Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
|
|
|
- Coral Quinn
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
2 Electrical Conduction Pathway
3 Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation
4 Cardiac Action Potential Phases
5 Electrical Pathway ECG Waveforms
6 Systole and Diastole ECG Waveforms
7 Leads
8 Einthoven s Triangle
9 MCL1 and MCL6
10 Leadwire Systems
11 Common Monitor Problems Artifact False-high rate Weak signals Wandering baseline Fuzzy baseline (electrical interference) Baseline (no waveforms)
12 Common Arrhythmia Interferences
13 Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: Small, round, before QRS (sinus) PRI: seconds QRS: < 0.12 seconds
14 ECG Paper Each small box is one millimeter (1mm) Each large box (5 small boxes) is 5 millimeters Standard paper speed is 25mm/second Each small box is 0.04 seconds Each large box is 0.20 seconds Convert seconds to milliseconds 1000 X number of boxes in seconds 0.04 sec. = = 40 ms
15 Sinus Bradycardia Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: sinus PRI: sec QRS: <0.12 sec Treatment Drugs: Atropine Epinephrine Intervention: Pacer
16 Sinus Tachycardia Rhythm: Regular Treatment Rate: bpm Treat cause, i.e. fever P wave: sinus PRI: sec QRS: < 0.12 sec
17 Sinus Arrhythmia Rhythm: Irregular Treatment Rate: Usually not necessary. P wave: sinus PRI: seconds QRS: <0.12 seconds
18 Sinus Arrest Rhythm: Irregular Treatment Rate: or < 60 Pacemaker P wave: sinus, absent in pause PRI: sec., absent in pause QRS: <0.12 sec., absent in pause
19 ESCAPE BEATS Sinus Escape Beat Junctional Escape Beat Ventricular Escape Beat
20 SINUS BLOCK Rhythm: Irregular Treatment Rate: or < 60 None P wave: sinus, absent in pause PRI: sec., absent in pause QRS: < 0.12 sec., absent in pause
21 WANDERING PACEMAKER Rhythm: Regular or Irregular Rate: bpm P wave: Change size, shape & direction PRI: < 0.12 seconds, may vary slightly QRS: < 0.12 seconds Treatment: Not usually necessary
22 PREMATURE ATRIAL CONTRACTION (PAC) Rhythm: Regular and irregular because of PAC Rate: Underlying rhythm P wave: Abnormal size, shape and/or direction PRI: or prolonged QRS: < 0.12 seconds Treatment: Not usually necessary
23 Non-conducted PAC Non-conducted P wave, which may occur before, during, or after the T wave preceding the pause. Possible distortion of the slope of the T wave preceding the pause; T wave difference in its height or shape. These are clues showing nonconducted P wave could be hidden in T wave
24 PAC Conduction EARLY A PAC occurring in the rhythm NON-CONDUCTED A premature, abnormally shaped P wave is seen without a QRS ABERRANTLY A PAC with a wide QRS
25 PAC Groupings Bigeminal every other beat is a PAC Trigeminal every third beat is a PAC Paroxsymal abruptly occurring in rhythm PAT Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia
26
27
28 ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA Rhythm: Regular Rate: P wave: Abnormal, hidden in T wave PRI: sec. if measurable QRS: < 0.12 sec. Treatment: Vagal maneuvers / Adenosine IV
29 PSVT
30 ATRIAL FLUTTER Rhythm: Regular or irregular Rate: Varies P wave: Flutter waves PRI: Not measurable QRS: < 0.12 seconds Treatment: Coagulation, Cardioversion, Medications
31 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Rhythm: Grossly irregular Rate: Controlled or Uncontrolled P wave: Fibrillatory waves; Coarse / Fine PRI: Not measurable QRS: < 0.12 seconds
32 P wave features with AV rhythms P wave inverted in Lead II P wave immediately before QRS P wave immediately after QRS P wave hidden in QRS
33 Premature Junctional Contraction (PJC) Rhythm: Regular except premature beat Rate: Underlying rhythm P wave: inverted, before, during or after QRS PRI: Short, <.12 seconds QRS: < 0.12 seconds Treatment: Not required
34 JUNCTIONAL ESCAPE RHYTHM Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: inverted before, during or after QRS PRI: Short, <0.12 seconds QRS: <0.12 seconds Treatment: Symptomatic-atropine, pacing, tx cause
35 Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: inverted before, during or after QRS PRI: Short, < 0.12 seconds QRS: < 0.12 seconds Treatment: Correct the cause if necessary
36 Junctional Tachycardia Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: usually hidden in preceding T wave PRI: Short, < 0.12 seconds, if present QRS: < 0.12 seconds Treatment: Correct cause or adenosine if needed
