amplification tech A Practical Guide to High Resolution Melt Analysis Genotyping
|
|
|
- Marilyn Perkins
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 amplification tech note 6004 A Practical Guide to High Resolution Melt Analysis Genotyping Sean Taylor, Rachel Scott, Richard Kurtz, Carl Fisher, Viresh Patel, and Frank Bizouarn, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA Introduction Classifying and understanding genetic variation between populations and individuals is an important aim in the field of genomics. Many common diseases (diabetes, cancer, osteoporosis, etc.) and clinically relevant phenotypic traits are elicited from the complex interaction between a subset of multiple gene products and environmental factors. The unique genetic profile of an individual confers susceptibility to a given trait or disease. Consequently, there is a rapidly growing interest in quantifiable methods for mutation screening in life science research. Such methods are used for detecting genes responsible for diverse traits in organisms from all biological kingdoms. Some notable examples include resistance to parasites or yield in plants (Dracatos et al. 2008, Alves et al. 2008), drug resistance in microorganisms (Zhao et al. 2010), and genetic susceptibility to cancer in humans (Lascorz et al. 2010). High resolution melt (HRM) analysis is the quantitative analysis of the melt curve of a DNA fragment following amplification by PCR and can be considered the next-generation application of amplicon melting analysis. It requires a real-time PCR detection system with excellent thermal stability and sensitivity and HRM-dedicated software. The combination of improved qpcr instrumentation and saturating DNA binding dyes has permitted the identification of genetic variation in nucleic acid sequences by the controlled melting of a double-stranded PCR amplicon. New instrument calibration methods coupled with HRM-compatible software permit the rapid analysis of the resulting data sets and the discrimination of DNA sequences based on their composition, length, GC content, or strand complementarity (Garritano et al. 2009). HRM experiments generate DNA melt curve profiles that are both specific and sensitive enough to distinguish nucleic acid species based on small sequence differences, enabling mutation scanning, methylation analysis, and genotyping (Garritano et al. 2009). For example, HRM can be used to detect single-base sequence variations or to discover unknown genetic mutations. It can also be used to quantitatively detect a small proportion of variant DNA in a background of wild-type sequence at sensitivities approaching 5% to study somatically acquired mutations or changes in methylation state (Malentacchi et al. 2009). Furthermore, HRM is a nondestructive method and subsequent characterization of the associated amplicon using gel electrophoresis or sequencing, for example, can be performed after melt analysis. High Resolution Melt Analysis: An Accessible Technique to Screen Targeted SNPs in Multiple Samples The completion of the human genome sequence (Lander et al. 2001, Venter et al. 2001) enabled the identification of millions of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and the construction of a high-density haplotype map (International HapMap Consortium 2005, Frazer et al. 2007). These combined data have opened the door for both small- and large-scale genotyping of case versus control populations of any organism. The government-funded project dbsnp ( is a publicly accessible database of all catalogued SNPs in the genomes of a growing list of model organisms and has become an important resource in the design of SNP profiling experiments. The ongoing discovery and study of new SNPs will help unravel the complex combinations of genetic modifications contributing to important traits in health and disease. Genetic mutations may comprise a single nucleotide change or multiple base changes, insertions, and/or deletions. The detection and genotyping of SNPs, representative of the smallest genetic change, highlights the sensitivity of HRM analysis. SNPs have been categorized into four classes as summarized in Table 1. The class IV SNPs are both the rarest and most difficult to identify because they differ by a single hydrogen bond, resulting in the smallest melt curve temperature shift compared to class I through III. Table 1. SNP classification and frequency. Frequency in the Human Genome SNP Class Base Change (Venter et al. 2001) I C>T, T>C, G>A, A>G 64% II C>A, A>C, G>T, T>G 20% III C>G, G>C 9% IV A>T, T>A 7%
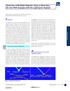
2 In order to perform successful HRM experiments and reliably detect subtle and rare sequence variants, such as Class IV SNPs, careful experimental design and HRM-specific analysis tools are required. Processing Melt Curve Data for High Resolution Melt Analysis Melt curves are run routinely for qpcr experiments to ensure primer specificity, with data typically collected over a temperature range between 65 and 95ºC in 0.5ºC increments. For HRM experiments, data are generally collected at narrower temperature increments than for standard melt curve protocols, commonly in 0.2ºC increments. Depending on the particular template and experimental conditions, the increased density of data points collected can assist with melt profile generation and subsequent sequence discrimination. HRM software is then used to identify areas of stable pre- and post-melt fluorescence intensity from the HRM curve (Figure 1A). These signals are then automatically normalized to relative values of 1.0 and 0, respectively (Figure 1B), eliminating differences in background fluorescence and increasing the ability to detect subtle melt profile differences. Both melting temperature shifts and curve shape are used to identify sequence differences. Homozygous allelic/sequence variants are typically characterized