Management of Urinary Incontinence. Sheri J. Ross, BSc, DVM, PhD, Dipl. ACVIM (Internal Medicine)
|
|
|
- Ashlee Charles
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Management of Urinary Incontinence Sheri J. Ross, BSc, DVM, PhD, Dipl. ACVIM (Internal Medicine) Managing Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is very prevalent among older animals. In this group of animals it is important to consider the impact of non-urinary conditions as well. Correct identification of the underlying cause and aggressive management may improve the quality of life for both the patient and owner. Micturition is the act of urination and includes both a storage phase and a voiding phase. Animals presenting with urinary incontinence typically have one or more problems with the storage phase of micturition, which can usually be categorized as; insufficient urethral closure pressure; failure of the bladder to relax and accommodate urine; or abnormal anatomy of the bladder, ureter(s) and/or urethra. Pathophysiology The main organs involved in urination are the bladder and the urethra. The smooth muscle of the bladder, known as the detrusor muscle, is innervated by sympathetic nerve fibers from the lumbar spinal cord and parasympathetic fibers from the sacral spinal cord. The internal urethral sphincter consists of smooth muscle bundles that pass on either side of the urethra. More distal along the urethra is the external urethral sphincter which is composed of skeletal muscle and is innervated by the somatic pudendal nerve which originates in Onuf's nucleus in the cord. In healthy animals, the lower urinary tract has two discrete phases: the storage phase and the voiding phase. The muscles controlling micturition are controlled by both the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. Storage phase During the storage phase the internal urethral sphincter remains tense and the detrusor muscle relaxed by sympathetic stimulation. The storage phase is controlled via stimulation of beta receptors in the bladder wall; causing detrusor muscle relaxation and alpha-1 receptors in the proximal urethra; causing urethral contraction. Sympathetic (adrenergic) input from the hypogastric nerve regulates the stimulation of these receptors. Skeletal muscle in the more distal urethra also contributes to urethral closure pressure and continence. This skeletal muscle is under voluntary control and is innervated by the somatic nervous system, principally through the pudendal nerve. Stimulation of the pudendal nerve with the neurotransmitters norepinephrine (NE) and serotonin (5-HT) results in contraction of the striated component of the urethral sphincter. Voiding phase
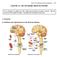
2 During voiding, parasympathetic stimulation causes the detrusor muscle to contract and the internal urethral sphincter to relax. As the bladder fills, sensory receptors in the bladder wall ascend the spinal cord to both the pontine micturition center and the cerebrum transmit the need to urinate. Once the voluntary signal to begin voiding has been issued, neurons in pontine micturition center fire maximally, causing excitation of sacral preganglionic neurons. The firing of these neurons results in contraction of the detrusor muscle and expulsion of urine from the bladder. The pontine micturition center also causes inhibition of Onuf's nucleus, resulting in relaxation of the external urinary sphincter. Under parasympathetic (cholinergic) control via the pelvic nerve, alphaadrenergic input to the bladder neck and proximal urethra is inhibited resulting in relaxation. Mechanism of storage and voiding reflexes. A. Storage reflexes. B. Voiding reflexes. (From Chancellor MB, Yoshimura N: Physiology and pharmacology of the bladder and urethra. In Walsh PC (ed): Campbell's Urology, pp Philadelphia, Saunders, 2002). Urethral sphincter mechanism incompetence In canines, incontinence is most often a result of inadequate urethral closure pressure. Urethral sphincter mechanism incompetence (USMI) is also known as "spay incontinence" or "hormone responsive incontinence". USMI is very common occurring in up to 30% of spayed dogs; most frequently in young to middle-aged, larger-breed dogs that have been spayed in the past 4 years. Factors contributing to the development of USMI may include an age related decline in collagenous support structures around the urethra and/or a decrease in sensitivity of adrenergic receptors within the urethra. An abnormally positioned bladder, obesity and anatomic abnormalities in the vagina and
3 vestibule may also contribute to the problem. Although much more common in females, USMI may occur in males as well. Medical Management of Incontinence Alpha-Adrenergic Agonists - Alpha-adrenergic agonists are one of the more common groups of drugs used in the management of canine urinary incontinence. These medications increase urethral tone my acting on the muscle in the urethral wall. The usual medication for canine use is phenylpropanolamine (Proin ) and is typically given two or three times daily. Increased blood pressure and behavioural changes are the most commonly observed side effects. Other side effects may include a decrease in appetite and irritability. Most dogs tend to tolerate phenylpropanolamine quite well and side effects are not common. It is important to monitor blood pressure periodically and to use with caution in patients with heart disease. There is a sustained release version of phenylpropanolamine available called cystolamine. This medication maintains a more stable blood concentration that does phenylpropanolamine and is thus more effective at controlling incontinence. Unfortunately this medication has been on indefinite back-order in the United States and Canada for the past 2 years. Estrogens - Estrogens are used to manage incontinence in post-menopausal women as well as dogs. Many dogs develop incontinence after being spayed due to the decrease in estrogen in their systems. Estrogens have also been helpful in managing incontinence from