See Sepsis Management Adult Algorithm and use Sepsis Order Set.
|
|
|
- Christian Allen
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANC less than 1,000/mm 3 or temperature greater than or Patient presents with fever or develops fever at MDACC -Consider Sepsis 1 Complete Physical Exam Start IV fluids Heme Survey with ANC, BUN, creatinine, Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, CO2 Urinalysis Lactic Acid Urine culture and sensitivity, Blood Cultures (with a set collected from each lumen simultaneously if CVC present, and 1 peripheral. If no CVC present, 2 blood cultures from peripheral site) and other cultures as clinically indicated. CXR if clinically indicated (signs/symptoms of respiratory involvement) or other tests as clinically indicated. Hemodynamically stable? (Does patient meet SIRS criteria 1 ) See Appendix A for signs of organ dysfunction Yes No See Sepsis Management Adult Algorithm and use Sepsis Order Set. If pneumonia is suspected, see algorithm for Pneumonia in Adult Patients (18 years and older) with Cancer and on Therapy. See Early Intervention for Suspected Adult Sepsis Algorithm and Early Intervention Sepsis Order Set. See Pages 2-4 to determine appropriate antibiotic regimen and use Inpatient Neutropenic Fever Order Set. 1 SIRS Criteria (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome) Patient exhibits two or more of the following : Temperature greater than 38 o C (100.4 o F) or less than 36 o C (96.8 o F) Heart Rate greater than 90 beats/minute Respiratory rate greater than or equal to 20 breaths/minute or PaCO 2 less than or equal to 32 mmhg WBC greater than or equal to 12,000/mm 3 or less than or equal to 4,000/mm 3 Suspected or proven infection Please call MERIT See Sepsis Management Adult Algorithm and use Sepsis Order Set. Consider adding ICU Addendum Severe Sepsis or Septic Shock Order Set.
2 Criteria for Selecting Antibiotics (antibiotics should be given within 2 hrs) SIRS patients refer to sepsis treatment algorithm. When selecting antibiotic regimen, take into account the following: -Recent culture and sensitivity results -History of positive VRE, MRSA, Multi- Drug Resistant organisms (i.e. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia) -CVC in place -Antibiotic history and prophylaxis -Source of infection if identified -Antibiotic allergies (see page 4 for beta lactam allergy) -Organ dysfunction 1 Consider Meropenem if patient has: - allergy to alternative agents or - failed treatment with cefepime or piperacillin/ tazobactam or - infection with ESBL (extended spectrum beta-lactamase) organism - infection with organism only susceptible to carbapenem 2 Double gram negative coverage should be considered with complicated tissue based infections, neutropenic enterocolitis, pneumonia and perirectal infections. If quinolone prophylaxis, add vancomycin to the regimen. NOTE: Antibiotics for gram negative coverage should be given first and may be infused via y-site with other antibiotics if compatible. FINDINGS Neutropenic Fever Suspected Line Infection and/or Bacteremia MRSA Colonization/ Skin and Soft Tissue Infection/ Mucositis greater than or equal to Grade 2 A B C ANTIMICROBIAL THERAPY RECOMMENDATIONS Choose one: Piperacillin and Tazobactam 4.5 grams IVPB every 6 hours or Cefepime 2 grams IVPB every 8 hours or Meropenem 1 1 grams IVPB every 8 hours If indicated, for double gram negative coverage 2, add one of the following: Beta-lactam allergy: see Page 4 for antibiotic options Choose one: Daptomycin 6-8 mg/kg IVPB every 24 hours (if no evidence of pneumonia) Piperacillin and Tazobactam 4.5 grams IVPB every 6 hours or Cefepime 2 grams IVPB every 8 hours or Meropenem 1 1 gram IVPB every 8 hours If indicated, for double gram negative coverage 2, add one of the following: Beta-lactam allergy: see Page 4 for antibiotic options Choose one: Daptomycin 6-8 mg/kg IVPB every 24 hours (if no evidence of pneumonia) or Linezolid 600 mg IVPB every 12 hours Piperacillin and Tazobactam 4.5 grams IVPB every 6 hours or Cefepime 2 grams IVPB every 8 hours or Meropenem 1 1 gram IVPB every 8 hours If indicated, for double gram negative coverage 2, add one of the following: Beta-lactam allergy: see Page 4 for antibiotic options See Pages 3 and 4 for additional findings and antibiotic options ANC less than 1,000/mm 3 or temperature greater than or NOTE: Doses indicated are for patients with normal renal/hepatic function. See Page 5 for Day 5 Re-assessment
3 Continued from previous page see Page 2 for Antibiotic Selection Criteria ANC less than 1,000/mm 3 or temperature greater than or FINDINGS Antimicrobial Therapy Recommendations NOTE: Doses indicated are for patients with normal renal/hepatic function. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Consider adding one of the following antibiotics to one of the regimens from Box A, B, or C on Page 2 or 3 of this algorithm: Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim (TMP) 3.75 mg TMP/kg IVPB or oral every 6 hours or If sulfa allergy, Tigecycline 100 mg IVPB times 1 dose then 50 mg IVPB every 12 hours Multi-drug resistent Organisms Consider Infectious Disease Consult Consider adding the following antibiotic to one of the regimens from Box A, B, or C on Page 2 or 3 of this algorithm: Colistin 2.5 mg/kg every 12 hours See Page 5 for Day 5 Re-assessment VRE Colonization or Infected Patients Consider using one of the following antibiotics, in place of vancomycin, with one of the regimens from Box A, B, or C on Page 2 of this algorithm: Linezolid 600 mg IVPB every 12 hours or Daptomycin 6-8 mg/kg IVPB every 24 hours (if no evidence of pneumonia) NOTE: Antibiotics for gram negative coverage should be given first and may be infused via y-site with other antibiotics if compatible.
