Investigations with Polyhedra
|
|
|
- Morgan Watts
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigations with Polyhedra When to use this project: In schools the subject of geometry, whether plane or solid, is often treated in a very abstract way. During this project students are motivated by the desire to create one of these beautiful figures and in doing so, they have hands-on experience with nets and solid geometry concepts. The applications of this construction activity are many. Our earth science classes have coordinated units on crystal structure that meld well with this activity. Students learn to make polyhedral examples of various crystal shapes. Real-world networking uses notions of 3- dimmensional connectivity. Molecular structure is another topic that can be illustrated well with polyhedra. Appropriate for students in 7th through 12th grades. Vocabulary and concepts polygon polyhedron, polyhedra regular polygon regular polyhedra truncation
2 stellation compound enanomorphic face edge vertex Motivation I generally begin this project after the winter vacation. Students have more indoor time in the winter. The anticipation for this project is another motivation for my students. In our classroom and around the school, there are lovely, student-made polyhedra dangling by fishing line or double strands of sewing thread from the braces between our ceiling tiles. These hanging polyhedra represents years of gifts from students to me or favorite teachers or favorite places in our school. The possibilities for the students are clear. Background necessary for students Several weeks before the projects begin, I try to make one polyhedra during team time or in the morning before classes begin so that students can observe my progress, the technique, and ask me questions about my creation. We do the actual construction in an opening 2 hour-long, block-scheduled class. But, prior to that class, students need to understand the vocabulary and appreciate the possibilities. About a week before the construction day, I show them the five Platonic Solids: tetrahedron, hexahedron, octahedron, dodecahedron and icosahedron. I indicate faces, regular faces (equal angles and equal sides), edges, vertices, and consistent interior angles. It's a good idea to have many models in student hands around the classroom. I like to get kids to wonder about why there are only 5 possible regular constructions. Lesson 1: About one week before construction To allow students to understand why there are only 5 regular solids, I have created sets of cardboard equilateral triangles, squares, pentagon and hexagons. Pattern blocks can also be used. Students equipped with these regular figures can investigate these questions. 1. How many different ways can you place equilateral triangles together to create the vertex of a polyhedron? Students find that 3 triangles held together make a very sharp point; 4 triangles make a less sharp vertex and 5 triangles held together make a rather dull vertex angle. However, 6 triangles don t create a vertex angle at all. 6 triangles together lay flat. Appropriate observations and review: What is the angle measure of one of your equilateral triangles? When you place 6 together what is the total angle measure of their union? Why do you suppose 6 triangles together don t make a vertex 2
3 angle of a polyhedra at all? 2. What would the figures look like if the vertex angle that you have just created were consistent throughout the figure? Students discover tetrahedron, octahedron, and icosahedron. 3. Now ask students to build a vertex with squares. They can only build a corner with 3 squares. What would a polyhedron made with vertices containing 3 squares each look like? Students discover a hexahedron = cube. Can you put 4 squares together in a vertex? What would the sum of four right angles be if you could create a vertex angle with them? 4. Now build vertices with pentagons. One interior vertex angle of a pentagon is 108 degrees. Review how you can figure out this measurement. Three pentagons together can be constructed to form a polyhedral vertex but four pentagons together have a vertex angle that adds up to more than 360 degrees making a concave vertex. What completed figure could you build with pentagons where every vertex had 3 adjacent pentagons? Students realize dodecahedron. 5. Now try to build vertices with hexagons. Each interior angle of a hexagon has 120 degrees. Three hexagons together create a flat vertex - no polygon. Therefore, there are only 5 regular solids. Hopefully throughout this investigation, words like vertices, faces, edges, regular angles will begin to be commonly understood. 3
4 Lesson 2: Familiarity with terms and notions of augmentation Before the actual construction class, students need to become familiar with the new vocabulary and concepts. I like to distribute my Platonic models and ask students to identify the following; 1. The name of the model 2. The shape of the faces in the model. 3. The number of faces in the model 4. The number of vertices in the model 5. The number of edges in the model *** Euler s formula makes an interesting insert here *** vertices + faces - edges = 2 This counting encourages students to explain to their classmates how they considered the model as they counted the number of edges, for instance, on an icosahedron. They also have the opportunity to use the terms and become familiar with their meanings. By now students are familiar with the five Platonic solids and understand the meaning of regular figures. It is time to introduce semi-regular figures. Semi-regular polyhedra are those that have regular faces but also contain more than one kind of regular polygon. There are several types of semi-regular figures 13 in all. Truncation: Getting students to understand truncation is not difficult if you have a model of a tetrahedron and a model of a truncated tetrahedron or a cube and a truncated cube. Truncating Platonic solids produce 5 new figures. Each of the 5 Platonic solids can be truncated. There are 8 other semi-regular convex polygons that are created by slicing sides and vertices again. But there are only 13 possible semi-regular polyhedrons. This is a very deep investigation but an option for a motivated student. Combining two or more polyhedra that appear to intersect each other can create more polyhedra. These are called Compounded polyhedra. Again, show models. 4
5 intersection of an octahedron and a cube two intersecting tetrahedra five intersecting tetrahedra The next important concept is the augmentation of the Platonic solids by stellation. If we extend the edges of all of the faces on an icosahedron, we obtain protrusions on each face. These protrusions would look like little pyramids attached to each face = stellations. Show stellated models. Point to the steepness of the stellation decided by the extended edges of the core polyhedra. A lovely stellation is the stellated icosahedron. At this point I like to show how the coloring of the models can emphasize different aspects of it. On the stellated icosahedron, I can use only one color to create a star or I can use six colors to emphasize the parallel facial planes and the two-d pentagrams that can be seen from each angle. A stellated model of an octahedron can be colored to look like an eight pointed star or done in two colors, as below, to look like two intersecting tetrahedron. 5
