GSM: system architecture
|
|
|
- Brett Baker
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
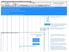
1 SS7 GSM: system architecture radio subsystem network and switching subsystem fixed partner networks MS MS U m MSC ISDN PSTN BTS BTS A bis BSC EIR HLR BTS BTS BS S BSC A MSC IWF VLR ISDN PSTN PSPDN CSPDN
2 System architecture: radio subsystem radio subsystem MS BTS BTS BTS BTS BSS MS U m A bis BSC BSC A network and switching subsystem MSC MSC Components MS (Mobile Station) BSS (Base Station Subsystem): consisting of BTS (Base Transceiver Station): sender and receiver BSC (Base Station Controller): controlling several transceivers Interfaces U m : radio interface A bis : standardized, open interface with 16 kbit/s user channels A: standardized, open interface with 64 kbit/s user channels
3 SS7 System architecture: network and switching subsystem MSC network subsystem EIR fixed partner networks ISDN PSTN Components MSC (Mobile Services Switching Center): IWF (Interworking Functions) ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) PSPDN (Packet Switched Public Data Net.) CSPDN (Circuit Switched Public Data Net.) MSC IWF HLR VLR ISDN PSTN PSPDN CSPDN Databases HLR (Home Location Register) VLR (Visitor Location Register) EIR (Equipment Identity Register)
4 Radio subsystem The Radio Subsystem (RSS) comprises the cellular mobile network up to the switching centers Components Base Station Subsystem (BSS): Base Transceiver Station (BTS): radio components including sender, receiver, antenna - if directed antennas are used one BTS can cover several cell-areas Base Station Controller (BSC): switching between BTSs, controlling BTSs, managing of network resources, mapping of radio channels (U m ) onto terrestrial channels (A interface) BSS = BSC + sum(bts) + interconnection Mobile Stations (MS) Page 4
5 GSM: cellular network possible radio coverage of the cell cell idealized shape of the cell use of several carrier frequencies not the same frequency in adjoining cells cell sizes vary from some 100 m up to max 35 km (due to time advance restriction of 6 bit) depending on user density, geography, transceiver power etc. hexagonal shape of cells is idealized (cells overlap, shapes depend on geography) if a mobile user changes cells handover of the connection to the neighbor cell
6 Example coverage of GSM networks ( T-Mobile (GSM-900/1800) Berlin Vodafone (GSM-900/1800) e-plus (GSM-1800) O 2 (GSM-1800) Page 6
7 Base Transceiver Station and Base Station Controller Tasks of a BSS are distributed over BSC and BTS BTS comprises radio specific functions BSC is the switching center for radio channels Functions BTS BSC Management of radio channels X Frequency hopping (FH) X X Management of terrestrial channels X Mapping of terrestrial onto radio channels X Channel coding and decoding X Rate adaptation X Encryption and decryption X X Paging X X Uplink signal measurements X Traffic measurement X Authentication X Location registry, location update X Handover management X Page 7
8 Mobile station 1 Terminal for the use of GSM services A mobile station (MS) comprises several functional groups MT (Mobile Termination): offers common functions used by all services the MS offers corresponds to the network termination (NT) of an ISDN access end-point of the radio interface (U m ) TA (Terminal Adapter): terminal adaptation, hides radio specific characteristics TE (Terminal Equipment): peripheral device of the MS, offers services to a user does not contain GSM specific functions SIM (Subscriber Identity Module): personalization of the mobile terminal, stores user parameters TE TA MT R S Page 8 U m
9 Mobile station 2 Each MS contains an International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) The SIM personalizes a MS Contains Information for: authentication Key Accounting data Personal numbers Contract and service details PIN PUK International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) after being connected: Key for data encryption Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (LMSI) Location Area Identity (LAI) Transmit power for GSM 900 2W for GSM1800 1W Page 9
10 Network and switching subsystem NSS is the main component of the public mobile network GSM switching, mobility management, interconnection to other networks, system control; inter BSS Handover; inter MSC Handover, international location of terminals; roaming between network-operators Components Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC) controls all connections via a separated network to/from a mobile terminal within the domain of the MSC - several BSC can belong to a MSC Has mainly same task as ISDN switch Databases (important: scalability, high capacity, low latency) Home Location Register (HLR) central master database containing all user data, permanent and semipermanent data of all subscribers assigned to the HLR (one provider can have several HLRs, but consider virtually as a distributed system) Visitor Location Register (VLR) local database for a subset of user data, including data about all user currently in the domain of the VLR Page 10