37 First Degree AV Heart Block Rhythm: Underlying rhythm Treatment Rate: Usually sinus Monitor P wave: Sinus Review Drugs PRI: greater 0.20 seconds & constant QRS: < 0.12 seconds
38 2 nd Degree AV Heart Block (Mobitz I or Type I or Wenckebach) Rhythm: Irregular Treatment Rate: Less than Atrial rate Atropine P wave: Sinus Review Drugs PRI: Progressively lengthens until missing QRS (MIA) (PRI after missing QRS is shorter than the last PRI) QRS: < 0.12 seconds
39 2 nd Degree AV Heart Block (Mobitz II or Type II) Rhythm: Regular unless the conduction varies Rate: # impulses conducted (< 60 bpm) P wave: More than # QRS (ratio or variable) PRI: 0.12 sec. or prolonged, but CONSTANT QRS: < 0.12 seconds, but could be wide Treatment: Pacemaker, Dopamine or Epinephrine
40 3 rd Degree AV Heart Block (Complete Heart Block (CHB) ) Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm (usually) P wave: More p waves than QRS complexes PRI: Varies greatly, no relationship with QRS QRS: < 0.12 if junctional, > 0.12 sec. if ventricular focus Treatment: Pacemaker, atropine (if narrow QRS)
41 Intraventricular Conduction Defect Rhythm: Regular Rate: Usually sinus P wave: Sinus PRI: Normal QRS: Wide, greater than 0.10 sec Treatment: Not necessary
42 Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC) Rhythm: Irregular due to premature beat Rate: Underlying rhythm P wave: None with PVC PRI: Not measurable QRS: Premature, wide, greater than 0.12 sec T wave is usually opposite direction of R wave Treatment: Not necessary or reversible causes
43 Idioventricular Rhythm (Ventricular Escape Rhythm) Rhythm: Usually regular Treatment Rate: bpm or slower Atropine P wave: Absent Pacemaker PRI: Not measurable QRS: Wide, greater than 0.10
44 Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Treatment Rate: bpm No treatment needed P wave: Absent PRI: Not measurable QRS: Wide, greater than 0.10 seconds
45 Ventricular Tachycardia Rhythm: Regular, may be slightly irregular Rate: bpm P wave: None PRI: Not measurable QRS: Wide, greater than 0.12 sec. (T opposite R) Treatment: CPR, Defibrillation, Amiodarone, Epinephrine, Lidocaine (cardioversion with pulse)
46 Torsades de Pointes
47 Ventricular Fibrillation Rhythm: Chaotic, irregular Rate: 0 P wave: Absent PRI: Not measurable QRS: Absent Treatment: CPR, Defibrillation, Epinephrine, Amiodarone, Lidocaine, causes.
48 Ventricular Flutter Rhythm: usually regular Rate: ventricular rate is bpm P waves: None seen PRI: None measurable QRS complex: Very wide, regular Treatment Defibrillation CPR Antiarrhythmics
49 Ventricular Standstill Rhythm: None Rate: Atrial only P wave: Present PRI: Not measurable QRS: Absent Treatment CPR Epinephrine Atropine
50 Ventricular Asystole Rhythm: No rhythm Rate: 0 P wave: None PRI: None QRS: Wide fading until none Treatment CPR Epinephrine Atropine
51 Agonal Wicked Witch is MELTING
52 Pulseless Electrical Activity Rhythm: Fairly regular (not sinus) Rate: bpm P wave: Usually present PRI: Normal QRS: Narrow or Wide Treatment: CPR, Epinephrine, Atropine
53 Indications for Pacing Complete Heart Block Symptomatic type II 2 nd degree AV block Sick sinus syndrome Symptomatic bradycardias with syncope 2 nd degree AV block with episodic ventricular arrhythmias Severe CHF and dilated cardiomyopathy Prevent Atrial fibrillation Hypersensitive carotid sinus syndrome Neurocardiogenic syncope (vasovagle syncope) Long QT syndrome Sleep Apnea
54 Components of Pacing System Pulse Generator Pacing Lead Pacing cable
55 Temporary Pacing Treat symptomatic bradycardia after AMI Treat symptomatic bradycardia after cardiac surgery Hyperkalemia Drug toxicity Before permanent pacemaker implantation in symptomatic patients Bacterial endocarditis Lyme disease Cardiac trauma
56 Types of Temporary Pacemakers Transvenous Epicardial Transcutaneous
57 Transvenous Pacemaker QQYjw6no
58 Epicardial Pacing Cardiac surgery Epicardium One or two atrial or ventricular leads
59 Transcutaneous Pacing
60 Permanent Pacemakers
61 Types of Pacing Single-Chamber Pacing Dual-Chamber Pacing Biventricular Pacing
62 Pacemaker Operation Bipolar Unipolar Asynchronous (Fixed-Rate) Demand
63 Codes for Permanent Pacemakers