6 Lastly, two other polyhedra producing techniques should be shown. If a dimple (indentation) were placed on each face of a regular polyhedron, I might obtain a very different looking figure. The Great Dodecahedron can be viewed as a dimpled icosahedron. Lesson 3 - Day of construction Supplies: Ask students to gather at home and bring to class on this day: Thin cardboard (not corrugated), from back of pads of paper or from cereal boxes, shirt cardboard, etc. ball point pens straight edges old magazine to be used under the template and construction paper in the vertex stabbing procedure. I supply; compass points or T-pins school scissors white glue construction paper bobby pins (we call them math clamps ) I ask students to bring their own scissors if they prefer to work with tools that are more precise than my school scissors. Objective: Students will create a Platonic Solid in order to learn the technique of polyhedra construction. Their actual project will be due 10 days to two weeks later and is somewhat restricted in scope. 1. I have students gather around a set of tables that have been pushed together to observe the technique. I show them a perfect triangle that I have created with straight edge, compass, and scissors or on the computer with a drawing program that I will use as my 6
7 template. I glue the paper triangle onto the thin cardboard and suggest that they consider three ways to think about cutting out their template; leave the line on, cut the line off, or split the line. I suggest that they try to cut out their template by barely leaving their line on. Their templates will not be traced around. To make a good model, the template cannot be damaged during the construction. So, I show them how to mark the vertices with a hole poked just outside of their template with compass point on their construction paper (backed with a magazine) and then to connect the vertices dots with straight edge and ballpoint pen. The purpose of using the ballpoint pen is to score the construction paper and allow for perfect folds. Students who will be making models involving other faces than a triangle will need to have faces produced from the computer to insure regular construction and then glued onto cardboard backings. The final cropping of their template (leaving the line on but just barely) should not be done until the glue has dried. When the template is dried and trimmed (leaving the line on), I demonstrate the vertex punching, pen and straight-edge scoring, cutting out construction paper piece with tabs left on each side and the folding. Once a construction paper triangle has been drawn. I show students that they need to cut out the face but leave on enough material to glue the faces together = tabs or seam allowance. They also need to understand that the need to bevel the ends of their tabs so that paper won t get crumpled into the corner joints. 3. I glue two faces together and point out the necessity of keeping vertices aligned and looking at the good side of the joint for evenness in the facial planes. I clamp the glued surfaces together with math clamps (bobby pins) and set the piece aside for 5 minutes. I alternate gluing and cutting in order to allow joints to dry. 4. When affixing the final face of the polyhedron, I ask students to think of closing the lid of a box. We glue one hinge joint, let it dry, and then glue both of the remaining joints at the same time as we lower the lid to the box and hold it for 5 minutes - Voila! Students then choose one of the five Platonic solids to try to create. The technique requires patience and good fine motor ability. I try to encourage students to expect a poor first construction. This first construction is merely to learn the technique and become accustomed to the timing and process required. Construction begins. Students generally help each other and also require my help. This is a very social and pleasurable one-hour experience. 7
8 Assignment: Students are assigned to build (in accordance with their enthusiasm and fine motor talent) any model that they see in the room or on the posters (other than the Platonic Solids). I often help them create templates with the computer s ability to make regular polygons of any size and number of sides. In building a polyhedra that contains, for example, octagons and triangles (a truncated hexahedron) it is necessary to create two templates... one, of an octahedron with the same size side as a second template, a triangle. Assessment: Students are very concerned about the pressure of making a detailed, elaborate, time-consuming construction. Fine motor ability and art project patience varies dramatically from student to student. During the 2-hour construction day, it is easy to note who is talented at accurately and neatly gluing joints and which students find this task very difficult. When students are choosing their projects I make sure that they understand the rubric. Your project must be more complex than a platonic solid Your project must be neatly assembled Your project must be appropriate to your skill level which I have just observed. You must use color to show facial planes and parallel planes (There are often wonderful exceptions to this color requirement. Soccer balls; red stars of good luck; glittery decorations...) 8
9 Polyhedra Assignment You are assigned to build (according to your fine motor ability and enthusiasm) any model that you see in the room, on the posters, or in my polyhedra book. You must see me individually to get your polyhedra templates and permission to attempt the figure that you have chosen to complete. Your project will be graded according to accuracy, neatness, effort expended and color. The difficulty of your project will not affect your grade. You should begin immediately in order to have enough time to peacefully build your polyhedra allowing for plenty of gluedrying time and time for getting help. Beginning soon will also help you remember the steps that we have practiced in our block schedule class. Enjoy! 9
Shape Dictionary YR to Y6
 Shape Dictionary YR to Y6 Guidance Notes The terms in this dictionary are taken from the booklet Mathematical Vocabulary produced by the National Numeracy Strategy. Children need to understand and use
Shape Dictionary YR to Y6 Guidance Notes The terms in this dictionary are taken from the booklet Mathematical Vocabulary produced by the National Numeracy Strategy. Children need to understand and use
Star and convex regular polyhedra by Origami.
 Star and convex regular polyhedra by Origami. Build polyhedra by Origami.] Marcel Morales Alice Morales 2009 E D I T I O N M O R A L E S Polyhedron by Origami I) Table of convex regular Polyhedra... 4
Star and convex regular polyhedra by Origami. Build polyhedra by Origami.] Marcel Morales Alice Morales 2009 E D I T I O N M O R A L E S Polyhedron by Origami I) Table of convex regular Polyhedra... 4
SOLIDS, NETS, AND CROSS SECTIONS
 SOLIDS, NETS, AND CROSS SECTIONS Polyhedra In this section, we will examine various three-dimensional figures, known as solids. We begin with a discussion of polyhedra. Polyhedron A polyhedron is a three-dimensional
SOLIDS, NETS, AND CROSS SECTIONS Polyhedra In this section, we will examine various three-dimensional figures, known as solids. We begin with a discussion of polyhedra. Polyhedron A polyhedron is a three-dimensional
Teaching and Learning 3-D Geometry
 This publication is designed to support and enthuse primary trainees in Initial Teacher Training. It will provide them with the mathematical subject and pedagogic knowledge required to teach 3-D geometry
This publication is designed to support and enthuse primary trainees in Initial Teacher Training. It will provide them with the mathematical subject and pedagogic knowledge required to teach 3-D geometry
3D shapes. Level A. 1. Which of the following is a 3-D shape? A) Cylinder B) Octagon C) Kite. 2. What is another name for 3-D shapes?
