Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.2 OBJECTIVES
|
|
|
- Calvin Barnett
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized and various operations performed to perform a specific task. You would have observed that instructions have to be fed into the computer in a systematic order to perform a specific task. Computer components are divided into two major categories, namely, hardware and software. In this lesson we will discuss about hardware, i.e., the machine itself and its connected devices such as monitor, keyboard, mouse etc., as well as software that makes use of hardware for performing various functions. 1.2 OBJECTIVES After going through this lesson you would be able to: explain basic organization of computer system explain different types of input and output devices define Software and its classification distinguish between system software and application software describe computer language and its classification
2 2 :: Data Entry Operations 1.3 WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Computer is a device that transforms data into meaningful information. Data can be anything like marks obtained by you in various subjects. It can also be name, age, sex, weight, height, etc. of all the students in a class. Computer can also be defined in terms of functions it can perform. A computer can i) accept data, ii) store data, iii) process data as desired, and iv) retrieve the stored data as and when required and v) print the result in desired format. The major characteristics of a computer are high speed, accuracy, diligence, versatility and storage Computer Organisation The block diagram of computer is shown in Fig Memory Unit Input unit Control Unit Output unit Arithmetic Logic Unit Fig. 1.1 Block diagram of Computer Organisation The computer performs basically five major operations of functions irrespective of their size and make. These are 1) it accepts data or instruction by way of input, 2) it stores data, 3) it can process data as required by the user, 4) it gives results in the form of output, and 5) it controls all operations inside a computer. We discuss below each of these operations. 1. Input: this is the process of entering data and programs into the computer system.
3 Basics of Computer :: 3 2. Control Unit (CU): The process of input, output, processing and storage is performed under the supervision of a unit called 'Control Unit'. It decides when to start receiving data, when to stop it, where to store data, etc. It takes care of step -by-step processing of all operations in side the computer. 3. Memory Unit: Computer is used to store data and instructions. 4. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The major operations performed by the ALU are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, logic and comparison. 5. Output: This is the process of producing results from the data for getting useful information. The ALU and the CU of a computer system are jointly known as the central processing unit (CPU). You may call CPU as the brain of any computer system. INTEXT QUESTIONS 1. What are the five basic operations performed by the computer? 2. Define ALU, CU and CPU. 3. Choose the correct answer. (a) The task of performing arithmetic and logical operations is called: (i) ALU (ii) editing (iii) storage (iv) Output (b) The ALU and CU jointly are known as (i) RAM (ii) ROM (iii) CPU (iv) None of above (c) The process of producing results from the data for getting useful information is called: (i) output (ii) input (iii) processing (iv) storage 1.4 PERIPHERAL DEVICES Peripheral devices are connected to the computer externally. These devices are used for performing some specific functions. Peripheral devices are as follows: 1. Input Devices 2. Output Devices 3. Other Peripherals
4 4 :: Data Entry Operations Monitor Disk drives Keyboard Mouse Fig. 1.2 Different peripheral devices of Computer 1.5 INPUT DEVICES Input devices accept data and instructions from the user. Following are the examples of various input devices, which are connected to the computer for this purpose. 1. Keyboard 2. Mouse 3. Light Pen 4. Optical/magnetic Scanner 5. Touch Screen 6. Microphone for voice as input 7. Track Ball Keyboard A keyboard (as shown in figure 1.3) is the most common input device. Several kinds of keyboards are available, but they resemble each other with minor variations. The keyboard in most common use is the QWERTY board. Generally standard keyboard has 104 keys. In these keyboards, the cursor control keys are duplicated to allow easier use of the Fig. 1.3 Keyboard numeric pad.
5 Basics of Computer :: Mouse A mouse is an electro-mechanical, hand-held device (as shown in figure 1. 4). It is used as a pointer. It can perform functions like selecting menu commands, moving icons, resizing windows, starting programs, and choosing options. Fig. 1.4 Mouse The most common mouse uses an internal, magnetically coated ball, to detect the movement of the mouse across a flat surface, usually a desktop. Now a days Optical or laser mouse is used to detect the movement. All windows based applications today are designed to work with a mouse. A mouse is used to replace hard -to-remember key combinations with easier "Point and Click" actions. However, it cannot substitute all keyboard operations. It can be alternative for commands based operations Light pen An input device that utilizes a light-sensitive detector to select objects on a display screen. A light pen is similar to a mouse (as shown in figure 1.5), except that with a light pen you can move the pointer and select objects on the display screen by directly pointing to the objects with the pen Optical Scanner Fig. 1.5 Light Pen These devices are used for automatic data collection. The devices of this category completely eliminate manual input of data. For example, the bar-code reader is actually just a special type of image scanner. An image scanner translates printed
6 6 :: Data Entry Operations images into an electronic format that can be stored in a computer s memory, and with the right kind of software, one can alter a stored image. Another example of scanner is optical character recognition (OCR) device, used by banks to convert the scanned image of a typed or printed page into text that can be edited on the computer. Fig. 1.6 Scanner Touch Screen Touch panel displays and pads are now being offered as alternatives to keyboard. Here the input can be given through the computer screen, that accepts the input through monitor; users touch electronic buttons displayed on the screen or they may use light pen Microphone Fig. 1.7 Touch Screen Monitor Microphone is an input device, which takes voice as input. The voice communication is more error-prone than information through keyboard. There are two types of microphones available (as shown in figure 1.8): 1. Desktop Microphone 2. Hand held Microphone Fig. 1.8 Desktop microphone and Hand-held Microphone
7 Basics of Computer :: Track Ball Trackball, a pointing device, is a mouse lying on its back (as shown in figure 1. 9). To move the pointer, you rotate the ball with your thumb, your fingers, or the palm of your hand. There are usually one to three buttons next to the ball, which you use just like mouse buttons. Fig. 1.9 Track Ball The advantage of trackballs over mouse is that the trackball is stationary so it does not require much space to use it. In addition, you can place a trackball on any type of surface, including your lap. For both these reasons, trackballs are popular pointing devices for portable computers. 1.6 OUTPUT DEVICES Output devices return processed data that is information, back to the user. Some of the commonly used output devices are: 1. Monitor (Visual Display Unit) 2. Printers 3. Plotter 4. Speakers Monitor Out of all the output devices, monitor (as shown in figure 1.10) is perhaps the most important output device because people interact with this device most intensively than others. Computer Fig CRT and LCD Monitor information is displayed, visually with a video adapter card and monitor. Information processed within the CPU, that needs to be visually displayed, is sent to video adapter. The video adapter converts information from the format used, in the same manner as a television displays information sent to it by a cable service.