11 Mobile Services Switching Center The MSC (mobile switching center) plays a central role in GSM switching functions additional functions for mobility support management of network resources interworking functions via Gateway MSC (GMSC) access to several databases Functions of a MSC specific functions for paging and call forwarding termination of SS7 (signaling system no. 7) mobility specific signaling location registration and forwarding of location information provision of (new) services (fax, data calls) support of short message service (SMS) generation and forwarding of accounting and billing information Page 11
12 Operation subsystem The OSS (Operation Subsystem) enables centralized operation, management, and maintenance of all GSM subsystems Components Authentication Center (AUC) generates user specific authentication parameters on request of a VLR authentication parameters used for authentication of mobile terminals and encryption of user data on the air interface within the GSM system Equipment Identity Register (EIR) registers GSM mobile stations and user rights stolen or malfunctioning mobile stations can be locked and sometimes even localized Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC) different control capabilities for the radio subsystem and the network subsystem using TMN (Telecommunication Management Network) Page 12
13 Air Interface Facts and Figures: Uses many of the introduced Multiplexing technologies SDMA for Cell structure and multi-segment BTS FDD for separation between up and down channel TDMA for more users per radio channel GSM900: 124 carrier frequencies for up and 124 frequencies for down channel, 200 khz/channel; channel 1 and 124 not used; 32 channels used for OAM purposes GSM1800: 2*374 carrier frequencies for up/down with 200KHz ea ch Frame structure: duration 4,615 ms 8 time slots of 577ms each TDMA shift: each logical channel will be shifted be 3 time-slots in up and down direction Data Burst: 546 ms+ 30,5 ms guard time for different path delays; theoretical throughput 33,8 kb/s Page 13
14 GSM - TDMA/FDMA MHz 124 channels (200 khz) downlink GSM TDMA frame MHz 124 channels (200 khz) uplink higher GSM frame structures time ms guard space GSM time-slot (normal burst) tail user data S Training S user data tail 3 bits 57 bits 1 26 bits 1 57 bits 3 guard space µs 577 µs
15 Burst Structure Each data-burst contains: Training sequence of 26 bit 2 data fields of 57 bits + 1control bit each 2 tail sequences of 3 bit each set to 0 for modulation control Other bust types: Access Burst: for connection establishment Synchronization Burst Frequency Correction Burst Dummy Burst Page 15
16 Logical Channels 1 Two different logical channels: Traffic channel (TCH) Control channel (CCH) Traffic Channel Types: Full-Rate (TCH/F) 22,8 kb/s 13kb/s for speech coding Rest for FEC Half-Rate 11,4 kb/s 5,6 kb/s for speech coding Rest for FEC For data transmission TCH/4.8; TCH/9.6; TCH/14.4 (TCH/FS) (TCH/HS) Using different coder and FEC mechanisms Page 16
17 Logical Channels 2 Control Channel Types Used for Media Access und User Mobility 3 types of control channel (with several sub-types): Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) Data to all MS in a cell Contains Cell-ID; Frequency Hopping type; available frequencies in this cell, adjacent cell frequencies Subtypes: Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH); Synchronization Channel (SCH) Common Control Channel (CCCH) BTS/MS connection establishment data Paging channel (PCH) for BTS to MS call Random Access Channel (RACH) for MS connection request Access Grant Channel (AGCH) for BTS to MS channel association Page 17
18 Logical Channels 3 Dedicated Control Channel (DCCH) Bidirectional Channels Stand Allone DCH (SDCCH) for signalling between MS and BTS Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH)(for each TCH and SDCCH) Fast Associated Control Channel (FACCH) (uses time slots of regular TCHs) Page 18
19 Frame Structure Not all combinations of frames are permitted: Each TCH/F is associated with a SACCH TTTTTTTTTTTTSTTTTTTTTTTTTXTTTTTTTTTTTTS 12* TCH 12* TCH 12* TCH 26 Slots Data Rate of TCH/F = 24/26*24,7kb/s= 22,8 kb/s Data Rata of SACCH= 1/26*24,7kb/s= 950b/s Page 19
20 GSM hierarchy of frames hyperframe h 28 min s superframe s multiframe slot burst frame 120 ms Traffic multiframe ms Control multiframe ms 577 µs Page 20
21 GSM protocol layers for signaling U m A bis A MS BTS BSC MSC CM CM MM MM RR LAPD m RR LAPD m BTSM LAPD RR BTSM LAPD BSSAP SS7 BSSAP SS7 radio radio PCM PCM PCM PCM 16/64 kbit/s 64 kbit/s / Mbit/s CM: Call Management; MM: Mobility Management; RR: Radio Resource LAPD: Line Access Protocol; PCM: Pulse Code Modulation; BSSAP BSS Application Part; BTSM: BTS Management; SS7 Signaling System 7 Page 21
22 Tasks of the different protocol layers 1 Physical Layer: All radio specific functions Generation of Burst-typs; Generation of TDMA-frame; Synchronisation with BTS, Free channel detection; Measurement of channel quality GMSK is used as modulation (Gausscian Minimal Shift Keying) Coding and FEC Voice Activity detection /Comfort Noise generation Interleaving for minimizing burst error influence (scrambling) Coding and Interleaving causes an additional delay of ms. For Internet services that might have bad impact on TCP performance Encryption function for transmission to BTS (no protection between users but only transport protection for all data transmission together) Synchronization: Contains the correction of individual path delays Time advance determines the number of 3,69 ms slots the MS has to send the signal earlier; the time advance value can go up to 63 (Cell-Size max =63*3,69ms*3*10 5 km/s/2=35 km) Allows to reduce Guard Time to 5% of bust-time and increases throughput Page 22