 Level A 1. Which of the following is a 3-D shape? A) Cylinder B) Octagon C) Kite 2. What is another name for 3-D shapes? A) Polygon B) Polyhedron C) Point 3. A 3-D shape has four sides and a triangular
Level A 1. Which of the following is a 3-D shape? A) Cylinder B) Octagon C) Kite 2. What is another name for 3-D shapes? A) Polygon B) Polyhedron C) Point 3. A 3-D shape has four sides and a triangular
Teaching Guidelines. Knowledge and Skills: Can specify defining characteristics of common polygons
 CIRCLE FOLDING Teaching Guidelines Subject: Mathematics Topics: Geometry (Circles, Polygons) Grades: 4-6 Concepts: Property Diameter Radius Chord Perimeter Area Knowledge and Skills: Can specify defining
CIRCLE FOLDING Teaching Guidelines Subject: Mathematics Topics: Geometry (Circles, Polygons) Grades: 4-6 Concepts: Property Diameter Radius Chord Perimeter Area Knowledge and Skills: Can specify defining
Activity Set 4. Trainer Guide
 Geometry and Measurement of Solid Figures Activity Set 4 Trainer Guide Mid_SGe_04_TG Copyright by the McGraw-Hill Companies McGraw-Hill Professional Development GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT OF SOLID FIGURES
Geometry and Measurement of Solid Figures Activity Set 4 Trainer Guide Mid_SGe_04_TG Copyright by the McGraw-Hill Companies McGraw-Hill Professional Development GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT OF SOLID FIGURES
G3-33 Building Pyramids
 G3-33 Building Pyramids Goal: Students will build skeletons of pyramids and describe properties of pyramids. Prior Knowledge Required: Polygons: triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons Vocabulary:
G3-33 Building Pyramids Goal: Students will build skeletons of pyramids and describe properties of pyramids. Prior Knowledge Required: Polygons: triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons Vocabulary:
E XPLORING QUADRILATERALS
 E XPLORING QUADRILATERALS E 1 Geometry State Goal 9: Use geometric methods to analyze, categorize and draw conclusions about points, lines, planes and space. Statement of Purpose: The activities in this
E XPLORING QUADRILATERALS E 1 Geometry State Goal 9: Use geometric methods to analyze, categorize and draw conclusions about points, lines, planes and space. Statement of Purpose: The activities in this
Line Segments, Rays, and Lines
 HOME LINK Line Segments, Rays, and Lines Family Note Help your child match each name below with the correct drawing of a line, ray, or line segment. Then observe as your child uses a straightedge to draw
HOME LINK Line Segments, Rays, and Lines Family Note Help your child match each name below with the correct drawing of a line, ray, or line segment. Then observe as your child uses a straightedge to draw
Warning! Construction Zone: Building Solids from Nets
 Brief Overview: Warning! Construction Zone: Building Solids from Nets In this unit the students will be examining and defining attributes of solids and their nets. The students will be expected to have
Brief Overview: Warning! Construction Zone: Building Solids from Nets In this unit the students will be examining and defining attributes of solids and their nets. The students will be expected to have
Topological Treatment of Platonic, Archimedean, and Related Polyhedra
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 15 (015) 43 51. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Topological Treatment of Platonic, Archimedean, and Related Polyhedra Tom M. Apostol and Mamikon A. Mnatsakanian Abstract. Platonic
Forum Geometricorum Volume 15 (015) 43 51. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Topological Treatment of Platonic, Archimedean, and Related Polyhedra Tom M. Apostol and Mamikon A. Mnatsakanian Abstract. Platonic
SEGMENTED WOODTURNING
 Notes on: SEGMENTED WOODTURNING Malcolm Tibbetts www.tahoeturner.com malcolm@tahoeturner.com (530) 541-6135 MATHEMATICAL FORMULAS AND CONCEPTS: A circle contains 360 Circumference = Diameter x π(3.1416)
Notes on: SEGMENTED WOODTURNING Malcolm Tibbetts www.tahoeturner.com malcolm@tahoeturner.com (530) 541-6135 MATHEMATICAL FORMULAS AND CONCEPTS: A circle contains 360 Circumference = Diameter x π(3.1416)
56 questions (multiple choice, check all that apply, and fill in the blank) The exam is worth 224 points.
 6.1.1 Review: Semester Review Study Sheet Geometry Core Sem 2 (S2495808) Semester Exam Preparation Look back at the unit quizzes and diagnostics. Use the unit quizzes and diagnostics to determine which
6.1.1 Review: Semester Review Study Sheet Geometry Core Sem 2 (S2495808) Semester Exam Preparation Look back at the unit quizzes and diagnostics. Use the unit quizzes and diagnostics to determine which
Geometry of Minerals
 Geometry of Minerals Objectives Students will connect geometry and science Students will study 2 and 3 dimensional shapes Students will recognize numerical relationships and write algebraic expressions
Geometry of Minerals Objectives Students will connect geometry and science Students will study 2 and 3 dimensional shapes Students will recognize numerical relationships and write algebraic expressions
DISCOVERING 3D SHAPES
 . DISCOVERING 3D SHAPES WORKSHEETS OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2009 1 . Worksheet 1. Cut out and stick the shapes. SHAPES WHICH ROLL SHAPES WHICH SLIDE 2 . Worksheet 2: COMPLETE THE CHARTS Sphere, triangle, prism,
. DISCOVERING 3D SHAPES WORKSHEETS OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2009 1 . Worksheet 1. Cut out and stick the shapes. SHAPES WHICH ROLL SHAPES WHICH SLIDE 2 . Worksheet 2: COMPLETE THE CHARTS Sphere, triangle, prism,
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 These students are setting up a tent. How do the students know how to set up the tent? How is the shape of the tent created? How could students find the amount of material needed to make the tent? Why
These students are setting up a tent. How do the students know how to set up the tent? How is the shape of the tent created? How could students find the amount of material needed to make the tent? Why
Lesson #13 Congruence, Symmetry and Transformations: Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Math Buddies -Grade 4 13-1 Lesson #13 Congruence, Symmetry and Transformations: Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Goal: Identify congruent and noncongruent figures Recognize the congruence of plane
Math Buddies -Grade 4 13-1 Lesson #13 Congruence, Symmetry and Transformations: Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Goal: Identify congruent and noncongruent figures Recognize the congruence of plane
Which shapes make floor tilings?
 Which shapes make floor tilings? Suppose you are trying to tile your bathroom floor. You are allowed to pick only one shape and size of tile. The tile has to be a regular polygon (meaning all the same
Which shapes make floor tilings? Suppose you are trying to tile your bathroom floor. You are allowed to pick only one shape and size of tile. The tile has to be a regular polygon (meaning all the same
Platonic Solids. Some solids have curved surfaces or a mix of curved and flat surfaces (so they aren't polyhedra). Examples:
 Solid Geometry Solid Geometry is the geometry of three-dimensional space, the kind of space we live in. Three Dimensions It is called three-dimensional or 3D because there are three dimensions: width,
Solid Geometry Solid Geometry is the geometry of three-dimensional space, the kind of space we live in. Three Dimensions It is called three-dimensional or 3D because there are three dimensions: width,
Dear Grade 4 Families,
 Dear Grade 4 Families, During the next few weeks, our class will be exploring geometry. Through daily activities, we will explore the relationship between flat, two-dimensional figures and solid, three-dimensional
Dear Grade 4 Families, During the next few weeks, our class will be exploring geometry. Through daily activities, we will explore the relationship between flat, two-dimensional figures and solid, three-dimensional
Glow-in-the-Dark Geometry
 The Big Idea Glow-in-the-Dark Geometry This week you ll make geometric shapes out of glow sticks. The kids will try all sizes and shapes of triangles and quadrilaterials, then lay out sticks in mystical
The Big Idea Glow-in-the-Dark Geometry This week you ll make geometric shapes out of glow sticks. The kids will try all sizes and shapes of triangles and quadrilaterials, then lay out sticks in mystical
Volume of Right Prisms Objective To provide experiences with using a formula for the volume of right prisms.
 Volume of Right Prisms Objective To provide experiences with using a formula for the volume of right prisms. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game
Volume of Right Prisms Objective To provide experiences with using a formula for the volume of right prisms. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game
Angles that are between parallel lines, but on opposite sides of a transversal.
