The methods of graphical statics and their relation to the structural form
|
|
|
- Kelly Bell
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the First nternational Congress on Construction History, Madrid, 20th-24th January 2003, ed. S. Huerta, Madrid:. Juan de Herrera, SEdHC, ETSAM, A. E. Benvenuto, COAM, F. Dragados, The methods of graphical statics and their relation to the structural form Rolf Gerhardt Karl-Eugen Kurrer Gerhard Pichler n the preface of the 2nd edition of his main work «Die graphische Statik» (\ 875), Karl Cu]mann was pleased to report that graphical statics had been taken up wide]y, but at the same time he complained that it was taught without the mathematica] base of the projective geometry. Subsequently, the «Graphostatik» (graphostatics), characterised by its recipe-like structure, became generally accepted. The graphostatics formed an essential means of intellectual engineering practice. t still referred to the unity of design, calculation and construction. Various examp]es demonstrate the option of deriving fram the graphical examination not only the interna] forces required for dimensioning, but a]so criteria for optimising the structura] formo Nevertheless, with the comp]etion of the classic structural theory after ] 890, the decline of the graphica] statics in favour of analytical calculation methods was a]ready becoming apparent. This corresponded with the desire to rationalise the engineer' s work, but it led to the disintegration of the unity of design, calcu]ation and construction. Today unlike in engineering practice, graphica] methods still play an important ra]e in ]ecturing on structures. The clarity of graphical techniques has a high didactic value, since interdependencies, e.g. between forces and structura] geometry, can be directly experienced visually. Architecture and structura] engineering students thus are provided with a suitable means of evaluating not least historie structures. Recent examples from engineering practice demonstrate how he]pfu] the know-]edge and use of graphica] methods can be for the eva]uation and preservation of historic structures: The history of structura] methods is therefore an important facet of construction history. GRAPHCAL STATlCS AND GRAPHOSTATCS N THE WORK OF CULMANN Graphical statics started with the publication of the monograph under the same title between 1864 and Karl Cu]mann ( ) had been lecturing graphical statics at Zurich Polytechnic (now known as ETH) since ] 860 (Maurer 1998). According to its creator, it is an attempt «to solve engineering tasks that are accessib]e to geometric treatment with the aid of the new geometry» (Cu]mann ]864/1866, V]). With «new geometry», Culmann refers to the prajective geometry going back to the pub]ication by lean Victor Poncelets (1788-] 867) entitled «Traité des propriétés prajectives des figures» (Poncelet ] 822), investigating the prajective characteristics of figures. How does this prajective geometry, which is after all freed fram metrics, i.e. fram dimensions and numbers, and which is only interested in the relative position of geometric figures, relate to graphical statics, with the ]atter dea]ing specifically with the measuring of geometrie parameters?
2 998 R. Gerhardt K. Kurrer, G. Pichler The answer is provided by means of an example, based on Cu\mann's mathematical proof of the projective relationship between funicular polygon and force polygon, which had already been introduced by Pierre Varignon ( ) (Figure 1). For the special case of an equilibrium system of torces with one point of application, Culmann found the «structural relatíon between funicular polygon and force poly gon via aplanar correlation of the projective geometry» (Scholz 1989, \74). Funicular polygon and force polygon are interchangeable in so far as it does not matter which of the polygons is regarded as the system of the lines of action in addition to the associated funicular polygon. Culmann describes such figures as reciprocal (Figure 2). o Et \\"\. Ft. ""'" '. G -:~~J! $ Hr/ / j./ i :/ R ' V 11 p /' - M Figure 1 Funicular polygon and force pojygon according to Varignon, (Varignon 1725), N force polygon O 4 Pl "" 1 P4 "" Al Pz ~~O' 2 /pole P3 / 3 reciprocal funicular Figure 2 A'4 polygon f\3 funicular O A4 recíprocal force polygon pole Q 141,/ p; 01'\ polygon 110,"" l' 1\ 1\ ""',... 1\ "... 1\ ""... : \ "''''''''..., P 4 ', " 3' 21 Reciproca1 diagrams 01' funicular pojygons and force polygons for plane systems 01'forces according to Culmann. (Kurrer 2002, 224) Soon after the publication of Culmann' s «Graphische Statik», graphical statics became separated from its applications in the form of graphostatics. Evidence for this can be found in the even more mathematically oriented second edition pub lished in 1875, in which Culmann promises the reader to elaborate on the applications in a second volume (Culmann 1875, XV). However, this never happened, beca use Cu]mann's scientific thinking was too much determined by the ideal of an axiomatic substantíation of graphical statics, Culmann's visualisation of beam statics vía the funicular polygon (Figure 3), which is an important component of graphostatics, is dominated by the operational side that is restrained in the means/purpose relation. Relying on measures and numbers, it rationalises and mechanises an important side of the working process of the engíneer through informational consolidation in the form of graphical
3 The methods of graphical statics and their relation to the structural form 999 P, P2 P3 ANWENDUNGEN 5 " " "" A ~t~ ~':.-:;c- 8-._5 DEl! GRAPHSCHEN STATK. M=H'll! PROFESSOR NACH DR. C. CULMANN P, " " A " " P2 -- " " '-'=-:~~pole " B P ~ H Figure3 Graphical solution rcpresenting the bending moment diagrarn of a sirnply supported beam according to Culmann. (Kurrer 2002, 224) W. RTTER, PROPE5S0R AM EDGE1\OSS8CBE..'\ rolyt:t::chnkt"m zu ZÜRTCH. Erstcr Teíl. llíe ilu nneren eines Bttlkens wirkenden K'Mte. Mit 65 Textfiguren und 6 Tafeln. BEARDE1'ET methods. Graphostatics mediates between the manpower of the engineer and his object, here in the form of ideal static models. Graphostatics represents an important intellectua] tool of the engineer, which had its heyday in the last third of the ] 9th century within the structure of fundamenta] engineering sciences and structural engineering. While graphical statics was the keystone of the establishment phase of the structural theory that had started with the trussed framework theory ( ), the emancipation of graphostatics from graphical statics and its cognitive expansion was an important moment in the completion phase of the structural theory ( ). Even Culmann's student and successor at ETH Zurich, Wilhe]m Ritter ( ), became disloyal to graphical statics and his own view of its basis on projective geometry, as it was formulated in the foreword of his four-volume work published betwecn ] 888 and 1906 «Anwendungen der graphischen Statik. Nach Professor D. C. Culmann», Figure 4: He wrote a work on graphostatics, in which this view only ZÜRlcn VBHT,AG VON JEYER &; ZELLER (Re;_nÚ,h. n"hhan~nng) Figure 4 Title page 01' Rítter's «Anwendungen der graphischen Statib. (Ritter 1888) appcared in the form of a mere «manner of speaking» (Schol 1989). n 1882, Ludwig Tetmajer ( ) recognised the influence of Culmann's graphostatics as foj]ows: «The grand bridge arches that were constructed in Switzerland since 1876 have all been cajculated according to Culmann's theory, with contributions from construction enterprises such as Holzmann and Benkieser in Frankfurt, Eiffel in Paris, (... ) in order to be able to utilise the results of Culmann's research in their constructionbureaus.» (quotedafter Stüssi 1951,2).
