1. Application of Computer Graphics
|
|
|
- Asher O’Connor’
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Application of Computer Graphics Computer-Aided Design for engineering and architectural systems etc. Objects maybe displayed in a wireframe outline form. Multi-window environment is also favored for producing various zooming scales and views. Animations are useful for testing performance. Presentation Graphics To produce illustrations which summarize various kinds of data. Except 2D, 3D graphics are good tools for reporting more complex data. Computer Art Painting packages are available. With cordless, pressure-sensitive stylus, artists can produce electronic paintings which simulate different brush strokes, brush widths, and colors. Photorealistic techniques, morphing and animations are very useful in commercial art. For films, 24 frames per second are required. For video monitor, 30 frames per second are required. Entertainment Motion pictures, Music videos, and TV shows, Computer games Education and Training Training with computer-generated models of specialized systems such as the training of ship captains and aircraft pilots. Visualization For analyzing scientific, engineering, medical and business data or behavior. Converting data to visual form can help to understand mass volume of data very efficiently. Image Processing Image processing is to apply techniques to modify or interpret existing pictures. It is widely used in medical applications. Graphical User Interface Multiple window, icons, menus allow a computer setup to be utilized more efficiently. 2. Overview of Graphics Systems 2.1 Cathode-Ray Tubes (CRT) - still the most common video display device presently Electrostatic deflection of the electron beam in a CRT An electron gun emits a beam of electrons, which passes through focusing and deflection systems and hits on the phosphor-coated screen. The number of points displayed on a CRT is referred to as the 1
2 resolution (eg. 1024x768). Different phosphors emit small light spots of different colors, which can combine to form a range of colors. A common methodology for color CRT display is the Shadowmask method. Illustration of a shadow-mask CRT The light emitted by phosphor fades very rapidly, so it needs to redraw the picture repeatedly. There are 2 kinds of redrawing mechanisms: Raster-Scan and Random-Scan Raster-Scan The electron beam is swept across the screen one row at a time from top to bottom. As it moves across each row, the beam intensity is turned on and off to create a pattern of illuminated spots. This scanning process is called refreshing. Each complete scanning of a screen is normally called a frame. The refreshing rate, called the frame rate, is normally 60 to 80 frames per second, or described as 60 Hz to 80 Hz. Picture definition is stored in a memory area called the frame buffer. This frame buffer stores the intensity values for all the screen points. Each screen point is called a pixel (picture element). On black and white systems, the frame buffer storing the values of the pixels is called a bitmap. Each entry in the bitmap is a 1-bit data which determine the on (1) and off (0) of the intensity of the pixel. On color systems, the frame buffer storing the values of the pixels is called a pixmap (Though nowadays many graphics libraries name it as bitmap too). Each entry in the pixmap occupies a number of bits to represent the color of the pixel. For a true color display, the number of bits for each entry is 24 (8 bits per red/green/blue channel, each channel 2 8 =256 levels of intensity value, ie. 256 voltage settings for each of the red/green/blue electron guns). 2
3 Random-Scan (Vector Display) The CRT's electron beam is directed only to the parts of the screen where a picture is to be drawn. The picture definition is stored as a set of line-drawing commands in a refresh display file or a refresh buffer in memory. Random-scan generally have higher resolution than raster systems and can produce smooth line drawings, however it cannot display realistic shaded scenes. 2.2 Flat-Panel Displays - will be the most common video display device very soon. Reduced thickness, volumn, weight, and power requirements compared to CRT. Liquid-Crystal Displays (LCDs) - Liquid crystal refers to compounds which are in crystalline arrangement, but can flow like liquid. - The light source passes through a liquid-crystal material that can be aligned to either block or transmit the light. - 2 glass plates, each containing a light polarizer at right angles to the other, sandwich a liquid crystal material. - Rows of horizontal transparent conductors are built into one glass page. Columns of vertical conductors are put into the other plate. The intersection of 2 conductors defines a pixel position. - - Passive-matrix LCD - In the "on" state, polarized light passing through the material is twisted so that it will pass through the opposite polarizer. - Different materials can display different colors. - By placing thin-film transistors at pixel locations, voltage at each pixel can be controlled. -- Active-matrix LCD. 3
4 2.3. Graphics Systems Block diagram of a CRT graphics system In this context we discuss the graphics systems of raster-scan devices. A graphics processor accepts graphics commands from the CPU and executes the graphics commands which may involve drawing into the frame buffer. The frame buffer acts as a temporary store of the image and also as a decoupler to allow the graphics processor and the display controller to operate at different speeds. The display controller reads the frame buffer line by line and generates the control signals for the screen. Graphics commands: - Draw point - Draw polygon - Draw text - Clear frame buffer - Change drawing color 2 kinds of graphics processors: 2D graphics processors execute commands in 2D coordinates. When objects overlap, the one being drawn will obscure objects drawn previously in the region. BitBlt operations (Bit Block Transfer) are usually provided for moving/copying one rectangular region of frame buffer contents to another region. 3D graphics processors execute commands in 3D coordinates. When objects overlap, it is required to determine the visibility of the objects according to the z values. Display Controller for a raster display device reads the frame buffer and generates the control signals for the screen, ie. the signals for horizontal scanning and vertical scanning. Most display controllers include a colormap (or video look-up table). The major function of a colormap is to provide a mapping between the input pixel value to the output color Input Devices Common devices: keyboard, mouse, trackball and joystick Specialized devices: Data gloves are electronic gloves for detecting fingers' movement. In some applications, a sensor is also attached to the glove to detect the hand movement as a whole in 3D space. 4