 GLOSSARY Appendix A Appendix A: Glossary Acute Angle An angle that measures less than 90. Acute Triangle Alternate Angles A triangle that has three acute angles. Angles that are between parallel lines,
GLOSSARY Appendix A Appendix A: Glossary Acute Angle An angle that measures less than 90. Acute Triangle Alternate Angles A triangle that has three acute angles. Angles that are between parallel lines,
12 Surface Area and Volume
 12 Surface Area and Volume 12.1 Three-Dimensional Figures 12.2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volumes of Pyramids
12 Surface Area and Volume 12.1 Three-Dimensional Figures 12.2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volumes of Pyramids
Plumbing and Pipe-Fitting Challenges
 Plumbing and Pipe-Fitting Challenges Students often wonder when they will use the math they learn in school. These activities answer that question as it relates to measuring, working with fractions and
Plumbing and Pipe-Fitting Challenges Students often wonder when they will use the math they learn in school. These activities answer that question as it relates to measuring, working with fractions and
Shapes & Designs Notes
 Problem 1.1 Definitions: regular polygons - polygons in which all the side lengths and angles have the same measure edge - also referred to as the side of a figure tiling - covering a flat surface with
Problem 1.1 Definitions: regular polygons - polygons in which all the side lengths and angles have the same measure edge - also referred to as the side of a figure tiling - covering a flat surface with
2. If C is the midpoint of AB and B is the midpoint of AE, can you say that the measure of AC is 1/4 the measure of AE?
 MATH 206 - Midterm Exam 2 Practice Exam Solutions 1. Show two rays in the same plane that intersect at more than one point. Rays AB and BA intersect at all points from A to B. 2. If C is the midpoint of
MATH 206 - Midterm Exam 2 Practice Exam Solutions 1. Show two rays in the same plane that intersect at more than one point. Rays AB and BA intersect at all points from A to B. 2. If C is the midpoint of
Third Grade Shapes Up! Grade Level: Third Grade Written by: Jill Pisman, St. Mary s School East Moline, Illinois Length of Unit: Eight Lessons
 Third Grade Shapes Up! Grade Level: Third Grade Written by: Jill Pisman, St. Mary s School East Moline, Illinois Length of Unit: Eight Lessons I. ABSTRACT This unit contains lessons that focus on geometric
Third Grade Shapes Up! Grade Level: Third Grade Written by: Jill Pisman, St. Mary s School East Moline, Illinois Length of Unit: Eight Lessons I. ABSTRACT This unit contains lessons that focus on geometric
SA B 1 p where is the slant height of the pyramid. V 1 3 Bh. 3D Solids Pyramids and Cones. Surface Area and Volume of a Pyramid
 Accelerated AAG 3D Solids Pyramids and Cones Name & Date Surface Area and Volume of a Pyramid The surface area of a regular pyramid is given by the formula SA B 1 p where is the slant height of the pyramid.
Accelerated AAG 3D Solids Pyramids and Cones Name & Date Surface Area and Volume of a Pyramid The surface area of a regular pyramid is given by the formula SA B 1 p where is the slant height of the pyramid.
ME 111: Engineering Drawing
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture # 14 (10/10/2011) Development of Surfaces http://www.iitg.ernet.in/arindam.dey/me111.htm http://www.iitg.ernet.in/rkbc/me111.htm http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~psr/ Indian
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture # 14 (10/10/2011) Development of Surfaces http://www.iitg.ernet.in/arindam.dey/me111.htm http://www.iitg.ernet.in/rkbc/me111.htm http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~psr/ Indian
Problem of the Month: Cutting a Cube
 Problem of the Month: The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common Core State Standards:
Problem of the Month: The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common Core State Standards:
Discovering Math: Exploring Geometry Teacher s Guide
 Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Mathematics Lesson Duration: Three class periods Program Description Discovering Math: Exploring Geometry From methods of geometric construction and threedimensional
Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6 8 Curriculum Focus: Mathematics Lesson Duration: Three class periods Program Description Discovering Math: Exploring Geometry From methods of geometric construction and threedimensional
Tessellating with Regular Polygons
 Tessellating with Regular Polygons You ve probably seen a floor tiled with square tiles. Squares make good tiles because they can cover a surface without any gaps or overlapping. This kind of tiling is
Tessellating with Regular Polygons You ve probably seen a floor tiled with square tiles. Squares make good tiles because they can cover a surface without any gaps or overlapping. This kind of tiling is
Chapter 18 Symmetry. Symmetry of Shapes in a Plane 18.1. then unfold
 Chapter 18 Symmetry Symmetry is of interest in many areas, for example, art, design in general, and even the study of molecules. This chapter begins with a look at two types of symmetry of two-dimensional
Chapter 18 Symmetry Symmetry is of interest in many areas, for example, art, design in general, and even the study of molecules. This chapter begins with a look at two types of symmetry of two-dimensional
Geometric Patterns. Introduction. Geometric Patterns 1 ~ Border Patterns. Geometric Patterns 2 ~ Tile Patterns
 Geometric Patterns Geometric Patterns Introduction In working with shapes, whether mathematically or artistically, it is necessary to have a good feeling for how more complex shapes can be made from simpler
Geometric Patterns Geometric Patterns Introduction In working with shapes, whether mathematically or artistically, it is necessary to have a good feeling for how more complex shapes can be made from simpler
Mathematics Materials for Tomorrow s Teachers
 M2T2 E 1 Geometry Mathematics Materials for Tomorrow s Teachers STATE GOAL 9: Use geometric methods to analyze, categorize, and draw conclusions about points, lines, planes, and space. Statement of Purpose:
M2T2 E 1 Geometry Mathematics Materials for Tomorrow s Teachers STATE GOAL 9: Use geometric methods to analyze, categorize, and draw conclusions about points, lines, planes, and space. Statement of Purpose:
Using 3D Computer Graphics Multimedia to Motivate Teachers Learning of Geometry and Pedagogy
 Using 3D Computer Graphics Multimedia to Motivate Teachers Learning of Geometry and Pedagogy Tracy Goodson-Espy Associate Professor goodsonespyt@appstate.edu Samuel L. Espy Viz Multimedia Boone, NC 28607
Using 3D Computer Graphics Multimedia to Motivate Teachers Learning of Geometry and Pedagogy Tracy Goodson-Espy Associate Professor goodsonespyt@appstate.edu Samuel L. Espy Viz Multimedia Boone, NC 28607
UNIT H1 Angles and Symmetry Activities
 UNIT H1 Angles and Symmetry Activities Activities H1.1 Lines of Symmetry H1.2 Rotational and Line Symmetry H1.3 Symmetry of Regular Polygons H1.4 Interior Angles in Polygons Notes and Solutions (1 page)
UNIT H1 Angles and Symmetry Activities Activities H1.1 Lines of Symmetry H1.2 Rotational and Line Symmetry H1.3 Symmetry of Regular Polygons H1.4 Interior Angles in Polygons Notes and Solutions (1 page)
Penultimate Polyhedra. James S. Plank. University oftennessee. 107 Ayres Hall. Knoxville, TN 37996. plank@cs.utk.edu.