4 1000 R. Gerhardt, K. Kurrer, G. Pichler The renunciation of static calculations, partly caused by the graphostatics, is a historic product of an increasing conditioning of the work of the structural engineer towards static techniques. Nevertheless, during the classic phase of structural theory it offered the opportunity to create fine iron structures. One could even go as far as saying that the graphostatics did not only rationalise the design work of the structural engineer, but at the same time aestheticised it, bearing in mind that the force and construction drawings appear in the dual shape of both the sensory consciousness and the sensory needs (Figure 5). This development reached its peak during the 1880s and 1890s; a prominent example is the Eiffel Tower, which was analysed by Culmann's former student Maurice Koechlin ( ) using graphostatical techniques. Nevertheless, with the completion of the c1assic theory of structures after 1890, the decline of the graphical methods in favour of analytical calculation methods was already becoming apparent. This corresponded with the desire to rationalise the engineering process, but it led to the disintegration of the unity of design, calculation and construction. THE SGNFCANCE OF GRAPHCAL METHODS FOR LECTURNG ON STRUCTURES Visual experientiality of interrelations Whilst in modern engineering practice, graphostatics is largely seen as a historic variety of structural analysis, its techniques are still relevant in lecturing JÚ'iiilcpolygon. r;v,/',,/"..k)'! t),/, /~/..~V'..~ Jú~ BLECHKRA.'\'. uni SolpolyS"', ris,1. Quel'M:luUUSmO\'~l\lC. fi'ig.4 40, Tal'. }Ú...!'utob 1:W Figure 5 Graphical solution of a metal crane according to Ritter. (Ritter 1888)
5 The methods of graphical statics and their relation to the structural form 1001 on structures. The clarity of the graphical method has a high didactic value, since interrelations and interdependencies, e.g. between structural geometry and forces, can be directly experienced visually. The Cremona diagram shown in Figure 6, for example, clearly illustrates how a reduction of the forces acting in the members of a framework can be achieved by increasing the depth of the trussed girder under consideration. t,, b ~3 }. ~5 f\rv1/1 L ", :""b-!-: V3: ':..+-- ~~~É~L, / : //" V4~ // V D F, Maszstab Lageplan --+--j o m t B.Om -+ B.O m =160m. 1 + Maszstab Krafteplan ---t-+--t O kN R ",DH O \0, Figure 7 Symmetrical frame with three hinges. Graphical determination of the supporting torees by means of the thrust line. (Gerhardt 2002a, 65) / ~ A~ Figure 6 Cremona's diagram of forces for a trussed girder. Comparison of two girders with different depths. Optimisation of the structural design Design, dimensioning and construction and their mutual influences can be experienced as a unit in graphical solutions. Criteria for the optimisation of the structural form are almost imposing themselves: The optimisation options are directly apparent and can be implemented directly in the design without the need for complicated calculations. An example is the three-hinged frame shown in Figure 7. Based on the theory of the thrust line, the supporting forces can easily be determined, and therefore also the bending moments at critical points (comer joints). The graphical optimisation shown in Figure 8 leads to a more balanced distribution of bending moments with significantly reduced maximum values by relocating the hinge. The interrelation between hinge relocation, thrust line and reduction of horizontal reaction forces can clearly be seen in the graphical solution. For lecturing on the theory of structures it has proven useful to extend the application of graphical Maszstab Lageplan o m ~--~320kN Maszstab Krafteplan j t-+ o 80 kn / t\ Flo M,. 1\ l' -l-- A '~'" J. V m: h!::.y h = 5.0 m! R -t-- A O -1-+ f. =2.35m t m- - 1=16.0m -- =t= 1 H=64kN U Figure 8 Frame with three hinges. Graphical optimisation of the position of a hinge in order to minimise the bending moments. (Gerhardt 2002a, 69) solution techniques to statically indeterminate systems, as far as possible with simple procedures. '. ' AH The principe of the thrust line can thus also be used, for example, for examining statically indeterminate frames, Figure 9, by assuming realistic ratios of beam Ay
6 1002 R. Gerhardl, K. Kurrer, G. Pichler stiffness to post stiffness. The zone in which all 'reasonable' bending moment curves and thrust lines respectively are located can thus be defined quite exactly, despite the statical indeterminacy (Führer, ngendaaij, Stein [1984] 1995, 201-6; Gerhardt 2002b, 381-3). «The aim of this procedure is to make the relationship between structural form, external load and the resulting bending moments directly experienceable through experiments with hanging chains.» (Gerhardt 2002a, 8) '!!lill!!i!!!llillilll!!! i1 lr B / //r", / max!1.y \\line of thrust / \ \ \ \ / \ ' -++- / A M ~.,y. H B ",>" ",..." "'.." ",.. ""'"... Figure 9 Bending moment diagram of a framc with two hinges. Optimised structural form as it approaches the hne of thrust. (Gerhardt 2002b, 383) Figure 10 Overhanging beam. Experimentally derived polygon representing the bending 'diagram'.(gerhardt 1998, 35) funicular moment The use of demonstration models in lecturing on graphostatics Experiments with demonstration models have proven didactically helpful for communicating theoretical facts in lecturing on structures. Studies show that theories are easily understood and lastingly memorised by students due to the illustrative quality of model experiments (Faisst 1975). The graphical method of determining bending moments via force polygon and funicular polygon can also easily be experimentally demonstrated with hanging chains. Here, the behaviour of a hanging chain under load, which resembles the bending moment curve of a beam under the same load, is utilised. The representation of the bending moment diagram via hanging chains as shown in Figure 10 is the materialisation of the graphical funicular polygon. «For the dimensioning of structural components, the magnitude and distribution of bending moments are a basic criterion and are often crucia!. Whilst the internal moments acting in a structural element subject to bending stress are often difficult to imagine, it is much easier to do so for the deformation of a hanging chain under an equivalent load. Via the analogy of the catenary, the qualitative shape of the bending moment curve is thus directly comprehensible. The method of experimental representation of bending moments can thus contribute to the safe estimation of bending stresses independent of calculations, and to the optimisation of load-bearing structures even during the design phase.» (Gerhardt 2002a, 8)
7 The methods of graphieal statics and their relation to the structural forrn 1003 Distribution of forces and structural form The correspondenee of struetural form and physieal stress inevitably implies both struetural and formal aesthetie qualities (Figure 11). distribution of force s in the examined structural elements in an excellent way and thus are able to have a positive intluence on the design process for loadbearing struetures, in the sense of the unity of design, calculation and construction mentioned above. Analysis of historie structures ~ ~~~" "\ \\::, \'-.\~ ''-.\'" ~ ~~ \.', '\ '\,.~ Figure 1] Park Gúell ( ). Retaining wall towards Muntanya Pelada. The diagram of forees demonstrates the way Gaudí was deterrnining the most effectivc shape of retaining walls. (Sweency and Sert 1960,74) Load-bearing struetures or struetural elements that are shaped aeeording to the tlow of forees are eonvineing not only due to their eonsisteney regarding the transfer of loads, but in addition they possess an aesthetie harmony that can positively shape the whole arehiteetural appearanee of a building. n view of the formal randomness of shape that prevails in the design 01' many buildings, even in times of high-teeh arehiteeture, the training 01' both arehiteets and struetural engineers has to eommunieate the eapability to derive a sensible design from the function of load transfer. The graphical methods have a special significance in achieving this aim, since they visualise the One of the tasks of lecturing on structures is the critical examination of historie constructions. Through the graphostatical techniques, students become acquainted with an appropriate tool for analysing, evaluating and preserving historie supporting structures. Suspended models based on the theory of the thrust line are partieularly useful for the anajysis of historie vault or arch structures. This gives architecture and structural engineering students the opportunity to examine for example the loadbearing behaviour of masonry domes, without having to aequire deep knowledge of the complex and abstract mathematieal teehniques 01'structural vault analysis. However, such an approach is inconceivable without any knowledge of graphostatics and the graphical techniq ues of representing force s as vectors. Figure 12 shows a suspended model produced by architecture students at Aachen U ni versity for analysing the distribution of 1'orces within the cupola of the cathedral at Aachen (S. Seyedahmadi and T. Daniel. Lehrstuhl für Baugeschichte und DenkmaJptlege und Lehrstuhl für Baukonstruktion (Tragwerklehre). Tutors: B. Schindler, R. Gerhardt). The three-dimensional suspended model gave an insight into the annular tension torees acting within the wrought-iron ties inserted into the basis of the vaulted masonry construction. The model also enabled statements to be made about the weight of the stones in the upper zone of the eupola. RECENT APPLlCATONS OF GRAPHlCAL METHODS N ENGNEERNG PRACTCE With examples from engineering practice, the consulting engineer' s office 'Pichler lngenieure', with contributions by Karen Eisenloffel and Marko Ludwig, demonstratcs how graphostatics as a «language of the engineef» (Culmann 1875,5) can be