by the temperature (x-axis) shift observed in an HRM melt curve (Figure 1, red and blue traces), whereas heterozygotes are commonly characterized by a change in melt curve shape generated from basepairing mismatches (Figure 1, green trace) generated as a result of destabilized heteroduplex annealing between some of the wild-type and variant strands. Analyzing the data in temperature-shifted view can assist in discriminating these duplex types. HRM data are often plotted using a difference curve to visually magnify the melt profile differences between different clusters of the same genotype (Figure 1C). HRM-Compatible Instrumentation Various designs of HRM-compatible qpcr instruments are available. Access to the following features enables rapid generation of robust HRM data: Flexible input sample volume compatible (5 50 µl) Standard 96- or 384- well format for increased throughput and streamlined reagent dispensing Gradient-enabled thermal block for fast reaction optimization No requirement for proprietary dyes, consumables, or reagents Fast and uniform thermal control with proven ability and A. Melt Curve Unprocessed RFU (x 10 3 ) B. Normalized Melt Curve 1.0 Normalized RFU C. Difference Curve Difference RFU C/C Fig. 1. HRM melt curve analysis. Data were generated using the CFX96 real-time PCR detection system and analyzed using Precision Melt Analysis software. Pre-melt (initial) and post-melt (final) fluorescence signals of all samples (A) were normalized to relative values of 1.0 and 0 (B). Curve differences were magnified by subtracting each curve from the most abundant type or from a userdefined reference (C). RFU, relative fluorescence units. C/T T/T sensitivity to resolve class I through IV SNPs
3 HRM-Compatible Software While all qpcr instruments are packaged with analysis software, not all software packages are suitable for HRM analysis. HRM-compatible software should allow the user to: Compare and combine data from multiple experiments by combining run results into a single melt study Display a plate view for easy identification of sample genotypes A B Share analysis settings among experiments Analyze multiple experiments from a single plate View all charts in a single window for simplified data analysis and interpretation Experimental Design Considerations for Successful High Resolution Melt Analysis Sample Selection and Quality Control qpcr with HRM analysis is a robust technology but, as with most assays, good sample preparation will result in solid, quantifiable data. To ensure quality data, the following points should be considered when preparing DNA for HRM. 1. Target sample purity with A 260/280 and A 260/230 ratios in the range of and , respectively, is recommended. 2. DNA integrity should be examined by gel electrophoresis to ensure the presence of undegraded, high molecular weight DNA fragments. 3. Although a DNA sample may display good integrity and apparent purity, appropriate reference gene(s) amplification is beneficial as an internal positive control and to normalize for concentration variation between samples. 4. The EDTA concentration should be minimized in the DNA solution because EDTA can interfere with the activity of some of the enzymes used in the downstream reactions, particularly when at high concentrations (>0.5 mm). HRM-Compatible Saturating Dyes HRM analysis relies upon the ability to analyze subtle changes in melt kinetics that typically require a dsdna intercalating, saturating dye (Figure 2). These dyes are much less inhibitory to PCR than SYBR Green I and, consequently, can be used at higher (saturating) concentrations to enable consistent and superior discrimination of PCR-amplified DNA (Monis et al. 2005, Mao et al. 2007). Several dye choices are available, the most prevalent being EvaGreen, LCGreen, SYBR GreenER, and SYTO 9. Fig. 2. Saturating and non-saturating dyes. A, when using a non-saturating dye, such as SYBR Green I, dye molecules can relocate to unmelted regions of dsdna during melting of DNA, which results in a small or nonuniform temperature shift in the melt curve; B, when using a saturating dye, the dye molecules from the melted region cannot relocate to the unmelted portion of the fully saturated amplicon, resulting in melt profiles that more accurately reflect DNA sequence. Primer Design and Amplicon Length Analyzing short DNA amplicons can assist with genotype discrimination in HRM experiments. Wherever possible, analyzing amplicons smaller than 100 bp is preferable, especially when sites with a known polymorphism are investigated. It is possible to detect sequence variations with longer amplicons; however, a single base variation influences the melting behavior of a 50 bp amplicon more than a 100 bp amplicon (Figure 3). Reducing amplicon size increases the difference in signal at a given temperature (maximal at the melting temperature [T m ]) between two sequences that differ at only one nucleotide position. This in turn will increase the statistical confidence in calling particular SNPs between samples to give data of higher reliability for publication. A number of programs are available to help design primer pairs and pick target sequences. Primer-BLAST ( cgi?link_loc=blasthomead), a freeware option for designing oligonucleotides, is a program developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information that uses the algorithm Primer3. Primer sequences are compared to the user-selected databases to ensure they are unique and specific for the gene of interest. Beacon Designer (PREMIER Biosoft International), a commercially available program, is also recommended. Beacon Designer designs HRM-specific primers that flank an SNP of interest so that the shortest possible amplicons with detectable melting temperature variation are generated. It is good practice to design and validate three sets of primers to increase the chances of identifying a highly robust pair.
