Diagnosis and types of Kidney Cancer
|
|
|
- Evangeline Fleming
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 Fact sheet Introduction Our series of kidney cancer fact sheets have been developed to help you understand more about kidney cancer. This fact sheet provides information about the tests you may have if your doctor thinks you may have kidney cancer. It also gives information about the different types and stages of kidney cancer. For more information relating to other aspects of kidney cancer please see our other fact sheets: Kidney Cancer Localised Kidney Cancer Advanced Kidney Cancer Support for Kidney Cancer Advanced Kidney Cancer Dealing with the side effects of medication: targeted therapy Kidney Cancer Make the most of your visit to the doctor These fact sheets are meant as an introduction only and are not meant to be a substitute for your doctor s or healthcare professional s advice. Always consult your doctor or healthcare professional for more advice. What tests will I need to have? Your doctor will use different tests to diagnose and get more information about your kidney cancer. The tests done for kidney cancer can be divided into blood and urine tests, imaging, tissue biopsy and cystoscopy. The tests you have will depend on your particular situation. You may not necessarily need to have all the tests described below. 1. Blood and urine tests Blood tests: Chemical tests of the blood can detect findings associated with kidney cancer. Urine test (urinalysis): A common sign of a kidney cancer is blood in the urine. Remember that blood in the urine can be caused by conditions other than cancer as well. This test can also detect other abnormalities in the urine such as protein.
2 Page 2 2. Imaging Imaging is important for the diagnosis and classification of kidney cancer. The most common imaging techniques used are ultrasound scans, computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. You may have more than one type of scan. Ultrasound A type of scan where sound waves are used to produce a picture of the internal organs on a computer screen. Any abnormalities in the kidney and other organs can be seen on the screen. An ultrasound takes about minutes A gel is spread over your back or side and an ultrasound probe is slid over the skin CT scan A CT scan uses x-rays to get detailed pictures of organs in the body. They provide information about: Where the tumour is located in the kidney and its size Whether a tumour looks like it maybe cancer (malignant) or not cancer (benign) Whether there are enlarged lymph nodes or not Whether the tumour has spread to other parts of the body (metastasised). A CT scan takes about minutes The CT scanner is like a large round metal doughnut. You lie still on a table that goes through the hole of the scanner You may be given contrast MRI scan An MRI scan uses a combination of magnetism and radio waves to get detailed pictures of organs in the body. They provide different details to a CT scan and give information about: Whether the tumour has spread into the veins Whether the tumour has spread into the spinal cord. An MRI takes about minutes The MRI scanner is a large magnetic metal cylinder open at both ends. You lie still on a table inside the cylinder You may be given contrast However, the scanner can be noisy and some people feel anxious about being in a small space. Talk to you doctor if you think this may be a problem for you. Bone scan A bone scan is used to see if cancer has spread to the bones. A bone scan takes about 5 hours A small and harmless amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein The substance slowly moves through your blood into your bones. It particularly goes into the cancer cells After 3 4 hours a scan is done that detects radioactivity. If the cancer has spread to the bones it will show up as a large amount of radioactivity PET scan A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a specialised scan that uses radioactivity to show the chemical function of an organ or tissue. It can detect cancers even before they are seen on other types of scans. PET scans can create an image of the entire body. This means that they can show if (and where) cancer is spreading to other parts of the body. PET scans can also be used to see if tumours, are benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer) and to tell the difference between tumour or scar tissue. A PET scan takes about 2 hours You may need to not eat or drink before the scan You will be given an injection of radioactive material The amount of radiation you receive is small Chest x-ray An x-ray of organs and bones within the chest: A chest X-ray takes a few minutes Contrast Most CT and MRI scans are done with contrast (a kind of dye). Contrast is administered through a drip line in one of your veins (intravenous line), usually your arm. The contrast highlights the arteries and veins, giving more information about the tumour. It may make you feel hot and flushed for a few minutes. Some people are allergic to contrast so let the person doing the scan know if you feel unwell.