8 1004 R. Gerhardt, K. Kurrer, G. Pichler overload of the vaults and whether the structure could withstand the envisaged load increase. Due to the type of damage, a steel girder grid to relieve the vault had been considered initially» (Pichler et al. 1998, 227). t appeared sensible to use graphostatics to check anew whether the existing construction would be able to withstand the expected loads. «The force diagrams and thrust lines of the graphical solution were drawn using CAD, so that the iteration steps required for the branched ribbed vault could be carried out without excessive effort and could be checked using a drawing of the existing vault. The result of the first calculations taking into account the additionallive load was not surprising. For unilateral loads, the thrust hne was outside the vault, i.e. the vault would fail. The advantage of the graphical method -in contrast to spatial computer calculations- is that it indicates a solution through ~--- Figure 12 Three dimensional suspended model to analyse the tlow of forces in the cupola of the cathedral at Aachen. (Seyedahmadi und Daniel 2002) utilised even today with the aid of the computer (Pichler et al. 1998). A particularly good example of this approach is the statical examination of the largespan ribbed vault above the main staircase of the city hall «Rotes Rathaus» in Berlin (Figure 13). Cracks had appeared in the plastered brickwork of the ribbed vault, the reasons for which had to be found. The intention was to turn the space above the ribbed vault into a banqueting hall: «We had to investigate whether the damage may have been caused' by an Figure '..->1'...\0 "...,." ".",.<1'., '\'".,-'\'.~,-",,-,-"'--' ',"-, ~ - Computer-aided graphostatical investigation of the crossvault spanning the foyer of the Berlin city hall «Rotes Rathaus». (EisenloffeJ and Ermer 2000, 85)
9 The methods of graphieal staties and their relation to the struetural form 1005 its clarity, namely that increasing the dead loads would prevent the thrust line from leaving the vault. With a ballasting sand ]ayer of 20 cm thickness above the vault, the course of the thrust line could be influenced in such a way that, for a unilateral live load of 3.5 kn/m"= with a maximum compressive strain of 1.5 N/mm,,=, the vault could be shown to be safe.» (Eisenloffe and Ermer 2000, 84-6) The initially envisaged additional support grid thus became superfluous. The combination of graphostatics and CAD not only enables the examination of vector and shapeactive structures, but al so mas s-active structures such as 1100r slabs (Pichler et al. 1998, 229). Building Structure: Part of a building that deals with the Joad~bear ng funetían required for assuring the funetían ofthe building (e.g. metal crane) Structural system: Computer~ Mode! of the structure that was abstracted under the aspect airlad of the load-bearing funetían (e. g. bent cantilever beam) grapho~ Statical system: statics Structural system that was made more precise through additional geometricaf/mechanical details tor the purpose of quantitative ana!ysis (e.g. fixed ben! elastic bar) Applied mechanics Applied mathematics Lecturing on structures Structural theory Figure 14 Subjeet and position of eomputer-aided graphostaties. (Kurrer 1998, 209) OUTLOOK The increasing rationalisation of the engineer's work during the completion phase of the theory of structures ( ) soon lead to the disintegration of graphicaj statics into respective individual methods, i.e. graphostatics, representing merely graphical recipes. n a development that is comparable with the later introduction of computer statics, graphostatics made structura] engineers move away from the design process in so far as graphostatical recipes became a mere means of intellectual techniques, i.e. a technical means or 'techne'. The aesthetic component also faded from the design work of structural engineers. Computer statics reinforced the tendency towards structural design based purely on analytical calculation. Nevertheless, modern information and communication technology already points towards a systemic design practice that enables structural engineers to regain lost design competency and enables architects lo regain lost structural competency on a higher ]evel. One option for moving away from structura] design purely based on analytical calculation is the creation of computeraided graphostatics, positioned at the interface between the practice of structural engineers and of architects in the theory of structures (Figure 14). Computer-aided graphostatics would have to be designed modularly, so that the user would be ab]e to mobilise each individual structure, e.g. the funicular polygon, through specially developed graphics editors, disp1ay it on the screen and combine it with other graphics editors into concrete structures in the sense of graphostatics. Such graphics editors and dimensioning modules based on approximation methods could enable the results of the graphostatical synthesis to be transferred directly to the ]evel of the structural system. Computer-aided graphostatics would thus become the hinge between design and construction. Not least it would be a suitable didactic means to bring together structural engineering and architecture students in the theory of structures. Further elements could be deduced from the kinematic structural theory developed in the 1880s (Kurrer 2000, 44). For example, the graphical techniques derived from the in11uence line theory created by atto Mohr ( ), Emil Winkler ( ), Johann Jakob Weyrauch ( ), Heinrich Müller-Breslau ( ) and in particular Robert Land ( ) during the 1870s and 1880s would provide an appropriate representation for adapted graphics software. Land's theorem would be a nice example for the rediscovery of the visualisation of statics; its graphic representation through the symbolic machine of the computer could significantly increase the 'statical feeling' ofthe user for the int1uence of moving effects on the force and displacement parameters. Computer-aided graphostatics could make the aesthetic component in design work become reality again, since it would facilitate the lost 'statical feeling' at the interface of design and construction becoming second nature again to the user: science
10 1006 R. Gerhardt. K. Kurrer. G. Pichler would become sensory and poetry would become scientific. t could break the established role behaviour of structural engineers and architects. REFERENCE LST Cu1mann. Karl. 1864/1866. Die graphisehe Statik. Zürich: Verlag van Meyer & Zel1er. Cu1mann. Karl Die graphisehe Statik. 20" ed. Zürich: Meycr & Zel1er. Eisen1offel. Karen and ngeborg Ermer eds Tragwerkstatt Gerhard Piehler. Entwii1je - Bauten - Kanstrllktian. Berlin: Gebr. Mann Verlag. Faisst. Kurt Veransehallliehung van Tragsvstemen dureh Modelle. Untersllehungen Üher den LemerjÓlg. Dissertation. Karlsruhe: Technische Universitat Karlsruhe. Führer. Wilfried; Susanne ngendaaij and Friedhelm Stein. [1984J Der EntwUlj' van Tragwerken. KOn: R. Mül1er. Gerhardt. Rolf Darstellung von Biegemomenten. hre experimentel1e Ermittlung mit Hilfe del' Seil1inie. Baukllltllr, 6: Gerhardt. Ro1f. 2002a. Ansehallliehe Tragwerklehre. Experimentelle Darstellung van Biegemomenten mit Hilfe del' Seillinie. Aachen: Shaker. Gerhardt. Rolf. 2002b. Reflections on the application of graphical methods to statica1 problems. n: Towards a Historv ofcanstrlletion. edited by A. Becchi. M. Corradi. F. Foce and O. Pedemonte Base1/Boston/Ber1in: Birkhauser. Kurrer. Karl-Eugen Baustatik und Ásthetik. Anmerkungen zur Neuausgabe des Werkes «Eisenbauten. hre Geschiehte und Ásthetib von Alfred Gotthold Meyer. Stahlhau, 67: Kurrer. KarJ-Eugen Baustatik und Ásthetik. Van del' Mogliehkeil des Ásthetischen beim statischen Rechnen. Baukultur, 8: Kurrer. KarJ-Eugen Geschiehte del' Ballstatik. Berlin: Ernst & Sohn. Maurer. Bertram Karl Culmann und die graphisehe Statik. BerJin/Diepholz/Stuttgart: Verlag für Geschichte del' Naturwissenschaft und del' Technik. Pich1er. Gerhard; Karen Eisenloffel and Marko Ludwig Die graphische Statik in Studium und Praxis. n: BrÜckenschliige. Festsehnft jür Herm Univ.-Pro! Dr.- ng. Wilhelm Friedrich FÜhrer zur Vollendllng des 60. Lehen.\jahres. edited by Lehrstuhl für Baukonstruktion (Tragwerk1ehre) Aachen: Freunde des Reiff. Aachen University. Ponce1et. Jean Victor Trailé des propriétés projeetives des jigures. Paris. Ritter. Wilhelm Anwendungen del' graphischen Slatik. Naeh Professor C. Clllmann. Enter Teil: Die im nneren eines Balkel1s wirkenden Kriifle. Zürich: Verlag von Meyer & Zel1er. Scholz. Erhard Symmetrie. Gruppe, Dllalitiit. Zur Beziehung zwischen hearelischer Malhematik lnd Anwendungen in Kristallographie und Bauslatik des /9. Jahrhunderts. Basel: Birkhauser. Seyedahmadi, Soheil and Tobias Daniel Geschichte der Konslrukliol1. Die Kuppel der Aachener Pfalzkapelle. Studienarbeit Aachen University (RWTH Aachen). Aachen: Lehrstuhl für Baugeschichte und Denkmalpflege and Lehrstuhl für Baukonstruktion (Tragwerklehre). Stüssi, Fritz Karl Culmann und dic graphische Statik. Schweizerische Bauzeilung, 69: 1-3. Sweeney, James Johnson and Josep Lluis Sert Antoni Gaudí. Stuttgart: G. Hatje. Varignon, Pierre NOllvelle mécanique ou slatiqlle. 2 Vols. Paris: C. Jombert.