 Penultimate Polyhedra James S. Plank Department of Computer Science University oftennessee 107 Ayres Hall Knoxville, TN 37996 plank@cs.utk.edu July 18, 1994 Introduction These are some notes that I originally
Penultimate Polyhedra James S. Plank Department of Computer Science University oftennessee 107 Ayres Hall Knoxville, TN 37996 plank@cs.utk.edu July 18, 1994 Introduction These are some notes that I originally
Contents. Grades K-2 1. Math Notebook Cover Template 2. Table of Contents Template
 Getting started with Interactive Math Notebooks Contents Grade 3-5 1. Math Notebook Expectations 2. Preparing your Math Notebook 3. Math Notebook Cover Template 4. Hints for Implementing Math Notebooks
Getting started with Interactive Math Notebooks Contents Grade 3-5 1. Math Notebook Expectations 2. Preparing your Math Notebook 3. Math Notebook Cover Template 4. Hints for Implementing Math Notebooks
SGS4.3 Stage 4 Space & Geometry Part A Activity 2-4
 SGS4.3 Stage 4 Space & Geometry Part A Activity 2-4 Exploring triangles Resources required: Each pair students will need: 1 container (eg. a rectangular plastic takeaway container) 5 long pipe cleaners
SGS4.3 Stage 4 Space & Geometry Part A Activity 2-4 Exploring triangles Resources required: Each pair students will need: 1 container (eg. a rectangular plastic takeaway container) 5 long pipe cleaners
Unit 8 Angles, 2D and 3D shapes, perimeter and area
 Unit 8 Angles, 2D and 3D shapes, perimeter and area Five daily lessons Year 6 Spring term Recognise and estimate angles. Use a protractor to measure and draw acute and obtuse angles to Page 111 the nearest
Unit 8 Angles, 2D and 3D shapes, perimeter and area Five daily lessons Year 6 Spring term Recognise and estimate angles. Use a protractor to measure and draw acute and obtuse angles to Page 111 the nearest
Grade 8 Mathematics Geometry: Lesson 2
 Grade 8 Mathematics Geometry: Lesson 2 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
Grade 8 Mathematics Geometry: Lesson 2 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
12 Surface Area and Volume
 CHAPTER 12 Surface Area and Volume Chapter Outline 12.1 EXPLORING SOLIDS 12.2 SURFACE AREA OF PRISMS AND CYLINDERS 12.3 SURFACE AREA OF PYRAMIDS AND CONES 12.4 VOLUME OF PRISMS AND CYLINDERS 12.5 VOLUME
CHAPTER 12 Surface Area and Volume Chapter Outline 12.1 EXPLORING SOLIDS 12.2 SURFACE AREA OF PRISMS AND CYLINDERS 12.3 SURFACE AREA OF PYRAMIDS AND CONES 12.4 VOLUME OF PRISMS AND CYLINDERS 12.5 VOLUME
Making tessellations combines the creativity of an art project with the challenge of solving a puzzle.
 Activities Grades 6 8 www.exploratorium.edu/geometryplayground/activities EXPLORING TESSELLATIONS Background: What is a tessellation? A tessellation is any pattern made of repeating shapes that covers
Activities Grades 6 8 www.exploratorium.edu/geometryplayground/activities EXPLORING TESSELLATIONS Background: What is a tessellation? A tessellation is any pattern made of repeating shapes that covers
How to Build Your Own CornHole Game
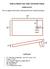 How to Build Your Own CornHole Game DIMENSIONS Here is a diagram with the basic measurements for the Cornhole board game. SUPPLIES 1/2 thick sheet of plywood one 4 x4 or two 2 x4 s 8 long 2 4 s (4) 4 1/2
How to Build Your Own CornHole Game DIMENSIONS Here is a diagram with the basic measurements for the Cornhole board game. SUPPLIES 1/2 thick sheet of plywood one 4 x4 or two 2 x4 s 8 long 2 4 s (4) 4 1/2
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116
 MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
Grade 7/8 Math Circles November 3/4, 2015. M.C. Escher and Tessellations
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Tiling the Plane Grade 7/8 Math Circles November 3/4, 2015 M.C. Escher and Tessellations Do the following
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Tiling the Plane Grade 7/8 Math Circles November 3/4, 2015 M.C. Escher and Tessellations Do the following
Geometry Progress Ladder
 Geometry Progress Ladder Maths Makes Sense Foundation End-of-year objectives page 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 2 End-of-block objectives page 3 Maths Makes Sense 3 4 End-of-block objectives page 4 Maths Makes
Geometry Progress Ladder Maths Makes Sense Foundation End-of-year objectives page 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 2 End-of-block objectives page 3 Maths Makes Sense 3 4 End-of-block objectives page 4 Maths Makes
Angle - a figure formed by two rays or two line segments with a common endpoint called the vertex of the angle; angles are measured in degrees
 Angle - a figure formed by two rays or two line segments with a common endpoint called the vertex of the angle; angles are measured in degrees Apex in a pyramid or cone, the vertex opposite the base; in
Angle - a figure formed by two rays or two line segments with a common endpoint called the vertex of the angle; angles are measured in degrees Apex in a pyramid or cone, the vertex opposite the base; in
Grade 1 Geometric Shapes Conceptual Lessons Unit Outline Type of Knowledge & SBAC Claim Prerequisite Knowledge:
 Grade 1 Geometric Shapes Conceptual Lessons Unit Outline Type of Knowledge & SBAC Claim Prerequisite Knowledge: Standards: Lesson Title and Objective/Description Shape names: square, rectangle, triangle,
Grade 1 Geometric Shapes Conceptual Lessons Unit Outline Type of Knowledge & SBAC Claim Prerequisite Knowledge: Standards: Lesson Title and Objective/Description Shape names: square, rectangle, triangle,
Florida Geometry EOC Assessment Study Guide
 Florida Geometry EOC Assessment Study Guide The Florida Geometry End of Course Assessment is computer-based. During testing students will have access to the Algebra I/Geometry EOC Assessments Reference
Florida Geometry EOC Assessment Study Guide The Florida Geometry End of Course Assessment is computer-based. During testing students will have access to the Algebra I/Geometry EOC Assessments Reference
Actually Doing It! 6. Prove that the regular unit cube (say 1cm=unit) of sufficiently high dimension can fit inside it the whole city of New York.