8 8 :: Data Entry Operations Two basic types of monitors are used with microcomputers, which are as follows: 1. CRT 2. LCD Cathode Ray Tube (CRT): CRT or Cathode Ray Tube Monitor is the typical monitor that you see on a desktop computer. It looks a lot like a television screen, and works the same way. This type uses a large vacuum tube, called cathode ray tube (CRT). Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD): This type of monitors are also known as flat panel monitor. Most of these employ liquid crystal displays (LCDs) to render images. These days LCD monitor are very popular. When people talk about the capabilities of various monitors, one critical statistic is the resolution of the monitor. Most monitors have a resolution of at least 800 x 600 pixels. High-end monitors can have resolutions of 1024 x 768 pixels or even 1280 x 1024 pixels. Thus monitors are available either in low resolution or in high resolution Printer After a document is created on the computer, it can be sent to a printer for a hard copy (printout). Some printers offer special features such as colored and large page formats. Some of the most commonly used printers are: 1. Laser Printer 2. Ink Jet Printer 3. Dot Matrix Printer 4. Line Printer Laser Printer: A laser printer produces high quality print that one normally finds in publishing. It is extremely fast and quiet. Moreover, the operation of a laser printer is easy with automatic paper loading and no smudging or messing up of ink ribbons. The fastest laser printer Fig Laser Printer
9 Basics of Computer :: 9 can print up to 200 pages per minute in monochrome (black and white) and up to 100 pages per minute in colour. Ink-Jet Printer: An ink-jet printer creates an image directly on paper by spraying ink through as many as 64 tiny nozzles. Although the image it produces is not generally quite as sharp as the output of a laser printer, the quality of ink-jet images is still high. In general, ink-jet printer offers an Fig Ink-Jet Printer excellent middle ground between dot matrix and laser printer. Like laser printer, an ink-jet printer is quiet and convenient, but not particularly fast. Typically, an ink-jet printer is more expensive than a dot-matrix printer, but costs only half as much as a laser printer. Dot Matrix Printer: The dot matrix printer was very popular at one point of time. It is a very versatile and inexpensive output device. In dot matrix printer the print head physically "hits" the paper through the ribbon and produces text (or images) by combinations of dots; hence the name dot matrix printer. Its speed is measured in characters per second (CPS). Although it is less expensive, it is louder, slower and produces lower print quality. Line Printer: A line printer is generally used with large computer systems to produce text based data processing reports. Line printers are high-speed printers with speeds ranging anywhere from 100 to about 3800 lines per minute. In the past, print quality on line printers was not high. Developments in technology are improving the print quality on line printers. These are in the cost range of lacs of Rupees. Fig Dot Matrix Printer Fig Line Printer
10 10 :: Data Entry Operations Plotter A plotter is a special kind of output device that, like a printer, produces images on paper, but does so in a different way. Plotters are designed to produce large drawings or images, such as construction plans for buildings or blueprints for mechanical objects. A plotter can be connected to the port normally used by a printer. An array of different colored pens in a clip rack and a robotic arm is part of plotter. The instructions that a plotter receives from a computer consist of a color, and beginning and ending coordinates for a line. With that information, the plotter picks up the appropriate pen through its arm, positions it at the beginning coordinates drops the pen down to the surface of the paper and draws to the ending coordinates. Plotters draw curves by creating a sequence of very short straight lines. Plotters usually come in two designs: 1. Flat Bed: Plotters of small size to be kept on table with restriction of paper size. 2. Drum: These plotters are of big size using rolls of paper of unlimited length Speaker Fig Flat bed and Drum Plotter Speakers (as shown in figure 1.16) are another type of output device, which allow you to listen to voice like music, and conversation with people. Fig Speaker
11 Basics of Computer :: 11 INTEXT QUESTION 4. Write True or False for the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 1.7 SOFTWARE Mouse is an output device. OCR stands for Optical Content Reader. LCD Monitor is used in notebook computer. Speed of DOT Matrix Printer is measured in Characters Per Second. Plotters are used to produce high quality drawings and images, such as construction plans for buildings or blueprints for mechanical objects. As you are aware, computer cannot do anything on its own. It is the user who instructs computer; what to do, how to do and when to do. In order to perform any task, you have to give a set of instructions in a particular sequence to the computer. These sets of instructions are called Programs. Software refers to a set of programs that makes the hardware perform a particular set of tasks in particular order. Software can be classified mainly into following categories and sub-categories are shown in Figure Software System Software Application Software Operating System Utilities Generalized Packages Customized Packages Fig Classification of Software
12 12 :: Data Entry Operations System Software When you switch on the computer the programs stored in ROM are executed which activates different units of your computer and makes it ready for you to work on it. This set of programs can be called system software. System softwares are sets of programs, responsible for running the computer, controlling various operations of computer systems and management of computer resources. Operating System (OS) falls under this category. An operating system is a system software that provides an interface for a user to communicate with the computer, manages hardware devices (disk drives, keyboard, monitor, etc), manages and maintains disk file systems and supports application programs. Some popular Operating systems are UNIX, Windows and Linux. Although operating system provides all the features users need to use and maintain their systems, inevitably, they still do not meet everyone s expectations. This has led to another type of system software called "Utilities". These are programs that bridge the gap between the functionality of an OS and the needs of users. Utility programs are a broad category of software such as compress (zip)/uncompress (unzip) files software, anti virus software, split and join files software, etc Application Software Application software is a set of programs, which are written to perform specific tasks, for example: An application package for managing library known as library information system is used to manage information of library such as: keeping book details, account holder details, book issue details, book return details etc. Another application package for managing student details is called student s information system, manages student s roll no, name, parents name, address, class, section, processing of examination results etc. Application software can be broadly classified into two types: (a) (b) Generalized packages Customized packages