As Hangs the Flexible Line:
 Philippe Block Matt DeJong John Ochsendorf Building Technology Program MIT Room 5-418 Cambridge MA 02139 USA [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Keywords: limit analysis, graphic statics, thrust
Philippe Block Matt DeJong John Ochsendorf Building Technology Program MIT Room 5-418 Cambridge MA 02139 USA [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Keywords: limit analysis, graphic statics, thrust
Statics of Structural Supports
 Statics of Structural Supports TYPES OF FORCES External Forces actions of other bodies on the structure under consideration. Internal Forces forces and couples exerted on a member or portion of the structure
Statics of Structural Supports TYPES OF FORCES External Forces actions of other bodies on the structure under consideration. Internal Forces forces and couples exerted on a member or portion of the structure
MAJOR LEARNING OUTCOMES ARCHITECTURE AND URBAN PLANNING 1ST CYCLE PROGRAMS GENERAL ACADEMIC PROFILE
 MAJOR LEARNING OUTCOMES Faculty: Major: Course level: ARCHITECTURE ARCHITECTURE AND URBAN PLANNING 1ST CYCLE PROGRAMS GENERAL ACADEMIC PROFILE Positioning of major in the study area The major in Architecture
MAJOR LEARNING OUTCOMES Faculty: Major: Course level: ARCHITECTURE ARCHITECTURE AND URBAN PLANNING 1ST CYCLE PROGRAMS GENERAL ACADEMIC PROFILE Positioning of major in the study area The major in Architecture
Structural Analysis - II Prof. P. Banerjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture - 02
 Structural Analysis - II Prof. P. Banerjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 02 Good morning. Today is the second lecture in the series of lectures on structural
Structural Analysis - II Prof. P. Banerjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 02 Good morning. Today is the second lecture in the series of lectures on structural
DESIGN OF SLABS. 3) Based on support or boundary condition: Simply supported, Cantilever slab,
 DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
Approximate Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Structures
 Approximate Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Structures Every successful structure must be capable of reaching stable equilibrium under its applied loads, regardless of structural behavior. Exact analysis
Approximate Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Structures Every successful structure must be capable of reaching stable equilibrium under its applied loads, regardless of structural behavior. Exact analysis
How To Write An Analysis System For Bridge Test
 Study of Analysis System for Bridge Test Chen Ke, Lu Jian-Ming, Research Institute of Highway, 100088, Beijing, China ([email protected], [email protected]) Summary Analysis System for Bridge Test (Chinese
Study of Analysis System for Bridge Test Chen Ke, Lu Jian-Ming, Research Institute of Highway, 100088, Beijing, China ([email protected], [email protected]) Summary Analysis System for Bridge Test (Chinese
INTRODUCTION TO BEAMS
 CHAPTER Structural Steel Design LRFD Method INTRODUCTION TO BEAMS Third Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Part II Structural Steel Design and Analysis
CHAPTER Structural Steel Design LRFD Method INTRODUCTION TO BEAMS Third Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Part II Structural Steel Design and Analysis
The elements used in commercial codes can be classified in two basic categories:
 CHAPTER 3 Truss Element 3.1 Introduction The single most important concept in understanding FEA, is the basic understanding of various finite elements that we employ in an analysis. Elements are used for
CHAPTER 3 Truss Element 3.1 Introduction The single most important concept in understanding FEA, is the basic understanding of various finite elements that we employ in an analysis. Elements are used for
INTRODUCTION TO LIMIT STATES
 4 INTRODUCTION TO LIMIT STATES 1.0 INTRODUCTION A Civil Engineering Designer has to ensure that the structures and facilities he designs are (i) fit for their purpose (ii) safe and (iii) economical and
4 INTRODUCTION TO LIMIT STATES 1.0 INTRODUCTION A Civil Engineering Designer has to ensure that the structures and facilities he designs are (i) fit for their purpose (ii) safe and (iii) economical and
PLANE TRUSSES. Definitions
 Definitions PLANE TRUSSES A truss is one of the major types of engineering structures which provides a practical and economical solution for many engineering constructions, especially in the design of
Definitions PLANE TRUSSES A truss is one of the major types of engineering structures which provides a practical and economical solution for many engineering constructions, especially in the design of
Deflections. Question: What are Structural Deflections?
 Question: What are Structural Deflections? Answer: The deformations or movements of a structure and its components, such as beams and trusses, from their original positions. It is as important for the
Question: What are Structural Deflections? Answer: The deformations or movements of a structure and its components, such as beams and trusses, from their original positions. It is as important for the
Advanced Structural Analysis. Prof. Devdas Menon. Department of Civil Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Module - 5.3.
 Advanced Structural Analysis Prof. Devdas Menon Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 5.3 Lecture - 29 Matrix Analysis of Beams and Grids Good morning. This is
Advanced Structural Analysis Prof. Devdas Menon Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 5.3 Lecture - 29 Matrix Analysis of Beams and Grids Good morning. This is
SMIP05 Seminar Proceedings VISUALIZATION OF NONLINEAR SEISMIC BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERSTATE 5/14 NORTH CONNECTOR BRIDGE. Robert K.