4 FINDINGS Neutropenic Fever 1 Antimicrobial Therapy Recommendations NOTE: Doses indicated are for patients with normal renal/hepatic function. Choose: Aztreonam 2 grams IVPB every 8 hours Linezolid 600 mg IVPB every 12 hours ANC less than 1,000/mm 3 or temperature greater than or Serious beta-lactam allergy Suspected Line infection and/or Bacteremia 1 MRSA colonization/ Skin and Soft Tissue infection 1 Mucositis 1 greater than or equal to Grade 2 Choose: Aztreonam 2 grams IVPB every 8 hours Plus one of the following Daptomycin 6-8 mg/kg IVPB every 24 hours (if no evidence of pneumonia) Choose: Aztreonam 2 grams IVPB every 8 hours Linezolid 600 mg IVPB every 12 hours or Daptomycin 6-8 mg/kg IVPB every 24 hours (if no evidence of pneumonia) Choose: Aztreonam 2 grams IVPB every 8 hours and Clindamycin 900 mg IVPB every 8 hours and Tobramycin 7 mg/kg IVPB daily Linezolid 600 mg IVPB every 12 hours See Page 4 for Day 5 Re-assessment 1 NOTES: Double gram negative coverage recommended due to reduced aztreonam susceptibility to gram negative pathogens according to local antibiograms Antibiotics for gram negative coverage should be given first and may be infused via y-site with other antibiotics if compatible.
5 ANC less than 1,000/mm 3 or temperature greater than or Patient afebrile Cultures, susceptibilities and X-rays negative? Yes No Continue treatment for at least 2 days and until ANC is greater than 500 and rising Treat for appropriate duration based on nature of infection (UTI, bacteremia, pneumonia) 72 Hour Evaluation Patient febrile Cultures, susceptibilities and X-rays negative? Yes No Repeat cultures CT sinuses and Chest, serology CMV/aspergillus, other diagnostic work-up as clinically indicated Re-evaluate antibiotics Consider antifungals and/or antivirals Check susceptibilities Make necessary changes in antibiotic regimen CT scans, serology and other diagnostic work-up as clinically indicated Consider antifungals and/or antiviral Reassess at Day 5 Fever persists? Yes No Consider Infectious Disease consult CT of chest and/or other diagnostic tests if clinically indicated Observe; monitor counts, cultures and sensitivity results, CXR negative Disposition based on ID consult recommendations and/or diagnostic test results Complete antibiotic regimen and disposition per MD
6 ANC less than 1,000/mm 3 or temperature greater than or APPENDIX A: Suspicion of Organ Dysfunction Decreased perfusion (capillary refill greater than 3 seconds, skin mottling, cold extremities, lactate greater than 2 mmol/l) Circulatory (SBP less than 90 mmhg, MAP less than 65 mmhg, decrease in SBP greater than 40 mmhg) Respiratory (PaO 2 /FiO 2 less than 300; PaO 2 less than 70 mmhg; SaO 2 less than 90%) Hepatic (jaundice; total bilirubin greater than 4 mg/dl; increased LFT s; increased PT) Renal (creatinine greater than 0.3 mg/dl; urine output less than 0.5 ml/kg/hour for at least 2 hours) Central nervous system (altered consciousness, confusion, psychosis) Coagulopathy (INR greater than 1.5 or aptt greater than 60 seconds); thrombocytopenia (platelets less than 100,000/mm 3 ) Splanchnic circulation (absent bowel sounds) APPENDIX B: Criteria for ICU Admission Major Criteria - one required for admission to ICU: Need for mechanical ventilation Septic shock with the need of vasopressor(s) (See Institutional Sepsis Algorithm) Minor Criteria - at least 3 required for admission to ICU: Noninvasive ventilation PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio less than 250 Respiratory rate greater than 30 breaths per minute Systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmhg Oxygen supplementation greater than 50% Hypotension requring aggressive fluid resuscitation Acute renal failure Multilobar pulmonary infiltrates Confusion BUN greater than 20 mg/dl WBC less than 4,000/mm 3 Thrombocytopenia less than 100,000/mm 3 Hypothermia (less than 36 O C)
7 SUGGESTED READINGS Baden LR, Bensinger W, Angarone M, et al. (2012). Prevention and treatment of cancer related infections. J Natl Compr Canc Netw; 10: Bow EJ, Rotstein C, Noskin GA, et al. (2006). A randomized, open-label, multicenter comparative study of the efficacy and safety of piperacillin-tazobactam and cefepime for the empirical treatment of febrile neutropenic episodes in patients with hematologic malignancies. Clin Infect Dis; 43(4): Caillot D, Casasnovas O, Bernard A, et al. (1997). Improved management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients using early thoracic computed tomographic scan and surgery. J Clin Oncol; 15(1): Corapcioglu F, Sarper N, Zengin E. (2006). Monotherapy with piperacillin/tazobactam versus cefepime as empirical therapy for febrile neutropenia in pediatric cancer patients: a randomized comparison. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 23(3): Cornely OA, Maertens J, Winston DJ, et al. (2007). Posaconazole vs. fluconazole or itraconazole prophylaxis in patients with neutropenia. see comment. N Engl J Med. 356(4): Cruciani M, Rampazzo R, Malena M, et al. (1996). Prophylaxis with fluoroquinolones for bacterial infections in neutropenic patients: a meta-analysis. see comment. Clin Infect Dis; 23(4): Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, et al. (2013). Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sever sepsis and septic shock: Crit Care Med; 41(2): doi: /ccm.0b013e31827e83af. Dykewicz CA, Centers for Disease C, Prevention, et al. (2001). Summary of the guidelines for preventing opportunistic infections among hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis; 33(2): Freifeld A, Bow E, Sepkowitz K, et al. (2010). Executive summary clinical practice guidelines for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 update by the Infectious Disease Society of America. Clin Infect Dis; 52(4) : Hachem R, Hanna H, Kontoyiannis D, et al. (2008). The changing epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: Candida glabrata and Candida krusei as the leading causes of candidemia in hematologic malignancy. see comment. Cancer. 