An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
|
|
|
- Posy Ross
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human body and the major components of each system Explain the concept of homeostasis and its significance to organisms Describe how positive feedback and negative feedback are involved in homeostatic regulation Use anatomical terms to describe body sections, body regions and relative positions Identify the major body cavities, their subdivisions, and the membranes that line these cavities and cover the associated organs An Introduction to Studying the Human Body The study of anatomy and physiology will familiarize you with the structures and functions of the human body. Most terms used in anatomy and physiology stem from Greek words because the Greeks were among the first to study this subject 2000 years ago. Learning the roots of these words will help you understand many scientific terms without having to look them up. Anatomy describes the structures of the body -- their scientific names, composition, location, and associated structures. Anatomy ( a cutting open ) is a plan or map of the body. Physiology studies the function of each structure, individually and in combination with other structures (-ology = the study of ). Anatomy and physiology always work together. As we examine each part of the body, always consider both its structure and its function. The study of anatomy is divided into 2 major fields: 1. Gross anatomy is the study of large visible structures 2. Microscopic anatomy is the study of structures that are too small to see, such as cells and molecules. Gross anatomy, also called macroscopic anatomy, is separated into 5 major divisions: 1. Surface anatomy describes surface forms and marks 1
2 2. Regional anatomy describes the organization of specific areas of the body such as the head or hand. This approach is used mostly in professional schools: medical, dental, physical therapy Systemic anatomy describes groups of organs that function together for a single purpose. We will use a systemic anatomy approach in this class. 4. Developmental anatomy describes the structural changes in an organism from fertilized egg to maturity. Embryology is the anatomical study of early development. 5. Clinical anatomy describes various medical specialties, including medical anatomy (changes that occur during illness), and radiographic anatomy Microscopic anatomy is divided into two major divisions: 1. Cytology, the study of cells and their structures. 2. Histology, the study of tissues and their structures. Physiology has many specialties. The 4 basic divisions are: 1. Cell physiology, including chemical and molecular processes within and between cells. 2. Special physiology, the study of specific organs such as the heart. 3. Systemic physiology, the cooperative functions of all the organs in an organ system. We will use a systemic physiology approach in this class. 4. Pathological physiology, the effects of diseases on organs and organ systems. When a patient visits his physician, s/he examines his gross anatomy, his microscopic anatomy (blood tests) and observes the way he functions -- his physiology. These observations are part of the scientific method, the basis of all science. Levels of Organization Our bodies are organized at many different levels. The levels of organization of living things, from smallest to largest, are: 1. Atoms, the smallest functional units of matter. 2. Molecules, active chemicals. 3. Organelles, specialized structures within a cell. 4. Cells, the smallest living units. 5. Tissues, a group of similar cells that work together. 6. Organs, two or more tissue types working together. 7. Organ systems, two or more organs working together. 8. Organism, a single individual, including all of the above. 2
3 Systemic Human Anatomy will be our approach The human body is divided into 11 interconnected organ systems. All organ systems work together, and many organs function in more than 1 organ system. Homeostasis The foundation of all physiology is homeostasis ( staying the same ). When the body does not function within its normal range, organ systems malfunction, resulting in disease. As our internal and external environment changes, physiological systems work together to maintain a stable internal environment, the condition of homeostasis. For example, systems monitor and adjust the volume and composition of body fluids, and keep body temperature within normal limits. A homeostatic regulatory mechanism consists of 3 parts: 1. Receptors, sensors that respond to a stimulus. 2. The control center, receives information from sensors and sends out commands. 3. Effectors, the cell or organ that responds to the control center. When the response of an effector opposes the original stimulus, that is called negative feedback because it negates the stimulus. An example of negative feedback is the temperature thermostat in your home. Temperature sensors turn the air conditioner off and on to maintain air temperature within a specific, limited range. In the same way, the brain controls normal body-temperature homeostasis by negative feedback. When body temperature is too high or too low, the control center instructs an effector to oppose the effects of the stimulus by increasing or decreasing blood flow and sweat production. In the opposite response, positive feedback, the effector adds to the initial stimulus instead of negating it, speeding up the process. Positive feedback examples include, blood clotting (a little clotting provokes more clotting) and the birthing process (contractions get closer). 3