64 Pacemaker Functions Capture Strength of stimulus (ma) Pulse width Pacemaker spike Indicated by a wide QRS complex Temporary pulse generators
65 Pacemaker Functions Sensing Millivolts (mv) see intrinsic activity Increase sensitivity decrease mv Decrease sensitivity increase mv Sensitivity threshold testing with temporary pacemakers
66 Pacemaker Functions Stimulation Threshold Testing Temporary pacemakers Minimum pacemaker output for capture Peak threshold Chronic stable threshold Performed each shift
67 Ventricular Paced Rhythm
68 Atrial Pacmaker
69 AV Sequential Pacemaker
70 Pacemaker Malfunctions Loss of capture Inadequate stimulus strength Pacing lead out of position Pacing lead positioned in infarcted tissue Electrolyte imbalances or drug effects Delivery of a pacing stimulus during ventricle s refractory period
71 Undersensing Pacing Malfunctions Asynchronous pacing mode Pacing catheter out of position Intrinsic QRS voltage too low Break in connections, battery failure, or faulty pulse generator Intrinsic ventricular activity occurring during pacemaker s refractory period
72 Pacemaker Malfunctions
73 Pacemaker Malfunctions Oversensing Too sensitive Inhibits ouput Interference from internal and external signals
74 Problems with Pacing
75 Analyzing Paced Rhythms
76 Paced Interval
77 Analyzing Paced Rhythms
78 Pacemaker Rhythm: Regular Rate: Set or own P wave: Present or spike PRI: Normal QRS: Present or spike
79 Sick Sinus Syndrome Rhythm: irregular with sinus pauses Rate: fast, slow or alternating; abrupt changes P wave; varies with changes; may be absent PRI: usually normal; varies with changes QRS: normal; varies with changes
80 Non-Sinus Atrial Rhythm Regular Rate: P wave: inverted before each QRS complex PRI: 0.12 seconds or greater QRS: <0.12 seconds
81 ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA Rhythm: Regular Rate: P wave: Abnormal, hidden in T wave PRI: sec. if measurable QRS: < 0.12 sec. Treatment: Vagal maneuvers / Adenosine IV
82 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Irregular Rate 150 to 250 bpm P wave: changing shapes & mixed with T wave PRI: varies QRS: <0.12 Treatment: Adenosine
83 Supraventricular Arrhythmias Supraventricular Arrhythmias Atrial Fibrillation Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias (PSVT) AV nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) AV reentry tachycardia (AVRT) -WPW -AV reentry over concealed bypass tract Atrial Tachycardia
84 Types of SVT
85 Arrhythmias from Abnormal Conduction Pathways Definition Clinical Implications
86 Physiology of the Accessory Pathway Kent Bundles James Bundle Mahaim s fibers Atriofascicular bypass tracts Concealed accessory pathway
87 Accessory Pathways
88 Location of Accessory Pathways
89 ECG Characteristics
90 Degrees of Preexcitation None Minimal Less than maximum Maximum preexcitation
91 Degrees of Preexcitation
92 Interpretation of Preexcitation Arrhythmia Obtain 12 Lead ECG Compare with resting or normal ECG Assess PR interval Look for delta wave ECG Characteristics Rate and regularity P waves (P ) PRI QRS
93 Accessory Pathway Arrhythmias RECIPROCATING TACHYCARDIA Circus-movement Tachycardia Reentry tachycardia Orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia
94 Reentry
95 AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT) AVNRT Dual AV node physiology both fast and slow conduction pathways are present in the AV node rapidly conducting tissue has a long recovery time -fast boat, long wake slow-conducting pathway has a relatively short recovery time -slow boats can follow more closely
96 AVNRT: Initiation of tachycardia
97 AVNRT
98 ORTHODROMIC TACHYCARDIA
99 ANTIDROMIC TACHYCARDIA
100 LOWN-GANONG-LEVINE SYNDROME
101 3 Criteria for LGL Syndrome 1. Short PR interval (0.12second or less) 2. Normal QRS configuration 3. Recurrent paroxysmal tachycardia
102 WOLF-PARKINSON-WHITE
103
104 WOLF-PARKINSON-WHITE
105 WPW ECG CHARACTERISTICS OVERT WPW Regular, bpm P wave: upright, normal, and appearing only before each QRS PRI: less than 0.12 seconds and constant QRS: great than 0.10 sec. in duration; a delta wave, slurred on the initial upstroke or downstroke of the QRS
106 WPW CHARACTERISTICS Non-evident WPW Regular, bpm; tendency for unprovoked PSVT, atrial flutter, or A fib P wave: upright, normal, and appearing only before each QRS PRI: second and constant QRS: 0.10 sec.