23 Tasks of the different protocol layers 2 LAPD m for signalling on layer 2: Derivate of Link Access Procedure for D-channel of ISDN Reduced LAPD protocol No synchronization and no CRC (already on layer 1 in GSM) Offers reliable data-transport, is connection oriented, preserves the order, conducts flow-control Offers segmentation and reassembly of data-packets as well as confirmed and unconfirmed messaging Network-Layer (switching layer) Contains several sub-layer Radio Resource Management (RR) Controls the use of the radio frequencies; uses the BTSM to access radio quality parameters directly; offers a reliable data transmission service to next higher layer Mobility Management (MM) Contains functions for registration; authentication; deviceidentification; location-update; TMSI management; offers a reliable transmission service to next higher sub-layer Page 23
24 Tasks of the different protocol layers 3 Call Management (CM) Contains functions for Call Control (CC), Short Message Service (SMS) and supplementary services (SS) CC offers point to point service between to terminals; in band signalling using DTMF (Dual Tone Multiple Frequencies). (DTMF cannot be transmitted via ordinary TCH cannels because the speech coding would influence the signalling tones) SMS uses control channels SDCCH and SACCH if no other signalling data has to be transmitted Additional Signalling Protocols Between BTS and BCS A bis Between BCS und MSC A Both protocols use PCM modulation with 64 transparent channels 4*16kb/s channels are co-located in a single PCM channel via A bis From BCS to MSC Primary multiplex channel of 2Mb/s are often available. Often dedicated microwave links are used LAPD is used on layer 2 for signalling Page 24
25 Mobile Terminated Call 1: calling a GSM subscriber 2: forwarding call to GMSC 3: signal call setup to HLR 4, 5: request MSRN (Mobile Subscriber Roaming Number) from VLR 6: reply to responsible GMSC 7: forward call to current MSC 8, 9: get current status of MS 10, 11: paging of MS 12, 13: MS answers 14, 15: security checks 16, 17: set up connection 18, 19, 20: set-up confirmation calling station HLR PSTN GMSC VLR MSC BSS BSS BSS MS Page 25
26 Mobile Originated Call 1, 2: connection request 3, 4: security check 5-8: check resources (free circuit) 9-10: set up call PSTN 6 5 GMSC 7 8 VLR 3 4 MSC 2 9 MS 1 10 BSS Page 26
27 Information necessary for localization Mobile Subscriber International ISDN Number (MSISDN) Consists of country code (CC); National Destination Code (NDC); Subscriber Number (SN) Is the only number of use for the subscriber International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) GSM internal unique identification number; consists of Mobile Country Code (MCC); Mobile Network Code (MNC); Mobile Subscriber Identity (MSI) Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI) To hide user identity; TMSI given by VLR; valid only in Local Area (LA); TMSI and LAI can identify a user uniquely Can be changed on demand of either BCS or MS Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN) Hide user identity and location; VLR generates MSRN on demand of MSC; is stored as part of the HLR of each active user; MSRN contains Visitor Country Code (VCC); Visitor National Destination Number (VNDC); actual MSC ID and subscriber number Page 27
28 MTC/MOC MS MTC BTS paging request channel request immediate assignment paging response authentication request authentication response ciphering command ciphering complete setup call confirmed assignment command assignment complete alerting connect connect acknowledge data/speech exchange MS MOC BTS channel request immediate assignment service request authentication request authentication response ciphering command ciphering complete setup call confirmed assignment command assignment complete alerting connect connect acknowledge data/speech exchange Page 28
29 4 types of handover MS MS MS MS BTS BTS BTS BTS BSC BSC BSC MSC MSC Page 29
30 Handover decision receive level BTS old receive level BTS old HO_MARGIN MS MS BTS old BTS new Trade-off for HO_Margin If HO_Margin to high the connection can be lost If HO_Margin to low the handover overhead increases dramatically Solution: relative low HO_Margin and defined Hysteresis Value Page 30
31 MS measurement report BTS old measurement result Handover procedure (Make before Brake) BSC old MSC BSC new BTS new HO command HO decision HO required HO command HO command HO access Link establishment clear command clear command clear complete clear complete HO request resource allocation ch. activation HO request ack ch. activation ack HO complete HO complete After the link is established the MS has no further influence on the old resources Page 31
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Global System for Mobile (GSM) Global System for Mobile (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