4 The body is constantly working, changing and responding to stimuli, a state of dynamic equilibrium. All body systems must work together (systems integration) to maintain homeostasis. Frames of Reference for Anatomical Studies Anatomical descriptions refer to standard anatomical position: standing with the hands at the sides, palms facing forward, feet together. Anatomical directions refer to the patient s left or right. Each direction is paired with an opposite; caudal is the opposite of cranial, anterior is the opposite of posterior. A lateral view is from the side. An anterior view is from the front. An area may be nearer to (proximal) or farther away from (distal) the medial or central region of the body. Moving from exterior references to the internal organs requires a 3-dimensional description, imagined as an axis or plane cut through the body. A specific slice along these planes is called a section. The 3 sectional planes are: 1. Sagittal plane (the length of the body, front to back), including the midsagittal or median section and left or right parasagittal sections. 2. Frontal plane (the length of the body, side to side), also called coronal plane, resulting in anterior and posterior portions. 3. Transverse plane (at right angles to the sagittal and frontal planes), also called a transverse section or cross section, resulting in inferior and superior portions. Body Cavities and Serous Membranes Internal compartments called body cavities protect internal organs, hold them in place, and allow them to change size and shape. All the internal organs found within these cavities are called viscera. Moist layers of connective tissue called serous membrane cover both the walls of internal cavities (parietal layer) and the visceral organs themselves (visceral layer), providing a double layer of membrane between an organ and its surroundings. Serous membrane contains a watery lubricant that reduces friction, allowing organs to expand and contract freely. 4
5 The ventral body cavity (coelom) is divided by the diaphragm muscle into 2 parts: 1. A superior thoracic cavity, containing the (a) pleural cavity (left and right, divided by the mediastinum) organs: lungs membranes: visceral and parietal pleura (b) pericardial cavity organs: heart membranes: visceral and parietal pericardium 2. and an inferior abdominopelvic cavity, containing the (a) peritoneal cavity membranes: visceral and parietal peritoneum (b) abdominal cavity (superior peritoneal) organs: liver, stomach, spleen, intestine (c) pelvic cavity (inferior peritoneal) organs: intestine, bladder, reproductive organs. 5
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) repair and completely restore itself during any type
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) repair and completely restore itself during any type
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology by Body Systems PART II
 Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology by Body Systems PART II An Overview of Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology CHAPTER 3 Good work is not accomplished in haste. Ancient Chinese Proverb HIGHLIGHTS Let s begin
Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology by Body Systems PART II An Overview of Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology CHAPTER 3 Good work is not accomplished in haste. Ancient Chinese Proverb HIGHLIGHTS Let s begin
Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1 Key Terms abdomen, p 11 abdominal, p 13 amplifier, p 16 anatomical position, p 9 anatomy, p 2 anterior, p 9 brachial, p 11 cardiovascular physiology, p 8 carpal, p 11
Introduction and Basic Concepts 1 Key Terms abdomen, p 11 abdominal, p 13 amplifier, p 16 anatomical position, p 9 anatomy, p 2 anterior, p 9 brachial, p 11 cardiovascular physiology, p 8 carpal, p 11
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
A&P Basics. a. 1,6,3,4,5,2 b. 2,4,5,6,1,3 c. 1, 3,6,5,4,2 d. 3,1,5,6,4,2 e. 1,6,3,2,5,4
 1. Which of the following disciplines is MOST likely to concentrate on the structure and function of organelles? a. Gross anatomy b. Histology c. Cytology d. Embryology 2. Which of the following disciplines
1. Which of the following disciplines is MOST likely to concentrate on the structure and function of organelles? a. Gross anatomy b. Histology c. Cytology d. Embryology 2. Which of the following disciplines
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
1. DEFINITION OF PHYSIOLOGY. Study of the functions of the healthy human body. How the body works. Focus on mechanisms of action.