3 Page 3 3. Kidney (renal) biopsy Sometimes your doctor will recommend that you have a kidney biopsy. A kidney biopsy is where samples of tissue are taken from the tumour so that the cells can then be examined under a microscope. This gives the doctors more information about what sort of kidney tumour is present. In the majority of cases of kidney cancer a biopsy is not necessary. This is because the CT or MRI scan has already given enough information for your doctor to recommend surgery or other treatments for your kidney cancer. However, a biopsy may be recommended if: The results of your scan suggest that the tumour is benign The tumour is small and can be treated with active surveillance, radiotherapy ablation or cryotherapy (see later in the treatment section). A kidney biopsy takes about an hour and is done as an outpatient Local anaesthetic is given to numb the area The biopsy is taken whilst a scan is being done so the tumour can be found A fine needle is used to get one or two samples of the tumour Biopsies may cause a small amount of blood in the urine, which is normal. You will have to lie flat for 4 hours after the biopsy Then you should expect to take it easy for the rest of the day Rarely a biopsy can cause more severe bleeding and if this happens when you are home you should go straight back to the hospital. 4. Cystoscopy If you have blood in your urine you may have a cystoscopy. This is a test that lets your doctor look into your bladder and urethra using a telescope with a lens and a light. It is used to see if the blood in your urine is coming from your bladder or urethra. A cystoscopy takes about an hour and is done as an outpatient (you will not need to stay overnight in the hospital) You will be given either a local or general anaesthetic A telescope is passed into your bladder through the urethra You should take it easy for the rest of the day You may feel a burning sensation when having a wee or notice blood in your urine. This is normal but let your doctor know if it lasts more than a few days.
4 Page 4 What are the different types of kidney cancer? Not all kidney cancers are the same. The results of the tests you have had give information about: 1. The exact subtype of kidney cancer how the cancer cells look under a microscope and other features. Different subtypes come from different cells in the kidney. 2. The grade of kidney cancer how abnormal the cells are and how fast they ll probably grow. 3. The stage of kidney cancer how large the cancer is and how far it has spread. This information can be used by your doctor to guide treatment and help plan long-term follow-up care. 1. Different subtypes of kidney cancer There are different types of kidney cancer based on what the cancer cells look like under a microscope and other factors. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer and the second most common type is urothelial carcinoma. This series of fact sheets mainly gives information about RCC. The type of kidney cancer is not usually important for surgery, but it can be very important if more treatment is needed. If more treatment is needed, knowing the type of kidney cancer helps your doctor to talk with you about the best treatment options. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) 9 out of 10 kidney cancers Comes from the cells of the kidney s nephrons Subtypes: Clear cell about 75 out of 100 RCC are this type Papillary cell about 10 out of 100 RCC are this type Chromophobe about 5 out of 100 RCC are this type Others Urothelial carcinoma 1 out of 10 kidney cancers Comes from the cells of the drainage system of the kidney (the renal pelvis or ureters) Behaves like bladder cancer and so is treated differently to RCC Also known as transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) 2. The grades of kidney cancer Kidney cancer can also be described as aggressive (quickly growing) or non-aggressive (slowly growing).