-The equipment was limited to operate only within the boundaries of each country. -The market for each mo bile equipment was limited.
 1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning
 GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing
 GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Bölüm 8. GSM. 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar!
 Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure
 GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3-
 Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems
 Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020502Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020502Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04. Simon Sörman
 Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
1. Introduction: The Evolution of Mobile Telephone Systems
 IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G
 CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
RELEASE NOTE. Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08. Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90
 ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks
 Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM
 Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0
 GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
How To Test Gsm Cell Phone Network On A Cell Phone
 G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Durresi@cis.ohio-state.edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
GLOSARIO. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Estándar de comunicación celular basado en TDMA.
 GLOSARIO A AC o AuC Ack AGCH A-key AMPS ANSI-136 ó IS-136 ARFCN ASE Authentication Center. Acknowledgement. Access Grant Channel. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Advanced
GLOSARIO A AC o AuC Ack AGCH A-key AMPS ANSI-136 ó IS-136 ARFCN ASE Authentication Center. Acknowledgement. Access Grant Channel. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Advanced
The Network Layer Layer 3
 CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Cellular mobile communication is based on the. The Cellular Concept. GSM and PCNs. Moe Rahnema
 GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing
 Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: solutions@wg.com http://www.wg.com
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: solutions@wg.com http://www.wg.com
ETSI TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06)
 TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
GSM Databases. Virginia Location Area HLR Vienna Cell Virginia BSC. Virginia MSC VLR
 Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Mobile Communications II Chapter 2: GSM
 Mobile Communications II Chapter 2: GSM Global System for Mobile Communications Architectures and Overview Data services in GSM GSM: Overview GSM formerly: Groupe Spéciale Mobile (founded 1982) now: Global
Mobile Communications II Chapter 2: GSM Global System for Mobile Communications Architectures and Overview Data services in GSM GSM: Overview GSM formerly: Groupe Spéciale Mobile (founded 1982) now: Global
Using TEMS Pocket. Johan Montelius
 Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Mobile Communication Systems: DECT Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunication
 Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034. Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301. Agenda item: 6.3.3
 TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034 Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301 Source: TSG-RAN WG2 Agenda item: 6.3.3 Doc-1st- Spec CR Rev Subject Cat Version Versio R2-000213 25.301 032 Correction
TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034 Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301 Source: TSG-RAN WG2 Agenda item: 6.3.3 Doc-1st- Spec CR Rev Subject Cat Version Versio R2-000213 25.301 032 Correction
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: Cellular Networking
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: Cellular Networking Professor Patrick Traynor 9/13/2012 The Big Picture Details create the big picture. -Sanford I. Weill 2 Overview Evolution Architecture
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: Cellular Networking Professor Patrick Traynor 9/13/2012 The Big Picture Details create the big picture. -Sanford I. Weill 2 Overview Evolution Architecture
LTE Tutorial GSM Tutorial i
 GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
Cellular Technology Sections 6.4 & 6.7
 Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
GSM Network Structure and Network Planning. Contents: Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre
 GSM Network Structure and Network Planning Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre Contents: 1. Geographical structures in a GSM network 2. Methods of network planning 2.1. Principles
GSM Network Structure and Network Planning Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre Contents: 1. Geographical structures in a GSM network 2. Methods of network planning 2.1. Principles
How To Understand The Performance Of A Cell Phone Network
 Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