5 A tablet contains a stylus and a drawing surface and it is mainly used for the input of drawings. A tablet is usually more accurate than a mouse, and is commonly used for large drawings. Scanners are used to convert drawings or pictures in hardcopy format into digital signal for computer processing. Touch panels allow displayed objects or screen positions to be selected with the touch of a finger. In these devices a touch-sensing mechanism is fitted over the video monitor screen. Touch input can be recorded using optical, electrical, or acoustical methods. 2.5 Hard-Copy Devices Directing pictures to a printer or plotter to produce hard-copy output on 35-mm slides, overhead transparencies, or plain paper. The quality of the pictures depend on dot size and number of dots per inch (DPI). Types of printers: line printers, laserjet, ink-jet, dot-matrix Laserjet printers use a laser beam to create a charge distribution on a rotating drum coated with a photoelectric material. Toner is applied to the drum and then transferred to the paper. To produce color outputs, the 3 color pigments (cyan, magenta, and yellow) are deposited on separate passes. Inkjet printers produce output by squirting ink in horizontal rows across a roll of paper wrapped on a drum. To produce color outputs, the 3 color pigments are shot simultaneously on a single pass along each print line on the paper. Inkjet or pen plotters are used to generate drafting layouts and other drawings of normally larger sizes. A pen plotter has one or more pens of different colors and widths mounted on a carriage which spans a sheet of paper. 2.6 Coordinate Representations in Graphics General graphics packages are designed to be used with Cartesian coordinate representations (x,y,z). Usually several different Cartesian reference frames are used to construct and display a scene: Modeling coordinates are used to construct individual object shapes. World coordinates are computed for specifying the placement of individual objects in appropriate positions. Normalized coordinates are converted from world coordinates, such that x,y values are ranged from 0 to 1. Device coordinates are the final locations on the output devices. 5
6 3. Output Primitives Shapes and colors of objects can be described internally with pixel arrays or sets of basic geometric structures such as straight line segments and polygon color areas. The functions provided by graphics programming packages to deal with these basic geometric structures are called output primitives. For example: Drawing a point: Drawing a line: SetPixel(100,200,RGB(255,255,0)); MoveTo(100,100); LineTo(100,200); Drawing some text: SetText(100,200,"Hello"); Drawing an ellipse: Ellipse(100,100,200,200); Painting a picture: BitBlt(100,100,50,50,srcImage,0,0,SRCCOPY); 3.1 Drawing a Thin Line in Raster Devices This is to compute intermediate discrete coordinates along the line path between 2 specified endpoint positions. The corresponding entry of these discrete coordinates in the frame buffer is then marked with the line color wanted. The basic concept is: - A line can be specified in the form: y = mx + c - Let m be between 0 to 1, then the slope of the line is between 0 and 45 degrees. - For the x-coordinate of the left end point of the line, compute the corresponding y value according to the line equation. Thus we get the left end point as (x1,y1), where y1 may not be an integer. - Calculate the distance of (x1,y1) from the center of the pixel immediately above it and call it D1 - Calculate the distance of (x1,y1) from the center of the pixel immediately below it and call it D2 - If D1 is smaller than D2, it means that the line is closer to the upper pixel than the lower pixel, then, we set the upper pixel to on; otherwise we set the lower pixel to on. - Then increatement x by 1 and repeat the same process until x reaches the right end point of the line. - This method assumes the width of the line to be zero 6
7 Bresenham's Line Algorithm This algorithm is very efficient since it use only incremental integer calculations. Instead of calculating the non-integral values of D1 and D2 for decision of pixel location, it computes a value, p, which is defined as: p = (D2-D1)* horizontal length of the line if p>0, it means D1 is smaller than D2, and we can determine the pixel location accordingly However, the computation of p is very easy: The initial value of p is 2 * vertical height of the line - horizontal length of the line. At succeeding x locations, if p has been smaller than 0, then, we increment p by 2 * vertical height of the line, otherwise we increment p by 2 * (vertical height of the line - horizontal length of the line) All the computations are on integers. The incremental method is applied to void BresenhamLine(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { int x, y, p, const1, const2; /* initialize variables */ p=2*(y2-y1)-(x2-x1); const1=2*(y2-y1); const2=2*((y2-y1)-(x2-x1)); x=x1; y=y1; SetPixel(x,y); while (x<xend) { x++; if (p<0) { p=p+const1; else { y++; p=p+const2; SetPixel(x,y); 7
8 3.2 Drawing a Circle in Raster Devices A circle can be specified in the form: (x-x c ) 2 + (y-y c ) 2 = r 2 where (x c,y c ) is the center of the circle. To save time in drawing a circle, we can make use of the symmetrical property of a circle which is to draw the segment of the circle between 0 and 45 degrees and repeat the segment 8 times as shown in the diagram to produce a circle. Ths algorithm also employs the incremental method which further improves the efficiency. void PlotCirclePoints(int centerx, int centery, int x, int y) { SetPixel(centerx+x,centery+y); SetPixel(centerx-x,centery+y); SetPixel(centerx+x,centery-y); SetPixel(centerx-x,centery-y); SetPixel(centerx+y,centery+x); SetPixel(centerx-y,centery+x); SetPixel(centerx+y,centery-x); SetPixel(centerx-y,centery-x); void BresenhamCircle(int centerx, int centery, int radius) { int x=0; int y=radius; int p=3-2*radius; while (x<y) { PlotCirclePoints(centerx,centery,x,y); if (p<0) { p=p+4*x+6; else { p=p+4*(x-y)+10; y=y-1; x=x+1; PlotCirclePoints(centerx,centery,x,y); 8
9 3.3 Scan-Line Polygon Fill Algorithm - Basic idea: For each scan line crossing a polygon, this algorithm locates the intersection points of the scan line with the polygon edges. These intersection points are shorted from left to right. Then, we fill the pixels between each intersection pair. - Some scan-line intersection at polygon vertices require special handling. A scan line passing through a vertex as intersecting the polygon twice. In this case we may or may not add 2 points to the list of intersections, instead of adding 1 points. This decision depends on whether the 2 edges at both sides of the vertex are both above, both below, or one is above and one is below the scan line. Only for the case if both are above or both are below the scan line, then we will add 2 points. - Inside-Outside Tests: The above algorithm only works for standard polygon shapes. However, for the cases which the edges of the polygon intersects, we need to identify whether a point is an interior or exterior point. Students may find interesting descriptions of 2 methods to solve this problem in many text books: odd-even rule and nonzero winding number rule. 9