5 Page 5 3. Stage of kidney cancer What is a staging system for kidney cancer? A staging system is a standard way for your healthcare team to describe how large the cancer is and how far it has spread. There are a number of ways to stage kidney cancer. The most common one is known as the TNM system. What are the stages of kidney cancer? Once the T, N, and M scores are known they can be used to give the kidney cancer overall stage of I, II, III, or IV. Each different stage groups cancers together that have a similar outcome (prognosis) and are treated in a similar way. Stage of kidney cancer: TNM staging system T (tumour) 1-4 Tx N (nodes) 0-1 Nx M (metastasis) 0-1 Indicates the size of the primary kidney tumour and whether it has spread into nearby areas. A higher number of T means that the tumour is larger, or has spread to areas around the kidney. Indicates the tumour cannot be assessed. Indicates whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes (part of the immune system). 0 means the cancer has not spread, 1 means the cancer has spread. Indicates lymph nodes can not be assessed. Indicates whether the cancer has spread (metastasised) to distant parts of the body. 0 means the cancer has not spread; 1 means the cancer has spread. STAGE Stage I Localised Stage II Localised Stage III Locally advanced Stage IV Advanced SIZE Less than 7cm Larger than 7cm Any size Any size LOCATION Only in the kidney Only in the kidney Spread to local lymph nodes, blood vessels and tissues Spread beyond the kidney metastasised TREATMENT If the cancer can be removed, surgery is a good treatment option If the cancer can be removed, surgery is a good treatment option The chance of being cured by surgery is lower but not zero; medication may be used Unlikely to be cured but various treatment options can slow growth SURVIVAL Survival decreases as stage increases
6 Page 6 A note on 5 year survival rates Survival rates are often used by doctors as a way of discussing how long a person will live after a diagnosis of cancer their prognosis. The 5 year survival rate refers to the percentage of patients who live at least 5 years after their cancer is diagnosed. Of course, many people live much longer than 5 years, many are cured, and some people die from causes other than their cancer. 5 year survival rates only give a general idea, they cannot predict what will happen in any individual person s case. Many things can affect a person s prognosis, such as the grade of the cancer, the treatment received, age and overall health. If you want to know your prognosis, your doctor can give you a general idea. Survival from kidney cancer has improved. In the 1980s, only 45 out of every 100 people with kidney cancer survived at least five years. Now about 73 out of every 100 people with kidney cancer survive at least 5 years. This improvement in survival from kidney cancer is due to kidney cancer being diagnosed earlier and better treatments. Who can I contact for more support & information? Both Kidney Health Australia and the Cancer Council offer a free and confidential service for further support and information. Kidney Health Australia Cancer Support & Information Service Kidney Health Australia provides support and information for kidney cancer patients, their families and carers in a variety of different ways. Free call: kidneycancer@kidney.org.au kidneycancer.org.au forum.kidney.org.au Cancer Council offers reliable cancer information and support to anyone affected by cancer, including patients, carers, families, friends, and healthcare professionals. They can connect you with others who have been through a similar experience and link you to practical, emotional and financial support in your area. Free call: cancer.org.au For more information about kidney or urinary health, please contact our free call Kidney Health Information Service (KHIS) on Or visit our website kidney.org.au to access free health literature. This is intended as a general introduction to this topic and is not meant to substitute for your doctor s or healthcare professional s advice. All care is taken to ensure that the information is relevant to the reader and applicable to each state in Australia. It should be noted that Kidney Health Australia recognises that each person s experience is individual and that variations do occur in treatment and management due to personal circumstances, the healthcare professional and the state one lives in. Should you require further information always consult your doctor or healthcare professional. If you have a hearing or speech impairment, contact the National Relay Service on or relayservice.com.au For all types of services ask for
7 Page 7 What does that word mean? Anaesthetic A drug that stops a person feeling pain during a medical procedure. A general anaesthetic affects the whole of your body by making you temporarily unconscious. A local anaesthetic affects only part of your body by making that area numb. Biopsy Removal of a small sample of tissue from the body to be examined under the microscope to help diagnose a disease. Bone scan A scan using small amounts of radioactive material to see if the cancer has spread to the bones. Computed tomography scan (CT) A scan using X-rays to produce detailed pictures of the body. Contrast medium/agent/dye A substance injected into a vein before a scan that gives more information about the tumour. Cystoscopy A test using a special telescope to look into the bladder. Grade A description of a tumour based on how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope and how quickly it is likely to grow and spread. Grading A score that is used to describe how quickly a tumour is likely to grow and how likely it is to spread. Intravenous line (iv line) A small plastic tube inserted into a vein (blood vessel) using a needle. Once in place, the needle is removed. It is used to give fluids and medications. Magnetic resonance imaging scan (MRI) - A scan using magnetic and radio waves to produce detailed pictures of the body. Positron emission tomography scan (PET) A scan using radioactivity to produce detailed pictures of the body. Prognosis The likely outcome or course of a disease, the chance of recovery or recurrence. Stage The extent of the cancer in the body (how large it is, whether it has spread to lymph nodes, and whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body). Staging Performing physical examinations and diagnostic tests to determine the extent of the cancer in the body (the stage). Ultrasound A scan that uses soundwaves to generate a picture of parts of the body. Urinanalysis A test of the urine.