 1: 1. Compute a random 4-dimensional polytope P as the convex hull of 10 random points using rand sphere(4,10). Run VISUAL to see a Schlegel diagram. How many 3-dimensional polytopes do you see? How many
1: 1. Compute a random 4-dimensional polytope P as the convex hull of 10 random points using rand sphere(4,10). Run VISUAL to see a Schlegel diagram. How many 3-dimensional polytopes do you see? How many
30a. 31a. 30b 12. 31b. 29a 28a 1/48SCALEHEMSDAUPHIN PAGE2/10
 9 11 10 43 42 49 50 32 7 51 52 48 58 5 6 8 59 2 3 4 1 24 30a 31a 30 30b 12 31b 31 28 13 29 29a 28a 1/48SCALEHEMSDAUPHIN PAGE2/10 38 82 38f 85 84 86 83 37d 35 38a 37 60 17 21 20 16 15 87 27 34 40c 36b 36a
9 11 10 43 42 49 50 32 7 51 52 48 58 5 6 8 59 2 3 4 1 24 30a 31a 30 30b 12 31b 31 28 13 29 29a 28a 1/48SCALEHEMSDAUPHIN PAGE2/10 38 82 38f 85 84 86 83 37d 35 38a 37 60 17 21 20 16 15 87 27 34 40c 36b 36a
Hyperbolic Islamic Patterns A Beginning
 Hyperbolic Islamic Patterns A Beginning Douglas Dunham Department of Computer Science University of Minnesota, Duluth Duluth, MN 55812-2496, USA E-mail: ddunham@d.umn.edu Web Site: http://www.d.umn.edu/
Hyperbolic Islamic Patterns A Beginning Douglas Dunham Department of Computer Science University of Minnesota, Duluth Duluth, MN 55812-2496, USA E-mail: ddunham@d.umn.edu Web Site: http://www.d.umn.edu/
Geometry Software for Three-Dimensional Visualization and Modeling
 1 Geometry Software for Three-Dimensional Visualization and Modeling Carl W. Lee Department of Mathematics University of Kentucky Lexington, KY lee@ms.uky.edu www.ms.uky.edu/~lee/nctmdenver/nctmdenver.html
1 Geometry Software for Three-Dimensional Visualization and Modeling Carl W. Lee Department of Mathematics University of Kentucky Lexington, KY lee@ms.uky.edu www.ms.uky.edu/~lee/nctmdenver/nctmdenver.html
Objective To guide exploration of the connection between reflections and line symmetry. Assessment Management
 Line Symmetry Objective To guide exploration of the connection between reflections and line symmetry. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game Family
Line Symmetry Objective To guide exploration of the connection between reflections and line symmetry. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game Family
Chapter 8 Geometry We will discuss following concepts in this chapter.
 Mat College Mathematics Updated on Nov 5, 009 Chapter 8 Geometry We will discuss following concepts in this chapter. Two Dimensional Geometry: Straight lines (parallel and perpendicular), Rays, Angles
Mat College Mathematics Updated on Nov 5, 009 Chapter 8 Geometry We will discuss following concepts in this chapter. Two Dimensional Geometry: Straight lines (parallel and perpendicular), Rays, Angles
Which two rectangles fit together, without overlapping, to make a square?
 SHAPE level 4 questions 1. Here are six rectangles on a grid. A B C D E F Which two rectangles fit together, without overlapping, to make a square?... and... International School of Madrid 1 2. Emily has
SHAPE level 4 questions 1. Here are six rectangles on a grid. A B C D E F Which two rectangles fit together, without overlapping, to make a square?... and... International School of Madrid 1 2. Emily has
alternate interior angles
 alternate interior angles two non-adjacent angles that lie on the opposite sides of a transversal between two lines that the transversal intersects (a description of the location of the angles); alternate
alternate interior angles two non-adjacent angles that lie on the opposite sides of a transversal between two lines that the transversal intersects (a description of the location of the angles); alternate
Level 1 - Maths Targets TARGETS. With support, I can show my work using objects or pictures 12. I can order numbers to 10 3
 Ma Data Hling: Interpreting Processing representing Ma Shape, space measures: position shape Written Mental method s Operations relationship s between them Fractio ns Number s the Ma1 Using Str Levels
Ma Data Hling: Interpreting Processing representing Ma Shape, space measures: position shape Written Mental method s Operations relationship s between them Fractio ns Number s the Ma1 Using Str Levels
PUZZLES WITH POLYHEDRA AND PERMUTATION GROUPS
 PUZZLES WITH POLYHEDRA AND PERMUTATION GROUPS JORGE REZENDE. Introduction Consider a polyhedron. For example, a platonic, an arquemidean, or a dual of an arquemidean polyhedron. Construct flat polygonal
PUZZLES WITH POLYHEDRA AND PERMUTATION GROUPS JORGE REZENDE. Introduction Consider a polyhedron. For example, a platonic, an arquemidean, or a dual of an arquemidean polyhedron. Construct flat polygonal
Volume of Pyramids and Cones
 Volume of Pyramids and Cones Objective To provide experiences with investigating the relationships between the volumes of geometric solids. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms
Volume of Pyramids and Cones Objective To provide experiences with investigating the relationships between the volumes of geometric solids. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms
Pardon My Garden Quilt
 Pardon My Garden Quilt ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ A classic quilt made up of diamonds looks wonderful in any setting and this one will be a favourite for many years to come. The diamonds are framed by narrow
Pardon My Garden Quilt ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ A classic quilt made up of diamonds looks wonderful in any setting and this one will be a favourite for many years to come. The diamonds are framed by narrow
Notes ~ 1. Frank Tapson 2004 [trolxp:2]
![Notes ~ 1. Frank Tapson 2004 [trolxp:2] Notes ~ 1. Frank Tapson 2004 [trolxp:2]](/thumbs/40/21105847.jpg) Pentominoes 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234
Pentominoes 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234 8901234
Lesson Plans. Isaiah A.J. Walters Designer Educator
 Lesson Plans Isaiah A.J. Walters Designer Educator Symmetry Activity Centre #1 Complete the Photograph Materials: Magazine Picture Glue Stick Pencils and Pencil Crayons Scissors Blank Paper Instructions:
Lesson Plans Isaiah A.J. Walters Designer Educator Symmetry Activity Centre #1 Complete the Photograph Materials: Magazine Picture Glue Stick Pencils and Pencil Crayons Scissors Blank Paper Instructions:
Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters
 Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters Name Lesson 8.1: Areas of Rectangle (and Square) and Parallelograms How do we measure areas? Area is measured in square units. The type of the square unit you choose
Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters Name Lesson 8.1: Areas of Rectangle (and Square) and Parallelograms How do we measure areas? Area is measured in square units. The type of the square unit you choose
Duplicating Segments and Angles
 CONDENSED LESSON 3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles In this lesson, you Learn what it means to create a geometric construction Duplicate a segment by using a straightedge and a compass and by using patty
CONDENSED LESSON 3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles In this lesson, you Learn what it means to create a geometric construction Duplicate a segment by using a straightedge and a compass and by using patty
Drawing Lines of Symmetry Grade Three
 Ohio Standards Connection Geometry and Spatial Sense Benchmark H Identify and describe line and rotational symmetry in two-dimensional shapes and designs. Indicator 4 Draw lines of symmetry to verify symmetrical
Ohio Standards Connection Geometry and Spatial Sense Benchmark H Identify and describe line and rotational symmetry in two-dimensional shapes and designs. Indicator 4 Draw lines of symmetry to verify symmetrical
Geometry and Measurement
 The student will be able to: Geometry and Measurement 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the principles of geometry and measurement and operations using measurements Use the US system of measurement for
The student will be able to: Geometry and Measurement 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the principles of geometry and measurement and operations using measurements Use the US system of measurement for
11.3 Curves, Polygons and Symmetry
 11.3 Curves, Polygons and Symmetry Polygons Simple Definition A shape is simple if it doesn t cross itself, except maybe at the endpoints. Closed Definition A shape is closed if the endpoints meet. Polygon
11.3 Curves, Polygons and Symmetry Polygons Simple Definition A shape is simple if it doesn t cross itself, except maybe at the endpoints. Closed Definition A shape is closed if the endpoints meet. Polygon
2.1. Inductive Reasoning EXAMPLE A
 CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Inductive Reasoning In this lesson you will Learn how inductive reasoning is used in science and mathematics Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures about sequences of numbers
CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Inductive Reasoning In this lesson you will Learn how inductive reasoning is used in science and mathematics Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures about sequences of numbers
Kindergarten to Grade 3. Geometry and Spatial Sense
 Kindergarten to Grade 3 Geometry and Spatial Sense Every effort has been made in this publication to identify mathematics resources and tools (e.g., manipulatives) in generic terms. In cases where a particular
Kindergarten to Grade 3 Geometry and Spatial Sense Every effort has been made in this publication to identify mathematics resources and tools (e.g., manipulatives) in generic terms. In cases where a particular
Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 314 318)
 Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 34 38) Any side of a parallelogram or triangle can be used as a base. The altitude of a parallelogram is a line segment perpendicular to the base
Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 34 38) Any side of a parallelogram or triangle can be used as a base. The altitude of a parallelogram is a line segment perpendicular to the base
Copyright 2008 OLYMPUS CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. Paper Craft Assembly Manual
 Paper Craft Assembly Manual Before assembly: 1/9 Tips on assembly: Print all the parts (Photo-quality paper is recommended for ink-jet printers and paper of medium thickness (0.20 mm) for laser printers.)
