
4 Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small ions PORES: medium-sized molecules (sweat) TRANSPORT PROTEINS
5 Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small ions PORES: medium-sized molecules (sweat) TRANSPORT PROTEINS
6 Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small ions PORES: medium-sized molecules (sweat) TRANSPORT PROTEINS
7 Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small ions PORES: medium-sized molecules (sweat) TRANSPORT PROTEINS
8 Electrolyte Movement Depolarize: to become positive from baseline Overshoot: more positive than the threshold potential Repolarization: to become negative from a positive potential Hyperpolarization ( or undershoot): to become more negative than baseline potential
9 Sodium Channels
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 HEART BLOCKS NORMAL PR-interval : <0.2sec FIRST DEGREE HEART BLOCK: fixed and prolonged PR-interval Problem is AT the SA node or BETWEEN the SA node and the AV node NO treatment necessary Speeding up the heart rate( exercise) will make the block disappear
17 HEART BLOCKS, cont SECOND DEGREE HEART BLOCK MOBITZ 1: progressive lengthening of PR-interval until QRS is dropped Early ischemia at the AV node Also called WENCKEBACK S Put in pacemaker if symptomatic; do nothing if asymptomatic
18 HEART BLOCKS, cont MOBITZ II: PR-interval is normal; QRS complexes are dropped erratically Late ischemia at the AV node Some cells are negative; some cells are positive ALL must have a pacemaker
19 HEART BLOCKS, cont THIRD DEGREE HEART BLOCK COMPLETE AV DISSOCIATION AV-node has INFARCTED P-waves and QRS complexes have NO relationship ALL must have a pacemaker
20 QRS COMPLEXES Premature ventricular complex (PVC) No P- wave; wide QRS complex; a pause following the QRS complex BIGEMINY: A PVC every other beat TRIGEMINY: A PVC every third beat VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA: three or more consecutive PVCs with a minimum heart rate of 150 VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION: NO recognizable QRS complexes
21 VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA IF PATIENT STABLE: treat with medication IF PATIENT UNSTABLE: SHOCK with 200joules SHOCK with 300joules SHOCK with 360(max)joules LIDOCAINE SHOCK BRETYLIUM or AMIODORONE
22 VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION EPINEPHRINE TREAT LIKE VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
23 ATRIAL ARRHYTHMIAS Premature atrial contraction (PAC) Multifocal atrial tachycardia Paroxysmal supraventricular tachcardia Atrial flutter Atrial fibrillation If ACUTE and STABLE: treat with medication If ACUTE and UNSTABLE: DEFIBRILLATE If CHRONIC: treat medically; put on coumadin May defibrillate after minimum 2 weeks on coumadin TX: use synchronized button
24 ELECTROLYTES AFFECT DEPOLARIZATIONS FOUR SPECIALIZED MEMBRANES NEURONS SKELETAL MUSCLES SMOOTH MUSCLES CARDIAC MUSCLE ATRIUM: uses calcium to depolarize VENTRICLE: uses sodium to depolarize; uses intracellular calcium to contract; depends on extracellular calcium to trigger off intracellular calcium release
25 HYPERMAGNESEMIA LESS LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE AFFECTS CALCIUM AND POTASSIUM GETS IN THE WAY OF SODIUM TX: IV normal saline; loop diuretic
26 HYPOMAGNESEMIA MORE LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE AFFECTS CALCIUM and POTASSIUM AFFECTS all KINASES TX: magnesium sulphate
27 HYPERCALCEMIA LESS LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE everywhere except the atrium( more likely) SMOOTH MUSCLE: initially less likely (blocks nerve) to depolarize, then more likely to CONTRACT (due to second messenger systems) TX: IV normal saline; loop diuretics
28 HYPOCALCEMIA MORE LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE everywhere except the atrium( less likely) WILL AFFECT SECOND MESSENGER SYSTEMS SMOOTH MUSCLE: initially more likely to depolarize( nerve fires more) followed by less likely to CONTRACT (affects second messenger systems)
29 HYPERKALEMIA Initially MORE LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE Potassium will flow into the cell, taking the membrane potential closer to threshold Potassium gets trapped INSIDE the cell during repolarization; repolarization therefore takes longer > LESS LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE Peaked T waves Widened T waves Prolonged QT interval Predisposes to arrythmias
30 HYPOKALEMIA LESS LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE Potassium will rush out of the cells, making them more negative Cells repolarize even faster Cells repolarize too much Narrow T waves Flat T waves Flipped and inverted T wave The U wave( exaggerated flipped T wave)