4 A Difference RFU B Difference RFU Fig. 3. Effect of amplicon size on melt curves. Difference plots for melt curves of 50 bp (A) and 100 bp (B) amplicons of wild type (A/A, ), heterozygote (A/T, ), and homozygote SNP (T/T, ) are compared. Clustering and the confidence percentage are increased by using smaller amplicons. Each trace represents a replicate. RFU, relative fluorescence units. Inconsistent data may be the result of secondary structures in single-stranded or partially denatured DNA. Amplicon sequences should be tested with MFOLD ( bioinfo.rpi.edu/cgi-bin/dna-form1.cgi) to ensure they do not form secondary structures during PCR that can increase the complexity of melting profile interpretation. The DINAMelt server ( is also a useful tool to assess target melt domain complexity. PCR Reaction Optimization The success of HRM analysis depends on the quality of the individually amplified PCR products as much as the post-pcr melting protocol and the specific sequence under investigation. Each experimental parameter must be controlled and highly reproducible from sample to sample to ensure successful and reproducible results. Analyzing real-time PCR amplification data prior to HRM analysis can be extremely useful when troubleshooting HRM experiments. Consider the recommended guidelines below for the development of successful HRM experiments. 1. Amplicon quality. HRM software may not be able to discriminate nonspecific reaction products if their melt profiles are similar to the target sequence of interest. Ensure only target amplicons of interest are being amplified by generating post-amplification low resolution melt profiles (0.5 C steps) and, ideally, assessing PCR products from each primer pair using agarose gel electrophoresis. 2. Use sufficient amplification template. Samples should have a threshold or quantification cycle (C q ) less than 30 cycles. Products that amplify late due to limited starting template amount, template degradation, or PCR inhibition produce variable HRM results. 3. Normalize input template concentration. For best results, the amount of template added to the reaction should be consistent. Normalize the starting concentrations so that all amplification plots are within three C q s of each other, that is, within less than a 10-fold range of one another. 4. Use an optimized annealing temperature and reaction efficiency. Annealing temperature has a great impact on reaction specificity and efficiency. Efficient and robust reactions generate reproducible data. Reactions should be optimized using a temperature gradient to determine the appropriate annealing temperature. Test primers and samples for reaction efficiency, which should be between 90 and 110%. 5. Check for aberrant amplification plots. Carefully examine amplification data for abnormal amplification curve shapes. A curve with a jagged log-linear phase or one that reaches a low signal plateau compared to other reactions can indicate poor amplification or a fluorescence signal that is too low for analysis. Unsuccessful amplification can be caused by reaction inhibitors, too little dye, or incorrect reaction setup. HRM from such samples can cause low resolution and poor or inconsistent classification. 6. Normalize input amplicon concentrations. DNA fragment concentration affects its melting temperature. Ensure every reaction has amplified to the plateau phase for reliable and reproducible melt comparisons. 7. Ensure sample-to-sample uniformity. Within an experiment, samples must be of equal volume and contain the same concentration of binding dye. DNA melting behavior is affected by salts in the reaction mix, so the concentration of buffer, Mg 2+, and other salts should be as uniform as possible in all samples.
5 8. Allow sufficient data collection for normalization of pre- and post-melt regions. For easier data interpretation and results with tighter replicates, sufficient baseline data points must be collected. This can be easily accomplished by capturing HRM data points over at least a 10 C (or greater) window, centered over the observed melting temperature of the amplified product. A good HRM analysis software, such as Precision Melt Analysis software from Bio-Rad, will help automate most of these processes to ensure consistent data analysis between samples. Beacon Designer is a trademark of PREMIER Biosoft International. EvaGreen is a trademark of Biotium, Inc. GreenER, SYBR, and SYTO are trademarks of Molecular Probes, Inc. HRM is a trademark of Corbett Life Science. LCGreen is a trademark of Idaho Technology Inc. Bio-Rad s real-time thermal cyclers are licensed real-time thermal cyclers under Applera s United States Patent Number 6,814,934 B1 for use in research, human in vitro diagnostics, and all other fields except veterinary diagnostics. Bio-Rad s real-time thermal cyclers are covered by one or more of the following U.S. patents or their foreign counterparts owned by Eppendorf AG: U.S. Patent Numbers 6,767,512 and 7,074,367. Information in this tech note was current as of the date of writing (2010) and not necessarily the date this version (rev A, 2010) was published. Conclusions HRM is a low-cost, readily accessible technique that can be used to rapidly analyze multiple genetic variants. Careful sample preparation and planning of experimental and assay design are crucial for robust and reproducible results. Following the guidelines above will assist in the development of such assays. References Alves DM et al. (2008). Development and use of single nucleotide polymorphism markers for candidate resistance genes in wild peanuts (Arachis spp). Genet Mol Res 7, Dracatos PM et al. (2008). Discovery and genetic mapping of single nucleotide polymorphisms in candidate genes for pathogen defence response in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Theor Appl Genet 117, Frazer KA et al. (2007). A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature 449, Garritano S et al. (2009). Determining the effectiveness of high resolution melting analysis for SNP genotyping and mutation scanning at the TP53 locus. BMC Genet 10, 5. International HapMap Consortium (2005). A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437, Lander ES et al. (2001). Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, Lascorz J et al. (2010). Genome-wide association study for colorectal cancer identifies risk polymorphisms in German familial cases and implicates MAPK signalling pathways in disease susceptibility. Carcinogenesis 31, Malentacchi F et al. (2009). Quantitative evaluation of DNA methylation by optimization of a differential-high resolution melt analysis protocol. Nucleic Acids Res 37, e86. Mao F et al. (2007). Characterization of EvaGreen and the implication of its physicochemical properties for qpcr applications. BMC Biotechnol 7, 76. Monis PT et al. (2005). Comparison of SYTO9 and SYBR Green I for real-time polymerase chain reaction and investigation of the effect of dye concentration on amplification and DNA melting curve analysis. Anal Biochem 340, Venter JC et al. (2001). The sequence of the human genome. Science 291, Zhao F et al. (2010). Sequencing and genetic variation of multidrug resistance plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS One 5, e10141.