 VISUALIZATION OF NONLINEAR SEISMIC BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERSTATE 5/14 NORTH CONNECTOR BRIDGE Robert K. Dowell Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering San Diego State University Abstract This paper
VISUALIZATION OF NONLINEAR SEISMIC BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERSTATE 5/14 NORTH CONNECTOR BRIDGE Robert K. Dowell Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering San Diego State University Abstract This paper
Rigid and Braced Frames
 Rigid Frames Rigid and raced Frames Rigid frames are identified b the lack of pinned joints within the frame. The joints are rigid and resist rotation. The ma be supported b pins or fied supports. The
Rigid Frames Rigid and raced Frames Rigid frames are identified b the lack of pinned joints within the frame. The joints are rigid and resist rotation. The ma be supported b pins or fied supports. The
ARCHITECTURE. Asst. Prof. Meltem VATAN KAPTAN [email protected]
 STRUCTURES IN ARCHITECTURE Asst. Prof. Meltem VATAN KAPTAN [email protected] Istanbul Aydin University, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture ISTANBUL, TURKEY December 15, 2011 - GAZIANTEP If
STRUCTURES IN ARCHITECTURE Asst. Prof. Meltem VATAN KAPTAN [email protected] Istanbul Aydin University, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture ISTANBUL, TURKEY December 15, 2011 - GAZIANTEP If
Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge
 Journal of Civil Engineering (IEB), 34 (1) (26) 1-14 Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge Tanvir Manzur and Alamgir Habib Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
Journal of Civil Engineering (IEB), 34 (1) (26) 1-14 Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge Tanvir Manzur and Alamgir Habib Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
The Basics of FEA Procedure
 CHAPTER 2 The Basics of FEA Procedure 2.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the spring element, especially for the purpose of introducing various concepts involved in use of the FEA technique. A spring
CHAPTER 2 The Basics of FEA Procedure 2.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the spring element, especially for the purpose of introducing various concepts involved in use of the FEA technique. A spring
Lecture 4. Case Study of 16 th C Church in Old Goa
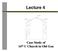 Lecture 4 Case Study of 16 th C Church in Old Goa Case Study: 16 th C. Church in Goa,, India 16th C. Church in Goa,, India 16th C. Church in Goa,, India 13.4 m 15.2 m 12.5 m 2.7 m 9.0 m 2.7 m Unit weight
Lecture 4 Case Study of 16 th C Church in Old Goa Case Study: 16 th C. Church in Goa,, India 16th C. Church in Goa,, India 16th C. Church in Goa,, India 13.4 m 15.2 m 12.5 m 2.7 m 9.0 m 2.7 m Unit weight
Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments
 Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments Positive Internal Forces Acting Recall from mechanics of materials that the internal forces P (generic axial), V (shear) and M (moment) represent resultants
Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments Positive Internal Forces Acting Recall from mechanics of materials that the internal forces P (generic axial), V (shear) and M (moment) represent resultants
A COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF THE VINCENT THOMAS SUSPENSION BRIDGE
 A COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF THE VINCENT THOMAS SUSPENSION BRIDGE 81 Raymond W. Wolfe Hany J. Farran A COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF THE VINCENT THOMAS SUSPENSION BRIDGE Civil Engineering Civil Engineering Given the
A COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF THE VINCENT THOMAS SUSPENSION BRIDGE 81 Raymond W. Wolfe Hany J. Farran A COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF THE VINCENT THOMAS SUSPENSION BRIDGE Civil Engineering Civil Engineering Given the
8.2 Elastic Strain Energy
 Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993
 Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993 Abstract: This Technical Notes is a design aid for the Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (ACI 530/ASCE 5/TMS 402-92) and Specifications
Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993 Abstract: This Technical Notes is a design aid for the Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (ACI 530/ASCE 5/TMS 402-92) and Specifications
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS This is the second tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises.
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS This is the second tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises.
Reinforced Concrete Design
 FALL 2013 C C Reinforced Concrete Design CIVL 4135 ii 1 Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1. Reading Assignment Chapter 1 Sections 1.1 through 1.8 of text. 1.2. Introduction In the design and analysis of reinforced
FALL 2013 C C Reinforced Concrete Design CIVL 4135 ii 1 Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1. Reading Assignment Chapter 1 Sections 1.1 through 1.8 of text. 1.2. Introduction In the design and analysis of reinforced
Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus. Second Semester 2013-2014
 Finite Element Method Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus Second Semester 2013-2014 Objectives Understand the basic theory of the FEM Know the behaviour and usage of each type of elements covered
Finite Element Method Finite Element Method (ENGC 6321) Syllabus Second Semester 2013-2014 Objectives Understand the basic theory of the FEM Know the behaviour and usage of each type of elements covered
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
EFFECTS ON NUMBER OF CABLES FOR MODAL ANALYSIS OF CABLE-STAYED BRIDGES
 EFFECTS ON NUMBER OF CABLES FOR MODAL ANALYSIS OF CABLE-STAYED BRIDGES Yang-Cheng Wang Associate Professor & Chairman Department of Civil Engineering Chinese Military Academy Feng-Shan 83000,Taiwan Republic
EFFECTS ON NUMBER OF CABLES FOR MODAL ANALYSIS OF CABLE-STAYED BRIDGES Yang-Cheng Wang Associate Professor & Chairman Department of Civil Engineering Chinese Military Academy Feng-Shan 83000,Taiwan Republic
THE GOTHIC CHOIR OF THE N-D CATHEDRAL OF TOURNAI (B) : STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF THE FLYING-BUTTRESSES.
 10 th Canadian Masonry Symposium, Banff, Alberta, June 8 12, 2005 THE GOTHIC CHOIR OF THE N-D CATHEDRAL OF TOURNAI (B) : STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF THE FLYING-BUTTRESSES. D. Lamblin 1, L. Deléhouzée 2, L.
10 th Canadian Masonry Symposium, Banff, Alberta, June 8 12, 2005 THE GOTHIC CHOIR OF THE N-D CATHEDRAL OF TOURNAI (B) : STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF THE FLYING-BUTTRESSES. D. Lamblin 1, L. Deléhouzée 2, L.
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME 2 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS
 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
8 EXTRA LIGHT GRC SANDWICH ELEMENTS FOR ROOFING IN INDUSTRIAL BUILDINGS
 8 EXTRA LIGHT GRC SANDWICH ELEMENTS FOR ROOFING IN INDUSTRIAL BUILDINGS MARICA DELLA BELLA and DIEGO CIAN Precompressi Centro Nord S.p.A., Italy SUMMARY: Secondary roofing elements, complementary to the
8 EXTRA LIGHT GRC SANDWICH ELEMENTS FOR ROOFING IN INDUSTRIAL BUILDINGS MARICA DELLA BELLA and DIEGO CIAN Precompressi Centro Nord S.p.A., Italy SUMMARY: Secondary roofing elements, complementary to the
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TEST FOR DETERMINATION OF TENSILE STRENGTH OF CONCRETE BLOCKS
 1 th Canadian Masonry Symposium Vancouver, British Columbia, June -5, 013 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TEST FOR DETERMINATION OF TENSILE STRENGTH OF CONCRETE BLOCKS Vladimir G. Haach 1, Graça Vasconcelos and Paulo
1 th Canadian Masonry Symposium Vancouver, British Columbia, June -5, 013 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TEST FOR DETERMINATION OF TENSILE STRENGTH OF CONCRETE BLOCKS Vladimir G. Haach 1, Graça Vasconcelos and Paulo
An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis
 CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
 Graphic User Interface Graphic User Interface Modeling Features Bridge Applications Segmental Bridges Cable Bridges Analysis Features Result Evaluation Design Features 02 07 13 17 28 34 43 48 2 User Interface
Graphic User Interface Graphic User Interface Modeling Features Bridge Applications Segmental Bridges Cable Bridges Analysis Features Result Evaluation Design Features 02 07 13 17 28 34 43 48 2 User Interface
BOFIRE A FEM-programm for non-linear analysis of structural members under fire conditions