31 HYPERNATREMIA MORE LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE SODIUM rushes into the cells, making them more positive After sometime, the NA-K ATP-ase kicks Into high gear, making the cells more negative( less likely to depolarize) TX: IV normal saline; correct slowly
32 HYPONATREMIA MORE LIKELY TO DEPOLARIZE SODIUM will now leak out of a cell by Na- K exchange When calcium leaks INTO cell in exchange for sodium leaking OUT, cells become more positive TX: IV normal saline; correct slowly Use 3% saline if sodium under 120 with symptoms Use fluid restriction if hyponatremia due to SIADH
33 Hyponatremia
34 The End: Turn off the lytes
35 Antiarrhythmics
36 Class 1: Na channel blockers 1a Quinidine Procainamide Disepyramide 1b Lidocaine Tocainide Mixelitine Phenytoin 1c Encainide Flecainide propofenone
37 Class II: Beta Blockers All end in lol Specific beta 1: begins with A thru M, but NOT L or C Blocks B-1 and B-2: begins with N thru Z, including L and C
38 Class II: Beta Blockers Propanolol Esmalol Sotalol Timalol Butexalol Labetalol Carvedilol Acebutalol Atenalol Pindalol
39 Class III: K Channel blockers Napa ( from procainamide) Sotalol Bretylium Amiodorone
40 Class IV: Ca Channel blocker Verapamil Diltiazem Nifedipine Nicardipine Nimodipine Femlodipine Amlodipine Quinidine Procainamide Phenytoin
41 IF YOU PLAY WITH LYTES
42 You may go down IN FLAMES
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT. Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
Interpretation of Laboratory Values
 Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response
 Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
Cardiovascular System & Its Diseases. Lecture #4 Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrhythmias
 Cardiovascular System & Its Diseases Lecture #4 Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrhythmias Dr. Derek Bowie, Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics, Room 1317, McIntyre Bldg, McGill University derek.bowie@mcgill.ca
Cardiovascular System & Its Diseases Lecture #4 Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrhythmias Dr. Derek Bowie, Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics, Room 1317, McIntyre Bldg, McGill University derek.bowie@mcgill.ca
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome
 Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
School of Health Sciences
 School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
 ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
Introduction to Cardiac Electrophysiology, the Electrocardiogram, and Cardiac Arrhythmias INTRODUCTION
 Introduction to Cardiac Electrophysiology, the Electrocardiogram, and Cardiac Arrhythmias Alfred E. Buxton, M.D., Kristin E. Ellison, M.D., Malcolm M. Kirk, M.D., Gregory F. Michaud, M.D. INTRODUCTION
Introduction to Cardiac Electrophysiology, the Electrocardiogram, and Cardiac Arrhythmias Alfred E. Buxton, M.D., Kristin E. Ellison, M.D., Malcolm M. Kirk, M.D., Gregory F. Michaud, M.D. INTRODUCTION
Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse
 PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
Anti Arrhythmic Agents
 Introduction to Antiarrhythmic Agents Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Anti Arrhythmic Agents Introduction to anti arrhythmic agents Mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis Management
Introduction to Antiarrhythmic Agents Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Anti Arrhythmic Agents Introduction to anti arrhythmic agents Mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis Management
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide
 Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION IN THE 21 ST CENTURY TIMOTHY DOWLING, D.O. FAMILY PHYSICIAN GOALS AND OBJECTIVES At The end of this talk you should understand: What is Atrial Fibrillation Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
Bi 360: Midterm Review
 Bi 360: Midterm Review Basic Neurobiology 1) Many axons are surrounded by a fatty insulating sheath called myelin, which is interrupted at regular intervals at the Nodes of Ranvier, where the action potential
Bi 360: Midterm Review Basic Neurobiology 1) Many axons are surrounded by a fatty insulating sheath called myelin, which is interrupted at regular intervals at the Nodes of Ranvier, where the action potential
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
TOP 5. The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac. Arrhythmias in Dogs & Cats. Sinus Arrhythmia. TOP 5 Arrhythmias Seen in Dogs & Cats
 Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date. The Resting Membrane Potential
 REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
The Action Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.