10 3.4 Boundary-Fill Algorithm - This algorithm starts at a point inside a region and paint the interior outward towards the boundary. - This is a simple method but not efficient: 1. It is recursive method which may occupy a large stack size in the main memory. void BoundaryFill(int x, int y, COLOR fill, COLOR boundary) { COLOR current; current=getpixel(x,y); if (current<>boundary) and (current<>fill) then { SetPixel(x,y,fill); BoundaryFill(x+1,y,fill,boundary); BoundaryFill(x-1,y,fill,boundary); BoundaryFill(x,y+1,fill,boundary); BoundaryFill(x,y-1,fill,boundary); - More efficient methods fill horizontal pixel spands across scan lines, instead of proceeding to neighboring points. 3.5 Flood-Fill Algorithm - Flood-Fill is similar to Boundary-Fill. The difference is that Flood-Fill is to fill an area which I not defined by a single boundary color. void BoundaryFill(int x, int y, COLOR fill, COLOR old_color) { if (GetPixel(x,y)== old_color) { SetPixel(x,y,fill); BoundaryFill(x+1,y,fill,boundary); BoundaryFill(x-1,y,fill,boundary); BoundaryFill(x,y+1,fill,boundary); BoundaryFill(x,y-1,fill,boundary); 10
11 3.6 Drawing Text - A character is defined by its outline which is usually comoposed of lines and curves. - We can use a method similar the one for rendering polygon to render a character - However, because text is used very oftenly, we usually convert them into bitmaps in advance to improve the drawing efficiency. - To draw a character on the screen, all we need to do is to copy the corresponding bitmap to the specified coordinate. - The problem with this method is that scaling a character with a bitmap to produce different character sizes would result in a block-like structures (stair-case, aliasing). Hence we normally render a few bitmaps for a single character to represent different sizes of the same character. 3.7 Bitmap - A graphics pattern suh as an icon or a character may be needed frequently, or may need to be reused. - Generating the pattern every time when needed may waste a lot of processing time. - A bitmap can be used to store a pattern and duplicate it to many places on the image or on the screen with simple copying operations. 11
12 3.8 Properties - In graphical output primitives, objects are normally associated with properties. Eg. Point: Line: Polygon: Text: color width, style, color edge color, filling color font size, color, bold or not bold, italic or not, underlined or not, etc. In graphical packages, we can specify such properties, eg. In Powerpoint, we can modify the properties of objects by a format command. In programming tools, we may pass the properties as arguments when we call the functions of these primitives, or we may pre-select the properties before calling the functions. 12
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions)
 www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions) Q 1. Can you give some basic features of computer graphics? Ans. The salient feature of computer graphics
www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions) Q 1. Can you give some basic features of computer graphics? Ans. The salient feature of computer graphics
Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays
 Display technology Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays Vector displays generally display lines, specified by their endpoints. Vector display
Display technology Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays Vector displays generally display lines, specified by their endpoints. Vector display
Lecture Notes, CEng 477
 Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Comp 410/510. Computer Graphics Spring 2016. Introduction to Graphics Systems
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2016 Introduction to Graphics Systems Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware (PC with graphics card)
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2016 Introduction to Graphics Systems Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware (PC with graphics card)
Important Question with Answer
 Important Question with Answer Q1. What do you mean by computer graphics? Ans. The branch of science and technology concerned with methods and techniques for converting data to or from visual presentation
Important Question with Answer Q1. What do you mean by computer graphics? Ans. The branch of science and technology concerned with methods and techniques for converting data to or from visual presentation
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS. NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions.
 B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
Computer Graphics. Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer
 Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware Software Applications Computer graphics is using computers to generate and display images based on
Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware Software Applications Computer graphics is using computers to generate and display images based on
Computer Graphics Lecture Notes
 Computer Graphics Lecture Notes DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING SHRI VISHNU ENGINEERING COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (Approved by AICTE, Accredited by NBA, Affiliated to JNTU Kakinada) BHIMAVARAM 534
Computer Graphics Lecture Notes DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING SHRI VISHNU ENGINEERING COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (Approved by AICTE, Accredited by NBA, Affiliated to JNTU Kakinada) BHIMAVARAM 534
Overview. Raster Graphics and Color. Overview. Display Hardware. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
 Raster Graphics and Color Greg Humphreys CS445: Intro Graphics University of Virginia, Fall 2004 Color models Color models Display Hardware Video display devices Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display
Raster Graphics and Color Greg Humphreys CS445: Intro Graphics University of Virginia, Fall 2004 Color models Color models Display Hardware Video display devices Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display
Working With Animation: Introduction to Flash
 Working With Animation: Introduction to Flash With Adobe Flash, you can create artwork and animations that add motion and visual interest to your Web pages. Flash movies can be interactive users can click
Working With Animation: Introduction to Flash With Adobe Flash, you can create artwork and animations that add motion and visual interest to your Web pages. Flash movies can be interactive users can click
Graphic Design. Background: The part of an artwork that appears to be farthest from the viewer, or in the distance of the scene.