6 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Life Science Group Web site USA Australia Austria Belgium Brazil Canada China Czech Republic Denmark Finland France Germany Greece Hong Kong Hungary India Israel Italy Japan Korea Mexico The Netherlands New Zealand Norway Poland Portugal Russia Singapore South Africa Spain Sweden Switzerland Taiwan United Kingdom Bulletin 6004 Rev A US/EG Sig 1109
amplification tech Optical Design of CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System Eliminates the Requirement of a Passive Reference Dye
 amplification tech note 6047 Optical Design of CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System Eliminates the Requirement of a Passive Reference Dye Liz Jordan and Richard Kurtz, Gene Expression Division, io-rad
amplification tech note 6047 Optical Design of CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System Eliminates the Requirement of a Passive Reference Dye Liz Jordan and Richard Kurtz, Gene Expression Division, io-rad
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Image Lab Software for the GS-900 Densitometer
 Image Lab Software for the GS-900 Densitometer Quick Start Guide Catalog # 170-9690 Bio-Rad Technical Support For help and technical advice, please contact the Bio-Rad Technical Support department. In
Image Lab Software for the GS-900 Densitometer Quick Start Guide Catalog # 170-9690 Bio-Rad Technical Support For help and technical advice, please contact the Bio-Rad Technical Support department. In
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR
 Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Technical Note. Roche Applied Science. No. LC 18/2004. Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR
 Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System. Real-Time PCR: CFX96 System
 Real-Time R Detection System Real-Time R: System Life Science Group Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Web site www.bio-rad.com USA 800 4BIORAD Australia 61 02 9914 2800 Austria 01 877 89 01 Belgium 09 385 55
Real-Time R Detection System Real-Time R: System Life Science Group Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Web site www.bio-rad.com USA 800 4BIORAD Australia 61 02 9914 2800 Austria 01 877 89 01 Belgium 09 385 55
Fast PCR: General Considerations for Minimizing Run Times and Maximizing Throughput
 amplification tech note 5362 Fast PCR: General Considerations for Minimizing Run Times and Maximizing Throughput Daniel Sullivan, Babette Fahey, and David Titus, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Waltham, MA
amplification tech note 5362 Fast PCR: General Considerations for Minimizing Run Times and Maximizing Throughput Daniel Sullivan, Babette Fahey, and David Titus, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Waltham, MA
Introduction to High Resolution Melt Analysis
 Introduction to High Resolution Melt Analysis Contents Page Introduction 3 Overview of the Melting Profile Principle 3 The Intercalating Dye Non-saturating dyes Saturating dyes Release-on-demand dyes Instruments
Introduction to High Resolution Melt Analysis Contents Page Introduction 3 Overview of the Melting Profile Principle 3 The Intercalating Dye Non-saturating dyes Saturating dyes Release-on-demand dyes Instruments
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
A guide to the analysis of KASP genotyping data using cluster plots
 extraction sequencing genotyping extraction sequencing genotyping extraction sequencing genotyping extraction sequencing A guide to the analysis of KASP genotyping data using cluster plots Contents of
extraction sequencing genotyping extraction sequencing genotyping extraction sequencing genotyping extraction sequencing A guide to the analysis of KASP genotyping data using cluster plots Contents of
LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System. High Resolution Melting: Optimization Strategies. Technical Note No. 1
 LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System Technical Note No. 1 High Resolution Melting: Optimization Strategies High resolution melting (HRM) is a novel, closed-tube, post-pcr technique allowing genomic researchers
LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System Technical Note No. 1 High Resolution Melting: Optimization Strategies High resolution melting (HRM) is a novel, closed-tube, post-pcr technique allowing genomic researchers
Image Lab Software How to Obtain Stain-Free Gel and Blot Images. Instructions
 Image Lab Software How to Obtain Stain-Free Gel and Blot Images Instructions Table of Contents Obtaining Stain-Free Gel images...1 5 Obtaining Stain-Free Blot Images...6 9 If the Gel Doc XR+ or ChemiDoc
Image Lab Software How to Obtain Stain-Free Gel and Blot Images Instructions Table of Contents Obtaining Stain-Free Gel images...1 5 Obtaining Stain-Free Blot Images...6 9 If the Gel Doc XR+ or ChemiDoc
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System
 PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
2.500 Threshold. 2.000 1000e - 001. Threshold. Exponential phase. Cycle Number
 application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Gene Expression Assays
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
Highly specific and sensitive quantitation
 PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
DNA Integrity Number (DIN) For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments
 DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
ProteinChip Energy Absorbing Molecules (EAM)
 ProteinChip Energy Absorbing Molecules (EAM) Instruction Manual Catalog #C30-00001, #C30-00002, #C30-00003, #C30-00004 For technical support, call your local Bio-Rad office, or in the US, call 1-800-4BIORAD
ProteinChip Energy Absorbing Molecules (EAM) Instruction Manual Catalog #C30-00001, #C30-00002, #C30-00003, #C30-00004 For technical support, call your local Bio-Rad office, or in the US, call 1-800-4BIORAD
LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System
 Roche Applied Science LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System Planned introduction of the LightCycler 480 System: September 2005 Rapid by nature, accurate by design The LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System
Roche Applied Science LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System Planned introduction of the LightCycler 480 System: September 2005 Rapid by nature, accurate by design The LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR System
Precision Melt Analysis Software Instruction Manual
 Precision Melt Analysis Software Instruction Manual Catalog #184-5025 Copyright 2009 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Reproduction in any form, either print or electronic, is prohibited without written permission
Precision Melt Analysis Software Instruction Manual Catalog #184-5025 Copyright 2009 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Reproduction in any form, either print or electronic, is prohibited without written permission
Computer Specifications
 Computer Specifications Specifications Imaging Systems Bulletin 6126 These tables list current specifications for Bio-Rad imaging systems. Refer to the following pages for information about each imaging
Computer Specifications Specifications Imaging Systems Bulletin 6126 These tables list current specifications for Bio-Rad imaging systems. Refer to the following pages for information about each imaging
PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit
 - PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit Catalog Number KA2102 50 tests/kit Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Introduction and Background Intended use The PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit
- PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit Catalog Number KA2102 50 tests/kit Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Introduction and Background Intended use The PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds. Overview. Data Analysis Tutorial
 Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
National Genetics Reference Laboratory (Wessex) Technology Assessment. Mutation scanning by high resolution melt analysis.