1 Introduction. 2 Assumptions. Implementing roaming for OpenBTS
 Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Analysis of GSM Network for Different Transmission Powers
 Analysis of GSM Network for Different Transmission Powers Mandeep Singh 1, Supreet Kaur 2 1,2 (Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India) Abstract: To
Analysis of GSM Network for Different Transmission Powers Mandeep Singh 1, Supreet Kaur 2 1,2 (Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India) Abstract: To
Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description
 C1 Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description C1. Parameters included in the modelling In the modelling the number of mobiles and their positioning with respect to the wired device needs to be taken
C1 Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description C1. Parameters included in the modelling In the modelling the number of mobiles and their positioning with respect to the wired device needs to be taken
Cellular Phone Systems
 Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
Positioning in GSM. Date: 14th March 2003
 Positioning in GSM Date: 14th March 2003 Overview of seminar Potential applications in cellular network Review of localization system and techniques Localization in GSM system Progress of the project with
Positioning in GSM Date: 14th March 2003 Overview of seminar Potential applications in cellular network Review of localization system and techniques Localization in GSM system Progress of the project with
PART 4 GSM Radio Interface
 PRT 4 GSM Radio Interface Lecture 4. Physical channels Frequency [MHz] 960 OWNLINK BS MS 95 95 UPLINK MS BS 890 GSM Radio Spectrum 890.4 890.2 guard band 2 x 25 Mhz band uplex spacing: 45 MHz 24 carriers
PRT 4 GSM Radio Interface Lecture 4. Physical channels Frequency [MHz] 960 OWNLINK BS MS 95 95 UPLINK MS BS 890 GSM Radio Spectrum 890.4 890.2 guard band 2 x 25 Mhz band uplex spacing: 45 MHz 24 carriers
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013
 EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude skangude@lyle.smu.edu Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude skangude@lyle.smu.edu Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services Cellular networks GSM Network and Services 2G1723 Johan Montelius 1 The name of the game The number one priority for mobile/cellular networks is to implement full-duplex voice
GSM Network and Services Cellular networks GSM Network and Services 2G1723 Johan Montelius 1 The name of the game The number one priority for mobile/cellular networks is to implement full-duplex voice
Supplementary material: Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT)
 Supplementary material: Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 History Analog cordless phones came into use in the early 1980s. They enabled communications between handsets
Supplementary material: Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 History Analog cordless phones came into use in the early 1980s. They enabled communications between handsets
NETWORK AND RF PLANNING
 NETWORK AND RF PLANNING Introduction Achieving maximum capacity while maintaining an acceptable grade of service and good speech quality is the main issue for the network planning. Planning an immature
NETWORK AND RF PLANNING Introduction Achieving maximum capacity while maintaining an acceptable grade of service and good speech quality is the main issue for the network planning. Planning an immature
Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov. Keywords: Data broadcasting, cellular mobile systems, WCDMA, GSM.
 Аnalysis of data broadcasting in modern cellular mobile systems of ground radio communications Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov At the analysis of channel formation in WCDMA networks the
Аnalysis of data broadcasting in modern cellular mobile systems of ground radio communications Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov At the analysis of channel formation in WCDMA networks the
Chapter 6: Broadcast Systems. Mobile Communications. Unidirectional distribution systems DVB DAB. High-speed Internet. architecture Container
 Mobile Communications Chapter 6: Broadcast Systems Unidirectional distribution systems DAB DVB architecture Container High-speed Internet Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC
Mobile Communications Chapter 6: Broadcast Systems Unidirectional distribution systems DAB DVB architecture Container High-speed Internet Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS
 RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]
![[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]](/thumbs/26/8506801.jpg) JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系
 Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
RADIUS. Brief brochure. Product Purpose
 Product Purpose The Product is designed for searching, intercepting, registering and analyzing of communication sessions as well as service information circulating in cellular GSM networks without encryption
Product Purpose The Product is designed for searching, intercepting, registering and analyzing of communication sessions as well as service information circulating in cellular GSM networks without encryption