 Graphic Design Active Layer- When you create multi layers for your images the active layer, or the only one that will be affected by your actions, is the one with a blue background in your layers palette.
Graphic Design Active Layer- When you create multi layers for your images the active layer, or the only one that will be affected by your actions, is the one with a blue background in your layers palette.
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal
 Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
ICS : 435. Computer Graphics Applications. Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh
 ICS : 435 Computer Graphics Applications Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh Course Outline Applications CAD/CAM, Art, Entertainment, Education, Training, Visualization, GUI, Image Processing. Overview of Computer
ICS : 435 Computer Graphics Applications Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh Course Outline Applications CAD/CAM, Art, Entertainment, Education, Training, Visualization, GUI, Image Processing. Overview of Computer
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING. Chapter 4 Output Devices
 CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input device for text and numbers.
 Standard Methods of Input Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input
Standard Methods of Input Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input
Computers: Tools for an Information Age. Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection
 Computers: Tools for an Information Age Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection Objectives Describe the user relationship with computer input and output Explain how data is input into a computer
Computers: Tools for an Information Age Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection Objectives Describe the user relationship with computer input and output Explain how data is input into a computer
Displays. Cathode Ray Tube. Semiconductor Elements. Basic applications. Oscilloscope TV Old monitors. 2009, Associate Professor PhD. T.
 Displays Semiconductor Elements 1 Cathode Ray Tube Basic applications Oscilloscope TV Old monitors 2 1 Idea of Electrostatic Deflection 3 Inside an Electrostatic Deflection Cathode Ray Tube Gun creates
Displays Semiconductor Elements 1 Cathode Ray Tube Basic applications Oscilloscope TV Old monitors 2 1 Idea of Electrostatic Deflection 3 Inside an Electrostatic Deflection Cathode Ray Tube Gun creates
COMPUTER GRAPHICS IMPORTANT QUESTION AND ANSWERS. Computer graphics
 Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT IMAGING
 AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
Scan-Line Fill. Scan-Line Algorithm. Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list
 Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
MMGD0203 Multimedia Design MMGD0203 MULTIMEDIA DESIGN. Chapter 3 Graphics and Animations
 MMGD0203 MULTIMEDIA DESIGN Chapter 3 Graphics and Animations 1 Topics: Definition of Graphics Why use Graphics? Graphics Categories Graphics Qualities File Formats Types of Graphics Graphic File Size Introduction
MMGD0203 MULTIMEDIA DESIGN Chapter 3 Graphics and Animations 1 Topics: Definition of Graphics Why use Graphics? Graphics Categories Graphics Qualities File Formats Types of Graphics Graphic File Size Introduction
B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN
 COURSE GUIDE B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN GRD 126 COMPUTER GENERATED GRAPHIC DESIGN I UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION, WINNEBA DEPARTMENT OF GRAPHIC DESIGN Copyright Acknowledgements The facilitating agent of the course
COURSE GUIDE B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN GRD 126 COMPUTER GENERATED GRAPHIC DESIGN I UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION, WINNEBA DEPARTMENT OF GRAPHIC DESIGN Copyright Acknowledgements The facilitating agent of the course
Discovering Computers. Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet. Chapter 7. Input and Output
 Discovering Computers Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet Chapter 7 Input and Output Objectives Overview Differentiate among various types of keyboards: standard, compact,
Discovering Computers Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet Chapter 7 Input and Output Objectives Overview Differentiate among various types of keyboards: standard, compact,
Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.2 OBJECTIVES
 Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics
 A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
Adobe Illustrator CS5
 What is Illustrator? Adobe Illustrator CS5 An Overview Illustrator is a vector drawing program. It is often used to draw illustrations, cartoons, diagrams, charts and logos. Unlike raster images that store
What is Illustrator? Adobe Illustrator CS5 An Overview Illustrator is a vector drawing program. It is often used to draw illustrations, cartoons, diagrams, charts and logos. Unlike raster images that store
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices
 Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
Computer Graphics with OpenGL 3e
 Computer Graphics with OpenGL 3e Chapter1 A surveys of Computer Graphics Computer Graphics Applications Graphs and Charts Computer-Aided Design Virtual-Reality Environments Data Visualizations Educations
Computer Graphics with OpenGL 3e Chapter1 A surveys of Computer Graphics Computer Graphics Applications Graphs and Charts Computer-Aided Design Virtual-Reality Environments Data Visualizations Educations
Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 1: Introduction to Illustrator
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 1: Introduction to Illustrator Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 1: Introduction to Illustrator Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading
Chapter 5 Understanding Input. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 5 Understanding Input Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Define input and differentiate among a program, command, and user response Identify
Chapter 5 Understanding Input Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Define input and differentiate among a program, command, and user response Identify
TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices
 TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ Input devices allow us to enter raw data into a computer. The computer processes the data and then produces
TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ Input devices allow us to enter raw data into a computer. The computer processes the data and then produces
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology
 Practical List 1) WAP to implement line generation using DDA algorithm 2) WAP to implement line using Bresenham s line generation algorithm. 3) WAP to generate circle using circle generation algorithm
Practical List 1) WAP to implement line generation using DDA algorithm 2) WAP to implement line using Bresenham s line generation algorithm. 3) WAP to generate circle using circle generation algorithm
Chapter 5 Objectives. Chapter 5 Input
 Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
Computer Graphics. Dr. S.M. Malaek. Assistant: M. Younesi