112(11): Hughes WT, Armstrong D, Bodey GP, et al. (2002) guidelines for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer. see comment. Clin Infect Dis; 34(6):730. Jaksic B, Martinelli G, Perez-Oteyza J, et al. (2006). Efficacy and safety of linezolid compared with vancomycin in a randomized, double-blind study of febrile neutropenic patients with cancer. Clin Infect Dis; (5): Kim SH, Kwon JC, Choi SM, et al. (2013). Escherichia coli and klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia in patients with neutropenic fever: factors associated with extended-spectrum b- lactamase production and its impact on outcome. Ann Hematol; 95: doi: /s y Klastersky J, Paesmans M, Rubenstein EB, et al. (2000). The multinational associated for supportive care in cancer risk index: a multinational scoring system for identifying low-risk febrile neutropenic cancer patients. J Clin Oncol; 15: Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Siegelman SS. (1985). Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in acute leukemia: characteristic findings on CT, the CT halo sign, and the role of CT in early diagnosis. Radiology. 157(3): Lee A, Mirrett S, Reller LB, Weinstein MP. (2007). Detection of bloodstream infections in adults: how many blood cultures are needed? see comment. J Clin Microbiol; 45(11): Leibovici L, Paul M, Cullen M, et al. (2006).Antibiotic prophylaxis in neutropenic patients: new evidence, practical decisions. Review 46 refs. Cancer. 107(8): Continued on Next Page Continued on Next Page
8 SUGGESTED READINGS - continued Limaye AP, Huang ML, Leisenring W, et al. (2001). Cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA load in plasma for the diagnosis of CMV disease before engraftment in hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients. J Infect Dis; 183(3): Lodise TP Jr., Patel N, Kwa A, et al. (2007). Predictors of 30-day mortality among patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections: impact of delayed appropriate antibiotic selection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother; 51(10): Maertens J, Theunissen K, Verhoef G, et al. (2005). Galactomannan and computed tomography-based preemptive antifungal therapy in neutropenic patients at high risk for invasive fungal infection: a prospective feasibility study. see comment. Clin Infect Dis. 41(9): Marti F, Cullen M, Roila F, et al. (2009). Management of febrile neutropenia: ESMO clinical recommendations. Annals of Oncology; 20(4): doi: /annonc/mdp163 Martino R, Ramila E, Rabella N, et al. (2003). Respiratory virus infections in adults with hematologic malignancies: a prospective study. Clin Infect Dis; 36(1):1-8. Morris PG, Hassan T, McNamara M, et al. (2008). Emergence of MRSA in positive blood cultures from patients with febrile neutropenia--a cause for concern. Support Care Cancer; 16(9): Nichols WG, Guthrie KA, Corey L, et al. (2004). Influenza infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: risk factors, mortality, and the effect of antiviral therapy. see comment. Clin Infect Dis; 39(9): Nucci M, Landau M, Silveira F, et al. (2001). Application of the IDSA guidelines for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients: impact on reducing the use of glycopeptides. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol; 22(10): Owens RC, Owens CA, Holloway WJ. (2000). Reduction in vancomycin consumption in patients with fever and neutropenia [abst 458]. Clin Infect Dis. 31:291. Pacheco-Rosas DO, Huelgas-Plaza AC, Miranda-Novales MG, et al. (2014). Serum lactate as a biomarker of sever sepsis in children with cancer, neutropenia and fever. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc; 52(2):S24-9. PMID: Paul M, Schlesinger A, Grozinsky-Glasberg S, et al. (2003). Beta-lactam versus beta-lactam-aminoglycoside combination therapy in cancer patients with neutropenia. Cochrane Database of Sys Rev; (3)2003, Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD Raad, II, Escalante C, Hachem RY, et al. (2003). Treatment of febrile neutropenic patients with cancer who require hospitalization: a prospective randomized study comparing imipenem and cefepime. Cancer. 98(5): Segal BH, Almyroudis NG, Battiwalla M, et al. (2007). Prevention and early treatment of invasive fungal infection in patients with cancer and neutropenia and in stem cell transplant recipients in the era of newer broad-spectrum antifungal agents and diagnostic adjuncts. Clin Infect Dis. 44(3): Walsh TJ, Pappas P, Winston DJ, et al. (2002). Voriconazole compared with liposomal amphotericin B for empirical antifungal therapy in patients with neutropenia and persistent fever. N Engl J Med; 346(4): Wisplinghoff H, Seifert H, Wenzel RP, et al. (2003). Current trends in the epidemiology of nosocomial bloodstream infections in patients with hematological malignancies and solid neoplasms in hospitals in the United States. see comment. Clin Infect Dis; 36(9):1103. Zuckermann J, Moreira LB, Stoll P, et al. (2008) Compliance with a critical pathway for the management of febrile neutropenia and impact on clinical outcomes. Ann Hematol; 87(2):
9 DEVELOPMENT CREDITS This practice consensus algorithm is based on majority expert opinion of the Neutropenic Fever Work Group at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. It was developed using a multidisciplinary approach that included input from the following core group members: Roy F. Chemaly, MD Ŧ Tami N. Johnson, PharmD, BCPS, FCCM Joseph L. Nates, MD Terry W. Rice, MD Ŧ Kenneth V. Rolston, MD Frank P. Tverdek, PharmD, BCPS Ŧ Core Development Team Lead
Sepsis Reassess patient Monitor and maintain respiratory/ hemodynamic status
 Patient exhibits two or more of the following SIRS criteria: Temperature greater than 38 o C (100.4 o F) or less SIRS than criteria 36 o C (96.8 o F) Heart Rate greater than 90 beats/minute Respiratory
Patient exhibits two or more of the following SIRS criteria: Temperature greater than 38 o C (100.4 o F) or less SIRS than criteria 36 o C (96.8 o F) Heart Rate greater than 90 beats/minute Respiratory
Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Antifungal Therapy. Empiric Therapy, Combination Therapy, and the Question of Central Venous Catheters
 Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Antifungal Therapy Empiric Therapy, Combination Therapy, and the Question of Central Venous Catheters Douglas Fish, Pharm.D. Professor of Pharmacy, University of Colorado
Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Antifungal Therapy Empiric Therapy, Combination Therapy, and the Question of Central Venous Catheters Douglas Fish, Pharm.D. Professor of Pharmacy, University of Colorado