107 WPW CHARACTERISTICS CONCEALED WPW Regular, bpm; tendency for unprovoked PSVT. P wave: upright, normal, and appearing only before each QRS PRI: sec and constant QRS: 0.10 second in duration
108 Mahaim s Fibers Right sided muscular bridges Originate below AV node into the ventricular wall Normal PR interval with a delta wave
109 Clinical Significance of Arrhythmias of Abnormal Conduction Pathways ASSESSMENT: Leads I, II, III, V1 and V6 in PSVT Assess Heart Rates Assess Ventricular Rate Assess Ventricular Rhythm Assess for history of onset
110 Proposed Interventions for Arrhythmias of Abnormal Conduction Pathways. Avoid AV nodal blocking agents in preexcitation syndromes Consider Amiodarone and Magnesium Paroxysms of tachycardia: EP testing Consider surgery or transvenous radio frequency catheter ablation
111 Table of Accessory Pathways
112 Romano-Ward syndrome
113 Atrio-Ventricular Dissociation One P wave for each QRS P wave moves in and out of QRS complex
114 Aberrant Ventricular Conduction Abnormal conduction pathway QRS complex that has the appearance of PVC Seen with Atrial Fibrillation and MAT Single beat or as a run of beats MCL1 lead
115 Ashman s Phenomenon Rhythm: irregular Rate: reflects the underlying rhythm P wave: abnormal configuration; unchanged if in the underlying rhythm RPI: commonly changes on the premature beat; if measurable at all QRS: altered configuration with right bundle-branch block pattern
116 Bundle Branch Blocks QRS wider than.12 in duration V1 Incomplete vs Complete
117 Right & Left-sided PVCs Determined by the direction of the QRS complex ECG strip in MCL1 lead PVC negative right ventricle PVC positive left ventricle
118 Interpolated PVC PVC falls close to the middle of 2 sinus QRS complexes No change in R R interval
119 End-diastolic PVC PVC falls at the very end of the sinus p wave PVC will have a sinus p wave & short PRI
120 Hyperkalemia ECG Changes
121 Hyperkalemia EKG Tracing
122 Hypokalemia ECG Changes Flatten T waves U waves merge with T wave ST segment depressed
123 Hypokalemia EKG
124 Hypercalcemia ECG Changes
125 Hypocalcemia ECG Changes
126 ECG Effects of Digoxin
127 Induced Arrhythmias CAD: monomorphic VT and atrial fib. Inferior MI: Bradycardia, sinus block, JR, AJR, AV Blocks, AVR Acute MIs: AT, Aflutter, Vfib Myocardial Ischemia: Vfib, VT, Premature beats Ischemic heart disease: 2 nd AVB and PVCs Acute Anteroseptal MI: 2 nd AVB-type II, RBBB Coronary thrombus: PEA
128 Radiofrequency Ablation AV Node Ablation Pulmonary Vein Ablation
129 Arrhythmias Treated with Ablation AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT) Accessory Pathway Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter Ventricular tachycardia
130 Ablation Procedure
131 Surgical Ablation The Maze procedure Minimally invasive surgical ablation The modified Maze procedure
132 12 Lead EKG Introduction 10 leads = 12 views of the heart 3 Limb leads, 3 augmented leads and 6 chest leads Monitoring for ST segment, T wave and Q wave changes
133 Lecture Resources Huff, Jane. ECG Workout: Exercises in Arrhythmia Interpretation. 5 th edition. Lippincott Thaler, Malcom S. The Only EKG Book You ll Ever Need. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Walraven,Gail. Basic Arrhythmias. 6 th edition. Pearson/Prentice Hall. Aehlert, Barbara. ECGs Made Easy. 3 rd edition. Mosby; Elsevier ECG Strip Ease; an arrhythmia interpretation Workbook, Lippincott Williams & Wiilkins Lewis, Kathryn. ECG Practical Applications Pocket Reference Guide, Cengage Learning
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
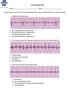 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
COVERAGE GUIDANCE: ABLATION FOR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Question: How should the EGBS Coverage Guidance regarding ablation for atrial fibrillation be applied to the Prioritized List? Question source: Evidence
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide
 Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response
 Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1
 Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109
 Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109 Interventions to prevent cardiac arrest + Airway management + Ventilation support + Treatment of bradyarrhythmias & Tachyarrhythmias Treat cardiac arrest
Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109 Interventions to prevent cardiac arrest + Airway management + Ventilation support + Treatment of bradyarrhythmias & Tachyarrhythmias Treat cardiac arrest
