Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions)
|
|
|
- Arnold Little
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions) Q 1. Can you give some basic features of computer graphics? Ans. The salient feature of computer graphics is the creation and manipulation of graphics (artificial images) by computer. Q 2. Can you tell which major components (hardware and software) are needed for computer graphics? Ans. Besides the basic computer, some special devices and software may be required especially for computer graphics. For hardware, a special high-resolution, color monitor is often demanded and some input tools, e.g. mouse and joy-sticker, and hard-copy devices, e.g. high-resolution color printer, may be required. For software, some special purpose utilities (device-dependent and deviceindependent) are needed for handling processing in computer graphics. Q 3. Can you list at least three important applications of computer graphics? Ans. There are many interesting applications of computer graphics. Three common applications are graphic user interface (GUI), computer-aided design (CAD), and computer games. Q 4. Define Computer Graphics. Ans. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or graphical representation of objects in a computer. Q 5. What is meant by scan code? Ans. When a key is pressed on the keyboard, the keyboard controller places a code carry to the key pressed into a part of the memory called as the keyboard buffer. This code is called as the scan code. Q 6. What does refreshing of the screen mean? Ans. Some method is needed for maintaining the picture on the screen. Refreshing of screen is done by keeping the phosphorus glowing to redraw the picture repeatedly. i.e. by quickly directing the electronic beam back to the same points.
2 Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 2 Q 7. Define Random Scan/Raster Scan displays. Ans. Random scan is a method in which the display is made by the electronic beam, which is directed, only to the points or part of the screen where the picture is to be drawn. The Raster scan system is a scanning technique in which the electrons sweep from top to bottom and from left to right. The intensity is turned on or off to light and unlight the pixel. Q 8. Explain the merits and demerits of Penetration techniques. Ans. The merits and demerits of the Penetration techniques are as follows: 1. It is an inexpensive technique. 2. It has only four colors. 3. The quality of the picture is not good when it is compared to other techniques. 4. It can display color scans in monitors. Q 9. Explain the merits and demerits of DVST. Ans. The merits and demerits of direct view storage tubes (DVST) are as follows: 1. It has a flat screen. 2. Refreshing of screen is not required. 3. Selective or part erasing of screen is not possible. 4. It has poor contrast. 5. Performance is inferior to the refresh CRT. Q 10. What do you mean by emissive and non-emissive displays? Ans. EMISSIVE: The emissive display converts electrical energy into light energy. The plasma panels, thin film electro-luminescent displays are the examples. NON-EMISSIVE: They are optical effects to convert the sunlight or light from any other source to graphic form. Liquid crystal display is an example. Q 11. Explain the merits and demerits of Plasma panel display. Ans. ADVANTAGES: 1. Refreshing is not required. 2. Produce a very steady image free of Flicker. 3. Less bulky than a CRT.
3 Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 3 DISADVANTAGES: 1. Poor resolution of up to 60 d.p.i. 2. It requires complex addressing and wiring. 3. It is costlier than CRT. Q 12. What is persistence? Ans. The time it takes the emitted light from the screen to decay one tenth of its original intensity is called as persistence. Q 13. What is resolution? Ans. The maximum number of points that can be displayed without an overlap on a CRT is called as resolution. Q 14. What is Aspect Ratio? Ans. The ratio of vertical points to the horizontal points necessary to produce length of lines in both directions of the screen is called Aspect Ratio. Usually the aspect ratio is ¾. Q 15. What is meant by Addressability? Ans. Addressability is the number of individual dots per inch (d.p.i.) that can be created. If the address of the current dot is (x, y) then the next dot will be (x + y), (x + y + 1) etc. Q 16. What is a dot size? Ans. Dot size may be defined as the diameter of a single dot on the devices output. Dot size is also called as the Spot size. Q 17. What is interdot distance? Ans. Interdot distance is the reciprocal of addressability. If the addressability is large, the interdot distance will be less. The interdot distance should be less to get smooth shapes. Q 18. What is the difference between impact and non-impact printers? Ans. Impact printers press formed character faces against an inked ribbon on to the paper. A line printer and dot-matrix printer are examples.