 Computer Graphics Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Computer Graphics Time: Textbook: Sunday/Tuesday 13:30-15 روشهاي مدلسازي در محيط مجازي كامپيوتر دكتر سيدمحمدباقر ملاي ك معصومه يونسي COMPUTER GRAPHICS,
Computer Graphics Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Computer Graphics Time: Textbook: Sunday/Tuesday 13:30-15 روشهاي مدلسازي در محيط مجازي كامپيوتر دكتر سيدمحمدباقر ملاي ك معصومه يونسي COMPUTER GRAPHICS,
ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide
 Adobe Training Services Exam Guide ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide Adobe Training Services provides this exam guide to help prepare partners, customers, and consultants who are actively seeking accreditation
Adobe Training Services Exam Guide ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide Adobe Training Services provides this exam guide to help prepare partners, customers, and consultants who are actively seeking accreditation
10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES
 FORM 4 COMPUTER STUDIES Chapter 10: Input and Output Devices March, 01 10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES The main function of an input device is to The main function of an output device is to
FORM 4 COMPUTER STUDIES Chapter 10: Input and Output Devices March, 01 10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES The main function of an input device is to The main function of an output device is to
How many PIXELS do you need? by ron gibbs
 How many PIXELS do you need? by ron gibbs We continue to move forward into the age of digital photography. The basic building block of digital images is the PIXEL which is the shorthand for picture element.
How many PIXELS do you need? by ron gibbs We continue to move forward into the age of digital photography. The basic building block of digital images is the PIXEL which is the shorthand for picture element.
Computer Peripherals
 Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Blender Notes. Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine
 Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
 LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
CAD/CAM. Hardware and software. CAD/CAM/CAE System. Shahrood University. Display Processing Unit
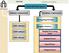 CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
Elfring Fonts, Inc. PCL MICR Fonts
 Elfring Fonts, Inc. PCL MICR Fonts This package contains five MICR fonts (also known as E-13B), to print magnetic encoding on checks, and six Secure Number fonts, to print check amounts. These fonts come
Elfring Fonts, Inc. PCL MICR Fonts This package contains five MICR fonts (also known as E-13B), to print magnetic encoding on checks, and six Secure Number fonts, to print check amounts. These fonts come
Pages 304 305. Figure 6-1. Page 305
 What Is Output? Output is data that has been processed into a useful form Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Figure -1 Objectives Overview Describe the types of output
What Is Output? Output is data that has been processed into a useful form Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Figure -1 Objectives Overview Describe the types of output
Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5.
 Chapter 1 Drawing Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketcher Workbench-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5. Start a new file in the Part
Chapter 1 Drawing Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketcher Workbench-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5. Start a new file in the Part
ClarisWorks 5.0. Graphics
 ClarisWorks 5.0 Graphics Level 1 Training Guide DRAFT Instructional Technology Page 1 Table of Contents Objectives... Page 3 Course Description and Organization... Page 4 Technology Requirements... Page
ClarisWorks 5.0 Graphics Level 1 Training Guide DRAFT Instructional Technology Page 1 Table of Contents Objectives... Page 3 Course Description and Organization... Page 4 Technology Requirements... Page
Thea Omni Light. Thea Spot Light. Light setup & Optimization
 Light setup In this tutorial we will learn how to setup lights inside Thea Studio and how to create mesh lights and optimize them for faster rendering with less noise. Let us have a look at the different
Light setup In this tutorial we will learn how to setup lights inside Thea Studio and how to create mesh lights and optimize them for faster rendering with less noise. Let us have a look at the different
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES
 INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
Help. Contents Back >>
 Contents Back >> Customizing Opening the Control Panel Control Panel Features Tabs Control Panel Lists Control Panel Buttons Customizing Your Tools Pen and Airbrush Tabs 2D Mouse and 4D Mouse Tabs Customizing
Contents Back >> Customizing Opening the Control Panel Control Panel Features Tabs Control Panel Lists Control Panel Buttons Customizing Your Tools Pen and Airbrush Tabs 2D Mouse and 4D Mouse Tabs Customizing
TABLE OF CONTENTS. INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE...
 Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
MassArt Studio Foundation: Visual Language Digital Media Cookbook, Fall 2013
 INPUT OUTPUT 08 / IMAGE QUALITY & VIEWING In this section we will cover common image file formats you are likely to come across and examine image quality in terms of resolution and bit depth. We will cover
INPUT OUTPUT 08 / IMAGE QUALITY & VIEWING In this section we will cover common image file formats you are likely to come across and examine image quality in terms of resolution and bit depth. We will cover
Index SNo Lesson Lesson Name Author Vetter. 1 1 Overview of Computer Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia
 Index SNo Lesson Lesson Name Author Vetter No. Overview of Computer Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia Graphics Display Devices Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia 3 3 Scan Conversion Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep
Index SNo Lesson Lesson Name Author Vetter No. Overview of Computer Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia Graphics Display Devices Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia 3 3 Scan Conversion Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep
Using SMART Notebook (Overview)
 Using SMART Notebook (Overview) A SMART Notebook is an electronic notebook that can capture and save images, objects and notes that are created on a SMART Board i.e. you can write student responses over
Using SMART Notebook (Overview) A SMART Notebook is an electronic notebook that can capture and save images, objects and notes that are created on a SMART Board i.e. you can write student responses over
Fixplot Instruction Manual. (data plotting program)
 Fixplot Instruction Manual (data plotting program) MANUAL VERSION2 2004 1 1. Introduction The Fixplot program is a component program of Eyenal that allows the user to plot eye position data collected with
Fixplot Instruction Manual (data plotting program) MANUAL VERSION2 2004 1 1. Introduction The Fixplot program is a component program of Eyenal that allows the user to plot eye position data collected with
The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input device for text and numbers.