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY
 ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY June, 2011 Question 1: Question 2: There is no pulse with this rhythm. Question 3: Question 4: Question 5: Question 6: Question 7: Question 8: Question 9: Question 10:
ACLS PRE-TEST ANNOTATED ANSWER KEY June, 2011 Question 1: Question 2: There is no pulse with this rhythm. Question 3: Question 4: Question 5: Question 6: Question 7: Question 8: Question 9: Question 10:
School of Health Sciences
 School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
An ECG Primer. Quick Look. I saw it, but I did not realize it. Elizabeth Peabody
 4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
EKG Abnormalities. I. Early repolarization abnormality:
 I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
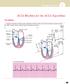 ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
TOP 5. The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac. Arrhythmias in Dogs & Cats. Sinus Arrhythmia. TOP 5 Arrhythmias Seen in Dogs & Cats
 Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
American Heart Association ACLS Pre-Course Self Assessment Dec., 2006. ECG Analysis. Name the following rhythms from the list below:
 American Heart Association ACLS Pre-Course Self Assessment Dec., 2006 ECG Analysis This pre-test is exactly the same as the pretest on the ACLS Provider manual CD. This paper version can be completed in
American Heart Association ACLS Pre-Course Self Assessment Dec., 2006 ECG Analysis This pre-test is exactly the same as the pretest on the ACLS Provider manual CD. This paper version can be completed in
Official Online ACLS Exam
 \ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
\ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
JAPI VOL. 52 NOVEMBER 2004 www.japi.org 883
 Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Review Article Wide Complex Tachycardia : Recognition and Management in the Emergency Room IB Ray Abstract Cardiac arrhythmias often present as urgent medical conditions requiring immediate care. Patient
Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 11, No. 3, July 2010 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol11/jul2010/89015.htm Recurrent AF: Choosing the Right Medication. Basamad Z. * Assistant Professor, Department
Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD
 92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist
 Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station Checklist VF/VT 00 American Heart Association Adult Cardiac Arrest Shout for Help/Activate Emergency Response Epinephrine every - min Amiodarone Start CPR
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA
 Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA Intrinsic Conduction Automaticity-cardiac cells ability to spontaneously depolarize and initiate impulse Depolarization-cardiac cells go to a+ intracellular and
Michael Hartman, CRNA, DNP, MSN, BSN, BA Intrinsic Conduction Automaticity-cardiac cells ability to spontaneously depolarize and initiate impulse Depolarization-cardiac cells go to a+ intracellular and
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians
 Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
If you do not wish to print the entire pre-test you may print Page 2 only to write your answers, score your test, and turn in to your instructor.
 This is a SAMPLE of the pretest you can access with your AHA PALS Course Manual at Heart.org/Eccstudent using your personal code that comes with your PALS Course Manual The American Heart Association strongly
This is a SAMPLE of the pretest you can access with your AHA PALS Course Manual at Heart.org/Eccstudent using your personal code that comes with your PALS Course Manual The American Heart Association strongly
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
IU Health ACLS Study Guide
 IU Health ACLS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming ACLS Class REVISED SEPTEMBER 2011 ON APRIL 1, 2011 WE BEGAN TEACHING THE 2010 AHA GUIDELINES. WE HIGHLY RECOMMEND REVIEWING THE NEW ALGORYHMS FOUND
IU Health ACLS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming ACLS Class REVISED SEPTEMBER 2011 ON APRIL 1, 2011 WE BEGAN TEACHING THE 2010 AHA GUIDELINES. WE HIGHLY RECOMMEND REVIEWING THE NEW ALGORYHMS FOUND
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR. Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University
 Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
Table of Contents Error! Bookmark not defined.
 Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Introduction. Sinus Rhythms. Premature Beats. Secondary article. John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
 John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT. Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO SVT Graham C. Wong MD MPH Division of Cardiology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART SA node His bundle Left bundle AV node Right
Advanced EKG Interpretation
 Advanced EKG Interpretation JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS AND NURSING INTERVENTIONS Objectives Identify specific cardiac dysrhythmias Describe appropriate nursing interventions for specific dysrhythmias Junctional
Advanced EKG Interpretation JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS AND NURSING INTERVENTIONS Objectives Identify specific cardiac dysrhythmias Describe appropriate nursing interventions for specific dysrhythmias Junctional
Ngaire has Palpitations
 Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Ngaire has Palpitations David Heaven Cardiac Electrophysiologist/Heart Rhythm Specialist Middlemore, Auckland City and Mercy Hospitals Auckland Heart Group MCQ Ms A is 45, and a healthy marathon runner.
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
2 ECG basics. Leads and planes. Leads. Planes. from different perspectives, which are called leads and planes.
 558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
 ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767 Copyright 2010 American Heart Association ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm Neumar, R. W. et al. Circulation 2010;122:S729-S767
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias
 Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls
 Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
CCAD Training Manual. Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM)
 CCAD Training Manual Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM) Version 1.0 A D Cunningham 19/3/2008 Introduction This manual is intended to assist users of the Notes Client version of the CCAD Cardiac Rhythm Management
CCAD Training Manual Cardiac Rhythm Management (CRM) Version 1.0 A D Cunningham 19/3/2008 Introduction This manual is intended to assist users of the Notes Client version of the CCAD Cardiac Rhythm Management
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
2 Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology
 2 Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Andrew C. Rankin F. Russell Quinn Alan P. Rae 2.1 Introduction... 54 2.2 History of Clinical Electrophysiology... 54 2.3 Methodology... 55 2.3.1 Electrophysiological
2 Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Andrew C. Rankin F. Russell Quinn Alan P. Rae 2.1 Introduction... 54 2.2 History of Clinical Electrophysiology... 54 2.3 Methodology... 55 2.3.1 Electrophysiological
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, ARRHYTHMIAS AND PACING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
Know the histology and gross anatomy of the normal sinoatrial node, atrial conduction pathways, atrioventricular (AV) junction and nod, His bundle, conduction fascicles and terminal intra-ventricular conduction
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008
 Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
Atrial Fibrillation Peter Santucci, MD Revised May, 2008 Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular, disorganized rhythm characterized by a lack of organized mechanical atrial activity. The atrial rate is
UCSF Anesthesia Resident Pearls: Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Pacemakers and ICDs Table of Contents
 UCSF Anesthesia Resident Pearls: Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Pacemakers and ICDs Table of Contents Page 1 Intro Indications for Pacers and ICDs Page 2 Differentiating between Pacers and ICDs
UCSF Anesthesia Resident Pearls: Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Pacemakers and ICDs Table of Contents Page 1 Intro Indications for Pacers and ICDs Page 2 Differentiating between Pacers and ICDs
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
TABLE 1 Clinical Classification of AF. New onset AF (first detected) Paroxysmal (<7 days, mostly < 24 hours)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Deborah Ritchie RN, MN, Robert S Sheldon MD, PhD Cardiovascular Research Group, University of Calgary, Alberta Partly
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery
 Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
 Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ACLS Study Guide BLS Overview CAB
 ACLS Study Guide The ACLS Provider exam is 50-mutiple choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. For students taking ACLS for the first time or renewing students with a current
ACLS Study Guide The ACLS Provider exam is 50-mutiple choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. For students taking ACLS for the first time or renewing students with a current
Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians
 Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians May 2011 Notices These coding suggestions and coverage guidelines do not replace seeking coding advice from the payer and/or your coding staff. The ultimate responsibility
Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians May 2011 Notices These coding suggestions and coverage guidelines do not replace seeking coding advice from the payer and/or your coding staff. The ultimate responsibility
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics. The Myocardial Cell. Chapter 1- Thaler
 Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm
 Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
New resuscitation science and American Heart Association treatment guidelines were released October 28, 2010!
 ACLS Study Guide 2010 Bulletin: New resuscitation science and American Heart Association treatment guidelines were released October 28, 2010! The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains
ACLS Study Guide 2010 Bulletin: New resuscitation science and American Heart Association treatment guidelines were released October 28, 2010! The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal
 How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