 BOFIRE A FEM-programm for non-linear analysis of structural members under fire conditions Prof. P. Schaumann, Dipl.-Ing. F. Kettner DESCRIPTION BOFIRE is a transient, non-linear, incremental computer code
BOFIRE A FEM-programm for non-linear analysis of structural members under fire conditions Prof. P. Schaumann, Dipl.-Ing. F. Kettner DESCRIPTION BOFIRE is a transient, non-linear, incremental computer code
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra
 Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
Thermal Stress & Strain. 07 Thermal Stress and Strain Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-05 press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 3
 Thermal Stress & Strain 07 Thermal Stress and Strain Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-05 press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 3 Thermal Stress & Strain 07 Thermal Stress and Strain Copyright G G
Thermal Stress & Strain 07 Thermal Stress and Strain Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-05 press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 3 Thermal Stress & Strain 07 Thermal Stress and Strain Copyright G G
REPAIR AND STRENGTHENING OF HISTORICAL CONCRETE BRIDGE OVER VENTA RIVER IN LATVIA
 1 REPAIR AND STRENGTHENING OF HISTORICAL CONCRETE BRIDGE OVER VENTA RIVER IN LATVIA Verners Straupe, M.sc.eng., Rudolfs Gruberts, dipl. eng. JS Celuprojekts, Murjanu St. 7a, Riga, LV 1024, Latvia e-mail:
1 REPAIR AND STRENGTHENING OF HISTORICAL CONCRETE BRIDGE OVER VENTA RIVER IN LATVIA Verners Straupe, M.sc.eng., Rudolfs Gruberts, dipl. eng. JS Celuprojekts, Murjanu St. 7a, Riga, LV 1024, Latvia e-mail:
Integration of Sustainable Approaches in the Building Design Process
 Integration of Sustainable Approaches in the Building Design Process U. Forgber, N. Kohler, V. Koch, University of Karlsruhe Englerstrasse 7 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany F. Schmidt, R. Haller, University of
Integration of Sustainable Approaches in the Building Design Process U. Forgber, N. Kohler, V. Koch, University of Karlsruhe Englerstrasse 7 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany F. Schmidt, R. Haller, University of
DESIGNING AESTHETIC FREEFORM OBJECTS: A COURSE FOR INDUSTRIAL DESIGN ENGINEERING STUDENTS
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ENGINEERING AND PRODUCT DESIGN EDUCATION 4 & 5 SEPTEMBER 2008, UNIVERSITAT POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA, BARCELONA, SPAIN DESIGNING AESTHETIC FREEFORM OBJECTS: A COURSE FOR INDUSTRIAL
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ENGINEERING AND PRODUCT DESIGN EDUCATION 4 & 5 SEPTEMBER 2008, UNIVERSITAT POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA, BARCELONA, SPAIN DESIGNING AESTHETIC FREEFORM OBJECTS: A COURSE FOR INDUSTRIAL
EFFECTIVE BENDING CAPACITY OF DOWEL-TYPE FASTENERS
 EFFECTIVE BENDING CAPACITY OF DOWEL-TYPE FASTENERS Hans Joachim Blass 1), Adriane Bienhaus 1) and Volker Krämer 1) 1) Lehrstuhl für Ingenieurholzbau und Baukonstruktionen, University of Karlsruhe, Germany
EFFECTIVE BENDING CAPACITY OF DOWEL-TYPE FASTENERS Hans Joachim Blass 1), Adriane Bienhaus 1) and Volker Krämer 1) 1) Lehrstuhl für Ingenieurholzbau und Baukonstruktionen, University of Karlsruhe, Germany
Structural Integrity Analysis
 Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
Structural Integrity Analysis 1. STRESS CONCENTRATION Igor Kokcharov 1.1 STRESSES AND CONCENTRATORS 1.1.1 Stress An applied external force F causes inner forces in the carrying structure. Inner forces
FOUNDATION DESIGN. Instructional Materials Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples
 FOUNDATION DESIGN Proportioning elements for: Transfer of seismic forces Strength and stiffness Shallow and deep foundations Elastic and plastic analysis Foundation Design 14-1 Load Path and Transfer to
FOUNDATION DESIGN Proportioning elements for: Transfer of seismic forces Strength and stiffness Shallow and deep foundations Elastic and plastic analysis Foundation Design 14-1 Load Path and Transfer to
SECTION 5 ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS SPANS DEVELOPED BY THE PTI EDC-130 EDUCATION COMMITTEE LEAD AUTHOR: BRYAN ALLRED
 SECTION 5 ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS SPANS DEVELOPED BY THE PTI EDC-130 EDUCATION COMMITTEE LEAD AUTHOR: BRYAN ALLRED NOTE: MOMENT DIAGRAM CONVENTION In PT design, it is preferable to draw moment diagrams
SECTION 5 ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS SPANS DEVELOPED BY THE PTI EDC-130 EDUCATION COMMITTEE LEAD AUTHOR: BRYAN ALLRED NOTE: MOMENT DIAGRAM CONVENTION In PT design, it is preferable to draw moment diagrams
THE DEVELOPMENT OF DESIGN METHODS FOR REINFORCED AND UNREINFORCED MASONRY BASEMENT WALLS J.J. ROBERTS
 THE DEVELOPMENT OF DESIGN METHODS FOR REINFORCED AND UNREINFORCED MASONRY BASEMENT WALLS J.J. ROBERTS Technical Innovation Consultancy Emeritus Professor of Civil Engineering Kingston University, London.
THE DEVELOPMENT OF DESIGN METHODS FOR REINFORCED AND UNREINFORCED MASONRY BASEMENT WALLS J.J. ROBERTS Technical Innovation Consultancy Emeritus Professor of Civil Engineering Kingston University, London.
New proposals for static consolidation of a damaged monument in Ani
 New proposals for static consolidation of a damaged monument in Ani Lorenzo JURINA, 1 (1) A.B.C. Department, Politecnico di Milano, Italy [email protected] Preface The ancient city of Ani represents
New proposals for static consolidation of a damaged monument in Ani Lorenzo JURINA, 1 (1) A.B.C. Department, Politecnico di Milano, Italy [email protected] Preface The ancient city of Ani represents
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar. Fig. 7.21 some of the trusses that are used in steel bridges
 7.7 Truss bridges Fig. 7.21 some of the trusses that are used in steel bridges Truss Girders, lattice girders or open web girders are efficient and economical structural systems, since the members experience
7.7 Truss bridges Fig. 7.21 some of the trusses that are used in steel bridges Truss Girders, lattice girders or open web girders are efficient and economical structural systems, since the members experience
SLAB DESIGN. Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems:
 Reading Assignment SLAB DESIGN Chapter 9 of Text and, Chapter 13 of ACI318-02 Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems: 13.6.1 Direct Design Method (DDM) For slab systems
Reading Assignment SLAB DESIGN Chapter 9 of Text and, Chapter 13 of ACI318-02 Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems: 13.6.1 Direct Design Method (DDM) For slab systems
Visualization of the healing process on reinforced concrete beams by application of Digital Image Correlation (DIC)
 Materials Characterisation VI 283 Visualization of the healing process on reinforced concrete beams by application of Digital Image Correlation (DIC) E. Tsangouri 1, K. Van Tittelboom 2, D.Van Hemelrijck
Materials Characterisation VI 283 Visualization of the healing process on reinforced concrete beams by application of Digital Image Correlation (DIC) E. Tsangouri 1, K. Van Tittelboom 2, D.Van Hemelrijck
2.0 External and Internal Forces act on structures
 2.0 External and Internal Forces act on structures 2.1 Measuring Forces A force is a push or pull that tends to cause an object to change its movement or shape. Magnitude, Direction, and Location The actual
2.0 External and Internal Forces act on structures 2.1 Measuring Forces A force is a push or pull that tends to cause an object to change its movement or shape. Magnitude, Direction, and Location The actual
MATERIALS AND SCIENCE IN SPORTS. Edited by: EH. (Sam) Froes and S.J. Haake. Dynamics
 MATERIALS AND SCIENCE IN SPORTS Edited by: EH. (Sam) Froes and S.J. Haake Dynamics Analysis of the Characteristics of Fishing Rods Based on the Large-Deformation Theory Atsumi Ohtsuki, Prof, Ph.D. Pgs.
MATERIALS AND SCIENCE IN SPORTS Edited by: EH. (Sam) Froes and S.J. Haake Dynamics Analysis of the Characteristics of Fishing Rods Based on the Large-Deformation Theory Atsumi Ohtsuki, Prof, Ph.D. Pgs.
Ponti pedonali con una struttura di pannelli di tavole accostate Brettstapel
 14. Internationales Holzbau-Forum 08 Stress-laminated arch construction for footbridges A. Kermani/Dr. G. Freedman 1 Fussgängerbrücken in Brettstapelbauweise Stress-laminated arch construction for footbridges
14. Internationales Holzbau-Forum 08 Stress-laminated arch construction for footbridges A. Kermani/Dr. G. Freedman 1 Fussgängerbrücken in Brettstapelbauweise Stress-laminated arch construction for footbridges
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 1 STRESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following.