Paper Craft Assembly Manual Before assembly: 1/9 Tips on assembly: Print all the parts (Photo-quality paper is recommended for ink-jet printers and paper of medium thickness (0.20 mm) for laser printers.)
Circles Galore Quilt. Sewing supplies: Approximate size: 60 (152cm)
 Sewing supplies: PFAFF creative 3.0 sewing and embroidery machine PFAFF creative QUILTERS HOOP 200x200 (820940096) PFAFF Extension Table with Adjustable Guide (821031096) PFAFF 0A Standard Foot for IDT
Sewing supplies: PFAFF creative 3.0 sewing and embroidery machine PFAFF creative QUILTERS HOOP 200x200 (820940096) PFAFF Extension Table with Adjustable Guide (821031096) PFAFF 0A Standard Foot for IDT
Skirt 1 / 4. The Skirt. The skirt patterns were downloaded from Mark's site but they need expanding before they can be used.
 Skirt 1 / 4 The Patterns The Skirt The skirt patterns were downloaded from Mark's site but they need expanding before they can be used. I used Corel Draw's real world dimensions to expand the patterns
Skirt 1 / 4 The Patterns The Skirt The skirt patterns were downloaded from Mark's site but they need expanding before they can be used. I used Corel Draw's real world dimensions to expand the patterns
Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1. 2. 3. 12in
 Area Review Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1 A 2 bh or A bh 2 Solve: Find the area of each triangle. 1. 2. 3. 5in4in 11in 12in 9in 21in 14in 19in 13in
Area Review Area of a triangle: The area of a triangle can be found with the following formula: 1 A 2 bh or A bh 2 Solve: Find the area of each triangle. 1. 2. 3. 5in4in 11in 12in 9in 21in 14in 19in 13in
I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE:
 Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Surface Area of Boxes I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In the Surface Area of Boxes activity, students will first discuss what surface area is and
Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Surface Area of Boxes I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In the Surface Area of Boxes activity, students will first discuss what surface area is and
Geometry Notes PERIMETER AND AREA
 Perimeter and Area Page 1 of 57 PERIMETER AND AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the area of given geometric figures. Calculate the perimeter
Perimeter and Area Page 1 of 57 PERIMETER AND AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the area of given geometric figures. Calculate the perimeter
Calendar Models. Frank Tapson 2005 [trolqc00:1]
![Calendar Models. Frank Tapson 2005 [trolqc00:1] Calendar Models. Frank Tapson 2005 [trolqc00:1]](/thumbs/27/9768586.jpg) Calendar Models I made my first calendar model, based on the regular dodecahedron, after reading about it in Martin Gardner's famous column in the Scientific American. (Late 70's?) I then went on to 'calendarise'
Calendar Models I made my first calendar model, based on the regular dodecahedron, after reading about it in Martin Gardner's famous column in the Scientific American. (Late 70's?) I then went on to 'calendarise'
GEOMETRY. Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12
 GEOMETRY Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12 OBJECTIVE Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic
GEOMETRY Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12 OBJECTIVE Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic
Please refer to the pack Design Tutorial for direction on how to embroider the blocks and sew them together.