Decreasing Sepsis Mortality at the University of Colorado Hospital
 Decreasing Sepsis Mortality at the University of Colorado Hospital Maureen Dzialo, RN, BSN - Nurse Manager, Cardiac Intensive Care Unit Olivia Kerveillant, RN Clinical Nurse III, Medical Intensive Care
Decreasing Sepsis Mortality at the University of Colorado Hospital Maureen Dzialo, RN, BSN - Nurse Manager, Cardiac Intensive Care Unit Olivia Kerveillant, RN Clinical Nurse III, Medical Intensive Care
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment
 Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS
 ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
Subject: Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock Published Date: August 9, 2013 Scope: Hospital Wide Original Creation Date: August 9, 2013
 Stony Brook Medicine Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock Recognition and Treatment Protocols Subject: Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock Published Date: August 9, 2013 Scope: Hospital Wide Original Creation Date: August
Stony Brook Medicine Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock Recognition and Treatment Protocols Subject: Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock Published Date: August 9, 2013 Scope: Hospital Wide Original Creation Date: August
SE5h, Sepsis Education.pdf. Surviving Sepsis
 Surviving Sepsis 1 Scope and Impact of the Problem: Severe sepsis is a major healthcare problem that affects millions of people around the world each year with an extremely high mortality rate of 30 to
Surviving Sepsis 1 Scope and Impact of the Problem: Severe sepsis is a major healthcare problem that affects millions of people around the world each year with an extremely high mortality rate of 30 to
Lynda Richardson, RN, BSN Sepsis/Septic Shock Abstractor. No disclosures
 Lynda Richardson, RN, BSN Sepsis/Septic Shock Abstractor No disclosures 1 2 3 Discuss data requirements -3 hour bundle -6 hour bundle Challenges and compliance issues Success 4 Based on the Surviving Sepsis
Lynda Richardson, RN, BSN Sepsis/Septic Shock Abstractor No disclosures 1 2 3 Discuss data requirements -3 hour bundle -6 hour bundle Challenges and compliance issues Success 4 Based on the Surviving Sepsis
Klinik für Infektiologie und Institut für Infektionskranhkeiten
 Klinik und Poliklinik für Kinderchirurgie Infektiöse Komplikationen der Neutropenie Prof. Martin Täuber Klinik für Infektiologie und Institut für Infektionskranhkeiten This patient has most likely bacteremia
Klinik und Poliklinik für Kinderchirurgie Infektiöse Komplikationen der Neutropenie Prof. Martin Täuber Klinik für Infektiologie und Institut für Infektionskranhkeiten This patient has most likely bacteremia
IDSA GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 IDSA GUIDELINES Clinical Practice Guideline for the Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Neutropenic Patients with Cancer: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America Alison G. Freifeld, 1 Eric
IDSA GUIDELINES Clinical Practice Guideline for the Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Neutropenic Patients with Cancer: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America Alison G. Freifeld, 1 Eric
CIBMTR Infection Data and the New Infection Inserts.
 CIBMTR Infection Data and the New Infection Inserts. Marcie Tomblyn, MD, MS Scientific Director, CIBMTR Infection and Immune Reconstitution Working Committee Overview Indication for expanded data collection
CIBMTR Infection Data and the New Infection Inserts. Marcie Tomblyn, MD, MS Scientific Director, CIBMTR Infection and Immune Reconstitution Working Committee Overview Indication for expanded data collection
The Sepsis Puzzle: Identification, Monitoring and Early Goal Directed Therapy
 The Sepsis Puzzle: Identification, Monitoring and Early Goal Directed Therapy Cindy Goodrich RN, MS, CCRN Content Description Sepsis is caused by widespread tissue injury and systemic inflammation resulting
The Sepsis Puzzle: Identification, Monitoring and Early Goal Directed Therapy Cindy Goodrich RN, MS, CCRN Content Description Sepsis is caused by widespread tissue injury and systemic inflammation resulting
Core Measures SEPSIS UPDATES
 Patricia Walker, RN-BC, BSN Evidence Based Practice Manager Quality Management Services UCLA Health System, Ronald Reagan Medical Center Core Measures SEPSIS UPDATES Sepsis Core Measures Bundle Requirements
Patricia Walker, RN-BC, BSN Evidence Based Practice Manager Quality Management Services UCLA Health System, Ronald Reagan Medical Center Core Measures SEPSIS UPDATES Sepsis Core Measures Bundle Requirements
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis*
 Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
Recommendations: Other Supportive Therapy of Severe Sepsis* K. Blood Product Administration 1. Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of extenuating circumstances, such as myocardial
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia
 Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
Treatment of Fever and Infection in Children with Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia Document Information Version: 2 Date: June 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees, Sue Height (consultant
Hematologic Malignancies/Stem Cell Transplantation Program Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095
 Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095 CS 6.2 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIA Location: Clinical Section Supersedes/Replaces: B3.421g Document drive\path\name Effective
Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095 CS 6.2 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIA Location: Clinical Section Supersedes/Replaces: B3.421g Document drive\path\name Effective
Hemodialysis catheter infection
 Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
DRG 416 Septicemia. ICD-9-CM Coding Guidelines
 oding uidelines Septicemia ICD-9-CM Coding Guidelines The below listed septicemia guidelines are not inclusive. The coder should refer to the applicable Coding Clinic guidelines for additional information.
oding uidelines Septicemia ICD-9-CM Coding Guidelines The below listed septicemia guidelines are not inclusive. The coder should refer to the applicable Coding Clinic guidelines for additional information.