 National Genetics Reference Laboratory (Wessex) Technology Assessment Mutation scanning by high resolution melt analysis. Evaluation of Rotor Gene 6000 (Corbett Life Science), HR 1 and 384 well LightScanner
National Genetics Reference Laboratory (Wessex) Technology Assessment Mutation scanning by high resolution melt analysis. Evaluation of Rotor Gene 6000 (Corbett Life Science), HR 1 and 384 well LightScanner
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit
 ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform
 QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist [email protected] Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist [email protected] Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
Bio-Rad Laboratories. QC data management solutions. Introduce Your Laboratory to a Whole New World of Unity Data Management Solutions
 Bio-Rad Laboratories QC data management solutions QC Data Management Solutions Introduce Your Laboratory to a Whole New World of Unity Data Management Solutions Bio-Rad Laboratories QC data management
Bio-Rad Laboratories QC data management solutions QC Data Management Solutions Introduce Your Laboratory to a Whole New World of Unity Data Management Solutions Bio-Rad Laboratories QC data management
PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase
 Cat. # R010A For Research Use PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 Features...3 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction
Cat. # R010A For Research Use PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 Features...3 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction
VLLM0421c Medical Microbiology I, practical sessions. Protocol to topic J10
 Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR. Results Interpretation Guide
 PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
GENOTYPING ASSAYS AT ZIRC
 GENOTYPING ASSAYS AT ZIRC A. READ THIS FIRST - DISCLAIMER Dear ZIRC user, We now provide detailed genotyping protocols for a number of zebrafish lines distributed by ZIRC. These protocols were developed
GENOTYPING ASSAYS AT ZIRC A. READ THIS FIRST - DISCLAIMER Dear ZIRC user, We now provide detailed genotyping protocols for a number of zebrafish lines distributed by ZIRC. These protocols were developed
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
SEQUENCING. From Sample to Sequence-Ready
 SEQUENCING From Sample to Sequence-Ready ACCESS ARRAY SYSTEM HIGH-QUALITY LIBRARIES, NOT ONCE, BUT EVERY TIME The highest-quality amplicons more sensitive, accurate, and specific Full support for all major
SEQUENCING From Sample to Sequence-Ready ACCESS ARRAY SYSTEM HIGH-QUALITY LIBRARIES, NOT ONCE, BUT EVERY TIME The highest-quality amplicons more sensitive, accurate, and specific Full support for all major
Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR
 Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR 02 Real-time PCR basic principles PCR or the Polymerase Chain Reaction has become the cornerstone of modern molecular biology the world over. Real-time PCR is an advanced
Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR 02 Real-time PCR basic principles PCR or the Polymerase Chain Reaction has become the cornerstone of modern molecular biology the world over. Real-time PCR is an advanced
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology
 Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit
 Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
Foreign Taxes Paid and Foreign Source Income INTECH Global Income Managed Volatility Fund
 Income INTECH Global Income Managed Volatility Fund Australia 0.0066 0.0375 Austria 0.0045 0.0014 Belgium 0.0461 0.0138 Bermuda 0.0000 0.0059 Canada 0.0919 0.0275 Cayman Islands 0.0000 0.0044 China 0.0000
Income INTECH Global Income Managed Volatility Fund Australia 0.0066 0.0375 Austria 0.0045 0.0014 Belgium 0.0461 0.0138 Bermuda 0.0000 0.0059 Canada 0.0919 0.0275 Cayman Islands 0.0000 0.0044 China 0.0000
Methylation Analysis Using Methylation-Sensitive HRM and DNA Sequencing
 APPLICATION NOTE Methylation Analysis Using Methylation-Sensitive HRM and DNA Sequencing Methylation Analysis Using Methylation Sensitive HRM and DNA Sequencing Abstract DNA methylation is a key epigenetic
APPLICATION NOTE Methylation Analysis Using Methylation-Sensitive HRM and DNA Sequencing Methylation Analysis Using Methylation Sensitive HRM and DNA Sequencing Abstract DNA methylation is a key epigenetic
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA
 Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Installation Qualification/Operational Qualification Protocols and Instructions. Experion Automated Electrophoresis Station and Software
 Installation Qualification/Operational Qualification Protocols and Instructions Experion Automated Electrophoresis Station and Software Validation Kit (Catalog #700-7051) Security Edition Software (Catalog
Installation Qualification/Operational Qualification Protocols and Instructions Experion Automated Electrophoresis Station and Software Validation Kit (Catalog #700-7051) Security Edition Software (Catalog
Fluorescent dyes for use with the
 Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products
 Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Troubleshooting Sequencing Data
 Troubleshooting Sequencing Data Troubleshooting Sequencing Data No recognizable sequence (see page 7-10) Insufficient Quantitate the DNA. Increase the amount of DNA in the sequencing reactions. See page
Troubleshooting Sequencing Data Troubleshooting Sequencing Data No recognizable sequence (see page 7-10) Insufficient Quantitate the DNA. Increase the amount of DNA in the sequencing reactions. See page
Co Extra (GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability) Outcomes of Co Extra
 GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
Methods and Application Guide. Introduction to Quantitative PCR
 Methods and Application Guide Introduction to Quantitative PCR Introduction to Quantitative PCR Methods and Application Guide Stratagene USA and Canada Order: 800-424-5444 x3 Technical Services: 800-894-1304
Methods and Application Guide Introduction to Quantitative PCR Introduction to Quantitative PCR Methods and Application Guide Stratagene USA and Canada Order: 800-424-5444 x3 Technical Services: 800-894-1304
Real-time qpcr Assay Design Software www.qpcrdesign.com
 Real-time qpcr Assay Design Software www.qpcrdesign.com Your Blueprint For Success Informational Guide 2199 South McDowell Blvd Petaluma, CA 94954-6904 USA 1.800.GENOME.1(436.6631) 1.415.883.8400 1.415.883.8488
Real-time qpcr Assay Design Software www.qpcrdesign.com Your Blueprint For Success Informational Guide 2199 South McDowell Blvd Petaluma, CA 94954-6904 USA 1.800.GENOME.1(436.6631) 1.415.883.8400 1.415.883.8488
Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation
 PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
Optimizing and Analyzing Real-Time Assays on the SmartCycler II System
 Optimizing and Analyzing Real-Time Assays on the SmartCycler II System Cepheid Technical Support Overview This technical note provides guidelines on transferring, optimizing, and evaluating real-time PCR