4 Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 4 Non-impact printer and plotters use Laser techniques, inkjet sprays, Xerographic process, electrostatic methods and electro thermal methods to get images onto the papers. Examples are: Inkjet/Laser printers. Q 19. What is the features of Inkjet printers? Ans. Features of inkjet printers: 1. They can print 2 to 4 pages/minutes. 2. Resolution is about 360d.p.i. Therefore better print quality is achieved. 3. The operating cost is very low. The only part that requires replacement is ink cartridge. 4. Four colors cyan, yellow, magenta, black are available. Q 20. What are the advantages of laser printers? Ans. Advantages of laser printer: 1. High speed, precision and economy. 2. Cheap to maintain. 3. Quality printers. 4. Lasts for longer time. 5. Toner power is very cheap. Q 21. What is the advantages of electrostatic plotters? Ans. Advantages of electrostatic plotters: 1. They are faster than pen plotters and very high quality printers. 2. Recent electrostatic plotters include a scan-conversion capability. 3. Color electrostatic plotters are available. They make multiple passes over the paper to plot color pictures. Q 22. Explain the differences between a general graphics system designed for a programmer and one designed for a specific application, such as architectural design? Ans. Basically, packages designed for graphics programming contain functions for setting primitives, attributes, and parameters for various graphics operations such as viewing and transformations. Packages designed for applications allow a user to create scenes in terms of the particular application, rather than in terms of graphics functions.
5 Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 5 Q 23. Consider three different raster systems with resolutions of 640 x 480, 1280 x 1024 and 2560 x a) What size is frame buffer (in bytes) for each of these systems to store 12 bits per pixel? b) How much storage (in bytes) is required for each system if 24 bits per pixel are to be stored? Ans. a) Because eight bits constitute a byte, frame-buffer sizes of the systems are as follows: 640 x 480 x 12 bits π 8 = 450KB 1280 x 1024 x 12 bits π 8 = 1920KB 2560 x 2048 x 12 bits π 8 = 7680KB b) Similarly, each of the above results is just doubled for 24 (12x2) bits of storage per pixel. Q 24. Consider two raster systems with the resolutions of 640 x 480 and 1280 x a) How many pixels could be accessed per second in each of these systems by a display controller that refreshes the screen at a rate of 60 frames per second? b) What is the access time per pixel in each system? Ans. a) Since 60 frames are refreshed per second and each frame consists of 640 x 480 pixels, the access rate of such a system is: (640 x 480) * 60 = x 107 pixels/second. Likewise, for the 1280 x 1024 system, the access rate is: (1280 x 1024) * 60 = x 107 pixels/second. b) According to the definition of access rate, we know that the access time per pixel should be 1/(access rate). Therefore, the access time is around 54 nanoseconds/pixel for the 640 x 480 system, and the access time is around 12.7 nanoseconds/pixel for the 1280 x 1024 system. Q 25. Consider a raster system with the resolution of 1024 x 768 pixels and the color palette calls for 65,536 colors. What is the minimum amount of video RAM that the computer must have to support the above-mentioned resolution and number of colors? Ans. Recall that the color of each pixel on a display is represented with some number of bits. Hence, a display capable of showing up to 256 colors is using 8 bits per pixels (i.e., 8-bit color ).
6 Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 6 Notice, first that the color palette calls for 65,536 colors. This number is but 216, which implies that 16 bits are being used to represent the color of each pixel on the display. The display s resolution is 1024 by 768 pixels, which implies that there is a total of 786,432 ( ) pixels on the display. Hence, the total number of bits required to display any of 65,536 colors on each of the screen s 786,432 pixels is 12,582,912 (786,432 16). Dividing this value by 8 yields an answer of 1,572,864 bytes. Dividing that value by 1,024 yields an answer of 1,536 KB. Dividing that value by 1,024 yields an answer of 1.5 MB.