 Standard Methods of Input Keyboard Mouse Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still
Standard Methods of Input Keyboard Mouse Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still
 Edinburgh COLLEGE of ART ARCHITECTURE 3D Modelling in AutoCAD - tutorial exercise The screen The graphics area This is the part of the screen in which the drawing will be created. The command prompt area
Edinburgh COLLEGE of ART ARCHITECTURE 3D Modelling in AutoCAD - tutorial exercise The screen The graphics area This is the part of the screen in which the drawing will be created. The command prompt area
Computers Are Your Future. 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
 Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
Optical Design Tools for Backlight Displays
 Optical Design Tools for Backlight Displays Introduction Backlights are used for compact, portable, electronic devices with flat panel Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) that require illumination from behind.
Optical Design Tools for Backlight Displays Introduction Backlights are used for compact, portable, electronic devices with flat panel Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) that require illumination from behind.
Digital Image Basics. Introduction. Pixels and Bitmaps. Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color
 Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction When using digital equipment to capture, store, modify and view photographic images, they must first be converted to a set
Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction When using digital equipment to capture, store, modify and view photographic images, they must first be converted to a set
Computer Peripherals
 Computer Peripherals School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore These notes are part of a 3rd year undergraduate course called "Computer Peripherals", taught at Nanyang Technological
Computer Peripherals School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore These notes are part of a 3rd year undergraduate course called "Computer Peripherals", taught at Nanyang Technological
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203.
 VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
Otis Photo Lab Inkjet Printing Demo
 Otis Photo Lab Inkjet Printing Demo Otis Photography Lab Adam Ferriss Lab Manager [email protected] 310.665.6971 Soft Proofing and Pre press Before you begin printing, it is a good idea to set the proof
Otis Photo Lab Inkjet Printing Demo Otis Photography Lab Adam Ferriss Lab Manager [email protected] 310.665.6971 Soft Proofing and Pre press Before you begin printing, it is a good idea to set the proof
A System for Capturing High Resolution Images
 A System for Capturing High Resolution Images G.Voyatzis, G.Angelopoulos, A.Bors and I.Pitas Department of Informatics University of Thessaloniki BOX 451, 54006 Thessaloniki GREECE e-mail: [email protected]
A System for Capturing High Resolution Images G.Voyatzis, G.Angelopoulos, A.Bors and I.Pitas Department of Informatics University of Thessaloniki BOX 451, 54006 Thessaloniki GREECE e-mail: [email protected]
2013 Getting Started Guide
 2013 Getting Started Guide The contents of this guide and accompanying exercises were originally created by Nemetschek Vectorworks, Inc. Vectorworks Fundamentals Getting Started Guide Created using: Vectorworks
2013 Getting Started Guide The contents of this guide and accompanying exercises were originally created by Nemetschek Vectorworks, Inc. Vectorworks Fundamentals Getting Started Guide Created using: Vectorworks
ELFRING FONTS INC. MICR FONTS FOR WINDOWS
 ELFRING FONTS INC. MICR FONTS FOR WINDOWS This package contains ten MICR fonts (also known as E-13B) used to print the magnetic encoding lines on checks, and eight Secure Fonts for use in printing check
ELFRING FONTS INC. MICR FONTS FOR WINDOWS This package contains ten MICR fonts (also known as E-13B) used to print the magnetic encoding lines on checks, and eight Secure Fonts for use in printing check
Overview of the Adobe Flash Professional CS6 workspace
 Overview of the Adobe Flash Professional CS6 workspace In this guide, you learn how to do the following: Identify the elements of the Adobe Flash Professional CS6 workspace Customize the layout of the
Overview of the Adobe Flash Professional CS6 workspace In this guide, you learn how to do the following: Identify the elements of the Adobe Flash Professional CS6 workspace Customize the layout of the
Drawing Lines with Pixels. Joshua Scott March 2012
 Drawing Lines with Pixels Joshua Scott March 2012 1 Summary Computers draw lines and circles during many common tasks, such as using an image editor. But how does a computer know which pixels to darken
Drawing Lines with Pixels Joshua Scott March 2012 1 Summary Computers draw lines and circles during many common tasks, such as using an image editor. But how does a computer know which pixels to darken
Scanners and How to Use Them
 Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction A scanner is a device that converts images to a digital file you can use with your computer. There are many different types
Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction A scanner is a device that converts images to a digital file you can use with your computer. There are many different types
PowerPoint 2007 Basics Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/
 Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ PowerPoint is the presentation program included in the Microsoft Office suite. With PowerPoint, you can create engaging presentations that can be presented in person, online,
Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ PowerPoint is the presentation program included in the Microsoft Office suite. With PowerPoint, you can create engaging presentations that can be presented in person, online,