BUNDLES IN 2013: SURVIVING SEPSIS CAMPAIGN
 BUNDLES IN 2013: SURVIVING SEPSIS CAMPAIGN R. Phillip Dellinger MD, MSc, MCCM Professor of Medicine Cooper Medical School of Rowan University Professor of Medicine University Medicine and Dentistry of
BUNDLES IN 2013: SURVIVING SEPSIS CAMPAIGN R. Phillip Dellinger MD, MSc, MCCM Professor of Medicine Cooper Medical School of Rowan University Professor of Medicine University Medicine and Dentistry of
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS IN CANCER PATIENTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS IN CANCER PATIENTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Systemic cancer treatments and immunological therapies can suppress the ability of the bone
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS IN CANCER PATIENTS 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Systemic cancer treatments and immunological therapies can suppress the ability of the bone
Surveillance cultures PRO. Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen
 Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
INFECTIONS IN PATIENTS WITH CANCER
 INFECTIONS IN PATIENTS WITH CANCER TM Robert K. Sylvester, Pharm.D. Reviewed by Deborah Blamble, Pharm.D., BCOP; and H. William Kelly, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS Learning Objectives 1. Assess the relative morbidity
INFECTIONS IN PATIENTS WITH CANCER TM Robert K. Sylvester, Pharm.D. Reviewed by Deborah Blamble, Pharm.D., BCOP; and H. William Kelly, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS Learning Objectives 1. Assess the relative morbidity
Guideline for Primary Antifungal Prophylaxis for Pediatric Patients with Cancer or Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients
 Guideline for Primary Antifungal Prophylaxis for Pediatric Patients with Cancer or Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients The C 17 Primary Antifungal Prophylaxis for Pediatric Hematology / Oncology
Guideline for Primary Antifungal Prophylaxis for Pediatric Patients with Cancer or Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients The C 17 Primary Antifungal Prophylaxis for Pediatric Hematology / Oncology
Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support. Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident
 Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Objectives Define septic shock and briefly review pathophysiology Outline receptor
Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Objectives Define septic shock and briefly review pathophysiology Outline receptor
Research priorities in medical mycology
 Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
Practice Guidelines. Updated Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Intra-abdominal Infections
 Updated Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Intra-abdominal Infections CARRIE ARMSTRONG Guideline source: Surgical Infection Society, Infectious Diseases Society of America Literature search described?
Updated Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Intra-abdominal Infections CARRIE ARMSTRONG Guideline source: Surgical Infection Society, Infectious Diseases Society of America Literature search described?
Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements
 Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements Salmaan Kanji, Pharm.D. The Ottawa Hospital The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Conflict of Interest No financial, proprietary
Atrial Fibrillation in the ICU: Attempting to defend 4 controversial statements Salmaan Kanji, Pharm.D. The Ottawa Hospital The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Conflict of Interest No financial, proprietary
SPONTANEOUS PNEUMOTHORAX AS A COMPLICATION OF SEPTIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN AN INTRAVENOUS DRUG USER: A CASE REPORT
 Spontaneous pneumothorax in an IV drug user SPONTANEOUS PNEUMOTHORAX AS A COMPLICATION OF SEPTIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN AN INTRAVENOUS DRUG USER: A CASE REPORT Chau-Chyun Sheu, Jhi-Jhu Hwang, Jong-Rung
Spontaneous pneumothorax in an IV drug user SPONTANEOUS PNEUMOTHORAX AS A COMPLICATION OF SEPTIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN AN INTRAVENOUS DRUG USER: A CASE REPORT Chau-Chyun Sheu, Jhi-Jhu Hwang, Jong-Rung
Suffolk County Community College School of Nursing NUR 133 ADULT NURSING I
 Suffolk County Community College School of Nursing NUR 133 ADULT NURSING I Page # 1 Instructions for students: Case study # 1 For this lab, you are planning to provide care to the following client: CB
Suffolk County Community College School of Nursing NUR 133 ADULT NURSING I Page # 1 Instructions for students: Case study # 1 For this lab, you are planning to provide care to the following client: CB
Solid Organ Transplantation
 Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
KING FAISAL SPECIALIST HOSPITAL AND RESEARCH CENTRE (GEN. ORG.) NURSING AFFAIRS. Scope of Service PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT (PICU)
 PICU-Jan.2012 Page 1 of 7 Number of Beds: 18 Nurse Patient Ratio: 1:1-2 : The Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) provides 24 hour intensive nursing care for patients aged neonate through adolescence.
PICU-Jan.2012 Page 1 of 7 Number of Beds: 18 Nurse Patient Ratio: 1:1-2 : The Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) provides 24 hour intensive nursing care for patients aged neonate through adolescence.