Important Question with Answer
 Important Question with Answer Q1. What do you mean by computer graphics? Ans. The branch of science and technology concerned with methods and techniques for converting data to or from visual presentation
Important Question with Answer Q1. What do you mean by computer graphics? Ans. The branch of science and technology concerned with methods and techniques for converting data to or from visual presentation
COMPUTER GRAPHICS IMPORTANT QUESTION AND ANSWERS. Computer graphics
 Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING. Chapter 4 Output Devices
 CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
Lecture Notes, CEng 477
 Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Comp 410/510. Computer Graphics Spring 2016. Introduction to Graphics Systems
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2016 Introduction to Graphics Systems Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware (PC with graphics card)
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2016 Introduction to Graphics Systems Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware (PC with graphics card)
Pages 304 305. Figure 6-1. Page 305
 What Is Output? Output is data that has been processed into a useful form Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Figure -1 Objectives Overview Describe the types of output
What Is Output? Output is data that has been processed into a useful form Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Figure -1 Objectives Overview Describe the types of output
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices
 Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
Overview. Raster Graphics and Color. Overview. Display Hardware. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
 Raster Graphics and Color Greg Humphreys CS445: Intro Graphics University of Virginia, Fall 2004 Color models Color models Display Hardware Video display devices Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display
Raster Graphics and Color Greg Humphreys CS445: Intro Graphics University of Virginia, Fall 2004 Color models Color models Display Hardware Video display devices Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal
 Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays
 Display technology Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays Vector displays generally display lines, specified by their endpoints. Vector display
Display technology Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays Vector displays generally display lines, specified by their endpoints. Vector display
The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input device for text and numbers.
 Standard Methods of Input Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input
Standard Methods of Input Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input
1. Application of Computer Graphics
 1. Application of Computer Graphics Computer-Aided Design for engineering and architectural systems etc. Objects maybe displayed in a wireframe outline form. Multi-window environment is also favored for
1. Application of Computer Graphics Computer-Aided Design for engineering and architectural systems etc. Objects maybe displayed in a wireframe outline form. Multi-window environment is also favored for
Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
 LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
Graphic Communication
 Graphic Communication St Pauls RC Academy Computer Hardware CDT Department Hardware Devices Hardware is the name given to any piece of equipment that is used along side a computer (including the main computer
Graphic Communication St Pauls RC Academy Computer Hardware CDT Department Hardware Devices Hardware is the name given to any piece of equipment that is used along side a computer (including the main computer
TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices
 TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ Input devices allow us to enter raw data into a computer. The computer processes the data and then produces
TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ Input devices allow us to enter raw data into a computer. The computer processes the data and then produces
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module
 Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Tomorrow s Technology and You
 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT IMAGING
 AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software
 What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
Discovering Computers. Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet. Chapter 7. Input and Output
 Discovering Computers Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet Chapter 7 Input and Output Objectives Overview Differentiate among various types of keyboards: standard, compact,
Discovering Computers Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet Chapter 7 Input and Output Objectives Overview Differentiate among various types of keyboards: standard, compact,
Computer Hardware Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of MCA
 A Seminar report On Computer Hardware Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of MCA SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org www.studymafia.org Preface I have
A Seminar report On Computer Hardware Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of MCA SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org www.studymafia.org Preface I have
10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES
 FORM 4 COMPUTER STUDIES Chapter 10: Input and Output Devices March, 01 10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES The main function of an input device is to The main function of an output device is to
FORM 4 COMPUTER STUDIES Chapter 10: Input and Output Devices March, 01 10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES The main function of an input device is to The main function of an output device is to
WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING
 What You should Know About Scanning WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING If you re thinking about purchasing a scanner, you may already know some of the ways they can add visual interest and variety to
What You should Know About Scanning WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING If you re thinking about purchasing a scanner, you may already know some of the ways they can add visual interest and variety to
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
Computers: Tools for an Information Age. Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection
 Computers: Tools for an Information Age Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection Objectives Describe the user relationship with computer input and output Explain how data is input into a computer
Computers: Tools for an Information Age Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection Objectives Describe the user relationship with computer input and output Explain how data is input into a computer
Computer Graphics. Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer
 Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware Software Applications Computer graphics is using computers to generate and display images based on
Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware Software Applications Computer graphics is using computers to generate and display images based on
Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.2 OBJECTIVES
 Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS
 CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
The six steps of Printing 1. Cleaning
 The Printer Laser Printers Laser Printers Ink-Jet printers Dot Matrix Printers Advantages/Disadvantages Laser Printers Advantages Fast Good image Quality Reliable Durable water resistant image Excellent
The Printer Laser Printers Laser Printers Ink-Jet printers Dot Matrix Printers Advantages/Disadvantages Laser Printers Advantages Fast Good image Quality Reliable Durable water resistant image Excellent
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O
 Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
How many PIXELS do you need? by ron gibbs
 How many PIXELS do you need? by ron gibbs We continue to move forward into the age of digital photography. The basic building block of digital images is the PIXEL which is the shorthand for picture element.