The causes of kidney cancer are unknown. However, there are several factors that may increase your risk including:
 Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Types of surgery for kidney cancer
 Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
KIDNEY CANCER (ADULT) - RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
 KIDNEY CANCER (ADULT) - RENAL CELL CARCINOMA What is cancer? Cancer develops when cells in a part of the body begin to grow out of control. Although there are many kinds of cancer, they all start because
KIDNEY CANCER (ADULT) - RENAL CELL CARCINOMA What is cancer? Cancer develops when cells in a part of the body begin to grow out of control. Although there are many kinds of cancer, they all start because
Understanding Kidney Cancer
 Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends Cancer information www.cancervic.org.au Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families
Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends Cancer information www.cancervic.org.au Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families
Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma What is cancer?
 Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma What is cancer? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early
Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma What is cancer? The body is made up of hundreds of millions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Understanding Kidney Cancer
 Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends Cancer information www.cancercouncil.com.au Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families
Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends Cancer information www.cancercouncil.com.au Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma What is cancer?
 Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early
Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early
Kidney Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant
 Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Understanding Metastatic Disease
 Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Your bladder cancer diary. WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network
 Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Genetics Gender plays a role in kidney cancer, as men are twice as likely as women to develop RCC
 What is kidney cancer? Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common kind of kidney cancer. 1 Normally, your kidneys filter your blood and excrete waste in urine. Although our kidneys are important, we
What is kidney cancer? Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common kind of kidney cancer. 1 Normally, your kidneys filter your blood and excrete waste in urine. Although our kidneys are important, we
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T)
 Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to help you understand the surgery you are about to undergo. It will give you information
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (T.U.R.B.T) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to help you understand the surgery you are about to undergo. It will give you information
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
Contents. Overview. Removing the womb (hysterectomy) Overview
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed In this fact sheet: How is prostate cancer diagnosed? What tests are done by my GP? What tests will I have at the hospital? What do my biopsy results mean? Will I need
How prostate cancer is diagnosed In this fact sheet: How is prostate cancer diagnosed? What tests are done by my GP? What tests will I have at the hospital? What do my biopsy results mean? Will I need
What is kidney cancer?
 Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma Overview This overview is based on the more detailed information in our document, Kidney Cancer (Adult) Renal Cell Carcinoma. You can get this document and
Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma Overview This overview is based on the more detailed information in our document, Kidney Cancer (Adult) Renal Cell Carcinoma. You can get this document and
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Ovarian cancer. Patient information from the BMJ Group. What is ovarian cancer? What are the symptoms?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
Localized Kidney Cancer
 Patient Information English 3 Localized Kidney Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. If you are diagnosed with localized kidney cancer, your doctor can recommend treating the cancer with
Patient Information English 3 Localized Kidney Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. If you are diagnosed with localized kidney cancer, your doctor can recommend treating the cancer with
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
For further information on screening and early detection of prostate cancer, see the Section entitled Screening for Prostate Cancer.
 Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Prostate Cancer For many older men, prostate cancer may be present but never cause symptoms or problems and many men will die with their prostate cancer rather than of their prostate cancer. Yet it remains
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men
 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men 2 Prostate cancer A guide for newly diagnosed men About this booklet This booklet is for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It is
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Treating Melanoma S kin Cancer A Quick Guide
 Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
Understanding Kidney Cancer. A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends.
 Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends. Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends. First published January 2008
Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends. Understanding Kidney Cancer A guide for people with cancer, their families and friends. First published January 2008
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER. How Will I Know If My Prostate Cancer Returns?
 WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER?
 PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
PROSTATE CANCER 101 WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? Prostate cancer is cancer that begins in the prostate. The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in
The recommendations made throughout this book are by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC).
 INTRODUCTION This book has been prepared for people with bowel cancer, their families and friends. The first section is for people with bowel cancer, and is intended to help you understand what bowel cancer
INTRODUCTION This book has been prepared for people with bowel cancer, their families and friends. The first section is for people with bowel cancer, and is intended to help you understand what bowel cancer
Breast Cancer. CSC Cancer Experience Registry Member, breast cancer
 ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
Localised prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Diagnosis Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Localised prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is localised prostate cancer? How is localised prostate cancer diagnosed? What do my
Prostate Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Prostate Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
PATIENT GUIDE. Localized Prostate Cancer
 PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
PATIENT GUIDE Localized Prostate Cancer The prostate* is part of the male reproductive system. It is about the same size as a walnut and weighs about an ounce. As pictured in Figure 1, the prostate is
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
How To Plan A Staging Investigation For Cancer Of The Oesophagus Or Stomach
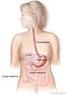 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
Advanced prostate cancer
 1 Advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is advanced (metastatic) prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose advanced prostate cancer? What do my test results mean? What are my treatment
1 Advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is advanced (metastatic) prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose advanced prostate cancer? What do my test results mean? What are my treatment
Multiple Myeloma. Understanding your diagnosis
 Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis Multiple Myeloma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer
 Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet
 Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed In this fact sheet: How is prostate cancer diagnosed? What tests are done by my GP? What tests will I have at the hospital? What do my biopsy results mean? Will I need
How prostate cancer is diagnosed In this fact sheet: How is prostate cancer diagnosed? What tests are done by my GP? What tests will I have at the hospital? What do my biopsy results mean? Will I need
Thyroid Cancer Overview
 Thyroid Cancer Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document, Thyroid Cancer. This document and other information
Thyroid Cancer Overview The information that follows is an overview of this type of cancer. It is based on the more detailed information in our document, Thyroid Cancer. This document and other information
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
Testing for Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
Testing for Prostate Cancer Should I be tested? Is it the right choice for me? Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find it early. There may be benefits and risks with testing. Research
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Skin cancer Patient information
 Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Having a kidney biopsy
 Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Mesenteric Angiography
 Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
A start to help you understand prostate cancer
 A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
A start to help you understand prostate cancer If you are reading this because you have worries or concerns about yourself or someone you know then the best thing to do is make an appointment with your
Kidney Stones. This reference summary will help you understand kidney stones and how to treat and prevent them. Kidney
 Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
The TV Series. www.healthybodyhealthymind.com INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK
 The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
Advanced prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is advanced (metastatic) prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose advanced prostate cancer?
Diagnosis Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is advanced (metastatic) prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose advanced prostate cancer?
Non-Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours
 Non-Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours NET Patient Foundation Non-Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours This booklet is intended to provide patients and their carers with information
Non-Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours NET Patient Foundation Non-Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours This booklet is intended to provide patients and their carers with information
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Bowel (Colorectal) Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
 Bowel (Colorectal) Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Introduction The information in this document has been reproduced with the permission of the Colorectal and Stoma Care Team, Barts & the London NHS Trust.
Bowel (Colorectal) Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Introduction The information in this document has been reproduced with the permission of the Colorectal and Stoma Care Team, Barts & the London NHS Trust.
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary
 X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