UPDATE ON PNEUMONIA COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA - UPDATE. PNEUMONIA Incidence. Michael E. Hanley, M.D. University of Colorado
 UPDATE ON PNEUMONIA Michael E. Hanley, M.D. University of Colorado COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA - UPDATE Epidemiology and definitions Risk factors and mortality Determining severity Management PNEUMONIA
UPDATE ON PNEUMONIA Michael E. Hanley, M.D. University of Colorado COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA - UPDATE Epidemiology and definitions Risk factors and mortality Determining severity Management PNEUMONIA
Disease Site Breast. Less than 120 kg: Cefazolin 2 grams IV Greater than or equal to 120 kg: Cefazolin 3 grams IV. Head & Neck
 Patients scheduled for surgery should have the following antibiotics administered prior to their procedure Vancomycin and Ciprofloxacin are to be initiated 60 to 120 minutes prior to incision and all other
Patients scheduled for surgery should have the following antibiotics administered prior to their procedure Vancomycin and Ciprofloxacin are to be initiated 60 to 120 minutes prior to incision and all other
Hematologic Malignancies/Stem Cell Transplantation Program Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095
 Hematologic Malignancies/Stem Cell Transplantation Program Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095 CS 6.4 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV) INFECTION AND DISEASE Location:
Hematologic Malignancies/Stem Cell Transplantation Program Clinical Section UCLA Health System Los Angeles, CA 90095 CS 6.4 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV) INFECTION AND DISEASE Location:
Develop an understanding of the differential diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Clostridium difficile infection has recently emerged in populations without any known risk factors. This presentation will focus on the historical background, diagnosis,
Antimicrobial Therapy in Immunocompromised and Critically Ill Patients: Management and Perspectives Palazzo dei Congressi - LUGANO 29-30 May 2014
 Antimicrobial Therapy in Immunocompromised and Critically Ill Patients: Management and Perspectives Palazzo dei Congressi - LUGANO 29-30 May 2014 BACKGROUND The incidence and diagnosis of viral, bacterial
Antimicrobial Therapy in Immunocompromised and Critically Ill Patients: Management and Perspectives Palazzo dei Congressi - LUGANO 29-30 May 2014 BACKGROUND The incidence and diagnosis of viral, bacterial
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER
 Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
Medical Direction and Practices Board WHITE PAPER Use of Pressors in Pre-Hospital Medicine: Proper Indication and State of the Science Regarding Proper Choice of Pressor BACKGROUND Shock is caused by a
SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS: ANTIBIOTIC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADULT PATIENTS
 Page 1 of 8 TITLE: SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS: ANTIBIOTIC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADULT PATIENTS GUIDELINE: Antibiotics are administered prior to surgical procedures to prevent surgical site infections. PURPOSE:
Page 1 of 8 TITLE: SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS: ANTIBIOTIC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ADULT PATIENTS GUIDELINE: Antibiotics are administered prior to surgical procedures to prevent surgical site infections. PURPOSE:
VASOPRESSOR AGENTS IN SEPTIC SHOCK
 VASOPRESSOR AGENTS IN SEPTIC SHOCK Daniel De Backer Head Dept Intensive Care, CHIREC hospitals, Belgium Professor of Intensive Care, Université Libre de Bruxelles President European Society of Intensive
VASOPRESSOR AGENTS IN SEPTIC SHOCK Daniel De Backer Head Dept Intensive Care, CHIREC hospitals, Belgium Professor of Intensive Care, Université Libre de Bruxelles President European Society of Intensive
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Do statins improve outcomes of patients with sepsis and pneumonia? Jordi Carratalà Department of Infectious Diseases Statins for sepsis & community-acquired pneumonia Sepsis and CAP are major healthcare
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
MSHP Annual Meeting 11/7/2014
 Using Clinical Decision Support (CDS): Meeting Quality Measures and Beyond Michael D. Kraft, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Associate Professor University of Michigan College of Pharmacy Assistant Director-Education
Using Clinical Decision Support (CDS): Meeting Quality Measures and Beyond Michael D. Kraft, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Associate Professor University of Michigan College of Pharmacy Assistant Director-Education
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline
 Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
International Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock
 International Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Sponsoring organizations: American Association of Critical-Care Nurses American College of Chest Physicians American College of
International Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Sponsoring organizations: American Association of Critical-Care Nurses American College of Chest Physicians American College of
Received 4 July 2010; returned 10 August 2010; revised 27 September 2010; accepted 30 September 2010
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2011; 66: 205 209 doi:10.1093/jac/dkq404 Advance Access publication 8 November 2010 Sustained reduction in antimicrobial use and decrease in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
J Antimicrob Chemother 2011; 66: 205 209 doi:10.1093/jac/dkq404 Advance Access publication 8 November 2010 Sustained reduction in antimicrobial use and decrease in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies
 Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Inpatient Code Sepsis March Update. Sarah Prebil
 Inpatient Code Sepsis March Update Sarah Prebil 3 hour bundle Time is life Kumar et al. Crit Care Med 2006; 34:1589-1596 But Sarah, why are you harassing us about sepsis? Pilot Results 10 Code Sepsis pabents
Inpatient Code Sepsis March Update Sarah Prebil 3 hour bundle Time is life Kumar et al. Crit Care Med 2006; 34:1589-1596 But Sarah, why are you harassing us about sepsis? Pilot Results 10 Code Sepsis pabents
Bachir K. Younes, M.D., M.P.H.