How many PIXELS do you need? by ron gibbs We continue to move forward into the age of digital photography. The basic building block of digital images is the PIXEL which is the shorthand for picture element.
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203.
 VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
Computers Are Your Future. 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
 Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
WHO CARES ABOUT RESOLUTION?
 WHO CARES ABOUT RESOLUTION? At Poli we certainly do not care about resolution as a concept! However we do care deeply about resolution when used as a measure of quality. Resolution is a very dry and technical
WHO CARES ABOUT RESOLUTION? At Poli we certainly do not care about resolution as a concept! However we do care deeply about resolution when used as a measure of quality. Resolution is a very dry and technical
Unit A451: Computer systems and programming. Section 2: Computing Hardware 4/5: Input and Output Devices
 Unit A451: Computer systems and programming Section 2: Computing Hardware 4/5: Input and Output Devices Input and Output devices Candidates should be able to: (a) understand the need for input and output
Unit A451: Computer systems and programming Section 2: Computing Hardware 4/5: Input and Output Devices Input and Output devices Candidates should be able to: (a) understand the need for input and output
Scanners and How to Use Them
 Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction A scanner is a device that converts images to a digital file you can use with your computer. There are many different types
Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction A scanner is a device that converts images to a digital file you can use with your computer. There are many different types
Primary Memory. Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit)
 Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Graphic Design. Background: The part of an artwork that appears to be farthest from the viewer, or in the distance of the scene.
 Graphic Design Active Layer- When you create multi layers for your images the active layer, or the only one that will be affected by your actions, is the one with a blue background in your layers palette.
Graphic Design Active Layer- When you create multi layers for your images the active layer, or the only one that will be affected by your actions, is the one with a blue background in your layers palette.
Digital printing? Digital C Print. Inkjet. i.e. pictures from Target, Wal-Mart, or Walgreens. i.e. Epson, Canon, Hewlett-Packard
 Jeremy Moore Digital printing? Digital printing refers to printing (specifically photographs in our case) where at least one step is entirely in the digital realm. Two main methods of digital printing
Jeremy Moore Digital printing? Digital printing refers to printing (specifically photographs in our case) where at least one step is entirely in the digital realm. Two main methods of digital printing
Technology in Action. Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy. Tenth Edition. Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers Understanding
Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers Understanding
MassArt Studio Foundation: Visual Language Digital Media Cookbook, Fall 2013
 INPUT OUTPUT 08 / IMAGE QUALITY & VIEWING In this section we will cover common image file formats you are likely to come across and examine image quality in terms of resolution and bit depth. We will cover
INPUT OUTPUT 08 / IMAGE QUALITY & VIEWING In this section we will cover common image file formats you are likely to come across and examine image quality in terms of resolution and bit depth. We will cover
Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices. A PC in Every Home. Assembling a Computer System
 C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies
 Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
Graphic Design Basics. Shannon B. Neely. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Graphics and Multimedia Design Group
 Graphic Design Basics Shannon B. Neely Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Graphics and Multimedia Design Group The Design Grid What is a Design Grid? A series of horizontal and vertical lines that evenly
Graphic Design Basics Shannon B. Neely Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Graphics and Multimedia Design Group The Design Grid What is a Design Grid? A series of horizontal and vertical lines that evenly
Digital Image Basics. Introduction. Pixels and Bitmaps. Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color
 Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction When using digital equipment to capture, store, modify and view photographic images, they must first be converted to a set
Written by Jonathan Sachs Copyright 1996-1999 Digital Light & Color Introduction When using digital equipment to capture, store, modify and view photographic images, they must first be converted to a set
Computer Hardware HARDWARE. Computer Hardware. Mainboard (Motherboard) Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN
 Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview
 Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS. NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions.
 B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
So you say you want something printed...