 1. DEFINITION OF PHYSIOLOGY Study of the functions of the healthy human body. How the body works. Focus on mechanisms of action. Anatomy & Physiology: inseparable & complementary They are complementary
1. DEFINITION OF PHYSIOLOGY Study of the functions of the healthy human body. How the body works. Focus on mechanisms of action. Anatomy & Physiology: inseparable & complementary They are complementary
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Concepts of the. Human Body. chapter outline. 1 The Human Body and Disease. The Study of the. Human Body. Organization of the.
 1 UNIT 1 The Human Body and Disease Concepts of the Human Body chapter outline The Study of the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Body Cavities, Regions, and Quadrants Anatomical Terminology LifeS
1 UNIT 1 The Human Body and Disease Concepts of the Human Body chapter outline The Study of the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Body Cavities, Regions, and Quadrants Anatomical Terminology LifeS
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more
 BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Diseases of peritoneum Lect. Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32
 Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Physiology Chapter 1 Lecture
 Physiology Chapter 1 Lecture I. Anatomy and Physiology - structure and function. *many subdivisions in both areas. See Table 1.1, page 2 *structure and function are interrelated, the structure often determines
Physiology Chapter 1 Lecture I. Anatomy and Physiology - structure and function. *many subdivisions in both areas. See Table 1.1, page 2 *structure and function are interrelated, the structure often determines
Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112)
 Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY
 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
Anatomy and Physiology for Engineers
 fl Course Description: fl Introduction to the subject of human anatomy and physiology. fl Concentration on physiology and bioengineering. fl Springboard for exploring bioengineering in greater detail.
fl Course Description: fl Introduction to the subject of human anatomy and physiology. fl Concentration on physiology and bioengineering. fl Springboard for exploring bioengineering in greater detail.
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Peritoneal Carcinosis
 Peritoneal Carcinosis What is it and how to cure it Peritoneum Peritoneum is a thin and transparent membrane that covers the internal part of the abdominal and pelvic cavity and all the viscera contained
Peritoneal Carcinosis What is it and how to cure it Peritoneum Peritoneum is a thin and transparent membrane that covers the internal part of the abdominal and pelvic cavity and all the viscera contained
The Human Body: An Orientation
 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology (pp. 2 3) Topics of Anatomy (p. 2) Topics of Physiology (pp. 2 3) Complementarity of Structure and Function (p. 3) Levels of Structural Organization (pp. 3 4) Maintaining
An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology (pp. 2 3) Topics of Anatomy (p. 2) Topics of Physiology (pp. 2 3) Complementarity of Structure and Function (p. 3) Levels of Structural Organization (pp. 3 4) Maintaining
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Test Bank. Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI) Jason LaPres LONE STAR COLLEGE NORTH HARRIS
 Test Bank Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI) Jason LaPres LONE STAR COLLEGE NORTH HARRIS Judi L. Nath LOURDES UNIVERSITY Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology
Test Bank Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI) Jason LaPres LONE STAR COLLEGE NORTH HARRIS Judi L. Nath LOURDES UNIVERSITY Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (BIO 2311) SYLLABUS
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (BIO 2311) SYLLABUS NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY The City University Of New York School of Arts and Sciences Department of Biological Sciences Course Information Course
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (BIO 2311) SYLLABUS NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY The City University Of New York School of Arts and Sciences Department of Biological Sciences Course Information Course
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Lassen Community College Course Outline
 Lassen Community College Course Outline BIOL-25 Human Anatomy and Physiology I 4.0 Units I. Catalog Description First semester of a two semester sequence covering structure and function, integration and
Lassen Community College Course Outline BIOL-25 Human Anatomy and Physiology I 4.0 Units I. Catalog Description First semester of a two semester sequence covering structure and function, integration and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program
 Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program The S.A.V.E. EMT Program prepares adult students to become certified emergency medical technicians and to work in the EMT field where
Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program The S.A.V.E. EMT Program prepares adult students to become certified emergency medical technicians and to work in the EMT field where
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
General Body and Directional Terms
 General Body and Directional Terms Course Anatomy & Physiology Unit I Orientation to the Human Body Essential Question What common terminology is used to describe human anatomy? TEKS 130.206 (c) 2A 6A,
General Body and Directional Terms Course Anatomy & Physiology Unit I Orientation to the Human Body Essential Question What common terminology is used to describe human anatomy? TEKS 130.206 (c) 2A 6A,
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Focused assessment of sonography in trauma
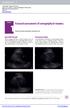 Chapter1 Focused assessment of sonography in trauma Patricia Fermin and John Christian Fox Epicardial fat pad When imaging the heart, careful attention must be made in identifying any surrounding fluid.