 The Action Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) ** If this is not printed in color, it is suggested you
The Action Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) ** If this is not printed in color, it is suggested you
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication. Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South
 Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
Medical management of CHF: A New Class of Medication Al Timothy, M.D. Cardiovascular Institute of the South Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Amgen Background Chronic systolic congestive heart failure remains
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Welcome to Vibrationdata
 Welcome to Vibrationdata Acoustics Shock Vibration Signal Processing December 2004 Newsletter Ni hao Feature Articles One of my goals is to measure a wide variety of oscillating signals. In some sense,
Welcome to Vibrationdata Acoustics Shock Vibration Signal Processing December 2004 Newsletter Ni hao Feature Articles One of my goals is to measure a wide variety of oscillating signals. In some sense,
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
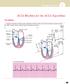 ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR. Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University
 Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
PSIO 603/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 2007 MRB 422; 626-6833 jburt@u.arizona.edu. MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle
 SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
EXCITABILITY & ACTION POTENTIALS page 1
 page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Excitable Tissue: able to generate Action Potentials (APs) (e.g. neurons, muscle cells) B. Neurons (nerve cells) a. components 1) soma (cell body): metabolic center (vital, always
page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Excitable Tissue: able to generate Action Potentials (APs) (e.g. neurons, muscle cells) B. Neurons (nerve cells) a. components 1) soma (cell body): metabolic center (vital, always
Lecture Outline. Cardiovascular Physiology. Cardiovascular System Function. Functional Anatomy of the Heart
 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE. MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011
 ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
Antiarrhythmic drug pharmacology
 Antiarrhythmic drug pharmacology Samuel C. Dudley, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. 6/7/2003 1 Setting the membrane potential Nernst E eq [ S] = 61log i [ S] o Current I Na Equil. Pot. +60 mv Effect on E m Depolarize
Antiarrhythmic drug pharmacology Samuel C. Dudley, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. 6/7/2003 1 Setting the membrane potential Nernst E eq [ S] = 61log i [ S] o Current I Na Equil. Pot. +60 mv Effect on E m Depolarize
LAST NAME VAT NUMBER. PHONE (Important for possible case discussion)
 Long QT Panel CUSTOMER INFORMATION FIRST NAME LAST NAME ORGANIZATION VAT NUMBER BILLING ADDRESS 1ST LINE BILLING ADDRESS 2ND LINE POST CODE CITY COUNTRY EMAIL (Required) PHONE (Important for possible case
Long QT Panel CUSTOMER INFORMATION FIRST NAME LAST NAME ORGANIZATION VAT NUMBER BILLING ADDRESS 1ST LINE BILLING ADDRESS 2ND LINE POST CODE CITY COUNTRY EMAIL (Required) PHONE (Important for possible case
Lethal Arrhythmias: Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130
 Lethal Arrhythmias: Advanced Rhythm Interpretation Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for five (5.0) contact hours. This course expires January 24,
Lethal Arrhythmias: Advanced Rhythm Interpretation Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for five (5.0) contact hours. This course expires January 24,
Lab 1: Simulation of Resting Membrane Potential and Action Potential
 Lab 1: Simulation of Resting Membrane Potential and Action Potential Overview The aim of the present laboratory exercise is to simulate how changes in the ion concentration or ionic conductance can change
Lab 1: Simulation of Resting Membrane Potential and Action Potential Overview The aim of the present laboratory exercise is to simulate how changes in the ion concentration or ionic conductance can change
UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD. Ex parte VINOD SHARMA and DANIEL C. SIGG
 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD Ex parte VINOD SHARMA and DANIEL C. SIGG Appeal 2012-000284 Technology Center 1600 Before ERIC GRIMES, FRANCISCO C. PRATS,
UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD Ex parte VINOD SHARMA and DANIEL C. SIGG Appeal 2012-000284 Technology Center 1600 Before ERIC GRIMES, FRANCISCO C. PRATS,
EKG Abnormalities. I. Early repolarization abnormality:
 I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It?