QUICK REFERENCE: ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS2 AND CS3 SECTION 1: CS3 TOOL BOX: PAGE 2 SECTION 2: CS2 TOOL BOX: PAGE 11
 QUICK REFERENCE, ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR, PAGE 1 QUICK REFERENCE: ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS2 AND CS3 CS2 SECTION 1: CS3 TOOL BOX: PAGE 2 SECTION 2: CS2 TOOL BOX: PAGE 11 SECTION 3: GENERAL CONCEPTS: PAGE 14 SELECTING
QUICK REFERENCE, ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR, PAGE 1 QUICK REFERENCE: ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS2 AND CS3 CS2 SECTION 1: CS3 TOOL BOX: PAGE 2 SECTION 2: CS2 TOOL BOX: PAGE 11 SECTION 3: GENERAL CONCEPTS: PAGE 14 SELECTING
Flash MX 2004 Animation Lesson
 Flash MX 2004 Animation Lesson By Tonia Malone Technology & Learning Services 14-102 Lesson Opening a document To open an existing document: 1. Select File > Open. 2. In the Open dialog box, navigate to
Flash MX 2004 Animation Lesson By Tonia Malone Technology & Learning Services 14-102 Lesson Opening a document To open an existing document: 1. Select File > Open. 2. In the Open dialog box, navigate to
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview
 Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
CREATING POSTERS WITH POWERPOINT
 CREATING POSTERS WITH POWERPOINT PowerPoint files will be required for Posters on CD-Rom with very few exceptions. WHY POWERPOINT? Although there are many software programs that will create posters, PowerPoint
CREATING POSTERS WITH POWERPOINT PowerPoint files will be required for Posters on CD-Rom with very few exceptions. WHY POWERPOINT? Although there are many software programs that will create posters, PowerPoint
The six steps of Printing 1. Cleaning
 The Printer Laser Printers Laser Printers Ink-Jet printers Dot Matrix Printers Advantages/Disadvantages Laser Printers Advantages Fast Good image Quality Reliable Durable water resistant image Excellent
The Printer Laser Printers Laser Printers Ink-Jet printers Dot Matrix Printers Advantages/Disadvantages Laser Printers Advantages Fast Good image Quality Reliable Durable water resistant image Excellent
C O M P U T E R G R A P H I C S. Computer Graphics. Introduction I. Guoying Zhao 1 / 58
 Computer Graphics Introduction I Guoying Zhao 1 / 58 A Survey of Computer Graphics What is computer graphics? Interactive computer graphics The history of computer graphics Computer graphics applications
Computer Graphics Introduction I Guoying Zhao 1 / 58 A Survey of Computer Graphics What is computer graphics? Interactive computer graphics The history of computer graphics Computer graphics applications
CHAPTER 6: GRAPHICS, DIGITAL MEDIA, AND MULTIMEDIA
 CHAPTER 6: GRAPHICS, DIGITAL MEDIA, AND MULTIMEDIA Multiple Choice: 1. created the World Wide Web, the URL scheme, HTML and HTTP A. Bill Gates B. Andy Grove C. Jeff Bezos D. Tim Berners-Lee Answer: D Reference:
CHAPTER 6: GRAPHICS, DIGITAL MEDIA, AND MULTIMEDIA Multiple Choice: 1. created the World Wide Web, the URL scheme, HTML and HTTP A. Bill Gates B. Andy Grove C. Jeff Bezos D. Tim Berners-Lee Answer: D Reference:
Chapter 5 Input. Chapter 5 Objectives. What Is Input? What Is Input? The Keyboard. The Keyboard
 Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Input Define input List characteristics of of a keyboard Describe different mouse types and how they work Summarize how pointing devices work Explain how a digital camera
Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Input Define input List characteristics of of a keyboard Describe different mouse types and how they work Summarize how pointing devices work Explain how a digital camera
Guide To Creating Academic Posters Using Microsoft PowerPoint 2010
 Guide To Creating Academic Posters Using Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 INFORMATION SERVICES Version 3.0 July 2011 Table of Contents Section 1 - Introduction... 1 Section 2 - Initial Preparation... 2 2.1 Overall
Guide To Creating Academic Posters Using Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 INFORMATION SERVICES Version 3.0 July 2011 Table of Contents Section 1 - Introduction... 1 Section 2 - Initial Preparation... 2 2.1 Overall
Lab 3. GIS Data Entry and Editing.
 Lab 3. GIS Data Entry and Editing. The goal: To learn about the vector (arc/node) and raster data types entry and editing. Objective: Create vector and raster datasets and visualize them. Software for
Lab 3. GIS Data Entry and Editing. The goal: To learn about the vector (arc/node) and raster data types entry and editing. Objective: Create vector and raster datasets and visualize them. Software for
Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners
 Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners Background The lateral response artifact (LRA) in radiochromic film images from flatbed scanners was first pointed
Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners Background The lateral response artifact (LRA) in radiochromic film images from flatbed scanners was first pointed
CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING MICROSCOPY TUTORIAL
 CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING MICROSCOPY TUTORIAL Robert Bagnell 2006 This tutorial covers the following CLSM topics: 1) What is the optical principal behind CLSM? 2) What is the spatial resolution in X, Y,
CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING MICROSCOPY TUTORIAL Robert Bagnell 2006 This tutorial covers the following CLSM topics: 1) What is the optical principal behind CLSM? 2) What is the spatial resolution in X, Y,
ACADEMIC TECHNOLOGY SUPPORT
 ACADEMIC TECHNOLOGY SUPPORT Adobe Photoshop Introduction Part 1 (Basics- Image Manipulation) [email protected] 439-8611 www.etsu.edu/ats Table of Contents: Overview... 1 Objectives... 1 Basic Graphic Terminology...