13 Basics of Computer :: 13 Generalized Packages These are user friendly softwares written to cater to user s very general needs such as preparing documents, drawing pictures, database to manage data/information, preparing presentations, play games etc. It is a group of programs that provide general purpose tools to solve specific problems. Some of the generalized packages are listed below: Word Processing Software(for preparing documents): Word Perfect, MS-Word, OpenOffice.org Writer Spreadsheets (Data Analysis): Lotus Smart suites, MS- Excel, OpenOffice.org Calc, Apple Numbers Presentations : Presentation Graphics, MS-PowerPoint, OpenOffice.org Impress Database Management System: MS-Access, OpenOffice.org Base, MS-SQL Server, ORACLE Graphics Tools: Paint shop pro, Adobe Photoshop Customized Packages These are the applications that are customized (or developed) to meet the specific requirements of an organization/institution. For Example: Student information details, Payroll packages, inventory control etc. These packages are developed using high-level computer language. 1.8 COMPUTER LANGUAGES Languages are a means of communication. Normally people interact with each other through a language. On the same pattern, communication with computers is carried out through a language. This language is understood both by user and the machine. Just as every language like English, Hindi has its grammatical rules; every computer language is bound by rules known as SYNTAX of that language. The user is bound by that syntax while communicating with the computer system.
14 14 :: Data Entry Operations Computer languages are broadly classified as: 1. Low Level Language: The term low level means closeness to the way in which machine understand. The low level languages are: a. Machine Language: This is the language (in the form of 0 s and 1 s, called binary numbers) understood directly by the computer. It is machine dependent. It is difficult to learn and even more difficult to write programs. b. Assembly Language: This is the language where the machine codes comprising of 0 s and 1 s are substituted by symbolic codes (called mnemonics) to improve their understanding. It is the first step to improve programming structure. Assembly language programming is simpler and less time consuming than machine level programming, it is easier to locate and correct errors in assembly language than in machine language programs. It is also machine dependent. Programmers must have knowledge of the machine on which the program will run. 2. High Level Language You know that low level language requires extensive knowledge of the hardware since it is machine dependent. To overcome the limitation, high level language has been evolved which uses normal English like, easy to understand statements to solve any problem. Higher level languages are computer independent and programming becomes quite easy and simple. Various high level languages are given below: BASIC (Beginners All Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code): It is widely used, easy to learn general purpose language. Mainly used in microcomputers in earlier days.
15 Basics of Computer :: 15 COBOL (Common Business Oriented language): A standardized language used for commercial applications. FORTRAN (Formula Translation): Developed for solving mathematical and scientific problems. One of the most popular languages among scientific community. C: Structured Programming Language used for all purpose such as scientific application, commercial application, developing games etc. C++: Popular object oriented programming language, used for general purpose. 1.9 COMPILER AND ASSEMBLER As you know that High Level language is machine independent and assembly language though it is machine dependent yet mnemonics that are being used to represent instructions are not directly understandable by machine. Hence to make the machine understand the instructions provided by both the languages, Compiler and Assembler are required to convert these instructions into machine language. The software (set of programs) that reads a program written in high level language and translates it into an equivalent program in machine language is called as Compiler. The program written by the programmer in high level language is called source program and the program generated by the compiler after translation is called as object program. Source Program (Higher Level Language) Compiler Object Program (Machine Language) Fig Compiler The software (set of programs) that reads a program written in assembly language and translates it into an equivalent program in machine language is called as Assembler.
16 16 :: Data Entry Operations Source Program (Assembling Language) Assembler Object Program (Machine Language) Fig Assembler INTEXT QUESTION 5. Write True or False for the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Operating System (OS) is an Application Software. High level languages are easy to program than low level language. Computer language FORTRAN is used to solve Scientific and Mathematical problems. C is an object oriented programming language. Compiler converts high level languages into machine language WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNT A computer is useful only when it interacts with the external devices such as keyboard, mouse, monitor, speaker, which are called as peripheral devices. In this lesson we have discussed in details about major peripheral devices of a computer system. You have learnt that only hardware does not do anything of its own without the help of software. Hence we have explained in details about software, its types and the computer languages used to prepare the software TERMINAL QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? Draw a block diagram to illustrate the basic organisation of a computer system and explain the functions of various units. 2. What is an input device? Briefly describe varioius important input devices. 3. Discuss two basic types of monitors CRT and LCD.