 So you say you want something printed... Well, that s great! You ve come to the right place. Whether you re having us design and edit your work, or you fancy yourself a designer and plan to hand over your
So you say you want something printed... Well, that s great! You ve come to the right place. Whether you re having us design and edit your work, or you fancy yourself a designer and plan to hand over your
Chapter 5 Understanding Input. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 5 Understanding Input Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Define input and differentiate among a program, command, and user response Identify
Chapter 5 Understanding Input Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Define input and differentiate among a program, command, and user response Identify
Index SNo Lesson Lesson Name Author Vetter. 1 1 Overview of Computer Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia
 Index SNo Lesson Lesson Name Author Vetter No. Overview of Computer Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia Graphics Display Devices Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia 3 3 Scan Conversion Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep
Index SNo Lesson Lesson Name Author Vetter No. Overview of Computer Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia Graphics Display Devices Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep Bhatia 3 3 Scan Conversion Abhesik Taneja Dr. Pradeep
1 PERSONAL COMPUTERS
 PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
COMPUTER BASICS. Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre
 COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
Computer Peripherals
 Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Introduction to Computer Applications CISY 1225. Dr. Zahoor Khan
 Introduction to Computer Applications CISY 1225 Dr. Zahoor Khan Last updated: May 2014 Why Computer is Important HOME COMPUTING COMMERCE NOT THIS EDUCATION ENGINEERING Medical THE FUTURE? Computer-literate
Introduction to Computer Applications CISY 1225 Dr. Zahoor Khan Last updated: May 2014 Why Computer is Important HOME COMPUTING COMMERCE NOT THIS EDUCATION ENGINEERING Medical THE FUTURE? Computer-literate
2. Keyboard-An input device similar to a typewriter, for the entry of text, numbers and punctuation.
 Computer Hardware: 1. System Unit- The main part of a personal computer. The system unit includes the chassis, microprocessor, main memory, bus, and ports, but does not include the keyboard or monitor,
Computer Hardware: 1. System Unit- The main part of a personal computer. The system unit includes the chassis, microprocessor, main memory, bus, and ports, but does not include the keyboard or monitor,
1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2
 1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2 06-02408 Level 3 10 credits in Semester 2 Professor Aleš Leonardis Slides by Professor Ela Claridge What is computer graphics? The art of 3D graphics is the art of fooling the
1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2 06-02408 Level 3 10 credits in Semester 2 Professor Aleš Leonardis Slides by Professor Ela Claridge What is computer graphics? The art of 3D graphics is the art of fooling the
MEMORY STORAGE CALCULATIONS. Professor Jonathan Eckstein (adapted from a document due to M. Sklar and C. Iyigun)
 1/29/2007 Calculations Page 1 MEMORY STORAGE CALCULATIONS Professor Jonathan Eckstein (adapted from a document due to M. Sklar and C. Iyigun) An important issue in the construction and maintenance of information
1/29/2007 Calculations Page 1 MEMORY STORAGE CALCULATIONS Professor Jonathan Eckstein (adapted from a document due to M. Sklar and C. Iyigun) An important issue in the construction and maintenance of information
EPSON SCANNING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Epson Perfection 3170 Scanner
 EPSON SCANNING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Epson Perfection 3170 Scanner SELECT A SUITABLE RESOLUTION The best scanning resolution depends on the purpose of the scan. When you specify a high resolution,
EPSON SCANNING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Epson Perfection 3170 Scanner SELECT A SUITABLE RESOLUTION The best scanning resolution depends on the purpose of the scan. When you specify a high resolution,
White Paper. Advances in Imaging to Improve Output Quality. April 2015. The Xerox Versant and EFI Fiery Digital Front End.
 White Paper April 2015 Advances in Imaging to Improve Output Quality The Xerox Versant and EFI Fiery Digital Front End Service Area On Demand Printing & Publishing Consulting Service Comments or Questions?
White Paper April 2015 Advances in Imaging to Improve Output Quality The Xerox Versant and EFI Fiery Digital Front End Service Area On Demand Printing & Publishing Consulting Service Comments or Questions?