ACADEMIC TECHNOLOGY SUPPORT Adobe Photoshop Introduction Part 1 (Basics- Image Manipulation) [email protected] 439-8611 www.etsu.edu/ats Table of Contents: Overview... 1 Objectives... 1 Basic Graphic Terminology...
Lession: 2 Animation Tool: Synfig Card or Page based Icon and Event based Time based Pencil: Synfig Studio: Getting Started: Toolbox Canvas Panels
 Lession: 2 Animation Tool: Synfig In previous chapter we learn Multimedia and basic building block of multimedia. To create a multimedia presentation using these building blocks we need application programs
Lession: 2 Animation Tool: Synfig In previous chapter we learn Multimedia and basic building block of multimedia. To create a multimedia presentation using these building blocks we need application programs
Tomorrow s Technology and You
 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Maya 2014 Basic Animation & The Graph Editor
 Maya 2014 Basic Animation & The Graph Editor When you set a Keyframe (or Key), you assign a value to an object s attribute (for example, translate, rotate, scale, color) at a specific time. Most animation
Maya 2014 Basic Animation & The Graph Editor When you set a Keyframe (or Key), you assign a value to an object s attribute (for example, translate, rotate, scale, color) at a specific time. Most animation
Preparing Images for PowerPoint, the Web, and Publication
 What is Resolution?... 2 How Resolution Affects File Memory Size... 2 Physical Size vs. Memory Size... 3 Thinking Digitally... 4 What Resolution is Best For Printing?... 5 Professional Publications...
What is Resolution?... 2 How Resolution Affects File Memory Size... 2 Physical Size vs. Memory Size... 3 Thinking Digitally... 4 What Resolution is Best For Printing?... 5 Professional Publications...
Visualization of 2D Domains
 Visualization of 2D Domains This part of the visualization package is intended to supply a simple graphical interface for 2- dimensional finite element data structures. Furthermore, it is used as the low
Visualization of 2D Domains This part of the visualization package is intended to supply a simple graphical interface for 2- dimensional finite element data structures. Furthermore, it is used as the low
REVISED JUNE 2011. PLEASE DISCARD ANY PREVIOUS VERSIONS OF THIS GUIDE. Graphic Style Guide
 REVISED JUNE 2011. PLEASE DISCARD ANY PREVIOUS VERSIONS OF THIS GUIDE. Graphic Style Guide 1 Introduction 2 Logo Fonts 4 Logo Color 6 Logo Size & Clear Space 8 Logo Composition 10 Logo Application 16 Corporate
REVISED JUNE 2011. PLEASE DISCARD ANY PREVIOUS VERSIONS OF THIS GUIDE. Graphic Style Guide 1 Introduction 2 Logo Fonts 4 Logo Color 6 Logo Size & Clear Space 8 Logo Composition 10 Logo Application 16 Corporate
Digital Video-Editing Programs
 Digital Video-Editing Programs Digital video-editing software gives you ready access to all your digital video clips. Courtesy Harold Olejarz. enable you to produce broadcastquality video on classroom
Digital Video-Editing Programs Digital video-editing software gives you ready access to all your digital video clips. Courtesy Harold Olejarz. enable you to produce broadcastquality video on classroom
Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software
 What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
So you say you want something printed...
 So you say you want something printed... Well, that s great! You ve come to the right place. Whether you re having us design and edit your work, or you fancy yourself a designer and plan to hand over your
So you say you want something printed... Well, that s great! You ve come to the right place. Whether you re having us design and edit your work, or you fancy yourself a designer and plan to hand over your
CHAPTER 3: DIGITAL IMAGING IN DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY. 3.1 Basic Concepts of Digital Imaging
 Physics of Medical X-Ray Imaging (1) Chapter 3 CHAPTER 3: DIGITAL IMAGING IN DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY 3.1 Basic Concepts of Digital Imaging Unlike conventional radiography that generates images on film through
Physics of Medical X-Ray Imaging (1) Chapter 3 CHAPTER 3: DIGITAL IMAGING IN DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY 3.1 Basic Concepts of Digital Imaging Unlike conventional radiography that generates images on film through
SketchUp Instructions
 SketchUp Instructions Every architect needs to know how to use SketchUp! SketchUp is free from Google just Google it and download to your computer. You can do just about anything with it, but it is especially
SketchUp Instructions Every architect needs to know how to use SketchUp! SketchUp is free from Google just Google it and download to your computer. You can do just about anything with it, but it is especially
Intro to Excel spreadsheets
 Intro to Excel spreadsheets What are the objectives of this document? The objectives of document are: 1. Familiarize you with what a spreadsheet is, how it works, and what its capabilities are; 2. Using
Intro to Excel spreadsheets What are the objectives of this document? The objectives of document are: 1. Familiarize you with what a spreadsheet is, how it works, and what its capabilities are; 2. Using
Solving Simultaneous Equations and Matrices
 Solving Simultaneous Equations and Matrices The following represents a systematic investigation for the steps used to solve two simultaneous linear equations in two unknowns. The motivation for considering
Solving Simultaneous Equations and Matrices The following represents a systematic investigation for the steps used to solve two simultaneous linear equations in two unknowns. The motivation for considering
Vector storage and access; algorithms in GIS. This is lecture 6
 Vector storage and access; algorithms in GIS This is lecture 6 Vector data storage and access Vectors are built from points, line and areas. (x,y) Surface: (x,y,z) Vector data access Access to vector
Vector storage and access; algorithms in GIS This is lecture 6 Vector data storage and access Vectors are built from points, line and areas. (x,y) Surface: (x,y,z) Vector data access Access to vector