17 Basics of Computer :: What is a software? Discuss its various categories with the help of diagram. 5. Distinguish between system and application software. 6. Write short notes on: (a) (b) (c) (d) Laser Printer High level language Compiler Plotter 7. Write a note on Computer language and its classification FEEDBACK TO INTEXT QUESTIONS 1. The five basic operations that a computer performs are input, storage, processing, output and control. 2. ALU : Arithmetic Logic Unit CU : Control Unit CPU : Central Processing Unit 3. (a) i (b) iii (c) i 4. (a) False (b) False (c) True (d) True (e) True 5. (a) False (b) True (c) True (d) False (e) True
3 SOFTWARE AND PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
 3 SOFTWARE AND PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous lesson we discussed about the different parts and configurations of computer. It has been mentioned that programs or instructions have
3 SOFTWARE AND PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous lesson we discussed about the different parts and configurations of computer. It has been mentioned that programs or instructions have
1 PERSONAL COMPUTERS
 PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input device for text and numbers.
 Standard Methods of Input Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input
Standard Methods of Input Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input
TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices
 TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ Input devices allow us to enter raw data into a computer. The computer processes the data and then produces
TH2. Input devices, processing and output devices http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/ict/ Input devices allow us to enter raw data into a computer. The computer processes the data and then produces
The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still the primary input device for text and numbers.
 Standard Methods of Input Keyboard Mouse Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still
Standard Methods of Input Keyboard Mouse Input device enables you to input information and commands into the computer. The Keyboard One of the first peripherals to be used with a computer and is still
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices
 Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
Chapter 3 Input Devices
 CSCA0101 COMPUTING BASICS Chapter 3 1 Topics: Examples of Input Device Keyboard Pointing Devices Graphic and Video Audio 2 Any peripheral (piece of computer hardware equipment) used to provide data and
CSCA0101 COMPUTING BASICS Chapter 3 1 Topics: Examples of Input Device Keyboard Pointing Devices Graphic and Video Audio 2 Any peripheral (piece of computer hardware equipment) used to provide data and
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal
 Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES
 FORM 4 COMPUTER STUDIES Chapter 10: Input and Output Devices March, 01 10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES The main function of an input device is to The main function of an output device is to
FORM 4 COMPUTER STUDIES Chapter 10: Input and Output Devices March, 01 10.1 FUNCTIONS OF INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES The main function of an input device is to The main function of an output device is to
Internet and Computing Core Certification Guide Module A Computing Fundamentals
 Lesson 4: Using Input/Output Devices input/output devices common input devices common output devices specialized devices how a device connects what a port is what a device driver is What are Input/Output
Lesson 4: Using Input/Output Devices input/output devices common input devices common output devices specialized devices how a device connects what a port is what a device driver is What are Input/Output
Discovering Computers. Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet. Chapter 7. Input and Output
 Discovering Computers Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet Chapter 7 Input and Output Objectives Overview Differentiate among various types of keyboards: standard, compact,
Discovering Computers Technology in a World of Computers, Mobile Devices, and the Internet Chapter 7 Input and Output Objectives Overview Differentiate among various types of keyboards: standard, compact,
Chapter 5 Objectives. Chapter 5 Input
 Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
Chapter 5 Input Describe two types of input List characteristics of a Identify various types of s Identify various types of pointing devices Chapter 5 Objectives Explain how voice recognition works Understand
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS World ORT Union I n p u t d e v i c e s Where would you find the letters QUERTY? A. Mouse B. Keyboard C.Numeric Keypad How did the computer mouse get its name? A.
Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
 LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
Computer Hardware HARDWARE. Computer Hardware. Mainboard (Motherboard) Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN
 Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
Computer Hardware HARDWARE Hardware: the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering 1. Case and inside 2. Peripherals
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING. Chapter 4 Output Devices
 CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
Chap-02, Hardware and Software. Hardware Model
 Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
Philadelphia University School of Business Administration INFO-101 Information Systems Prof London Chap-02, Hardware and Software Hardware Components Central processing unit (CPU) Arithmetic/logic unit
Chapter 5 Understanding Input. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 5 Understanding Input Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Define input and differentiate among a program, command, and user response Identify
Chapter 5 Understanding Input Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Define input and differentiate among a program, command, and user response Identify
Primary Memory. Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit)
 Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Graphic Communication
 Graphic Communication St Pauls RC Academy Computer Hardware CDT Department Hardware Devices Hardware is the name given to any piece of equipment that is used along side a computer (including the main computer
Graphic Communication St Pauls RC Academy Computer Hardware CDT Department Hardware Devices Hardware is the name given to any piece of equipment that is used along side a computer (including the main computer
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS
 CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
CHAPTER 3: HARDWARE BASICS: PERIPHERALS Multiple Choice: 1. is the early operating system developed by Microsoft A. Monitor B. MS-DOS C. Mouse D. Video games Answer: B Reference: Bill Gates Rides the Digital
Chapter 5 Input. Chapter 5 Objectives. What Is Input? What Is Input? The Keyboard. The Keyboard
 Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Input Define input List characteristics of of a keyboard Describe different mouse types and how they work Summarize how pointing devices work Explain how a digital camera
Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Input Define input List characteristics of of a keyboard Describe different mouse types and how they work Summarize how pointing devices work Explain how a digital camera
Chapter One Introduction to Computer
 Chapter One Introduction to Computer Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according
Chapter One Introduction to Computer Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according
Chapter 1. The largest computers, used mainly for research, are called a. microcomputers. b. maxicomputers. c. supercomputers. d. mainframe computers.
 Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
Tomorrow s Technology and You
 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Tomorrow s Technology and You 8 th Edition Slide 1 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e Hardware Basics: Peripherals Slide 2 Objectives List several examples of input devices and explain how they can make
Overview of MIS Professor Merrill Warkentin
 Management Systems (MIS) Mississippi State University Data raw numbers - not processed facts, lists, numbers, tables of value to an organization 1 2 Data Processing (DP) the restructuring of data to improve
Management Systems (MIS) Mississippi State University Data raw numbers - not processed facts, lists, numbers, tables of value to an organization 1 2 Data Processing (DP) the restructuring of data to improve
COMPUTER AND COMPUTERISED ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
 MODULE - 2 Computer and Computerised Accounting System 12 COMPUTER AND COMPUTERISED ACCOUNTING SYSTEM With the expansion of business the number of transactions increased. The manual method of keeping and
MODULE - 2 Computer and Computerised Accounting System 12 COMPUTER AND COMPUTERISED ACCOUNTING SYSTEM With the expansion of business the number of transactions increased. The manual method of keeping and
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O
 Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
COMPUTER - INPUT DEVICES
 COMPUTER - INPUT DEVICES http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_fundamentals/computer_input_devices.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Following are few of the important input devices which are used in a
COMPUTER - INPUT DEVICES http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_fundamentals/computer_input_devices.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Following are few of the important input devices which are used in a
Unit A451: Computer systems and programming. Section 2: Computing Hardware 4/5: Input and Output Devices
 Unit A451: Computer systems and programming Section 2: Computing Hardware 4/5: Input and Output Devices Input and Output devices Candidates should be able to: (a) understand the need for input and output
Unit A451: Computer systems and programming Section 2: Computing Hardware 4/5: Input and Output Devices Input and Output devices Candidates should be able to: (a) understand the need for input and output
2. Keyboard-An input device similar to a typewriter, for the entry of text, numbers and punctuation.
 Computer Hardware: 1. System Unit- The main part of a personal computer. The system unit includes the chassis, microprocessor, main memory, bus, and ports, but does not include the keyboard or monitor,
Computer Hardware: 1. System Unit- The main part of a personal computer. The system unit includes the chassis, microprocessor, main memory, bus, and ports, but does not include the keyboard or monitor,
Computers Are Your Future. 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
 Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
Computers Are Your Future 2005 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 5 Input/Output and Storage 200 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About The purpose of special keys and
Fall 2009. Lecture 1. Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345. Introduction to Operating Systems. Mostafa Z. Ali. [email protected].
 Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali [email protected] 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali [email protected] 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
Computers: Tools for an Information Age. Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection
 Computers: Tools for an Information Age Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection Objectives Describe the user relationship with computer input and output Explain how data is input into a computer
Computers: Tools for an Information Age Chapter 5 Input and Output: The User Connection Objectives Describe the user relationship with computer input and output Explain how data is input into a computer
Input and Output. Chapter 6
 Input and Output Chapter 6 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be
Input and Output Chapter 6 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be
Management Challenge. Managing Hardware Assets. Central Processing Unit. What is a Computer System?
 Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Computer Hardware Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of MCA
 A Seminar report On Computer Hardware Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of MCA SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org www.studymafia.org Preface I have
A Seminar report On Computer Hardware Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of MCA SUBMITTED TO: SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org www.studymafia.org Preface I have
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module
 Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Created by the St. Dorothy s Project Team Updated by Oksana Maibroda
 Computer Basics ICT Training Updated: May 2002 Job Aid Created by the St. Dorothy s Project Team Updated by Oksana Maibroda Introduction to computer basics for Macintosh computers Welcome to this training
Computer Basics ICT Training Updated: May 2002 Job Aid Created by the St. Dorothy s Project Team Updated by Oksana Maibroda Introduction to computer basics for Macintosh computers Welcome to this training
Pages 304 305. Figure 6-1. Page 305
 What Is Output? Output is data that has been processed into a useful form Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Figure -1 Objectives Overview Describe the types of output
What Is Output? Output is data that has been processed into a useful form Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Figure -1 Objectives Overview Describe the types of output
TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS
 TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Changes that you make in virtual machines do not affect your physical computer. 2. The size of a bus
TEST CHAPTERS 1 & 2 OPERATING SYSTEMS True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Changes that you make in virtual machines do not affect your physical computer. 2. The size of a bus
ICT THEORY 4 MAIN AREAS
 ICT THEORY RE- CAP & REVISION (SUMMARY OF THE THEORY HANDOUT) 4 MAIN AREAS 1. HARDWARE 2. SOFTWARE 3. NETWORKS, CONNECTIVITY, COMMUNICATION & THE INTERNET. 4. USE/MISUSE AND CARE OF COMPUTERS 1 Hardware
ICT THEORY RE- CAP & REVISION (SUMMARY OF THE THEORY HANDOUT) 4 MAIN AREAS 1. HARDWARE 2. SOFTWARE 3. NETWORKS, CONNECTIVITY, COMMUNICATION & THE INTERNET. 4. USE/MISUSE AND CARE OF COMPUTERS 1 Hardware
Chapter 9: Input-Output Devices
 Slide 1/58 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Input/Output (I/O) devices Commonly used input devices Commonly used output devices Other concepts related to I/O devices 148 Slide
Slide 1/58 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Input/Output (I/O) devices Commonly used input devices Commonly used output devices Other concepts related to I/O devices 148 Slide
5COMPUTER SCIENCE For Class IX (marks 55)
 5COMPUTER SCIENCE For Class IX (marks 55) 1. Introduction to Computers o History and development of computers - Types of computers (analogue, digital, hybrid) - Classification of digital computers (micro,
5COMPUTER SCIENCE For Class IX (marks 55) 1. Introduction to Computers o History and development of computers - Types of computers (analogue, digital, hybrid) - Classification of digital computers (micro,
Parts of a Computer. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. 1 1999 Micron Technology Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
COMPUTER BASICS. Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre
 COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT)
 Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
Alternative Methods Of Input. Kafui A. Prebbie [email protected] 82
 Alternative Methods Of Input Kafui A. Prebbie [email protected] 82 This lesson includes the following sections: Devices for the Hand Optical Input Devices Audio-Visual (Multimedia) Input Devices Kafui A.