Computer Peripherals
 Computer Peripherals School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore These notes are part of a 3rd year undergraduate course called "Computer Peripherals", taught at Nanyang Technological
Computer Peripherals School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore These notes are part of a 3rd year undergraduate course called "Computer Peripherals", taught at Nanyang Technological
Chapter 1. The largest computers, used mainly for research, are called a. microcomputers. b. maxicomputers. c. supercomputers. d. mainframe computers.
 Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
Understanding Digital Components
 Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics
 A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
Preliminary Draft May 19th 1992. Video Subsystem
 Video Subsystem 2 Preliminary Draft May 19th 1992 Video Subsystem Section 1. Introduction....................... 1-1 Video Subsystem.......................... 1-2 Section 2. VGA Function......................
Video Subsystem 2 Preliminary Draft May 19th 1992 Video Subsystem Section 1. Introduction....................... 1-1 Video Subsystem.......................... 1-2 Section 2. VGA Function......................
Chapter 9: Input-Output Devices
 Slide 1/58 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Input/Output (I/O) devices Commonly used input devices Commonly used output devices Other concepts related to I/O devices 148 Slide
Slide 1/58 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Input/Output (I/O) devices Commonly used input devices Commonly used output devices Other concepts related to I/O devices 148 Slide
Computers are now making it possible to combine sound, images and motion
 Hardware and Software for Multimedia Development 3 Computers are now making it possible to combine sound, images and motion together. In earlier sections, you have read about definitions of multimedia
Hardware and Software for Multimedia Development 3 Computers are now making it possible to combine sound, images and motion together. In earlier sections, you have read about definitions of multimedia
Created by the St. Dorothy s Project Team Updated by Oksana Maibroda
 Computer Basics ICT Training Updated: May 2002 Job Aid Created by the St. Dorothy s Project Team Updated by Oksana Maibroda Introduction to computer basics for Macintosh computers Welcome to this training
Computer Basics ICT Training Updated: May 2002 Job Aid Created by the St. Dorothy s Project Team Updated by Oksana Maibroda Introduction to computer basics for Macintosh computers Welcome to this training
designed and prepared for california safe routes to school by circle design circledesign.net Graphic Standards
 Graphic Standards Table of Contents introduction...2 General Usage...2 Logo lockups: color...3 LOGO LOCKUPS: GRAYSCALE...4 Minimum Staging Area...5 Minimum Logo Size...6 Type Family...7 Color Palettes...8
Graphic Standards Table of Contents introduction...2 General Usage...2 Logo lockups: color...3 LOGO LOCKUPS: GRAYSCALE...4 Minimum Staging Area...5 Minimum Logo Size...6 Type Family...7 Color Palettes...8
ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide
 Adobe Training Services Exam Guide ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide Adobe Training Services provides this exam guide to help prepare partners, customers, and consultants who are actively seeking accreditation
Adobe Training Services Exam Guide ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide Adobe Training Services provides this exam guide to help prepare partners, customers, and consultants who are actively seeking accreditation
Chapter 5 Objectives. Chapter 5 Input
 Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
CAD/CAM. Hardware and software. CAD/CAM/CAE System. Shahrood University. Display Processing Unit
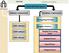 CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
Input and Output. Chapter 6
 Input and Output Chapter 6 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be
Input and Output Chapter 6 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be
2 COMPUTER ORGANISATION
 2 COMPUTER ORGANISATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous lesson we discussed about the evolution of computer. In this lesson we will provide you with an overview of the basic design of a computer. You
2 COMPUTER ORGANISATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous lesson we discussed about the evolution of computer. In this lesson we will provide you with an overview of the basic design of a computer. You
Lesson 10: Video-Out Interface
 Lesson 10: Video-Out Interface 1. Introduction The Altera University Program provides a number of hardware controllers, called cores, to control the Video Graphics Array (VGA) Digital-to-Analog Converter
Lesson 10: Video-Out Interface 1. Introduction The Altera University Program provides a number of hardware controllers, called cores, to control the Video Graphics Array (VGA) Digital-to-Analog Converter
Main Memory & Backing Store. Main memory backing storage devices
 Main Memory & Backing Store Main memory backing storage devices 1 Introduction computers store programs & data in two different ways: nmain memory ntemporarily stores programs & data that are being processed
Main Memory & Backing Store Main memory backing storage devices 1 Introduction computers store programs & data in two different ways: nmain memory ntemporarily stores programs & data that are being processed
Displays. Cathode Ray Tube. Semiconductor Elements. Basic applications. Oscilloscope TV Old monitors. 2009, Associate Professor PhD. T.