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant
 International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. 3 Issue. 3 Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant 1, M. S. Abo_Elkhair, 2, M. E. Abo-Elnor,
International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. 3 Issue. 3 Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant 1, M. S. Abo_Elkhair, 2, M. E. Abo-Elnor,
Copyright 2011 Casa Software Ltd. www.casaxps.com. Centre of Mass
 Centre of Mass A central theme in mathematical modelling is that of reducing complex problems to simpler, and hopefully, equivalent problems for which mathematical analysis is possible. The concept of
Centre of Mass A central theme in mathematical modelling is that of reducing complex problems to simpler, and hopefully, equivalent problems for which mathematical analysis is possible. The concept of
Tall Building Form Generation by Parametric Design Process
 ctbuh.org/papers Title: Authors: Subject: Keywords: Tall Building Form Generation by Parametric Design Process Mahjoub Elnimeiri, Professor, Illinois Institute of Technology Sang Min Park, PhD Candidate,
ctbuh.org/papers Title: Authors: Subject: Keywords: Tall Building Form Generation by Parametric Design Process Mahjoub Elnimeiri, Professor, Illinois Institute of Technology Sang Min Park, PhD Candidate,
SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES
 SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES RANJITH DISSANAYAKE DEPT. OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF PERADENIYA, SRI LANKA ABSTRACT Many existing reinforced concrete structures in present
SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES RANJITH DISSANAYAKE DEPT. OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF PERADENIYA, SRI LANKA ABSTRACT Many existing reinforced concrete structures in present
Miss S. S. Nibhorkar 1 1 M. E (Structure) Scholar,
 Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings
 Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings In Turkey H. Sucuoğlu & A. Yakut Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey J. Kubin & A. Özmen Prota Inc, Ankara, Turkey SUMMARY Over the past
Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings In Turkey H. Sucuoğlu & A. Yakut Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey J. Kubin & A. Özmen Prota Inc, Ankara, Turkey SUMMARY Over the past
Rotation: Moment of Inertia and Torque
 Rotation: Moment of Inertia and Torque Every time we push a door open or tighten a bolt using a wrench, we apply a force that results in a rotational motion about a fixed axis. Through experience we learn
Rotation: Moment of Inertia and Torque Every time we push a door open or tighten a bolt using a wrench, we apply a force that results in a rotational motion about a fixed axis. Through experience we learn
Two-Year Post-Professional Degree (Path A) MASTERS OF ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN & URBANISM (MADU) With a Concentration in Classical Architecture
 Two-Year Post-Professional Degree (Path A) MASTERS OF ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN & URBANISM (MADU) With a Concentration in Classical Architecture ARCH 61011 Introduction to Architectural Representation 0 TOTAL
Two-Year Post-Professional Degree (Path A) MASTERS OF ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN & URBANISM (MADU) With a Concentration in Classical Architecture ARCH 61011 Introduction to Architectural Representation 0 TOTAL
COMPUTATIONAL ACCURACY ANALYSIS OF A COORDINATE MEASURING MACHINE UNDER STATIC LOAD
 COMPUTATIONAL ACCURACY ANALYSIS OF A COORDINATE MEASURING MACHINE UNDER STATIC LOAD Andre R. Sousa 1 ; Daniela A. Bento 2 CEFET/SC Federal Center of Technological Education Santa Catarina Av. Mauro Ramos,
COMPUTATIONAL ACCURACY ANALYSIS OF A COORDINATE MEASURING MACHINE UNDER STATIC LOAD Andre R. Sousa 1 ; Daniela A. Bento 2 CEFET/SC Federal Center of Technological Education Santa Catarina Av. Mauro Ramos,
METHOD OF STATEMENT FOR STATIC LOADING TEST
 Compression Test, METHOD OF STATEMENT FOR STATIC LOADING TEST Tension Test and Lateral Test According to the American Standards ASTM D1143 07, ASTM D3689 07, ASTM D3966 07 and Euro Codes EC7 Table of Contents
Compression Test, METHOD OF STATEMENT FOR STATIC LOADING TEST Tension Test and Lateral Test According to the American Standards ASTM D1143 07, ASTM D3689 07, ASTM D3966 07 and Euro Codes EC7 Table of Contents
Truss. are both simple and A Matsuo Example continuous trusses. The
 Girder Bridge A girder bridge is perhaps the most common and most basic bridge. A log across a creek is an example of a girder bridge in its simplest form. In modern steel girder bridges, the two most
Girder Bridge A girder bridge is perhaps the most common and most basic bridge. A log across a creek is an example of a girder bridge in its simplest form. In modern steel girder bridges, the two most
NEW MEXICO Grade 6 MATHEMATICS STANDARDS
 PROCESS STANDARDS To help New Mexico students achieve the Content Standards enumerated below, teachers are encouraged to base instruction on the following Process Standards: Problem Solving Build new mathematical
PROCESS STANDARDS To help New Mexico students achieve the Content Standards enumerated below, teachers are encouraged to base instruction on the following Process Standards: Problem Solving Build new mathematical
Fire and Concrete Structures
 Fire and Concrete Structures Authors: David N. Bilow, P.E., S.E., Director, Engineered Structures, Portland Cement Association 5420 Old Orchard Road, Skokie, IL 60077,Phone 847-972-9064, email: [email protected]
Fire and Concrete Structures Authors: David N. Bilow, P.E., S.E., Director, Engineered Structures, Portland Cement Association 5420 Old Orchard Road, Skokie, IL 60077,Phone 847-972-9064, email: [email protected]
Status quo of stress simulation for hot and warm work piece temperatures in forging
 Status quo of stress simulation for hot and warm work piece temperatures in forging Dipl.-Ing. Johannes Knust, Dr.-Ing. Malte Stonis, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd-Arno Behrens IPH - Institute of Integrated Production
Status quo of stress simulation for hot and warm work piece temperatures in forging Dipl.-Ing. Johannes Knust, Dr.-Ing. Malte Stonis, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd-Arno Behrens IPH - Institute of Integrated Production
Numerical Analysis of the Moving Formwork Bracket Stress during Construction of a Curved Continuous Box Girder Bridge with Variable Width
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 9, No. 6; 2015 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Numerical Analysis of the Moving Formwork Bracket Stress during Construction
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 9, No. 6; 2015 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Numerical Analysis of the Moving Formwork Bracket Stress during Construction
DESIGN OF SLABS. Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
 DESIGN OF SLABS Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction Types of Slab Slabs are plate elements
DESIGN OF SLABS Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction Types of Slab Slabs are plate elements
2.75 6.525 Problem Set 1 Solutions to ME problems Fall 2013
 2.75 6.525 Problem Set 1 Solutions to ME problems Fall 2013 2. Pinned Joint problem Jacob Bayless a) Draw a free-body diagram for the pin. How is it loaded? Does the loading depend on whether the pin is
2.75 6.525 Problem Set 1 Solutions to ME problems Fall 2013 2. Pinned Joint problem Jacob Bayless a) Draw a free-body diagram for the pin. How is it loaded? Does the loading depend on whether the pin is
Draft Table of Contents. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14
 Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
Chapter 8. Flexural Analysis of T-Beams
 Chapter 8. Flexural Analysis of T-s 8.1. Reading Assignments Text Chapter 3.7; ACI 318, Section 8.10. 8.2. Occurrence and Configuration of T-s Common construction type.- used in conjunction with either
Chapter 8. Flexural Analysis of T-s 8.1. Reading Assignments Text Chapter 3.7; ACI 318, Section 8.10. 8.2. Occurrence and Configuration of T-s Common construction type.- used in conjunction with either
ADVANCED SYSTEMS FOR RATIONAL SLAB REINFORCEMENT
 ADVANCED SYSTEMS FOR RATIONAL SLAB REINFORCEMENT CASPER ÅLANDER M. Sc. (Civ. Eng.) Development manager Fundia Reinforcing Abstract This paper deals with rational and fast ways to reinforce concrete slabs.