Alternative Methods Of Input Kafui A. Prebbie [email protected] 82 This lesson includes the following sections: Devices for the Hand Optical Input Devices Audio-Visual (Multimedia) Input Devices Kafui A.
TYPES OF COMPUTERS AND THEIR PARTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies
 Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
Software: Systems and Application Software
 Software: Systems and Application Software Computer Software Operating System Popular Operating Systems Language Translators Utility Programs Applications Programs Types of Application Software Personal
Software: Systems and Application Software Computer Software Operating System Popular Operating Systems Language Translators Utility Programs Applications Programs Types of Application Software Personal
Lesson Plan. Preparation
 Lesson Plan Course Title: Principles of Information Technology Lesson Duration: 45 Minutes Session Title: Keyboards, Mice, and Other Input Devices Performance Objective: Upon completion of this assignment,
Lesson Plan Course Title: Principles of Information Technology Lesson Duration: 45 Minutes Session Title: Keyboards, Mice, and Other Input Devices Performance Objective: Upon completion of this assignment,
Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software
 What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now
 1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
ZIMBABWE SCHOOL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL. COMPUTER STUDIES 7014/01 PAPER 1 Multiple Choice SPECIMEN PAPER
 ZIMBABWE SCHOOL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level COMPUTER STUDIES 7014/01 PAPER 1 Multiple Choice SPECIMEN PAPER Candidates answer on the question paper Additional materials:
ZIMBABWE SCHOOL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level COMPUTER STUDIES 7014/01 PAPER 1 Multiple Choice SPECIMEN PAPER Candidates answer on the question paper Additional materials:
Computer Organization
 Basics Machine, software, and program design JPC and JWD 2002 McGraw-Hill, Inc. Computer Organization CPU - central processing unit Where decisions are made, computations are performed, and input/output
Basics Machine, software, and program design JPC and JWD 2002 McGraw-Hill, Inc. Computer Organization CPU - central processing unit Where decisions are made, computations are performed, and input/output
ERA6 OBJECTIVE QUSESTION
 1)Database Management Question:- ERA6 OBJECTIVE QUSESTION 1) While Creating a Table using the MS Access, you will get an interface, as shown on the screen this Interface shows, you are Working on the View
1)Database Management Question:- ERA6 OBJECTIVE QUSESTION 1) While Creating a Table using the MS Access, you will get an interface, as shown on the screen this Interface shows, you are Working on the View
SB101 SMART Board 101
 SB101 SMART Board 101 Pieces and Parts SMART Board with cable connected to a laptop or desktop computer LCD projector with cable connected to the computer Computer SMART Board cable (use the appropriate
SB101 SMART Board 101 Pieces and Parts SMART Board with cable connected to a laptop or desktop computer LCD projector with cable connected to the computer Computer SMART Board cable (use the appropriate
Basic Computer Hardware and Software
 Overview: This lesson is an introduction to basic computer hardware and software. If possible, have one or more types of computers available to show students the hardware components found on different
Overview: This lesson is an introduction to basic computer hardware and software. If possible, have one or more types of computers available to show students the hardware components found on different
A Computer Glossary. For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses
 A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
Introduction to Computers and Programming
 M01_GADD7119_01_SE_C01.QXD 1/30/08 12:55 AM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming TOPICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Hardware and Software 1.3 How Computers Store Data 1.4 How a Program Works
M01_GADD7119_01_SE_C01.QXD 1/30/08 12:55 AM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming TOPICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Hardware and Software 1.3 How Computers Store Data 1.4 How a Program Works
2 COMPUTER ORGANISATION
 2 COMPUTER ORGANISATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous lesson we discussed about the evolution of computer. In this lesson we will provide you with an overview of the basic design of a computer. You
2 COMPUTER ORGANISATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous lesson we discussed about the evolution of computer. In this lesson we will provide you with an overview of the basic design of a computer. You
Introduction to Mac Operating System: Snow Leopard
 Introduction to Mac Operating System: Snow Leopard Switching the Computer On 1. Press the round button on the back of the computer to turn the computer on. If the screen is black, but the lights are lit
Introduction to Mac Operating System: Snow Leopard Switching the Computer On 1. Press the round button on the back of the computer to turn the computer on. If the screen is black, but the lights are lit
SUMMARIES OF VIDEOS GRADE 11 SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES
 SUMMARIES OF VIDEOS GRADE 11 SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES 1. Case Study - Understanding Computers and Computing A computer is an electronic device that can accept, process and store data by following instructions
SUMMARIES OF VIDEOS GRADE 11 SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES 1. Case Study - Understanding Computers and Computing A computer is an electronic device that can accept, process and store data by following instructions
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations. General Certificate of Secondary Education ICT FOUNDATION TIER. Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes Total marks: 90
 GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education ICT FOUNDATION TIER Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes Total marks: 90 Answer all questions in the spaces provided 1. Information can be
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education ICT FOUNDATION TIER Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes Total marks: 90 Answer all questions in the spaces provided 1. Information can be