Chapter1 Focused assessment of sonography in trauma Patricia Fermin and John Christian Fox Epicardial fat pad When imaging the heart, careful attention must be made in identifying any surrounding fluid.
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Unit 1 Levels of Organization 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Learning Outcomes After studying this chapter, you should be able to do the following: A wooden toe on an ancient Egyptian mummy
Unit 1 Levels of Organization 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Learning Outcomes After studying this chapter, you should be able to do the following: A wooden toe on an ancient Egyptian mummy
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn external anatomy of the pig. 2. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. I. Introduction: Humans (Homo sapiens) and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa) are
The Digestive System Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn external anatomy of the pig. 2. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. I. Introduction: Humans (Homo sapiens) and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa) are
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130)
 Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130) Gastrointestinal & Urogenital Systems Recommended Text: TEXTBOOK OF ANATOMY: ROGERS Published by Churchill Livingstone
Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130) Gastrointestinal & Urogenital Systems Recommended Text: TEXTBOOK OF ANATOMY: ROGERS Published by Churchill Livingstone
Bio 348 Human Anatomy & Physiology Lapsansky 2014
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES NOTE: Please review the objectives for both the lecture and lab in preparation for lecture exams. Although lab questions will not be on the lecture exams, many of the objectives overlap,
LEARNING OBJECTIVES NOTE: Please review the objectives for both the lecture and lab in preparation for lecture exams. Although lab questions will not be on the lecture exams, many of the objectives overlap,
MORPHOPHYSIOLOGY I Human Anatomy & Physiology I
 MORPHOPHYSIOLOGY I Human Anatomy & Physiology I Semester Credits: 4 In-class Hours: 48 Out-of-Class Hours: 96 Level: 1 st year OVERVIEW Morphophysiology I introduces students to the study of anatomy and
MORPHOPHYSIOLOGY I Human Anatomy & Physiology I Semester Credits: 4 In-class Hours: 48 Out-of-Class Hours: 96 Level: 1 st year OVERVIEW Morphophysiology I introduces students to the study of anatomy and
Health Science Career Field Allied Health and Nursing Pathway (JM)
 Health Science Career Field Allied Health and Nursing Pathway (JM) ODE Courses Possible Sinclair Courses CTAG Courses for approved programs Health Science and Technology 1 st course in the Career Field
Health Science Career Field Allied Health and Nursing Pathway (JM) ODE Courses Possible Sinclair Courses CTAG Courses for approved programs Health Science and Technology 1 st course in the Career Field
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
How To Understand How Cancer Works
 Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
RAD 223. Radiography physiology. Lecture Notes. First lecture: Cell and Tissue
 RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Diseases. Inflammations Non-inflammatory pleural effusions Pneumothorax Tumours
 Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus
 Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB
 BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Presented and Approved: January 12, 2012 Effective: 2012-13 FA Prefix & Number BIO 201 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Presented and Approved: January 12, 2012 Effective: 2012-13 FA Prefix & Number BIO 201 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Emergency Ultrasound Course
 Emergency Ultrasound Course Dr Justin Bowra ED Course Manual 2: EFAST Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma JUSTIN BOWRA 1 The Questions: 1. Is there free fluid (FF) a. In the pleural space?
Emergency Ultrasound Course Dr Justin Bowra ED Course Manual 2: EFAST Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma JUSTIN BOWRA 1 The Questions: 1. Is there free fluid (FF) a. In the pleural space?
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