other causes as well. In dogs, DES (diethylstilbestrol) is the most common estrogen used, though it is now only available through compounding pharmacies. Typically, the patient is treated daily for 5 days and then the dosage is decreased to 1-2 times a week. Once continence has been attained, the frequency of dosing should be reduced the lowest possible dosage that will control the clinical signs. Although much less common with the newer estrogens such as DES, side effects are still possible and include bone marrow blood problems and hair loss. Side effects are more common in older animals and with high dosages. To monitor for any bone marrow problems, regular bloodwork is recommended. Proin and DES are often used in combination, and seem to be synergistic. Non-medical treatments Although medications or combinations of medications work for most patients to control the incontinence, if the leaking is not controlled there are surgical options to consider: colposuspension and/or urethropexy and collagen injections. Colposuspension/Urethropexy: is the most commonly performed procedure in females. Here, the vagina is tacked to the ventral wall entrapping and compressing the urethra. Fibers from the urethral muscles can also be tacked down to increase the tension and hopefully improve urethral tone. Medications listed above are used in conjunction with surgery. After urethropexy, 56% of affected dogs were continent and 27% had improvement of incontinence. A similar success rate was observed after colposuspension, with 53% of the female dogs continent and 38% with marked improvement. Hydraulic Occluder Cuff: Another option for controlling incontinence is the placement of a hydrolic occlude cuff around the trigone and proximal urethral. This cuff is placed
4 surgically and, after the patient has healed from surgery, is inflated to an appropriate pressure to prevent leakage, but still permitting conscious urination. Urethral Collagen Injections: Another option for the management of refractory incontinence is the injection of collagen into the urethra to decrease the luminal diameter and thus decrease leaking. Collagen injections are also useful in managing incontinence in cases where the patient can not be treated with the medications described above due to other medical conditions. Due to technical and size limitations, the cystoscopic method of collagen delivery is only appropriate for medium to larger female dogs. For smaller females and males, the collagen must be delivered via surgery or laparoscopy so that the urethra may be visualized. The most recent data suggest that approximately 68% of treated dogs will regain continence, although most still require medical therapy as well. The average duration of continence following collagen injections is reported to be 17 months with a range of 1-64 months. As the collagen tends to flatten with time, the injections may need to be repeated. At present, there is no data describing the success of repeated collagen injections, but we suspect that the success rate will be slightly lower due to scarring and difficulty with placement of the new injections. Collagen injection compares well to established surgical methods for treatment of refractory incontinence and is much less invasive. Table 1. Common Causes of Urinary Incontinence Non-neurogenic causes Urethral sphincter mechanism incompetence Detrusor hyper/hypocontractility Inflammation of the bladder or urethra urinary tract infction uroliths neoplasia Anatomic abnormalities ectopic ureters pelvic bladder vestibulovaginal malformations Neurogenic causes Trauma or spinal lesion FeLV (cats) Dysautonomia Increased urethral tone reflex dyssynergia upper motor neuron bladder Congenital (Manx cats) Table 2. Some Useful Drugs in the Management of Canine Urinary Incontinence Agent Classification Recommended Dosage (Dogs) Phenylpropanolamine Alpha agonist 1.5 mg/kg PO q 8-12 hrs
5 Cystolamine Alpha agonist 1-2 mg/kg PO q 24 hrs (sustained release phenylpropanolamine) no longer available in North America Diethylstilbestrol (DES) Reproductive hormone mg/dog PO q 24 hrs for 5-7 days, then weekly or as needed Imipramine Antimuscarinic, 5-15 mg PO q 12 hrs alpha/beta agonist Oxybutynin Antimuscarinic 0.2 mg/kg PO q 8-12 hrs Cats/small dogs: mg total dose Larger dogs: mg total dose
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Loss of voluntary control of urination, usually observed as involuntary urine leakage while resting SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET Species
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Loss of voluntary control of urination, usually observed as involuntary urine leakage while resting SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET Species
Canine Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence in the Bitch Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt, CAFCI, CCRT Urinary Incontinence = Involuntary leakage of urine during storage Micturation disorders (non-neurologic): 61% = Urethral
Urinary Incontinence in the Bitch Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt, CAFCI, CCRT Urinary Incontinence = Involuntary leakage of urine during storage Micturation disorders (non-neurologic): 61% = Urethral
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
Women suffer in silence
 Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Women suffer in silence Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure. In people who suffer with this condition, forms of exertion such
Urinary Continence. Second edition FAST FACTS. by Julian Shah and Gary Leach. Anatomy and physiology 7. Investigations and diagnosis 11
 FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
FAST FACTS Urinary Continence Second edition Indispensable Guides to by Julian Shah and Gary Leach Clinical Practice Anatomy and physiology 7 Investigations and diagnosis 11 Detrusor instability 28 Primary
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to. women, and is a serious condition that can lead to. significant lifestyle changes.
 Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
URINARY INCONTINENCE CASE PRESENTATION #1. Urinary Incontinence - History 2014/10/07. Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract
 Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Bladder pressure 2014/10/07 Structure of the Female Lower Urinary Tract Ureter URINARY INCONTINENCE Clinical Clerkship Lecture Series Outer peritoneal coat Detrusor smooth muscle Mucosa Trigone Proximal
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Electroneuromyographic studies
 Electroneuromyographic studies in the diagnosis of Pudendal Entrapment Syndrome BY NAGLAA ALI GADALLAH PROFESSOR OF PHYSICAL MEDICINE, RHEUMATOLOGY& REHABILITATION AIN SHAMS UNIVERSITY Pudendal neuralgia
Electroneuromyographic studies in the diagnosis of Pudendal Entrapment Syndrome BY NAGLAA ALI GADALLAH PROFESSOR OF PHYSICAL MEDICINE, RHEUMATOLOGY& REHABILITATION AIN SHAMS UNIVERSITY Pudendal neuralgia
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006
 Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006 What treatment options are available for a woman with stress urinary incontinence (SUI)? Behavioral therapy, medication, pessary,
Stress Urinary Incontinence: Treatment Manisha Patel, MD April 10, 2006 What treatment options are available for a woman with stress urinary incontinence (SUI)? Behavioral therapy, medication, pessary,
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9
 Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Minimally invasive techniques for the relief of stress urinary incontinence (Adapted from the
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL
 GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
GENUINE STRESS AND URGE INCONTINENCE PROTOCOL Using the NeuroTrac ETSTM in combination of electrostimulation and EMG Biofeedback in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Anna Pawlaczyk Specialist
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler
 Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
Urinary Incontinence Dr. Leffler The involuntary loss of urine at socially unacceptable times occurs in both women and men, but more commonly in women. It has multiple, far-reaching effects on daily activities,
Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology
 Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology R Hamid MD (Res), FRCS (Urol) Consultant Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & University College London Hospitals Micturition Micturition can be visualized as
Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology R Hamid MD (Res), FRCS (Urol) Consultant Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & University College London Hospitals Micturition Micturition can be visualized as
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
Urinary Incontinence. Anatomy and Terminology Overview. Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS
 Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Urinary Incontinence Anatomy and Terminology Overview Moeen Abu-Sitta, MD, FACOG, FACS Purpose Locate and describe the anatomy of the Female Urinary System Define terminology related to Incontinence Describe
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling
 Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
Mixed urinary incontinence - sling or not sling 吳 銘 斌 Ming-Ping Wu, M.D.,Ph.D. Director, Div. Urogynecology & Pelvic Floor Reconstruction, Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan Assistant Professor,
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN
 TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Bladder Management Options Following Spinal Cord Injury
 Bladder Management Options Following Spinal Cord Injury September 2015 This fact sheet tells you about some of the more common methods to manage your bladder if it is not working correctly following your
Bladder Management Options Following Spinal Cord Injury September 2015 This fact sheet tells you about some of the more common methods to manage your bladder if it is not working correctly following your
An illustrated guide to the management of incontinence.
 An illustrated guide to the management of incontinence. 1 The problem of incontinence The ACA describes incontinence as an involuntary loss of urine and/or bowel motion. The amount can vary from slight
An illustrated guide to the management of incontinence. 1 The problem of incontinence The ACA describes incontinence as an involuntary loss of urine and/or bowel motion. The amount can vary from slight
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence
 Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
NUR 111 Anne Marie Holler RN MSN(c)
 NUR 111 Anne Marie Holler RN MSN(c) Assignments Required Readings: Potter & Perry: pp. 1042-1085 Skills book: 809-840 Knowledge Base Anatomy Control Mechanisms Factors that inhibit micturation (voiding)
NUR 111 Anne Marie Holler RN MSN(c) Assignments Required Readings: Potter & Perry: pp. 1042-1085 Skills book: 809-840 Knowledge Base Anatomy Control Mechanisms Factors that inhibit micturation (voiding)
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 1988, Vol. 95, pp. 77-81 Urinary incontinence during sexual intercourse: a common, but rarely volunteered, symptom PAUL HILTON Summary. A total of 4
Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone
 Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION.
 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
 Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS. Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center. Bladder Dysfunction
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Urinary Incontinence. Types
 Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
A Physical Therapist s Perspective
 You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men
 Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Managing Urinary Incontinence
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Managing Urinary Incontinence www.nshealth.ca Managing Urinary Incontinence What is the urinary system? Urine (pee) is made in the kidneys. It flows through tubes called ureters.
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Managing Urinary Incontinence www.nshealth.ca Managing Urinary Incontinence What is the urinary system? Urine (pee) is made in the kidneys. It flows through tubes called ureters.
Testosterone Therapy for Women
 Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Bladder and Bowel Control
 Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
URINARY RETENTION-WHEN THE BLADDER WON T EMPTY
 URINARY RETENTION-WHEN THE BLADDER WON T EMPTY Diane K Newman, RNC MSN CRNP FAAN Co Director, PENN Center for Continence and Pelvic Health Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
URINARY RETENTION-WHEN THE BLADDER WON T EMPTY Diane K Newman, RNC MSN CRNP FAAN Co Director, PENN Center for Continence and Pelvic Health Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence. Overview of Lecture
 Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Lifestyle changes. Pelvic floor muscle training
 Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