www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions)
 www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions) Q 1. Can you give some basic features of computer graphics? Ans. The salient feature of computer graphics
www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions) Q 1. Can you give some basic features of computer graphics? Ans. The salient feature of computer graphics
SMART Board User Guide for Mac
 SMART Board User Guide for Mac What is it? SMART Board is an interactive whiteboard available in an increasing number of classrooms at the University of Tennessee. While your laptop image is projected
SMART Board User Guide for Mac What is it? SMART Board is an interactive whiteboard available in an increasing number of classrooms at the University of Tennessee. While your laptop image is projected
After going through this lesson you would be able to:
 18 :: Data Entry Operations 2 Operating System 2.1 INTRODUCTION The operating system in these days uses a graphical user interface (GUI). Here you do not have to remember all the commands by heart. The
18 :: Data Entry Operations 2 Operating System 2.1 INTRODUCTION The operating system in these days uses a graphical user interface (GUI). Here you do not have to remember all the commands by heart. The
Module A. Computing Fundamentals
 Module A Computing Fundamentals Module A Computing Fundamentals Computing Fundamentals The Computing Fundamentals examination covers subjects needed for a foundational understanding of computing, including
Module A Computing Fundamentals Module A Computing Fundamentals Computing Fundamentals The Computing Fundamentals examination covers subjects needed for a foundational understanding of computing, including
SMART Board Menu. Full Reference Guide
 SMART Board Full Reference Guide Start-Up After entering Windows, click on the desktop icon SMART Board Tools. The SMART Board icon will appear in the system tray on the bottom right of the screen. Turn
SMART Board Full Reference Guide Start-Up After entering Windows, click on the desktop icon SMART Board Tools. The SMART Board icon will appear in the system tray on the bottom right of the screen. Turn
2. Advance Certificate Course in Information Technology
 Introduction: 2. Advance Certificate Course in Information Technology In the modern world, information is power. Acquiring information, storing, updating, processing, sharing, distributing etc. are essentials
Introduction: 2. Advance Certificate Course in Information Technology In the modern world, information is power. Acquiring information, storing, updating, processing, sharing, distributing etc. are essentials
CS 3530 Operating Systems. L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson
 CS 3530 Operating Systems L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Operating Systems Computer Systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components,
CS 3530 Operating Systems L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Operating Systems Computer Systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components,
What s New in SMART Board Software 9.0 for Windows Operating Systems
 What s New in SMART Board Software 9.0 for Windows Operating Systems If you ve used SMART Board software before, you ll notice many changes in version 9.0. In this document, we ll introduce version 9.0
What s New in SMART Board Software 9.0 for Windows Operating Systems If you ve used SMART Board software before, you ll notice many changes in version 9.0. In this document, we ll introduce version 9.0
Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices. A PC in Every Home. Assembling a Computer System
 C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
SECTION 2 Input and Output Devices
 SECTION 2 Input and Output Devices 2.a. Input Devices Keyboard Input device that contains keys users press to enter data and instructions into a computer. The keyboard translates key selections into digital
SECTION 2 Input and Output Devices 2.a. Input Devices Keyboard Input device that contains keys users press to enter data and instructions into a computer. The keyboard translates key selections into digital
Technology in Action. Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy. Tenth Edition. Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers Understanding
Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers Understanding
Lower School. Third Grade
 Lower School The goal of the Lower School Computer curriculum is to continue to develop technology skills for both academic learning and personal productivity in the 21 st century. Students learn the science
Lower School The goal of the Lower School Computer curriculum is to continue to develop technology skills for both academic learning and personal productivity in the 21 st century. Students learn the science
Tukwila School District #406. Technology Department 4205 South 142nd Street Tukwila, WA 98168 (206) 901-8080. Computer and Phone Support Handbook
 Tukwila School District #406 Technology Department 4205 South 142nd Street Tukwila, WA 98168 (206) 901-8080 Computer and Phone Support Handbook Revised: July 2009 Table of Contents Network Systems Department
Tukwila School District #406 Technology Department 4205 South 142nd Street Tukwila, WA 98168 (206) 901-8080 Computer and Phone Support Handbook Revised: July 2009 Table of Contents Network Systems Department
How To Understand The Computer (For A Computer)
 Computer Fundamental Compiled by: Hemanta Baral Computer Fundamentals What is Computer? Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user and processes these data under
Computer Fundamental Compiled by: Hemanta Baral Computer Fundamentals What is Computer? Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user and processes these data under
SMART Board 9 Software Tips and Tricks
 SMART Board 9 Software Tips and Tricks Tips for Writing and Adding Content Drawing (or erasing) fine lines For precise control of the digital ink, change the pen setting to use the thinnest line width.
SMART Board 9 Software Tips and Tricks Tips for Writing and Adding Content Drawing (or erasing) fine lines For precise control of the digital ink, change the pen setting to use the thinnest line width.