 The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
The Emerging Atrial Fibrillation Epidemic: Treat It, Leave It or Burn It? Indiana Chapter-ACC 17 th Annual Meeting Indianapolis, Indiana October 19, 2013 Deepak Bhakta MD FACC FACP FAHA FHRS CCDS Associate
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways. for the primary care physicians
 Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
Atrial fibrillation (AF) care pathways for the primary care physicians by University of Minnesota Physicians Heart, October, 2011 Evaluation by the primary care physician: 1. Comprehensive history and
Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. A Guide for Adults
 Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Adults Fast Facts n There are different ways to treat atrial fibrillation (A-fib). One kind of treatment involves putting the heart back into
Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Adults Fast Facts n There are different ways to treat atrial fibrillation (A-fib). One kind of treatment involves putting the heart back into
Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109
 Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109 Interventions to prevent cardiac arrest + Airway management + Ventilation support + Treatment of bradyarrhythmias & Tachyarrhythmias Treat cardiac arrest
Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109 Interventions to prevent cardiac arrest + Airway management + Ventilation support + Treatment of bradyarrhythmias & Tachyarrhythmias Treat cardiac arrest
JAPI VOL. 52 NOVEMBER 2004 www.japi.org 883
 Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Table of Contents Error! Bookmark not defined.
 Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Tachyarrhythmias in the ICU
 Tachyarrhythmias in the ICU ACNP/PA Critical Care Boot Camp Vanderbilt University Medical Center September 21, 2015 Ariel Kappa RN, MSN, ACNP-BC Acute Arrhythmias are the gremlins of the ICU because they
Tachyarrhythmias in the ICU ACNP/PA Critical Care Boot Camp Vanderbilt University Medical Center September 21, 2015 Ariel Kappa RN, MSN, ACNP-BC Acute Arrhythmias are the gremlins of the ICU because they
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
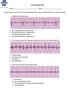 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
An ECG Primer. Quick Look. I saw it, but I did not realize it. Elizabeth Peabody
 4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
Trust Guideline for the Management of New-born Babies with abnormal heart rhythm
 A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
Premature Ventricular Contractions. Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS
 Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue
 12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, ARRHYTHMIAS AND PACING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
TABLE 1 Clinical Classification of AF. New onset AF (first detected) Paroxysmal (<7 days, mostly < 24 hours)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
MEDICATIONS USED IN ADULT CODE BLUE EMERGENCIES. Source: ACLS Provider Manual. American Heart Association. 2001, 2002. Updated 2003.
 MEDICATIONS USED IN ADULT CODE BLUE EMERGENCIES Source: ACLS Provider Manual. American Heart Association. 2001, 2002. Updated 2003. 1 ET Administration Atropine o First drug for symptomatic sinus bradycardia
MEDICATIONS USED IN ADULT CODE BLUE EMERGENCIES Source: ACLS Provider Manual. American Heart Association. 2001, 2002. Updated 2003. 1 ET Administration Atropine o First drug for symptomatic sinus bradycardia
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
Atrial Fibrillation Centre
 About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Monitoring EKG. Evaluation copy
 Monitoring EKG Computer 28 An electrocardiogram, or EKG, is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. A typical EKG tracing consists of five identifiable deflections. Each
Monitoring EKG Computer 28 An electrocardiogram, or EKG, is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. A typical EKG tracing consists of five identifiable deflections. Each
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AF) DRUG INFORMATION
 Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AF) DRUG INFORMATION Copyright
Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AF) DRUG INFORMATION Copyright
Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
HEART RHYTHM DISORDERS CRAIG A. McPHERSON, M.D., AND LYNDA E. ROSENFELD, M.D.
 HEART RHYTHM DISORDERS CRAIG A. McPHERSON, M.D., AND LYNDA E. ROSENFELD, M.D. INTRODUCTION Heart rhythm disorders, called arrhythmias, pose one of the paradoxes of medicine. Almost anyone s heart will
HEART RHYTHM DISORDERS CRAIG A. McPHERSON, M.D., AND LYNDA E. ROSENFELD, M.D. INTRODUCTION Heart rhythm disorders, called arrhythmias, pose one of the paradoxes of medicine. Almost anyone s heart will
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias
 Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Simulation of an Action Potential using the Hodgkin-Huxley Model in Python. Nathan Law 250560559. Medical Biophysics 3970
 Simulation of an Action Potential using the Hodgkin-Huxley Model in Python Nathan Law 250560559 Medical Biophysics 3970 Instructor: Dr. Ian MacDonald TA: Nathaniel Hayward Project Supervisor: Dr. Andrea
Simulation of an Action Potential using the Hodgkin-Huxley Model in Python Nathan Law 250560559 Medical Biophysics 3970 Instructor: Dr. Ian MacDonald TA: Nathaniel Hayward Project Supervisor: Dr. Andrea
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist
 Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
The Action Potential
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46526 1 The Action Potential OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m46526 1 The Action Potential OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you