 Displays Semiconductor Elements 1 Cathode Ray Tube Basic applications Oscilloscope TV Old monitors 2 1 Idea of Electrostatic Deflection 3 Inside an Electrostatic Deflection Cathode Ray Tube Gun creates
Displays Semiconductor Elements 1 Cathode Ray Tube Basic applications Oscilloscope TV Old monitors 2 1 Idea of Electrostatic Deflection 3 Inside an Electrostatic Deflection Cathode Ray Tube Gun creates
Module 1 Concepts of Infor mation Technology (IT) Module Goals
 Module 1 Concepts of Infor mation Technology (IT) The following is the Syllabus for Module 1, Concepts of Information Technology (IT), which provides the basis for the theory-based test in this module
Module 1 Concepts of Infor mation Technology (IT) The following is the Syllabus for Module 1, Concepts of Information Technology (IT), which provides the basis for the theory-based test in this module
ICT THEORY 4 MAIN AREAS
 ICT THEORY RE- CAP & REVISION (SUMMARY OF THE THEORY HANDOUT) 4 MAIN AREAS 1. HARDWARE 2. SOFTWARE 3. NETWORKS, CONNECTIVITY, COMMUNICATION & THE INTERNET. 4. USE/MISUSE AND CARE OF COMPUTERS 1 Hardware
ICT THEORY RE- CAP & REVISION (SUMMARY OF THE THEORY HANDOUT) 4 MAIN AREAS 1. HARDWARE 2. SOFTWARE 3. NETWORKS, CONNECTIVITY, COMMUNICATION & THE INTERNET. 4. USE/MISUSE AND CARE OF COMPUTERS 1 Hardware
CRT and LCD monitors properties and problems. Maarten Demeyer October 27 2010
 CRT and LCD monitors properties and problems Maarten Demeyer October 27 2010 Overview Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Comparing CRT and LCD The future of computer displays Overview
CRT and LCD monitors properties and problems Maarten Demeyer October 27 2010 Overview Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Comparing CRT and LCD The future of computer displays Overview
BASIC CONCEPTS IN COMPUTER HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE
 BASIC CONCEPTS IN COMPUTER HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE THE NEED FOR COMPUTER LITERACY Information is power and Computers are amplifiers of information When a pregnant woman collapsed into hepatic coma, a surgeon
BASIC CONCEPTS IN COMPUTER HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE THE NEED FOR COMPUTER LITERACY Information is power and Computers are amplifiers of information When a pregnant woman collapsed into hepatic coma, a surgeon
Parts of a Computer. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. 1 1999 Micron Technology Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
HIGH-RESOLUTION INKJET THERMAL TRANSFER LABELS FOR BARCODING
 HIGH-RESOLUTION INKJET VS. THERMAL TRANSFER LABELS FOR BARCODING TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Technology 1 Consumable Costs 2 Barcode Printing Capability 2 Print Contrast 4 Product Handling Requirements
HIGH-RESOLUTION INKJET VS. THERMAL TRANSFER LABELS FOR BARCODING TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Technology 1 Consumable Costs 2 Barcode Printing Capability 2 Print Contrast 4 Product Handling Requirements
Hardware for Multimedia. Input and Output Devices. Most important components of a multimedia system. Devices classified as per their use
 Hardware for Multimedia Input and Output Devices Most important components of a multimedia system Devices classified as per their use Key devices for multimedia output Monitors for text and graphics (still
Hardware for Multimedia Input and Output Devices Most important components of a multimedia system Devices classified as per their use Key devices for multimedia output Monitors for text and graphics (still
Understanding Resolution and the meaning of DPI, PPI, SPI, & LPI
 Understanding Resolution and the meaning of DPI, PPI, SPI, & LPI 2003, 2006, and 2012 David Creamer I.D.E.A.S. Publishing Consultant & Trainer Authorized Adobe Training Provider for Photoshop, Illustrator,
Understanding Resolution and the meaning of DPI, PPI, SPI, & LPI 2003, 2006, and 2012 David Creamer I.D.E.A.S. Publishing Consultant & Trainer Authorized Adobe Training Provider for Photoshop, Illustrator,
Digitisation Disposal Policy Toolkit
 Digitisation Disposal Policy Toolkit Glossary of Digitisation Terms August 2014 Department of Science, Information Technology, Innovation and the Arts Document details Security Classification Date of review
Digitisation Disposal Policy Toolkit Glossary of Digitisation Terms August 2014 Department of Science, Information Technology, Innovation and the Arts Document details Security Classification Date of review
B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN
 COURSE GUIDE B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN GRD 126 COMPUTER GENERATED GRAPHIC DESIGN I UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION, WINNEBA DEPARTMENT OF GRAPHIC DESIGN Copyright Acknowledgements The facilitating agent of the course
COURSE GUIDE B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN GRD 126 COMPUTER GENERATED GRAPHIC DESIGN I UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION, WINNEBA DEPARTMENT OF GRAPHIC DESIGN Copyright Acknowledgements The facilitating agent of the course
Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 110 Course Title: Computer Literacy
 Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 11 Course Title: Computer Literacy Course Length: 3 credits 3 5-minute meetings per week or equivalent Course Description: An introduction to the
Montgomery College Course Designator/Course Number: CS 11 Course Title: Computer Literacy Course Length: 3 credits 3 5-minute meetings per week or equivalent Course Description: An introduction to the
What Resolution Should Your Images Be?
 What Resolution Should Your Images Be? The best way to determine the optimum resolution is to think about the final use of your images. For publication you ll need the highest resolution, for desktop printing
What Resolution Should Your Images Be? The best way to determine the optimum resolution is to think about the final use of your images. For publication you ll need the highest resolution, for desktop printing
Links. Blog. Great Images for Papers and Presentations 5/24/2011. Overview. Find help for entire process Quick link Theses and Dissertations
 Overview Great Images for Papers and Presentations May 26, 2011 Web Tips Definitions Using the Michigan Tech logo Photography 101 Great images from others Great images you create PDF conversion Final words
Overview Great Images for Papers and Presentations May 26, 2011 Web Tips Definitions Using the Michigan Tech logo Photography 101 Great images from others Great images you create PDF conversion Final words
Tips for optimizing your publications for commercial printing
 Tips for optimizing your publications for commercial printing If you need to print a publication in higher quantities or with better quality than you can get on your desktop printer, you will want to take
Tips for optimizing your publications for commercial printing If you need to print a publication in higher quantities or with better quality than you can get on your desktop printer, you will want to take
CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING MICROSCOPY TUTORIAL
 CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING MICROSCOPY TUTORIAL Robert Bagnell 2006 This tutorial covers the following CLSM topics: 1) What is the optical principal behind CLSM? 2) What is the spatial resolution in X, Y,
CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING MICROSCOPY TUTORIAL Robert Bagnell 2006 This tutorial covers the following CLSM topics: 1) What is the optical principal behind CLSM? 2) What is the spatial resolution in X, Y,
Digital Imaging and Image Editing
 Digital Imaging and Image Editing A digital image is a representation of a twodimensional image as a finite set of digital values, called picture elements or pixels. The digital image contains a fixed
Digital Imaging and Image Editing A digital image is a representation of a twodimensional image as a finite set of digital values, called picture elements or pixels. The digital image contains a fixed
Alternative Methods Of Input. Kafui A. Prebbie [email protected] 82
 Alternative Methods Of Input Kafui A. Prebbie [email protected] 82 This lesson includes the following sections: Devices for the Hand Optical Input Devices Audio-Visual (Multimedia) Input Devices Kafui A.
Alternative Methods Of Input Kafui A. Prebbie [email protected] 82 This lesson includes the following sections: Devices for the Hand Optical Input Devices Audio-Visual (Multimedia) Input Devices Kafui A.
The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input device for text and numbers.
 Standard Methods of Input Keyboard Mouse Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still
Standard Methods of Input Keyboard Mouse Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still
Management Challenge. Managing Hardware Assets. Central Processing Unit. What is a Computer System?
 Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Chap-02, Hardware and Software. Hardware Model
 Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