QUIT MACSCHOOL AND DRAG YOUR SERVER ICONS TO THE TRASH OR HIT THE DISCONNECT BUTTON BESIDE THE SERVER ICON IN THE TOP SIDEBAR
 Macintosh Operating System OSX 10.3.x STARTING YOUR COMPUTER Logging in Whenever you start your computer, you will need to enter your computer password at the log in screen. When the log in screen appears,
Macintosh Operating System OSX 10.3.x STARTING YOUR COMPUTER Logging in Whenever you start your computer, you will need to enter your computer password at the log in screen. When the log in screen appears,
Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware. Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA
 Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Information System Layers Learning Objectives Task Statements
Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Information System Layers Learning Objectives Task Statements
A Practical Approach to Starting and Growing Your Own Law Firm
 Hanging Your Shingle: A Practical Approach to Starting and Growing Your Own Law Firm Technology Planning for Startup Law Firms General Considerations Computers Deciding on the type of computer and the
Hanging Your Shingle: A Practical Approach to Starting and Growing Your Own Law Firm Technology Planning for Startup Law Firms General Considerations Computers Deciding on the type of computer and the
Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2
 Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2 Do Now 1. What is the main reason why flash
Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2 Do Now 1. What is the main reason why flash
Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2
 Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2 Definition of a Computer What does IPOS stand for? Input Process Output Storage Other types of Computers Name some examples of other types of computers, other than a typical
Computer Basics: Chapters 1 & 2 Definition of a Computer What does IPOS stand for? Input Process Output Storage Other types of Computers Name some examples of other types of computers, other than a typical
Tutorial for Programming the LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT
 Tutorial for Programming the LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT Table of contents 1 LEGO MINDSTORMS Overview 2 Hardware 2.1 The NXT Brick 2.2 The Servo Motors 2.3 The Sensors 3 Software 3.1 Starting a Program 3.2 The
Tutorial for Programming the LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT Table of contents 1 LEGO MINDSTORMS Overview 2 Hardware 2.1 The NXT Brick 2.2 The Servo Motors 2.3 The Sensors 3 Software 3.1 Starting a Program 3.2 The
WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING
 What You should Know About Scanning WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING If you re thinking about purchasing a scanner, you may already know some of the ways they can add visual interest and variety to
What You should Know About Scanning WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING If you re thinking about purchasing a scanner, you may already know some of the ways they can add visual interest and variety to
SMART Board Tips & Tricks (version 9.0) Getting Started. SMART Tools vs. SMART Notebook software
 SMART Board Tips & Tricks (version 9.0) Getting Started SMART Tools vs. SMART Notebook software Click the SMART Board icon (in the system tray at the bottom right of your screen) to access the SMART Board
SMART Board Tips & Tricks (version 9.0) Getting Started SMART Tools vs. SMART Notebook software Click the SMART Board icon (in the system tray at the bottom right of your screen) to access the SMART Board
EPSON PERFECTION SCANNING BASICS
 EPSON PERFECTION SCANNING BASICS SCANNING A DOCUMENT 1. start a new Word document 2. select Insert, Picture, From Scanner or Camera choose Web or Print quality, depending on what you are scanning a. if
EPSON PERFECTION SCANNING BASICS SCANNING A DOCUMENT 1. start a new Word document 2. select Insert, Picture, From Scanner or Camera choose Web or Print quality, depending on what you are scanning a. if
CAD/CAM. Hardware and software. CAD/CAM/CAE System. Shahrood University. Display Processing Unit
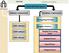 CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
Mobile Devices and Systems Lesson 02 Handheld Pocket Computers and Mobile System Operating Systems
 Mobile Devices and Systems Lesson 02 Handheld Pocket Computers and Mobile System Operating Systems Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Handheld Pocket Computers Come in many manifestations
Mobile Devices and Systems Lesson 02 Handheld Pocket Computers and Mobile System Operating Systems Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Handheld Pocket Computers Come in many manifestations
Lecture Notes, CEng 477
 Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Understanding Digital Components
 Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT IMAGING
 AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION DATA PROCESSING OPERATIONS SERIES CLASS TITLE POSITION CODE EFFECTIVE
 ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION DATA PROCESSING OPERATIONS SERIES CLASS TITLE POSITION CODE EFFECTIVE DATA PROCESSING OPERATOR 11425 4-16-89 DATA PROCESSING ASSISTANT
ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION DATA PROCESSING OPERATIONS SERIES CLASS TITLE POSITION CODE EFFECTIVE DATA PROCESSING OPERATOR 11425 4-16-89 DATA PROCESSING ASSISTANT
lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System
 essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Paper 1 May/June 2014 2 hours
 *3483070646* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY 047/ Paper May/June 04 hours Candidates answer
*3483070646* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY 047/ Paper May/June 04 hours Candidates answer
Topics. Introduction. Java History CS 146. Introduction to Programming and Algorithms Module 1. Module Objectives
 Introduction to Programming and Algorithms Module 1 CS 146 Sam Houston State University Dr. Tim McGuire Module Objectives To understand: the necessity of programming, differences between hardware and software,
Introduction to Programming and Algorithms Module 1 CS 146 Sam Houston State University Dr. Tim McGuire Module Objectives To understand: the necessity of programming, differences between hardware and software,
THE SOCIETY OF BUSINESS PRACTITIONERS
 THE SOCIETY OF BUSINESS PRACTITIONERS CERTIIFIICATE IIN BUSINESS ADMIINIISTRATI ION This is an introductory course to the fundamental principles of business studies. Students who have the necessary GCE
THE SOCIETY OF BUSINESS PRACTITIONERS CERTIIFIICATE IIN BUSINESS ADMIINIISTRATI ION This is an introductory course to the fundamental principles of business studies. Students who have the necessary GCE