 Work: 36923 Cook St. # 103 Palm Desert, CA 92211 Phone (760) 636-1336 Fax (760) 636-1335 Bachir K. Younes, M.D., M.P.H. Personal Born: Jan. 1 st, 1971 in Lebanon Marital Status: Married to Roula Sleilati
Work: 36923 Cook St. # 103 Palm Desert, CA 92211 Phone (760) 636-1336 Fax (760) 636-1335 Bachir K. Younes, M.D., M.P.H. Personal Born: Jan. 1 st, 1971 in Lebanon Marital Status: Married to Roula Sleilati
Postoperative management in adults
 Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Net work 77 Postoperative management in adults A practical guide to postoperative care for clinical staff 1 Introduction 1 2 Clinical assessment and monitoring 3 3 Cardiovascular
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Net work 77 Postoperative management in adults A practical guide to postoperative care for clinical staff 1 Introduction 1 2 Clinical assessment and monitoring 3 3 Cardiovascular
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
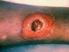 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance
 Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Guidance Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common indication for antimicrobial use in hospitals and a significant proportion of this use is
MANAGEMENT OF CANDIDA INFECTIONS IN SURGICAL PATIENTS
 DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto
 Is fever dangerous? Do we need to treat it? Episode 48 Pediatric Fever with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto prepared by Claire Heslop, edited by Anton Helman, July 2014 Pediatric Fever Fever in a child
Is fever dangerous? Do we need to treat it? Episode 48 Pediatric Fever with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto prepared by Claire Heslop, edited by Anton Helman, July 2014 Pediatric Fever Fever in a child
Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Acute Leukemia and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients
 27 Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Acute Leukemia and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients Maxim Norkin and John R. Wingard University of Florida College of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology,
27 Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Acute Leukemia and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients Maxim Norkin and John R. Wingard University of Florida College of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology,
Lothian Diabetes Handbook MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS
 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS 90 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS Diagnosis elevated plasma and/or urinary ketones metabolic acidosis (raised H + /low serum bicarbonate) Remember that hyperglycaemia,
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS 90 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS Diagnosis elevated plasma and/or urinary ketones metabolic acidosis (raised H + /low serum bicarbonate) Remember that hyperglycaemia,
Staphyloccus aureus sepsis: follow- up practice guidelines
 Staphyloccus aureus sepsis: follow- up practice guidelines March 17, 2012 National Study Day Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship prof. dr. Dirk Vogelaers, Ghent University Hospital apr. Franky Buyle, Ghent
Staphyloccus aureus sepsis: follow- up practice guidelines March 17, 2012 National Study Day Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship prof. dr. Dirk Vogelaers, Ghent University Hospital apr. Franky Buyle, Ghent
Prior Authorization Guideline
 Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: PS Inj - Alimta Therapeutic Class: Antineoplastic Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Antifolates Client: PS Inj Approval Date: 8/2/2004 Revision Date: 12/5/2006 I. BENEFIT
Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: PS Inj - Alimta Therapeutic Class: Antineoplastic Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Antifolates Client: PS Inj Approval Date: 8/2/2004 Revision Date: 12/5/2006 I. BENEFIT
James T. Dwyer DO, FACOI
 Antibiotics in the Surgical Patient James T. Dwyer DO, FACOI Objectives Define current prophylactic recommendations for the use of antibiotics in the surgical patient List current antibiotics available
Antibiotics in the Surgical Patient James T. Dwyer DO, FACOI Objectives Define current prophylactic recommendations for the use of antibiotics in the surgical patient List current antibiotics available
GRANIX (tbo-filgrastim)
 RATIONALE FOR INCLUSION IN PA PROGRAM Background Neutropenia is a hematological disorder characterized by an abnormally low number of neutrophils. A person with severe neutropenia has an absolute neutrophil
RATIONALE FOR INCLUSION IN PA PROGRAM Background Neutropenia is a hematological disorder characterized by an abnormally low number of neutrophils. A person with severe neutropenia has an absolute neutrophil
Update on Small Animal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)- is anything new?
 Update on Small Animal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)- is anything new? DVM, DACVA Objective: Update on the new Small animal guidelines for CPR and a discussion of the 2012 Reassessment Campaign on
Update on Small Animal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)- is anything new? DVM, DACVA Objective: Update on the new Small animal guidelines for CPR and a discussion of the 2012 Reassessment Campaign on
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Sites: Columbia University Medical Center Guideline: Medication Use Manual Page 1 of 12
 Page 1 of 12 TITLE: ANTIBIOTICS IN ADULT PATIENTS EMPIRIC USE GUIDELINES, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MEDICATION GUIDELINE PURPOSE: These are the 2011 guidelines for the empiric use of antibiotics
Page 1 of 12 TITLE: ANTIBIOTICS IN ADULT PATIENTS EMPIRIC USE GUIDELINES, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MEDICATION GUIDELINE PURPOSE: These are the 2011 guidelines for the empiric use of antibiotics
Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy
 Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy Jason E. Bowling, MD a,b, *, James S. Lewis II, PharmD c,d, Aaron D. Owens, MD a,e KEYWORDS Outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy Antibiotics Adverse events
Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy Jason E. Bowling, MD a,b, *, James S. Lewis II, PharmD c,d, Aaron D. Owens, MD a,e KEYWORDS Outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy Antibiotics Adverse events
Acute Pancreatitis. Questionnaire. if yes: amount (cigarettes/day): since when (year): Drug consumption: yes / no if yes: type of drug:. amount:.
 The physical examination has to be done AT ADMISSION! The blood for laboratory parameters has to be drawn AT ADMISSION! This form has to be filled AT ADMISSION! Questionnaire Country: 1. Patient personal
The physical examination has to be done AT ADMISSION! The blood for laboratory parameters has to be drawn AT ADMISSION! This form has to be filled AT ADMISSION! Questionnaire Country: 1. Patient personal
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model
 Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
Musculoskeletal Infection Care Process Model Musculoskeletal infections are serious and potentially life-threatening. Musculoskeletal infections include necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis,
BCCA Protocol Summary for Advanced Therapy for Relapsed Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Using PACLitaxel, Ifosfamide and CISplatin (TIP)
 BCCA Protocol Summary for Advanced Therapy for Relapsed Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Using PACLitaxel, Ifosfamide and CISplatin (TIP) Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician UGUTIP Genitourinary Dr.
BCCA Protocol Summary for Advanced Therapy for Relapsed Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Using PACLitaxel, Ifosfamide and CISplatin (TIP) Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician UGUTIP Genitourinary Dr.
John Gasman, MD Alec Jamieson, RN, MSN Kim Clifforth, RN, BSN, MSN, CNS Thomas T. Lam, MD. June 18, 2013
 John Gasman, MD Alec Jamieson, RN, MSN Kim Clifforth, RN, BSN, MSN, CNS Thomas T. Lam, MD June 18, 2013 Objectives Acquire knowledge on defining sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock Recognize SIRS criteria.
John Gasman, MD Alec Jamieson, RN, MSN Kim Clifforth, RN, BSN, MSN, CNS Thomas T. Lam, MD June 18, 2013 Objectives Acquire knowledge on defining sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock Recognize SIRS criteria.