Optimizing and Analyzing Real-Time Assays on the SmartCycler II System Cepheid Technical Support Overview This technical note provides guidelines on transferring, optimizing, and evaluating real-time PCR
Sequencing Guidelines Adapted from ABI BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit and Roswell Park Cancer Institute Core Laboratory website
 Biomolecular Core Facility AI Dupont Hospital for Children, Rockland Center One, Room 214 Core: (302) 651-6712, Office: (302) 651-6707, [email protected] Katia Sol-Church, Ph.D., Director Jennifer Frenck
Biomolecular Core Facility AI Dupont Hospital for Children, Rockland Center One, Room 214 Core: (302) 651-6712, Office: (302) 651-6707, [email protected] Katia Sol-Church, Ph.D., Director Jennifer Frenck
Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein Barr)
 Techne qpcr test Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein Barr) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein
Techne qpcr test Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein Barr) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein
SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus-
 Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Gene Mapping Techniques
 Gene Mapping Techniques OBJECTIVES By the end of this session the student should be able to: Define genetic linkage and recombinant frequency State how genetic distance may be estimated State how restriction
Gene Mapping Techniques OBJECTIVES By the end of this session the student should be able to: Define genetic linkage and recombinant frequency State how genetic distance may be estimated State how restriction
WATERS QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS solutions
 More sensitivity. More speed. What more can you ask for in a complete quantitative analysis solution? WATERS QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS solutions THE CHALLENGE OF QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS Tandem mass spectrometry,
More sensitivity. More speed. What more can you ask for in a complete quantitative analysis solution? WATERS QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS solutions THE CHALLENGE OF QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS Tandem mass spectrometry,
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
Introduction to Quantitative PCR
 Introduction to Quantitative PCR Methods and Applications Guide Introduction to Quantitative PCR Methods and Applications Guide IN 70200 D US and Canada Orders: 800-227-9770 x3 Technical Service: 800-227-9770
Introduction to Quantitative PCR Methods and Applications Guide Introduction to Quantitative PCR Methods and Applications Guide IN 70200 D US and Canada Orders: 800-227-9770 x3 Technical Service: 800-227-9770
[ Care and Use Manual ]
![[ Care and Use Manual ] [ Care and Use Manual ]](/thumbs/26/8588921.jpg) PREP Calibration Mix DIOS Low i. Introduction Pre-packaged PREP Calibration Mixtures eliminate the need to purchase and store large quantities of the component calibration reagents, simplifying sample
PREP Calibration Mix DIOS Low i. Introduction Pre-packaged PREP Calibration Mixtures eliminate the need to purchase and store large quantities of the component calibration reagents, simplifying sample
Application of Automated Data Collection to Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS)
 Application Note: 52020 Application of Automated Data Collection to Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Timothy O. Deschaines, Ph.D., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Madison, WI, USA Key Words Array Automation
Application Note: 52020 Application of Automated Data Collection to Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Timothy O. Deschaines, Ph.D., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Madison, WI, USA Key Words Array Automation
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
DNA Sequence Analysis
 DNA Sequence Analysis Two general kinds of analysis Screen for one of a set of known sequences Determine the sequence even if it is novel Screening for a known sequence usually involves an oligonucleotide
DNA Sequence Analysis Two general kinds of analysis Screen for one of a set of known sequences Determine the sequence even if it is novel Screening for a known sequence usually involves an oligonucleotide
quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476
 BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
2. True or False? The sequence of nucleotides in the human genome is 90.9% identical from one person to the next. False (it s 99.
 1. True or False? A typical chromosome can contain several hundred to several thousand genes, arranged in linear order along the DNA molecule present in the chromosome. True 2. True or False? The sequence
1. True or False? A typical chromosome can contain several hundred to several thousand genes, arranged in linear order along the DNA molecule present in the chromosome. True 2. True or False? The sequence
TruSeq Custom Amplicon v1.5
 Data Sheet: Targeted Resequencing TruSeq Custom Amplicon v1.5 A new and improved amplicon sequencing solution for interrogating custom regions of interest. Highlights Figure 1: TruSeq Custom Amplicon Workflow
Data Sheet: Targeted Resequencing TruSeq Custom Amplicon v1.5 A new and improved amplicon sequencing solution for interrogating custom regions of interest. Highlights Figure 1: TruSeq Custom Amplicon Workflow
360 Master Mix. , and a supplementary 360 GC Enhancer.
 Product Bulletin AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix and 360 DNA Polymerase AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix AmpliTaq Gold 360 DNA Polymerase 360 Coverage for a Full Range of Targets AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix
Product Bulletin AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix and 360 DNA Polymerase AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix AmpliTaq Gold 360 DNA Polymerase 360 Coverage for a Full Range of Targets AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix
CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Genetic engineering is possible
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Genetic engineering is possible
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr
 DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
QIAsymphony RGQ Protocol Sheet
 QIAsymphony RGQ Protocol Sheet Settings to run the artus CT/NG QS-RGQ Kit (Rotor-Gene Q software.) Check availability of new electronic labeling revisions at www.qiagen.com/products/artusctngqsrgqkitce.aspx
QIAsymphony RGQ Protocol Sheet Settings to run the artus CT/NG QS-RGQ Kit (Rotor-Gene Q software.) Check availability of new electronic labeling revisions at www.qiagen.com/products/artusctngqsrgqkitce.aspx
Application Note. Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics. Kit: A Real-Time PCR Extension
 Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit: Table of Contents Introduction.............................................. 2 Learning Objectives......................................
Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit: Table of Contents Introduction.............................................. 2 Learning Objectives......................................
Thermo Scientific PepFinder Software A New Paradigm for Peptide Mapping
 Thermo Scientific PepFinder Software A New Paradigm for Peptide Mapping For Conclusive Characterization of Biologics Deep Protein Characterization Is Crucial Pharmaceuticals have historically been small
Thermo Scientific PepFinder Software A New Paradigm for Peptide Mapping For Conclusive Characterization of Biologics Deep Protein Characterization Is Crucial Pharmaceuticals have historically been small
Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) genesig Standard Kit. DNA testing. Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
A Guide to High Resolution Melting (HRM) Analysis
 A Guide to High Resolution Melting (HRM) Analysis.5 8. 8.5 81. 81.5 82. 82.5 83. 83.5 84. 84.5 85. 85.5 86. Temperature (C) erozygote Hom - wild type Hom - varian A Guide to High Resolution Melting (HRM)
A Guide to High Resolution Melting (HRM) Analysis.5 8. 8.5 81. 81.5 82. 82.5 83. 83.5 84. 84.5 85. 85.5 86. Temperature (C) erozygote Hom - wild type Hom - varian A Guide to High Resolution Melting (HRM)
The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics
 The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics The GS Junior System The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing on Your Benchtop Proven technology: Uses the same long
The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics The GS Junior System The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing on Your Benchtop Proven technology: Uses the same long
Introduction. Preparation of Template DNA
 Procedures and Recommendations for DNA Sequencing at the Plant-Microbe Genomics Facility Ohio State University Biological Sciences Building Room 420, 484 W. 12th Ave., Columbus OH 43210 Telephone: 614/247-6204;
Procedures and Recommendations for DNA Sequencing at the Plant-Microbe Genomics Facility Ohio State University Biological Sciences Building Room 420, 484 W. 12th Ave., Columbus OH 43210 Telephone: 614/247-6204;
Chapter 8: Recombinant DNA 2002 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 8: Recombinant DNA 2002 by W. H. Freeman and Company
 Genetic engineering: humans Gene replacement therapy or gene therapy Many technical and ethical issues implications for gene pool for germ-line gene therapy what traits constitute disease rather than just
Genetic engineering: humans Gene replacement therapy or gene therapy Many technical and ethical issues implications for gene pool for germ-line gene therapy what traits constitute disease rather than just
Protocols. Internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) region. Niklaus J. Grünwald, Frank N. Martin, and Meg M. Larsen (2013)
 Protocols Internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) region Niklaus J. Grünwald, Frank N. Martin, and Meg M. Larsen (2013) The nuclear ribosomal RNA (rrna) genes (small subunit, large subunit and 5.8S) are
Protocols Internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) region Niklaus J. Grünwald, Frank N. Martin, and Meg M. Larsen (2013) The nuclear ribosomal RNA (rrna) genes (small subunit, large subunit and 5.8S) are
Real-time PCR handbook
 Real-time PCR handbook Single-tube assays 96- and 384-well plates 384-well TaqMan Array cards OpenArray plates The image on this cover is of an OpenArray plate which is primarily used for mid-density real-time
Real-time PCR handbook Single-tube assays 96- and 384-well plates 384-well TaqMan Array cards OpenArray plates The image on this cover is of an OpenArray plate which is primarily used for mid-density real-time
Applications Guide. Real-Time PCR Applications Guide
 Applications Guide Real-Time PCR Applications Guide table of contents Table of Contents 1. Overview of Real-Time PCR 2 1.1 Key Concepts of Real-Time PCR 2 1.1.1 What Is Real-Time PCR? 2 1.1.2 How Real-Time
Applications Guide Real-Time PCR Applications Guide table of contents Table of Contents 1. Overview of Real-Time PCR 2 1.1 Key Concepts of Real-Time PCR 2 1.1.1 What Is Real-Time PCR? 2 1.1.2 How Real-Time
MystiCq microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C
 microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
How To Install A Gel Doc Xr+ Camera On A Computer Or Mouse Or Tv (For A Powerbook) With A Zoom Lens (For An Ipa) With An Iphone Or Ipa (For Mac) With The Zoom Lens
 Molecular Imager Gel Doc XR+ Installation Guide To install your Gel Doc XR+, perform these seven steps in the following order: 1. Unpack the Gel Doc XR+ system. 2. Install Image Lab software. 3. Set up
Molecular Imager Gel Doc XR+ Installation Guide To install your Gel Doc XR+, perform these seven steps in the following order: 1. Unpack the Gel Doc XR+ system. 2. Install Image Lab software. 3. Set up
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System
 qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix. Protocol
 TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
SeqScape Software Version 2.5 Comprehensive Analysis Solution for Resequencing Applications
 Product Bulletin Sequencing Software SeqScape Software Version 2.5 Comprehensive Analysis Solution for Resequencing Applications Comprehensive reference sequence handling Helps interpret the role of each
Product Bulletin Sequencing Software SeqScape Software Version 2.5 Comprehensive Analysis Solution for Resequencing Applications Comprehensive reference sequence handling Helps interpret the role of each
Intended Use: The kit is designed to detect the 5 different mutations found in Asian population using seven different primers.
 Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
Thermo Scientific Dionex Chromeleon 7 Chromatography Data System Software
 Thermo Scientific Dionex Chromeleon 7 Chromatography Data System Software Frank Tontala, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germering, Germany Technical Note 708 Key Words Chromeleon Chromatography Data System,
Thermo Scientific Dionex Chromeleon 7 Chromatography Data System Software Frank Tontala, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germering, Germany Technical Note 708 Key Words Chromeleon Chromatography Data System,
Time-Correlated Multi-domain RF Analysis with the MSO70000 Series Oscilloscope and SignalVu Software
 Time-Correlated Multi-domain RF Analysis with the MSO70000 Series Oscilloscope and SignalVu Software Technical Brief Introduction The MSO70000 Series Mixed Oscilloscope, when coupled with SignalVu Spectrum
Time-Correlated Multi-domain RF Analysis with the MSO70000 Series Oscilloscope and SignalVu Software Technical Brief Introduction The MSO70000 Series Mixed Oscilloscope, when coupled with SignalVu Spectrum
Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene. genesig Advanced Kit. DNA testing
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
bitter is de pil Linos Vandekerckhove, MD, PhD
 4//24 Current HIV care HIV copies/ ml plasma Viral load Welcome to the Digital droplet PCR age! bitter is de pil Linos Vandekerckhove, MD, PhD Latent HIV reservoir Time at Ghent University Hospital 2 HIV
4//24 Current HIV care HIV copies/ ml plasma Viral load Welcome to the Digital droplet PCR age! bitter is de pil Linos Vandekerckhove, MD, PhD Latent HIV reservoir Time at Ghent University Hospital 2 HIV
Plexor Systems Instrument Setup and Data Analysis for the Applied Biosystems 7300 and 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems
 Technical Manual Plexor Systems Instrument Setup and Data Analysis for the Applied Biosystems 7300 and 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS A4011, A4021, A4031, A4041, A4051 AND
Technical Manual Plexor Systems Instrument Setup and Data Analysis for the Applied Biosystems 7300 and 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS A4011, A4021, A4031, A4041, A4051 AND
CISCO MDS 9000 FAMILY PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
 WHITE PAPER CISCO MDS 9000 FAMILY PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT As storage area networks (SANs) grow, so do the challenges for monitoring and resolving performance issues. Summary views of networkwide historical
WHITE PAPER CISCO MDS 9000 FAMILY PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT As storage area networks (SANs) grow, so do the challenges for monitoring and resolving performance issues. Summary views of networkwide historical
Pitfalls in qpcr. Primer and probe design and synthesis. Mary Span Eurogentec S.A.
 Pitfalls in qpcr Primer and probe design and synthesis Mary Span Eurogentec S.A. Steps in qpcr assay Set up experiment statistical relevant # samples/experimental group controls Design and synthesis primers
Pitfalls in qpcr Primer and probe design and synthesis Mary Span Eurogentec S.A. Steps in qpcr assay Set up experiment statistical relevant # samples/experimental group controls Design and synthesis primers
Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR. so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed
 Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR or.. for this audience so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed Nigel Walker, Ph.D. Laboratory of Computational Biology and Risk Analysis, Environmental
Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR or.. for this audience so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed Nigel Walker, Ph.D. Laboratory of Computational Biology and Risk Analysis, Environmental
DNA Core Facility: DNA Sequencing Guide
 DNA Core Facility: DNA Sequencing Guide University of Missouri-Columbia 216 Life Sciences Center Columbia, MO 65211 http://biotech.missouri.edu/dnacore/ Table of Contents 1. Evaluating Sequencing Data..
DNA Core Facility: DNA Sequencing Guide University of Missouri-Columbia 216 Life Sciences Center Columbia, MO 65211 http://biotech.missouri.edu/dnacore/ Table of Contents 1. Evaluating Sequencing Data..
Thermo Scientific ClinQuan MD Software For In Vitro Diagnostic Use. Confidence in Results With Data Integrity
 Thermo Scientific ClinQuan MD Software For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Confidence in Results With Data Integrity 2 Make the World Healthier With the LC-MS Tests You Run Confidence in Test Results With Data
Thermo Scientific ClinQuan MD Software For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Confidence in Results With Data Integrity 2 Make the World Healthier With the LC-MS Tests You Run Confidence in Test Results With Data
The Techniques of Molecular Biology: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting
 Revised Fall 2011 The Techniques of Molecular Biology: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting The techniques of molecular biology are used to manipulate the structure and function of molecules such as DNA and proteins
Revised Fall 2011 The Techniques of Molecular Biology: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting The techniques of molecular biology are used to manipulate the structure and function of molecules such as DNA and proteins
CABIOS. Q-RT-PCR: data analysis software for measurement of gene expression by competitive RT-PCR
 CABIOS Vol. 73 no. 6 1997 Pages 587-591 Q-RT-PCR: data analysis software for measurement of gene expression by competitive RT-PCR Peter A. Doris 2, Amanda Hayward-Lester and Jon K. Hays Sr 1 Department
CABIOS Vol. 73 no. 6 1997 Pages 587-591 Q-RT-PCR: data analysis software for measurement of gene expression by competitive RT-PCR Peter A. Doris 2, Amanda Hayward-Lester and Jon K. Hays Sr 1 Department