ADVANCED SYSTEMS FOR RATIONAL SLAB REINFORCEMENT CASPER ÅLANDER M. Sc. (Civ. Eng.) Development manager Fundia Reinforcing Abstract This paper deals with rational and fast ways to reinforce concrete slabs.
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope
 Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
4.2 Free Body Diagrams
 CE297-FA09-Ch4 Page 1 Friday, September 18, 2009 12:11 AM Chapter 4: Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies A (rigid) body is said to in equilibrium if the vector sum of ALL forces and all their moments taken about
CE297-FA09-Ch4 Page 1 Friday, September 18, 2009 12:11 AM Chapter 4: Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies A (rigid) body is said to in equilibrium if the vector sum of ALL forces and all their moments taken about
Use of Computers in Mechanics Education at Ohio State University*
 Int. J. Engng Ed. Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 394±400, 2000 0949-149X/91 $3.00+0.00 Printed in Great Britain. # 2000 TEMPUS Publications. Use of Computers in Mechanics Education at Ohio State University* GEORGE
Int. J. Engng Ed. Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 394±400, 2000 0949-149X/91 $3.00+0.00 Printed in Great Britain. # 2000 TEMPUS Publications. Use of Computers in Mechanics Education at Ohio State University* GEORGE
Pragmatic multi-scale and multi-physics analysis of Charles Bridge in Prague
 Pragmatic multi-scale and multi-physics analysis of Charles Bridge in Prague Jiří Šejnoha 1,2 Michal Šejnoha 1,2 Jan Zeman 1 Jan Novák 1,2 with Zdeněk Janda, Jiří Maděra, Jan Vorel and Jan Sýkora 1 Department
Pragmatic multi-scale and multi-physics analysis of Charles Bridge in Prague Jiří Šejnoha 1,2 Michal Šejnoha 1,2 Jan Zeman 1 Jan Novák 1,2 with Zdeněk Janda, Jiří Maděra, Jan Vorel and Jan Sýkora 1 Department
Solid Mechanics. Stress. What you ll learn: Motivation
 Solid Mechanics Stress What you ll learn: What is stress? Why stress is important? What are normal and shear stresses? What is strain? Hooke s law (relationship between stress and strain) Stress strain
Solid Mechanics Stress What you ll learn: What is stress? Why stress is important? What are normal and shear stresses? What is strain? Hooke s law (relationship between stress and strain) Stress strain
ENGINEERING SCIENCE H1 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS EDEXCEL HNC/D ENGINEERING SCIENCE LEVEL 4 H1 FORMERLY UNIT 21718P
 ENGINEERING SCIENCE H1 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS EDEXCEL HNC/D ENGINEERING SCIENCE LEVEL 4 H1 FORMERLY UNIT 21718P This material is duplicated in the Mechanical Principles module H2 and those
ENGINEERING SCIENCE H1 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS EDEXCEL HNC/D ENGINEERING SCIENCE LEVEL 4 H1 FORMERLY UNIT 21718P This material is duplicated in the Mechanical Principles module H2 and those
P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatsky MT07 Lecture 3 Statically Indeterminate Structures
 4 Stress and Strain Dr... Zavatsky MT07 ecture 3 Statically Indeterminate Structures Statically determinate structures. Statically indeterminate structures (equations of equilibrium, compatibility, and
4 Stress and Strain Dr... Zavatsky MT07 ecture 3 Statically Indeterminate Structures Statically determinate structures. Statically indeterminate structures (equations of equilibrium, compatibility, and
TABLE OF CONTENTS. INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE...
 Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
Compression load testing straw bale walls. Peter Walker Dept. Architecture & Civil Engineering University of Bath Bath BA2 7AY.
 Compression load testing straw bale walls Peter Walker Dept. Architecture & Civil Engineering University of Bath Bath BA2 7AY May 2004 1. Introduction Over the last 10 years a growing number of loadbearing
Compression load testing straw bale walls Peter Walker Dept. Architecture & Civil Engineering University of Bath Bath BA2 7AY May 2004 1. Introduction Over the last 10 years a growing number of loadbearing
2. Designing with Grammars
 CAAD futures Digital Proceedings 1991 33 2. Designing with Grammars Terry W. Knight Graduate School of Architecture and Urban Planning University of California Los Angeles, CA 90024-1467 U.S.A. Shape grammars
CAAD futures Digital Proceedings 1991 33 2. Designing with Grammars Terry W. Knight Graduate School of Architecture and Urban Planning University of California Los Angeles, CA 90024-1467 U.S.A. Shape grammars
FUNICULAR FUNNEL SHELLS
 FUNICULAR FUNNEL SHELLS MATTHIAS RIPPMANN, PHILIPPE BLOCK ABSTRACT This paper introduces a new typology of structurally efficient, funnel-shaped shells for light and open architectural applications. We
FUNICULAR FUNNEL SHELLS MATTHIAS RIPPMANN, PHILIPPE BLOCK ABSTRACT This paper introduces a new typology of structurally efficient, funnel-shaped shells for light and open architectural applications. We
Estimation of Work Hardening in Bent Sheet Metal Products at an Early Stage of Virtual Product Development
 Estimation of Work Hardening in Bent Sheet Metal Products at an Early Stage of Virtual Product Development RokneddinAzizi HosseinAmiryousefi Department of Mechanical Engineering Blekinge Institute of Technology
Estimation of Work Hardening in Bent Sheet Metal Products at an Early Stage of Virtual Product Development RokneddinAzizi HosseinAmiryousefi Department of Mechanical Engineering Blekinge Institute of Technology
US 51 Ohio River Bridge Engineering and Environmental Study
 US 51 Ohio River Bridge Engineering and Environmental Study ITEM NOS. 1-100.00 & 1-1140.00 Prepared by: Michael Baker Jr., Inc. 9750 Ormsby Station Rd Louisville, KY 40223 August 16, 2013 Table of Contents
US 51 Ohio River Bridge Engineering and Environmental Study ITEM NOS. 1-100.00 & 1-1140.00 Prepared by: Michael Baker Jr., Inc. 9750 Ormsby Station Rd Louisville, KY 40223 August 16, 2013 Table of Contents
National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying. Principles and Practice of Engineering Structural Examination
 Structural Effective Beginning with the April 2011 The structural engineering exam is a breadth and exam examination offered in two components on successive days. The 8-hour Vertical Forces (Gravity/Other)
Structural Effective Beginning with the April 2011 The structural engineering exam is a breadth and exam examination offered in two components on successive days. The 8-hour Vertical Forces (Gravity/Other)
ETABS. Integrated Building Design Software. Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA
 ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all
ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all
New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design
 New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design Part 1: 3D model based analysis using general beam-column FEM Ferenc Papp* and József Szalai ** * Associate Professor, Department of Structural
New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design Part 1: 3D model based analysis using general beam-column FEM Ferenc Papp* and József Szalai ** * Associate Professor, Department of Structural
Design of reinforced concrete columns. Type of columns. Failure of reinforced concrete columns. Short column. Long column
 Design of reinforced concrete columns Type of columns Failure of reinforced concrete columns Short column Column fails in concrete crushed and bursting. Outward pressure break horizontal ties and bend
Design of reinforced concrete columns Type of columns Failure of reinforced concrete columns Short column Column fails in concrete crushed and bursting. Outward pressure break horizontal ties and bend
Introductory Examples. InfoCAD Program System
 Introductory Examples InfoCAD Program System The description of program functions within this documentation should not be considered a warranty of product features. All warranty and liability claims arising
Introductory Examples InfoCAD Program System The description of program functions within this documentation should not be considered a warranty of product features. All warranty and liability claims arising
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31)
 Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