Acute on Chronic Liver Failure: Current Concepts. Disclosures
 Acute on Chronic Liver Failure: Current Concepts Vandana Khungar, MD MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine September 20, 2015 None to declare Disclosures
Acute on Chronic Liver Failure: Current Concepts Vandana Khungar, MD MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine September 20, 2015 None to declare Disclosures
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis
 Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
Introduction to Antimicrobial Therapy
 Introduction to Antimicrobial Therapy Christine Kubin, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Case #1 L.G. is a 78 yo woman admitted for cardiac cath. 3-vessel disease was identified and
Introduction to Antimicrobial Therapy Christine Kubin, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Case #1 L.G. is a 78 yo woman admitted for cardiac cath. 3-vessel disease was identified and
Telemedicine Resuscitation & Arrest Trials (TreAT)
 Telemedicine Resuscitation & Arrest Trials (TreAT) Telemedicine within the ED for treating Severe Sepsis: A Hub and Spoke Telemedicine pilot SUMR Intern: Karole Collier Mentor: Dr. Brendan Carr & Dr. Anish
Telemedicine Resuscitation & Arrest Trials (TreAT) Telemedicine within the ED for treating Severe Sepsis: A Hub and Spoke Telemedicine pilot SUMR Intern: Karole Collier Mentor: Dr. Brendan Carr & Dr. Anish
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections
 Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Marnie Peterson, Pharm.D., BCPS Dept. of Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical School University of Minnesota Intra-abdominal abdominal Infections Intra-abdominal abdominal
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer [email protected] 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer [email protected] 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan
 Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Mean Duration (days) ± SD b. n = 587 n = 587
 Online Table 1. Length of stay in matched cohorts of patients with VA and patients without VA a MS-DRG opulation (Code) ECMO or tracheostomy with mechanical ventilation 96 hours or principal diagnosis
Online Table 1. Length of stay in matched cohorts of patients with VA and patients without VA a MS-DRG opulation (Code) ECMO or tracheostomy with mechanical ventilation 96 hours or principal diagnosis
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Guidelines for Antimicrobial Stewardship in Hospitals in Ireland. A Strategy for the Control of Antimicrobial Resistance in Ireland
 A Strategy for the Control of Antimicrobial Resistance in Ireland Guidelines for Antimicrobial Stewardship in Hospitals in Ireland Hospital Antimicrobial Stewardship Working Group Guidelines for Antimicrobial
A Strategy for the Control of Antimicrobial Resistance in Ireland Guidelines for Antimicrobial Stewardship in Hospitals in Ireland Hospital Antimicrobial Stewardship Working Group Guidelines for Antimicrobial
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D.
 ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
BCCA Protocol Summary for Palliative Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer using Trastuzumab Emtansine (KADCYLA)
 BCCA Protocol Summary for Palliative Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer using Trastuzumab Emtansine (KADCYLA) Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician UBRAVKAD Breast Dr Stephen Chia ELIGIBILITY:
BCCA Protocol Summary for Palliative Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer using Trastuzumab Emtansine (KADCYLA) Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician UBRAVKAD Breast Dr Stephen Chia ELIGIBILITY:
GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America Guidelines for Developing an Institutional Program to Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship Timothy
GUIDELINES Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America Guidelines for Developing an Institutional Program to Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship Timothy
A 7-year study of the distribution of nosocomial candidemia in children with cancer
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 225-229 Original A 7-year study of the distribution of nosocomial candidemia in children with cancer İlker Devrim 1, Bengü Demirağ 2, Yöntem Yaman 2, Nuri Bayram
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 225-229 Original A 7-year study of the distribution of nosocomial candidemia in children with cancer İlker Devrim 1, Bengü Demirağ 2, Yöntem Yaman 2, Nuri Bayram
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma
 Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital
 Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Using Predictive Analytics to Improve Sepsis Outcomes 4/23/2014
 Using Predictive Analytics to Improve Sepsis Outcomes 4/23/2014 Ryan Arnold, MD Department of Emergency Medicine and Value Institute Christiana Care Health System, Newark, DE Susan Niemeier, RN Chief Nursing
Using Predictive Analytics to Improve Sepsis Outcomes 4/23/2014 Ryan Arnold, MD Department of Emergency Medicine and Value Institute Christiana Care Health System, Newark, DE Susan Niemeier, RN Chief Nursing
TREATMENT OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS (PD) RELATED PERITONITIS. General Principles
 WA HOME DIALYSIS PROGRAM (WAHDIP) GUIDELINES General Principles 1. PD related peritonitis is an EMERGENCY early empiric treatment followed by close review is essential 2. When culture results and sensitivities
WA HOME DIALYSIS PROGRAM (WAHDIP) GUIDELINES General Principles 1. PD related peritonitis is an EMERGENCY early empiric treatment followed by close review is essential 2. When culture results and sensitivities
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options. John Kuruvilla
 Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Sepsis Management. National Clinical Guideline No. 6
 Sepsis Management National Clinical Guideline No. 6 November 2014 Using this National Clinical Guideline The aim of the National Clinical Guideline is to facilitate the early recognition and appropriate
Sepsis Management National Clinical Guideline No. 6 November 2014 Using this National Clinical Guideline The aim of the National Clinical Guideline is to facilitate the early recognition and appropriate
MULTIPLE MYELOMA Review & Update for Primary Care. Dr. Joseph Mignone 21st Century Oncology
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA Review & Update for Primary Care Dr. Joseph Mignone 21st Century Oncology OVERVIEW Identify the diagnostic criteria for multiple myeloma Compare first & second line therapies, using data
MULTIPLE MYELOMA Review & Update for Primary Care Dr. Joseph Mignone 21st Century Oncology OVERVIEW Identify the diagnostic criteria for multiple myeloma Compare first & second line therapies, using data
Appendix M: Guidelines for the Prophylaxis and Management of Intraabdominal, Biliary, and Appendiceal Infections
 Appendix M: Guidelines for the Prophylaxis and Management of Intraabdominal, Biliary, and Appendiceal Infections University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics Intraabdominal Infections Prophylaxis and Management
Appendix M: Guidelines for the Prophylaxis and Management of Intraabdominal, Biliary, and Appendiceal Infections University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics Intraabdominal Infections Prophylaxis and Management