 The Following is a tutorial on how to Back and Bind your Quilt. This is the way to do, however, there are other ways to finish your quilt. If you prefer a different method, do what works for you, it s
The Following is a tutorial on how to Back and Bind your Quilt. This is the way to do, however, there are other ways to finish your quilt. If you prefer a different method, do what works for you, it s
Jinny Beyer Border Prints. Creative Ideas & Tips for Quilters
 Jinny Beyer Border Prints Creative Ideas & Tips for Quilters Border Prints the Jinny Beyer Way W hile living in India in the early 1970s, I became fascinated with block-printed Indian cotton fabrics. These
Jinny Beyer Border Prints Creative Ideas & Tips for Quilters Border Prints the Jinny Beyer Way W hile living in India in the early 1970s, I became fascinated with block-printed Indian cotton fabrics. These
GAP CLOSING. 2D Measurement GAP CLOSING. Intermeditate / Senior Facilitator s Guide. 2D Measurement
 GAP CLOSING 2D Measurement GAP CLOSING 2D Measurement Intermeditate / Senior Facilitator s Guide 2-D Measurement Diagnostic...4 Administer the diagnostic...4 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions...4
GAP CLOSING 2D Measurement GAP CLOSING 2D Measurement Intermeditate / Senior Facilitator s Guide 2-D Measurement Diagnostic...4 Administer the diagnostic...4 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions...4
THE USE OF ORIGAMI IN THE TEACHING OF GEOMETRY
 THE USE OF ORIGAMI IN THE TEACHING OF GEOMETRY Sue Pope St. Martin s College, Lancaster This paper describes how Origami was used as a source of mathematical problemsolving in a series of lessons with
THE USE OF ORIGAMI IN THE TEACHING OF GEOMETRY Sue Pope St. Martin s College, Lancaster This paper describes how Origami was used as a source of mathematical problemsolving in a series of lessons with
Grade 3 Core Standard III Assessment
 Grade 3 Core Standard III Assessment Geometry and Measurement Name: Date: 3.3.1 Identify right angles in two-dimensional shapes and determine if angles are greater than or less than a right angle (obtuse
Grade 3 Core Standard III Assessment Geometry and Measurement Name: Date: 3.3.1 Identify right angles in two-dimensional shapes and determine if angles are greater than or less than a right angle (obtuse
12-1 Representations of Three-Dimensional Figures
 Connect the dots on the isometric dot paper to represent the edges of the solid. Shade the tops of 12-1 Representations of Three-Dimensional Figures Use isometric dot paper to sketch each prism. 1. triangular
Connect the dots on the isometric dot paper to represent the edges of the solid. Shade the tops of 12-1 Representations of Three-Dimensional Figures Use isometric dot paper to sketch each prism. 1. triangular
1 Symmetries of regular polyhedra
 1230, notes 5 1 Symmetries of regular polyhedra Symmetry groups Recall: Group axioms: Suppose that (G, ) is a group and a, b, c are elements of G. Then (i) a b G (ii) (a b) c = a (b c) (iii) There is an
1230, notes 5 1 Symmetries of regular polyhedra Symmetry groups Recall: Group axioms: Suppose that (G, ) is a group and a, b, c are elements of G. Then (i) a b G (ii) (a b) c = a (b c) (iii) There is an
LONDON JUBILEE AND OLYMPIC CELEBRATION ITEMS BY HILARY GOODING FOR MAKOWER UK
 LONDON JUBILEE AND OLYMPIC CELEBRATION ITEMS BY HILARY GOODING FOR MAKOWER UK 118 Grey s Road, Henley on Thames, Oxon RG9 1QW www.makoweruk.com Email: info@makoweruk.com www.andoverfabrics.com LONDON Designed
LONDON JUBILEE AND OLYMPIC CELEBRATION ITEMS BY HILARY GOODING FOR MAKOWER UK 118 Grey s Road, Henley on Thames, Oxon RG9 1QW www.makoweruk.com Email: info@makoweruk.com www.andoverfabrics.com LONDON Designed
TECHNICAL DRAWING (67)
 TECHNICAL DRAWING (67) (Candidates offering Technical Drawing Applications are not eligible to offer Technical Drawing.) Aims: 1. To develop competence among the students to pursue technical courses like
TECHNICAL DRAWING (67) (Candidates offering Technical Drawing Applications are not eligible to offer Technical Drawing.) Aims: 1. To develop competence among the students to pursue technical courses like
9 Area, Perimeter and Volume
 9 Area, Perimeter and Volume 9.1 2-D Shapes The following table gives the names of some 2-D shapes. In this section we will consider the properties of some of these shapes. Rectangle All angles are right
9 Area, Perimeter and Volume 9.1 2-D Shapes The following table gives the names of some 2-D shapes. In this section we will consider the properties of some of these shapes. Rectangle All angles are right
Geometry Chapter 1. 1.1 Point (pt) 1.1 Coplanar (1.1) 1.1 Space (1.1) 1.2 Line Segment (seg) 1.2 Measure of a Segment
 Geometry Chapter 1 Section Term 1.1 Point (pt) Definition A location. It is drawn as a dot, and named with a capital letter. It has no shape or size. undefined term 1.1 Line A line is made up of points
Geometry Chapter 1 Section Term 1.1 Point (pt) Definition A location. It is drawn as a dot, and named with a capital letter. It has no shape or size. undefined term 1.1 Line A line is made up of points
1 N o t e p a d P o r t f o l i o P a t t e r n
 Mrs. Langley s Notepad Cover Pattern 1 N o t e p a d P o r t f o l i o P a t t e r n Notepad Cover Pattern By The Hip Home Ec Teacher and Tamara Morris Langley Materials needed: Fabric see #1 under sewing
Mrs. Langley s Notepad Cover Pattern 1 N o t e p a d P o r t f o l i o P a t t e r n Notepad Cover Pattern By The Hip Home Ec Teacher and Tamara Morris Langley Materials needed: Fabric see #1 under sewing
Target To know the properties of a rectangle
 Target To know the properties of a rectangle (1) A rectangle is a 3-D shape. (2) A rectangle is the same as an oblong. (3) A rectangle is a quadrilateral. (4) Rectangles have four equal sides. (5) Rectangles
Target To know the properties of a rectangle (1) A rectangle is a 3-D shape. (2) A rectangle is the same as an oblong. (3) A rectangle is a quadrilateral. (4) Rectangles have four equal sides. (5) Rectangles
Mathematics Geometry Unit 1 (SAMPLE)
 Review the Geometry sample year-long scope and sequence associated with this unit plan. Mathematics Possible time frame: Unit 1: Introduction to Geometric Concepts, Construction, and Proof 14 days This
Review the Geometry sample year-long scope and sequence associated with this unit plan. Mathematics Possible time frame: Unit 1: Introduction to Geometric Concepts, Construction, and Proof 14 days This
Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles Circles, Circles, Circles March 19/20, 2013
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G Introduction Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles Circles, Circles, Circles March 9/20, 203 The circle is a very important shape. In fact of all shapes, the circle is
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G Introduction Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles Circles, Circles, Circles March 9/20, 203 The circle is a very important shape. In fact of all shapes, the circle is
ANCIENT EGYPT FUN AND ENGAGING LESSONS
 ANCIENT EGYPT FUN AND ENGAGING LESSONS NILE RIVER 3D CUBES MODERN DAY TOMB COLLECTIONS ILLUSTRATED MUMMIFICATION WHEEL EGYPTIAN TIME TRAVEL SCRAPBOOK HIEROGLYPHIC CARTOUCHE PENDANTS FUN AND ENGAGING LESSONS
ANCIENT EGYPT FUN AND ENGAGING LESSONS NILE RIVER 3D CUBES MODERN DAY TOMB COLLECTIONS ILLUSTRATED MUMMIFICATION WHEEL EGYPTIAN TIME TRAVEL SCRAPBOOK HIEROGLYPHIC CARTOUCHE PENDANTS FUN AND ENGAGING LESSONS
angle attribute Figure 1 4 right angles opposite sides parallel Lesson 14 5 Lesson 14 4 Vocab
 Vocab angle attribute 006_055_G4_VisV_101741.indd Page F46 2/13/10 11:27:36 PM u-s014 /Volumes/114/GO00403/GO00403_Natl_Visual_Voca_Cards_G4%0 Figure 1 4 right angles opposite sides parallel endpoint hexagon
Vocab angle attribute 006_055_G4_VisV_101741.indd Page F46 2/13/10 11:27:36 PM u-s014 /Volumes/114/GO00403/GO00403_Natl_Visual_Voca_Cards_G4%0 Figure 1 4 right angles opposite sides parallel endpoint hexagon
